Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 22(1); 2009 > Article
-
Original Article
- Double Tension Band Wire Fixation for Unstable Fracture of the Distal Clavicle
- Kyeong-Seop Song, M.D., Hyung-Gyu Kim, M.D., Byeong-Mun Park, M.D., Jong-Min Kim, M.D., Sung-Hoon Jung, M.D., Bong-Seok Yang, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2009;22(1):24-29.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.1.24
Published online: January 31, 2009
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kwangmyung Sung-Ae Hospital, Gwangmyeong, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Hyung-Gyu Kim, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kwangmyung Sung-Ae Hospital, 389, Chulsan 3-dong, Gwangmyung 423-711, Korea. Tel: 82-2-2680-7236, Fax: 82-2-2617-9039, khg0623@hanmail.net
• Received: October 11, 2008 • Accepted: November 10, 2008
Copyright © 2009 The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 353 Views
- 1 Download
Abstract
-
Purpose
- To evaluate the clinical results after operative treatment with the double tension band wire fixation in Neer type II and III distal clavicle fractures.
-
Materials and Methods
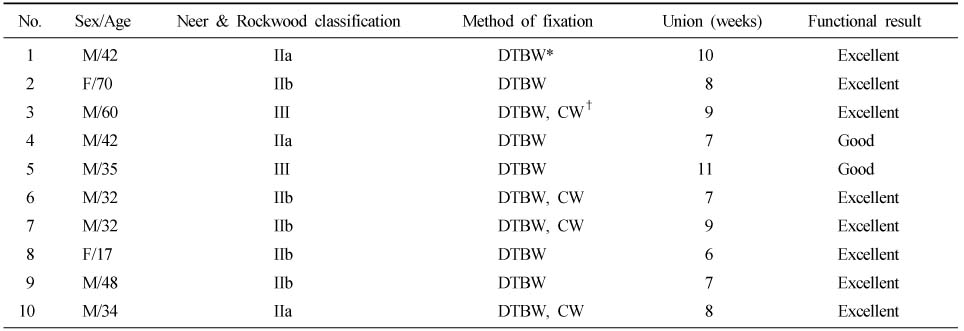
- Ten patients with type II and III distal clavicle fractures were evaluated, who operated with double tension band wire fixation technique, from Febrary 2007 to June 2008, and could be followed-up for more than 1 year after operation. Postoperative assessments were evaluated on plain x-ray, pain, and clinical finding according to the functional criteria by Kona et al.
-
Results
- Average duration from operation to fracture union was 8 weeks in all cases. There were 8 excellent and 2 good results. It was no other significant complications such as K-wire migration, breakage, infection, and AC joint arthritis.
-
Conclusion
- Double tension band wire fixation technique seems to be an effective method for type II or III distal clavicle fracture with multiple compressive axis, without injury of the AC joint and loosening of the fixation.
- 1. Caspi I, Ezra E, Oliver S, Lin E, Horoszowski H. Treament of Avulsed calvicle and recurrent subluxation of the ipsilateral shoulder by dynamic fixation. J Trauma, 1987;27:94-95.
- 2. Chun JM, Kim SY, Lee KW, Shin SJ, Kim EG. Modified tension band fixation for unstable fracture of the distal clavicle. J Korean Orthop Assoc, 2002;37:416-420.ArticlePDF
- 3. Craig EV. Fracture of the distal clavicle. In: Rockwood CA, Matsen FA, editors. The shoulder. Philadelphia, WB: Sauders; 1990. p. 367-412.
- 4. Edwards DJ, Kavanagh TG, Flannery MC. Fractures of the distal clavicle: a case for fixation. Injury, 1992;23:44-46.Article
- 5. Flinkkilä T, Ristiniemi J, Hyvönen P, Hämäläinen M. Surgical treatment of unstable fractures of the distal clavicle: a comparative study of Kirschner wire and clavicular hook plate fixation. Acta Orthop Scand, 2002;73:50-53.Article
- 6. Goldberg JA, Bruce WM, Sonnabend DH, Walsh WR. Type 2 fractures of the distal clavicle: a new surgical technique. J Shoulder Elbow Surg, 1997;6:380-382.Article
- 7. Hessmann M, Kirschner R, Baumgatel F, Gehling H, Gotzen L. Treatment of unstable distal clavicular fractures with and without lesions of the acromioclavicular joint. Injury, 1996;27:47-52.Article
- 8. Kang HJ, Park KK, Yoon HK, Song HK, Hahn SB. T plate fixation for unstable frature of distal clavicle. J Korean Fract Soc, 2006;19:329-334.Article
- 9. Kao FC, Chao EK, Chen CH, Yu SW, Chen CY, Yen CY. Treatment of distal clavicle fracture using Kirschner wires and tension-band wires. J Trauma, 2001;51:522-525.Article
- 10. Katznelson A, Nerubay J, Oliver S. Dynamic fixation of the avulsed clavicle. J Trauma, 1976;16:841-844.Article
- 11. Kona J, Bosse MJ, Staeheli JW, Rosseau RL. Type II distal clavicle fracture: a retrospective review of surgical treatment. J Orthop Trauma, 1990;4:115-120.
- 12. Lyons FA, Rockwood CA Jr. Migration of pins used in operations on the shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1990;72:1262-1267.Article
- 13. Moneim MS, Balduini FC. Coracoid fracture as a complication of surgical treatment by coracoclavicular tape fixation. A case report. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1982;168:133-135.
- 14. Neer CS II. Fracture of the distal third of the clavicle. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1968;58:43-50.
- 15. Neviaser RJ. Injuries to the clavicle and acromioclavicular joint. Orthop Clin North Am, 1987;18:433-438.Article
- 16. Nordqvist A, Petersson C, Redlund-Johnell I. The natural course of lateral clavicle fracture: 15(11~21) year follow-up of 110 cases. Acta Orthop Scand, 1993;64:87-91.
- 17. Parkes JC, Deland JT. A three-part distal clavicle fracture. J Trauma, 1983;23:437-438.Article
- 18. Park JH, Rha KW, Suh SW, Kim SK. Operative treatment of type 2 distal clavicle fractures. J Korean Fracture Soc, 1998;11:683-689.
- 19. Post M. Current concepts in the treatment of fractures of the clavicle. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1989;245:89-101.Article
- 20. Rockwood CA. Fracture of the outer clavicle in children and adults. Orthop Trans, 1982;6:472.
- 21. Yamaguchi H, Arakawa H, Kobayashi M. Results of the Bosworth method for unstable fractures of the distal clavicle. Int Orthop, 1998;22:366-368.ArticlePDF
REFERENCES
Fig. 1
Illustrations of the surgical technique of double tension band wire fixation for distal clavicle.
(A) Insertion two K-wires from distal to proximal and one K-wire from anteior to posterior for typical tension band wire fixation.
(B) Insertion of one more K-wire from anterior to posterior at distal fragment and another tension band wire fixation over the fracture site.
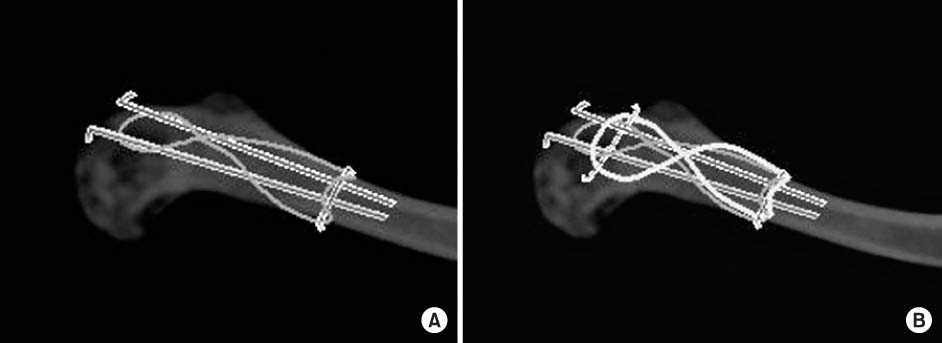

Fig. 3
A 32-years-old male was injured by traffic accident.
(A) The radiograph shows a type IIb unstable distal clavicle fracture with a long transverse fragment.
(B) The fracture is fixed with double tension band wire and additional two circular wires.
(C) After removal of the implats at postoperative 14 months, complete union of the fracture site is seen.
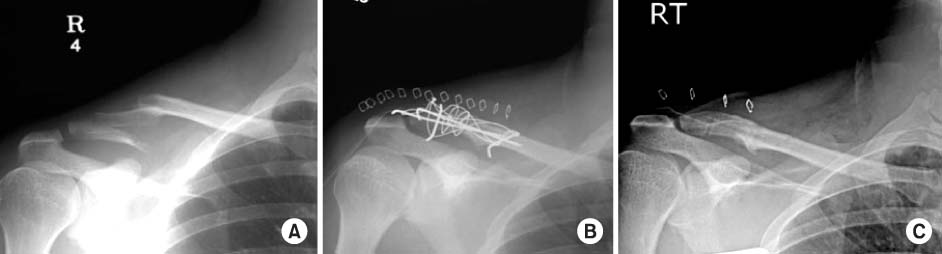

Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

Double Tension Band Wire Fixation for Unstable Fracture of the Distal Clavicle
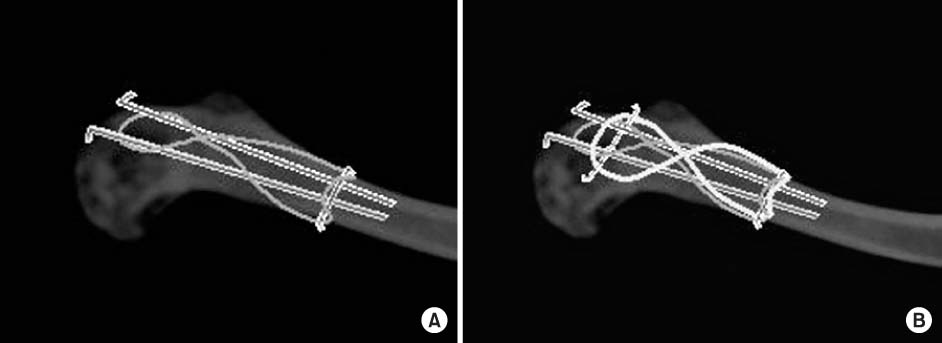
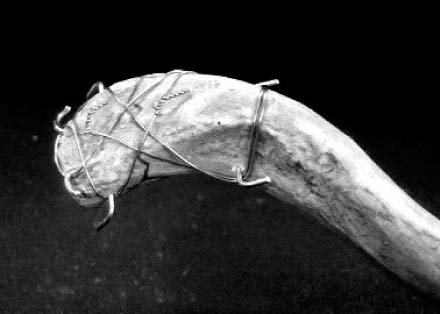
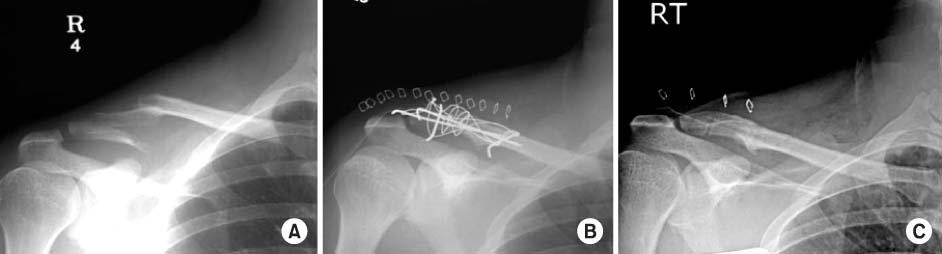
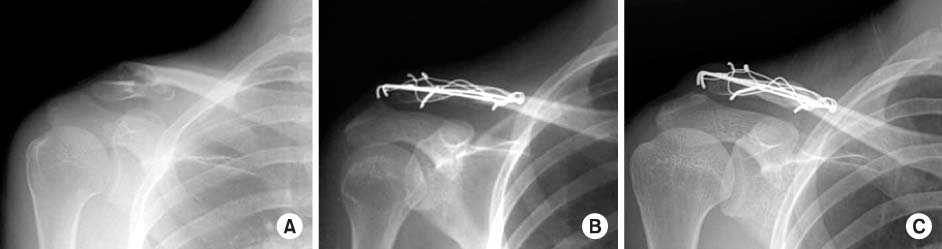
Fig. 1
Illustrations of the surgical technique of double tension band wire fixation for distal clavicle.
(A) Insertion two K-wires from distal to proximal and one K-wire from anteior to posterior for typical tension band wire fixation.
(B) Insertion of one more K-wire from anterior to posterior at distal fragment and another tension band wire fixation over the fracture site.
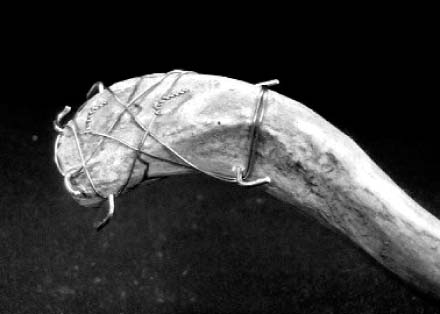
Fig. 2
A demonstration model of the double tension band wire fixation.
Fig. 3
A 32-years-old male was injured by traffic accident.
(A) The radiograph shows a type IIb unstable distal clavicle fracture with a long transverse fragment.
(B) The fracture is fixed with double tension band wire and additional two circular wires.
(C) After removal of the implats at postoperative 14 months, complete union of the fracture site is seen.
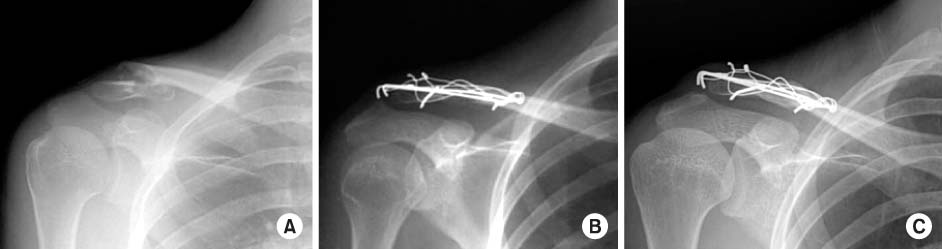
Fig. 4
A 17-years-old female was injured by slip down.
(A) The radiograph shows a type IIb unstable distal clavicle fracture.
(B) Postoperative radiograph shows the fracture fixed with double tension band wire.
(C) Fracture is united in 6 weeks after surgery on radiograph.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Double Tension Band Wire Fixation for Unstable Fracture of the Distal Clavicle
Demographic data of the patients
*Double tension band wire, †Circular wire.
Classification of functional results by Kona et al.
Table 1
Demographic data of the patients
*Double tension band wire, †Circular wire.
Table 2
Classification of functional results by Kona et al.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 Cite
Cite

