Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 24(2); 2011 > Article
-
Original Article
- Does Interfragmentary Cerclage Wire Fixation in Clavicle Shaft Fracture Interfere the Fracture Healing?
- Jae-Kwang Yum, M.D., Ph.D., Yong-Woon Shin, M.D., Hee-Sung Lee, M.D., Jae-Gu Park, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2011;24(2):138-143.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.2.138
Published online: April 19, 2011
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Yong-Woon Shin, M.D. Department of Orthopedic surgery, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, 761-1, Sanggye 7-dong, Nowon-gu, Seoul 139-707, Korea. Tel: 82-2-950-1032, Fax: 82-2-934-6342, woonysos@hanmail.net
• Received: November 22, 2010 • Revised: January 6, 2011 • Accepted: March 4, 2011
Copyright © 2011 The Korean Fracture Society
- 649 Views
- 0 Download
- 5 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- A technique of cerclage wire fixation in comminuted fracture of the clavicle shaft is thought to interfere the fracture healing, so authors studied radiographically and clinically about the cases of cerclage wiring of the fracture fragments with the plate and screws fixation in the comminuted fracture of the shaft of the clavicle.
-
Materials and Methods
- According to following inclusion criteria, total 18 patients (male: 15, female: 3) were investigated; Patients who visited hospital due to clavicle shaft comminuted fracture from February 2005 to April 2009, who underwent surgery utilizing more than 2 cerclage wire fixation for the fragments when open reduction and plate fixation were operated and who could be follow-up over one year. The duration for fracture union, functional outcome and complications were investigated retrospectively.
-
Results
- Radiological bone union was accomplished in average 13.3 weeks (12~16 weeks) and there was no complication such as nonunion, delayed union or infection. Range of motion of ipsilateral shoulder joint was recovered in all patients except one at the final follow-up.
-
Conclusion
- The clinical and radiographical results of the plate and screws fixation with cerclage wiring of the fragments in comminuted clavicle shaft fracture showed that the cerclage wiring does not interfere the fracture healing, so authors think that this method is a good alternative operation if it is performed carefully to minimize soft tissue dissection.
- 1. Altamimi SA, McKee MD. Canadian Orthopaedic Trauma Society. Nonoperative treatment compared with plate fixation of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. Surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2008;90:Suppl 2. (Pt 1):1-8.
- 2. Andermahr J, Jubel A, Elsner A, et al. Anatomy of the clavicle and the intramedullary nailing of midclavicular fractures. Clin Anat, 2007;20:48-56.Article
- 3. Baek DH, Sohn JM, Jahng J, Kim HK, Ha NK, Lim KS. Comparison of results between conservative treatment and operative treatment for clavicle fractures in adults. J Korean Orthop Assoc, 2000;35:77-82.ArticlePDF
- 4. Charnley J. The closed treatment of common fractures, 1961;3rd ed. Edinburgh and London, E. & S. Livingstone. 112-115.
- 5. Chung PH, Kang S, Hwang CS, et al. Operative treatment in midshaft fractures of clavicle using reconstruction plate and interfragmentary PDS suture. J Korean Fract Soc, 2006;19:335-339.Article
- 6. Coupe BD, Wimhurst JA, Indar R, Calder DA, Patel AD. A new approach for plate fixation of midshaft clavicular fractures. Injury, 2005;36:1166-1171.Article
- 7. Golish SR, Oliviero JA, Francke EI, Miller MD. A biomechanical study of plate versus intramedullary devices for midshaft clavicle fixation. J Orthop Surg Res, 2008;3:28. ArticlePDF
- 8. Ha SS, Sim JC, Hong KD, Kim JY, Kang JH, Park KH. Comparison of results in two operative treatments for clavicle shaft fractures in adult: comparison of results between open reduction and internal fixation with the plate and percutaneous reduction by towel clip and intramedullary fixation with steinmann. J Korean Fract Soc, 2007;20:233-238.Article
- 9. Huang JI, Toogood P, Chen MR, Wilber JH, Cooperman DR. Clavicular anatomy and the applicability of precontoured plates. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2007;89:2260-2265.Article
- 10. Kang KS, Ahn JI, Oh HY, Kang YS, Lee SJ. Clinical study of clavicle fracture. J Korean Orthop Assoc, 1984;19:367-372.ArticlePDF
- 11. Kim BH, Im JI, Yim UK, Kim JJ. Operative treatment of clavicle fracture. J Korean Soc Fract, 1998;11:658-664.Article
- 12. Kim IG, Kim JH, Hwang R, Hong YI. Operative treatment with the reconstruction plate for the displaced clavicle shaft fracture of adults. J Korean Soc Fract, 2000;13:941-947.Article
- 13. Kim W, McKee MD. Management of acute clavicle fractures. Orthop Clin North Am, 2008;39:491-505.Article
- 14. King GJ, Richards RR, Zuckerman JD, et al. A standardized method for assessment of elbow function. Research Committee, American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons. J Shoulder Elbow Surg, 1999;8:351-354.
- 15. Manske DJ, Szabo RM. The operative treatment of mid-shaft clavicular non-unions. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1985;67:1367-1371.Article
- 16. Neer CS 2nd. Nonunion of the clavicle. J Am Med Assoc, 1960;172:1006-1011.Article
- 17. Nowak J, Holgersson M, Larsson S. Sequelae from clavicular fractures are common: a prospective study of 222 patients. Acta Orthop, 2005;76:496-502.
- 18. Rhinelander FW. The normal microcirculation of diaphyseal cortex and its response to fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1968;50:784-800.Article
- 19. Robinson CM. Fractures of the clavicle in the adult. Epidemiology and classification. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1998;80:476-484.
- 20. Shen WJ, Liu TJ, Shen YS. Plate fixation of fresh displaced midshaft clavicle fractures. Injury, 1999;30:497-500.Article
- 21. Zenni EJ Jr, Krieg JK, Rosen MJ. Open reduction and internal fixation of clavicular fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1981;63:147-151.Article
REFERENCES
Fig. 1
(A) Two cerclage wires tie up the fracture fragment with minimal soft tissue dissection.
(B) Fracture fixation is performed in anatomical position with the reconstruction plate and screws.
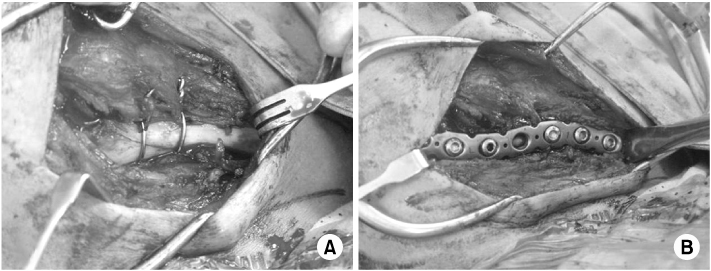

Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Surgical Management of Comminuted Midshaft Clavicle Fractures Using Reconstruction Plate and Circumferential Wiring: Does the Circumferential Wiring Interfere with the Bone Union?
Kyung-Tae Kim, Chung-Shik Shin, Young-Chul Park, Dong-hyun Kim, Min-Woo Kim
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2021; 56(3): 245. CrossRef - Supplementary Technique for Unstable Clavicle Shaft Fractures: Interfragmentary Wiring and Temporary Axial K-Wire Pinning
Jinmyoung Dan, Byung-Kook Kim, Ho-Jae Lee, Tae-Ho Kim, Young-Gun Kim
Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery.2018; 10(2): 142. CrossRef - Use of Composite Wiring on Surgical Treatments of Clavicle Shaft Fractures
Kyung Chul Kim, In Hyeok Rhyou, Ji Ho Lee, Kee Baek Ahn, Sung Chul Moon
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2016; 29(3): 185. CrossRef - TO EVALUATE THE SURGICAL OUTCOME OF NON-UNION CLAVICLE USING PLATE AND SLIVERS OF AUTOLOGOUS ILIAC CREST CORTICOCANCELLOUS BONE GRAFT
Mohammed Tauheed, Shashi Kumar Yalagach, Vivek Purushothaman, Anwar Shareef Kunnath K
Journal of Evidence Based Medicine and Healthcare.2016; 3(25): 1121. CrossRef - Anatomical Reduction of All Fracture Fragments and Fixation Using Inter-Fragmentary Screw and Plate in Comminuted and Displaced Clavicle Mid-Shaft Fracture
Kyoung Hwan Koh, Min Soo Shon, Seung Won Lee, Jong Ho Kim, Jae Chul Yoo
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2012; 25(4): 300. CrossRef
Does Interfragmentary Cerclage Wire Fixation in Clavicle Shaft Fracture Interfere the Fracture Healing?
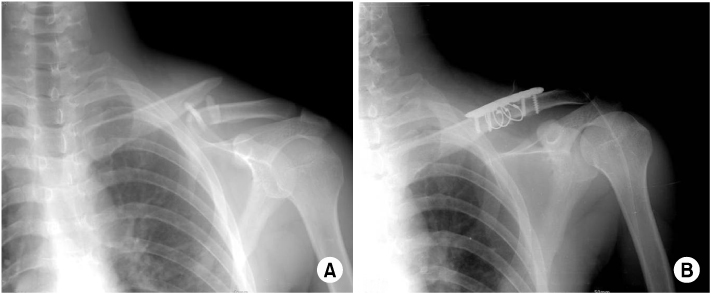
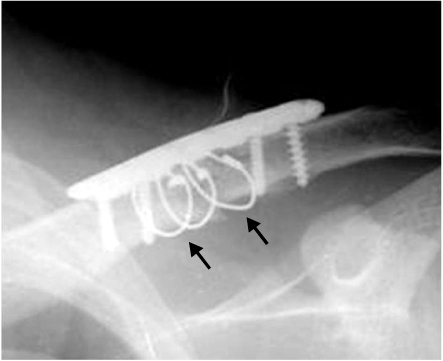
Fig. 1
(A) Two cerclage wires tie up the fracture fragment with minimal soft tissue dissection.
(B) Fracture fixation is performed in anatomical position with the reconstruction plate and screws.
Fig. 2
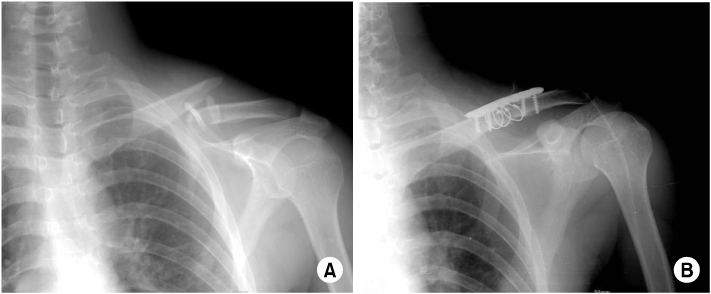
(A) The preoperative radiograph shows comminuted fracture of the clavicle shaft.
(B) Immediate postoperative radiograph shows comminuted clavicle shaft fracture is fixed by reconstruction plate and screws with three cerclage wires.
Fig. 3
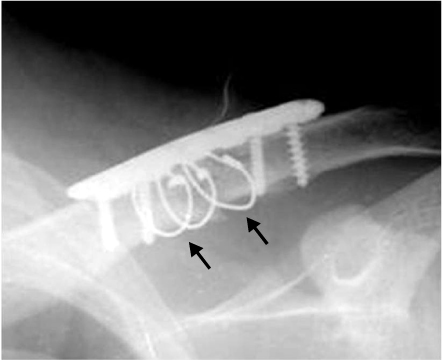
The simple radiograph shows gap between cortical bone and wires (black arrows).
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Does Interfragmentary Cerclage Wire Fixation in Clavicle Shaft Fracture Interfere the Fracture Healing?
Factors for evaluation of results and clinical scoring system by Kang et al
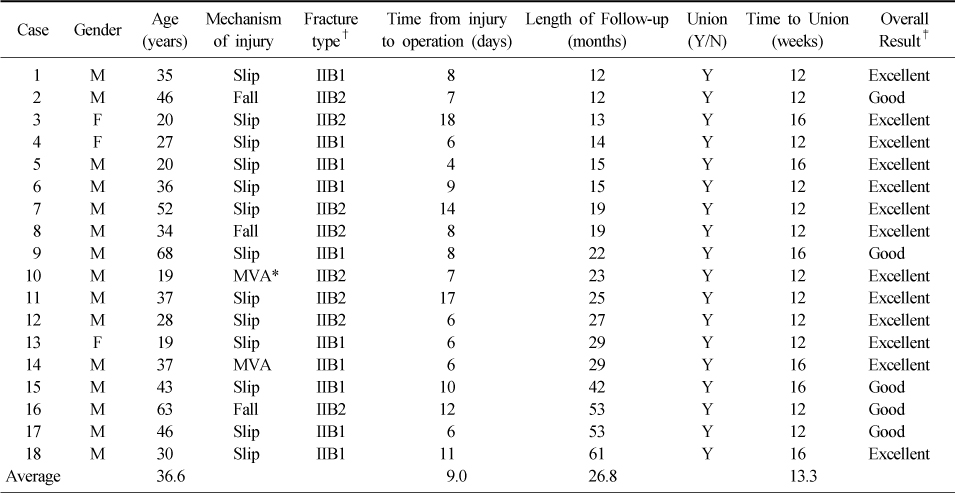
Details of 18 patients of clavicle shaft comminuted fractures treated by open reduction and internal fixation using plate and cerclage wires
*MVA: motor vehicle accident, †Edingurgh classification, ‡Kang's criteria.
Table 1
Factors for evaluation of results and clinical scoring system by Kang et al
Table 2
Details of 18 patients of clavicle shaft comminuted fractures treated by open reduction and internal fixation using plate and cerclage wires
*MVA: motor vehicle accident, †Edingurgh classification, ‡Kang's criteria.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 Cite
Cite

