Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 30(2); 2017 > Article
-
Original Article
- The Result of Using an Additional Mini-Locking Plate for Tibial Pilon Fractures
- Suenghwan Jo, M.D., Ph.D., Jun Young Lee, M.D., Ph.D., Boseon Kim, M.D., Kang Hyeon Ryu, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2017;30(2):75-82.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.2.75
Published online: April 18, 2017
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chosun University Hospital, Chosun University School of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea.
- Correspondence to: Jun Young Lee, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chosun University Hospital, Chosun University School of Medicine, 309 Pilmun-daero, Dong-gu, Gwangju 61452, Korea. Tel: +82-62-220-3147, Fax: +82-62-226-3379, leejy88@chosun.ac.kr
Copyright © 2017 The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 501 Views
- 4 Download
Abstract
-
Purpose
- We evaluated the usefulness of an additional, 2.7 mm mini-locking plate for tibial pilon fractures.
-
Materials and Methods
- We studied 21 patients (14 males and 7 females), who were treated with a 2.7 mm mini-locking plate via the anterolateral approach for tibial pilon fractures between September 2012 and April 2014. The mean age was 43.85 years, and the mean follow-up period was 16.6 months. The radiologic outcomes were graded by the Burwell and Charnley modified system and clinical outcomes were evaluated by the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) ankle-hind foot score and visual analogue scale (VAS) score.
-
Results
- The mean union period was 14.3 weeks. At the final follow-up, radiologic results showed 16 excellent results, 4 fair results, and 1 poor result. The average VAS was 3.4 points; the average AOFAS score was 81.8 points. During the follow-up period, there were three cases of posttraumatic osteoarthritis and one case of superficial skin infection.
-
Conclusion
- Additional anterolateral, 2.7 mm mini-locking plate may be a good treatment method to manage tibial pilon fractures.
- 1. Blauth M, Bastian L, Krettek C, Knop C, Evans S. Surgical options for the treatment of severe tibial pilon fractures: a study of three techniques. J Orthop Trauma, 2001;15:153-160.
- 2. Bone L, Stegemann P, McNamara K, Seibel R. External fixation of severely comminuted and open tibial pilon fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1993;(292):101-107.
- 3. Leung F, Kwok HY, Pun TS, Chow SP. Limited open reduction and Ilizarov external fixation in the treatment of distal tibial fractures. Injury, 2004;35:278-283.
- 4. Patterson MJ, Cole JD. Two-staged delayed open reduction and internal fixation of severe pilon fractures. J Orthop Trauma, 1999;13:85-91.
- 5. Baumgaertel F, Buhl M, Rahn BA. Fracture healing in biological plate osteosynthesis. Injury, 1998;29:Suppl 3. C3-C6.
- 6. Claes L, Heitemeyer U, Krischak G, Braun H, Hierholzer G. Fixation technique influences osteogenesis of comminuted fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1999;(365):221-229.
- 7. Gerber M, Richardson S, Cavallo F, et al. The role of diet history and biologic assays in the study of “diet and breast cancer”. Tumori, 1990;76:321-330.PDF
- 8. Jastifer JR. Topical review: locking plate technology in foot and ankle surgery. Foot Ankle Int, 2014;35:512-518.PDF
- 9. Dujardin F, Abdulmutalib H, Tobenas AC. Total fractures of the tibial pilon. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res, 2014;100:S65-S74.
- 10. Barei DP, Nork SE. Fractures of the tibial plafond. Foot Ankle Clin, 2008;13:571-591.
- 11. Chen L, O'Shea K, Early JS. The use of medial and lateral surgical approaches for the treatment of tibial plafond fractures. J Orthop Trauma, 2007;21:207-211.
- 12. Khazzam M, Della Rocca GJ, Wade AM, Murtha YM, Crist BD. Anterolateral approach to the distal tibia for fixation of pilon fractures: rate of wound complications in the early postoperative period. Curr Orthop Pract, 2012;23:111-115.
- 13. Howard JL, Agel J, Barei DP, Benirschke SK, Nork SE. A prospective study evaluating incision placement and wound healing for tibial plafond fractures. J Orthop Trauma, 2008;22:299-305. discussion 305-306.
- 14. Deivaraju C, Vlasak R, Sadasivan K. Staged treatment of pilon fractures. J Orthop, 2015;12:S1-S6.
- 15. Lee KB. Distal tibia fracture: plate osteosynthesis. J Korean Fract Soc, 2009;22:306-313.
- 16. Maffulli N, Toms AD, McMurtie A, Oliva F. Percutaneous plating of distal tibial fractures. Int Orthop, 2004;28:159-162.PDF
- 17. Ghera S, Santori FS, Calderaro M, Giorgini TL. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibial fractures: pitfalls and surgical guidelines. Orthopedics, 2004;27:903-905.
- 18. Lee HS, Kim JJ, Oh SK, Ahn HS. Treatment of distal tibial metaphyseal fracture using MIPPO technique. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc, 2004;8:166-170.
- 19. Vidyadhara S, Rao SK. Ilizarov treatment of complex tibial pilon fractures. Int Orthop, 2006;30:113-117.
- 20. Bozkurt M, Ocguder DA, Ugurlu M, Kalkan T. Tibial pilon fracture repair using Ilizarov external fixation, capsuloligamentotaxis, and early rehabilitation of the ankle. J Foot Ankle Surg, 2008;47:302-306.
- 21. Kim YJ, Jung HG, Lee JH, Byun WS, Lee ST. Comminuted pilon fractures: comparative outcome analysis according to surgical techniques. J Korean Fract Soc, 2007;20:6-12.
- 22. Lomax A, Singh A, N Jane M, C Senthil K. Complications and early results after operative fixation of 68 pilon fractures of the distal tibia. Scott Med J, 2015;60:79-84.PDF
REFERENCES
Fluroscopic image, 3.5 mm locking compression plate distal anterolateral plate is not contoured to the anatomy of tibia.
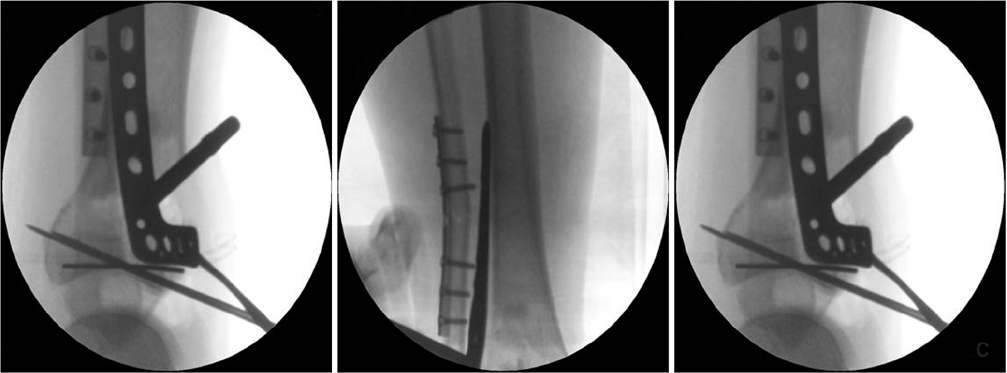
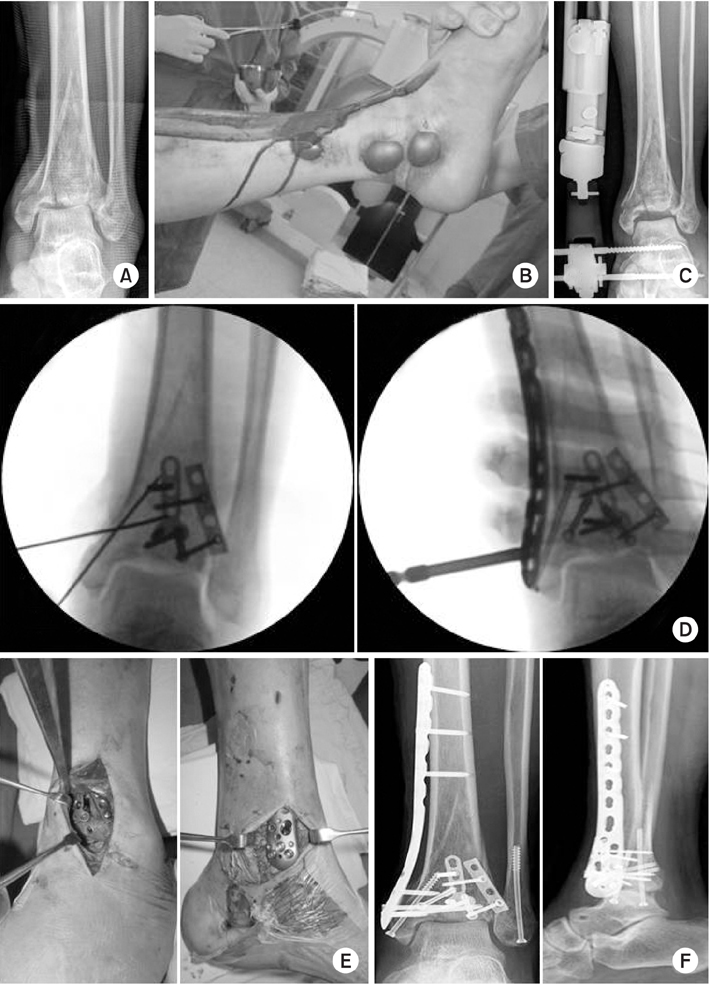
(A) A 47-year-old man suffered a traffic accident and sustained Rüedi-Allgower type III Pilon fracture. (B) The photographs show poor soft tissue condition and a bullous hemorrhagic lesions around the fracture site. (C) As the 1st stage treatment, the Pilon fracture was realigned and stabilized by an external fixator, using ligament taxis. The postoperative radiograph shows restoration of the tibial length, joint spanning, and articular surface reduction. (D) Intraoperative fluoroscopic image for articular surface reduction through the anterolateral approach using a 2.7 mm minilocking compression plate. Thereafter, the medial distal locking plate under Carm guidance (Synthes®) through limited medial approach was applied. (E) Intraoperative photographs. (F) Immediate postoperative radiographsdemonstrate a satisfactory articular reduction and restoration of distal tibial alignment.
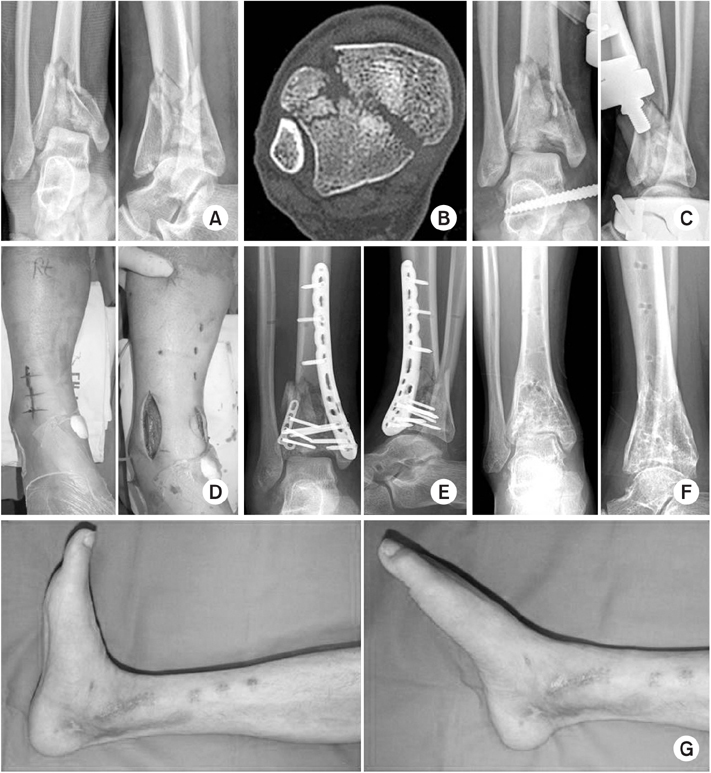
(A) A 17-year-old female experienced a fall-down injury and sustained a Rüedi-Allgower type II Pilon fracture. (B) The computed tomography scan shows comminution of tibia plafond with displaced articular fragments, especially anterolateral aspect of the tibia. (C) The patient underwent closed reduction and external fixation. (D) The surgical incision of the anterolateral and limited medial approach to metaphysis and ankle joint have been marked on the right ankle. (E) Immediate postoperative radiographs demonstrate a satisfactory articular reduction and restoration of the distal tibial alignment by locking compression plates (Synthes®) in the 2nd-staged operation. (F) At postoperative 13 months, the implant was removed. (G) The patient showed a mild stiff ankle with no pain, with a final American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society score of 75 points.
Patient Demographics
Radiologic Results, Clinical Outcomes and Postoperative Complications
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

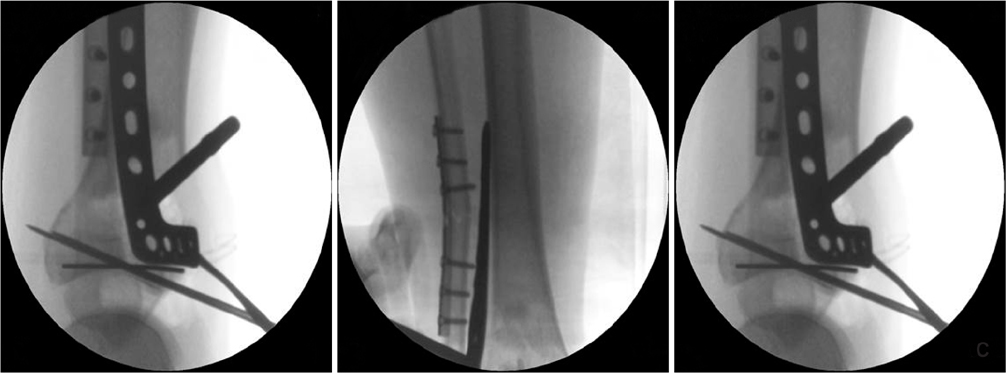
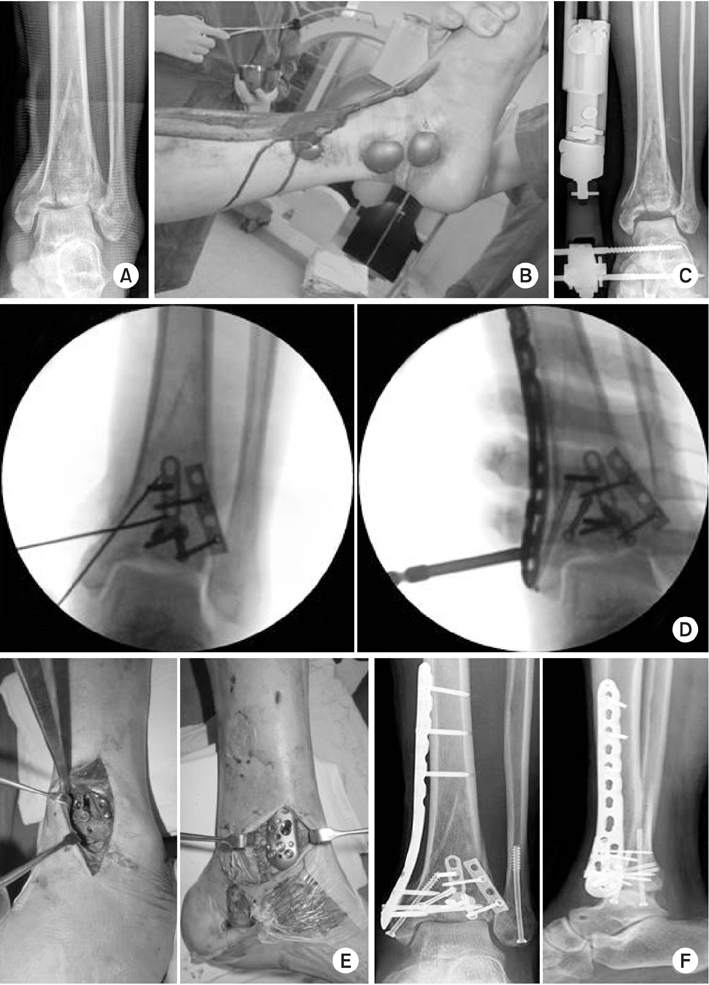
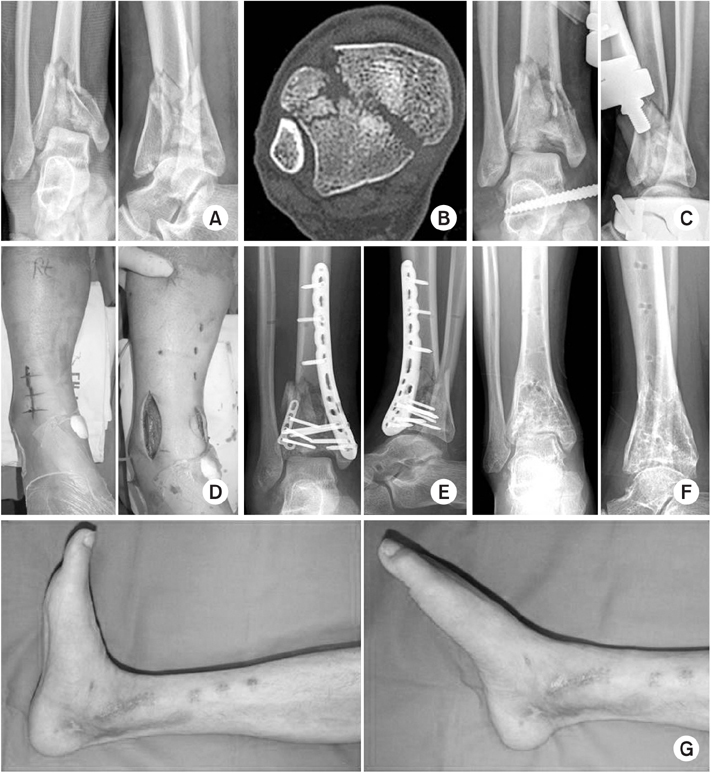
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Patient Demographics
| Case No. | Age (yr)/sex | Mechanism of injury | RA classification | Open fracture | Union time (wk) | Final F/U (mo) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 14/M | Slip down | II | - | 10 | 20 |
| 2 | 43/M | Fall down | III | - | 14 | 15 |
| 3 | 57/M | Direct injury | II | - | 11 | 18 |
| 4 | 55/F | Fall down | II | - | 15 | 15 |
| 5 | 20/F | Fall down | II | - | 11 | 12 |
| 6 | 73/M | Fall down | III | O | 16 | 18 |
| 7 | 73/M | MVA | III | O | 17 | 22 |
| 8 | 27/M | Fall down | II | - | 14 | 13 |
| 9 | 38/M | Slip down | III | - | 14 | 15 |
| 10 | 40/M | MVA | III | - | 12 | 11 |
| 11 | 39/F | Fall down | III | - | 21 | 36 |
| 12 | 34/M | Fall down | II | - | 13 | 20 |
| 13 | 17/F | Fall down | II | - | 13 | 18 |
| 14 | 47/M | MVA | III | - | 16 | 12 |
| 15 | 36/M | Fall down | II | - | 12 | 15 |
| 16 | 51/M | Fall down | III | - | 14 | 14 |
| 17 | 43/F | Fall down | III | - | 15 | 15 |
| 18 | 65/F | Slip down | II | - | 16 | 17 |
| 19 | 55/F | MVA | II | - | 13 | 15 |
| 20 | 54/M | Fall down | III | O | 19 | 12 |
| 21 | 40/M | Fall down | III | - | 14 | 15 |
| Mean | 43.85 | - | - | - | 14.3 | 16.6 |
RA: Rüedi-Allgower, F/U: follow-up, M: male, F: female, MVA: motor vehicle accident.
Radiologic Results, Clinical Outcomes and Postoperative Complications
| Case No. | AOFAS score | Radiologic result | Complication |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 98 | Anatomical | - |
| 2 | 80 | Fair | Osteoarthritis |
| 3 | 82 | Fair | Osteoarthritis |
| 4 | 84 | Anatomical | - |
| 5 | 78 | Anatomical | - |
| 6 | 60 | Fair | - |
| 7 | 87 | Anatomical | - |
| 8 | 87 | Anatomical | - |
| 9 | 85 | Anatomical | - |
| 10 | 90 | Anatomical | - |
| 11 | 70 | Fair | - |
| 12 | 89 | Anatomical | - |
| 13 | 75 | Anatomical | - |
| 14 | 88 | Anatomical | - |
| 15 | 92 | Anatomical | - |
| 16 | 87 | Anatomical | - |
| 17 | 91 | Anatomical | - |
| 18 | 79 | Anatomical | - |
| 19 | 82 | Anatomical | - |
| 20 | 48 | Poor | Osteoarthritis Superfical skin infection |
| 21 | 86 | Anatomical | - |
| Mean | 81.8 | - | - |
AOFAS: American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society.
RA: Rüedi-Allgower, F/U: follow-up, M: male, F: female, MVA: motor vehicle accident.
AOFAS: American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

