Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
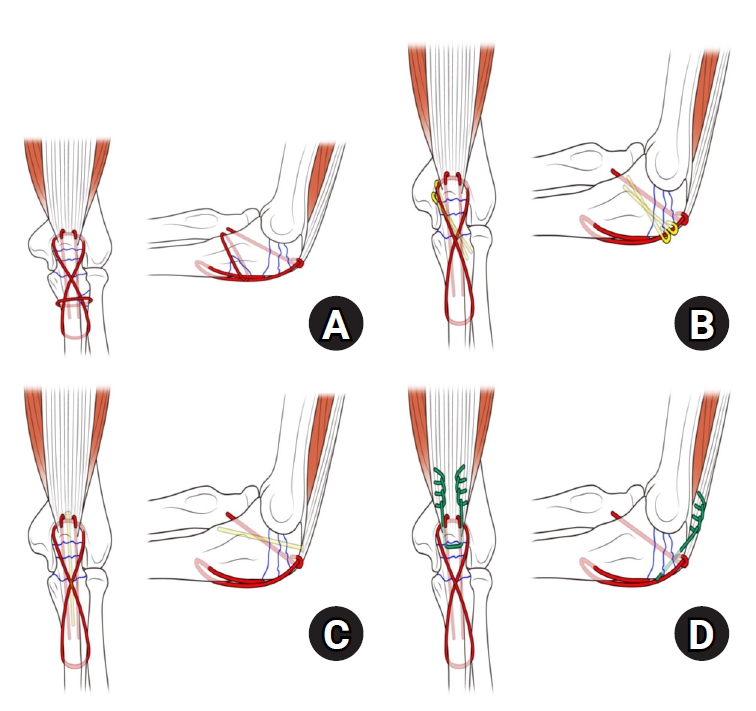
- Comparison of outcomes of reinforced tension band wiring and precontoured plate and screw fixation in the management of Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures
- Hyun Goo Kang, Tong Joo Lee, Samuel Jaeyoon Won
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):96-101. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00059
- Correction in: J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):168
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures are characterized by significant displacement and comminution, presenting a challenge in selecting the appropriate fixation technique. This study compared the clinical and radiographic outcomes, complications, and reoperation rates of reinforced tension band wiring (TBW) and precontoured plate and screw fixation (PF) in the surgical treatment of Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures.
Methods
This retrospective review analyzed 24 patients diagnosed with Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures, who were treated between 2005 and 2023. Of these, 11 patients underwent reinforced TBW, and 13 received precontoured PF. Clinical outcomes were assessed using Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH) scores and the Mayo Elbow Performance Score (MEPS). Radiographic outcomes focused on fracture union. Operative times, complication rates, and reoperation rates were compared between the groups.
Results
Both the reinforced TBW and PF groups achieved satisfactory clinical outcomes, with no significant between-group differences in DASH and MEPS scores (P>0.05). Radiographic union was achieved in all patients. The reinforced TBW group demonstrated a significantly shorter operative time than the PF group (93.6±7.4 min vs. 132.3±13.7 min; P<0.001). Complication rates were similar between the two groups (reinforced TBW, 38.4%; PF, 36.3%), but hardware-related irritation occurred more frequently in the reinforced TBW group. Reoperations were required in 15.8% of the reinforced TBW group due to hardware irritation, whereas no reoperations were necessary in the PF group.
Conclusions
Reinforced TBW and PF are both effective surgical options for managing Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures, yielding comparable clinical and radiographic outcomes. While reinforced TBW offers shorter operative times and lower costs, PF is associated with fewer hardware-related complications. Further prospective studies are needed to optimize treatment strategies for these complex fractures. Level of Evidence: Level III. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Are posterior olecranon locking plates a problem for patients after fracture healing because of prominence?
Reva Qiu, Mallika Makkar, Richard Buckley
Injury.2025; 56(11): 112769. CrossRef
- Are posterior olecranon locking plates a problem for patients after fracture healing because of prominence?
- 2,018 View
- 46 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review Article
- Avulsion Fractures around the Hip Joint and Pelvis
- Ha-Yong Kim, Hajun Jang, Jung-Taek Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Jun-Il Yoo, Won-Sik Choy, Yonghan Cha
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(3):150-157. Published online July 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.3.150
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Avulsion fractures occur when tendons or ligaments are subjected to forces greater than they can withstand at the apophysis or enthesis, regardless of the fusion status. Given the diverse muscular structures around the pelvis and hip joint, which serve as origins for multiple muscles leading to the lower extremities, these areas are vulnerable to such injuries. Pelvic avulsion fractures commonly af-fect young athletes, but they can also occur in adults. Diagnosis typically involves assessing the trauma history, clinical examination, and radiographic imaging. In cases of unclear diagnosis, additional tests, such as computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, may assist in treatment decisions and diagnosis. Although most avulsion fractures respond well to conservative treatment, surgical interven-tion may be preferred in severe displacements, significant retraction in active athletes, or when a faster recovery is necessary. Chronic or neglected injuries may lead to excessive osseous formation around the pelvis, causing impingement syndromes. Recognizing the characteristic radiological findings based on the pelvic anatomy aids in accurate diagnosis because chronic injuries might mimic tumors or infectious conditions, necessitating a careful differential diagnosis.
- 1,327 View
- 40 Download

Original Article
- Demographic and Radiographic Parameters as Predictors of Reduction Loss after Conservative Treatment of Distal Radius Fractures in Adults
- Kyu Jin Kim, Dae Won Shin, Seong Kee Shin
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(2):45-51. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.2.45
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the demographic and radiological risk factors for later reduction loss of distal radius fractures treated conservatively. Materials and Methods This study enrolled patients treated for distal radius fractures between January 2017 and December 2019. Seventy-eight patients were included in the analysis and divided into two groups. The patients who showed minimal reduction loss within an acceptable radiologic angle after initial manual reduction were classified as Group A. The patients who showed reduction loss out of an acceptable radiologic angle and finally malunited or converted to surgical treatments were classified as Group B. The patient’s age and bone marrow density were used as demographic data. The initial X-ray images were evaluated to determine the fracture type. Various radiological parameters were measured. Results The 78-patient study cohort consisted of nine men and 69 women with a mean age of 67 years. Forty-eight cases were sorted into Group A, and 30 cases into Group B. On logistic regression analysis, the age of 80 or older was a risk factor for later fracture displacement among the demographic factors (p=0.037, odds ratio=4.937). Among the radiographic factors, the presence of distal ulnar fracture and dorsal cortical comminution were disclosed as risk factors of later displacement (p=0.049, 0.003, odds ratio=3.429, 7.196). Conclusion When conservative management for distal radius fracture is decided in patients more than 80 years of age or accompanied by a distal ulnar fracture or with dorsal cortical comminution, the possibility of later displacement of the distal radius should be considered.
- 445 View
- 1 Download

Review Articles
- Treatment of Scaphoid Fractures and Nonunions
- Wan-Sun Choi
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(4):182-189. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.4.182
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A scaphoid fracture is one of the most common types of wrist fractures, and if treatment is delayed, there is a high possibility of nonunion due to anatomical factors such as limited blood supply to the injured bone. Therefore, it is important to suspect a scaphoid fracture based on the mechanism of wrist injury and physical examination of the patient. A computed tomography scan or magnetic resonance imaging can also aid early diagnosis of the fracture. Stable acute fractures can be treated conservatively, but unstable fractures require surgical treatment, and percutaneous screw fixation is usually performed. Nonunions require bone grafts and are treated with non-vascularized bone grafts and screw fixation. However, if the nonunion is located at the proximal pole, a vascularized bone graft may be considered because there is a possibility of avascular necrosis. Pedicled vascularized and free vascularized medial femoral condyle bone grafts are mainly used in such cases. The treatment of a proximal pole nonunion with impaired blood flow remains controversial. There are conflicting opinions on whether a nonvascularized bone graft is sufficient or whether a vascularized bone graft is necessary.
- 545 View
- 6 Download

- Current Treatment of Calcaneal Fractures and Dislocation
- Dae Jin Nam, Sung Hyun Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(2):74-82. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.2.74
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Calcaneal fractures are the most common fractures occurring in the tarsal bone. In the past, surgical treatments were not preferred because they were accompanied by severe comminution and soft tissue complications. In recent years, there have been great advancements in the treatment of calcaneal fractures owing to the development of new surgical techniques and instruments. However, a standard treatment method has not yet been established. In this review article, we summarize the latest information on the indications and treatment methods of calcaneal fractures.
- 438 View
- 13 Download

- Current Management of Talar Fractures
- Gun-Woo Lee, Keun-Bae Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(1):31-37. Published online January 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.1.31
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Talar fracture management is one of the most challenging tasks for orthopedic surgeons. High complication rates and functional impairments after talar fractures have been well documented, and thus, surgical strategies capable of perfect anatomic reduction and stable fixation are important. The current review was undertaken to provide recommendations regarding updated surgical strategies that include surgical timing, approach, fixation methods, and the prevention and treatment of possible complications.
- 515 View
- 4 Download

Case Report
- Recurrent Treatment Failure in Vancouver Classification Type C Periprosthetic Fractures around a Well Fixed Short Femoral Stem
- Byeong Yeol Choi, Hong-Man Cho, Jiyeon Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(1):16-20. Published online January 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.1.16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A short femoral stem (type 1 cementless stem) is being increasingly used to perform total hip arthroplasty; however, various types of intra- or postoperative periprosthetic fractures have been reported in recent times. A 66-year-old woman with a history of bilateral total hip arthroplasties using a type 1B femoral stem was admitted 2 months post-operation for a Vancouver type C periprosthetic fracture. She underwent open reduction and internal fixation; however, we observed recurrent non-union and plate breakage at the same site. In this case report, we discuss the factors associated with treatment failure in patients with a Vancouver type C periprosthetic fracture following type 1 femoral stem im-plantation.
- 308 View
- 0 Download

Review Article
- Ankle Fractures in Children: Classification and Treatment
- Ha-Yong Kim, Yong-Han Cha, Woo-Suk Kim, Won-Sik Choy
- J Korean Fract Soc 2021;34(2):87-95. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2021.34.2.87
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pediatric ankle fractures are defined as damage to the metaphysis, epiphyseal plate, and epiphysis of the distal tibia and fibula. Although the injury mechanism could be similar, the fracture patterns and treatment of pediatric ankle fractures are different from those of adults. In children, growth plate injuries are more common with a force that would cause sprains in adults because the ligaments are stronger than the growth plate cartilage in children. In the adolescent period, unique fractures, called “transitional fractures”, occur while the physis is closed. For a diagnosis, plain images of the anteroposterior, lateral, and mortise views are essential. Stress radiographs, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging can be used for suspected ligament injuries. The treatment goal is to restore the articular congruity, normal bony alignment, and preserve the epiphyseal plate to ensure normal growth. Pediatric ankle fractures frequently lead to premature physeal arrest, angular deformities, malunion, and posttraumatic arthritis even after anatomic reduction. Treating surgeons should follow-up children for a sufficient time and explain to the caregiver the possible complications before treatment.
- 1,215 View
- 29 Download

Original Article
- Treatment of Proximal Femur Fracture with a Newly Designed Nail: Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced (TFNA)
- Jae Youn Yoon, Ji Wan Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(4):189-195. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.4.189
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study evaluated the clinical results and implant safety of a newly developed implant, Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced (TFNA; DePuy Synthes), in the treatment of proximal femur fractures.
Materials and Methods
This was a retrospective cohort study of 26 patients diagnosed with proximal femur fracture and treated surgically with TFNA. The patients’ demographic data, surgical data, radiologic findings, and functional outcomes, including complications, were evaluated.
Results
The mean age of the patients was 71.2 years (95% confidence interval [CI], 68.2-74.2); 65.4% were female. The mean Carlson comorbidity index score was 5.4, and the mean Koval grade before fracture was 2.1. Fracture classification included four cases of AO/OTA 31.A1, nine cases of A2, six cases of A3, and seven cases of 32A including six cases of atypical femoral fractures. The mean operating time was 53.3 minutes (95% CI, 43.6-63.1). There were no early postoperative complications, such as postoperative infection, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, or in-hospital death, except one case of pneumonia. The mean Koval score at the postoperative six-month follow-up was 2.9. EuroQol-5 Dimension (EQ-5D) increased from 0.05 to 0.54 after three months and 0.72 at six months postoperatively. Bone union was observed in all cases with a mean union time of 12.9 weeks. No implant failure occurred, and no cases required secondary revision surgery.
Conclusion
A new intramedullary nail system, TFNA, showed excellent outcomes and safety in the surgical treatment of proximal femur fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intermediate Length Cephalomedullary Nails in Proximal Femoral Fractures: Review of Indications and Outcomes
Daniel Scott Horwitz, Ahmed Nageeb Mahmoud, Michael Suk
Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.2025; 33(19): 1071. CrossRef - Outcomes of Intertrochanteric Fracture Fixation Using the Trochanteric Fixation Nail Advanced (TFNA): A Retrospective Analysis
Ramprasad Jasti, Prithvi Mohandas, Mahesh K Ragavan, Sunil D Magadam, Umesh Kannadasan
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures Treated with Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced and Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation-II: Correlation between Lateral Sliding of the Helical Blade and Lateral Trochanteric Pain
Sung Yoon Jung, Myoung Jin Lee, Lih Wang, Hyeon Jun Kim, Dong Hoon Sung, Jun Ha Park
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2024; 59(3): 208. CrossRef - Prospective randomized multicenter noninferiority clinical trial evaluating the use of TFN-advancedTM proximal femoral nailing system (TFNA) for the treatment of proximal femur fracture in a Chinese population
Lidan Zhang, Zhijun Pan, Xiaohui Zheng, Qiugen Wang, Peifu Tang, Fang Zhou, Fan Liu, Bin Yu, Frankie K. L. Leung, Alex Wu, Suzanne Hughson, Zhuo Chen, Michael Blauth, Anthony Rosner, Charisse Sparks, Manyi Wang
European Journal of Trauma and Emergency Surgery.2023; 49(3): 1561. CrossRef - Risk of shortening in operatively treated proximal femur fractures with cephalomedullary nails with dynamically versus statically locked helical blades
Nathan Cherian, Lasun Oladeji, Cole Ohnoutka, Dan Touhey, Madeline Sauer, Kyle A. Schweser, Mauricio Kfuri, James L. Cook, Gregory J. Della Rocca, Brett D. Crist
Injury.2023; 54(2): 669. CrossRef - GS Hip Nail versus Affixus Hip Fracture Nail for the Intramedullary Nailing of Intertrochanteric Fractures
Seungcheol Kwon, Minjae Lee, Heeyeon Lee, Jihyo Hwang
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(21): 6720. CrossRef - Comparison of the Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of TFNA (Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced) and PFNA-II (Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation-II) Treatment in Elderly Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures
Min Sung Kwon, Young Bok Kim, Gyu Min Kong
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2022; 35(4): 162. CrossRef - Analysis of Clinical and Functional Outcomes according to the Blood Sugar Control Status at the Time of Ankle Fractures Resulting from Rotational Injuries
Jun Young Lee, Dong Seop Lim, Seung Hyun Lee, Seo Jin Park
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2022; 35(4): 135. CrossRef - Conventional versus helical blade screw insertion following the removal of the femoral head screw: a biomechanical evaluation using trochanteric gamma 3 locking nail versus PFN antirotation
Hong Man Cho, Kwang Min Park, Tae Gon Jung, Ji Yeon Park, Young Lee
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and Radiologic Outcome of Intertrochanteric Fracture Treatment Using TFNA (Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced)
Hyeon Joon Lee, Hyun Bai Choi, Ba Rom Kim, Seung Hwan Jo, Sang Hong Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2021; 34(3): 105. CrossRef
- Intermediate Length Cephalomedullary Nails in Proximal Femoral Fractures: Review of Indications and Outcomes
- 2,107 View
- 20 Download
- 10 Crossref

Review Articles
- Periprosthetic Fracture after Total Shoulder Arthroplasty
- Nam Su Cho, Myung Seo Kim, Jae Woo Yang, Jeung Hwan Seo, Dong Won Seo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(2):118-123. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.2.118
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Periprosthetic humeral fractures in patients with total shoulder arthroplasty are rare and difficult to treat. With the significant increase in the number of older patients who have undergone total shoulder arthroplasty in recent years, an increase in the number of periprosthetic shoulder fractures can be estimated. The decisions of treatment have to be taken individually, depending on the stability of the prosthesis, fracture location, and bone quality. On the other hand, there are limited data for treatment guidance and outcomes. This paper reviews the risk factors, classification, treatment, and outcomes of periprosthetic humeral fractures.
- 692 View
- 11 Download

- New Injury Mechanism and Treatment Algorithm of Posterior Elbow Dislocation
- In Hyeok Rhyou
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(1):61-71. Published online January 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.1.61
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Although the concept of a single elbow dislocation mechanism, in which all dislocations start from the lateral side of the elbow joint and progress to the medial side, has never been able to explain the various conflicting experimental and clinical observations thus far, new studies and proposals for a valid mechanism have not been reported. The new proposal for posteromedial and posterolateral dislocation of the elbow joint according to the authors' study and the new treatment algorithm based on this new study can explain the various clinical and experimental results that have been difficult to explain, and provide a reasonable approach to the treatment of elbow dislocations.
- 1,448 View
- 12 Download

- Treatment Options of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures
- Yu Mi Kim, Tae Kyun Kim, Dae Moo Shim, Kyeong Hoon Lim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(3):114-121. Published online July 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.3.114
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This paper reviews previous studies on the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in elderly patients to determine what factors should be considered for successful treatment. In osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures, the primary treatment is conservative treatments. Other treatments include osteoporosis treatment, pain control, orthosis, and physical therapy. Recently, percutaneous catheterization or balloon plasty is performed for rapid pain recovery and early ambulation. Percutaneous catheterization or balloon posterior plasty is effective in reducing pain and improving the activity ability. Surgical treatment should be considered in cases of nonunion or osteonecrosis, dent, deformation, and spinal cord compression after conservative treatment has failed. In surgical treatment, posterior spinal fixation and vertebroplasty are more advantageous in terms of the amount of bleeding, operation time compared to the anterior approach, but the most appropriate method should be selected through the patient's condition and understanding of each surgical method.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Maigne Syndrome and Thoracolumbar Compression Fracture – An Overlooked Combination in Low Back Pain: A Case Report
Jae-Yong Shim, Myung-Hoon Shin
The Nerve.2025; 11(1): 21. CrossRef - Effects of Herbal Medicines on Bone Mineral Density Score in Osteoporosis or Osteopenia: Study Protocol for a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Su Min Hong, Eun Jung Lee
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2021; 31(2): 49. CrossRef -
Spinal Stability Evaluation According to the Change in the Spinal Fixation Segment Based on Finite Element Analysis
Cheol-Jeong Kim, Seung Min Son, Jin-Young Heo, Chi-Seung Lee
Journal of the Computational Structural Engineering Institute of Korea.2020; 33(3): 145. CrossRef
- Maigne Syndrome and Thoracolumbar Compression Fracture – An Overlooked Combination in Low Back Pain: A Case Report
- 568 View
- 7 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Nonsurgical Treatment of a Distal Radius Fracture: When & How?
- Young Ho Shin, Jun O Yoon, Jae Kwang Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(2):71-78. Published online April 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.2.71
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Distal radius fractures are a common upper extremity fracture and a considerable number of patients have a stable fracture. In the treatment of distal radius fractures, there is considerable disagreement regarding the need for a strict anatomical restoration with operation in elderly patients. Therefore, nonsurgical treatment is a still important treatment option in distal radius fractures. The radiological parameters of before or after manual reduction are important for deciding whether to perform operation or not. The radiological parameters include dorsal angulation of the articular surface, radial shortening, extent of dorsal comminution, intra-articular displacement, concomitant ulnar metaphyseal fracture, shear fracture, and fracture-dislocation of the distal radio-ulnar joint. In addition, clinical situations of patients, including age, activity level, underline disease, and recovery level, which the patients wish should be considered, comprehensively. For the duration of a splint or cast, three to four weeks are recommended in impacted or minimally displaced fractures and five to six weeks in displaced fractures. After reduction of the displaced fractures, patients should undergo a radiologicical examination every week to check the redisplacement or deformity of the fracture site until two or three weeks post trauma. Arm elevation is important for controlling fracture site swelling and finger exercises, including metacarpophalangeal joint motion, are needed to prevent hand stiffness. Active range of motion exercise of the wrist should be initiated immediately after removing the splint or cast.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Clinical Effect of Complex Korean Medical Admission Treatment in Patients with Fractures of Distal Radius by Traffic Accident: 2 Cases Series Report
Gyu-cheol Choi, Ji-won Lee, Ji-Eun Bae, Dong-jin Kim, Jeong-su Hong, Da-hyun Kyung
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2021; 31(1): 187. CrossRef - The Clinical Effect of Rehabilitation Protocol for Distal Radius Fracture in Korean Medicine: A Report of 3 Cases
Won-Bae Ha, Ji-Hye Geum, Nak-Yong Koh, Jung-Han Lee
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2018; 28(3): 97. CrossRef
- The Clinical Effect of Complex Korean Medical Admission Treatment in Patients with Fractures of Distal Radius by Traffic Accident: 2 Cases Series Report
- 458 View
- 7 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Conservative Treatment of Proximal Humeral Fracture
- Hwansub Hyun, Jonghyun Ahn, Sang Jin Shin
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(1):29-35. Published online January 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.1.29
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A proximal humeral fracture is an osteoporotic fracture that often occurs in elderly women. Approximately 80% of all proximal humeral fractures are non-displaced fractures, which can be treated with conservative treatment to achieve stable union. The treatment plan for fractures involving displaced and comminuted fractures is controversial. Malunion, avascular necrosis of the humeral head, and shoulder stiffness due to conservative treatment can occur but the functional deterioration is low and the patient satisfaction is high. The indications for the conservative management of proximal humeral fractures include a non-displaced fracture and a 2-part fracture, low-functional demanded 3-part fracture, and operative-limited 4-part fracture. Recently, the surgical indications have expanded as technological advances in surgical fixation methods and functional needs of elderly patients are increasing. Current treatment policy decisions tend to be determined by the personal preference and expert opinion rather than by evidence-based decision-making.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Postoperative Korean Traditional Medicine for the of Proximal Humeral Fracture: A Case Report
Hyun Il Go, Hangyul Choi, Jieun Hong, Nam geun Cho
Journal of Acupuncture Research.2019; 36(1): 50. CrossRef
- The Effect of Postoperative Korean Traditional Medicine for the of Proximal Humeral Fracture: A Case Report
- 458 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Conservative Treatment of Mid-Clavicle Fractures
- Woong Kyo Jeong
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(1):22-28. Published online January 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.1.22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Clavicle fractures are very common injuries in adults and children and the majority of these fractures occur in the midshaft. Traditionally, mid-clavicle fractures have been treated with conservative methods and the clinical outcomes of this method are believed to be excellent. On the other hand, recent studies have shown that the clinical results of severe comminuted or markedly displaced fractures after conservative management were not as favorable as previously described. Despite these concerns, the conservative treatment of mid-clavicle fractures is still an efficient method, which can be applied to all patients as a primary care. This review focuses on the proper indication, technique, and limitations of conservative treatment of mid-clavicle fractures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Two Patients Who Were Hospitalized for Clavicle Fracture Caused by a Traffic Accident and Improved with Korean Medicine Complex Treatment
Deok Kang, ByungSoo Kang, Hwe-Joon Jeong, Dong-Hoon Shin, Kyung-Moon Shin, Ji-Hoon O, Jae-Woo Yang
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2022; 32(3): 179. CrossRef
- Two Patients Who Were Hospitalized for Clavicle Fracture Caused by a Traffic Accident and Improved with Korean Medicine Complex Treatment
- 414 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Report
- The Different Treatment Methods for Segmental Fractures of the Clavicle: Cases Report
- Sung Sik Ha, Ki Do Hong, Jae Cheon Sim, Yi Rak Seo, Tae Seok Nam
- J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(3):151-155. Published online July 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.3.151
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Segmental fractures of the clavicle are very rare. Therefore, to date, there has not been a clear, standardized method of management of segmental clavicle fractures. Herein, two patients with a segmental fracture are described: One patient was treated conservatively, while another patient was treated operatively. Both patients showed excellent results. We discuss the various management options with a literature review.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fratura segmentar da clavícula em paciente politraumatizado: Relato de caso
Carlos A. Sánchez, Pablo J. Coronel, Luisa F. García, Juan S. Afanador, Raúl Gonzalez
Revista Brasileira de Ortopedia.2024; 59(01): e139. CrossRef
- Fratura segmentar da clavícula em paciente politraumatizado: Relato de caso
- 815 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review Articles
- Treatment Strategy of Infected Nonunion
- Hyoung Keun Oh
- J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(1):52-62. Published online January 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.1.52
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The management of infected nonunion is based on a detailed evaluation of patients, the involved bone and soft tissues, stability of fixation, and type of bacterial pathogens. Preoperative surgical planning and strategies for each step is mandatory for the successful treatment of infected nonunion. The radical debridement of infected tissues, including the unstable implant, is one of the most important procedures. Adequate soft tissue coverage should be considered for the appropriate management of infection; a reconstructive procedure and stable skeletal stabilization by internal or external fixation is also necessary later. A restoration of bone defects and bony union can be accomplished with bone grafting, distraction osteogenesis, vascularized fibular grafting, and induced membrane technique.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Systematic Diagnosis and Treatment Principles for Acute Fracture-Related Infections
Jeong-Seok Choi, Jun-Hyeok Kwon, Seong-Hyun Kang, Yun-Ki Ryu, Won-Seok Choi, Jong-Keon Oh, Jae-Woo Cho
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2023; 36(4): 148. CrossRef - The Antibiotic Cement Coated Nail and Masquelet Technique for the Treatment of Infected Nonunion of Tibia with Bone Defect and Varus Deformity: A Case Report
Min Gu Jang, Jae Hwang Song, Dae Yeung Kim, Woo Jin Shin
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2022; 35(1): 26. CrossRef
- Systematic Diagnosis and Treatment Principles for Acute Fracture-Related Infections
- 1,384 View
- 23 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Scaphoid Fractures and Nonunion
- Jin Rok Oh
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(1):79-92. Published online January 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.1.79
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fracture of scaphoid is relatively common, and accurate and prompt diagnosis leads to bony union with good clinical outcome. However, it can be easily missed due to vague symptomatic complaints by patients, which in turn leads to negligence of a doctor in making the diagnosis or anatomical shape of scaphoid that causes minute fracture to be ignored while viewing simple radiography. When missed, nonunion of scaphoid gradually progresses to arthritic change in the wrist. Thus when fracture of the scaphoid is suspected, further evaluation should be initiated with care, and if the diagnosis is confirmed, a proper treatment plan must be set with assessment of stability of the fracture fragment. Internal fixation is usually proposed since solid fixation of the fracture provides early return to daily activity. When nonunion of the scaphoid is present, most patients can achieve bony union with avascular bone graft and internal fixation. However, if there is sclerotic change, large bone cyst or avascular necrosis of the fracture fragment, internal fixation with bone graft that includes vascular supply should be introduced in order to achieve bony union.
- 499 View
- 2 Download

Original Articles
- The Result of Conservative Treatment of Proximal Humerus Fracture in Elderly Patients
- Seung Gil Baek, Chang Wug Oh, Young Soo Byun, Jong Keon Oh, Joon Woo Kim, Jong Pil Yoon, Hyun Joo Lee, Hyung Sub Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(4):292-298. Published online October 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.4.292
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
With the increase in the old age population, proximal humerus fractures have been increasing recently. However, complications after operative treatment, such as fixation failure, are common because of osteoporosis. We treated proximal humerus fractures in patients with osteoporosis conservatively, and evaluated the radiographic and functional results by analyzing the factors affecting the results.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Nineteen out of 30 cases for whom the clinical follow-up was over 1 year were included in this retrospective study. There were 17 females and 2 males, and the mean age was 73.2 years. The causes were slip from a short height (18 cases) and a minor car accident (1 case). We evaluated the union period, nonunion, malunion and the Constant score and analyzed several factors affecting the functional result, such as age, fracture pattern, and malunion.
RESULTS
Seventeen cases (89.5%) obtained union within 12.8 weeks on average. Neck-shaft angle was 125.3degrees on average, with seven cases of malunion. The Constant score was 84.1 on average, and there were excellent scores in 11 cases, good scores in 4 cases, and fair scores in 2 cases. Fracture pattern, neck-shaft angle, or malunion did not affect the functional outcome, and elderly patients showed poorer shoulder function.
CONCLUSION
Proximal humeral fractures with osteoporosis may achieve a high rate of bony union when treated with conservative methods. Despite the common occurrence of malunion, a satisfactory functional outcome may be expected.
- 643 View
- 6 Download

- Clinical Results of Various Surgical Techniques for Isolated Fracture of Greater Tuberosity of Humerus
- Nam Su Cho, Seong Cheol Moon, Yong Girl Rhee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(2):133-139. Published online April 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.2.133
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To compare the clinical and radiologic outcomes of various surgical techniques for an isolated fracture of greater tuberosity of the humerus.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From February 2001 to December 2008, 31 patients, who underwent an operation for isolated greater tuberosity fracture and were followed up for more than 1 year, were enrolled in this study. The mean age at the time of operation was 49.3 years (range, 23-73 years). The operation methods included in this study were as follows: a transosseous suture using nonabsorbable suture material (16 cases), a fixation by cannulated screws (10 cases), tension band wiring (2 cases), bony fragment excision with rotator cuff repair (2 cases), and percutaneous pinning (1 case).
RESULTS
At the last follow-up, the average Constant score was 79.4 and Korean Shoulder Score (KSS) was 81.2. Among the various operation methods used in this study, the transosseous suture had the highest scores with 82.5 in Constant score and 89.3 in KSS. Bone union was achieved at average 10.3 weeks (range, 7-15 weeks), and there were 2 cases in which the reoperation was required due to internal fixation failure. Postoperative shoulder stiffness occurred in 3 cases, and all the cases were done with the deltopectoral approach.
CONCLUSION
Clinically and radiologically satisfactory results were obtained using various operation techniques for an isolated greater tuberosity fracture of the humerus. The transosseous suture showed relatively better results than the other methods used in this study. To achieve favorable clinical and radiologic results, it is important to select an appropriate surgical approach and fixation method according to the fracture site, degree of displacement, and size of fragment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biomechanical comparisons of hook plate and screw fixations in split-type greater tuberosity fractures of the humerus
Fa-Chuan Kuan, Kai-Lan Hsu, Chih-Kai Hong, Yueh Chen, Chen-Hao Chiang, Hao-Ming Chang, Wei-Ren Su
Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery.2022; 31(6): 1308. CrossRef
- Biomechanical comparisons of hook plate and screw fixations in split-type greater tuberosity fractures of the humerus
- 609 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Treatment of Non-union Distal Humerus Fractures after Operation
- Hyung Sik Kim, Ki Joon Jang, Yun Rak Choi, Il Hyun Koh, Ho Jung Kang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(4):310-316. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.4.310
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study is a retrospective analysis of patients who had undergone surgical treatment for non-union of distal humerus fracture. We evaluated them in terms of causes of injury, radiologic findings, and clinical outcomes such as prognosis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Seven consecutive radiologic patients who were confirmed to have nonunion of a distal humerus fracture underwent reoperations. These patients had already undergone operations for distal humerus fractures. This survey was held from 2005 to 2010. The average period up to diagnosis of non-union after the first operation was 7.4 months (4 to 16 months). The mean follow-up period was 24.6 months (12 to 65 months). Each patient was graded functionally according to the Mayo Elbow Performance Score and the Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand Score.
RESULTS
Osteosynthesis was performed by internal fixation with plates and screws and then a bone graft for non-union of the distal humerus fracture. The average range of motion within the elbow joints was found to be a flexion contracture of 18.8 degrees (0~30 degrees) and further flexion of 120.2 degrees (102~140 degrees). Among postoperative complications, three cases of medium-degree stiffness, two cases of medial column nonunion, and one case of dissociation of the internal fixator were reported.
CONCLUSION
Stable internal fixation for maintenance reduction status is essential after accurate initial anatomical reduction. We concluded that nonunion could be prevented by additional surgical treatment such as autogenous bone graft, if it is necessary. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Autogenous Inlay Bone Graft for Distal Humerus Nonunion with Metaphyseal Bone Defect: A Technical Note
Yong-Suk Lee, Dongmin Kim, Min-Sung Kang, Jong-Hwa Park, Sang-Uk Lee
Archives of Hand and Microsurgery.2020; 25(1): 39. CrossRef
- Autogenous Inlay Bone Graft for Distal Humerus Nonunion with Metaphyseal Bone Defect: A Technical Note
- 650 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Results of Two Stage Surgical Treatment of Pilon Fractures
- Hong Moon Sohn, Jun Young Lee, Sang Ho Ha, Sang Hong Lee, Gwang Chul Lee, Kwang Hyo Seo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(3):177-184. Published online July 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.3.177
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To report the good results of two-stage treatment in pilon fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A retrospective study of 23 patients among 30 patients with pilon fractures from March 2006 to November 2008, who underwent two-stage treatment of pilon fractures with a minimum of 24 months follow-up. The mean follow-up period was 28 months (24~41 months). In the first stage of the operation, open reduction of the articular surface and external fixation were performed after minimal incision. As the soft tissue healed, locking compression plate fixation was performed with the Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. Radiographic evaluation was graded by the criteria of Burwell and Charnley, and functional assessment of the ankle was evaluated by the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) ankle-hindfoot score.
RESULTS
The fractures were united within 16 weeks (12~30 weeks). The radiologic results showed anatomical reduction in 18 cases and a mean AOFAS score of 81. The mean range of ankle motion was 44 degrees. There were four complications: 1 case of wound infection and 3 cases of ankle osteoarthritis.
CONCLUSION
Two-stage treatment of pilon fractures is a good treatment method because it is designed to obtain early anatomical reduction, definitive stable fixation, low rates of soft tissue complication, and good range of ankle motion. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Current Concepts in Management of Pilon Fracture
Jun-Young Lee, Sang-Joon Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2014; 27(2): 173. CrossRef
- Current Concepts in Management of Pilon Fracture
- 647 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Report
- Conservative Treatment of Valgus Impacted Four-Part Fracture of the Proximal Humerus: A Case Report
- Moon Chan Kim, Jae Lim Cho, Hung Tae Chung, Dong Jun Kim, In Bo Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2011;24(1):96-99. Published online January 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.1.96
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - For valgus impacted four part fracture of the proximal humerus, surgical stabilization and early mobilization of the joint can produce the best clinical outcomes. But, we have experienced a case of conservative treatment and gained good clinical results. We have reported this case and included a review of the relevant literatures.
- 601 View
- 6 Download

Original Articles
- Arthroscopic Treatment of Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation Using TightRope(R): Preliminary Report
- Eui Sung Choi, Kyoung Jin Park, Yong Min Kim, Dong Soo Kim, Hyun Chul Shon, Byung Ki Cho, Ji Kang Park, Hyun Chul Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2010;23(3):310-316. Published online July 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.3.310
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the clinical and radiologic results of the arthroscopic treatment using TightRope(R) (Arthrex, Inc, Naples, FL) for management of acute acromioclavicular dislocation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twelve patients with acromioclavicular joint dislocation Rockwood type V are underwent the arthroscopic acromioclavicular joint reconstruction using TightRope(R) between March, 2008 and March, 2009. The average age was 40.4 years (range 25~63 years) and mean follow-up was 10 months (range 8~16 months). The shoulders were evaluated using parameters include radiologic measurements by comparing the clavicle posteroanterior and lateral radiographs with the contralateral one. Clinical evaluation was made for pain, function, and range of joint motion by Constant score and KSS (Korean Shoulder Score).
RESULTS
All twelve patients returned to their work without pain in 3 months after operation. The average Constant score and KSS score was 98.4 (range 97~100) and 97.8 (range 97~100) at the last follow-up. Because of technical error and indication error, two patients showed failures of TightRope(R) fixation on the coracoid side and the acromioclavicular joint was redislocated, so these cases were excluded. 10 patients were satisfied with functional results and cosmetic appearance.
CONCLUSION
Considering its less morbidity, less hospitalization, excellent cosmesis, early rehabilitation, this new technique offers an attractive alternative in acromioclavicular joint stabilization if the early technical error would be overcome. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Coracoclavicular Ligament Augmentation Using Tight-Rope®for Acute Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation - Preliminary Report -
Seok Hyun Kweon, Sang Su Choi, Seong In Lee, Jeong Woo Kim, Kwang Mee Kim
The Journal of the Korean Shoulder and Elbow Society.2013; 16(2): 115. CrossRef - Coracoclavicular Ligament Augmentation Using Endobutton for Unstable Distal Clavicle Fractures - Preliminary Report -
Chul-Hyun Cho, Gu-Hee Jung, Hong-Kwan Sin, Young-Kuk Lee, Jin-Hyun Park
The Journal of the Korean Shoulder and Elbow Society.2011; 14(1): 1. CrossRef
- Coracoclavicular Ligament Augmentation Using Tight-Rope®for Acute Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation - Preliminary Report -
- 550 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Clinical Outcome of Surgical Treatment for Intra-articular Distal Humerus Fracture
- Myung Jin Lee, Hyeon Jun Kim, Sung Keun Sohn, Kyu Yeol Lee, Sung Soo Kim, Chul Hong Kim, Lib Wang, Hyun Woo Sung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2010;23(2):201-205. Published online April 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.2.201
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate functions of the elbow joint according to surgical approach, time to exercise, and type of fracture after surgical treatment for the intra-articular comminuted fracture of the distal humerus.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
27 patients with the intra-articular comminuted fractures of the distal humerus underwent surgery from March, 2000 to January, 2007. We investigated the surgical approach, time for union, time to exercise and age. We also evaluated postoperative functions of the elbow joint according to the flexion contracture, the range of motion and the Mayo elbow performance score.
RESULTS
The average follow-up period was 37 months and the average time for union was 14 weeks. The average range of flexion was 115 degrees, the average flexion contracture was 10 degrees, and the Mayo elbow performance score with average value of 85 point showed good clinical results. There were no statistically significant differences in functions of the elbow joint according to the operative method and age. However, patients with early postoperative exercise within 6 days showed statistically better outcomes than patients with postoperative exercise after 7 days. Type C1, 2 fractures showed statistically better results than the type C3 fracture.
CONCLUSION
Stable fixation and early exercise are required to prevent postoperative complications and restore functions of the elbow joint with an intra-articular comminuted fracture of the distal humerus. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surgical Treatment Using a Transolecranon Approach with a Dual Locking Plate for Unstable Intercondylar Fractures of the Humerus
Ji-Kang Park, Yong-Min Kim, Dong-Soo Kim, Eui-Sung Choi, Hyun-Chul Shon, Kyoung-Jin Park, Byung-Ki Cho
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2012; 25(2): 129. CrossRef
- Surgical Treatment Using a Transolecranon Approach with a Dual Locking Plate for Unstable Intercondylar Fractures of the Humerus
- 664 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Surgical Treatment of Pathologic Humeral Fracture
- Ho Jung Kang, Byoung Yoon Hwang, Jae Jeong Lee, Kyu Ho Shin, Soo Bong Hahn, Sung Jae Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2010;23(2):187-193. Published online April 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.2.187
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate and analyze the radiographic and clinical outcomes after the surgical treatments of pathologic humeral fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From October 1993 to September 2007, a retrospective investigation was conducted with a total of 13 patients who underwent operations for pathologic humeral fractures. The methods of surgical treatment were as follows-four cases of open reduction and internal fixation; eight cases of closed reduction and internal fixation with intramedullary nailing; and one of radical excision and hemiarthroplasty.
RESULTS
Of nine patients with metastatic bone lesions, three were diagnosed with primary cancer after the incidence of pathologic humeral fracture. The mean period between the diagnosis of primary cancer and pathologic fracture in the latter six cases was 36.7 (2~144) months and the mean survival period after the surgical treatments was 22.8 (12~35) weeks in all patients with bone metastasis. Fracture unions were noted in all four cases of primary humeral bone lesion but none in metastatic cases. Pain relief and functional recovery were noted in eleven patients of this study.
CONCLUSION
Satisfactory clinical outcomes with sustained pain relief and functional recovery were observed after the surgical treatments of pathologic humeral fracture. Benign bone lesions require more active and early treatments in order to facilitate the functional recovery of upper extremities and fracture union. With pathologic humeral fractures originated from metastasis, palliative treatments were preferred to fracture union method for planning long-term pain relief and functional recovery. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The application of a dual-lead locking screw could enhance the reduction and fixation stability of the proximal humerus fractures: a biomechanical evaluation
Eunju Lee, Hyeon Jang Jeong, Yeon Soo Lee, Joo Han Oh
Frontiers in Surgery.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Therapeutic Approach to Humeral Pathologic Fracture Caused by Benign Bone Tumor
Jeung Il Kim, Um Ji Kim, Nam Hoon Moon, Hui Taek Kim, Tae Young Ahn, In Sook Lee, You Seon Song, Kyung Un Choi
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2016; 51(6): 509. CrossRef
- The application of a dual-lead locking screw could enhance the reduction and fixation stability of the proximal humerus fractures: a biomechanical evaluation
- 723 View
- 6 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Staged Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis of Proximal Tibial Fracture
- Joon Woo Kim, Chang Wug Oh, Jong Keon Oh, Hee Soo Kyung, Woo Kie Min, Byung Chul Park, Kyung Hoon Kim, Hee Joon Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(1):6-12. Published online January 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.1.6
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To assess the results of staged MIPO (Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis) for proximal tibial fractures with compromised soft tissue.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Eighteen proximal tibial fractures (AO 41:9 cases, AO 42:9 cases) included this study. Ten were open fractures. After temporary external fixation until soft tissue healed (mean 27.3 days), MIPO was performed secondarily without bone graft. We assessed the bony union and knee function, and affecting factors of the results were investigated.
RESULTS
All fractures united at 20 weeks (range, 11~32) except 1 case. Mean range of knee flexion was 134.4degrees and mean IOWA knee score was 89.1. There were 2 superficial and 2 delayed deep infections from open fractures (grade II:1 case, grade III:3 cases), although they healed after implant removal. Open fractures seem to influence the infection rate. Otherwise, there was no related factor affecting the results.
CONCLUSION
MIPO after temporary external fixation can provide favorable results in proximal tibial fractures with soft tissue injuries, but attention of delayed infection should be paid in open fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- MINIMALLY INVASIVE OSTEOSYNTHESIS WITH PLATE OR NAIL FOR META-DIAPHYSEAL TIBIAL FRACTURES - WHAT IS BETTER?
B. Makelov
Trakia Journal of Sciences.2023; 21(4): 357. CrossRef - Effect of Korean Medicine Treatments in Patients with Proximal Tibia Fracture: A Retrospective Observational Study
Jung Min Lee, Eun-Jung Lee
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2020; 30(3): 141. CrossRef - Comparison of Time to Operation and Efficacies of Ultrasound-Guided Nerve Block and General Anesthesia in Emergency External Fixation of Lower Leg Fractures (AO 42, 43, 44)
Chan Kang, Sang-Bum Kim, Youn-Moo Heo, You-Gun Won, Byung-Hak Oh, June-Bum Jun, Gi-Soo Lee
The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery.2017; 56(5): 1019. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Proximal Tibial Shaft Fracture
Young-Soo Byun, Ki-Chul Park, Hyun-Jong Bong, Chang-Hoon Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(1): 23. CrossRef - The Use of Fresh Frozen Allogenic Bone Graft in the Impacted Tibial Plateau Fractures
Yeung Jin Kim, Soo Uk Chae, Jung Hwan Yang, Ji Wan Lee, Dae Han Wi, Duk Hwa Choi
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(1): 26. CrossRef - Management of Open Fracture
Gu-Hee Jung
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(2): 236. CrossRef - Staged Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis of Distal Tibial Fractures
Sung-Ki Park, Chang-Wug Oh, Jong-Keon Oh, Kyung-Hoon Kim, Woo-Kie Min, Byung-Chul Park, Won-Ju Jeong, Joo-Chul Ihn
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(3): 289. CrossRef - Intramedullary Nailing of Proximal Tibial Fractures
Young-Soo Byun, Dong-Ju Shin
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(3): 197. CrossRef - Proximal Tibia Fracture: Plating
Ki-Chul Park
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(3): 206. CrossRef
- MINIMALLY INVASIVE OSTEOSYNTHESIS WITH PLATE OR NAIL FOR META-DIAPHYSEAL TIBIAL FRACTURES - WHAT IS BETTER?
- 580 View
- 0 Download
- 9 Crossref

- The Results of Surgical Treatment for Nonunion of Phalanges in the Hand
- Hee Dong Kim, Yoon Hong Kim, Yong Soo Choi, Heun Guyn Jung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2008;21(2):140-144. Published online April 30, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.2.140
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the results of internal fixation and autogenous bone graft for the phalangeal nonunion in the hand.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From Feb. 2000 until May 2006, thirteen cases that had been treated for non-union of phalanges in the hand were investigated retrospectively. Seven cases were treated with mini-plate fixation and autogenous cancellous graft and six cases with Kirschner wire fixation and autogenous cancellous graft. We analyzed bony union period radiographically and clinical results according to Belsky's score.
RESULTS
Thirteen cases obtained bony union. Seven cases of mini-plate fixation and bone graft, and six cases of K-wire fixation and bone graft achieved the bony union postoperatively on average 7.9 weeks and 6.3 weeks, respectively. Clinical results were "good" in four cases and "poor" in nine cases according to the Belsky's score. Only one of ten cases with associated injuries, such as tendon, nerve, arterial injuries and other finger fractures in the injured hand, had the good clinical result, but all three cases without associated injuries had the good one.
CONCLUSION
Internal fixation and autogenous bone graft can be a successful treatment of phalangeal nonunion. However, more careful choice of surgical treatment methods and preoperative explanation of poor post-operative results or complications should be made for phalangeal nonunion with associated injuries in the finger because of poor outcome in those cases.
- 546 View
- 3 Download

- The Surgical Outcomes for Isolated Greater Tuberosity Fracture of Proximal Humerus
- Eun Sun Moon, Myung Sun Kim, Young Jin Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(3):239-245. Published online July 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.3.239
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the adequate surgical methods and postoperative rehabilitation by analyzing the outcome of surgical treatment for isolated greater tuberosity fracture of proximal humerus.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Ten patients who allowed at least 1 year follow up after the surgical treatment of isolated greater tuberosity fractures were evaluated. Their mean age was 52.3 years (range, 28~67) and mean follow up duration was 23.8 months (range, 12~36). We choosed the different approaches and fixation methods according to size, location and presence of comminution of the fragment, and combined injury. The rehabilitation programs were indivisualized and we evaluated the clinical outcomes using UCLA and Constant scoring system.
RESULTS
According to the UCLA scoring system, 5 cases were excellent, 3 cases were satisfactory, and 2 cases were unsatisfactory. By the Constant scoring system, 8 cases were excellent and 2 cases were good. The average bony union time was 7.6 weeks (range, 6~8) except the 2 cases of revision surgery. Two cases were operated using cannulated screws alone, 3 cases using only nonabsorbable sutures and 5 cases using cannulated screws and nonabsorbable sutures. One out of two revision cases was developed from the negligence of preoperative shoulder anterior dislocation with rupture of subscapularis, and the other was caused by improper immobilization of the fracture site postoperatively.
CONCLUSION
Not only the adequate surgical approaches and the fixation methods according to the size and comminution of fragment, but also the identification of combined injuries were very important in the surgical treatment for the isolated greater tuberosity fracture. And we considered that the adequate postoperative rehabilitation and proper protection based on the intraoperative fixation stability play an important role for the better clinical and radiological outcomes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Features and Characteristics of Greater Tuberosity Fractures with or without Shoulder Dislocation
Dong-Wan Kim, Young-Jae Lim, Ki-Cheor Bae, Beom-Soo Kim, Yong-Ho Lee, Chul-Hyun Cho
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2018; 31(4): 139. CrossRef - The Surgical Outcomes of Isolated Greater Tuberosity Fractures of the Proximal Humerus Fixed with the Spring Plate
Dong-Ju Shin, Young-Soo Byun, Se-Ang Chang, Hee-Min Yun, Ho-Won Park, Jae-Young Park
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(3): 159. CrossRef
- Clinical Features and Characteristics of Greater Tuberosity Fractures with or without Shoulder Dislocation
- 594 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Surgical Treatment of Posterior Wall Fractures of the Acetabulum
- Young Soo Byun, Se Ang Chang, Young Ho Cho, Dae Hee Hwang, Sung Rak Lee, Sang Hee Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(2):123-128. Published online April 30, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.2.123
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the results of surgical treatment of posterior wall fractures of the acetabulum and to determine the factors affecting the results.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty-one posterior wall fractures were reviewed; 7 type A1-1, 19 type A1-2 and 5 type A1-3 by AO classification. Postoperatively, the accuracy of the reduction was evaluated. At the final follow-up, clinical and radiographic results were evaluated with medical records and radiographs. The factors affecting the results were determined.
RESULTS
The reduction was graded as anatomical in 22 patients, imperfect in seven and poor in two. The clinical result was excellent in 21 hips, good in six, fair in three and poor in one. The quality of the reduction was strongly associated with the clinical result. The radiographic result was excellent in 22 hips, good in five, fair in two and poor in two. The clinical result was related closely to the radiographic result. Complications were osteoarthritis in three patients, osteonecrosis of the femoral head in one, heterotopic ossification in one, penetration of a screw into the joint in one and iatrogenic sciatic nerve injury in one. The factors affecting the clinical results were fracture patterns, the surgeon's experience, the accuracy of the reduction and late complications.
CONCLUSION
In this present series of posterior wall fractures, as their prognosis depends on the severity of the injury and the accuracy of the reduction, satisfactory result can be obtained by anatomical reduction with thorough preoperative planning and the surgeon's experience.
- 401 View
- 1 Download

Case Report
- Surgical Treatment of the Myositis Ossificans in Supracondylar Fracture of the Humerus in Children: A Case Report
- Tai Seung Kim, Kee Cheol Park, Seung Pyo Seo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(4):482-485. Published online October 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.4.482
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- Supracondylar fracture of the humerus is a common injury in the pediatric patient. A less common complication is the development of myositis ossificans. Although frequently cited as a possible complication, there are few reported cases of this occurring in the pediatric patient. We present a case report of a 8 year old boy who developed myositis ossificans after a supracondylar fracture of the humerus. After one year of the injury, we could ascertained radiologically complete maturation of the mass which developed in front of the distal humerus and markedly made motion of the elbow joint limited. We could obtain further motion through the surgical resection and then physical therapy. Now, eleven months have lapsed since the mass was removed, the range of motion is almost normal, and the recurrence of myositis ossificans is not existed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recent Trends in Treatment of Supracondylar Fracture of Distal Humerus in Children
Soon Chul Lee, Jong Sup Shim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2012; 25(1): 82. CrossRef
- Recent Trends in Treatment of Supracondylar Fracture of Distal Humerus in Children
- 553 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Article
- Percutaneous Transphyseal Intramedullary K-wire Fixation for the Diaphyseal Forearm Fractures in Children
- Jung Hoei Ku, Young Chul Go, Man Jun Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(3):374-377. Published online July 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.3.374
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Although the standard treatment of diaphyseal forearm fractures in children is conservative treatment with closed reduction and cast immobilization, unstable or irreducible fractures are usually needed by surgical intervention. The aim of this article is to determine the efficacy of the percutaneous transphyseal intramedullary K-wires fixation for the forearm diaphyseal fractures in children.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In this retrospective study, we reviewed 18 cases of forearm diaphyseal fractures in children, which were treated with percutaneous transphyseal intramedullary nailing using K-wires from January 2001 to December 2004. We analyzed the period for radiologic bone union and the complications until the last follow-up.
RESULTS
The average period of follow-up was 15 months with mean age of 7.8 years. The average time to bone union was 6.2 weeks and nonunion, malunion, radio-ulnar synostosis and refracture were not found, just 2 local pin site infections were seen but healed by conservative treatment. Postoperative scar was small and the complications until the last follow-up were not found.
CONCLUSION
In the operative treatment of the forearm diaphyseal fractures in children, we think percutaneous transphyseal intramedullary K-wire fixation is one of the effective methods because of the minimal invasiveness, simplicity and easiness in removal.
- 388 View
- 0 Download

Randomized Controlled Trial
- Comparison of the Result of Vertebroplasty and Conservative Treatment in Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture
- Ye Soo Park, Woo Jin Cho, Jae Lim Cho
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(3):363-368. Published online July 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.3.363
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the results of vertebroplasty and conservative treatment in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients were divided randomly into 2 groups; Group I (conservative treatment) and Group II (vertebroplasty). There are 14 cases in group I and 16 cases in group II. Radiologically, the progression of compression was observed. Clinical evaluation was done using Denis pain scale. In both groups, prolonged pain with nonunion or avascular necrosis that resulted in surgical intervention was evaluated as complication. In group II, the complication associated the procedures were evaluated.
RESULTS
Group II was superior to conservative treatment in terms of maintaining vertebral height radiologically. The characteristics of symptom improvement were the same in two groups. There were cement leakage among group II but they did not influence to the results. In group I, 2 subjects needed surgery due to prolonged pain. In group II, 1 subject needed surgery due to prolonged pain and there were 3 cement leakage cases which were insignificant.
CONCLUSION
In vertebroplasty group, complications associated the procedures were noted. In conservative treatment group, more patients needed operation. Therefore, we should be very prudent when we choose the treatment of the osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Case Report of the Korean Medical Treatment of Dysphagia and Anorexia after Lumbar Compression Fracture
Hye-mi Jo, Eun-chang Lee, Hye-soo Youn, Choong-hyun Park, Da-young Han, Da-hae Jung, Jung-eun Lee
The Journal of Internal Korean Medicine.2022; 43(2): 219. CrossRef - A Retrospective Clinical Survey of Vertebral Compression Fractures
Ji Hye Oh, Yun Kyu Lee, Jae Soo Kim, Hyun Jong Lee, Sung Chul Lim
Journal of Acupuncture Research.2018; 35(4): 219. CrossRef - Lumbar Spine Fracture
Seung-Wook Back, Hyun-Joong Cho, Ye-Soo Park
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(3): 277. CrossRef
- A Case Report of the Korean Medical Treatment of Dysphagia and Anorexia after Lumbar Compression Fracture
- 1,305 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref

Original Articles
- Surgical Treatment of Displaced Intra-articular Calcaneal Fractures: Minimum of 2-year Follow-up
- Myung Ho Kim, Hong Geun Jung, Joong Bae Seo, You Jin Kim, Je Wook Yu
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(2):201-207. Published online April 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.2.201
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the overall clinical features and postoperative functional results of the intra-articular calcaneal fractures at more than 2 years follow-up, and also to compare the results at postoperative 1 year with the results at more than 2-year follow-up.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study is based on 39 intra-articular calcaneal fractures (34 patients) that underwent surgical treatment from March 1997 to May 2002 with at least 2 years follow-up. The overall postoperative results were evaluated with Creighton-Nebraska functional scale. The comparison of results at postoperative 1 year was also performed with results at more than 2-year follow-up.
RESULTS
By Sanders classifications, there were 13 type II fractures (33.3%), 20 type III (51.3%), and 6 type IV fractures (15.4%). Average follow-up period was 35 months (range: 24~87 months) and at final follow-up of more than 2 years, Creighton-Nebraska score was average 76.0 (range: 30~100) which significantly improved from postoperative 1-year results of 67.1 (range: 22~95) (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
The clinical outcome at more than 2 years after surgical treatment of intra-articular calcaneal fractures was quite promising, which significantly improved compared to 1-year results. Therefore, we concluded that functional results of calcaneal fractures should be evaluated at least 2 years after the treatment.
- 262 View
- 0 Download

- Operative Treatment in Fracture-Dislocations of Carpometacarpal Joints
- Jae Yeol Choi, Hun Kyu Shin, Kyung Mo Son, Chun Suk Ko
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(4):443-451. Published online October 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.4.443
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To present our operative experiences with carpometacarpal (CMC) injuries, excluding thumb.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty four fracture and dislocations of CMC joint excluding thumb were reviewed retrospectively. Emphases were placed on injury mechanisms, anatomical location, times between diagnosis and surgery, treatment and complications.
RESULTS
The average age of patients was 31.5 years. 19 cases of axial loading by blow as an injury mechanism. The 5th CMC joint was found to be the most frequently involved single joint (18 cases of 34 cases). Dorsal dislocation of CMC joints was present in 12 cases. Comminution of the carpal or metacarpal bone was present in 18 cases. The average time to surgery was 6 days. Twenty-seven cases were operated upon by closed reduction and percutaneous pinning. Seven cases were treated by open reduction and internal fixation. In the last follow up period, a clinically full hand function was restored in 31 cases. Intermittent pain was present in 6 cases in which there was grip weakness in 4 cases and limitation of motion in 3 cases. However, all cases were able to activities of daily living.
CONCLUSION
We obtained good outcomes in CMC joint injuries through the accurate diagnosis and proper operative treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Study on Percutaneous Intramedullary Bioresorbable Pin Fixation for Fourth and Fifth Metacarpal Bone Fracture
Sang Hwan Lee, Sang Hun Kim, Eun Soo Park, Seung Min Nam, Ho Seong Shin
Journal of the Korean Society for Surgery of the Hand.2017; 22(2): 105. CrossRef - Percutaneous retrograde intramedullary single wire fixation for metacarpal shaft fracture of the little finger
Soo-Hong Han, Seung-Yong Rhee, Soon-Chul Lee, Seung-Chul Han, Yoon-Sik Cha
European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology.2013; 23(8): 883. CrossRef - Operative Treatment in the Delayed Diagnosed Fracture and Dislocation of Hamatometacarpal Joint
Suk Ha Lee, Jong Wong Park, Jin Il Kim, Seoung Joon Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(3): 249. CrossRef - Comparison of Early Fixation and Late Fusion of 4, 5th Carpometacarpal Joint in the Intra-Articular Fractures of 4th and 5th Metacarpal Base
Chang Ho Yi, Jin Rok Oh
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(1): 60. CrossRef - Percutaneous Retrograde Intramedullary Pin Fixation for Isolated Metacarpal Shaft Fracture of the Little Finger
Soo Hong Han, Hyung Ku Yoon, Dong Eun Shin, Seung Chul Han, Young Woong Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(4): 367. CrossRef - Operative Treatment of Trapezium Fractures
Ho Jung Kang, Nam Heon Seol, Man Seung Heo, Soo-Bong Hahn
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(4): 276. CrossRef - Fracture-Dislocation of the Carpometacarpal Joint with the Fracture of Hamate
Jin Woong Yi, Whan Young Chung, Woo Suk Lee, Cheol Yong Park, Youn Moo Heo
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2008; 21(4): 297. CrossRef
- Clinical Study on Percutaneous Intramedullary Bioresorbable Pin Fixation for Fourth and Fifth Metacarpal Bone Fracture
- 503 View
- 0 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Nonoperative Treatment of Isolated Lateral Malleolar Fracture
- Woo Chun Lee, Jong Ho Ahn
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(3):291-293. Published online July 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.3.291
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the results of conservative treatment for isolated lateral malleolus fracture without medial ankle injury.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From March 1999 to February 2003, 25 ankles in 25 patients were treated for isolated lateral malleolus fracture and followed for more than one year. Mean age was 46.9 years (range, 20~71 years). Cases without any swelling or tenderness on the deltoid area, or cases with minimal pain, swelling or tenderness on the deltoid area and medial clear space 1 mm or less on stress radiograph were included for the study. Immediate weight bearing was allowed with below-knee cast immobilization in all cases.
RESULTS
All were supinatin-external rotation stage II injury and mean duration of cast immobilization was 6.3+/-1.6 weeks after injury. There was no case which showed widening of medial clear space during routine radiographic follow-up. There was no change in the degree of displacement in spite of immediate weight bearing with short leg cast on.
CONCLUSION
Because the lateral malleolus fracture without medial injury can be managed nonoperatively, we need to differentiate this type of fracture to avoid unnecessary surgery, and for early return to normal daily activity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Posterior Plating in Distal Fibular Fracture
Choong-Hyeok Choi, Young-A Cho, Jae-Hoon Kim, Il-Hoon Sung
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2007; 20(2): 161. CrossRef
- Posterior Plating in Distal Fibular Fracture
- 695 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Usefulness of Blocking Screw in Intramedullary Nail on Proximal Tibial Fracture
- Jun Young Yang, June Kyu Lee, Young Mo Kim, Chang Hwa Hong, Kyung Cheon Kim, Sung Hwan Ahn
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(1):17-21. Published online January 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.1.17
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the effectiveness of a blocking screw in intramedullary nailing at the tibia proximal shaft fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
63 tibia proximal shaft fractures from January 2000 to December 2002 treated with only intramedullary nailing were referred to as group I, and 8 fractures from January 2003 to December 2003 treated with both intramedullary nailing and the blocking screw were referred to as group II. Retrospective studies were done for group I and II. The incidence of nonunion and the postoperative angular alignments were compared. Malalignment was defined as an angle of 5 degrees anteroposteriorly or mediolaterally.
RESULTS
There were 7 nonunion (11%) in group I in compare with none in group II. There were 21 angular malalignments (33%) in group I and 1 in group II (12%) and most of them had valgus deformity or anterior anglulation. No complications were directly due to the use of the Blocking screw.
CONCLUSION
The technique of the blocking screw used to be one of the option for proximal tibial nailing at tibial proximal shaft fracture helps to overcome angular malalignments of bones.
- 340 View
- 0 Download

- A Comparison of Vertebroplasty Versus Conservative Treatment in Osteoporotic Compression Fractures
- Sang Ho Moon, Dong Joon Kim, Chung Soo Hwang, Sang Eon Lee, Se Won Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(4):374-379. Published online October 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.4.374
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To compare clinical and radiological results between vertebroplasty and conservative treatment in osteoporotic compression fractures of thoracolumbar spine.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
34 patients were reviewed with at least 1 year follow up. Vertebroplasty was used in 14 and conservative treatment was done in 20 fractures. These groups were compared by clinical results which were evaluated by the scoring system according to pain, mobility and analgesic usage at preoperative, postoperative 1 month and postoperative 1 year. And also compared by the increment of kyphosis and loss of vertebral body height in lateral films at the same time. We compared duration of hospitalization between two groups.
RESULTS
Vertebroplasty group showed statistically significant less pain and mobility than conservative treatment (p<0.05), but there was no differences in analgesic usage at postoperative 1 year while significant difference at 1 month. In radiological comparison, vertebroplasty showed less increment of kyphosis and loss of body height significantly (p<0.05). Also vertebroplasty group had shorter hospitalization stay significantly (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
Our retrospective analysis demonstrated that vertebroplasty provided significant pain relief, improvement of motion and reduction of analgesic usage and also provided considerable spinal stabilization that prevented further kyphosis and collapse. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Outcome Comparison between Percutaneous Vertebroplasty and Conservative Treatment in Acute Painful Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture
Hwa-Yeop Na, Young-Sang Lee, Tae-Hoon Park, Tae-Hwan Kim, Kang-Won Seo
Journal of Korean Society of Spine Surgery.2014; 21(2): 70. CrossRef - Large Pulmonary Embolus after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty - A Case Report -
Sang Ho Moon, Soo Won Lee, Byoung Ho Suh, Sung Hwan Kim
Journal of Korean Society of Spine Surgery.2009; 16(1): 46. CrossRef
- Outcome Comparison between Percutaneous Vertebroplasty and Conservative Treatment in Acute Painful Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture
- 743 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Treatment of Bony Mallet Finger: Closed Reduction Using Extension Block K-wire
- Jae Yeol Choi, Hwa Jae Jung, Ho Jin Lee, Kyung Mo Son, Young Hun Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(4):362-367. Published online October 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.4.362
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To review the result of bony mallet finger treated with a closed reduction using extension block K-wire MATERIALS AND METHODS: Between January 2001 and November 2002, among the patients with bony mallet finger underwent closed reduction using extension block K-wire, we retrospectively reviewed 14 patients with 14 fractures who had a minimum follow-up of 12 months.
RESULTS
There were 10 men and 4 women, with an average follow-up for all cases 15.7 months (range, 12 months~18 months). According to Crawford's evaluation criteria, we obtained 7 excellent, 5 good, 2 fair. We obtained bony union in all patients, with no remained pain. The average ROM was 67 degrees at postoperative 12 months. Postoperative complications occurred in two cases, which were nail deformity and mild osteoarthritis at the distal interphalangeal joint. There was no pin site infection.
CONCLUSION
This technique is not only easier but also less invasive than other techniques for reduction of mallet finger. Also, it shows excellent result with lower complication rate. So, it seems a reliable treatment for bony mallet finger. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Osteoarthritis after Extension Block Technique for the Bony Mallet Finger
Sung Hoon Koh, Jung Hyun Park, Jin Soo Kim, Si Young Roh, Kyung Jin Lee, Dong Chul Lee
Archives of Hand and Microsurgery.2021; 26(4): 238. CrossRef - Comparison of Surgical Outcomes of Percutaneous K-Wire Fixation in Bony Mallet Fingers with Use of Towel Clip versus 18-Gauge Needle
Ho-Seung Jeon, Chan-Sam Moon, Seo-Goo Kang, Kyeong-Seop Song, Uk-Hyun Choi
Journal of the Korean Society for Surgery of the Hand.2013; 18(1): 1. CrossRef - Percutaneous Kirschner Wire Fixation of Acute Mallet Fractures Percutaneousely Reduced by Towel Clip
Chung Soo Han, Duke Whan Chung, Bi O Jeong, Hyun Chul Park, Jin Young Kim, Cheol Hee Park, Jin Sung Park
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(4): 283. CrossRef
- Osteoarthritis after Extension Block Technique for the Bony Mallet Finger
- 513 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The Usefulness of Non-operative Treatment of Distal Radius Fracture in Elderly Patients
- Ki Ser Kang, Han Jun Lee, Sang Hak Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(4):345-349. Published online October 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.4.345
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To disclose the correlation between the functional and radiologic results of the treatment of distal radius fracture in elderly patients by non-operative versus operative treatment.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From January 1995 to December 2000, 36 patients, more than 60 years old with fractures of distal radius were treated and followed up for more than one year. We classified them using the Fernandez classification and evaluated functional and radiological results according to the subjective point system of Cole & Obletz and objective evaluation by Scheck.
RESULTS
In functional result, excellent to good results were obtained in 12 cases (71%) in the non-operative group and 14 cases (74%) in the operative group, there were no evidence of statistical difference between two groups (p>0.05). In radiographic results, mean radial inclination, loss of radial length and volar tilt were 13degree, 12.3 mm, 7.2degrees in the non-operative goup and 5.2degrees, 5.1 mm, 3.3degrees in the operative group on last follw-up radiographs, there were evidence of statistical difference between two groups (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
Operative treatment is radiographically better result in distal radius of elderly patients but functional satisfaction is not significantly related with radiographic result. When we decide the treatment of elderly patients, non-operative treatment can be useful method, considering with patient's age and activity status.
- 320 View
- 0 Download

- Conservative Treatment of the Displaced Clavicular Shaft Fracture in Multiple Injury
- Hyun Dae Shin, Kwang Jin Rhee, Young Mo Kim, Se Min Woo, Ho Sup Song
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(4):333-337. Published online October 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.4.333
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analyse the comparative clinical results between adults with multiple injury including the clavicular shaft fracture and only clavicular shaft fracture who had supportive care through retrospective aspect.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We had 48 adult patients in this hospital with simple fracture and multiple injury including the clavicular shaft whom we were able to evaluate at least more than a year. 12 of 48 patients were with only clavicular shaft fracture and the rest of them were with multiple injury. We classified patients into two groups those who had fracture with displacement for group A (A1 for the cases with over 50% of fracture surface contact rate and A2 for less than 50% from the images of simple X-ray) and those who had comminuted fracture for B. We compared the time of bone union, nonunion rate of only clavicular fractures and multiple injury, clinical results for patients who had supportive care with retrospective aspect.
RESULTS
A1 (7 cases), A2 (4 cases), B (1 case) were prevalent in the group of only clavicular shaft fracture and A1 (8 cases) and A2 (16 cases) and B (12 cases) were prevalent in the group of multiple injury. For the cases with supportive care, we could find 1 nonunion case (8%) and 11 union cases on average 2.91 months in the group of only clavicular shaft fracture and 7 nonunion cases (19%) and 29 union cases on average 3.58 months in the group of multiple injury. The best clinical results had occurred in 8 cases (67%) of only clavicular shaft fracture group and 19 cases (53%) of multiple injury group. We could find out the union from all 8 nonunion cases that took operation afterward.
CONCLUSION
Although the choice of treatment of clavicular fracture is supportive care, but multiple injury including the clavicular fracture is a high-energy injury, so the possibility of comminuted and displacement is high, so that nonunion rate is high. The possibility of early surgery must be considered seriously.
- 328 View
- 0 Download

- Operative Treatment of Proximal Tibial Plateau Fractures through Lateral Submeniscal Approach
- Hyug Su An, Se Ang Chang, Jun Woo Park, Jin Seok Lee, Hun Ho Bang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(3):237-242. Published online July 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.3.237
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was conducted to evaluate the clinical results of proximal tibial plateau fractures treated with open reduction and internal fixation through the lateral submeniscal approach and allowed early motion of the knee and to evaluate the effectiveness of the approach.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From January 1998 to December 2002, fifty four patients who underwent open reduction through the lateral submeniscal approach for proximal tibia plateau fracture and had a follow-up more than one year were included in this study. Clinical results were evaluated by postoperative radiographs taken at the last follow-up and Porter's assessment method.
RESULTS
Anatomical reduction was achieved under direct vision through the submeniscal approach in most of the cases in this study. The postoperative radiographs showed anatomical reduction in 32 cases (59%) and adequate reduction with displacement within 2 mm in 20 cases (37%). The clinical evaluation by Porter's assessment method revealed that 49 cases (91%) were acceptable results of excellent or good at the final follow-up CONCLUSION: This study indicates that open reduction and internal fixation through the lateral submeniscal approach can be a good option for proximal tibia plateau fractures because it allows accurate reduction of the articular fractures, which is confirmed directly during operation, identification and repair of associated soft tissue injuries are facilitated, sufficient bone graft and stable fixation of the articular fragments under direct vision allow early motion of the knee.
- 362 View
- 7 Download

- Operative Treatment of Floating Shoulder
- Ho Jung Kang, Gun Bo Park, Dong Joon Shim, Soo Bong Hahn, Eung Shick Kang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(1):38-42. Published online January 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.1.38
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
Conservative treatment of displaced ipsilateral compound fractures of clavicle and scapula neck or gleonoid cavity, causing a floating shoulder, cannot expect satisfactory results in all of them. We reviewed 9 operative cases of floating shoulders and analyzed the results with review of literature.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Nine patients with floating shoulders were operated from July 1996 to August 2000 were reviewed. Patient's age was in average 38.3 years old. Associated injuries were 4 cases of rib fractures and 1 case of humerus shaft fracture. Other injuries included 3 hemothorax, 2 pneumothorax, 1 brachial plexus injury, and 1 ulnar nerve injury. Operation for both clavicle and scapula fracture was done in 6 cases, and surgery was done for only clavicle in 3 cases. Internal fixation for clavicle was done with 3.5 mm AO reconstruction plate in 4 cases and Dynamic Compression Plate in 5 cases.
RESULTS
Clinical results by Hardegger method showed 7 cases of excellent, 1 case of good, and 1 case of poor. Complications include 2 cases of limitation of motion of shoulder joint and one case of residual pain.
CONCLUSION
Floating Shoulder is caused by high-energy trauma, therefore initial assessment of associated injuries should be done carefully. In evaluating the articular surface of the glenoid and positions of the fracture fragment, CT evaluation is very useful in planning the surgical treatment. Clinical results after surgery can give satisfactory results.
- 504 View
- 2 Download

- Results of Surgical Treatment in Schatzker Type VI Tibial Plateau Fracture
- Kyung Jin Song, Kwang Bok Lee, Seung Jin Moon, Joo Hong Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(1):32-37. Published online January 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.1.32
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the factors influencing the results for the treatment of the Schatzker type VI tibial plateau fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty-two cases of the 21 patients in Schatzker type VI tibial plateau fractures were analyzed. Treatment results were analyzed according to the type of fracture (open vs closed), method of operative treatment, angulation more than 5 degree and status of infection. The functional results was evaluated by Hohl's functional criteria. Student t-test was used for the statistical analysis.
RESULTS
Functional outcome demonstrated 5 excellent, 8 good, 6 fair and 3 poor results. There was no significant difference in the treatment results between type of fracture, method of operative treatment and status of infection. Among 9 cases with angular deformity of more than 5 degree, 2 showed excellent or good result and 7 showed fair or poor result (p<0.05). There was no significant difference between rate of postoperative infection and the mean period of the clinical bone union (p=0.66).
CONCLUSION
Accurate anatomical reduction and rigid fixation is essential for the treatment of Schatzker type VI tibial plateau fractures for the prevention of the angular deformity. And early weight bearing exercise should be controlled for the prevention of loss of reduction and loss of alignment leading to angular deformity.
- 411 View
- 12 Download

- Non-operative Treatment of Lateral Malleolar Fracture using Ankle Brace
- Nam Hong Choi, Ho Yoon Kwak, Baik Yong Song, Sang Wook Bae, In Mook Lee, Do Hyun Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(3):363-369. Published online July 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.3.363
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the outcome of conservative treatment for minimal displaced lateral mallolar fracture using ankle brace.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Eleven patients (eleven ankles) underwent conservative treatment with ankle brace for 8 weeks with full weight bearing ambulation. Inclusion criteria were minimal displacement (<3 mm) of fracture, no or mild tenderness or swelling on medial malleolar area and no lateral shift of talus. The patients were evaluated with AOFAS (the American Orthopedic Foot and Ankle society) Ankle-Hindfoot scale.
RESULTS
Average follow up was 103 weeks (36~192). All cases had normal range of motion of ankle. The average score of AOFAS Ankle-Hindfoot scale was 95 points.
CONCLUSION
The advantages of conservative treatment with ankle brace were early return to daily activity and work, comfort to the patients and a short period of rehabilitation. Conservative treatment with ankle brace for minimal displaced lateral malleolar fracture is recommended.
- 541 View
- 3 Download

- Treatment of Ipsilateral Femoral Neck and Shaft Fractures
- Jung Ryul Kim, Hyung Suk Lee, Myung Sik Park, Hee Chul Yu, Doo Hyun Yang
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(3):327-333. Published online July 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.3.327
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analyse the result of the treatment of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures and to consider effective method of the treatment.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Seventeen patients with ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures were treated from January 1992 to January 1999 and followed up more than 2 years. Radiologic bony union between each treatment method, complication were analysed. The functional results assessed with Iowa hip rating system and Swiontkowski system.
RESULTS
In femoral neck fractures, bony union was obtained in all cases, average 12 weeks. In femoral shaft fractures, bony union was obtained in all but one case. There was no statistical association bony union time between each treatment method (p>0.05). By Iowa hip rating system, nine hips had an excellent result; eight, a good result. According to rating system of Swiontkowski, the result was excellent in nine, good in six, fair in one, and poor in one.
CONCLUSION
We concluded that early diagnosis of all injuries was needed. To avoid further vascular damage of femoral head, early anatomical reduction of the femoral neck fracture should be performed. And then, shaft fracture was fixed with implants which were most appropriate for that combination of fractures.
- 336 View
- 0 Download

- Surgical and Conservative Treatment of Acetabular Fractures
- Chong Kwan Kim, Byung Woo Ahn, Saeng Guk Lee, Jae Ik Chung, Jin Woo Jin, Kwon Ho Kim, Kang Hoon Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(3):309-318. Published online July 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.3.309
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
Fractures of the acetabulum remain a major challenge to the orthopedic surgeons. Although the operative treatment for the complex fractures is preferred, inaccurate reduction and then incongruity of the hip joint lead to serious complication such as premature osteoarthritis. We evaluated the results of surgical and conservative treatment for acetabular fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From January 1996 to March 2001, we reviewed 55 cases retrospectively. Posterior wall fracture (13 cases) was the most common by Letournel's classification and followed by both column fracture (10 cases). Causes of injuries included 41 cases of traffic accident and 8 cases of falling down. We divided the cases into an operation group (28 cases) and conservative group (27 cases) and evaluated the results as excellent, good, fair or poor according to Matta's clinical and radiological grade criteria.
RESULTS
Anatomical or satisfactory reduction was obtained in 22 cases of operative group and clinical results were excellent in 7 cases, good in 13 cases. Conservative group revealed excellent and good clinical results in 15 of 27 cases.
CONCLUSION
In cases of the displaced complex fractures, posterior wall fracture with instability and displaced fractures involving the weight bearing dome of the acetabulum, open reduction and internal fixation after accurate evaluation of the fracture pattern could allow earlier ROM exercise and have the result in better prognosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Results of Surgical Treatment of Acetabular Fractures according to Quality of Reduction
Sang-Hong Lee, Min-Kyu Shin, Sueng-Hwan Jo
The Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2007; 42(2): 153. CrossRef
- Clinical Results of Surgical Treatment of Acetabular Fractures according to Quality of Reduction
- 626 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Correlation between Surgical Timing and Perioperative Complications in the Treatment of Displaced Supracondylar Humeral Fractures of Children
- Soo Hong Han, Duck Yun Cho, Hyung Ku Yoon, Byung Soon Kim, Jae Hwa Kim, Hyung Kun Park, Se Hyen Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(2):278-283. Published online April 30, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.2.278
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
Even though emergent percutaneous pinning after closed reduction is the popularized treatment of the displaced type II and type III pediatric supracondylar fractures of the humerus, the timing of pinning still presents controversy. The purpose of this study is to suggest an appropriate surgical time without significant perioperative complications.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From April 1995 to January 2002, 179 consecutive patients who had undergone surgical treatment were selected. They were divided to 5 groups [A group: 8 hours or less following injury (24 cases), B group: from 9 to 16 hours (63 cases), C group: from17 hours to 24 hours (63 cases), D group: from 25 hours to 48 hours (18 cases), and E group: from 49 hours to 72 hours (11 cases)] and reviewed retrospectively to analyze perioperative complications and operation time.
RESULTS
There was no significant difference between each group with respect to surgical wound infection, iatrogenic ulnar nerve injury, VIC, operation time and the necessity of reoperation (p>0.05).
CONCLUSION
Within the parameters outlined in our study, we could not find the any meaningful correlation between surgical timing and occurrence of perioperative complications and also, we think that the timing of percutaneous pinning can be delayed to the time when a surgeon considers it appropriate.
- 337 View
- 0 Download

- Surgical Treatment for Fractures of the Talus
- Ho Rim Choi, Jang Geun Lee, Hun Hwi Choi, Sung Woo Choi
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(1):67-73. Published online January 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.1.67
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the clinical results and develope guidelines for surgical treatment of talus fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Among the 60 cases that were treated during March 1990 to November 2000, 34 cases were treated operatively and followed up for more than one year( range: 1 4.4 years ). They were analyzed retrospectively with questionnaire directly or by telephone interview, radiograms and medical records. Clinical results were evaluated by Hawkins 'scoring system.
RESULTS
25 out of 34 cases showed satisfactory results. Unisatisfactory results were seen in cases that we couldn 't achieve anatomical reduction due to severe communition, and also in case of delayed treatment due to associated trauma and soft tissue injury. Six out of 8 cases that showed no Hawkins 'sign developed avascular necrosis. However, satisfactory results were achieved through conservative treatment.
CONCLUSION
Satisfactory results could be achieved through early anatomical reduction and rigid internal fixation followed by aggressive rehabilitation. There was no differences in clinical results either by the surgical approach or method of internal fixation. Avascular necrosis was not essentially related to the clinical results.
- 517 View
- 2 Download

- The results of Operative Treatment in the Proximal Tibial Plateau Fracture
- Kyung Jin Song, Keun Ho Yang, Joo Hong Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(4):489-496. Published online October 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.4.489
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - INTRODUCTION: The purpose of this study was to analyze the results, prognosis and complications in the treatment of proximal tibia plateau fractures, and to suggest the guideline for the proper management in the difficult cases of tibial plateau fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We have analyzed 27 cases, which surgically treated during recent five years with average 36.6 months follow-up. Patients ranged in age from 24 to 83 years at the time of hospitalization, consisting of 19 males(70.4%) and 8 females(29.6%). The type of fracture by Schatzker classification revealed in type I 3 cases(11.1%), type II 1 case(3.7%), type III 0 case(0%), type IV 3 cases(11.1%), type V 1 case(3.7%) and type VI 19 cases(70.4%). The associated injury occurred in 22 cases(81.5%), most of them were ipsilateral fibular, ipsilateral femoral and radioulnar fractures. The results were evaluated by Blokker 's criteria.
RESULTS
Screw fixation was done in 4 cases(18%) and plate fixation in 23 cases(85.2%), and bone grafting was done in 10 cases(37.0%). There were 10 postoperative complications with 3 cases of knee ankyosis, 3 cases of angular deformity, 3 cases of infection, and 1 case of traumatic arthritis. According to Blokker 's criteria, 22 cases(81.5%) had satisfactory results.
CONCLUSIONS
Accurate anatomical reduction and rigid internal fixation of the proximal tibial plateau fracture enabled early motion and normalization of injured soft tissues, and also provided functional improvement of the knee.
- 327 View
- 2 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


