Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 22(1); 2009 > Article
-
Original Article
- Staged Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis of Proximal Tibial Fracture
- Joon-Woo Kim, M.D., Chang-Wug Oh, M.D., Jong-Keon Oh, M.D., Hee-Soo Kyung, M.D., Woo-Kie Min, M.D., Byung-Chul Park, M.D., Kyung-Hoon Kim, M.D., Hee-Joon Kim, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2009;22(1):6-12.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.1.6
Published online: January 31, 2009
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
*Department of Orthopedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Chang-Wug Oh, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, 101, Dongin-dong 2-ga, Jung-gu, Daegu 700-422, Korea. Tel: 82-53-420-5630, Fax: 82-53-422-6605, cwoh@knu.ac.kr
Copyright © 2009 The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 704 Views
- 0 Download
- 9 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- To assess the results of staged MIPO (Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis) for proximal tibial fractures with compromised soft tissue.
-
Materials and Methods
- Eighteen proximal tibial fractures (AO 41:9 cases, AO 42:9 cases) included this study. Ten were open fractures. After temporary external fixation until soft tissue healed (mean 27.3 days), MIPO was performed secondarily without bone graft. We assessed the bony union and knee function, and affecting factors of the results were investigated.
-
Results
- All fractures united at 20 weeks (range, 11~32) except 1 case. Mean range of knee flexion was 134.4° and mean IOWA knee score was 89.1. There were 2 superficial and 2 delayed deep infections from open fractures (grade II:1 case, grade III:3 cases), although they healed after implant removal. Open fractures seem to influence the infection rate. Otherwise, there was no related factor affecting the results.
-
Conclusion
- MIPO after temporary external fixation can provide favorable results in proximal tibial fractures with soft tissue injuries, but attention of delayed infection should be paid in open fractures.
- 1. Blokker CP, Rorabeck CH, Bourne RB. Tibial plateau fractures. An analysis of the results of treatment in 60 patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1984;182:193-199.
- 2. Collinge C, Kuper M, Larson K, Protzman R. Minimally invasive plating of high-energy metaphyseal distal tibia fractures. J Orthop Trauma, 2007;21:355-361.
- 3. Covall DJ, Fowble CD, Foster TE, Whitelaw GP. Bicondylar tibial plateau fractures: principles of treatment. Contemp Orthop, 1994;28:115-122.
- 4. Egol KA, Tejwani NC, Capla EL, Wolinsky PL, Koval KJ. Staged management of high-energy proximal tibia fractures (OTA types 41): the results of a prospective, standardized protocol. J Orthop Trauma, 2005;19:448-455.
- 5. Haidukewych GJ. Temporary external fixation for the management of complex intra- and periarticular fractures of the lower extremity. J Orthop Trauma, 2002;16:678-685.
- 6. Krettek C, Miclau T, Grün O, Schandelmaier P, Tscherne H. Intraoperative control of axes, rotation and length in femoral and tibial fractures. Technical note. Injury, 1998;29:C29-C39.
- 7. Lachiewicz PF, Funcik T. Factors influencing the results of open reduction and internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1990;259:210-215.
- 8. Littenberg B, Weinstein LP, McCarren M, et al. Closed fractures of the tibial shaft: a meta-analysis of three methods of treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1998;80:174-183.
- 9. Mallik AR, Covall DJ, Whitelaw GP. Internal versus external fixation of bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. Orthop Rev, 1992;21:1433-1436.
- 10. Marsh JL, Smith ST, Do TT. External fixation and limited internal fixation for complex fracture of the tibial plateau. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1995;77:661-673.
- 11. Merchant TC, Dietz FR. Long-term follow-up after fractures of the tibia and fibular shafts. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1989;71:599-606.
- 12. Murphy CP, D'Ambrosia R, Dabezies EJ. The small pin circular fixator for proximal tibial fractures with soft tissue compromise. Orthopedics, 1991;14:273-280.
- 13. Oh CW, Oh JK, Jeon IH, et al. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate stabilization of proximal tibial fractures. J Korean Fract Soc, 2004;17:224-229.
- 14. Oh CW, Oh JK, Jeon IH, et al. Double plating of proximal tibial fractures using minimally invasive percutaneous osteosynthesis technique. J Korean Fract Soc, 2005;18:250-255.
- 15. Schatzker J, McBroom R, Bruce D. The tibial plateau fracture. The Toronto experience 1968-1975. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1979;138:94-104.
- 16. Shybut GT, Spiegel PG. Symposium. Rigid internal fixation of fractures. Tibial plateau fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1979;138:12-17.
- 17. Sirkin M, Sanders R, DiPasquale T, Herscovici D Jr. A staged protocol for soft tissue management in the treatment of complex pilon fractures. J Orthop Trauma, 2004;18:8 Suppl. S32-S38.
- 18. Stamer DT, Schenk R, Staggers B, Aurori K, Aurori B, Behrens FF. Condylar tibial plateau fractures treated with a hybrid ring external fixator: a preliminary study. J Orthop Trauma, 1994;8:455-461.
- 19. Tejwani NC, Achan P. Staged management of high-energy proximal tibia fractures. Bull Hosp Jt Dis, 2004;62:62-66.
- 20. Tscherne H, Lobenhoffer P. Tibial plateau fractures. Management and expected results. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1993;292:87-100.
- 21. Waddell JP, Johnson DW, Neidre A. Fractures of the tibial plateau: a review of ninety-five patients and comparison of treatment methods. J Trauma, 1981;21:376-381.
- 22. Watson JT. High-energy fractures of the tibial plateau. Orthop Clin North Am, 1994;25:723-752.
- 23. Whiteside LA, Lesker PA. The effects of extraperiosteal and subperiosteal dissection. II. On fracture healing. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1978;60:26-30.
- 24. Young MJ, Barrack RL. Complications of internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures. Orthop Rev, 1994;23:149-154.
REFERENCES
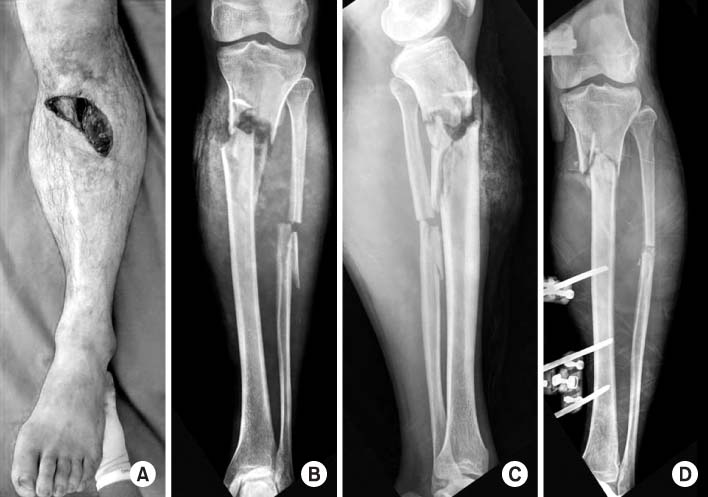
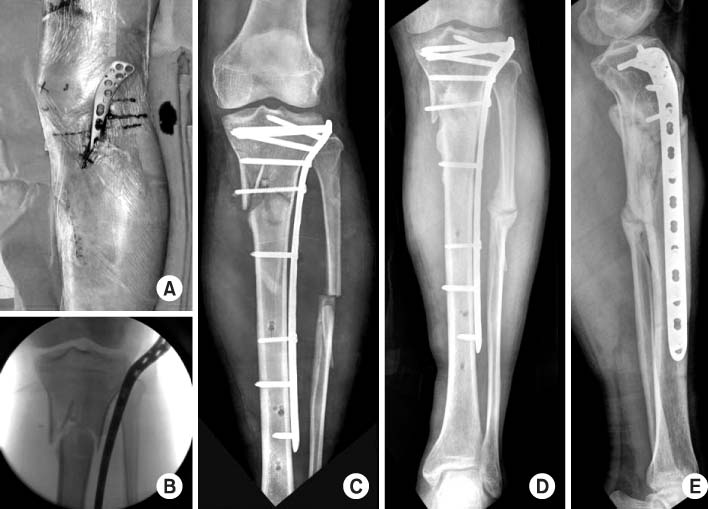
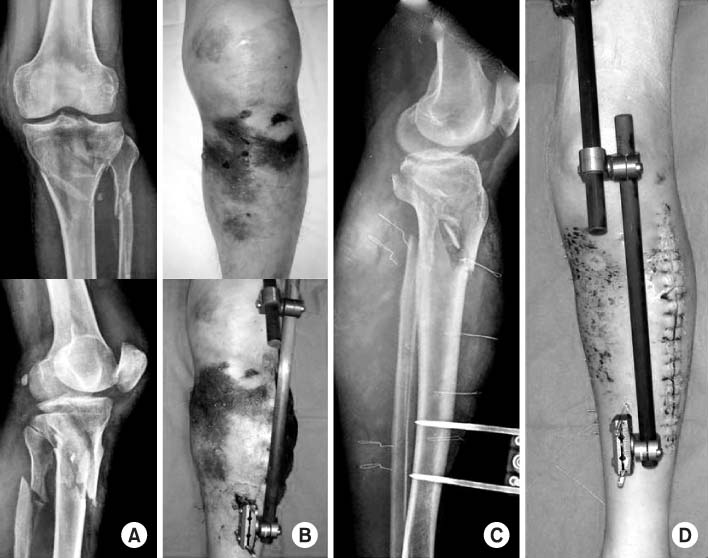
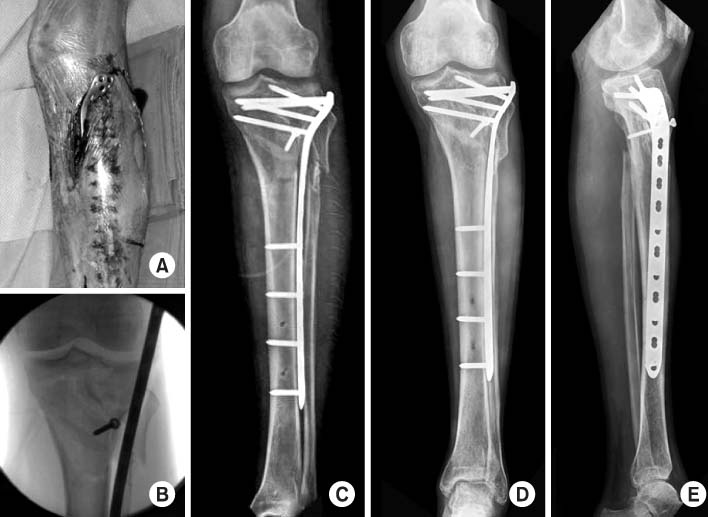
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- MINIMALLY INVASIVE OSTEOSYNTHESIS WITH PLATE OR NAIL FOR META-DIAPHYSEAL TIBIAL FRACTURES - WHAT IS BETTER?
B. Makelov
Trakia Journal of Sciences.2023; 21(4): 357. CrossRef - Effect of Korean Medicine Treatments in Patients with Proximal Tibia Fracture: A Retrospective Observational Study
Jung Min Lee, Eun-Jung Lee
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2020; 30(3): 141. CrossRef - Comparison of Time to Operation and Efficacies of Ultrasound-Guided Nerve Block and General Anesthesia in Emergency External Fixation of Lower Leg Fractures (AO 42, 43, 44)
Chan Kang, Sang-Bum Kim, Youn-Moo Heo, You-Gun Won, Byung-Hak Oh, June-Bum Jun, Gi-Soo Lee
The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery.2017; 56(5): 1019. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Proximal Tibial Shaft Fracture
Young-Soo Byun, Ki-Chul Park, Hyun-Jong Bong, Chang-Hoon Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(1): 23. CrossRef - The Use of Fresh Frozen Allogenic Bone Graft in the Impacted Tibial Plateau Fractures
Yeung Jin Kim, Soo Uk Chae, Jung Hwan Yang, Ji Wan Lee, Dae Han Wi, Duk Hwa Choi
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(1): 26. CrossRef - Management of Open Fracture
Gu-Hee Jung
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(2): 236. CrossRef - Staged Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis of Distal Tibial Fractures
Sung-Ki Park, Chang-Wug Oh, Jong-Keon Oh, Kyung-Hoon Kim, Woo-Kie Min, Byung-Chul Park, Won-Ju Jeong, Joo-Chul Ihn
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(3): 289. CrossRef - Intramedullary Nailing of Proximal Tibial Fractures
Young-Soo Byun, Dong-Ju Shin
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(3): 197. CrossRef - Proximal Tibia Fracture: Plating
Ki-Chul Park
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(3): 206. CrossRef
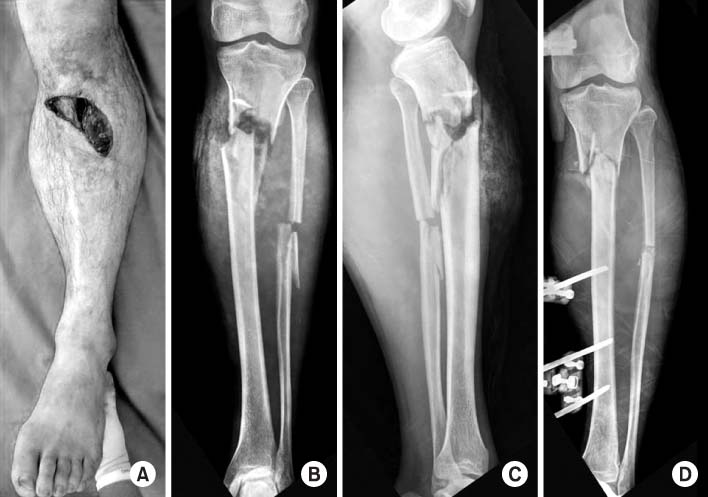
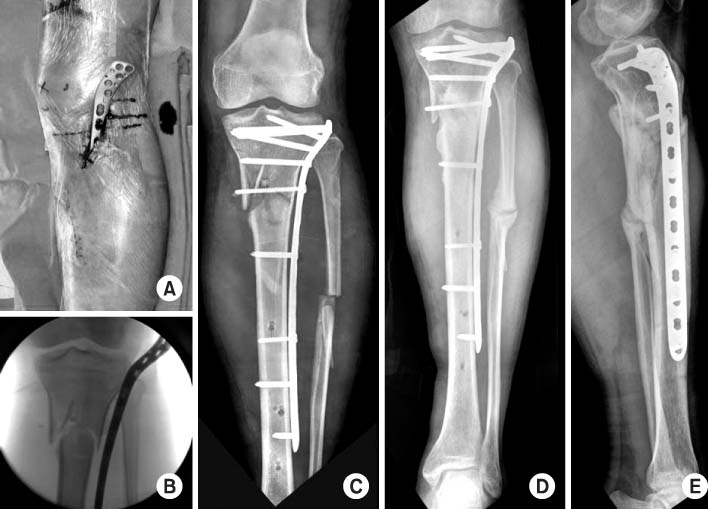
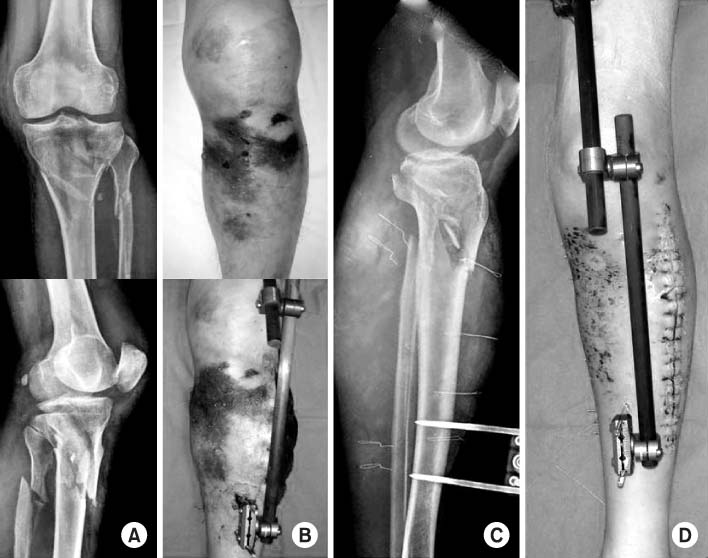
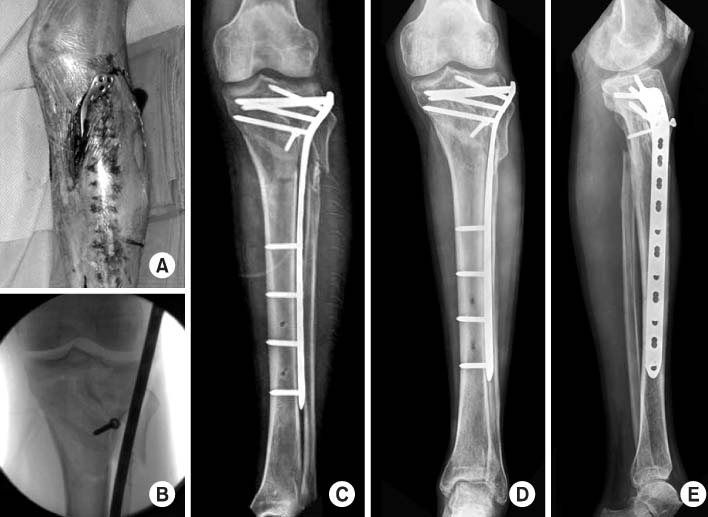
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
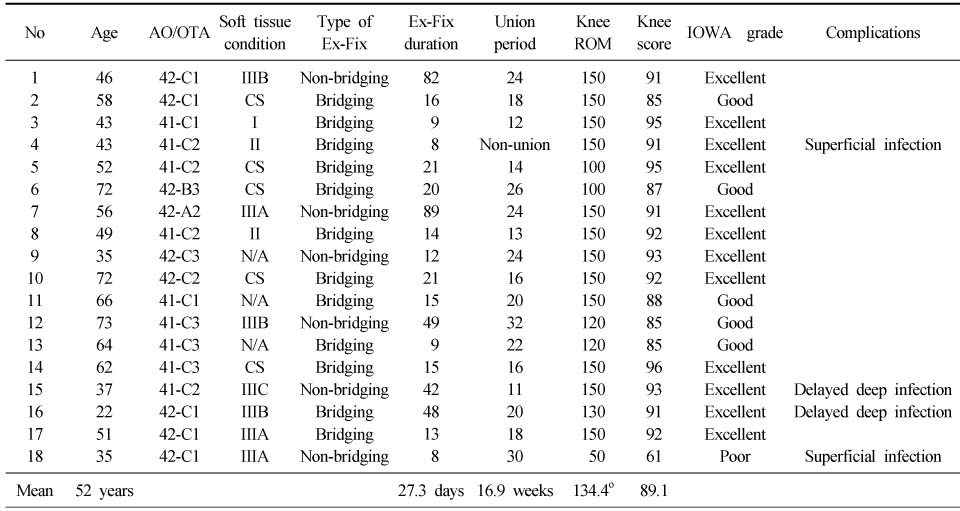
Proximal tibial fractures treated with staged percutaneous plate stabilization
AO/OTA: Fracture classification according to arbeitsgemeinschaft für osteosynthesefragen and orthopaedic trauma association, Soft tissue condition includes the type of open fracture or compartment syndrome, CS: Compartment syndrome, Ex-Fix: External fixator, ROM: Range of motion.
AO/OTA: Fracture classification according to arbeitsgemeinschaft für osteosynthesefragen and orthopaedic trauma association, Soft tissue condition includes the type of open fracture or compartment syndrome, CS: Compartment syndrome, Ex-Fix: External fixator, ROM: Range of motion.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

