Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 32(1); 2019 > Article
- Original Article Surgical Results of Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Fixation in the Treatment of Clavicle Shaft Fracture
- Seong Ho Yoo, Suk Woong Kang, Jae Seung Seo
-
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma 2019;32(1):21-26.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.1.21
Published online: January 31, 2019
2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea. redmaniak@naver.com
- 995 Views
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
Abstract
PURPOSE
This study analyzed the results of the midclavicle fracture treatment using the minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) technique in a retrospective manner.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between March 2013 and March 2017, this study analyzed 40 patients who received MIPO surgery. Excluding 1 patient who underwent surgery on another body part injury, and 4 patients who were lost to follow-up over 1 year, 40 patients were analyzed for their operation time, bone union, functional American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons score, scar lengths, pain relief (visual analogue scale), and complications.
RESULTS
All patients over a 1 year of follow-up achieved bone union, and American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons score 97.6 (94–100) on their shoulder functional scores. Their average operation time was 42.7 minutes, and the average scar length was 6.1 cm. Eighteen patients successfully received metal removal using the previous scar without additional incision. The clavicle length was similar in the normal and operated group.
CONCLUSION
Despite its small sample size, clavicle fixation using the MIPO technique can be considered an effective treatment because of its limited number of complications, such as nonunion and rotational angulations.
Published online Jan 25, 2019.
https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.1.21
Surgical Results of Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Fixation in the Treatment of Clavicle Shaft Fracture
Abstract
Purpose
This study analyzed the results of the midclavicle fracture treatment using the minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) technique in a retrospective manner.
Materials and Methods
Between March 2013 and March 2017, this study analyzed 40 patients who received MIPO surgery. Excluding 1 patient who underwent surgery on another body part injury, and 4 patients who were lost to follow-up over 1 year, 40 patients were analyzed for their operation time, bone union, functional American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons score, scar lengths, pain relief (visual analogue scale), and complications.
Results
All patients over a 1 year of follow-up achieved bone union, and American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons score 97.6 (94–100) on their shoulder functional scores. Their average operation time was 42.7 minutes, and the average scar length was 6.1 cm. Eighteen patients successfully received metal removal using the previous scar without additional incision. The clavicle length was similar in the normal and operated group.
Conclusion
Despite its small sample size, clavicle fixation using the MIPO technique can be considered an effective treatment because of its limited number of complications, such as nonunion and rotational angulations.
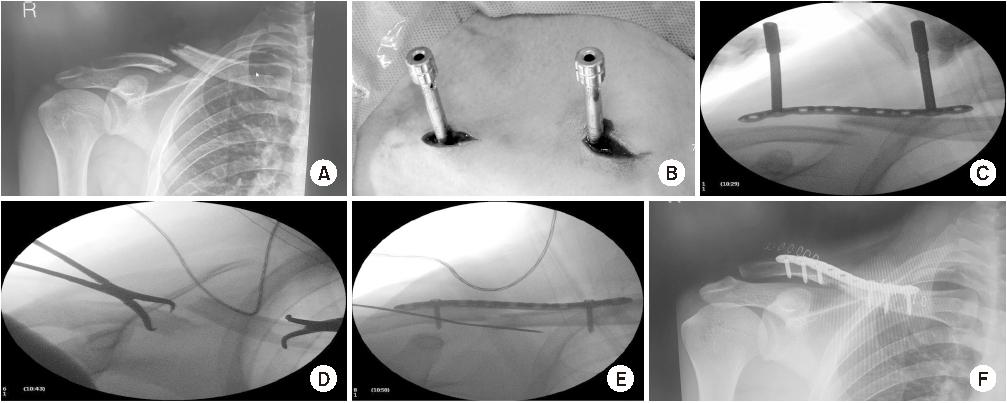
Fig. 1
(A) Preoperative radiography. (B) Plate was slid through the submuscular tunnel. (C) During operation, the anteroposterior view was checked to prevent fracture distraction. (D) Check axial view for preventing anteroposterior translation. (E) Temporary fixation by K-wire and screw fixation. (F) Postoperative radiography.
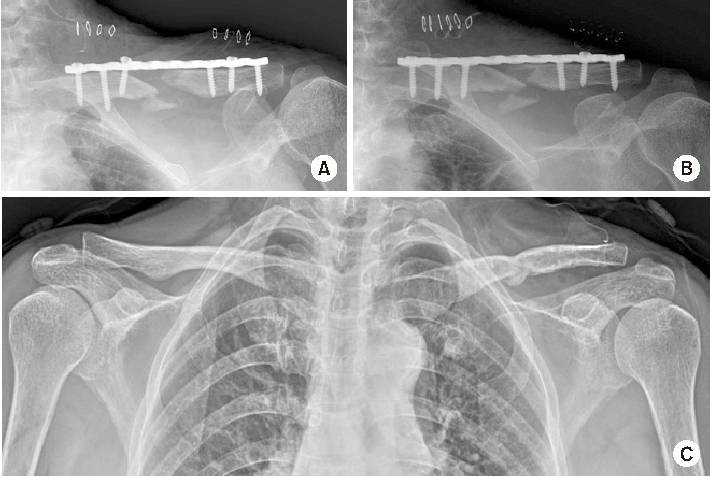
Fig. 2
(A) Postoperative day one, failure of reduction. (B) Reoperation for adequate reduction. (C) Metal removal after 1 year.
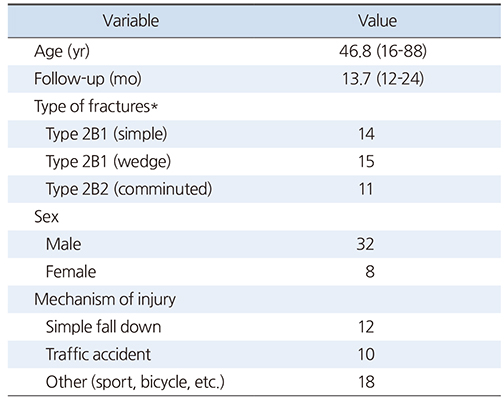
Table 1
Demographic Data and Injury Details of the 40 Patients
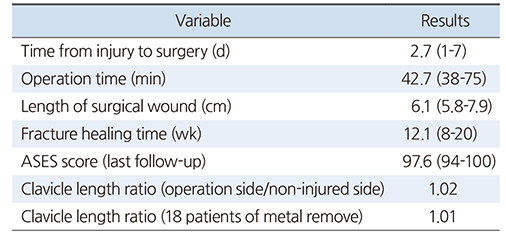
Table 2
Surgical Results of the Patients
Financial support:None.
Conflict of interests:None.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS


 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite

