Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 23(2); 2010 > Article
-
Original Article
- Clinical Outcome of Surgical Treatment for Intra-articular Distal Humerus Fracture
- Myung Jin Lee, M.D., Hyeon Jun Kim, M.D., Sung Keun Sohn, M.D., Kyu Yeol Lee, M.D., Sung Soo Kim, M.D., Chul Hong Kim, M.D., Lib Wang, M.D., Hyun Woo Sung, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2010;23(2):201-205.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.2.201
Published online: April 30, 2010
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Hyeon Jun Kim, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Dong-A University College of Medicine, 1, Dongdaesin-dong 3-ga, Seo-gu, Busan 602-715, Korea. Tel: 82-51-240-5167, Fax: 82-51-254-6757, campbellkim@naver.com
Copyright © 2010 The Korean Fracture Society
- 773 Views
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- To evaluate functions of the elbow joint according to surgical approach, time to exercise, and type of fracture after surgical treatment for the intra-articular comminuted fracture of the distal humerus.
-
Materials and Methods
- 27 patients with the intra-articular comminuted fractures of the distal humerus underwent surgery from March, 2000 to January, 2007. We investigated the surgical approach, time for union, time to exercise and age. We also evaluated postoperative functions of the elbow joint according to the flexion contracture, the range of motion and the Mayo elbow performance score.
-
Results
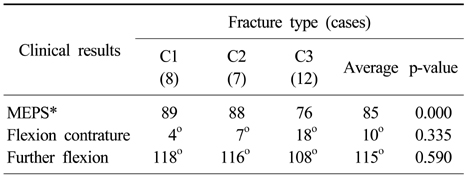
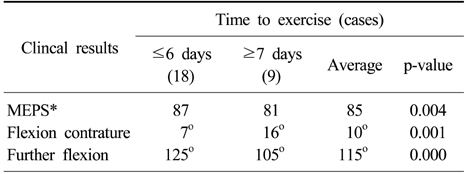
- The average follow-up period was 37 months and the average time for union was 14 weeks. The average range of flexion was 115 degrees, the average flexion contracture was 10 degrees, and the Mayo elbow performance score with average value of 85 point showed good clinical results. There were no statistically significant differences in functions of the elbow joint according to the operative method and age. However, patients with early postoperative exercise within 6 days showed statistically better outcomes than patients with postoperative exercise after 7 days. Type C1, 2 fractures showed statistically better results than the type C3 fracture.
-
Conclusion
- Stable fixation and early exercise are required to prevent postoperative complications and restore functions of the elbow joint with an intra-articular comminuted fracture of the distal humerus.
- 1. Aitken GK, Rorabeck CH. Distal humeral fracture in the adult. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1986;(207):191-197.
- 2. Aslam N. Surgical fixation of intra-articular fractures of the distal humerus in adults. Injury, 2005;36:804-805.
- 3. Bryan RS, Morrey BF. Extensive posterior exposure of the elbow. A tricepssparing approach. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1982;166:188-192.
- 4. Helfet DL, Schmeling GJ. Bicondylar intraarticular fractures of the distal humerus in adults. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1993;292:26-36.
- 5. Houben PF, Bongers KJ, Wildenberg FA. Double tension band osteosynthesis in supra- and transcondylar humeral fractures. Injury, 1994;25:305-309.
- 6. Husband JB, Hastings H 2nd. The lateral approach for operative release of posttraumatic contracture of the elbow. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1990;72:1353-1358.
- 7. Jupiter JB. Complex fractures of the distal part of the humerus and associated complications. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1994;76:1252-1264.
- 8. Kang SY, Lee HJ, Chung JW. Modified lateral approach to the distal humerus fractures. J Korean Orthop Assoc, 2000;35:705-710.PDF
- 9. Korner J, Lill H, Muller LP, et al. Distal humerus fractures in elderly patients: results after open reduction and internal fixation. Osteoporos Int, 2005;16:Suppl 2. S73-S79.PDF
- 10. Lee HJ, Kang SY, Kang KS, Lee SH, Kim CH. Surgical treatment of intercondylar fracture of the distal humerus through the modified triceps sparing approach. J Korean Orthop Assoc, 2003;38:584-587.PDF
- 11. McKee MD, Wilson TL, Winston L, Schemitsch EH, Richards RR. Functional outcome following surgical treatment of intra-articular distal humeral fractures through a posterior approach. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2000;82-A:1701-1707.
- 12. Morrey BF. Post-traumatic contracture of the elbow. Operative treatment, including distraction arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1990;72:601-618.
- 13. O'Driscoll SW. Optimizing stability in distal humeral fracture fixation. J Shoulder Elbow Surg, 2005;14:1 Suppl S. 186S-194S.
- 14. O'Driscoll SW. The triceps-reflecting anconeus pedicle (TRAP) approach for distal humeral fractures and nonunions. Orthop Clin North Am, 2000;31:91-101.
- 15. Pollock JW, Athwal GS, Steinmann SP. Surgical exposures for distal humerus fractures: a review. Clin Anat, 2008;21:757-768.
- 16. Rah SK, Kim SK, Choi JG, Kim YI, Choi CU. Comparison between transolecranon approach and posterior approach in comminuted intercondylar fracture of the distal humerus. J Korean Soc Fract, 1996;9:1069-1075.
- 17. Ring D, Jupiter JB. Complex fractures of the distal humerus and their complications. J Shoulder Elbow Surg, 1999;8:85-97.
- 18. Ring D, Jupiter JB. Fractures of the distal humerus. Orthop Clin North Am, 2000;31:103-113.
- 19. Soon JL, Chan BK, Low CO. Surgical fixation of intra-articular fractures of the distal humerus in adults. Injury, 2004;35:44-54.
- 20. Tyllianakis M, Panagopoulos A, Papadopoulos AX, Kaisidis A, Zouboulis P. Functional evaluation of comminuted intra-articular fractures of the distal humerus (AO type C). Long term results in twenty-six patients. Acta Orthop Belg, 2004;70:123-130.
- 21. Wang KC, Shin HN, Hsu KY, Shih CH. Intercondylar fracture of the distal humerus. Routine anterior subcutaneous transpositon of the ulnar nerve in posterior operative approach. J Trauma, 1994;36:770-773.
- 22. Werner CML, Ramseier LE, Trentz O, Heinzelmann M. Distal humeral fractures of the adult. Euro J Trauma, 2006;32:264-270.PDF
REFERENCES
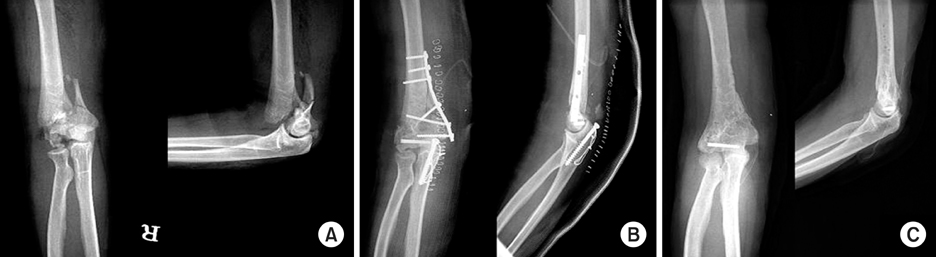
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Surgical Treatment Using a Transolecranon Approach with a Dual Locking Plate for Unstable Intercondylar Fractures of the Humerus
Ji-Kang Park, Yong-Min Kim, Dong-Soo Kim, Eui-Sung Choi, Hyun-Chul Shon, Kyoung-Jin Park, Byung-Ki Cho
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2012; 25(2): 129. CrossRef
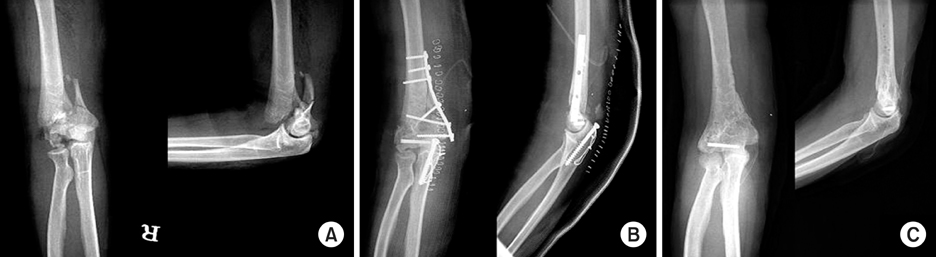
Fig. 1
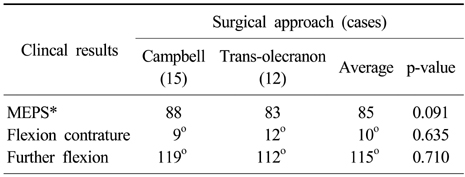
The relationship between surgical approach and postoperative functions of the elbow joint
*Mayo elbow performance score.
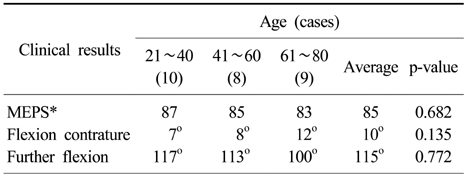
The relationship between age and postoperative functions of the elbow joint
*Mayo elbow performance score.
The relationship between fracture type and postoperative functions of the elbow joint
*Mayo elbow performance score.
The relationship between time to exercise and postoperative functions of the elbow joint
*Mayo elbow performance score.
*Mayo elbow performance score.
*Mayo elbow performance score.
*Mayo elbow performance score.
*Mayo elbow performance score.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

