Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Case Report
- Rim plate-assisted intramedullary nail and plate combination technique for complex tibial plateau-to-diaphysis fractures: a technical note and case series
- Whee Sung Son
- Received September 9, 2025 Accepted October 14, 2025 Published online December 4, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00290 [Epub ahead of print]
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Complex tibial plateau-to-diaphysis fractures present a significant surgical challenge due to their intricate fracture patterns and frequent association with severe soft tissue damage and concomitant injuries. This technical note introduces a novel fixation strategy: the rim plate-assisted intramedullary nail-plate combination (NPC) technique. In this approach, a rim plate simplifies the conventional NPC procedure by unifying the tibial plateau fracture into a single structural segment. This modification eliminates the need to address the articular and diaphyseal components simultaneously while enhancing articular stability. Furthermore, the technique preserves soft tissue integrity and promotes early rehabilitation. Clinical case examples demonstrate its successful application in managing complex tibial plateau-to-diaphysis injuries. Level of evidence: V.
- 184 View
- 7 Download

Review Article
- How to obtain the desired results from distal tibial nailing based on anatomy, biomechanics, and reduction techniques
- Jungtae Ahn, Se-Lin Jeong, Gu-Hee Jung
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):74-85. Published online March 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00024

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Distal tibial metaphyseal fractures are commonly caused by high-energy injuries in young men and osteoporosis in older women. These fractures should be clearly distinguished from high-energy pilon fractures. Although the optimal surgical intervention methods for distal tibial metaphyseal fractures remain uncertain and challenging, surgical treatments for nonarticular distal tibia fractures can be broadly divided into two types: plate fixation and intramedullary nail (IMN) fixation. Once functional reduction is achieved using an appropriate technique, distal tibial nailing might be slightly superior to plate fixation in reducing postoperative complications. Thus, the surgical strategy should focus on functional realignment and proceed in the following sequence: (1) restoring the original tibial length, regardless of whether fibular fixation is to be done; (2) making the optimal entry point through an anteroposterior (AP) projection based on the overlapping point between the fibular tip and lateral plateau margin; (3) placing Kirschner wires (Ø2.4 mm) as blocking pins (in the AP orientation for coronal control and in the mediolateral [ML] orientation for sagittal control) as close to the upper locking hole as possible without causing further comminution on the concave aspect of the short fragment; and (4) making the the distal fixation construct with at least two ML and one AP interlocking screw or two ML interlocking screws and blocking screws. After the IMN is adequately locked, blocking pins (Ø2.4 mm) need to be replaced by a 3.5 mm screw.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Foot Width on Patient-Reported Outcomes Assessed by 3-Dimensional Foot Morphometry in Hallux Valgus
Jungtae Ahn, Dae-Cheol Nam, Gu-Hee Jung
Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery.2025; 17(6): 1062. CrossRef
- Impact of Foot Width on Patient-Reported Outcomes Assessed by 3-Dimensional Foot Morphometry in Hallux Valgus
- 2,212 View
- 43 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Report
- Acute on Chronic Stress Fracture of a Varus Deformed Distal Tibia - A Case Report -
- Seong Kee Shin, Ki Chun Kim, Eli Schmidt, Seung Yeon Cho, Ki Chul Park
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2024;37(4):184-189. Published online October 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2024.37.4.184
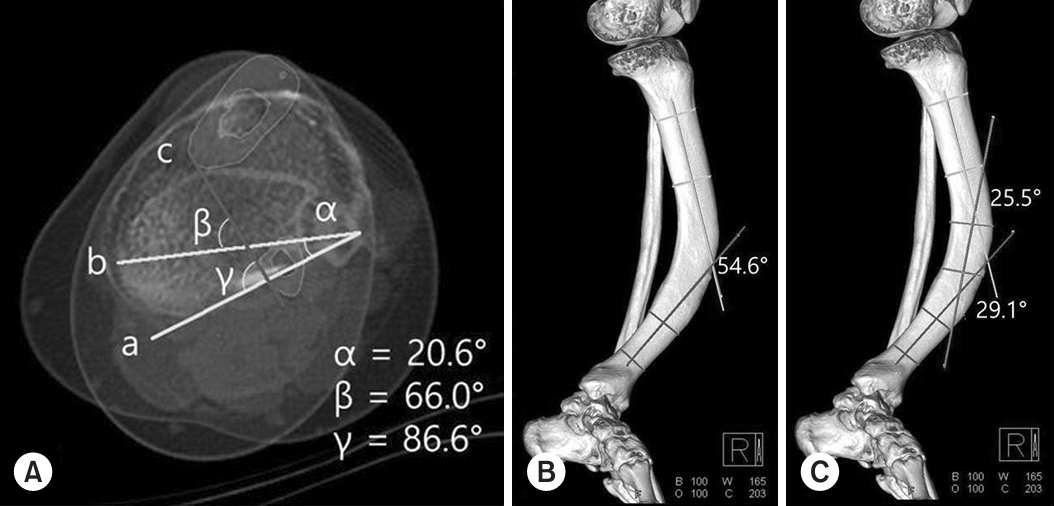
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A severe post-traumatic distal tibia vara deformity is an uncommon condition in orthopedics. Typical symptoms include intractable recurrent pain, fragility related to stress fractures over the tensile area, and a limping gait caused by leg length discrepancy. Surgical management should be performed on acute fractures extending from a stress fracture gap. For successful surgical results, deformity correction is important for sustaining axial load bearing for standing and walking. Procedures to manage this condition have been proposed, but there is a high risk of complications, including metal failure, nonunion, and weakness caused by a long period of rehabilitation. In this case, the authors report a successful result using a modified clamshell osteotomy combined with a proximal and distal wedge bone resection in a single stage.
- 897 View
- 32 Download

Original Articles
- Restoration of Lateral Tibial Plateau Widening and Articular Depression Is Necessary to Prevent Valgus Deformities after Arthroscopic Reduction and Internal Fixation in AO/OTA 41.B2 or B3 Fractures
- Jun-Ho Kim, Kang-Il Kim, Sang-Hak Lee, Gwankyu Son, Myung-Seo Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(3):125-136. Published online July 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.3.125
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the factors affecting valgus deformities after arthroscopic reduction and internal fixation (ARIF) in lateral joint-depression tibial plateau fractures.
Materials and Methods
Patients with lateral joint-depression tibial plateau fractures treated with ARIF were assessed retrospectively. The radiological evaluations included the articular depression distance (ADD) and the lateral plateau widening distance (LPWD) on preoperative and postoperative computed tomography. A postoperative valgus deformity was defined as valgus malalignment (mechanical axis ≥3°) and valgus deviation (Δmechanical axis of the operated knee from the healthy knee of ≥5°). Subgroup analyses based on a postoperative valgus deformity were performed to compare the clinical outcomes, including the range of motion, patient-reported outcomes measures, and failure and osteoarthritis progression. Furthermore, factors affecting the postoperative mechanical and Δmechanical axes were assessed.
Results
Thirty-nine patients were included with a mean follow-up of 44.6 months (range, 24-106 months). Valgus malalignment and valgus deviation were observed after ARIF in 10 patients (25.6%) and five patients (12.8%), respectively. The clinical outcomes were similar in patients with and without a postoperative valgus deformity. On the other hand, lateral compartment osteoarthritis progression was significantly higher in the valgus deformity group than in the non-valgus deformity group (valgus malalignment group: 50.0% vs 6.9%, p=0.007; valgus deviation group: 60.0% vs 11.8%, p=0.032). One patient with valgus deformity underwent realignment surgery at postoperative five years. The preoperative ADD and postoperative LPWD were significantly associated with the postoperative mechanical (both, p<0.001) and Δmechanical (ADD, p=0.001; LPWD, p=0.025) axes. Moreover, the lateral meniscectomized status during ARIF was significantly associated with the Δmechanical axis (p=0.019).
Conclusion
Osteoarthritis progression was highly prevalent in patients with postoperative valgus deformity. Thus, the restoration of lateral plateau widening and articular depression and preservation of the meniscus are necessary to prevent a valgus deformity after ARIF in lateral joint-depression tibial plateau fractures.
- 2,327 View
- 37 Download

- Biomechanical Investigation to Establish Stable Fixation Strategies for Distal Tibial Fractures in Various Situations: Finite Element Analysis Studies
- Sung Hun Yang, Jun Young Lee, Gu-Hee Jung, Hyoung Tae Kim, Ba Woo Ko
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(2):71-81. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.2.71
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the structural and mechanical stability as well as the clinical significance of various fixation constructs for distal tibial fractures using finite element analysis.
Materials and Methods
Fracture models with 20 mm and 120 mm defects were produced, and implants of an intramedullary nail and anatomical plate model were applied. An axial load of 800 N with 60% distribution in the medial compartment and 40% in the lateral compartment was applied and analyzed using Ansys ® software.
Results
In the intramedullary nail model, the maximum von Mises stress occurred at the primary lag screw hole and adjacent medial cortex, while in the plate model, it occurred at the locking holes around the fracture. The maximum shear stress on the bone and metal implant in the fracture model with a 20 mm defect was highest in the plate assembly model, and in the fracture model with a 120 mm defect, it was highest in the two-lag screw assembly model.
Conclusion
Based on an analysis of the maximum shear stress distribution, securing the fixation strength of the primary lag screw hole is crucial, and the assembly model of the intramedullary nail with two lag screws and a blocking screw applied was the model that best withstood the optimal load. Securing the locking hole directly above the fracture is believed to provide the maximum fixation strength because the maximum pressure in the plate model is concentrated in the proximal locking hole and the surrounding cortex. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How to obtain the desired results from distal tibial nailing based on anatomy, biomechanics, and reduction techniques
Jungtae Ahn, Se-Lin Jeong, Gu-Hee Jung
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(2): 74. CrossRef
- How to obtain the desired results from distal tibial nailing based on anatomy, biomechanics, and reduction techniques
- 832 View
- 17 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Triplane Fracture Management: Prediction of Periosteal Entrapment and the Need for Open Reduction by Measurements of the Physeal Fracture Gap in Preoperative Computed Tomography Scans
- Dae Hee Lee, Joo Han Kwon, Jae Uk Jung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(1):1-7. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study measured the physeal fracture gap on preoperative ankle computed tomography (CT) to predict the periosteal entrapment that requires an open reduction in distal tibia triplane fractures.
Materials and Methods
This study retrospectively reviewed patients who had undergone internal fixation for a triplane fracture from April 2004 to September 2022. The demographic data, including age,body mass index, and past medical history, were analyzed. In the radiographic evaluations, ankle CT and ankle simple radiographs, including anteroposterior (AP), lateral, and mortise views, were taken preoperatively. Postoperatively, simple ankle radiographs were obtained periodically, including AP, mortise, and lateral views. The physeal fracture gap was measured on ankle CT, and the larger gap between the coronal and sagittal view of CT was selected. The residual physeal gap <2 mm was considered an adequate reduction.
Results
Of 17 cases, three demonstrated successful reduction using closed reduction techniques. Periosteal entrapment was observed in 14 cases open reduction cases. In all three closed reduction cases, the physeal gap estimated on preoperative ankle CT was under 3 mm with a mean gap of 2.4±0.2 mm (range, 2.1-2.5 mm). In the remaining 14 open reduction cases, the measured physeal gap was over 3 mm, averaging 5.0±2.7 mm (range, 3.1-12.2 mm). There was a significant difference in the preoperative physeal gap between the two groups (p<0.01). Overall, good reduction was achieved in all 17 cases; the postoperative physeal gap was under 2 mm with a mean of 1.0±0.5 mm (closed reduction group, 0.5±0.2 mm; open reduction group, 1.1±0.5 mm).
Conclusion
Open reduction is strongly recommended for triplane fractures with a physeal fracture gap of 3 mm or more in preoperative ankle CT, suggesting the possibility of an entrapped periosteum in the fracture gap. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diagnostic values of radiographic indices for predicting periosteal entrapment in pediatric proximal phalangeal base physeal fractures of toes
Ho Young Park, Jeong-Seok Moon, Kiwook Kim
Skeletal Radiology.2026; 55(1): 97. CrossRef
- Diagnostic values of radiographic indices for predicting periosteal entrapment in pediatric proximal phalangeal base physeal fractures of toes
- 1,136 View
- 16 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Treatment Results of Reamed Exchange Nailing in Aseptic Nonunion of Tibial Shaft Fracture
- Yongjin Cho, Jun Young Lee, Jehong Ryu, Hyoung Tae Kim, Jong Jin Moon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(4):125-132. Published online October 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.4.125
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Intramedullary nailing is used widely for treating tibial diaphysis fractures because of its relatively rigid internal fixation, which allows weight bearing, resulting in rapid bone healing and functional recovery. This study evaluated the results of exchange nailing in treating aseptic nonunion of tibial shaft fractures.
Materials and Methods
From November 2015 to December 2021, a retrospective study was conducted on patients who had undergone intramedullary nailing for tibial diaphysis fractures. Among them, this study focused on patients diagnosed with nonunion and who underwent exchange nailing. Twenty patients with a minimum follow-up period of at least 12 months were included in the study.
Results
The mean ages of patients were 60 years (range, 30-79 years). Of the 20 cases in which exchange nailing was performed, bone union was achieved in 18 cases (90.0%), and the mean period was 23 weeks (range, 14-46 weeks). Among the 18 cases of bone union, one case exhibited delayed union and achieved union without additional treatment after 46 weeks, while two cases of nonunion failed to achieve union and were lost to follow-up until the final assessment.
Conclusion
Reamed exchange nailing performed on aseptic nonunion after intramedullary nailing for tibial diaphysis fractures had satisfactory clinical outcomes.
- 425 View
- 4 Download

Case Report
- Irreducible Ankle Fracture Dislocation due to Dislocated Tibialis Posterior Tendon - A Case Report -
- Seungyup Shin, Bum-Soo Kim, Ji-Won Lee, Euisun Yoon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(2):52-56. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.2.52
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - An irreducible ankle dislocation is a rare injury. The cause is a dislocation of the distal fibula anteriorly or posteriorly or the insertion of soft tissue, such as the deltoid ligament or posteromedial tendon. The tibialis posterior tendon can be dislocated through distal tibiofibular diastasis and prevent reduction of the ankle joint. The authors experienced anterolateral ankle fracture dislocation with a diastasis of the distal tibiofibular joint, and reduction was impossible because of impingement of the tibialis posterior tendon dislocated anteriorly through the distal tibiofibular diastasis. This paper reports the treatment of this injury.
- 480 View
- 11 Download

Original Articles
- Intra-Articular Alterations after Suprapatellar Nailing in Tibial Shaft Fractures: An Arthroscopic Evaluation
- GwangChul Lee, Sung Hun Yang, Sung Min Jo, Jeong Min Kook
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(4):129-134. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.4.129
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study attempted to study the intra-articular changes due to intramedullary nailing through the suprapatellar approach by evaluating the joint cartilage damage and presence of foreign bodies through a comparison of the pre- and post-operative status evaluated by knee arthroscopy.
Materials and Methods
This retrospective study analyzed fifteen patients who underwent intramedullary nailing through the suprapatellar approach for proximal tibial shaft fracture from January 2017 to March 2020. The condition of the joint cartilage and the presence of foreign substances in the patellofemoral joint were evaluated. The cartilage status of the patellofemoral joint was evaluated using the International Cartilage Repair Society (ICRS) grading system. Data from the ICRS grading and the visual analogue scale (VAS) scores of the femoral and patellar cartilage were compared to each independent variable surveyed.
Results
All the intra-articular structures before nailing were normal. In all cases after nailing, articular cartilage damage of the patellofemoral joint and intra-articular debris were observed. The average VAS score was 0.6 (0-1) before surgery and 2.27 (0-4) after surgery. There were no statistically significant differences except for the correlation in the diameter of the tibia nail and femoral ICRS grade (p=0.001) and the damage to the cartilage was greater in the femoral cartilage than that to the patella (p=0.001).
Conclusion
Intra-articular damage appears to be unavoidable in suprapatellar nailing. Further research is needed on the long-term effects of intra-articular damage and on methods to reduce this damage.
- 402 View
- 6 Download

- Assessment of Noncontiguous Posterior Malleolar Fractures in Distal One-Third Tibia Shaft Fractures with Proximal Fibula Fractures
- Dae-Geun Kim, Byung Hoon Kwack
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(3):103-108. Published online July 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.3.103
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Posterior malleolar fractures after intramedullary nail surgery rarely occur in distal tibia shaft fractures. The importance of preoperative ankle evaluation in preventing these fractures is also common knowledge. There are no studies in the literature on posterior malleolar fractures in distal onethird tibia shaft fractures except for distal metaphyseal tibia fractures to the best of our knowledge. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the incidence and radiological features of posterior malleolar fractures in distal one-third tibia shaft fractures with proximal fibula fractures.
Materials and Methods
Thirty-one patients diagnosed with distal one-third tibia shaft fractures with proximal fibula fractures from January 2016 to May 2021 were retrospectively reviewed. With the aid of plain radiographs and computed tomography (CT) scans, the fracture patterns of the tibia and fibula were classified according to the AO Foundation/Orthopedic Trauma Association (AO/OTA) classification, and posterior malleolar fractures were identified. The fracture pattern was classified according to the Haraguchi classification, and the angle between the bimalleolar axis and the posterior malleolar fracture line was measured when there was a posterior malleolar fracture.
Results
Out of the 31 distal one-third tibia shaft fractures with proximal fibula fractures, 16 cases (51.6%) had noncontiguous posterior malleolar fractures that were confirmed on a CT scan, while 3 cases (18.8%) were visible on initial plain radiographs. There was no statistically significant variation seen in the presence of a posterior malleolar fracture in the tibia (p=0.15) and fibula (p=0.87) fractures. According to the Haraguchi classification, there were 15 posterolateral-oblique fractures (Type I) and 1 medial-extension fracture (Type II), and the mean angle was 24.5°.
Conclusion
Noncontiguous posterior malleolar fractures occurred in approximately half of the distal one-third tibia shaft fractures with proximal fibula fractures, and a CT scan was considered necessary to diagnose posterior malleolar fractures before surgery
- 468 View
- 8 Download

Case Report
- The Antibiotic Cement Coated Nail and Masquelet Technique for the Treatment of Infected Nonunion of Tibia with Bone Defect and Varus Deformity
- Min Gu Jang, Jae Hwang Song, Dae Yeung Kim, Woo Jin Shin
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(1):26-30. Published online January 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.1.26
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Infective nonunion after fracture surgery can cause persistent pain and inflammatory exudate in patients, requiring long-term treatment. To treat infective nonunion, radical debridement of infective bone and soft tissue should be performed, followed by stable internal fixation and bone graft. Multiple treatment strategies need to be considered according to the classification of chronic osteomyelitis, size of the bone defect, degree of bone malalignment, and severity of the soft tissue injury. This paper reports a case of a patient treated with an antibiotic cement-coated nail and a Masquelet technique to treat the infected nonunion of the tibia with a bone defect and varus deformity.
- 295 View
- 4 Download

Original Articles
- Results of Intramedullary Nailing for Distal Metaphyseal Intra-Articular Fractures of Tibia
- Jun Young Lee, Yongjin Cho, Hyung Seok Park, Se Woong Jang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(4):196-203. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.4.196
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the results of internal fixation using an intramedullary nail in the treatment of distal metaphyseal fractures involving the articular surface.
Materials and Methods
From November 2009 to November 2018, distal tibia fractures involving the articular surface were treated with intramedullary nailing only for fractures corresponding to AO type 43 B and 43 C1, twenty-four cases were studied retrospectively. The tibial alignment was measured preoperatively and postoperatively, and the bone union time and nonunion were assessed. In addition, the clinical evaluation of ankle joint function was assessed using the Olerud and Molander ankle score (OMAS).
Results
Complete bone union was obtained in all cases, and the mean union time was 17.7±1.87 weeks (range, 15-20 weeks). The average preoperative coronal alignment was 6.4°±1.0° (range, 5.2°-8.4°), and sagittal alignment was 2.7°±0.6° (range, 1.9°-3.8°). The average postoperative coronal alignment was 2.5°±0.13° (range, 2.2°-2.6°) and sagittal alignment was 0.4°±0.25° (range, 0.09°-0.95°). There was no nonunion. The OMAS had an average of 85±7.9 points (range, 70-95 points).
Conclusion
In the treatment of distal metaphyseal fractures involving the articular surface, internal fixation using an intramedullary nail reduces complications and achieves satisfactory reduction and union. This method is considered an excellent treatment to obtain good clinical results.
- 426 View
- 4 Download

- Clinical Outcome after Treatment of Tibia Segmental Fracture with Intramedullary Nailing and Minimal Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis
- Jun Young Lee, Hyung Seok Park, Dong Hyuk Cha
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(3):142-147. Published online July 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.3.142
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the clinical outcomes after the treatment of a tibia segmental fracture with intramedullary nailing (IM nailing) and minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO).
Materials and Methods
From July 2012 to December 2017, 14 out of 17 cases from a treatment cohort of 32 cases of AO type 42 C2 tibia segmental fractures with IM nailing and MIPO were studied retrospectively. Periodic radiographs were used to evaluate the presence of union, union time, and radiographic evaluation of bony union (varus-valgus deformity, anteroposterior angular deformity, shortening). To evaluate the postoperative clinical function, modified Rasmussen’s system was used for proximal fractures, and the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society functional score was used for distal fractures.
Results
Bony union was achieved in all 14 cases, and the average union time was 26 weeks. In one case of soil contamination, there were no other complications other than simple debridement after a soft tissue infection. The mean varus was two degrees; the mean anteroposterior angular deformity was three degrees of anterior oblique; the mean length shortening was 5 mm (2-9 mm). The mean functional score of the knee joint with the Modified Rasmussen’s system measured for the postoperative clinical function was relatively good (excellent 9, good 4, fair 1, and poor 0). The results of the Molander and Olerud Functional scores of the ankle joints were also good (excellent 8, good 3, fair 2, poor 0).
Conclusion
The treatment of tibia segmental fractures with IM nailing and MIPO can effectively reduce the gap of fracture sites. Hence, it is possible to increase the bony union probability and obtain relatively satisfactory alignment. Overall, the treatment of tibia segmental fractures with IM nailing and minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis appears to be a useful treatment, considering the preservation of the soft tissue and the alignment of the tibia.
- 516 View
- 2 Download

- Comparison of a Novel Box-Frame External Fixator and Conventional Delta-Frame External Fixator in the Staged Treatment of Distal Tibia Fractures
- Yong-Cheol Yoon, MinKyu Shin, Chang-Wug Oh, Jong-Keon Oh
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(3):125-133. Published online July 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.3.125
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Distal tibia fractures with severe soft-tissue edema or intra-articular fractures are treated by staged operations using external fixators. Definitive surgery that maintains ligamentotaxis has been difficult using existing fixators. This study introduced a novel ‘box-frame’ external fixator and evaluated its clinical usefulness.
Materials and Methods
This study included 45 patients (32 males, 13 females) diagnosed with distal tibia fractures who underwent staged operations between March 2012 and March 2016, with a follow-up of at least one year. The patients were divided into two groups. In one group, fixation was performed with a box-frame external fixator (Group A). In the other group, fixation was performed with a delta-frame external fixator (Group B). The following outcomes were evaluated: the time until definitive surgery, operative time of the definitive surgery, radiation exposure time, bone union, time to achieve bone union, postsurgical complications, American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society anklehindfoot score, and ankle range of motion.
Results
Compared to the delta-frame, the box-frame showed a statistically significant reduction in the mean radiation-exposure time and operative time during the definitive surgery by 58 seconds and 25 minutes, respectively. The differences in the time until definitive surgery, bone union, time to achieve bone union, postsurgical complications, and functional scores were not significant.
Conclusion
The box-frame external fixator can be a useful treatment method in the staged surgery of distal tibia fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Temporary Circular External Fixation for Spanning the Traumatized Ankle Joint
Nando Ferreira, Niel Bruwer, Adriaan Jansen van Rensburg, Ernest Muserere, Shao-Ting Jerry Tsang
JBJS Essential Surgical Techniques.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Temporary circular external fixation for spanning the traumatised ankle joint: A cohort comparison study
William D. Harrison, Franklin Fortuin, Matthieu Durand-Hill, Etienne Joubert, Nando Ferreira
Injury.2022; 53(10): 3525. CrossRef
- Temporary Circular External Fixation for Spanning the Traumatized Ankle Joint
- 1,763 View
- 14 Download
- 2 Crossref

Case Reports
- Concurrent Posterolateral Corner Injury Associated with a Schatzker Type 2 Tibial Plateau Fracture: A Case Report
- Jae Cheon Sim, Choong Won Jung, Tae Seok Nam
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(1):27-31. Published online January 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.1.27
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Isolated posterolateral corner (PLC) injury associated with a Schatzker type 2 fracture is a very rare combination of injuries. A male who was driving a motor vehicle was injured after a collision accident. The plain radiographs and computed tomography scans of the knee showed a Schatzker type 2 fracture of the tibial plateau, mostly in the anterolateral portion of tibial plateau, and an avulsion fragment on the fibular tip. Magnetic resonance imaging showed no injury to cruciate ligaments, medial collateral ligament, or any meniscal injury. We performed an open reduction operation and internal fixation for treating the fracture. Six months later, he complained of instability. At 11 months later after initial operation, we performed the second operation for stabilizing the PLC. We present here a rare case of an isolated PLC injury associated with a Schatzker type 2 fracture. We discuss the mechanism of injury and review similar cases.
- 754 View
- 3 Download

- Surgical Repair of Tibialis Anterior Muscle Herniation Using a Synthetic Mesh That Was Beneath the Fascia after a Military Training Program: A Case Report
- Kyoung Ho Kim, Young Soo Shin
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(2):102-106. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.2.102
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Tibialis anterior muscle herniation is the most common type of skeletal muscle herniation of the lower legs. The treatment of muscle herniation relies on the patient's symptoms. For patients with chronic large fascial defects, fascial grafting with synthetic mesh can be considered. In this case of a patient who was exposed to excessive strain on his lower legs during a military training program, the use of a secure repair technique with synthetic mesh was required. This paper presents a case of tibialis anterior muscle herniation that was treated successfully with a monofilament knitted polypropylene mesh covered by the tibialis anterior fascia. The advantages of this technique include early rehabilitation and an early return to work. No significant difference in the clinical results compared to other methods were observed and there were no complications. The military training program appeared to have aggravated the patient's symptoms of tibialis anterior muscle herniation. On the other hand, larger scale study will be needed to determine if this program actually affects the clinical outcomes.
- 838 View
- 2 Download

- Pseudoaneurysm of the Anterior Tibial Artery after Reduction with Pointed Bone Reduction Forceps on a Spiral Fracture of the Distal Tibia: A Case Report
- Hyunseung Yoo, Youngho Cho, Seongmun Hwang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(1):43-46. Published online January 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.1.43
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This paper reports a pseudoaneurysm of the anterior tibial artery after reduction with pointed bone reduction forceps on a spiral fracture of the distal tibia. Most reported injuries occurred at the proximal part of anterior tibial artery during drilling of the proximal tibia. To the best of the authors' knowledge, injury of the distal part of anterior tibial artery has never been reported. This paper describes a 54-year-old woman with a pseudoaneurysm of the anterior tibial artery clinically detected 11 weeks after the index surgery. This report highlights the need for surgeons to be aware of and careful about this complication during and after surgical intervention.
- 487 View
- 1 Download

Original Articles
- Prediction of Concomitant Lateral Meniscus Injury with a Tibia Plateau Fracture Based on Computed Tomography Assessment
- Wonchul Choi, Yunseong Choi, Go Tak Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(4):132-138. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.4.132
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study examined whether any fracture pattern shown in computed tomography (CT) scan is associated with the presence of lateral meniscus (LM) injury in a tibia plateau fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fifty-three tibia plateau fractures with both preoperative CT and magnetic resonance imagings (MRI) available were reviewed. The patient demographics, including age, sex, body mass index, and energy level of injury were recorded. The fracture type according to the Schatzker classification, patterns including the lateral plateau depression (LPD), lateral plateau widening (LPW), fracture fragment location, and the number of columns involved were assessed from the CT scans. The presence of a LM injury was determined from the MRI. The differences in the factors between the patients with (Group 1) and without (Group 2) LM injuries were compared and the correlation between the factors and the presence of LM injury was analyzed.
RESULTS
The LM was injured in 23 cases (Group 1, 43.4%) and intact in 30 cases (Group 2, 56.6%). The LPD in Group 1 (average, 8.2 mm; range, 3.0–20.0 mm) and Group 2 (average, 3.8 mm; range, 1.4–12.1 mm) was significantly different (p < 0.001). The difference in LPW of Group 1 (average, 6.9 mm; range, 1.2–15.3 mm) and Group 2 (average, 4.8 mm; range, 1.4–9.4 mm) was not significant (p=0.097). The other fracture patterns or demographics were similar between in the two groups. Regression analysis revealed that an increased LPD (p=0.003, odds ratio [OR]=2.12) and LPW (p=0.048, OR=1.23) were significantly related to the presence of a LM tear.
CONCLUSION
LPD and LPW measured from the CT scans were associated with an increased risk of concomitant LM injury in tibia plateau fractures. If such fracture patterns exist, concomitant LM injury should be considered and an MRI may be beneficial for an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The value of magnetic resonance imaging in the preoperative diagnosis of tibial plateau fractures: a systematic literature review
Gregoire Thürig, Alexander Korthaus, Karl-Heinz Frosch, Matthias Krause
European Journal of Trauma and Emergency Surgery.2023; 49(2): 661. CrossRef
- The value of magnetic resonance imaging in the preoperative diagnosis of tibial plateau fractures: a systematic literature review
- 449 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Comparative Analysis of Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis and Intramedullary Nailing in the Treatment of the Distal Tibia Fractures
- Ho Min Lee, Young Sung Kim, Jong Pil Kim, Phil Hyun Chung, Suk Kang, Kaung Suk Jo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(3):94-101. Published online July 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.3.94
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study compared the radiological and clinical results of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) and intramedullary nailing (IMN) of distal tibial fractures, which were classified as the simple intra-articular group and extra-articular group.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fifty patients with distal tibial fractures, who could be followed-up more than 12 months, were evaluated. Group A consisted of 19 patients treated with MIPO and group B consisted of 31 patients treated with IMN. The results of each group were analyzed by radiological and clinical assessments.
RESULTS
The mean operation times in groups A and B were 72.4 minutes and 65.7 minutes, respectively. The mean bone union times in groups A and B were 16.4 weeks and 15.7 weeks, respectively. The bone union rate in groups A and B were 100% and 93%, respectively. The ranges of ankle motion were similar in the two groups at the last follow-up. The mean American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society score was similar: 90.1 in group A and 90.5 in group B. The radiological and clinical results were similar in the intra and extra-articular groups. In groups A and B, two cases of posterior angulation and five cases of valgus deformity of more than 5° were encountered.
CONCLUSION
Both MIPO and IMN achieved satisfactory results in extra-articular AO type A and simple articular extension type C1 and C2 distal tibia fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intramedullary Nailing versus Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Distal Tibia Shaft Fractures: Retrospective Comparison of Functional and Cosmetic Outcomes
Kahyun Kim, In Hee Kim, Geon Jung Kim, SungJoon Lim, Ji Young Yoon, Jong Won Kim, Yong Min Kim
Journal of Korean Foot and Ankle Society.2023; 27(3): 93. CrossRef
- Intramedullary Nailing versus Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Distal Tibia Shaft Fractures: Retrospective Comparison of Functional and Cosmetic Outcomes
- 438 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Report
- Atypical Fracture-Like Insufficiency Fracture of the Tibia with Prolonged Bisphosphonate Drug: A Case Report
- Min Jung Park, Su Jin Lee, Jin Hwa Kam, Yun Tae Lee, Ju Hyung Yoo, Hyun Cheol Oh, Joong Won Ha, Yung Park, Sang Hoon Park, Seong Hoon Kim, Han Kook Yoon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(3):137-141. Published online July 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.3.137
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Atypical femoral fracture related to a long-term bisphosphonate therapy has commonly been reported; however, a fracture at the site other than the femur has rarely been reported to date. Herein, we report a case of a patient on long-term bisphosphonate therapy who presented atypical tibial insufficiency fracture at the anterolateral aspect of diaphysis, without trauma. We, for the first time in Korea, present this case with a literature review.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Atypical Femoral Fracture Occurring at a Proximal Screw Insertion Site after Plate Removal in a Distal Femoral Fracture
Jin Woo Jin, Sung Jin Shin, Jong Min Jeon
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2024; 59(4): 314. CrossRef
- Atypical Femoral Fracture Occurring at a Proximal Screw Insertion Site after Plate Removal in a Distal Femoral Fracture
- 559 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Article
- The Result of Using an Additional Mini-Locking Plate for Tibial Pilon Fractures
- Suenghwan Jo, Jun Young Lee, Boseon Kim, Kang Hyeon Ryu
- J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(2):75-82. Published online April 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.2.75
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
We evaluated the usefulness of an additional, 2.7 mm mini-locking plate for tibial pilon fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We studied 21 patients (14 males and 7 females), who were treated with a 2.7 mm mini-locking plate via the anterolateral approach for tibial pilon fractures between September 2012 and April 2014. The mean age was 43.85 years, and the mean follow-up period was 16.6 months. The radiologic outcomes were graded by the Burwell and Charnley modified system and clinical outcomes were evaluated by the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) ankle-hind foot score and visual analogue scale (VAS) score.
RESULTS
The mean union period was 14.3 weeks. At the final follow-up, radiologic results showed 16 excellent results, 4 fair results, and 1 poor result. The average VAS was 3.4 points; the average AOFAS score was 81.8 points. During the follow-up period, there were three cases of posttraumatic osteoarthritis and one case of superficial skin infection.
CONCLUSION
Additional anterolateral, 2.7 mm mini-locking plate may be a good treatment method to manage tibial pilon fractures.
- 408 View
- 4 Download

Case Reports
- Pediatric Cartilaginous Tibia Eminence Fracture Overlooked on Plain Radiograph: A Report of Two Cases
- Seong Eun Byun, Yunseong Choi, Wonchul Choi
- J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(1):29-34. Published online January 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.1.29
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In children with open physis, avulsion fracture of the tibia eminence, as an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury, is more commonly observed than an ACL rupture. Pure cartilaginous avulsions of the ACL tibia insertion seldom occurs. In such case, cartilaginous lesion is frequently overlooked or misdiagnosed on plain radiograph and may result in a less favorable treatment outcome. We report two cases of cartilaginous tibia eminence fractures of the children that were initially overlooked from plain radiographs, and then diagnosed by magnetic resonance imaging, which was ultimately treated by arthroscopyassisted headless compression screw fixation.
- 399 View
- 4 Download

- Medial Plating of Distal Femoral Fracture with Locking Compression Plate-Proximal Lateral Tibia: Cases' Report
- Se Ang Jang, Young Soo Byun, In Ho Han, Dongju Shin
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(3):206-212. Published online July 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.3.206
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Generally, lateral plating is used for a comminuted fracture of the distal femur. However, in some cases, it has been shown that using a medial plate is necessary to achieve better outcome. Nevertheless, there are no available anatomical plates that fit either the distal medial femoral condyle or fracture fixation, except for the relatively short plate developed for distal femoral osteotomy. We found that locking compression plate-proximal lateral tibia (LCP-PLT) fits anatomically well for the contour of the ipsilateral medial femoral condyle. Moreover, LCP-PLT has less risk of breaking the thread holes since it rarely needs to be bent. We report a plastic bone model study and two cases of distal femoral fractures fixed with medial plating using LCP-PLT.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A novel anatomical locked medial femoral condyle plate: a biomechanical study
M. A. Ozer, S. Keser, D. Barıs, O. Yazoglu
European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology.2024; 34(5): 2767. CrossRef - Medial plating of distal femur: which pre-contoured angular stable plate fits best?
Shaam Achudan, Rex Premchand Antony Xavier, Sze Ern Tan
European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology.2024; 34(6): 3297. CrossRef - Medial augmentation of distal femur fractures using the contralateral distal femur locking plate: A technical note
Jaime Andrés Leal
OTA International.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The missing piece of the trauma armoury-medial femoral condyle plate
Piyush Upadhyay, Farhan Syed, Darryl N Ramoutar, Jayne Ward
Injury.2022; 53(3): 1237. CrossRef - Surgical Tips and Tricks for Distal Femur Plating
Christopher Lee, Dane Brodke, Ajay Gurbani
Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.2021; 29(18): 770. CrossRef - Medial minimally invasive helical plate osteosynthesis of the distal femur – a new technique
G.M. Hohenberger, A.M. Schwarz, P. Grechenig, B. Clement, Mario Staresinic, Bore Bakota
Injury.2021; 52: S27. CrossRef - Feature-Based Design of Personalized Anatomical Plates for the Treatment of Femoral Fractures
Xiaozhong Chen, Zhijian Mao, Xi Jiang
IEEE Access.2021; 9: 43824. CrossRef
- A novel anatomical locked medial femoral condyle plate: a biomechanical study
- 1,181 View
- 59 Download
- 7 Crossref

Original Article
- Usefulness of Computed Tomography on Distal Tibia Intra-Articular Fracture Associated with Spiral Tibia Shaft Fracture
- Seong Eun Byun, Sang June Lee, Uk Kim, Young Rak Choi, Soo Hong Han, Byong Guk Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(2):114-120. Published online April 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.2.114
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the usefulness of computed tomography (CT) for spiral tibia shaft fracture by analyzing associated distal tibia intra-articular fractures diagnosed by CT only which met the indication of surgical fixation and were fixed.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Ninety-five spiral tibia shaft fractures with preoperative ankle plain radiographs and CT were analyzed retrospectively. The incidence and type of associated distal tibia articular fractures were evaluated by reviewing ankle plain radiography and CT. The number of fractures diagnosed by CT that correspond with the indication of fixation and that were actually fixed were analyzed.
RESULTS
Among 95 spiral tibia shaft fractures, 62 cases (65.3%) were associated with distal tibia intra-articular fracture. There were 37 cases of posterior malleolar fracture, 5 cases of avulsion fracture of the distal anterior tibiofibular ligament, 5 cases of medial malleolar fracture, and 15 cases of complex fracture. Among 52 posterior malleolar fractures including complex fracture, 20 cases were diagnosed by ankle plain radiograph. Of these 20 cases, 16 posterior malleolar fractures (80.0%) met the indication of surgical fixation, and 14 cases were actually fixed with a screw. Among 32 posterior malleolar fractures diagnosed by CT only, 26 cases (81.3%) met the indication of surgical fixation and 18 cases (56.3%) were fixed by screw.
CONCLUSION
Approximately 50% of associated fractures were diagnosed by CT only and more than 80% of associated posterior malleolar fractures met the indication of surgical fixation and among these fractures, 18 cases (56.3%) were actually fixed by screw. This result suggests that CT is useful in diagnosis and treatment of distal tibia intra-articular fracture associated with spiral tibia shaft fracture. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Treatment of Distal Tibial Spiral Fractures Combined with Posterior Malleolar Fractures
Young Sung Kim, Ho Min Lee, Jong Pil Kim, Phil Hyun Chung, Soon Young Park
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2021; 56(4): 317. CrossRef
- Treatment of Distal Tibial Spiral Fractures Combined with Posterior Malleolar Fractures
- 527 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Reports
- Calcified Anterior Tibial Artery Entrapment in Distal Third Tibial Fracture: A Case Report
- Kyu Hyun Yang, Yougun Won, Sang Bum Kim, Won Kuen Park, You Sun Jung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(1):68-72. Published online January 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.1.68
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In the distal third of the tibia, the anterior tibial artery runs close to the anterolateral surface of the tibial cortex. In a clinical situation, without vascular evaluation, injury or entrapment of the anterior tibial artery is difficult to detect. Because, an intact dorsalis pedis pulse is supplied with the collateral vessels of the posterior tibial artery. An entrapped anterior tibial artery can be injured during closed reduction in an emergency room or open reduction and internal fixation in the operating room. Care must be taken to prevent iatrogenic anterior tibial artery. In this case, an entrapped anterior tibial artery was observed in a simple radiograph and computed tomograph without contrast media for the vessel. We report on a rare case of calcified anterior tibial artery entrapment in a distal tibial fracture.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Time to Operation and Efficacies of Ultrasound-Guided Nerve Block and General Anesthesia in Emergency External Fixation of Lower Leg Fractures (AO 42, 43, 44)
Chan Kang, Sang-Bum Kim, Youn-Moo Heo, You-Gun Won, Byung-Hak Oh, June-Bum Jun, Gi-Soo Lee
The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery.2017; 56(5): 1019. CrossRef
- Comparison of Time to Operation and Efficacies of Ultrasound-Guided Nerve Block and General Anesthesia in Emergency External Fixation of Lower Leg Fractures (AO 42, 43, 44)
- 586 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Extraction of Misplaced Endcap during Tibia Intramedullary Nailing by 'Fish-Hook' Technique: Technical Note
- Se Hyeok Yun, Jae Hyuk Yang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2015;28(3):194-197. Published online July 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.3.194
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Endcap placement after intramedullary nailing can be cumbersome. Misplacement of the endcap which may be difficult to extract may occur. In this report, a simple Kirschner wire device with 'fish-hook' technique may ease the procedure without further violating bony or soft tissues.
- 351 View
- 0 Download

Original Article
- A Comparison of Quality of Life Using Short Form 36 between Femoral Shaft Fracture and Tibia Shaft Fracture Treated with Antegrade Nailing
- Sangbong Ko, Hojin Chang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2015;28(3):163-168. Published online July 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.3.163
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
We sought to compare the quality of life between two similar groups of patients; one group who sustained an isolated femoral shaft fracture, and the other group who sustained an isolated tibial shaft fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From February 1995 to July 2010, two groups of 168 patients who underwent implant removal operations after intramedullary nailing for an isolated femoral shaft fracture or an isolated tibial shaft fracture were enrolled. Short Form 36 (SF-36) questionnaires were completed at the final follow-up visit. Data analysis was performed by another physician not otherwise involved with clinical evaluation or the surgeries.
RESULTS
Patients ranged in age from 18 to 37 years old. The two groups had similar characteristics, including age, gender ratio, body weight, smoking, and mean follow-up period (all p>0.05). No significant difference in functional outcome using SF-36 was observed between the groups except in the domain of physical functioning (PF) where femoral shaft fracture patients had a slightly higher score (p=0.002).
CONCLUSION
Femoral shaft fracture patients and tibial shaft fracture patients who underwent intramedullary nailing and subsequent implant removal after fracture union with similar epidemiological characteristics had similar functional outcomes using the SF-36 survey, except in the domain of PF, where femoral shaft fracture patients had a slightly better outcome. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health‐related quality of life outcomes after surgical treatment of atypical femur fractures: a multicenter retrospective cohort study
Jonathon Spanyer, Lauren A. Barber, Harrison Lands, Alexander Brown, Mary Bouxsein, Marilyn Heng, Madhusudhan Yakkanti
JBMR Plus.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Health‐related quality of life outcomes after surgical treatment of atypical femur fractures: a multicenter retrospective cohort study
- 547 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Report
- Chronic Osteomyelitis in Distraction Osteogenesis Area of Tibial Shaft: A Case Report
- Sanguk Bae, Baekyong Song, Jin Seon Moon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(4):321-326. Published online October 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.4.321
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Distraction osteogenesis with an Ilizarov external fixator is one of the most successful treatment options for large segmental bone defects after extensive debridement of chronic osteomyelitis in the tibial shaft. Its complications include skin irritation, pin tract infection, and non-union due to infection. There are few case reports on chronic osteomyelitis occurring in the distraction osteogenesis area. The authors experienced a chronic osteomyelitis in the distraction osteogenesis area of the tibial shaft and report this case with references.
- 457 View
- 7 Download

Original Articles
- The Efficacy of Preserved Posterior Cortex in the Treatment of Infected Nonunion of the Tibia
- Hyoung Min Kim, Il Jung Park, Youn Tae Roh, Byung Min Kang, Hyun Jin Lee, Jae Young Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(4):301-307. Published online October 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.4.301
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
We studied the efficacy of preserved posterior cortex connecting to adjacent muscle or periosteum during wide debridement in the treatment of infected nonunion of the tibia.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From January 2001 to May 2011, 12 cases of infected nonunion of the tibia with segmental defect larger than 4 cm after wide debridement were selected. The selected cases were categorized according to two groups; group 1 with preserved posterior cortex in the segmental defect site - six cases, group 2 without posterior cortex - six cases. The results were compared by assessing the size of bone defect, the interval between wide debridement and bone reconstruction, bony union time, complications, and clinical results.
RESULTS
The mean length of bone defect of group 1 was 7.6 cm (range 4.3-11.0 cm) and that of group 2 was 6.4 cm (range 4.0-12.0 cm). The interval between wide debridement and bone reconstruction was 10.0 weeks (range 5-18 weeks) for group 1, and 12.1 weeks (range 0-24 weeks) for group 2. The time for bony union of group 1 was 6.2 months (range 5-7 months), and that of group 2 was 10.8 months (range 7-18 months). In group 2, there were two cases of fatigue fracture and two cases of docking site nonunion after distraction osteogenesis.
CONCLUSION
The preserved posterior cortex after wide debridement of infected nonunion of the tibia helps bony union and reduces the treatment period.
- 381 View
- 2 Download

- Treatment of Type IIIb Open Tibial Fractures
- Seong Yeon Lim, Il Jae Lee, Jae Ho Joe, Hyung Keun Song
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(4):267-273. Published online October 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.4.267
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the outcome of treatment for patients with Type IIIb open tibial fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study targeted 35 adult patients for whom follow-up was possible over one year after undergoing surgical treatment. There were 29 males and six females with an average age of 45 years.
RESULTS
Fracture location was proximal in 10 cases, midshaft in 13 cases, and the distal part of the tibia in 12 cases. An average of 10 days was observed for definitive fixation with soft tissue coverage of the injury. The mean time to radiographic union was 27 weeks. Sixteen cases (45.7%) of complications were observed. Three cases of superficial infection, two cases of deep infection, four cases of partial flap necrosis, three cases of mal-alignment, three cases of joint stiffness, and one case of hardware breakage were observed. The mean lower extremity functional scale score was 68.5 and the factors influencing the clinical results were severity of open wound (p=0.000) and occurrence of complications (p=0.000) according to results of multiple regression analysis.
CONCLUSION
In treatment of Type IIIb open tibial fractures, good clinical results can be expected provided that complications are prevented through proper reduction, firm fixation, early soft tissue reconstruction, and early rehabilitation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Korean Medicine Treatments in Patients with Proximal Tibia Fracture: A Retrospective Observational Study
Jung Min Lee, Eun-Jung Lee
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2020; 30(3): 141. CrossRef
- Effect of Korean Medicine Treatments in Patients with Proximal Tibia Fracture: A Retrospective Observational Study
- 911 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Intramedullary Nailing of Distal Tibial Fractures with Percutaneous Reduction by Pointed Reduction Forceps
- Jae Kwang Hwang, Chung Hwan Kim, Young Joon Choi, Gi Won Lee, Hyun Il Lee, Tae Kyung Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(2):144-150. Published online April 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.2.144
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to analyze the radiographic and clinical results of intramedullary nailing after percutaneous reduction using pointed reduction forceps for spiral or oblique fractures of the distal tibia. The benefit of percutaneous reduction using pointed reduction forceps in anatomical reduction and maintenance was assessed.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From January 2005 to December 2009, 47 cases of distal one-third tibial fracture were managed by intramedullary nailing using pointed reduction forceps. Thirty-eight cases were spiral fracture and nine cases were oblique fracture. In all cases, the percutaneous reduction was achieved using pointed reduction forceps under fluoroscopy control. While maintaining the reduction with the pointed reduction forceps, the intramedullary nail was inserted. The pointed reduction forceps were removed after insertion of proximal and distal inter-locking screws. Alignment was evaluated with anterior-posterior and lateral radiographs taken immediately post-operation and at the time of union.
RESULTS
At immediate post-operation, the mean displacement of valgus and anterior angulation was 0.57degrees and 0.24degrees, respectively. That of valgus and anterior angulation at bone union was 0.37degrees and 0.16degrees, respectively. The average duration of bone union was 16.1 weeks.
CONCLUSION
Intramedullary nailing with percutaneous reduction using pointed reduction forceps for distal tibial fractures was an easy and effective method for achievement of accurate alignment intra-operatively. Accurate alignment was successfully maintained until bone union.
- 463 View
- 0 Download

- Ankle Fracture Associated with Tibia Shaft Fractures
- Ji Wan Kim, Hong Joon Choi, Dong Hyun Lee, Young Chang Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(2):136-143. Published online April 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.2.136
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the incidence of ankle injury in ipsilateral tibial shaft fractures and to assess the risk factors for ankle injury associated with tibial shaft fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sixty patients with tibial shaft fractures were enrolled in this retrospective study. The incidence and characteristics of ankle injury were evaluated, and fracture classification, fracture site, and fracture pattern of the tibial shaft fractures were analyzed for assessment of the risk factors for ankle injury combined with tibial shaft fractures.
RESULTS
Ankle injury occurred in 20 cases (33%). There were four cases of lateral malleolar fracture, four cases of posterior malleolar fracture, two cases of distal tibiofibular ligament avulsion fracture, and 10 cases of complex injury. Fourteen cases (70%) of 20 cases of ankle injury were diagnosed from x-ray films, and the other six cases were recognized in ankle computed tomography (CT). Ankle injury occurred in 45.1% of distal tibial shaft fractures and found in 41.4% of A type, but there was no statistical significance. Ankle injury was observed in 54% of cases of spiral pattern of tibial shaft fracture and the incidence was statistically higher than 19% of cases of non-spiral pattern tibial shaft fracture.
CONCLUSION
Ankle injury was observed in 33% of tibial shaft fractures; however, only 70% could be diagnosed by x-ray. Ankle injury occurred frequently in cases of spiral pattern of tibial shaft fracture, and evaluation of ankle injury with CT is recommended in these cases. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Usefulness of Computed Tomography on Distal Tibia Intra-Articular Fracture Associated with Spiral Tibia Shaft Fracture
Seong-Eun Byun, Sang-June Lee, Uk Kim, Young Rak Choi, Soo-Hong Han, Byong-Guk Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2016; 29(2): 114. CrossRef
- Usefulness of Computed Tomography on Distal Tibia Intra-Articular Fracture Associated with Spiral Tibia Shaft Fracture
- 668 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Reports
- Breakage of Reamer during Tibia Intramedullary Nailing: A Case Report
- Ho Yoon Kwak, Jin Su Kim, Ki Won Young, Joo Won Joh, Sae Min Hwang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(4):333-337. Published online October 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.4.333
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The reamer crack, followed by breakage at its distal part occurred during intramedullary nailing of tibial shaft fracture. The broken reamer was trapped in the intramedullary canal, making it very difficult to pull out. We successfully extracted the broken reamer by retrograde impaction through the fracture site and completed intramedullary nailing procedure. Thus, we present this case with a review of the literature.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clamshell Corticotomy: A Technique to Address Challenges of Narrow Medullary Canal during Intramedullary Nailing of Tibial Shaft Fracture Fixation
Ranjith Kumar Yalamanchili, Deepankar Satapathy, Deepak Kumar Maley, Syed Ifthekar, Maheshwar Lakkireddy
Journal of West African College of Surgeons.2025; 15(4): 481. CrossRef - A novel technique for retrieval of a broken flexible reamer during proximal femur nailing: A case report and review of the literature
Gowtham Sushruth, Sudhir Shankar Mane, Murali Krishna
Journal of Orthopaedic Reports.2025; : 100691. CrossRef - ‘Extended tibia osteotomy’: a technical tip for removal of incarcerated reamer with broken guide wire bead during tibia nailing and literature review
Pulak Vatsya, Samarth Mittal, Aashraya Karpe, Vivek Trikha
BMJ Case Reports.2022; 15(3): e247812. CrossRef - Removal of intra-operatively broken flexible reamer: An innovative use of jumbo cutter
Tankeshwar Boruah, Sapan Kumar, Mohit Kumar Patralekh, Shambhu Prashad, Vibash Chandra, Ijack Debbarma, Ramesh Kumar
Journal of Clinical Orthopaedics and Trauma.2019; 10(3): 620. CrossRef
- Clamshell Corticotomy: A Technique to Address Challenges of Narrow Medullary Canal during Intramedullary Nailing of Tibial Shaft Fracture Fixation
- 580 View
- 5 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Stabilization Using a Medial Locking Plate for Proximal Tibial Fractures: Technical Note
- Jae Ang Sim, Beom Koo Lee, Kwang Hui Kim, Yong Seuk Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(4):327-332. Published online October 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.4.327
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) is beneficial for proximal tibial fractures since these injuries are mostly caused by high energy traumas. The advantages of MIPO are minimization of soft tissue dissection and preservation of periosteal vascularization. Lateral plating has mostly developed as MIPO for proximal tibial fractures. We introduce minimal invasive percutaneous plate stabilization using a medial locking plate as alternative treatment for proximal tibial fractures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Korean Medicine Treatments in Patients with Proximal Tibia Fracture: A Retrospective Observational Study
Jung Min Lee, Eun-Jung Lee
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2020; 30(3): 141. CrossRef - Medial Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis in Proximal Tibial Comminuted Fractures
Jae-Ang Sim, Kwang-Hui Kim, Yong-Seuk Lee, Sang-Jin Lee, Beom-Koo Lee
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2014; 49(4): 278. CrossRef
- Effect of Korean Medicine Treatments in Patients with Proximal Tibia Fracture: A Retrospective Observational Study
- 633 View
- 17 Download
- 2 Crossref

Original Articles
- Outcomes and Analysis of Factors Affecting Bone Union after Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing in Segmental Tibia Fractures
- Sang Soo Park, Jun Young Lee, Sang Ho Ha, Sung Hae Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(4):275-283. Published online October 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.4.275
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the radiological results and complications of interlocking intramedullary nailing for segmental tibia fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty-six patients (26 cases) who underwent interlocking intramedullary nailing for segmental tibia fractures between January 2003 and May 2011 were followed for more than one year. We evaluated the complications and statistically analyzed the factors influencing bone union, including open fracture, fracture site, reaming, postoperative angulation, and postoperative fracture gap.
RESULTS
Nineteen cases (73%) achieved bone union with one operation at an average of 7 months (range, 5 to 11). Seven cases had secondary procedures before achieving union. Complications included 7 cases of nonunion, 3 cases of incomplete peroneal nerve injury, 2 cases of superficial infection, 1 case of compartment syndrome. Factors showing statistically significant differences were open fracture, postoperative angulation, and postoperative fracture gap. Factors showing no statistically significant difference were fracture site and reaming.
CONCLUSION
Nonunion is the most common complication in interlocking intramedullary nailing for segmental tibia fractures. To minimize this complication, comprehension of surgical techniques to reduce anatomically and careful evaluation of the fracture are required. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Outcome after Treatment of Tibia Segmental Fracture with Intramedullary Nailing and Minimal Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis
Jun Young Lee, Hyung Seok Park, Dong Hyuk Cha
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2020; 33(3): 142. CrossRef
- Clinical Outcome after Treatment of Tibia Segmental Fracture with Intramedullary Nailing and Minimal Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis
- 552 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Analysis of Risk Factors for the Posterolateral Articular Depression and Status of Posterolateral Fragment in Lateral Condylar and Bicondylar Tibial Plateau Fractures with Joint Depression
- Jung Yun Choi, Yong Woon Shin, Beom Jung Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(4):241-247. Published online October 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.4.241
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate risk factors of posterolateral articular depression and characteristics of the posterolateral fragment in lateral condylar and bicondylar tibial plateau fractures with joint depression.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed 48 patients of Schatzker type II and type V (type II 34, type V 14) and evaluated risk factors of posterolateral articular depression according to the posterolateral fragment, fibular fracture, and Schatzker classification. We evaluated the position of articular depression and anterolateral fracture line of the posterolateral fragment and measured anterior to posterior lengths of the posterolateral fragment.
RESULTS
Posterolateral articular depression was found in 20 of 34 cases (59%) with coexisting posterolateral fragment and in 16 of 21 cases (76%) with coexisting fibular fracture. There was a significant difference in the occurrence of posterolateral articular depression with the existence of the posterolateral fragment and fibular fracture (p<0.001). Multivariate regression analysis revealed that fibular fracture increased the occurrence of posterolateral articular depression (odds ratio 24.5, 95% confidence interval 2.2-267.2). Fifty-seven percentage of the anterolateral fracture line of the posterolateral fragment existed posterior to the anterior margin of the fibular head.
CONCLUSION
This study showed that fibular fracture affects posterolateral articular depression in Schatzker type II and V tibial plateau fractures. Selecting a fixation device and performing fracture reduction requires a careful consideration since the anterolateral fracture line of the posterolateral fragment exists posterior to the anterior margin of the fibular head. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Current Concepts in Management of Tibia Plateau Fracture
Sang Hak Lee, Kang-Il Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2014; 27(3): 245. CrossRef
- Current Concepts in Management of Tibia Plateau Fracture
- 577 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Arthroscopic Assisted Intra-Articular Reduction and Internal Fixation of Tibia Plateau Fracture
- Dong Hwi Kim, Gwang Chul Lee, Kwi Youn Choi, Sung Won Cho, Sang Ho Ha
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(3):191-198. Published online July 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.3.191
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
We evaluated the results of arthroscopic intra-articular reduction and internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures without cortical window along with any additional bone grafts.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From March 2006 to March 2009, twelve patients with arthroscopic intra-articular reduction and internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures over 5 mm in depression and displacement on the articular surface in computed tomography (CT) were enrolled in this study. We reduced or removed the depressed fracture fragment using freer without making a cortical window. Then, we accomplished internal fixation by a cannulated screw. All cases have not received bone graft. Both the postoperative clinical and radiological results were evaluated by the Rasmussen system.
RESULTS
The fractures were healed completely in an average of 9 (range from 7 to 12) weeks. According to Rasmussen classification, we obtained satisfactory clinical results as excellent in 8 cases, good in 3 cases, and fair in 1 case; and radiological results were excellent in 7 cases and good in 5 cases.
CONCLUSION
We consider that arthroscopic intra-articular reduction and internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures without cortical window and any additional bone grafts is are a useful methods for attaining satisfactory results. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Current Concepts in Management of Tibia Plateau Fracture
Sang Hak Lee, Kang-Il Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2014; 27(3): 245. CrossRef
- Current Concepts in Management of Tibia Plateau Fracture
- 514 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Analysis of the Result Treated with Locking Compression Plate-Distal Tibia and Zimmer Periarticular Locking Plate in Distal Tibia Fracture
- Jun Young Lee, Sang Ho Ha, Sung Won Cho, Sung Hae Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(2):118-125. Published online April 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.2.118
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the clinical and radiological results of minimally invasive plate, osteosynthesis, using either a locking compression plate-distal tibia (LCP-DT) or Zimmer periarticular locking plate (ZPLP) for distal tibia fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fifty one patients (51 cases), who underwent minimally invasive osteosynthesis using locking compression plate for distal tibia fractures between October 2008 and August 2011, were followed for more than six months. Eighteen patients were treated with LCP-DT and 33 patients with ZPLP. Time to bony union and anatomic alignment were evaluated radiologically. Clinically, American Orthopedic Foot & Ankle Society ankle-hindfoot scales (AOFAS score) and range of ankle motion were assessed and compared between two groups.
RESULTS
All patients achieved bony union at an average of 18 weeks on LCP-DT group and 16weeks on ZPLP group. The average American Orthopedic Foot & Ankle Society ankle-hindfoot scales was 83.3 points on the LCP-DT group, 84.6 points on the ZPLP group, and range of ankle motion averaged at 45 degrees, 48 degrees, respectively.
CONCLUSION
Both types of locking compression plates were effective when performing minimally invasive osteosynthesis for distal tibia fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biomechanical analysis and clinical effects of bridge combined fixation system for femoral fractures
Da-xing Wang, Ying Xiong, Hong Deng, Fu Jia, Shao Gu, Bai-lian Liu, Qun-hui Li, Qi Pu, Zhong-zi Zhang
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine.2014; 228(9): 899. CrossRef
- Biomechanical analysis and clinical effects of bridge combined fixation system for femoral fractures
- 472 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Clinical Outcomes of the Tibia Segmental Fractures Treated by Intramedullary Nail Using Various Reduction Techniques
- Oog Jin Shon, Ji Hoon Shin, Chul Wung Ha
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(1):50-55. Published online January 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.1.50
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
We evaluated the clinical outcomes of tibia segmental fractures treated by intramedullary nailing using various reduction techniques.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From January 2003 to June 2009, 18 segmental tibial fracture patients treated by intramedullary nail were enrolled with a minimum 12-month follow-up. The mean follow-up was 38 months (range 15-72). According to the AO classification, the fractures were types 42C2.1, 42C2.2, and 42C2.3 in four, ten, and four patients, respectively. Ten fractures were closed and eight were open. We used various techniques for reduction during operation and investigated bone union time and complication (non-union, malunion etc.).
RESULTS
Bone grafting was performed in three patients. Complete union was achieved in all patients. The mean time for union was 16.3 weeks (range 12-21), except in three delayed union patients. All radiological evaluations showed good alignment (less than 5 degree) except in two patients; and the mean deformity angle was 2.2 degree. Knee range of motion (ROM) was 129 degree, and ankle ROM was 68 degree. Local wound infection occurred in two patients.
CONCLUSION
Intramedullary nailing is a successful method in the acute management of segmental tibial fractures, if accompanied by appropriate reduction technique.
- 390 View
- 1 Download

Case Reports
- Anterior Tibial Muscle Hernia Treated with Local Periosteal Rotational Flap: A Case Report
- Jun Ku Lee, Hyung Ku Yoon, Dong Eun Shin, Jae hwa Kim, Dong Hoon Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(4):331-334. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.4.331
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Tibialis anterior muscle hernia is the most common hernia among lower extremity muscles. This condition can be diagnosed by physical examination and radiologic findings, especially by dynamic ultrasonography. There are surgical methods of treatment for muscle hernia, including direct repair, fasciotomy, fascial patch grafting using autologous fascia lata or synthetic mesh. We report a case of tibialis anterior muscle hernia treated with local periosteal rotational flap. Because there are several advantages to the local periosteal rotational flap, such as lack of donor site morbidity, lack of skin irritation, low cost, simplicity, and an easy approach, this technique could be an option for tibialis anterior muscle hernia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Muscle hernias of the leg: A case report and comprehensive review of the literature
Jesse T Nguyen, Jenny L Nguyen, Michael J Wheatley, Tuan A Nguyen
Canadian Journal of Plastic Surgery.2013; 21(4): 243. CrossRef
- Muscle hernias of the leg: A case report and comprehensive review of the literature
- 1,302 View
- 7 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Tension Band Plating for a Stress Fracture of the Anterior Tibial Cortex in a Basketball Player: A Case Report
- Chul Hyun Park, Woo Chun Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(4):323-326. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.4.323
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Stress fractures of the anterior tibial cortex are prone to complete fracture because these stress fractures occur on the tension side of the bone. Recently, surgical treatments are preferred in high-performance athletes requiring rapid return to sports. We report our experience of a case in which stress fracture of the anterior tibial cortex was treated using anterior tension band plating in a male athlete and successful bony union and rapid return to sports were achieved.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Stress fractures of the tibia
Jung Min Park, Ki Sun Sung
Arthroscopy and Orthopedic Sports Medicine.2015; 2(2): 95. CrossRef
- Stress fractures of the tibia
- 566 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- Treatment for Bone Defect of Open Tibial Fractures by Using Intramedullary Nail Fixation with Autogenous Iliac Bone Graft
- Hyub Sakong, Ki Cheor Bae, Chul Hyun Cho, Kyung Jae Lee, Eun Seok Son, Du Han Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(4):288-294. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.4.288
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study was conducted to evaluate the results of intramedullary nail fixation with autogenous iliac bone graft for defects of bone after tibial fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Ten patients with bone defects in tibial fractures who had been treated with intramedullary nail fixation with autogenous iliac bone graft between May 2005 and September 2008 with more than 12 month follow-up were subject to study. Of the 10 patients, 8 were male and 2 were female, and the mean age was 50.2 years (29~76 years). By cause of accident, motor vehicle accidents caused 9 cases, a crush caused 1 case, and the average follow-up period was 21.9 months (12~42 months). Radiologically, we analyzed the union of the bone defect on simple x-ray and clinical evaluation was performed using the estimate method of Mekhali.
RESULTS
This study reveals that there was radiological union in all 10 cases and the mean time to union was 8.4 months (5~18 months). By clinical evaluation according to Mekhali's estimate method, 9 patients had excellent outcomes and 1 patient had limitation of motion in the ankle joint rated as a fair clinical result. None of patients developed complications post-operatively.
CONCLUSION
Our study demonstrated that the intramedullary nail fixation with autogenous iliac bone graft can be a useful operative method because it can remove external fixators early and reduce complications, and autogenous bones have exceptional osteoconduction, osteoinduction, and bone-forming ability resulting in excellent union of bones.
- 474 View
- 5 Download

- Alteration of the Patella Tendon Length after Intramedullary Nail in Tibial Shaft Fractures
- Dong Eun Shin, Ki Shik Nam, Jin Young Bang, Ji Hoon Chang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(4):283-287. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.4.283
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To compare and analyze length change of patella tendon after intramedullary nailing of tibial shaft fracture using transtendinous approach.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty-two cases were analyzed from December, 1999 to December, 2005. Insall Salvati ratios were estimated. Severity of initial trauma, duration of nail retension, knee function and pain on change of length of patellar tendon was evaluated.
RESULTS
Mean duration of nail retention was twenty-two months. The shortening of patella tendon was observed in 25 cases (p<0.001). The effect of AO type and the duration of nail retension on the decrease of Insall Salvati ratio was not significant (p>0.05, p=0.778). Lysholom score decrease to 89.5. There was no significant difference between the shortening of patellar tendon length and knee pain (p=0.058).
CONCLUSION
After intramedullary nailing for closed tibia fracture, shortening of patellar tendon length is observed. That is irrelevant to the fracture type and the duration of nail retension. The shortening of patella tendon length may contribute to decreasing of knee function, but it was no significance of knee pain after intramedullary nailing.
- 401 View
- 0 Download

- The Results of Two Stage Surgical Treatment of Pilon Fractures
- Hong Moon Sohn, Jun Young Lee, Sang Ho Ha, Sang Hong Lee, Gwang Chul Lee, Kwang Hyo Seo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(3):177-184. Published online July 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.3.177
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To report the good results of two-stage treatment in pilon fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A retrospective study of 23 patients among 30 patients with pilon fractures from March 2006 to November 2008, who underwent two-stage treatment of pilon fractures with a minimum of 24 months follow-up. The mean follow-up period was 28 months (24~41 months). In the first stage of the operation, open reduction of the articular surface and external fixation were performed after minimal incision. As the soft tissue healed, locking compression plate fixation was performed with the Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. Radiographic evaluation was graded by the criteria of Burwell and Charnley, and functional assessment of the ankle was evaluated by the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) ankle-hindfoot score.
RESULTS
The fractures were united within 16 weeks (12~30 weeks). The radiologic results showed anatomical reduction in 18 cases and a mean AOFAS score of 81. The mean range of ankle motion was 44 degrees. There were four complications: 1 case of wound infection and 3 cases of ankle osteoarthritis.
CONCLUSION
Two-stage treatment of pilon fractures is a good treatment method because it is designed to obtain early anatomical reduction, definitive stable fixation, low rates of soft tissue complication, and good range of ankle motion. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Current Concepts in Management of Pilon Fracture
Jun-Young Lee, Sang-Joon Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2014; 27(2): 173. CrossRef
- Current Concepts in Management of Pilon Fracture
- 625 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Clinical Outcomes of Locking Compression Plate Fixation through Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis in the Treatment of Distal Tibia Fracture
- Jae Sung Yoo, Hyun Woo Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(2):117-122. Published online April 30, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.2.117
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analyze the clinical results of operative treatment of distal tibia fracture with locking compression plate fixation through a minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis technique.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The subjects were 46 patients (conventional open surgery: 22 patients, minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis: 24 patients) with fracture of the distal tibia who were treated with plating between November 2006 and June 2010. The time of bony union, complications, range of motion, and clinical functional outcome (according to American Orthopedic Foot and Ankle Society, AOFAS) were investigated.
RESULTS
In the minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis group, the average union time was 14.3 weeks, postoperative range of motion was an average of 55.2, average AOFAS was 96.9, and incidence of complications was 20.8%. In the open surgery group, the average union time was 18.9 weeks, postoperative range of motion was an average of 49.1, average AOFAS was 83.8, and incidence of complications was 32.6%. There were statistically significant differences (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
Surgical treatment with locking compression plate fixation through the minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis technique showed favorable results regarding its union time, postoperative functional outcome, and incidence of complications. The locking compression plate fixation through minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis technique can be an effective treatment option. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Fractures of Distal Tibia
Tae Hun Kim, So Hak Chung
Kosin Medical Journal.2014; 29(1): 23. CrossRef
- Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Fractures of Distal Tibia
- 529 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Treatment of Tibial Plateau Fractures Using a Locking Plate and Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Osteosynthesis Technique
- Hee Gon Park, Dae Hee Lee, Kyung Joon Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(2):110-116. Published online April 30, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.2.110
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To acknowledge the importance of precise reduction of articular surface of tibial plateau fractures and to make a guideline of treatment by evaluating outcomes and effectiveness of using locking plate and minimally invasive percutaneous osteosynthesis technique.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty-nine patients who underwent surgery for tibial plateau fracture from November 2005 to March 2010 were enrolled with 12 months follow-up in a retrograde manner. The Shatzker classification was used to classify fractures, and we used lateral submeniscal approach to make a precise reduction of articular surface. Radiologic evaluation was determined by presence of bone union, malalignment, and reduction loss or joint depression of articular surface. Post-operative infection, time of active movement of the knee joint, time of partial weight loading, and range of motion (ROM) of knee joint were evaluated. Lysholm Knee Score was used for functional evaluation.
RESULTS
Bone union took place in all but one case that developed osteomyelitis. Angulation deformity of more than 10degrees and reduction loss or joint depression of more than 5 mm were not observed. There was one case of osteomyelitis and one case of superficial surgical site infection. There were satisfactory clinical results, with an average time of active knee joint movement and weight loading of 6 weeks. The average ROM of knee joint was 125degrees in the last follow up. As for functional evaluation using Lysholm Knee Score, cases showed an average Lysholm Knee Score of 94 which was a satisfactory result.
CONCLUSION
In cases of tibial plateau fractures, if a surgeon accurately reduces the articular surface of joint and use minimally invasive locking plate it will help in bone union biologically, reducing the incidence of soft tissue injuries, and biomechanically maintaining the articular surface of the joint, proving itself to be a useful method of treatment.
- 685 View
- 5 Download

- Comparative Analysis of Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis Using Periarticular Plate and Intramedullary Nailing in Distal Tibial Metaphyseal Fractures
- Gwang Chul Lee, Jun Young Lee, Sang Ho Ha, Hong Moon Sohn, Yi Kyu Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(1):20-25. Published online January 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.1.20
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To compare results between minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis using a periarticular plate and intramedullary nailing in distal tibial metaphyseal fractures in two treatment groups.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sixty-one cases of distal tibial metaphyseal fractures from December 2008 to December 2009 were evaluated. The minimal follow-up period was 12 months. Thirty patients treated by minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis using a periarticular plate were Group A; 31 patients treated by intramedullary nailing were Group B. We compared and analyzed the results of each group by radiological and clinical assessments.
RESULTS
The mean bony union time was 16.4 weeks in Group A and 17.2 weeks in Group B. The mean operation time was 45 minutes in Group A and 48 minutes in Group B. The mean radiation exposure times were 4.2 minutes and 4.8 minutes, respectively. VAS scores were 0.7 points and 0.5 points in each respective group. In Group A, the VAS score was 1.7 points when we applied pressure on the skin around the plate. The mean Olerud and Molander Ankle Score was 87.4 points and 86.3 points, respectively. A superficial wound infection occurred in 1 case in each group, and angular deformities more than 5 degrees occurred in 2 Group B cases.
CONCLUSION
No significant differences in results were observed between the two groups. However, a higher incidence of angular deformity was seen in the intramedullary nailing group. Therefore, we must be careful during surgery. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Analysis of Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis and Intramedullary Nailing in the Treatment of the Distal Tibia Fractures
Ho-Min Lee, Young-Sung Kim, Jong-Pil Kim, Phil-Hyun Chung, Suk Kang, Kaung Suk Jo
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2018; 31(3): 94. CrossRef - A Comparison of the Results between Intramedullary Nailing and Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis in Distal Tibia Fractures
Chul-Hyun Park, Chi-Bum Choi, Bum-Jin Shim, Dong-Chul Lee, Oog-Jin Shon
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2014; 49(4): 285. CrossRef
- Comparative Analysis of Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis and Intramedullary Nailing in the Treatment of the Distal Tibia Fractures
- 510 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

Case Reports
- Treatment of Nonunion of Tibia with Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy: A Case Report
- Seung Yong Sung, Han Kook Yoon, Jeung Yeul Jung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2011;24(4):367-370. Published online October 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.4.367
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Almost tibia fractures can be surgically treated, but nonunion may occur in 10~30%, and they may accompany various complications by operation. This research was designed to review literatures and report a case of patient with nonunion of the tibia that showed good result when performing the extracorporeal shock wave therapy as a conservative treatment.
- 497 View
- 0 Download

- Checkrein Deformity by Incarcerated Posterior Tibial Tendon and Displaced Flexor Hallucis Longus Tendon following Ankle Dislocation: A Case Report
- Su Young Bae, Hyung Jin Chung, Man Young Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2011;24(3):271-276. Published online July 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.3.271
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We report a case of 20 year-old man who had unusual equinus and checkrein deformity following dislocation of his right ankle joint. He had been treated with distal tibiofibular screw fixation and external fixation. After removal of external fixator, he had suffered from progressive deformity of foot and ankle. Widening of distal tibiofibular joint and medial clear space was found on radiograph and it was revealed that posterior tibial tendon had been dislocated and incarcerated into the distal tibiofibular joint on MRI. We corrected the deformity with excision of incarcerated posterior tibial tendon, adhesiolysis and lengthening of flexor hallucis longus tendon, reconstruction of deltoid ligament and flexor digitorum longus tendon transfer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Management of Checkrein Deformity
Min Gyu Kyung, Yun Jae Cho, Dong Yeon Lee
Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery.2024; 16(1): 1. CrossRef - A Neglected Extensor Hallucis Longus Tendon Rupture Caused by Arthritic Adhesion
Sung Hun Won, Sung Hwan Kim, Young Koo Lee, Dong-Il Chun, Byung-Ryul Lee, Woo-Jong Kim
Medicina.2023; 59(6): 1069. CrossRef - The Checkrein Deformity of Extensor Hallucis Longus Tendon and Extensor Retinaculum Syndrome with Deep Peroneal Nerve Entrapment after Triplane Fracture: A Case Report
Hyungon Gwak, Jungtae Ahn, Jae Hoon Lee
Journal of Korean Foot and Ankle Society.2021; 25(3): 145. CrossRef - Checkrein Deformity Due to Flexor Digitorum Longus Adhesion after Comminuted Calcaneus Fracture: A Case Report
Jin Su Kim, Han Sang Lee, Ki Won Young, Keun Woo Lee, Hun Ki Cho, Sang Young Lee
Journal of Korean Foot and Ankle Society.2015; 19(1): 35. CrossRef
- Management of Checkrein Deformity
- 496 View
- 0 Download
- 4 Crossref

Original Article
- Anatomically Percutaneous Wiring Reduction in Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Distal Tibial Fractures
- Young Mo Kim, Chan Kang, Deuk Soo Hwang, Yong Bum Joo, Woo Yong Lee, Jung Mo Hwang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2011;24(3):230-236. Published online July 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.3.230
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To report the method of anatomical reduction and its maintenance by percutaneous wiring reduction in minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for distal tibial fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
17 cases that were diagnosed oblique, spiral or transverse fracture of distal tibia from August 2007 to February 2010 and were able to anatomically reduce by the method of percutanous wiring reduction in minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis were included in this study. Mean age was 50, and mean follow up period was 18 months. We investigated the period until bone union was achieved, degree of angulation angle, and complications. For postoperative evaluation, Olerud and Molander ankle score and VAS pain score in daily living were checked.
RESULTS
The mean varus/valgus angulation after bone union on AP radiograph was 0.9 degrees and the mean anterior/posterior angulation on lateral radiograph was 2.0 degrees The mean Olerud and Molander ankle score was 89.4, and mean pain score due to walk adjacent to metal plate was 0 points.
CONCLUSION
By the method of percutaneous wiring reduction in distal tibial fracture, anatomical reduction is easily acquired, and only by wire itself, reduction could be maintained, so that without additional manual reduction, plate could be easily fixed.
- 425 View
- 3 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


