Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
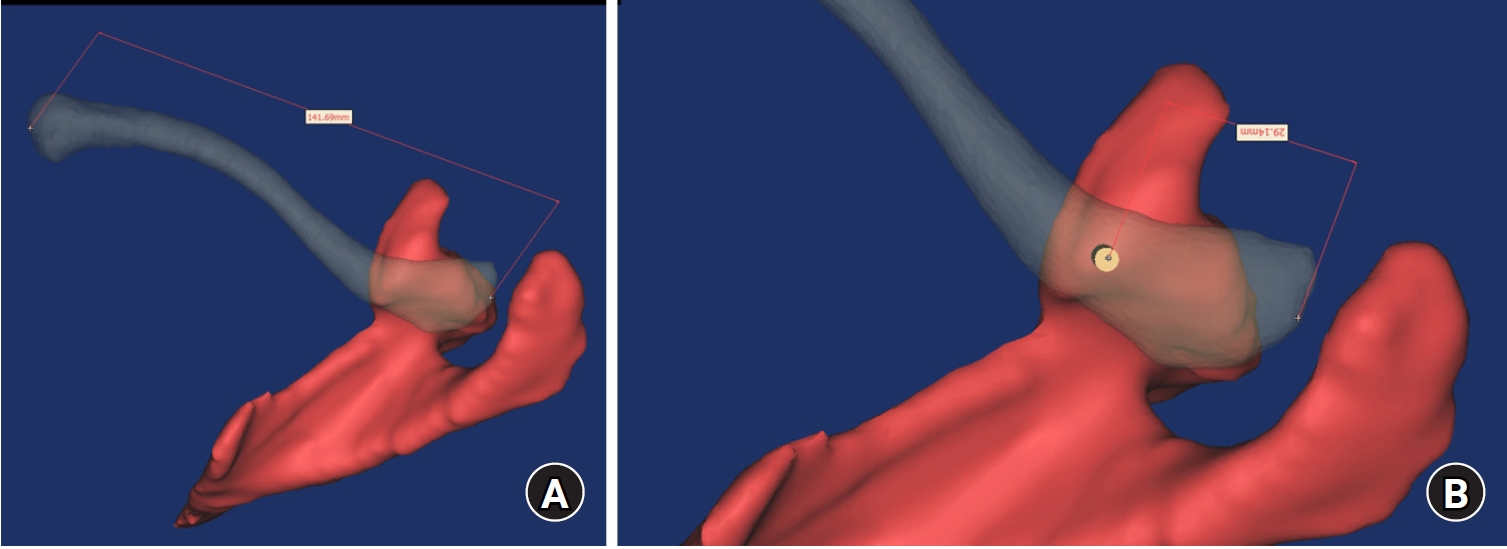
- Computational simulation of coracoclavicular screw insertion through the superior distal clavicular plate for clinical applications in Korean cadavers
- Hyung-Lae Cho, Ji Han Choi, Se-Lin Jeong, Gu-Hee Jung
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):143-151. Published online July 22, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00122
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The study was conducted to determine the practical area for inserting the coracoclavicular (CC) screw through the plate by analyzing three-dimensional (3D) shoulder models featuring virtually implanted, actual-size plates and screws.
Methods
Ninety cadaveric shoulders (41 males and 49 females) underwent continuous 1.0-mm slice computed tomography scans. The data were imported into image-processing software to generate a 3D shoulder model, including the scapula and clavicle. The overlapping area between the clavicle and the horizontal portion of the coracoid process (horizontal portion_CP) was analyzed in the cranial view. A curved pelvic recon plate was virtually placed on the upper surface of the distal clavicle, and an actual-size (3.5 mm) CC screw was inserted through the plate.
Results
The distal clavicle directly overlapped with the horizontal portion_CP in the vertical direction. The overlapping area was sufficient to place the 3.5 mm and 4.5 mm-sized screws. In all shoulder models, the CC screw could be inserted through the plate into the vertical direction, with an average length of 35.5 mm (range, 26.2–62.5 mm; standard deviation, 1.2 mm). In 87 models, the CC screw was inserted through the third hole from the lateral end of the plate. Two models were inserted through the second hole, and one model through the fourth hole.
Conclusions
The upper surface of the clavicle has sufficient overlapping area to place CC screws through the plate in the vertical direction in the corresponding hole. Supplemental CC screw fixation through the plate can be performed without additional or special equipment. Level of evidence: IV
- 544 View
- 19 Download

- Interpositional tricortical iliac bone graft in nonunion of midshaft clavicular fractures
- Eun-Seok Son, Bum-Soon Park, Chang-Jin Yon, Chul-Hyun Cho
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(1):23-31. Published online January 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00004

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The purpose of this study was to investigate the radiological and clinical outcomes after interpositional tricortical iliac bone graft with plate fixation for the nonunion of clavicle midshaft fractures. Methods: Between 2007 and 2020, 17 cases who were treated by interpositional tricortical iliac bone graft with plate fixation for the clavicle midshaft nonunion combined with bone defect were investigated. The mean age was 53 years (range, 22–70 years). The mean follow-up period was 102.2 months (range, 18–193 months). Serial plain radiographs were used to evaluate radiological outcomes. The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) score, American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons (ASES) score, and Quick-disabilities of the arm, shoulder, and hand (DASH) score were used to evaluate clinical outcomes. Complications were also evaluated. Results: All cases achieved complete bony union with mean healing time of 17.6 weeks (range, 14–22 weeks). The mean clavicle length difference was significantly decreased from 9.1 mm preoperatively to 2.6 mm postoperatively (P<0.001). The mean UCLA and ASES scores were significantly improved from 18.1 and 52.2 before surgery to 30.6 and 88.6 after surgery (both P<0.001), respectively. The mean final Quick-DASH score was 18.0. Three cases (17.6%) developed postoperative complications including two cases of shoulder stiffness and one case of screw irritation. Conclusions: Interpositional tricortical iliac bone graft with plate fixation for the clavicle midshaft nonunion demonstrated excellent radiological and clinical outcomes. In cases of atrophic nonunion combined with bone defect, this technique is an effective option that can provide structural support and restore clavicle length. Level of evidence: Level IV, case series.
- 1,674 View
- 40 Download

Case Reports
- Brachial Plexus Neuropathy after Revision of Clavicular Fracture Nonunion: A Case Report
- Youngwoo Kim, Suk Kyu Choo, Neunghan Jeon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(1):22-26. Published online January 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.1.22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We performed a revisionary open reduction and internal fixation for treating nonunion of the mid-shaft of the left clavicle with an autogenous cancellous bone graft. On postoperative day 4, the patient presented with neurologic deficits in the left upper extremity. We removed the implant and made a superior angulation to decompress the brachial plexus. At 6 months postoperatively, callus bridging and consolidation were visible and all hand and elbow functions were fully recovered. Our case suggests that brachial plexus neuropathy may be caused by stretching and compression after reduction and straightening of the nonunion site around adhesions or scar tissue. Therefore, care should be taken whether there are the risk factors that can cause brachial plexus neuropathy when revision surgery is performed for treating nonunion of a clavicle shaft fracture.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Arcuate osteoplasty for brachial plexus paralysis after plate fixation of mid-clavicle fracture: a case report and literature review
Dongju Shin, Jae Hwi Han
Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow.2025; 28(3): 394. CrossRef
- Arcuate osteoplasty for brachial plexus paralysis after plate fixation of mid-clavicle fracture: a case report and literature review
- 928 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Progressive Brachial Plexus Palsy after Fixation of Clavicle Shaft Nonunion: A Case Report
- Hong Ki Jin, Ki Bong Park, Hyung Lae Cho, Jung Il Kang, Wan Seok Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(2):97-101. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.2.97
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The brachial plexus palsy is a rare complication of a clavicle fracture, occurring in 0.5% to 9.0% of cases. This condition is caused by excessive callus formation, which can be recovered by a spur resection and surgical fixation. In contrast, only seven cases have been reported after surgical reduction and fixation. A case of progressive brachial plexus palsy was observed after fixation of the displaced nonunion of a clavicle fracture. The symptom were improved after removing the implant.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Arcuate osteoplasty for brachial plexus paralysis after plate fixation of mid-clavicle fracture: a case report and literature review
Dongju Shin, Jae Hwi Han
Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow.2025; 28(3): 394. CrossRef
- Arcuate osteoplasty for brachial plexus paralysis after plate fixation of mid-clavicle fracture: a case report and literature review
- 640 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Article
- Surgical Results of Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Fixation in the Treatment of Clavicle Shaft Fracture
- Seong Ho Yoo, Suk Woong Kang, Jae Seung Seo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(1):21-26. Published online January 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.1.21
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study analyzed the results of the midclavicle fracture treatment using the minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) technique in a retrospective manner.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between March 2013 and March 2017, this study analyzed 40 patients who received MIPO surgery. Excluding 1 patient who underwent surgery on another body part injury, and 4 patients who were lost to follow-up over 1 year, 40 patients were analyzed for their operation time, bone union, functional American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons score, scar lengths, pain relief (visual analogue scale), and complications.
RESULTS
All patients over a 1 year of follow-up achieved bone union, and American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons score 97.6 (94–100) on their shoulder functional scores. Their average operation time was 42.7 minutes, and the average scar length was 6.1 cm. Eighteen patients successfully received metal removal using the previous scar without additional incision. The clavicle length was similar in the normal and operated group.
CONCLUSION
Despite its small sample size, clavicle fixation using the MIPO technique can be considered an effective treatment because of its limited number of complications, such as nonunion and rotational angulations. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Additional fixation using a metal plate with bioresorbable screws and wires for robinson type 2B clavicle fracture
Woo Jin shin, Young Woo Chung, Seon Do Kim, Ki-Yong An
Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow.2020; 23(4): 205. CrossRef
- Additional fixation using a metal plate with bioresorbable screws and wires for robinson type 2B clavicle fracture
- 850 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review Article
- Conservative Treatment of Mid-Clavicle Fractures
- Woong Kyo Jeong
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(1):22-28. Published online January 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.1.22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Clavicle fractures are very common injuries in adults and children and the majority of these fractures occur in the midshaft. Traditionally, mid-clavicle fractures have been treated with conservative methods and the clinical outcomes of this method are believed to be excellent. On the other hand, recent studies have shown that the clinical results of severe comminuted or markedly displaced fractures after conservative management were not as favorable as previously described. Despite these concerns, the conservative treatment of mid-clavicle fractures is still an efficient method, which can be applied to all patients as a primary care. This review focuses on the proper indication, technique, and limitations of conservative treatment of mid-clavicle fractures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Two Patients Who Were Hospitalized for Clavicle Fracture Caused by a Traffic Accident and Improved with Korean Medicine Complex Treatment
Deok Kang, ByungSoo Kang, Hwe-Joon Jeong, Dong-Hoon Shin, Kyung-Moon Shin, Ji-Hoon O, Jae-Woo Yang
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2022; 32(3): 179. CrossRef
- Two Patients Who Were Hospitalized for Clavicle Fracture Caused by a Traffic Accident and Improved with Korean Medicine Complex Treatment
- 419 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Reports
- Atypical Bipolar Segmental Fracture of the Clavicle in an Adolescent: A Case Report
- Joong Bae Seo, Sung Hyun Yoon, Jun Kyom Kim, Sung Hyun Kim, Jae Sung Yoo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(1):18-21. Published online January 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.1.18
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Clavicular fractures commonly occur in adults and children. The usual site of these fractures is the mid clavicle with lateral end and medial end clavicular fractures being less common. Bipolar segmental clavicular injuries involving medial and lateral ends are rare but almost always occur in adults. This paper reports a very rare case of segmental clavicular fracture involving the medial and lateral end in an adolescent caused by direct trauma. The surgical management of a segmental fracture clavicle in an adolescent is reported with a discussion of the relevant literature.
- 251 View
- 3 Download

- The Different Treatment Methods for Segmental Fractures of the Clavicle: Cases Report
- Sung Sik Ha, Ki Do Hong, Jae Cheon Sim, Yi Rak Seo, Tae Seok Nam
- J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(3):151-155. Published online July 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.3.151
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Segmental fractures of the clavicle are very rare. Therefore, to date, there has not been a clear, standardized method of management of segmental clavicle fractures. Herein, two patients with a segmental fracture are described: One patient was treated conservatively, while another patient was treated operatively. Both patients showed excellent results. We discuss the various management options with a literature review.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fratura segmentar da clavícula em paciente politraumatizado: Relato de caso
Carlos A. Sánchez, Pablo J. Coronel, Luisa F. García, Juan S. Afanador, Raúl Gonzalez
Revista Brasileira de Ortopedia.2024; 59(01): e139. CrossRef
- Fratura segmentar da clavícula em paciente politraumatizado: Relato de caso
- 827 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- Use of Composite Wiring on Surgical Treatments of Clavicle Shaft Fractures
- Kyung Chul Kim, In Hyeok Rhyou, Ji Ho Lee, Kee Baek Ahn, Sung Chul Moon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(3):185-191. Published online July 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.3.185
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To introduce the technique of reducing displaced or comminuted clavicle shaft fracture using composite wiring and report the clinical results.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between March 2006 and December 2013, 31 consecutive displaced clavicle fractures (Edinburgh classification 2B) treated by anatomic reduction and internal fixation using composite wiring and plates were retrospectively evaluated. The fracture fragments were anatomically reduced and fixed with composite-wiring. An additional plate was applied. Radiographic assessments for the numbers of fragments, size of each fragment and amount of shortening and displacement were performed. The duration for fracture union and complications were investigated retrospectively. The mean fallow-up duration was 15.9 months.
RESULTS
The mean number of fragments was 1.7 (1-3) and the mean width of fracture fragment was 7.1 mm (4.5-10.6 mm). The mean shortening of the clavicle was 20.5 mm (10.3-36.2 mm). The mean number of composite wires used in fixation was 1.9 (1-3). Radiographic union was achieved in all patients with a mean time to union of 11.6 weeks. There were no complications including metal failure, pin migration, nonunion, or infection.
CONCLUSION
The composite wiring was suitable for fixation of small fracture fragment and did not interfere with the union, indicating that it is useful for treatment of clavicle shaft fracture.
- 312 View
- 1 Download

- Hypoesthesia after Open Reduction and Plate Fixation of Clavicular Midshaft Fractures: Correlation with Plate Location and Clinical Features of Hypoesthesia
- Seong Hun Kim, Joon Yub Kim, Kyoung Hwan Koh, Myung Gon Jung, Jae Ho Cho
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(2):121-127. Published online April 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.2.121
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The aim of this study is to evaluate the correlation between the location of the plate and the incidence of clavicular hypoesthesia and the clinical features of patients with clavicular hypoesthesia after open reduction and internal fixation of clavicular midshaft fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Seventy-eight patients who underwent open reduction and plate fixation for clavicle midshaft fractures between March 2013 and October 2014 were assessed for eligibility. The total clavicular length (A), the distance to the medial end of the plate from the sternoclavicular joint (B), and the distance to the lateral end of the plate from the sternoclavicular joint (C) were measured. Correlation between the location of the clavicular plate and the incidence of clavicular hypoesthesia was evaluated. In addition, the severity, and recovery of hypoesthesia were evaluated. Patient satisfaction, pain visual analogue scale were evaluated regarding hypoesthesia.
RESULTS
The incidence of hypoesthesia was 32.1% (25/78 patients). No correlation was observed with respect to the location of the clavicular plate and the incidence of clavicular hypoesthesia (p=0.666 at the medial end, p=0.369 at the lateral end). Recovery from hypoesthesia was observed in 23 out of 25 patients (p=0.008). Patient satisfaction and pain showed negative correlation with the incidence of hypoesthesia (p=0.002 and p=0.022).
CONCLUSION
There was no correlation between clavicular hypoesthesia and the plate location. Although most cases of hypoesthesia were recovered, we should try to avoid hypoesthesia due to the negative 'correlation' with patient satisfaction and pain.
- 394 View
- 0 Download

- Usefulness of the Additional K-Wire Fixation and Suture for Reinforce the Treatment of Distal Clavicle Fracture Using Modified Tension Band Wiring
- Seung Bum Chae, Chang Hyuk Choi, Dong Young Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(2):107-113. Published online April 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.2.107
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
We attempted to evaluate the clinical results of modified tension band wiring (MTBW) with additional K-wire fixation and suture for distal clavicle fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fifty-nine patients with a distal clavicle fracture from May 2009 to December 2013 treated with MTBW were enrolled in this study. Their fracture types were type 2, 12; and type 3, 33; type 4, 8; and type 5, 6 according to Craig classification group II; average age was 47.2 years with a mean follow-up period of 27.9 months. The operations were performed within a mean of 3.1 days a fter t rauma. The c linical results were evaluated u sing University of California at Los Angeles scores (UCLA), American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons scores (ASES) and Korean Shoulder Society scores (KSS) at 1 year after surgery.
RESULTS
Radiographic bone union was achieved at a mean of 3.7 months after the operation. In the last observation, their range of motion was forward flexion 159.0°, external rotation 59.8°, and internal rotation 4.3 points, and there were 2 cases of nonunion. Each average functional score was UCLA 31.3 points, KSS 91.6 points, and ASES 93.0 points.
CONCLUSION
For the surgical treatment of distal clavicle fractures, MTBW with additional K-wire fixation and suture is a useful technique allowing early range of motion exercises, minimizing soft tissue damage, and preserving the acromio-clavicular joint. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Treatment Results for Unstable Distal Clavicle Fractures Using Hybrid Fixations with Finger Trap Wire and Plate
Jeong-Seok Yu, Bong-Seok Yang, Byeong-Mun Park, O-Sang Kwon
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2022; 57(2): 135. CrossRef - Comparison of Locking Compression Plate Superior Anterior Clavicle Plate with Suture Augmentation and Hook Plate for Treatment of Distal Clavicle Fractures
Jun-Cheol Choi, Woo-Suk Song, Woo-Sung Kim, Jeong-Muk Kim, Chan-Woong Byun
Archives of Hand and Microsurgery.2017; 22(4): 247. CrossRef
- Treatment Results for Unstable Distal Clavicle Fractures Using Hybrid Fixations with Finger Trap Wire and Plate
- 710 View
- 6 Download
- 2 Crossref

Case Reports
- Periprosthetic Fracture after Hook Plate Fixation in Neer Type II Distal Clavicle Fracture: A Report of 3 Cases
- Kyung Yong Kim, Joon Yub Kim, Won Bok Lee, Myong Gon Jung, Jeong Hyun Yoo, Joo Hak Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(1):55-60. Published online January 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.1.55
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hook plate fixation is a treatment method for the displaced distal clavicle fracture with favorable results regarding bone union and shoulder function, however possible complications include impingement syndromes, subacrormial erosions, acromial fractures, and periprosthetic fractures. In this report, we observed 3 cases of periprosthetic fracture after hook plate fixation. All cases of periprosthetic fractures were initiated at the medial end screw holes. The causes of these periprosthetic fractures appeared to be the off centered fixation of medial end screws near the anterior or posterior cortex which were specific during operations with hook plates with more than 6 holes and the increased stress on the medial end screw by over-reduced or inferiorly reduced position of the distal end of the clavicle by the hook plate.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of a novel hybrid hook locking plate fixation method with the conventional AO hook plate fixation method for Neer type V distal clavicle fractures
Joongbae Seo, Kang Heo, Seong-Jun Kim, Jun-Kyom Kim, Hee-Jung Ham, Jaesung Yoo
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research.2020; 106(1): 67. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of a locking plate with an all-suture anchor versus hook plate fixation of Neer IIb distal clavicle fractures
Joong-Bae Seo, Kwon-young Kwak, Jae-Sung Yoo
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Locking Compression Plate Superior Anterior Clavicle Plate with Suture Augmentation and Hook Plate for Treatment of Distal Clavicle Fractures
Jun-Cheol Choi, Woo-Suk Song, Woo-Sung Kim, Jeong-Muk Kim, Chan-Woong Byun
Archives of Hand and Microsurgery.2017; 22(4): 247. CrossRef
- Comparison of a novel hybrid hook locking plate fixation method with the conventional AO hook plate fixation method for Neer type V distal clavicle fractures
- 583 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Infected Nonunion of Clavicle Shaft after Operation: A Case Report
- Ho Su Jang, Suk Hwan Jang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2015;28(1):77-81. Published online January 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.1.77
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The infected nonunion of clavicle with bone defect is an uncommon complication following clavicle shaft fracture. There were a few reports regarding treatment of the infected nonunion after clavicle fracture. We report on a case of infected clavicle nonunion successfully treated with autologous bone graft and dual plate fixation.
- 616 View
- 3 Download

Original Article
- The Surgical Outcome of Unstable Distal Clavicle Fractures Treated with 2.4 mm Volar Distal Radius Locking Plate
- Suk Kyu Choo, Ji Ho Nam, Youngwoo Kim, Hyoung Keun Oh
- J Korean Fract Soc 2015;28(1):38-45. Published online January 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.1.38
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study evaluated the surgical outcomes of unstable distal clavicular fractures treated with a 2.4 mm volar distal radius locking plate.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From August 2009 to August 2012, 16 patients with distal clavicle fractures underwent surgical treatment. Mean age was 36 years (18-62 years) and mean follow-up period was 12.9 months (6-32 months). Two cases were Neer type I, six cases IIa, three cases IIb, three cases III, and two cases V. For the radiologic assessment, union time and metal failure were evaluated, and coracoidiologic assessment, union time and metal failure were evaluatethe acromioclavicular joint. The clinical results were evaluated by range of motion, postoperative complication, and University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA) score.
RESULTS
Mean time to fracture union was 7.4 weeks (6-14 weeks) in all cases. No statistical difference in coracoid-clavicle distance was observed between immediate post-operation group and contra-lateral group (p=0.6), but an increase of 2.1 mm was observed in the last follow up group compared with the contra-lateral group (p<0.01). The UCLA scoring system showed excellent results in 15 cases and good results in one case. Acromial-clavicle instability occurred in one case so that metal removal and distal clavicle resection were performed.
CONCLUSION
A 2.4 mm volar distal radius locking plate can provide rigid fixation through several screw fixation in the short distal fragment and lead to satisfactory clinical outcomes in unstable distal clavicular fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Estudo retrospectivo da placa anterior superior como tratamento para fraturas instáveis da clavícula distal (tipo 2 de Neer)
Syed Ibrahim, Jimmy Joseph Meleppuram
Revista Brasileira de Ortopedia.2018; 53(3): 306. CrossRef - Retrospective study of superior anterior plate as a treatment for unstable (Neer type 2) distal clavicle fractures
Syed Ibrahim, Jimmy Joseph Meleppuram
Revista Brasileira de Ortopedia (English Edition).2018; 53(3): 306. CrossRef
- Estudo retrospectivo da placa anterior superior como tratamento para fraturas instáveis da clavícula distal (tipo 2 de Neer)
- 555 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

Case Report
- Granulation Tissue Formed by Stimulating K-Wire Mimicking Tuberculous Cervical Lymphadenopathy: A Case Report
- Gu Hee Jung, Tae Hun Kim, Hyun Ik Cho
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(3):227-231. Published online July 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.3.227
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pins and wires are still used frequently in surgeries of the shoulder; however, these can cause breakage or migration to surrounding tissues, leading to complications. We report on case of a patient with a neck mass who had a past history of pulmonary tuberculosis and distal clavicle fracture with internally fixated state. She was misdiagnosed as tuberculous cervical lymphadenopathy and treated for approximately one year, but was finally revealed as granulation tissue around the internally fixated distal clavicle fracture site, thus, mass excision and metal removal was performed. This case shows the importance of a proper selection device, internal fixation technique, duration, and close follow-up after the operation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Kirschner Wire Migration into SpinaL Canal after Acromioclavicular Joint Fixation (Literature Review and Clinical Case)
D. A. Gulyaev, D. S. Godanyuk, T. A. Kaurova, P. V. Krasnoshlyk, S. V. Maikov
Traumatology and Orthopedics of Russia.2018; 24(4): 121. CrossRef
- Kirschner Wire Migration into SpinaL Canal after Acromioclavicular Joint Fixation (Literature Review and Clinical Case)
- 475 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Article
- Tension Band Wiring for Distal Clavicle Fracture: Radiologic Analysis and Clinical Outcome
- Seong Cheol Moon, Chul Hee Lee, Jong Hoon Baek, Nam Su Cho, Yong Girl Rhee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(2):127-135. Published online April 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.2.127
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the radiologic and clinical outcomes after tension band wire fixation of Neer type II distal clavicle fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty-six patients with Neer type II distal clavicle fractures who underwent tension band wire fixation from March 2002 to May 2011 were included in the study. Fifteen cases were classified as Neer type IIa and 11 cases as type IIb. The postoperative mean follow-up period was 14.3 months. Clinical and radiologic evaluation was performed at two weeks, six weeks, three months, six months, and 12 months postoperatively.
RESULTS
Bony union on X-rays was observed at an average of 11.7 weeks (range 8-20 weeks) postoperatively. The overall visual analogue scale score for pain was 1.23+/-2.75 postoperatively. The overall postoperative University of California at Los Angeles score increased to 33.5+/-2.15 from the preoperative score of 21.6+/-1.91 (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
Among various methods of treatment for Neer type II distal clavicle fracture, K-wire and tension band fixation was used and relatively satisfactory radiological and clinical results were obtained. This surgical method yields excellent clinical results, owing to its relatively easy technique, fewer complications, and allowance of early rehabilitation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical and Radiologic Outcomes of Acute Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation: Comparison of Kirschner's Wire Transfixation and Locking Hook Plate Fixation
Yong Girl Rhee, Jung Gwan Park, Nam Su Cho, Wook Jae Song
Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow.2014; 17(4): 159. CrossRef
- Clinical and Radiologic Outcomes of Acute Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation: Comparison of Kirschner's Wire Transfixation and Locking Hook Plate Fixation
- 772 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Reports
- Acute Rupture of Subclavian Artery Pseudoaneurysm after Delayed Osteosynthesis of Clavicular Fracture: A Case Report
- Oog Jin Shon, Jee Hoon Kim, Kang Hyun Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(1):82-87. Published online January 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.1.82
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Subclavian vessels are well protected by muscles, fascia and sheaths, so vascular complications associated with clavicular fractures are rare. Pseudoaneurysms after clavicular fractures have been reported, and the occurrence or rupture of pseudoaneurysm has been reported rarely as a late complication. However, cases of pseudoaneurysm after rupture of the clavicular fracture following delayed osteosynthesis of the clavicular fracture have not been reported. A 58-year-old female that presented with a right clavicular shaft fracture obtained conservative treatment. Surgery was performed after 4 months because of non-union in the local medical center. After operation, rupture of the subclavian pseudoaneurysm occurred following osteosynthesis of the clavicular shaft fracture. We report this case here with a review of the literature.
- 413 View
- 0 Download

- Costoclavicular Syndrome Secondary to Nonunion of a Displaced Fracture of the Clavicle, Misdiagnosed as a Simple Muscle Strain: A Case Report
- Ho Seung Jeon, Haeng Kee Noh, Seo Goo Kang, Jong Min Kim, Seung Ju Jeon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(1):60-64. Published online January 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.1.60
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Thoracic outlet syndrome is a relatively common disease. However, costoclavicular syndrome as a condition secondary to nonunion of a displaced fracture of the clavicle is very rare. Most clavicular fractures in adults are united with no or minimal persistent symptoms. Also, symptomatic nonunion of a displaced fracture of the clavicle is rare. A 55-year-old male initially presented with persistent forearm pain after slip-down was initially diagnosed with simple muscle strain. However, he was given a delayed diagnosis of costoclavicular syndrome, caused by compression of the subclavian artery due to trauma in the fibrotic nonunion of the right clavicle without apparent symptoms. We obtained satisfactory results by surgical treatment. Here we report this case with a review of the literature.
- 336 View
- 0 Download

Original Articles
- Coracoclavicular Screw Fixation and Tension Band Wiring in Treatment of Distal Clavicle Fracture
- Dae Gyu Kwon, Tong Joo Lee, Kyung Ho Moon, Byoung Ki Shin, Min Su Woo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(1):1-7. Published online January 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to analyze the effectiveness of coracoclavicular screw fixation with tension band wiring in the treatment of displaced distal clavicle fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From October 2006 to December 2010, 18 patients with Neer type 2 displaced distal clavicle fracture were surgically treated. Fixation was performed, using coracoclavicular screw with tension band wiring. Radiographic and clinical evaluation was performed and the University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA) shoulder rating scale was employed for the assessment of shoulder joint function.
RESULTS
Osseous union was achieved approximately 9.5 weeks (8-11 weeks) in all patients. After the union, the screw and wire were removed under local anesthesia. All patients returned to the normal shoulder range of motion. Loosening of the screw was seen in two patients and breakage was seen in one patient. However, we could not observe the delayed union and complications, such as infection and refracture. All but one patient showed excellent results according to the UCLA shoulder score at one year after the operation.
CONCLUSION
Coracoclavicular screw fixation with tension band wiring in the treatment of displaced distal clavicle fractures is a clinically useful technique with good result and less complication.
- 478 View
- 1 Download

- Anatomical Reduction of All Fracture Fragments and Fixation Using Inter-Fragmentary Screw and Plate in Comminuted and Displaced Clavicle Mid-Shaft Fracture
- Kyoung Hwan Koh, Min Soo Shon, Seung Won Lee, Jong Ho Kim, Jae Chul Yoo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(4):300-304. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.4.300
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To report the treatment results of anatomical reduction of all fracture fragments and internal fixation using an inter-fragmentary screw and plate in displaced mid-shaft clavicle fracture with comminution.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between June 2005 and August 2011, 13 consecutive displaced clavicle fractures with comminution (Edinburgh classification IIB2) treated by anatomic reduction and internal fixation using inter-fragmentary screw and plate were retrospectively evaluated. There were 11 male and 2 female patients with a mean age of 37.4 years (15~55 years). The right clavicle was injured in 4 patients and the dominant arm was involved in 46%. The mean duration from trauma to surgery was 7.0 days. The cause of injury was a traffic accident in three, a fall in two, and sports activity or direct injury in eight patients. All of the fracture pieces were anatomically reduced and fixed with inter-fragmentary screws. An additional plate was applied to maintain and reinforce the reduction of the fracture. Radiographic assessments for the numbers of fragments and the amount of shortening and displacement were performed. To verify the fracture healing and determine the time from fracture surgery to union and complications, all of the radiographs taken after surgery were evaluated.
RESULTS
The number of fragments was 2 in 7 cases, 3 in 5 cases, and 6 in one case. The mean shortening of the clavicle was 1.1 cm (0.3~2.1 cm) and mean displacement between the main fragments was 2.6 cm (1.3~4.5 cm). The mean duration of follow-up was 16.5 months (8~26 months). Radiographic union was achieved in all patients with a mean time to union of 10.8 weeks (8~14 weeks). There were no complications including metal failure, nonunion, or infection.
CONCLUSION
Anatomical reduction of all the fracture fragments and fixation using inter-fragmentary screws in addition to the usual plate fixation showed good fracture healing in displaced clavicle fracture with comminution. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Additional fixation using a metal plate with bioresorbable screws and wires for robinson type 2B clavicle fracture
Woo Jin shin, Young Woo Chung, Seon Do Kim, Ki-Yong An
Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow.2020; 23(4): 205. CrossRef - Use of Composite Wiring on Surgical Treatments of Clavicle Shaft Fractures
Kyung Chul Kim, In Hyeok Rhyou, Ji Ho Lee, Kee Baek Ahn, Sung Chul Moon
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2016; 29(3): 185. CrossRef
- Additional fixation using a metal plate with bioresorbable screws and wires for robinson type 2B clavicle fracture
- 732 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Comparison of Plate Versus Threaded K-wire for Fixation of Midshaft Clavicular Fractures
- Young Jin Ko, Chul Hyun Park, Oog Jin Shon, Jae Sung Seo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(2):123-128. Published online April 30, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.2.123
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To compare clinical outcomes of the plate and threaded K-wire for fixation of midshaft clavicular fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From 2005 Jan to 2009 May, medical records of 18 patients who underwent open reduction and internal fixation with plate (group 1) and 13 others who underwent intramedullary fixation with threaded K-wire (group 2) were reviewed. The mean follow up periods were 21.9 and 18.9months. The Functional results were evaluated with The Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand (DASH) score and Constant shoulder score. The statistical evaluation was assessed with Paired T-test, Chi-square test.
RESULTS
The DASH score were 11.5+/-2.7 in group 1 and 12.4+/-4.3 in group 2. The constant shoulder score were 92.0+/-3.1 in group 1 and 87.1+/-2.8 in group 2. Length of surgical wound (cm) were 10.6+/-3.4 in group 1 and 4.8+/-1.5 in group 2. Postoperative pain and range of motion change were superior in group 1.
CONCLUSION
There was no significant difference between the two groups in functional and radiological results. But, there were patient's complaints about length of surgical wound in group 1 and hardware irritation in group 2. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comparison between Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis and Plate Fixation in the Treatment of Clavicle Midshaft Fracture
Seong-Ho Yoo, Suk-Woong Kang, Bu-Hwan Kim, Moo-Ho Song, Yeong-Joon Kim, Gyu-Taek Park, Chang-Hun Kwack
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2017; 52(1): 1. CrossRef - Plate fixation versus intramedullary fixation for midshaft clavicle fractures: Meta-analysis of complications and functional outcomes
Hao Xiao, Hengbo Gao, Tuokang Zheng, Jianhui Zhao, Yingping Tian
Journal of International Medical Research.2016; 44(2): 201. CrossRef - Meta-analysis of plate fixation versus intramedullary fixation for the treatment of mid-shaft clavicle fractures
Bing Zhang, Yanbin Zhu, Fei Zhang, Wei Chen, Ye Tian, Yingze Zhang
Scandinavian Journal of Trauma, Resuscitation and Emergency Medicine.2015;[Epub] CrossRef
- A Comparison between Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis and Plate Fixation in the Treatment of Clavicle Midshaft Fracture
- 570 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Complications of Hook-Plate Fixation for Distal Clavicle Fractures
- Su Han An, Hyung Chun Kim, Kwang Yeol Kim, Ji Hoon Lee, Seung Hyun Yoon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(1):38-45. Published online January 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.1.38
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To report on the complications of hook-plate fixation for distal clavicle fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Eighteen patients who underwent surgery for distal clavicle fracture with a hook-plate from April 2008 to April 2011 were enrolled with a minimum of 4 months follow-up. The reduction was qualified and evaluated according to the radiologic findings. We analyzed the results by UCLA score, Kona's functional evaluation, and VAS pain score.
RESULTS
By radiologic evaluation, 17 of 18 cases showed anatomical reduction and solid unions. Although satisfactory results were found in the clinical study as shown by the UCLA score, Kona's functional evaluation, and VAS pain score, complications arose in 7 cases, including osteolysis of the acromion in 2 cases, nonunion in 1 case, periprosthetic fracture in 2 cases, subacromial pain in 1 case, and skin irritation in 1 case. 2 cases of all required reoperation.
CONCLUSION
To reduce the complications of the hook-plate, a precise surgical technique and the choice of an appropriate size for the hook-plate are needed. We suggest that early removal of the plate is necessary to decrease the risk of subacromial impingement and erosion in hook-plate fixation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical outcomes of bending versus non-bending of the plate hook in acromioclavicular joint dislocation
Min Su Joo, Hoi Young Kwon, Jeong Woo Kim
Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow.2021; 24(4): 202. CrossRef - Surgical Treatment of Unstable Distal Clavicle Fractures: Comparison of Transacromial Pin Fixation and Hook Plate Fixation
Young Sung Kim, Ho Min Lee, Han Gil Jang
The Journal of the Korean Shoulder and Elbow Society.2013; 16(2): 123. CrossRef
- Clinical outcomes of bending versus non-bending of the plate hook in acromioclavicular joint dislocation
- 1,448 View
- 15 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Surgical Techniques for Percutaneous Reduction by Towel Clips and Percutaneous Intramedullary Fixation with Steinmann Pins for Clavicle Shaft Fractures
- Ki Do Hong, Jae Chun Sim, Sung Sik Ha, Tae Ho Kim, Jong Hyun Kim, Jong Seong Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(1):31-37. Published online January 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.1.31
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To report the clinical results of surgical treatment of clavicle shaft fracture by percutaneous reduction with towel clips and percutaneous intramedullary pin fixation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study reviewed the results of 80 cases of clavicle shaft fracture treated by percutaneous reduction with towel clips and percutaneous intramedullary pin fixation with Steinmann pins from January 2002 to August 2010, after follow-up for 12 months or more. We evaluated the clinical results, such as union time and complications.
RESULTS
Bone union was evident in all cases and the mean time for bone union to appear on radiological findings was 10.3 weeks. Using Kang's criteria, 78 of the 80 patients (97.5%) showed good results and there were no severe complications.
CONCLUSION
Percutaneous reduction with towel clips and the percutaneous intramedullary pin fixation method showed good results for treating clavicle shaft fracture. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Additional fixation using a metal plate with bioresorbable screws and wires for robinson type 2B clavicle fracture
Woo Jin shin, Young Woo Chung, Seon Do Kim, Ki-Yong An
Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow.2020; 23(4): 205. CrossRef - A Comparison between Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis and Plate Fixation in the Treatment of Clavicle Midshaft Fracture
Seong-Ho Yoo, Suk-Woong Kang, Bu-Hwan Kim, Moo-Ho Song, Yeong-Joon Kim, Gyu-Taek Park, Chang-Hun Kwack
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2017; 52(1): 1. CrossRef
- Additional fixation using a metal plate with bioresorbable screws and wires for robinson type 2B clavicle fracture
- 584 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Does Interfragmentary Cerclage Wire Fixation in Clavicle Shaft Fracture Interfere the Fracture Healing?
- Jae Kwang Yum, Yong Woon Shin, Hee Sung Lee, Jae Gu Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2011;24(2):138-143. Published online April 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.2.138
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
A technique of cerclage wire fixation in comminuted fracture of the clavicle shaft is thought to interfere the fracture healing, so authors studied radiographically and clinically about the cases of cerclage wiring of the fracture fragments with the plate and screws fixation in the comminuted fracture of the shaft of the clavicle.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
According to following inclusion criteria, total 18 patients (male: 15, female: 3) were investigated; Patients who visited hospital due to clavicle shaft comminuted fracture from February 2005 to April 2009, who underwent surgery utilizing more than 2 cerclage wire fixation for the fragments when open reduction and plate fixation were operated and who could be follow-up over one year. The duration for fracture union, functional outcome and complications were investigated retrospectively.
RESULTS
Radiological bone union was accomplished in average 13.3 weeks (12~16 weeks) and there was no complication such as nonunion, delayed union or infection. Range of motion of ipsilateral shoulder joint was recovered in all patients except one at the final follow-up.
CONCLUSION
The clinical and radiographical results of the plate and screws fixation with cerclage wiring of the fragments in comminuted clavicle shaft fracture showed that the cerclage wiring does not interfere the fracture healing, so authors think that this method is a good alternative operation if it is performed carefully to minimize soft tissue dissection. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surgical Management of Comminuted Midshaft Clavicle Fractures Using Reconstruction Plate and Circumferential Wiring: Does the Circumferential Wiring Interfere with the Bone Union?
Kyung-Tae Kim, Chung-Shik Shin, Young-Chul Park, Dong-hyun Kim, Min-Woo Kim
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2021; 56(3): 245. CrossRef - Supplementary Technique for Unstable Clavicle Shaft Fractures: Interfragmentary Wiring and Temporary Axial K-Wire Pinning
Jinmyoung Dan, Byung-Kook Kim, Ho-Jae Lee, Tae-Ho Kim, Young-Gun Kim
Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery.2018; 10(2): 142. CrossRef - Use of Composite Wiring on Surgical Treatments of Clavicle Shaft Fractures
Kyung Chul Kim, In Hyeok Rhyou, Ji Ho Lee, Kee Baek Ahn, Sung Chul Moon
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2016; 29(3): 185. CrossRef - TO EVALUATE THE SURGICAL OUTCOME OF NON-UNION CLAVICLE USING PLATE AND SLIVERS OF AUTOLOGOUS ILIAC CREST CORTICOCANCELLOUS BONE GRAFT
Mohammed Tauheed, Shashi Kumar Yalagach, Vivek Purushothaman, Anwar Shareef Kunnath K
Journal of Evidence Based Medicine and Healthcare.2016; 3(25): 1121. CrossRef - Anatomical Reduction of All Fracture Fragments and Fixation Using Inter-Fragmentary Screw and Plate in Comminuted and Displaced Clavicle Mid-Shaft Fracture
Kyoung Hwan Koh, Min Soo Shon, Seung Won Lee, Jong Ho Kim, Jae Chul Yoo
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2012; 25(4): 300. CrossRef
- Surgical Management of Comminuted Midshaft Clavicle Fractures Using Reconstruction Plate and Circumferential Wiring: Does the Circumferential Wiring Interfere with the Bone Union?
- 706 View
- 0 Download
- 5 Crossref

Case Report
- Simultaneous Fractures of the Ipsilateral Distal and Proximal Clavicle: Double Clavicle Fracture: A Case Report
- Kyoung Jun Park, Hoon Sang Sohn, Kyoung Young Baek
- J Korean Fract Soc 2011;24(1):92-95. Published online January 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.1.92
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Clavicular fracture is common injury in the upper extremity, but ipsilateral proximal, distal or middle-third clavicular fractures which occur simultaneously are an extremely rare. Seven cases have been reported in the English and Japanese literatures, but it has never been reported in Korea. We report a case of ipsilateral proximal and distal clavicular fracture caused by fall from height and describe its presumed mechanism, diagnosis, treatment with a review of literatures.
- 571 View
- 2 Download

Original Articles
- Comparison of Results of Tension Band Wire and Hook Plate in the Treatment of Unstable Fractures of the Distal Clavicle
- Chul Hyun Park, Oog Jin Shon, Jae Sung Seo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2011;24(1):55-59. Published online January 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.1.55
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To compare the clinical and radiological outcomes of two surgical methods with tension band wire and Hook plate for unstable distal clavicle fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty patients with type II distal clavicle fractures were evaluated, who were operated with tension band wire (Group I) and Hook plate (Group II) fixation, from June 2005 to June 2009, and could be followed-up for more than 1 year after operation. The reduction and union were evaluated by the immediate post-operative and final radiographs. The functional outcome was evaluated by Kona's system and Constant-Murley scoring system.
RESULTS
All 30 cases showed bony union. By Kona's functional evaluation, there were 16 cases with excellent and good results in Group I and 14 cases in Group II. The average Constant score was 88.3 (71~100) in Group I and 89.6 (72~100) in Group II, but there was no significant difference in both groups. As complications, there were 2 case with subacromial impingement, and 1 case showed subacromial erosion. There was no K-wire migration, deep infection and acromioclavicular joint arthritis.
CONCLUSION
Tension band and Hook plate fixation technique gave satisfactory clinical and radiological results in patients with type II distal clavicle fractures. These results suggest that tension band wire and Hook plate fixation technique seems to be an effective method for type II distal clavicle fracture. But we think thal early removal of plate is necessary due to risks for subacromial impingement and erosion in Hook plate fixation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hook Plate Fixation for Unstable Distal Clavicle Fractures: A Prospective Study
Kyung-Cheon Kim, Hyun-Dae Shin, Soo-Min Cha, Yoo-Sun Jeon
The Journal of the Korean Shoulder and Elbow Society.2011; 14(1): 6. CrossRef
- Hook Plate Fixation for Unstable Distal Clavicle Fractures: A Prospective Study
- 591 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Treatment of Distal Clavicle Fracture Using Hook Plate
- Su Han Ahn, Hyeong Jo Yoon, Kwang Yeol Kim, Hyung Chun Kim, In Yeol Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2011;24(1):48-54. Published online January 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.1.48
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the result of distal clavicle fracture treated by Hook plate (LCP clavicle hook plate, Synthes(R), Paoli, Switzerland).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
10 patients with distal clavicle fracture treated by Hook plate from April 2008 to March 2010 were analyzed. The average follow-up period was 10 (range 4 to 26) months. The reduction was qualified and evaluated according to the immediate post-operative, final radiographs. We analyze the result by UCLA score and Kona's functional evaluation.
RESULTS
By radiologic evaluation, all cases showed anatomical reduction and solid union. By Kona's functional evaluation, there are 7 cases with excellent results, 3 cases with good results. The UCLA score was average 33.3 (range 29 to 35) points followed by 6 excellent cases, 4 good cases. As complication, 1 case showed post-operative clavicle shaft fracture and 1 case showed acromial osteolysis on X-rays. We found no complications such as skin irritation, infection, loosening of screws, and plate failure.
CONCLUSION
The Hook plate fixation for distal clavicle fracture is considered effective method for satisfactory reduction and rigid fixation, a lower incidence of nonunion and excellent clinical result. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Locking Compression Plate Superior Anterior Clavicle Plate with Suture Augmentation and Hook Plate for Treatment of Distal Clavicle Fractures
Jun-Cheol Choi, Woo-Suk Song, Woo-Sung Kim, Jeong-Muk Kim, Chan-Woong Byun
Archives of Hand and Microsurgery.2017; 22(4): 247. CrossRef
- Comparison of Locking Compression Plate Superior Anterior Clavicle Plate with Suture Augmentation and Hook Plate for Treatment of Distal Clavicle Fractures
- 776 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Surgical Outcomes of Clavicle Lateral End Fractures Fixed with the Oblique T Locking Compession Plate
- Seung Oh Nam, Young Soo Byun, Dong Ju Shin, Jung Hoon Shin, Chung Yeol Lee, Tae Gyun Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2011;24(1):41-47. Published online January 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.1.41
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the surgical outcomes of the clavicle lateral end fracture fixed with an oblique T locking compression plate (LCP).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fourteen clavicle lateral end fractures were fixed with the oblique T-LCP and followed up for at least 1 year after the surgery. Thirteen cases were unstable Neer type II fractures and one case was nonunion of the Neer type I fracture. The mean age was 46 years of age (range, 26~70). In ten cases, augmenting sutures with the absorbable suture material were placed in the coraco-clavicular ligament and around the plate and the clavicle to improve the stability of fracture fixation. Autogenous iliac bone graft was done in four cases. The clinical outcomes were evaluated by using UCLA scoring system and KSS (Korean Shoulder Score).
RESULTS
The mean UCLA score was 33.5 and the mean KSS was 94.9. Average time of bone union was 11.9 weeks (range, 6~28), including 1 case with a delayed union. There was no complication such as loss of fixation or nonunion.
CONCLUSION
Fixation with the oblique T-LCP is a good option providing reliable functional results in clavicle lateral end fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Results of Hook Plate Fixation of Unstable Distal Clavicle Fractures
Hoon-Sang Sohn, Byung Chul Jo
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(4): 335. CrossRef
- Results of Hook Plate Fixation of Unstable Distal Clavicle Fractures
- 533 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Modified Spring Plate for Treatment of Unstable Distal Clavicle Fractures
- Sang Myung Lee, Il Jung Park, Hyung Min Kim, Jae Chul Park, Sung Gil Cho, Yoon Chung Kim, Seung Koo Rhee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2010;23(1):64-68. Published online January 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.1.64
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
Unstable distal clavicle fractures should be treated surgically but may be difficult in firm fixation because of small distal fragment. Although a variety of fixation methods have been currently used, none of the methods seem to be firm fixation and little pain. We present a new technique using a spring plate which was modified from one third tubular plate and report the early results.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Modified spring plate was made from one third tubular plate and the distal hole of the plate was cutting and sharpened by rasp. The sharp edge was bent just like an animal claw (C shape). Between May 2007 and June 2009, a total of six patients with distal clavicle fracture were treated using modified spring plate. A sling was applied in the immediate post operative period for six weeks and exercises were started immediately.
RESULTS
Union was achieved in all cases with excellent results without complication (mean Constant score, 96). All patients had returned to ordinary daily activities but mild limitation of abduction (150 degrees ) by seven weeks after surgery. After six months, the plate was removed.
CONCLUSION
The modified spring plate has provided stable fixation for unstable distal clavicle fixation without disturbance to the acromioclavicular joint, subacromial space, or rotator cuff.
- 333 View
- 1 Download

Case Report
- Clavicle Midshaft Fracture with Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation: A Case Report
- Chul Hyun Cho, Chul Hyung Kang, Soo Won Jung, Hyuk Jun Seo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(4):297-299. Published online October 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.4.297
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Clavicle fracture or acromioclavicular joint dislocation is common injury in the upper extremity. But ipsilateral clavicle midshaft fracture with acromioclavicular joint dislocation is a extremely rare. Seven cases has been reported in the English literature, but it has never been reported in Korea. We report a case of clavicle midshaft fracture with acromioclavicular joint dislocation caused by motor vehicle accident and describe its presumed mechanism, diagnosis, treatment with a review of literature.
- 392 View
- 4 Download

Original Article
- Double Tension Band Wire Fixation for Unstable Fracture of the Distal Clavicle
- Kyeong Seop Song, Hyung Gyu Kim, Byeong Mun Park, Jong Min Kim, Sung Hoon Jung, Bong Seok Yang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(1):24-29. Published online January 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.1.24
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the clinical results after operative treatment with the double tension band wire fixation in Neer type II and III distal clavicle fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Ten patients with type II and III distal clavicle fractures were evaluated, who operated with double tension band wire fixation technique, from Febrary 2007 to June 2008, and could be followed-up for more than 1 year after operation. Postoperative assessments were evaluated on plain x-ray, pain, and clinical finding according to the functional criteria by Kona et al.
RESULTS
Average duration from operation to fracture union was 8 weeks in all cases. There were 8 excellent and 2 good results. It was no other significant complications such as K-wire migration, breakage, infection, and AC joint arthritis.
CONCLUSION
Double tension band wire fixation technique seems to be an effective method for type II or III distal clavicle fracture with multiple compressive axis, without injury of the AC joint and loosening of the fixation.
- 382 View
- 1 Download

Case Report
- Bipolar Clavicular Dislocation: A Case Report
- Han Jun Lee, Jae Sung Lee, Young Bong Ko
- J Korean Fract Soc 2008;21(4):316-319. Published online October 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.4.316
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Bipolar clavicular dislocation is simultaneous dislocation of both poles of the clavicle (mainly an anterior dislocation of the sternoclavicular joint and a posterior dislocation of acromioclavicular joint) and rarely reported. We report a case of bipolar claviclular dislocation after a seat belt injury and describe its presumed mechanism and treatment with a review of literature.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Case of the Month #177: Bipolar Clavicular Dislocation: Radiologic Evaluation of a Rare Traumatic Injury
Michael P. Loreto, Dawn Pearce
Canadian Association of Radiologists Journal.2012; 63(2): 156. CrossRef - Clavicle Midshaft Fracture with Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation: A Case Report
Chul-Hyun Cho, Chul-Hyung Kang, Soo-Won Jung, Hyuk-Jun Seo
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(4): 297. CrossRef
- Case of the Month #177: Bipolar Clavicular Dislocation: Radiologic Evaluation of a Rare Traumatic Injury
- 542 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Crossref

Original Articles
- Comparison of Results in Two Operative Treatments for Clavicle Shaft Fractures in Adult: Comparison of Results between Open Reduction and Internal Fixation with the Plate and Percutaneous Reduction by Towel Clip and Intramedullary Fixation with Steinmann Pin
- Sung Sik Ha, Jae Chun Sim, Ki Do Hong, Jae Young Kim, Jung Ho Kang, Kwang Hee Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(3):233-238. Published online July 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.3.233
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the results between open reduction and internal fixation with the plate and percutaneous reduction by towel clip and intramedullary fixation with Steinmann pin for clavicle shaft fractures in adult.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We have studied the results in 33 cases with the plate, 35 cases with the Steinmann pin among total 68 cases of clavicle shaft fracture. The patients were followed up over a period of at least 12 months. The final postoperative outcome was analyzed with the clinical outcomes using Kang's criteria, radiological union time and operation time.
RESULTS
The clinical outcome that was good or excellent according to the Kang's criteria showed a distribution of 88% in the group using the plate with 29 cases out of total 33 cases, 91% in the group using the Steinmann pin with 32 cases out of total 35 cases. The mean radiological union time was 8.9 weeks in the group using the plate, 9.1 weeks in the group using Steinmann pin. The mean operation time was 72 minutes in the group using the plate, whereas was 18 minutes in the group using Steinmann pin.
CONCLUSION
In the treatment of adult clavicle shaft fracture, two groups did not show a significant statistical difference in clinical and radiological outcomes. However, the operation time and postoperative functional recovery was significantly shorter and faster in the group using Steinmann pin. Additionally economic and cosmetic aspect was more satisfactory in the group using Steinmann pin. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Anatomical Reduction of All Fracture Fragments and Fixation Using Inter-Fragmentary Screw and Plate in Comminuted and Displaced Clavicle Mid-Shaft Fracture
Kyoung Hwan Koh, Min Soo Shon, Seung Won Lee, Jong Ho Kim, Jae Chul Yoo
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2012; 25(4): 300. CrossRef - Does Interfragmentary Cerclage Wire Fixation in Clavicle Shaft Fracture Interfere the Fracture Healing?
Jae-Kwang Yum, Yong-Woon Shin, Hee-Sung Lee, Jae-Gu Park
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(2): 138. CrossRef
- Anatomical Reduction of All Fracture Fragments and Fixation Using Inter-Fragmentary Screw and Plate in Comminuted and Displaced Clavicle Mid-Shaft Fracture
- 656 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Operative Treatment in Midshaft Fractures of Clavicle using Reconstruction Plate and Interfragmentary PDS Suture
- Phil Hyun Chung, Suk Kang, Chung Soo Hwang, Jong Pil Kim, Young Sung Kim, Sung Pock Park, Jin Wook Chung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(3):335-339. Published online July 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.3.335
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We are reporting the result of comminuted midshaft fractures of clavicle treated by reconstruction plate fixation and PDS augmentation easily fixing butterfly fragments with minimal soft tissue dissection.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed 42 cases of operatively treated displaced comminuted midshaft fractures of clavicle at our hospital from March, 2001 to May 2004 whom were followed up for more than one year after the operation. According to Robinson classification, we grouped simple fractures as group A, and comminuted fractures as group B. Internal fixation using reconstruction plate has been chosen for type A fracture. Type B has been treated by reconstruction plate fixation with PDS augmentations. Shoulder function, union time and complications has been studied according to the fracture type retrospectively.
RESULTS
All cases had complete bone union with average union time of 8.6 weeks for type A and 8.9 weeks for type B. Weitzman functional evaluation did not show significant differences.
CONCLUSION
PDS augmentation in comminuted midshaft fracture of clavicle easily fix the butterfly fragments with least soft tissue damage and lessen the bone graft. Therefore it considered to be one of the available treatment methods for comminuted midshaft fracture of clavicle. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Does Interfragmentary Cerclage Wire Fixation in Clavicle Shaft Fracture Interfere the Fracture Healing?
Jae-Kwang Yum, Yong-Woon Shin, Hee-Sung Lee, Jae-Gu Park
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(2): 138. CrossRef
- Does Interfragmentary Cerclage Wire Fixation in Clavicle Shaft Fracture Interfere the Fracture Healing?
- 398 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- T Plate Fixation for Unstable Fracture of Distal Clavicle
- Ho Jung Kang, Kwan Kyu Park, Hong Kee Yoon, Hyung Keun Song, Soo Bong Hahn
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(3):329-334. Published online July 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.3.329
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To review clinical and radiological results after open reduction and internal fixation with T plate for unstable distal clavicle fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From July. 1999 to December 2002, nine patients with distal clavicle Neer type II fractures were treated by open reduction and internal fixation with T plate. The bony union was confirmed by plain radiography. The clinical results were analyzed according to the classification by Kona et al.
RESULTS
Average time to fracture union was 8 weeks in all cases. The functional results were as follows: excellent in 7 cases and good in 2 cases. Screw loosening occurred in one case, but bony union was achieved.
CONCLUSION
We recommend T plate fixation as another treatment method for unstable distal clavicle fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Usefulness of the Additional K-Wire Fixation and Suture for Reinforce the Treatment of Distal Clavicle Fracture Using Modified Tension Band Wiring
Seung-Bum Chae, Chang-Hyuk Choi, Dong-Young Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2016; 29(2): 107. CrossRef - Treatment of Distal Clavicle Fracture Using Hook Plate
Su-Han Ahn, Hyeong-Jo Yoon, Kwang-Yeol Kim, Hyung-Chun Kim, In-Yeol Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(1): 48. CrossRef - The Surgical Outcomes of Clavicle Lateral End Fractures Fixed with the Oblique T Locking Compession Plate
Seung-Oh Nam, Young-Soo Byun, Dong-Ju Shin, Jung-Hoon Shin, Chung-Yeol Lee, Tae-Gyun Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(1): 41. CrossRef - Results of Hook Plate Fixation of Unstable Distal Clavicle Fractures
Hoon-Sang Sohn, Byung Chul Jo
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(4): 335. CrossRef - Modified Spring Plate for Treatment of Unstable Distal Clavicle Fractures
Sang-Myung Lee, Il-Jung Park, Hyung-Min Kim, Jae-Chul Park, Sung-Gil Cho, Yoon-Chung Kim, Seung-Koo Rhee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(1): 64. CrossRef - Double Tension Band Wire Fixation for Unstable Fracture of the Distal Clavicle
Kyeong-Seop Song, Hyung-Gyu Kim, Byeong-Mun Park, Jong-Min Kim, Sung-Hoon Jung, Bong-Seok Yang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(1): 24. CrossRef
- Usefulness of the Additional K-Wire Fixation and Suture for Reinforce the Treatment of Distal Clavicle Fracture Using Modified Tension Band Wiring
- 468 View
- 0 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Clinical and Functional Result after Internal Fixation of Severely Displaced Floating Shoulder
- Sang Hun Ko, Chang Hyuk Choe, Sung Do Cho, Jae Sung Seo, Jong Oh Kim, Jaedu Yu, Sang Jin Shin, In Ho Jeon, Kwang Hwan Jung, Jong Keun Woo, Ji Young Jeong, Gwon Jae No
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(1):46-50. Published online January 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.1.46
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the follow-up result of 11 cases that were operated with internal fixation of scapular neck and internal fixation of clavicle or acromioclavicular dislocation for severely displaced floating shoulder which was high energy injury and unstable.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We examined the scapular neck fracture with clavicle fracture or acromioclavicular joint dislocation by multidisciplinary research from August 1997 to July 2004. The scapular neck fractures were operated in the case of translational displacement of more than 25 mm and angular displacement of more than 45 degrees with 3.5 mm reconstruction plate fixation and internal fixation for clavicle fracture or acromioclavicular joint perpormed simultaneously. And we evaluated 11 cases that can be followed up for more than 9 months.
RESULTS
We achieved bony union in all cases. In ASES functional score, we got average 89.2 (75~95) points. In Rowe functional score, we got average 89.1 (75~100) points. In complication, there was external rotation weakness in 1 case.
CONCLUSION
In severely displaced floating shoulder due to high energy injury, we got good clinical and functional result after internal fixation for scapular neck and clavicle or acromioclavicular joint.
- 303 View
- 0 Download

- Tension Band Fixation for Type II Fracture of the Distal Clavicle
- Jin Young Park, Joong Bae Seo, Myung Ho Kim, Je Wook Yu
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(4):421-425. Published online October 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.4.421
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the efficacy of the tension band wire fixation for type II distal clavicle fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty one patients with type II distal clavicle fractures were evaluated, who were operated with tension band fixation technique with sparing AC joint, from May 2000 to December 2003, and could be followed-up for more than 1 year after operation. Average age at injury is 40.7 years old (14~73). 13 cases were males and 8 were females. And 16 cases were classified as type IIa and 5 cases as type IIb. Judgement of union was based on plain x-ray and clinical finding and postoperative assessment was evaluated on ASES and Constant scoring system.
RESULTS
Outcomes in all patients showed more than good, average ASES score was 96.1 (88~98) and Constant score was 93.1 (82~100). Radiologic union was achieved at 11.7 (6~16) weeks postoperatively. One patient suffered from non union, and there was no other significant complications such as K-wire migrations, breakage, infection, and AC joint arthritis.
CONCLUSION
Tension band fixation technique for type II distal clavicle fracture seems to be a useful and effective method, which is relatively simple and provides rigid fixation without violating the AC joint. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Results of Tension Band Wire and Hook Plate in the Treatment of Unstable Fractures of the Distal Clavicle
Chul-Hyun Park, Oog-Jin Shon, Jae-Sung Seo
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(1): 55. CrossRef - Modified Spring Plate for Treatment of Unstable Distal Clavicle Fractures
Sang-Myung Lee, Il-Jung Park, Hyung-Min Kim, Jae-Chul Park, Sung-Gil Cho, Yoon-Chung Kim, Seung-Koo Rhee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(1): 64. CrossRef
- Comparison of Results of Tension Band Wire and Hook Plate in the Treatment of Unstable Fractures of the Distal Clavicle
- 614 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The Operative Treatment of Mid-Shaft Clavicular Nonunions: Intramedullary Fixation with Threaded Steinmann Pin and Bone Grafting
- Jeong Ro Yoon, Hak Jun Kim, Taik Seon Kim, Haeng Kee Noh
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(4):415-420. Published online October 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.4.415
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the clinical and radiological results of the treatment of mid-shaft clavicular nonunions using intramedullary fixation with threaded Steinmann pin and bone grafting. MATERIAL AND METHODS: In 16 patients treated with intramedullary fixation of threaded Steinmann pin and autogenous iliac bone grafting for the mid-shaft clavicular nonunions, 10 patients with follow-up over 1 year were investigated. All patients (10 clavicle fractures) underwent conservative treatment initially. The average age of patients was 56 years old (range, 18~70 years old). Eight cases were atrophic nonunions, two hypertrophic. A clinical assessment was evaluated postoperatively after 5 months according to the evaluation method of Kona et al.
RESULTS
According to the evaluation method of Kona et al, four cases achieved excellent results, five cases good, and one case achieved a fair result. The average period until bony union was 9 weeks (range, 7~12.5 weeks) without infection, pin migration or breakage. One case showed skin irritation by lateral margin of Steinmann pin, which was subsided by pin removal after bony union.
CONCLUSION
We obtained satisfactory results and have concluded that intramedullary fixation with threaded Steinmann pin and bone grafting could appropriately treat nonunions of the mid-clavicular fracture occurred after conservative treatment, because it minimizes soft tissue injury, gets relatively stable fixation and early ROM, predicts early bone union, facilitates pin removal under local anesthesia.
- 308 View
- 1 Download

- Internal Fixation of Clavicle Lateral and Fracture with Mini T-plate
- Byung Woo Ahn, Jong Ho Yoon, Chong Kwan Kim, Sung Won Chung, Young Il Kwan, Young Ho Lee, Chan Wan Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(4):410-414. Published online October 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.4.410
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the effectiveness of a mini T-plate fixation in clavicle lateral end fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed eleven cases of calvicle lateral end fracture which were treated with open reduction and internal fixion with mini T-plate from May 2000 to December 2004. The follow up period was 12 months minimum. The radiologic result, pain and shoulder function were evaluated by the ASES shoulder score.
RESULTS
All cases showed satisfactory results. Seven cases (63%) were excellent, and four (37%) cases were good. There were no fair or poor results. All cases showed radiologic union by the fifteenth week. No complications such as metal breakage, limited motion, infections were seen.
CONCLUSION
This study demonstrates that using a mini T-plate fixation which is easy and induces no injury of acromiocalvicular joint, contributes to provide stable fixation in clavicle lateral end fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Tension Band Wiring for Distal Clavicle Fracture: Radiologic Analysis and Clinical Outcome
Seong Cheol Moon, Chul Hee Lee, Jong Hoon Baek, Nam Su Cho, Yong Girl Rhee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2014; 27(2): 127. CrossRef - The Surgical Outcomes of Clavicle Lateral End Fractures Fixed with the Oblique T Locking Compession Plate
Seung-Oh Nam, Young-Soo Byun, Dong-Ju Shin, Jung-Hoon Shin, Chung-Yeol Lee, Tae-Gyun Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(1): 41. CrossRef - Comparison of Results of Tension Band Wire and Hook Plate in the Treatment of Unstable Fractures of the Distal Clavicle
Chul-Hyun Park, Oog-Jin Shon, Jae-Sung Seo
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(1): 55. CrossRef
- Tension Band Wiring for Distal Clavicle Fracture: Radiologic Analysis and Clinical Outcome
- 452 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Intramedullary Fixation in the Fracture of the Shaft of the Clavicle by Threaded Kirschner Wire
- Jae Kwang Yum, Se Jin Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(2):89-92. Published online April 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.2.89
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate and report the clinical result of the intramedullary fixation by threaded Kirschner wire in the clavicle shaft fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From May 2000 to April 2004, twenty patients who had the fracture of the shaft of the clavicle were treated by the intramedullary fixation with threaded Kirschner wire. Thirteen patients were followed up and the clinical and radiological results were analyzed.
RESULTS
All of the cases had satisfactory fracture union but there were four cases of skin irritation signs by the tip of threaded Kirschner wire. In one case, the Kirschner wire was bent at the fracture site with malunion. According to the clinical scoring system of Kang et al, eight cases were excellent and five cases were good.
CONCLUSION
Authors think that intramedullary fixation with threaded Kirschner wire in the fracture of the shaft of the clavicle is one of a good operative method because of small operative incision, easy operative method, satisfactory fracture union and easy removability of the implant.
- 325 View
- 2 Download

- Conservative Treatment of the Displaced Clavicular Shaft Fracture in Multiple Injury
- Hyun Dae Shin, Kwang Jin Rhee, Young Mo Kim, Se Min Woo, Ho Sup Song
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(4):333-337. Published online October 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.4.333
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analyse the comparative clinical results between adults with multiple injury including the clavicular shaft fracture and only clavicular shaft fracture who had supportive care through retrospective aspect.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We had 48 adult patients in this hospital with simple fracture and multiple injury including the clavicular shaft whom we were able to evaluate at least more than a year. 12 of 48 patients were with only clavicular shaft fracture and the rest of them were with multiple injury. We classified patients into two groups those who had fracture with displacement for group A (A1 for the cases with over 50% of fracture surface contact rate and A2 for less than 50% from the images of simple X-ray) and those who had comminuted fracture for B. We compared the time of bone union, nonunion rate of only clavicular fractures and multiple injury, clinical results for patients who had supportive care with retrospective aspect.
RESULTS
A1 (7 cases), A2 (4 cases), B (1 case) were prevalent in the group of only clavicular shaft fracture and A1 (8 cases) and A2 (16 cases) and B (12 cases) were prevalent in the group of multiple injury. For the cases with supportive care, we could find 1 nonunion case (8%) and 11 union cases on average 2.91 months in the group of only clavicular shaft fracture and 7 nonunion cases (19%) and 29 union cases on average 3.58 months in the group of multiple injury. The best clinical results had occurred in 8 cases (67%) of only clavicular shaft fracture group and 19 cases (53%) of multiple injury group. We could find out the union from all 8 nonunion cases that took operation afterward.
CONCLUSION
Although the choice of treatment of clavicular fracture is supportive care, but multiple injury including the clavicular fracture is a high-energy injury, so the possibility of comminuted and displacement is high, so that nonunion rate is high. The possibility of early surgery must be considered seriously.
- 328 View
- 0 Download

- Intramedullary Fixation of Clavicle Fracture Percutaneously Reduced By Towel Clip
- Ki Do Hong, Sung Sik Ha, Nam Sik Chung, Jae Cheon Sim, Gyoung Ho Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(4):328-332. Published online October 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.4.328
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To investigate the utility of surgical treatment of clavicle shaft fracture using a percutaneous towel clip reduction and intramedullary fixation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study was conducted for total 16 cases of patients who had no neurovascular injury and a few comminuted bone fragment among patients with clavicle shaft fracture from January 2002 to July 2003. The method of operation was percutaneous towel clip reduction and intramedullary fixation. The clinical and radiological results were evaluated.
RESULTS
Radiologically, 15 cases showed bone unions and the average time was 9.1 weeks. According to Kang's criteria clinically, there were 14 cases which were more than an excellence. One case substituted open reduction and nailing fixation due to a medial migration of K-wire and re- displacement of fracture even in 1 week. However, there wasn't any other major complication.
CONCLUSION
Due to its having no additional injury to soft tissues, no scar formations, and its short operation time, percutaneous towel clip reduction and intramedullary fixation will be very useful as one of the treatments of clavicular shaft fracture if it follows correct surgical indications. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Results in Two Operative Treatments for Clavicle Shaft Fractures in Adult: Comparison of Results between Open Reduction and Internal Fixation with the Plate and Percutaneous Reduction by Towel Clip and Intramedullary Fixation with Steinmann
Sung-Sik Ha, Jae-Chun Sim, Ki-Do Hong, Jae-Young Kim, Jung-Ho Kang, Kwang-Hee Park
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2007; 20(3): 233. CrossRef
- Comparison of Results in Two Operative Treatments for Clavicle Shaft Fractures in Adult: Comparison of Results between Open Reduction and Internal Fixation with the Plate and Percutaneous Reduction by Towel Clip and Intramedullary Fixation with Steinmann
- 829 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Clavicle Fracture in Newborn
- Kyeong Seop Song, Byeong Mun Park, Young Hun Kang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(1):55-58. Published online January 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.1.55
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to identify the incidence of clavicle fracture in birth trauma associated with delivery, fetal presentation, birth weight and to identify the difference of the prognosis of clavicle fracture when immobilization was performed or not.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Among the 12,738 live births from March 1996 to December 2000, we reveiwed retrospectively the medical records and radiographs of 39 cases of clavicle fracture which were followed for more than 6 months. Statistical analysis was measured P-value. Except 11 cases that diagnosis was delayed, 27 cases were treated with figure of 8-bandage, and 1 case, which was combined with humerus fracture, was treated with long arm cast.
RESULTS
Among 39 cases infants of clavicle fracture, 36 cases (0.57%) were delivered through vaginal delivery, 3 cases (0.04%) through ceasarean section. Fetal presentations were cephalic presentation in 29 cases, shoulder dystocia in 8 cases, breech presentation in 2 cases. The mean birth weight was 3.8 kg, the high prevalence (8.5%) was identified on large birth weight infants more than 4 kg (p<0.05). The fracture site was proximal portion in 12 cases, middle portion in 27 cases and right clavicle in 24 cases, left clavicle in 13 cases and both clavicle in 1 case. The combined injuries were the brachial plexus palsy (2 cases), skull fracture (1 case) and cephalhematoma (1 case). Finally all cases of clavicle fracture were shown radiographically bony union within 3 weeks.
CONCLUSION
The newborn clavicle fractures were remarkably low incidence in cesarean section delivery and were easily neglected, and were detected accidentally on simple chest X-ray that was performed for upper respiratory infection. As a conclusion, it is necessary of screening test through careful physical examination and X-ray interpretation.
- 484 View
- 9 Download

- Operative Treatment of the Clavicular Fracture with Cannulated Screw
- Byung Jik Kim, Suk Kyu Choo, Jin Hwan Kim, Sang Min Lee, Dong Soo Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(4):555-562. Published online October 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.4.555
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To investigate the utility of cannulated screw in operative treatment of the clavicular fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From December 1999 to December 2002, 23 patients with clavicular fracture were underwent operative treatment with cannulated screw. Their mean age was 40.1 years and the sites of fracture were 16 cases in middle 1/3, 7 cases in lateral 1/3, 12 cases were comminnuted fracture. The clinical and radiological results were evaluated.
RESULTS
According to the Kang's criteria, the clinical results were excellent in 18 cases (78.3%), good in 4 cases (17.4%) and fair in 1 case. Radiologically, all cases showed bone union and the average time was 7.9 weeks. Complications such as infection, nonunion, metal failure has not been observed.
CONCLUSION
Open reduction and internal fixation with cannulated screw could be considered as an alternative method of treatment in clavicular fracture, when indications for primary surgical treatment are presents.
- 335 View
- 0 Download

Case Report
- Distal Clavicle Fracture in Adolescence Mimicking Type IV Acromioclavicular Joint Injury
- Tae Woo Park, Sung Do Cho, Chae Chil Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(2):299-303. Published online April 30, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.2.299
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Distal clavicle fracture in children may mimic acromioclavicular joint separation, but have very different prognosis and treatment. We are reporting two cases of distal clavicle fracture in adolescence mimicking type IV acromioclavicular injury. This report demonstrates the importance of shoulder axillary view, computerized tomography as well as physical examination on diagnosis of the distal clavicle fracture in adolescence.
- 363 View
- 2 Download

Original Articles
- Delayed Brachial Plexus Palsy due to Clavicular Fracture: A Case Report
- Woo Suk Lee, Whan Yong Chung, Taek Soo Jeon, Yong Sang Kim, Nam Hyun Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(2):230-234. Published online April 30, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.2.230
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The brachial plexus palsies secondary to nonunion of the clavicle fracture are extremely rare. The nonunions are hypertrophic and usually in the middle third of the clavicle. Hypertrophic callus produced during healing process will cause a compression of the neurovascular bundle. This lesion requires operative treatment for decompression of the brachial plexus and internal fixation of nonunion. We present a case of delayed brachial plexus palsy due to nonunion and excessive callus formation of a clavicular fracture.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Progressive Brachial Plexus Palsy after Fixation of Clavicle Shaft Nonunion: A Case Report
Hong-Ki Jin, Ki Bong Park, Hyung Lae Cho, Jung-Il Kang, Wan Seok Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2019; 32(2): 97. CrossRef
- Progressive Brachial Plexus Palsy after Fixation of Clavicle Shaft Nonunion: A Case Report
- 470 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Operative Treatment of Nonunions of Midshaft Clavicular Fractures: Reconstruction Plate Fixation and Bone Grafting
- Young Soo Byun, Chan Hoon Yoo, Hyug Su An, Seong Gun Moon, Dong Ju Shin, Jun Woo Park
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(2):222-229. Published online April 30, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.2.222
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to present our experience with open reduction, 3.5-mm reconstruction plate fixation, bone-grafting, and postoperative early mobilization for nonunions of midshaft clavicular fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sixteen patients were treated operatively for nonunions of the midshaft of the clavicle from 1997 to 2001. Ten nonunions were atrophic and six were hypertrophic. Nonunion had been present for an average of 6.5 months. The operative technique included removing the fibrous tissue from the nonunion site and opening the medullary canal, reduction of the fracture and fixation with a 3.5-mm reconstruction plate, and bone-grafting. Postoperative mobilization started within one week.
RESULTS
The average duration of follow-up was 22.0 months. All fractures were united in an average of 10.0 weeks. All patients had full range of motion of the ipsilateral shoulder, but 3 out of 6 patients who were more than 50 years old complained occasional pain in the ipsilateral shoulder at the final follow-up examination. There were no major complications of postoperative infection, metal failure of the plate, loss of fixation, nonunion, and refracture after removal of the implant.
CONCLUSION
The technique of open reduction, reconstruction plate fixation, and bone-grafting is a safe and reliable method to allow early rehabilitation by stable fixation and to predict a high rate of union for nonunions of midshaft clavicular fractures.
- 320 View
- 0 Download

- Treatment of Distal Clavicle Type II Fracture using K-Wires and Tension Band Wiring
- Whan Yong Chung, Woo Suk Lee, Taek Soo Jeon, Dae Hwan Kim, Kwang Kyoon Kim, Jae Woo Lim
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(2):215-221. Published online April 30, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.2.215
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This is a retrospective study to analyze the clinical results of the usefulness of K-wires and tension band wiring that fix the fracture fragment directly without passing the acromioclavicular joint in distal clacivle type II fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From May 2000 to May 2001, eleven patients with distal clavicle type II fracture were treated by open reduction and internal fixation with K-wires and tension band wiring. The clinical results were analyzed according to modified shoulder rating scale for distal clavicle freacture. Radiological union, complication, and range of motion of the shoulder were assessed.
RESULTS
All fractures were united at 10 weeks (8~12 weeks) in average. Finally, full range of motion of the shoulder joint was achieved in all patients. No complication was found and the modified shoulder rating scale for distal clavicle fracture were as follows: excellent 9 and good 2.
CONCLUSION
K-wires and tension band wiring can be a good treatment method for distal clavicle type II fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Tension Band Wiring for Distal Clavicle Fracture: Radiologic Analysis and Clinical Outcome
Seong Cheol Moon, Chul Hee Lee, Jong Hoon Baek, Nam Su Cho, Yong Girl Rhee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2014; 27(2): 127. CrossRef
- Tension Band Wiring for Distal Clavicle Fracture: Radiologic Analysis and Clinical Outcome
- 624 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Internal fixation with K-wires for the clavicular shaft fractures in young women
- Do Young Kim, Yong Wook Park, Gun Il Im, Chang Kyun Lim, Sang Soo Lee, Hyun Chul Park
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(4):545-550. Published online October 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.4.545
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To know the advantages and disadvantages of this procedure by analyzing the results of internal fixation with K-wires for clavicular shaft fractures in young women.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twelve patients were followed for more than 1 year after the operation. All patients were female and average age was 28 years with average follow-up of 14 months. All cases were displaced fractures of the middle third with tenting of the skin and 2 cases were type 1 open fractures. After the operation, we investigated time to union, changes of K-wire, scar and disadvantages periodically.
RESULTS
There was no nonunion and time to union averaged 11.8 weeks. Migration and bending of the K-wires occured in one case. The length of surgical scar was about 4cm and the K-wires were easily removed under local anesthesia. But all patients complained of frequent radiographic evaluation, relatively long period of immobilization and irritation of the K-wires on medial part of the clavicle.
CONCLUSION
We think that internal fixation with the K-wires is one of the effective treatment options for the clavicular shaft fractures in young women.
- 270 View
- 0 Download

- The Cause of the Nonunion of the Mid-clavicle Fractures
- Jung Ro Yoon, Jae Ik Shim, Taek Seon Kim, Sung Jong Lee, Young Bae Kim, Hack Jun Kim, Kuk Whan Ahn, Jae Young Chang, Myung Pyo Hong
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(4):538-544. Published online October 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.4.538
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
Because the prognosis of the mid 1/3 clavicle fracture is good, the conservative treatment with a figure of 8 bandage is the gold standard and the nonunions are rare.However, recently surgical treatment is recommended when the shortening and displacement is severe because of the high nonunion rate and the poor clinical result. This study was undertaken to evaluate that the shortening and displacement at fracture site are associated with the development of nonunion.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We analysed the 194 fractures of mid 1/3 clavicle in adults which had been treated conservatively from February 1993 to January 2002 and did the retrospective study. Of these, 78cases were originally in the middle third of the clavicle and had been completely displaced. We reviewed 63 of these cases. The shortening and displacement at the fracture site was measured on the initial roentgenogram. And the analysis of the patients 'chart was done for another predisposing nonunion factors. Nonunion and delayed union are considered to be present when there has been little or no progression of clinical or radiographic healing at a minimum of 4 months after injury.
RESULTS
15 of the 63cases had developed nonunion.. The average 8.6mm(2mm-17mm) shortening and average 9.7mm(2-22mm) in the union patients. The average 14.5mm(3mm-37mm) shortening and average 17.3mm(4-25mm) in the nonunion patients. We found that initial shortening > or =1 8 m m ( Fisher's exact test, p <0.01) and initial displacement > or =16mm(Chi-square test, p <0.01) at the fracture site were siinificantly associated with the development of nonunion.
CONCLUSION
The conservative treatment with figure-8-bandage is the gold standard in the clavicle middle one third fracture. However, the nonunion is commonly occurs in the cases of more of severely shortened and displaced fractures. If there are no signs of callus formation and the patient complains of pain after several weeks, osteosynthesis should be considered.
- 349 View
- 0 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


