Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 23(1); 2010 > Article
-
Original Article
- Modified Spring Plate for Treatment of Unstable Distal Clavicle Fractures
- Sang-Myung Lee, M.D., Il-Jung Park, M.D., Hyung-Min Kim, M.D., Jae-Chul Park, M.D., Sung-Gil Cho, M.D., Yoon-Chung Kim, M.D., Seung-Koo Rhee, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2010;23(1):64-68.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.1.64
Published online: January 31, 2010
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
*Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Seung-Koo Rhee, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, 60, Yeouido-dong, Yeongdeungpo-gu, Seoul 150-713, Korea. Tel: 82-2-3779-1192, Fax: 82-2-783-0252, skrhee@catholic.ac.kr
• Received: July 8, 2009 • Revised: October 26, 2009 • Accepted: December 15, 2009
Copyright © 2010 The Korean Fracture Society
- 370 Views
- 1 Download
Abstract
-
Purpose
- Unstable distal clavicle fractures should be treated surgically but may be difficult in firm fixation because of small distal fragment. Although a variety of fixation methods have been currently used, none of the methods seem to be firm fixation and little pain. We present a new technique using a spring plate which was modified from one third tubular plate and report the early results.
-
Materials and Methods
- Modified spring plate was made from one third tubular plate and the distal hole of the plate was cutting and sharpened by rasp. The sharp edge was bent just like an animal claw (C shape). Between May 2007 and June 2009, a total of six patients with distal clavicle fracture were treated using modified spring plate. A sling was applied in the immediate post operative period for six weeks and exercises were started immediately.
-
Results
- Union was achieved in all cases with excellent results without complication (mean Constant score, 96). All patients had returned to ordinary daily activities but mild limitation of abduction (150°) by seven weeks after surgery. After six months, the plate was removed.
-
Conclusion
- The modified spring plate has provided stable fixation for unstable distal clavicle fixation without disturbance to the acromioclavicular joint, subacromial space, or rotator cuff.
- 1. Allman FL Jr. Fractures and ligamentous injuries of the clavicle and its articulation. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1967;49:774-778.
- 2. Constant CR, Murley AH. A clinical method of functional assessment of the shoulder. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1987;214:160-164.
- 3. Eiff MP, Hatch RL, Calmbach WL. Clavicle and scapula fractures. Fracture management for primary care, 1998;Philadelphia, Saunders Co. 131-142.
- 4. Eskola A, Vainionpää S, Myllynen P, Pätiälä H, Rokkanen P. Outcome of clavicular fracture in 89 patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, 1986;105:337-338.PDF
- 5. Flinkkilä T, Ristiniemi J, Hyvönen P, Hämäläinen M. Surgical treatment of unstable fractures of the distal clavicle: a comparative study of kirschner wire and clavicular hook plate fixation. Acta Orthop Scand, 2002;73:50-53.
- 6. Henkel T, Oetiker R, Hackenbruch W. Treatment of fresh Tossy III acromioclavicular joint dislocation by ligament suture and temporary fixation with the clavicular hooked plate. Swiss Surg, 1997;3:160-166.
- 7. Kang HJ, Park KK, Yoon HK, Song HK, Hahn SB. T plate fixation for unstable fracture of distal clavicle. J Korean Fract Soc, 2006;19:329-334.
- 8. Kona J, Bosse MJ, Staeheli JW, Rosseau RL. Type II distal clavicle fractures: a retrospective review of surgical treatment. J Orthop Trauma, 1990;4:115-120.
- 9. Mast J, Jakob R, Ganz R. Planning and reduction technique in fracture surgery, 1989;New York, Springer-Verlag.
- 10. Meda PV, Machani B, Sinopidis C, Braithwaite I, Brownson P, Frostick SP. Clavicular hook plate for lateral end fractures:-a prospective study. Injury, 2006;37:277-283.
- 11. Neer CS 2nd. Fracture of the distal clavicle with detachment of the coracoclavicular ligaments in adults. J Trauma, 1963;3:99-110.
- 12. Neer CS 2nd. 5 Fractures of the distal third of the clavicle. . Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1968;58:43-50.
- 13. Park JY, Seo JB, Kim MH, Yu JW. Tension band fixation for type II fracture of the distal clavicle. J Korean Fract Soc, 2005;18:421-425.
- 14. Rockwood CA. Fractures of the outer clavicle in children and adults. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1982;64:642.
REFERENCES
Fig. 1Close up photograph of modified spring plate. A newly designed spring plate which is made from ordinary one third tubular plate; The distal hole of the plate was cutting and sharpened by rasp. The sharp edge was bent just like an animal claw (C shape).
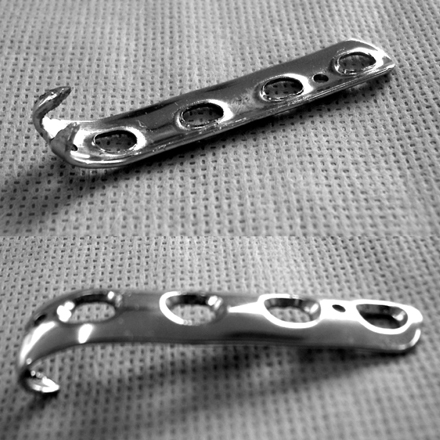


Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

Modified Spring Plate for Treatment of Unstable Distal Clavicle Fractures
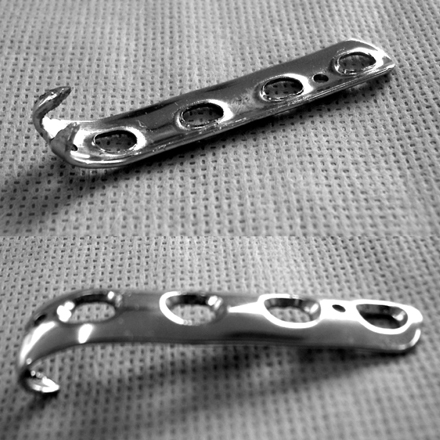

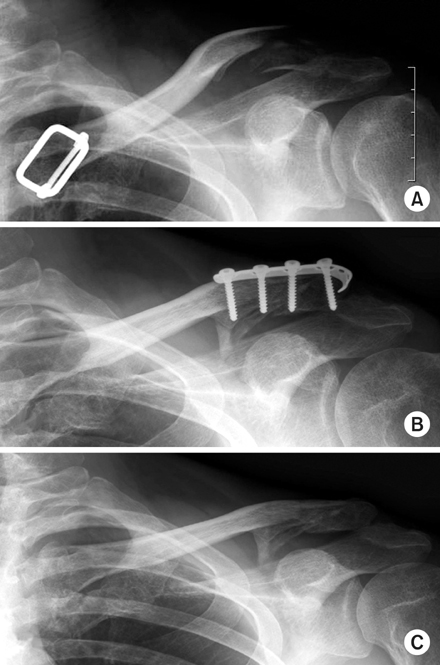
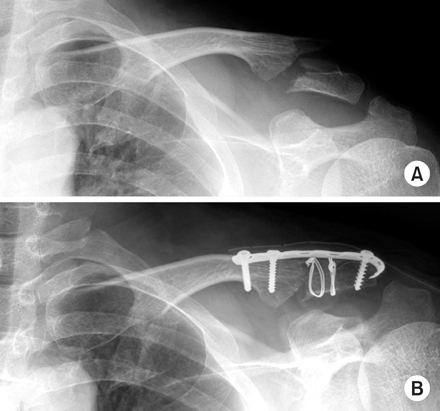
Fig. 1
Close up photograph of modified spring plate. A newly designed spring plate which is made from ordinary one third tubular plate; The distal hole of the plate was cutting and sharpened by rasp. The sharp edge was bent just like an animal claw (C shape).
Fig. 2
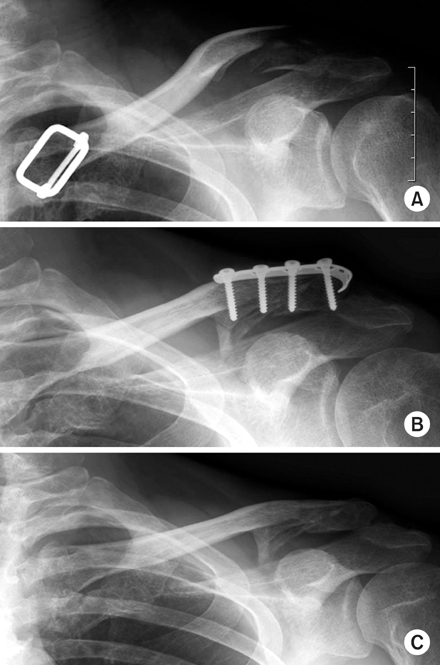
(A) Distal clavicle comminuted fracture in a 47-year-old man.
(B) After modified spring plate fixation. Note the acromioclavicular joint subluxation caused by acromioclavicular ligament damage.
(C) After removal of modified spring plate.
Fig. 3
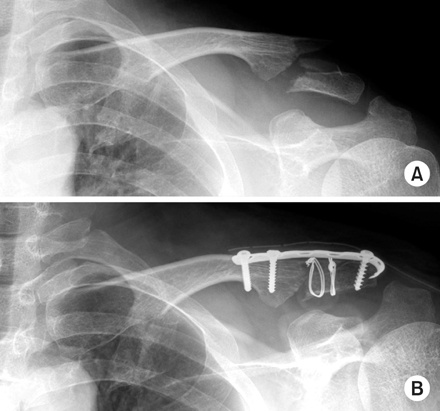
(A) Distal clavicle fracture in a 46-year-old man.
(B) After modified spring plate fixation.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Modified Spring Plate for Treatment of Unstable Distal Clavicle Fractures
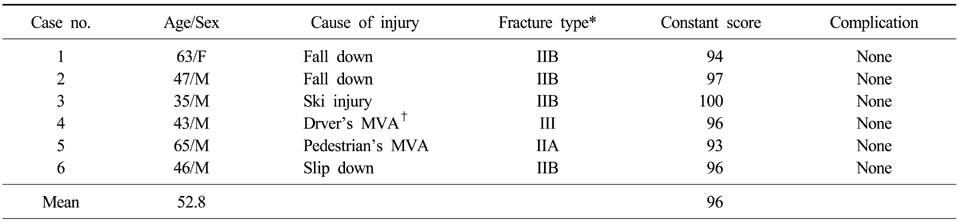
Summary of cases
*Fracture type by Neer classification (1963), †MVA: Motor vehicle accident.
Table 1
Summary of cases
*Fracture type by Neer classification (1963), †MVA: Motor vehicle accident.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

