Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Hook plate fixation for volar plate avulsion fractures of the middle phalanges in Korea: a case series
- Kang-San Lee, Sang-Woo Son, Hee-June Kim, Hyun-Joo Lee, Dong Hee Kim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2026;39(1):48-53. Published online January 25, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00339
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
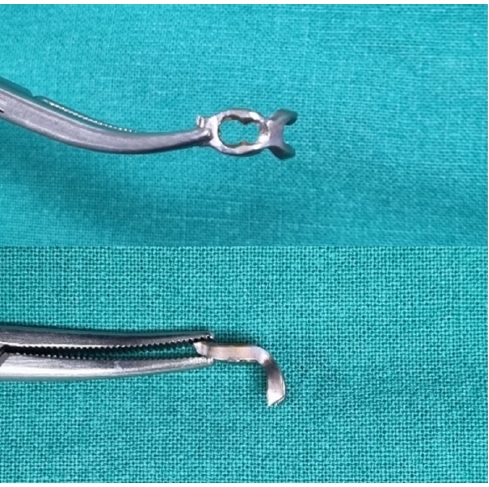
Volar plate avulsion fractures in phalanges are relatively common injuries. While surgical treatment can help reduce limitations in motion after injury, the small size of the fracture fragment can make the procedure challenging. In this study, we used hook plate fixation as a surgical technique for treating volar avulsion fractures in phalanges and evaluated its radiological and clinical outcomes.
Methods
The medical records of eight patients (nine digits) with volar plate avulsion fractures of the middle phalanx were retrospectively reviewed. All fractures were treated with a 1.5-mm hook plate after open reduction. Radiologic evaluations were performed using simple radiographs, and clinical outcomes were assessed through range of motion, instability, and pain.
Results
The mean follow-up period was 4.89 months (range, 1–9 months). All nine digits achieved bone union at the final follow-up. The mean union time was 2.2 months (range, 1–4 months). In all patients, the range of motion in the proximal interphalangeal joint was 85° (range, 70°–100°) before implant removal and 89.4° (range, 80°–100°) after implant removal. All patients demonstrated no joint instability and no residual pain.
Conclusion
Using a hook plate for volar plate avulsion fractures presents a promising alternative to existing fixation methods. Its biomechanical advantages and ease of fabrication make it a valuable tool in hand surgery. Level of evidence: IV.
- 90 View
- 6 Download

Technical Note
- Rim plate-assisted intramedullary nail and plate combination technique for complex tibial plateau-to-diaphysis fractures: a technical note and case series
- Whee Sung Son
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2026;39(1):62-71. Published online December 4, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00290

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Complex tibial plateau-to-diaphysis fractures present a significant surgical challenge due to their intricate fracture patterns and frequent association with severe soft tissue damage and concomitant injuries. This technical note introduces a novel fixation strategy: the rim plate-assisted intramedullary nail-plate combination (NPC) technique. In this approach, a rim plate simplifies the conventional NPC procedure by unifying the tibial plateau fracture into a single structural segment. This modification eliminates the need to address the articular and diaphyseal components simultaneously while enhancing articular stability. Furthermore, the technique preserves soft tissue integrity and promotes early rehabilitation. Clinical case examples demonstrate its successful application in managing complex tibial plateau-to-diaphysis injuries. Level of evidence: V.
- 410 View
- 18 Download

Original Articles
- Hook plate versus periarticular-type volar locking plate for distal radius fractures involving the volar lunate facet in Korea: a retrospective cohort study
- Hyun-Jae Park, Joo-Hak Kim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):221-228. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00241
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
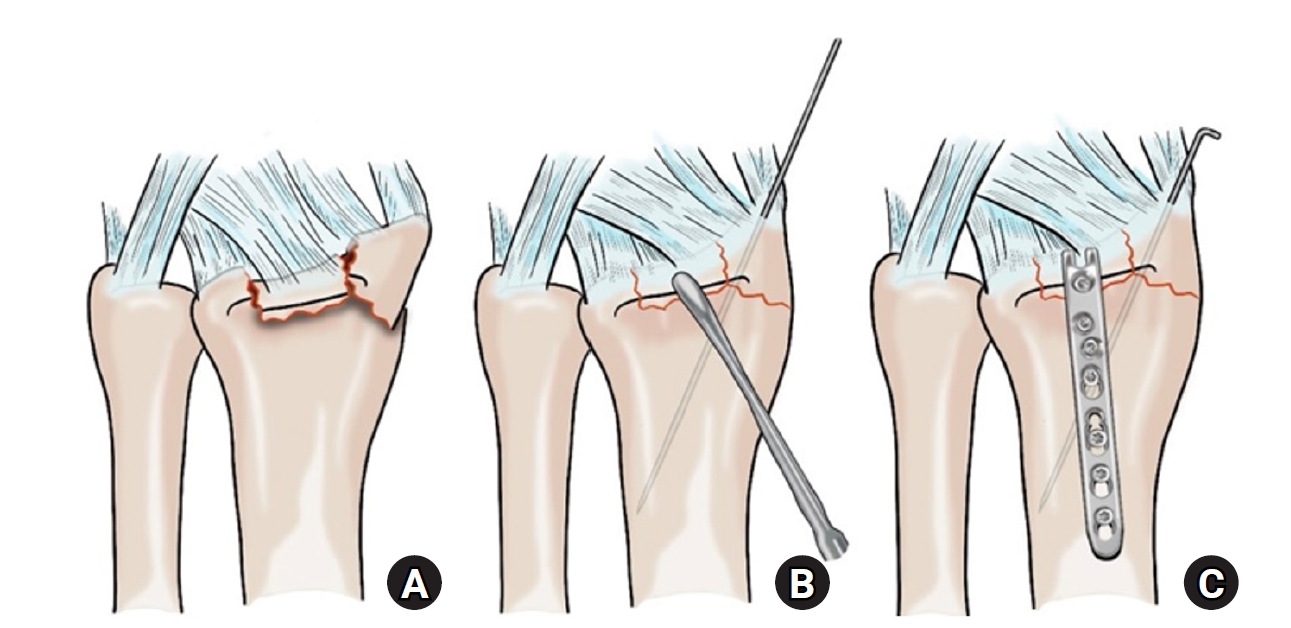
This study investigated the clinical and radiographic outcomes of hook plate (HP) fixation for volar lunate facet fractures, comparing them with periarticular-type volar locking plates (PVLPs).
Methods
A retrospective review was conducted on 24 patients with distal radius fractures involving volar lunate facet fragments who underwent surgery between January 2016 and April 2021. Patients were divided into two groups: HP (n=12) and PVLP (n=12). Radiographic union, wrist range of motion, Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand (DASH) scores, and implant-related complications were compared. Statistical analyses included the Mann-Whitney U test and Fisher exact test.
Results
Radiographic union was achieved in all patients (100%), without secondary displacement or hardware failure. No significant differences were observed between the two groups in wrist flexion (P=0.152), extension (P=0.832), pronation (P=0.792), or supination (P=0.328). The mean DASH scores were 12.8±5.5 in the HP group and 14.6±6.0 in the volar plate group (P=0.449). One patient in the HP group experienced mild flexor tendinopathy that resolved with conservative management. No cases of tendon rupture or early reoperation were reported.
Conclusions
Fixation of volar lunate facet fractures using a HP yielded clinical and radiographic outcomes comparable to those of PVLPs, with a low rate of complications and reliable bony union. Due to its mechanical stability, compatibility with standard surgical approaches, and low risk of flexor tendon irritation, the HP may serve as a valuable alternative for managing volar lunate facet fractures. Level of evidence: IV.
- 325 View
- 10 Download

- Comparison of outcomes of reinforced tension band wiring and precontoured plate and screw fixation in the management of Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures
- Hyun Goo Kang, Tong Joo Lee, Samuel Jaeyoon Won
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):96-101. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00059
- Correction in: J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):168
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
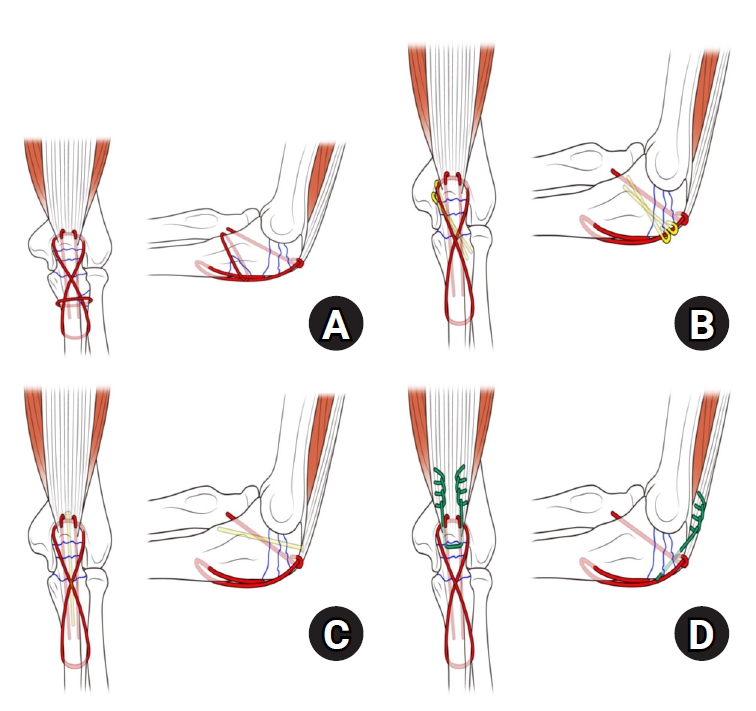
Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures are characterized by significant displacement and comminution, presenting a challenge in selecting the appropriate fixation technique. This study compared the clinical and radiographic outcomes, complications, and reoperation rates of reinforced tension band wiring (TBW) and precontoured plate and screw fixation (PF) in the surgical treatment of Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures.
Methods
This retrospective review analyzed 24 patients diagnosed with Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures, who were treated between 2005 and 2023. Of these, 11 patients underwent reinforced TBW, and 13 received precontoured PF. Clinical outcomes were assessed using Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH) scores and the Mayo Elbow Performance Score (MEPS). Radiographic outcomes focused on fracture union. Operative times, complication rates, and reoperation rates were compared between the groups.
Results
Both the reinforced TBW and PF groups achieved satisfactory clinical outcomes, with no significant between-group differences in DASH and MEPS scores (P>0.05). Radiographic union was achieved in all patients. The reinforced TBW group demonstrated a significantly shorter operative time than the PF group (93.6±7.4 min vs. 132.3±13.7 min; P<0.001). Complication rates were similar between the two groups (reinforced TBW, 38.4%; PF, 36.3%), but hardware-related irritation occurred more frequently in the reinforced TBW group. Reoperations were required in 15.8% of the reinforced TBW group due to hardware irritation, whereas no reoperations were necessary in the PF group.
Conclusions
Reinforced TBW and PF are both effective surgical options for managing Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures, yielding comparable clinical and radiographic outcomes. While reinforced TBW offers shorter operative times and lower costs, PF is associated with fewer hardware-related complications. Further prospective studies are needed to optimize treatment strategies for these complex fractures. Level of Evidence: Level III. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Are posterior olecranon locking plates a problem for patients after fracture healing because of prominence?
Reva Qiu, Mallika Makkar, Richard Buckley
Injury.2025; 56(11): 112769. CrossRef
- Are posterior olecranon locking plates a problem for patients after fracture healing because of prominence?
- 2,171 View
- 51 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Outcomes of open reduction and internal fixation using 2.0/2.4 mm locking compression plate in isolated greater tuberosity fractures of humerus
- Sung Choi, Dongju Shin, Sangwoo Kim, Byung Hoon Kwack
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(1):32-39. Published online January 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00005

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The purpose of this study was to retrospectively evaluate the radiographic and clinical results of a small single or double low-profile plate fixation of 2.0/2.4 mm locking compression plate (LCP) in treating isolated greater tuberosity (GT) fractures of the humerus. Methods: From June 2015 to October 2022, patients who underwent LCP in treating isolated GT fractures of the humerus were included in this study. The radiological and clinical results were analyzed in 15 patients who underwent open reduction and internal fixation used 2.0/2.4 mm LCP. Results: Bone union was achieved in 14 patients (93.3%) and one failed case was treated with a 2.4 mm single LCP fixation. Radiological union was achieved within 10–20 weeks. Complications occurred in two patients (13.3%), including the reduction failure and shoulder stiffness. At the final follow-up, the average clinical scores were as follows: a visual analog scale for pain of 2.1 (range, 0–5) and a University of California, Los Angeles score of 27.2 (range, 18–31). Regarding range of motion (ROM), the average active ROMs were 142° for forward flexion (range, 120°–150°), 147.1° for abduction (range, 120°– 180°), and 59.3° for external rotation (range, 45°–80°). For internal rotation, the average was observed to reach the 10th thoracic vertebra (range, 1st lumbar vertebra–7th thoracic vertebra). Conclusions: The clinical and radiologic outcomes of treating isolated GT fracture using 2.0/2.4 mm LCP were favorable, and double low-profile plate fixation may be beneficial for sufficient fracture stability if possible. Level of evidence: Level IV, case series.
- 1,895 View
- 55 Download

- Restoration of Lateral Tibial Plateau Widening and Articular Depression Is Necessary to Prevent Valgus Deformities after Arthroscopic Reduction and Internal Fixation in AO/OTA 41.B2 or B3 Fractures
- Jun-Ho Kim, Kang-Il Kim, Sang-Hak Lee, Gwankyu Son, Myung-Seo Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(3):125-136. Published online July 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.3.125
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the factors affecting valgus deformities after arthroscopic reduction and internal fixation (ARIF) in lateral joint-depression tibial plateau fractures.
Materials and Methods
Patients with lateral joint-depression tibial plateau fractures treated with ARIF were assessed retrospectively. The radiological evaluations included the articular depression distance (ADD) and the lateral plateau widening distance (LPWD) on preoperative and postoperative computed tomography. A postoperative valgus deformity was defined as valgus malalignment (mechanical axis ≥3°) and valgus deviation (Δmechanical axis of the operated knee from the healthy knee of ≥5°). Subgroup analyses based on a postoperative valgus deformity were performed to compare the clinical outcomes, including the range of motion, patient-reported outcomes measures, and failure and osteoarthritis progression. Furthermore, factors affecting the postoperative mechanical and Δmechanical axes were assessed.
Results
Thirty-nine patients were included with a mean follow-up of 44.6 months (range, 24-106 months). Valgus malalignment and valgus deviation were observed after ARIF in 10 patients (25.6%) and five patients (12.8%), respectively. The clinical outcomes were similar in patients with and without a postoperative valgus deformity. On the other hand, lateral compartment osteoarthritis progression was significantly higher in the valgus deformity group than in the non-valgus deformity group (valgus malalignment group: 50.0% vs 6.9%, p=0.007; valgus deviation group: 60.0% vs 11.8%, p=0.032). One patient with valgus deformity underwent realignment surgery at postoperative five years. The preoperative ADD and postoperative LPWD were significantly associated with the postoperative mechanical (both, p<0.001) and Δmechanical (ADD, p=0.001; LPWD, p=0.025) axes. Moreover, the lateral meniscectomized status during ARIF was significantly associated with the Δmechanical axis (p=0.019).
Conclusion
Osteoarthritis progression was highly prevalent in patients with postoperative valgus deformity. Thus, the restoration of lateral plateau widening and articular depression and preservation of the meniscus are necessary to prevent a valgus deformity after ARIF in lateral joint-depression tibial plateau fractures.
- 2,703 View
- 40 Download

- Comparison of Results between Minimally Invasive Plate Fixation and Antegrade Intramedullary Nailing of Recon-Type in Low-Energy Injury Distal Femoral Shaft Fractures
- Hong Moon Sohn, Gwangchul Lee, Ba Rom Kim, Jung Soo Oh
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(2):87-94. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.2.87
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study compared the outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis and antegrade intramedullary nailing for low-energy fracture of the distal femoral shaft.
Materials and Methods
A study was conducted on 30 patients who underwent surgery for low-energy fractures of the distal femoral shaft between January 2016 and April 2022. The study compared 15patients who underwent minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (Group P) with 15 patients who underwent recon-type antegrade intramedullary nailing (Group N). We evaluated intraoperative blood loss, operative time, C-arm exposure time, bone density, final union status, anatomical reduction, and clinical evaluation. The complications were also examined, and statistical analysis was conducted to compare the two groups.
Results
The blood loss, surgery time, and C-arm time were similar in the two groups. The radiographic assessments and clinical evaluations were also similar in the two groups. The clinical results showed no difference between the groups. Group N had one case of nonunion and one case of delayed union, while Group P had one case of nonunion and one case of peri-prosthetic fracture.
Conclusion
Antegrade intramedullary nailing of the recon-type demonstrated comparable results to minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. Hence, antegrade intramedullary nailing of the recon-type, which enhances stability by fixing the entire femur and providing additional fixation in the distal portion, is deemed appropriate for treating distal femoral shaft fractures.
- 750 View
- 17 Download

- Effect of Additional Medial Locking Plate Fixation and Autogenous Bone Graft for Distal Femur Nonunion after Lateral Locking Plate Fixation
- Ho Min Lee, Jong Pil Kim, In Hwa Baek, Han Sol Moon, Sun Kyo Nam
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(1):30-38. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.1.30
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the outcomes of additional medial locking plate fixation and autogenous bone grafting in the treatment of nonunions that occurred after initial fixation for distal femoral fractures using lateral locking plates.
Materials and Methods
The study involved eleven patients who initially underwent minimally invasive lateral locking plate fixation for distal femoral fractures between January 2008 and December 2020. The initial procedure was followed by additional medial locking plate fixation and autogenous bone grafting for clinically and radiographically confirmed nonunions, while leaving the stable lateral locking plate in situ. A clinical evaluation of the bone union time, knee joint range of motion, visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores, presence of postoperative complications, and functional evaluations using the lower extremity functional scale (LEFS) were performed.
Results
In all cases, bone union was achieved in an average of 6.1 months after the secondary surgery. The range of knee joint motion, weight-bearing ability, and VAS and LEFS scores improved at the final follow-up compared to the preoperative conditions. All patients could walk without walking assistive devices and did not experience pain at the fracture site. On the other hand, three patients complained of pain in the lateral knee joint caused by irritation by the lateral locking plate; hence, lateral hardware removal was performed. One patient complained of mild paresthesia at the anteromedial incision site. Severe complications, such as deep infection or metal failure, were not observed.
Conclusion
For nonunion with stable lateral locking plates after minimally invasive lateral locking plate fixation of distal femur fractures, additional medial locking plate fixation and autogenous bone grafting, while leaving the lateral locking plate intact, can achieve successful bone union.
- 361 View
- 5 Download

- Triplane Fracture Management: Prediction of Periosteal Entrapment and the Need for Open Reduction by Measurements of the Physeal Fracture Gap in Preoperative Computed Tomography Scans
- Dae Hee Lee, Joo Han Kwon, Jae Uk Jung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(1):1-7. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study measured the physeal fracture gap on preoperative ankle computed tomography (CT) to predict the periosteal entrapment that requires an open reduction in distal tibia triplane fractures.
Materials and Methods
This study retrospectively reviewed patients who had undergone internal fixation for a triplane fracture from April 2004 to September 2022. The demographic data, including age,body mass index, and past medical history, were analyzed. In the radiographic evaluations, ankle CT and ankle simple radiographs, including anteroposterior (AP), lateral, and mortise views, were taken preoperatively. Postoperatively, simple ankle radiographs were obtained periodically, including AP, mortise, and lateral views. The physeal fracture gap was measured on ankle CT, and the larger gap between the coronal and sagittal view of CT was selected. The residual physeal gap <2 mm was considered an adequate reduction.
Results
Of 17 cases, three demonstrated successful reduction using closed reduction techniques. Periosteal entrapment was observed in 14 cases open reduction cases. In all three closed reduction cases, the physeal gap estimated on preoperative ankle CT was under 3 mm with a mean gap of 2.4±0.2 mm (range, 2.1-2.5 mm). In the remaining 14 open reduction cases, the measured physeal gap was over 3 mm, averaging 5.0±2.7 mm (range, 3.1-12.2 mm). There was a significant difference in the preoperative physeal gap between the two groups (p<0.01). Overall, good reduction was achieved in all 17 cases; the postoperative physeal gap was under 2 mm with a mean of 1.0±0.5 mm (closed reduction group, 0.5±0.2 mm; open reduction group, 1.1±0.5 mm).
Conclusion
Open reduction is strongly recommended for triplane fractures with a physeal fracture gap of 3 mm or more in preoperative ankle CT, suggesting the possibility of an entrapped periosteum in the fracture gap. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diagnostic values of radiographic indices for predicting periosteal entrapment in pediatric proximal phalangeal base physeal fractures of toes
Ho Young Park, Jeong-Seok Moon, Kiwook Kim
Skeletal Radiology.2026; 55(1): 97. CrossRef
- Diagnostic values of radiographic indices for predicting periosteal entrapment in pediatric proximal phalangeal base physeal fractures of toes
- 1,325 View
- 20 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Bone Union Time of Simple Distal Femur Fractures in the Elderly according to Fracture Gap after Treated with Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis
- Young Ho Cho, Sangwoo Kim, Jaewook Koo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(4):133-138. Published online October 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.4.133
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the difference in bone union time according to the fracture gap after minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) for simple distal femoral fractures in elderly patients.
Materials and Methods
From January 2010 to December 2019, patients aged 60 years or older who underwent surgical treatment for distal femoral fractures due to a low-energy injury were investigated retrospectively. Forty patients were enrolled in the study. The patients were divided into two groups according to the fracture gap after reduction: no more than 2 mm (Group A) and more than 2 mm (Group B) in the anteroposterior and lateral plane. The demographic, operation time, presence or absence of cerclage wiring, plate screw density, plate span ratio, plate length, bone union period, non-union, and complications were evaluated.
Results
No statistical differences in operation time, cerclage wiring, plate screw density, plate span ratio, and plate length were observed between the two groups, and the bone union was achieved in all patients without complication. The bone union period was 17.24±1.48 weeks in Group A and 24.53± 5.20 weeks in Group B, which was statistically significant (p<0.001).
Conclusion
The bone union time in treating geriatric simple distal femur fractures using the MIPO tech-nique was significantly shorter in the 2 mm or less fracture gap than in the greater than 2 mm group.
- 713 View
- 5 Download

Technical Note
- Usefulness of Reduction and Internal Fixation Using a 2.4 mm Hand Plating System in Type AO 33-A3 Distal Femur Fracture - Technical Note -
- Bong-Ju Lee, Ja-Yeong Yoon, Seungha Woo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(1):25-28. Published online January 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.1.25
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Open reduction in an AO 33-A3 class distal femur transverse and comminuted fracture is often difficult due to frequent reduction loss during surgery, leading to longer operative time and increased blood loss intra-operation. In this study, the authors report a case in which the use of an offset grid plate (OsteoMed, USA) using 2.4 mm HPS (hand plating system) eased the process of fracture reduction and achieved a stable internal fixation, ultimately leading to successful osteosynthesis. The authors experienced no need for temporary fixation devices such as K-wires or screws, which are otherwise required to stabilize the reduction. The fracture reduction was stable throughout the primary fixation of the fracture using a locking plate and screws. The authors report that the advantage of the HPS plate is fitting into the cortical contour and providing stable maintenance of fracture reduction intra-operation, which would be beneficial in certain distal femoral fracture patterns.
- 508 View
- 9 Download

Original Articles
- Distal Femur Fractures Treated with Distal Femoral Locking Plate Fixation: A Retrospective Study of One Year Mortality and Risk Factors
- Kwang-Hwan Jung, Yoon-Seok Youm, Seung-Hyun Jung, Jae-Min Oh, Ki Bong Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(1):10-16. Published online January 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.1.10
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the one-year mortality after locking plate fixation for distal femur fractures and the risk factors related to death.
Materials and Methods
From July 2011 to June 2020, 128 patients who underwent locking plate fixation for distal femur fractures were analyzed retrospectively. Epidemiologic information of the patients, characteristics related to fracture and surgery, and death were investigated. The risk factors related to death were investigated using Cox analysis, and a subgroup analysis was also performed based on the age of 65 years.
Results
The one-year mortality rate after locking plate fixation for distal femur fractures was 3.9%, and the mortality rates in patients younger than 65 years and older than 65 years were 0% and 6.7%, respectively. There were no significant risk factors related to death in the total population. On the other hand, in patients aged 65 years or older, however, high-energy fracture and high comorbidity index increased the risk of death after surgery by 6.9-fold and 1.9-fold, respectively.
Conclusion
The one-year mortality rate for the total patients was 3.9%, but the mortality rate for patients over 65 years of age increased to 6.7%. High-energy fractures and high comorbidity index were risk factors related to death after surgery for distal femur fractures in patients aged 65 years or older.
- 485 View
- 3 Download

- Is It Essential to Apply Tension Band Wire Fixation in Non-Comminuted Displaced Transverse Fractures of the Olecranon (Mayo Type 2A)?
- In-Tae Hong, Cheungsoo Ha, Seongmin Jo, Wooyeol Ahn, Soo-Hong Han
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(3):97-102. Published online July 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.3.97
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Various problems have been reported with tension-band wire (TBW) fixation. With the devel-opment of anatomical plates and the improvement of fixation forces, plate fixation is currently being performed for non-comminuted, displaced, transverse olecranon fractures (Mayo Type 2A). This study compared the usefulness of the above two procedures applied in non-comminuted, displaced, transverse olecranon fractures.
Materials and Methods
Fifty-three patients with Mayo Type 2A were studied retrospectively. Twenty-nine patients underwent TBW fixation, while the other 24 underwent plate fixation. The averageoutpatient follow-up period was 10 months for both groups. Both groups were analyzed radiologically and clinically. The radiological assessment included the time to bone union, joint stability, and presence of traumatic osteoarthritis at the final follow-up. The clinical assessment included the operation time,range of motion of the elbow joint, Mayo Elbow Performance Score (MEPS), Disability of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand (DASH) score, and the presence of postoperative complications.
Results
Both groups showed stable elbow joints, proper union of fractures, and no traumatic osteo-arthritis at the final follow-up. The range of motion for the TBW fixation group was 142° (range, 3°-145°), while that of the plate fixation group was 135° (range, 4°-139°) at the final follow-up (p=0.219). The MEPS was 98.2 and 97.7 for the TBW fixation and plate fixation groups, respectively (p=0.675). The DASH score was 10.7 and 13.9 for the TBW fixation and plate fixation groups, respectively. Both groups showed excellent results, and the differences were not statistically significant (p=0.289).
Conclusion
TBW fixation and plate fixation were compared in non-comminuted, displaced, transverse olecranon fractures, and good results were obtained without significant differences between the two groups. Hence, surgeons should choose a technique they are more confident with and can be applied more efficiently.
- 370 View
- 2 Download

- Posterior Anti-Glide Plating for Supination External Rotation Type Lateral Malleolar Fractures: Clinical Comparison of Locking versus Non-Locking One-Third Semi-Tubular Plate Fixation
- Jun Young Lee, Yong Jin Cho, Dong Hyuk Cha, Hyun Bai Choi, Jung Ho Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(2):57-62. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.2.57
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate and compare the clinical and radiological outcomes between locking plates and non-locking plates using posterior anti-glide plating for supination external rotation type lateral malleolar fractures.
Materials and Methods
A total of 50 patients who underwent internal fixation of posterior anti-glide plating due to lateral malleolar fractures, classified as supination-external rotation (SER) as per the Lauge-Hansen classification system, at our hospital from January 2017 to November 2018 were retro-spectively evaluated. Patients were divided into two groups: 1/3 semi-tubular locking plate (24 patients) and 1/3 semi-tubular non-locking plate (26 patients). A radiographic assessment was performed after surgery to evaluate the time of bone union. The American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) ankle-hindfoot functional score was measured after the surgery to evaluate the clinical outcomes.
Results
The two groups showed similar distributions in sex, age, height, body mass index, fracture pattern, and mean follow-up period. Complete bone union was obtained in all cases and the mean bone union time was 13.00±3.38 weeks in Group 1 and 12.92±3.26 weeks in Group 2 (p=0.87). The mean AOFAS score at 24 weeks was 95.66±2.86 in Group 1 and 95.84±2.79 in Group 2 (p=0.82). The mean AOFAS score at 48 weeks was 97.25±3.54 in Group 1 and 96.57±3.07 in Group 2 (p=0.47). Two cases of complications were observed in the non-locking plate group.
Conclusion
For the treatment of Lauge-Hansen SER type lateral malleolar fracture, internal fixation us-ing locking 1/3 semi-tubular plate and non-locking 1/3 semi-tubular plate are both favorable fixation methods.
- 332 View
- 2 Download

- Comparing Outcomes of Retrograde Intramedullary Nail and Locking Plate Fixation in Distal Femoral Fractures
- Byung-Ho Yoon, Bo Kwon Hwang, Hyoung-Keun Oh, Suk Kyu Choo, Jong Min Sohn, Yerl-Bo Sung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2021;34(4):131-136. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2021.34.4.131
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
We compared the radiological and clinical results of fixation for distal femoral fracture (DFF) using a locking compression plate (LCP) or a retrograde intramedullary nail (RIN).
Materials and Methods
From October 2003 to February 2020, 52 cases of DFF with a minimum 1-year follow-up (with a mean follow-up of 19.1 months) were included: 31 were treated with LCP and 21 with RIN. The operation time, blood loss, and hospitalization period were compared, and the incidence of postoperative nonunion, malunion, delayed union and metal failure and other post-operative complications were evaluated and compared.
Results
There was no significant difference in the operating time between the two groups, but the mean blood loss was significantly higher in the LCP group (LCP 683.5 ml vs RIN; 134.9 ml; p=0.015). In 49 out of 52 cases, bone union was achieved without additional surgery in an average of 6.8 months, and a complete union was achieved after additional surgery in three cases of nonunion (LCP 2 cases vs RIN 1 case; p=0.065). One case of malunion and superficial infection was confirmed in each group.
Conclusion
Internal fixation using LCP and RIN give good outcomes with a low complication rate and can therefore be considered useful surgical treatments for DFF.
- 447 View
- 5 Download

- Primary Open Reduction and Plate Fixation in Open Comminuted Intra-Articular Distal Radius Fracture
- Jun-Ku Lee, Soonchul Lee, Weon Min Cho, Minkyu Kil, Soo-Hong Han
- J Korean Fract Soc 2021;34(1):16-22. Published online January 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2021.34.1.16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
There are no standard surgical treatments for open distal radius fractures (DRFs), and the fracture fixator is chosen by the surgeon’s own experience. This study compared the outcomes of open reduction and volar locking plating (OR VLP) between closed and open AO-OTA type C3 DRFs. Materials and Methods: Patient data were retrospectively collected between January 2010 and December 2018. Only patients aged >18 years with AO-OTA C3 DRFs were included. After further exclusion, the patients with DRFs were divided into two groups: 13 patients with open DRFs in Group 1 and 203 patients with closed DRFs in Group 2. Data on the patient characteristics and treatment-related factors were further investigated. For the radiological evaluation, the radial height, volar height, and volar titling were measured based on the final plain radiography, and the union time was measured. The wrist range of motion (ROM), pain visual analogue scale score, and modified Mayo wrist score for function were measured at the final outpatient follow-up. Finally, the complications associated with OR VLP fixa-tion were investigated. Results: In the demographic comparison, the patients with open fractures were older (mean age, 62years) than those with closed fractures (mean age, 57 years), without a statistically significant differ-ence. The patients with open DRFs had longer antibiotic therapy and hospital stay durations. Although they presented a higher radial inclination, with statistical significance, the clinical implication was low with a mean difference of 3°. No significant differences were observed for the remaining radiological parameters, wrist ROM, and functional scores. An open DRF did not increase the complication rates,including deep infection. Conclusion: Depending on the expertise of the operating surgeon, the primary OR VLP fixation in open intra-articular comminuted DRF did not increase the incidence of deep infections and yielded similar outcomes to a closed intra-articular comminuted DRF.
- 1,066 View
- 11 Download

- Clinical Outcome after Treatment of Tibia Segmental Fracture with Intramedullary Nailing and Minimal Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis
- Jun Young Lee, Hyung Seok Park, Dong Hyuk Cha
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(3):142-147. Published online July 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.3.142
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the clinical outcomes after the treatment of a tibia segmental fracture with intramedullary nailing (IM nailing) and minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO).
Materials and Methods
From July 2012 to December 2017, 14 out of 17 cases from a treatment cohort of 32 cases of AO type 42 C2 tibia segmental fractures with IM nailing and MIPO were studied retrospectively. Periodic radiographs were used to evaluate the presence of union, union time, and radiographic evaluation of bony union (varus-valgus deformity, anteroposterior angular deformity, shortening). To evaluate the postoperative clinical function, modified Rasmussen’s system was used for proximal fractures, and the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society functional score was used for distal fractures.
Results
Bony union was achieved in all 14 cases, and the average union time was 26 weeks. In one case of soil contamination, there were no other complications other than simple debridement after a soft tissue infection. The mean varus was two degrees; the mean anteroposterior angular deformity was three degrees of anterior oblique; the mean length shortening was 5 mm (2-9 mm). The mean functional score of the knee joint with the Modified Rasmussen’s system measured for the postoperative clinical function was relatively good (excellent 9, good 4, fair 1, and poor 0). The results of the Molander and Olerud Functional scores of the ankle joints were also good (excellent 8, good 3, fair 2, poor 0).
Conclusion
The treatment of tibia segmental fractures with IM nailing and MIPO can effectively reduce the gap of fracture sites. Hence, it is possible to increase the bony union probability and obtain relatively satisfactory alignment. Overall, the treatment of tibia segmental fractures with IM nailing and minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis appears to be a useful treatment, considering the preservation of the soft tissue and the alignment of the tibia.
- 609 View
- 4 Download

- Results of Single Small Incision Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis in the Treatment of the Distal Radius Fractures
- Young Sung Kim, Jong Pil Kim, Phil Hyun Chung, Ho Min Lee, Bo Sung Go
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(2):72-80. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.2.72
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study compared minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) using a single small skin incision and conventional open volar locking plate fixation (OP) for distal radius fracture to identify outcome difference.
Materials and Methods
Forty-three patients who underwent MIPO using a single small skin incision or OP for distal radius fractures were evaluated retrospectively. Of the patients, 21 were treated with MIPO using a single small skin incision and 22 with the OP method through the conventional volar approach. The postoperative radiographic results and clinical outcomes at the final follow-up in each group were compared.
Results
All patients achieved bone union in the MIPO and OP groups. No significant differences in the bone union time, alignment, range of motion, QuickDASH, or pain score were observed. On the other hand, the size of the incision was significant: 23 mm in the MIPO group and 55 mm in the OP group (p<0.001).
Conclusion
MIPO technique using a single small incision showed similar satisfactory radiographic and functional outcomes compared to conventional OP for distal radius fractures. The MIPO technique using a single small incision offered advantages, including cosmetic benefits and minimal soft tissue damage, is recommended, particularly in young women and high functional demand patients.
- 674 View
- 9 Download

- Treatment of Isolated Lateral Malleolar Fractures Using Locking Compression Plate Fixation and Tension Band Wiring Fixation
- Woojin Shin, Seondo Kim, Jiyeon Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(1):16-21. Published online January 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.1.16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to compare the clinical and radiological outcomes of locking compression plate (LCP)-screw fixation and tension band wiring (TBW) fixation in isolated lateral malleolar fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From May 2016 to August 2018, 52 patients with isolated lateral malleolar fracture were retrospectively reviewed. They were divided into 30 cases of the LCP fixation group (Group I) and 22 cases of the TBW fixation group (Group II). The clinical and radiological results of those groups were compared. Pearson chi-square tests and independent t-tests were used in the statistical analysis.
RESULTS
The mean length of the surgical incision was 8.3 cm in Group I and 4.9 cm in Group II. Radiological union was obtained at a mean of 8.4 weeks in both groups. The mean American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society score was 90 (range, 85–97) and 92 (range, 85–100) in Groups I and II, respectively, at the last follow up.
CONCLUSION
Both the LCP-screw and TBW techniques revealed excellent results in isolated lateral malleolar fractures. The tension band technique may be a fine alternative method of fixation in the treatment of isolated lateral malleolar fracture.
- 955 View
- 8 Download

- Use of Miniplate for Severe Comminuted Metadiaphyseal Fractures of the Distal Radius
- Jong Ryoon Baek, Yong Cheol Yoon, Seung Hyun Baek
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(4):204-210. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.4.204
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study investigated the clinical and radiological outcomes of patients undergoing provisional fixation in conjunction with locking plate fixation. Miniplates were used as the reduction plates for the surgical treatment of severe comminuted metadiaphyseal fractures with an intra-articular fracture of the distal radius.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The radial length, radial inclination, volar tilt, and radial intra-articular step-off were measured preoperatively, postoperatively, and at one year after surgery in 12 patients (eight males, four females, mean age 55.4 years old). The patients underwent volar locking plate fixation with miniplate as a reduction plate for severe comminuted metadiaphyseal fractures with an intra-articular fracture of the distal radius. Clinical evaluations were conducted using the modified Mayo wrist score (MMWS).
RESULTS
Bone union was achieved in all cases. The mean MMWS was 81.8 points, including two excellent, three good, and seven fair cases. Radiological improvements were observed in the average radial length (preoperative, 6.4 mm; postoperative, 11.8 mm), average radial inclination (10.2° to 22.4°), average volar tilt (−4.5° to 10.6°), and average radial intra-articular step-off (4.8–0.8 mm) (all, p<0.05). Radiographic measurements obtained immediately after surgery and at the final follow-up revealed insignificant decreases in radial length (0.6 mm), radial inclination (0.4°), and volar tilt (0.9°) (all, p>0.05).
CONCLUSION
Miniplate fixation can be an effective treatment option as a reduction plate for the treatment of distal radial fractures, which is challenging to reduce and maintain due to severely comminuted metadiaphysis fractures with the intra-articular fracture.
- 690 View
- 3 Download

- Outcomes following Treatment of Geriatric Distal Femur Fractures with Analyzing Risk Factors for the Nonunion
- Soo young Jeong, Jae Ho Lee, Ki Chul Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(4):188-195. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.4.188
- Correction in: J Musculoskelet Trauma 2020;33(1):62
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
Many international journals have published studies on the results of distal femoral fractures in elderly people, but only a few studies have been conducted on the Korean population. The aim of this study was to determine the factors that are associated with the outcomes and prognosis of fixation of distal femur fractures using the minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) technique in elderly patients (age≥60) and to determine the risk factors related witht he occurrence of nonunion.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study is a retrospective study. From January 2008 to June 2018, distal femur fracture (AO/OTA 33) patients who underwent surgical treatment (MIPO) were analyzed. A total of 52 patients were included in the study after removing 121 patients that met with the exclusion criteria. Medical records, including surgical records, were reviewed to evaluate the patients' underlying disease, bone mineral density, the number of days delayed from surgery, complications and mortality. In addition, follow-up radiographs were used to determine bone union, delayed union and nonunion.
RESULTS
The average time to achieve bone union was 19.95 weeks, the rate of nonunion was 20.0% (10/50) and the overall mortality was 3.8% (2/52). There were no significant differences in the clinical and radiological results of those patients with or without periprosthetic fracture. On the univariate analysis, which compared the union group vs. the nonunion group, no factors were identified as significant risk factors for nonunion. On the multiple logistic regression analysis, medical history of cancer was identified as a significant risk factor for nonunion (p=0.045).
CONCLUSION
The rate of nonunion is high in the Korean population of elderly people suffering from distal femur fracture, but the mortality rate appears to be low. A medical history of cancer is a significant risk factor for nonunion. Further prospective studies are required to determine other associated factors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Clinical Outcomes for Femoral Neck System and Cannulated Compression Screws in the Treatment of Femoral Neck Fracture
Jae Kwang Hwang, KiWon Lee, Dong-Kyo Seo, Joo-Yul Bae, Myeong-Geun Song, Hansuk Choi
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2023; 36(3): 77. CrossRef
- Comparison of Clinical Outcomes for Femoral Neck System and Cannulated Compression Screws in the Treatment of Femoral Neck Fracture
- 1,048 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Report
- Ulnar Insufficiency Fractures in Patients on Prolonged Bisphosphonate Therapy: A Case Report
- Kyu Min Kong, Yong Uk Kwon, Young Kyung Min, Doo Yeol Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(3):143-147. Published online July 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.3.143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Atypical fractures associated with prolonged bisphosphonate (BP) therapy rarely occur outside the femur, and the diagnostic criteria, appropriate treatment principles, and fixation methods for atypical ulnar fractures have not been established. The authors experienced the use of internal fixation with a metal plate and a new internal fixation method with an intramedullary nail in the treatment of an atypical ulnar fracture in a patient who had been on BP therapy for 10 to 20 years. This paper reports findings along with a review of the relevant literature.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Treatment of Atypical Ulnar Fracture Associated with Bisphosphonate Therapy: A Case Report
Dong-Soo Kim, Ji-Kang Park, Eui-Sung Choi, Ho-Seung Jeong, Seok-Hyun Hong, Byung-Hyun Ahn
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2020; 33(2): 101. CrossRef
- Treatment of Atypical Ulnar Fracture Associated with Bisphosphonate Therapy: A Case Report
- 795 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- Surgical Results of Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Fixation in the Treatment of Clavicle Shaft Fracture
- Seong Ho Yoo, Suk Woong Kang, Jae Seung Seo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(1):21-26. Published online January 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.1.21
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study analyzed the results of the midclavicle fracture treatment using the minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) technique in a retrospective manner.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between March 2013 and March 2017, this study analyzed 40 patients who received MIPO surgery. Excluding 1 patient who underwent surgery on another body part injury, and 4 patients who were lost to follow-up over 1 year, 40 patients were analyzed for their operation time, bone union, functional American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons score, scar lengths, pain relief (visual analogue scale), and complications.
RESULTS
All patients over a 1 year of follow-up achieved bone union, and American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons score 97.6 (94–100) on their shoulder functional scores. Their average operation time was 42.7 minutes, and the average scar length was 6.1 cm. Eighteen patients successfully received metal removal using the previous scar without additional incision. The clavicle length was similar in the normal and operated group.
CONCLUSION
Despite its small sample size, clavicle fixation using the MIPO technique can be considered an effective treatment because of its limited number of complications, such as nonunion and rotational angulations. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Additional fixation using a metal plate with bioresorbable screws and wires for robinson type 2B clavicle fracture
Woo Jin shin, Young Woo Chung, Seon Do Kim, Ki-Yong An
Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow.2020; 23(4): 205. CrossRef
- Additional fixation using a metal plate with bioresorbable screws and wires for robinson type 2B clavicle fracture
- 956 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Prediction of Concomitant Lateral Meniscus Injury with a Tibia Plateau Fracture Based on Computed Tomography Assessment
- Wonchul Choi, Yunseong Choi, Go Tak Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(4):132-138. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.4.132
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study examined whether any fracture pattern shown in computed tomography (CT) scan is associated with the presence of lateral meniscus (LM) injury in a tibia plateau fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fifty-three tibia plateau fractures with both preoperative CT and magnetic resonance imagings (MRI) available were reviewed. The patient demographics, including age, sex, body mass index, and energy level of injury were recorded. The fracture type according to the Schatzker classification, patterns including the lateral plateau depression (LPD), lateral plateau widening (LPW), fracture fragment location, and the number of columns involved were assessed from the CT scans. The presence of a LM injury was determined from the MRI. The differences in the factors between the patients with (Group 1) and without (Group 2) LM injuries were compared and the correlation between the factors and the presence of LM injury was analyzed.
RESULTS
The LM was injured in 23 cases (Group 1, 43.4%) and intact in 30 cases (Group 2, 56.6%). The LPD in Group 1 (average, 8.2 mm; range, 3.0–20.0 mm) and Group 2 (average, 3.8 mm; range, 1.4–12.1 mm) was significantly different (p < 0.001). The difference in LPW of Group 1 (average, 6.9 mm; range, 1.2–15.3 mm) and Group 2 (average, 4.8 mm; range, 1.4–9.4 mm) was not significant (p=0.097). The other fracture patterns or demographics were similar between in the two groups. Regression analysis revealed that an increased LPD (p=0.003, odds ratio [OR]=2.12) and LPW (p=0.048, OR=1.23) were significantly related to the presence of a LM tear.
CONCLUSION
LPD and LPW measured from the CT scans were associated with an increased risk of concomitant LM injury in tibia plateau fractures. If such fracture patterns exist, concomitant LM injury should be considered and an MRI may be beneficial for an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The value of magnetic resonance imaging in the preoperative diagnosis of tibial plateau fractures: a systematic literature review
Gregoire Thürig, Alexander Korthaus, Karl-Heinz Frosch, Matthias Krause
European Journal of Trauma and Emergency Surgery.2023; 49(2): 661. CrossRef
- The value of magnetic resonance imaging in the preoperative diagnosis of tibial plateau fractures: a systematic literature review
- 506 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Risk Factors for Knee Stiffness in Distal Femoral Fractures
- Dong Wook Son, Hyoung Soo Kim, Woo Young Choi
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(4):123-131. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.4.123
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The aims of this study were to evaluate risk factors for knee stiffness after the fixation of distal femoral fractures, and to analyze the clinical and radiologic outcomes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This is a retrospective case control study of 104 consecutive patients who have a distal femoral fracture and were treated with a submuscular locking plate. The case group comprised of patients with 12-month postoperative range of motion (ROM) ≤90° or a history of manipulation under anesthesia. The case group was compared with the control group of patients with a 12-month postoperative ROM >90°. The possible risk factors were evaluated by univariate and logistic regression analysis. The postoperative ROM and Knee Society clinical rating system was evaluated for the clinical assessment and the distal femoral angle on a whole-extremity scanogram was measured for radiologic assessments.
RESULTS
Fifty-four patients were included in the study (14 in the case group, 40 in the control group). Univariate analysis showed that comminuted fracture, intra-articular fracture, open fracture, temporary external fixation, severe osteoarthritis, and prolonged immobilization placed patients at an increased risk for knee stiffness. On the other hand, multivariate logistic regression showed that an extensor mechanism injury was the only significant predictor (p=0.001; odds ratio, 42.0; 95% confidence interval, 5.0–350.7). The ROM and Knee Society score were significantly lower in the case group; however, the coronal alignment was similar in the case and control group.
CONCLUSION
Various factors that delay postoperative knee motion place patients at increased risk of knee stiffness. Understanding these risk factors may help surgeons prevent postoperative knee stiffness after distal femoral fractures. In particular, extensor mechanism injury, such as patella fracture or open quadriceps injury, was found to be an independent predictable factor associated with knee stiffness. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comprehensive Approach to Stiffness in Total Knee Arthroplasty
Brian P. Chalmers, Linda I. Suleiman, Peter K. Sculco, Matthew P. Abdel
The Journal of Arthroplasty.2025; 40(9): S59. CrossRef - Staged Management for Distal Femur Fractures: Impacts on Reoperation, Stiffness, and Overall Outcomes
Matthew T. Yeager, Robert W. Rutz, Alex Roszman, Gerald McGwin, James E. Darnley, Joseph P. Johnson, Clay A. Spitler
Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma.2024; 38(11): 577. CrossRef - Outcome of the Masquelet Technique for Complex Bilateral Distal Femoral Bone Defects
Ziad A Aljaafri, Abdullah Alzahrani, Ali Alshehri, Ahmed AlHussain, Faisal Alzahrani, Khalid Alsheikh
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of non-operative treatment of patients with knee arthrofibrosis using high-intensity home mechanical therapy: a retrospective review of 11,000+ patients
Shaun K. Stinton, Samantha J. Beckley, Thomas P. Branch
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Distal Femoral Replacement and Extensor Mechanism Repair Reinforced With Synthetic Mesh for Distal Femur Fracture With Patellar Ligament Avulsion
Charles Powell, Kristopher Sanders, Neal Huang, Luis Felipe Colón, Colton Norton
Arthroplasty Today.2022; 16: 31. CrossRef - The fragility of statistical significance in distal femur fractures: systematic review of randomized controlled trials
Michael Megafu, Hassan Mian, Emmanuel Megafu, Sulabh Singhal, Alexander Lee, Richawna Cassie, Paul Tornetta, Robert Parisien
European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology.2022; 33(6): 2411. CrossRef - Association Between Femoral “Spike” Size After Intramedullary Nailing and Subsequent Knee Motion Surgery
Michael G. Schloss, Nathan N. O'Hara, Syed M. R. Zaidi, Zachary D. Hannan, Dimitrius Marinos, Jared Atchison, Alexandra Mulliken, Jason W. Nascone, Robert V. O'Toole
Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma.2021; 35(2): 100. CrossRef - Distal Femur Replacement Versus Surgical Fixation for the Treatment of Geriatric Distal Femur Fractures: A Systematic Review
Brett P. Salazar, Aaron R. Babian, Malcolm R. DeBaun, Michael F. Githens, Gustavo A. Chavez, L. Henry Goodnough, Michael J. Gardner, Julius A. Bishop
Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma.2021; 35(1): 2. CrossRef
- A Comprehensive Approach to Stiffness in Total Knee Arthroplasty
- 645 View
- 10 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Comparative Analysis of Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis and Intramedullary Nailing in the Treatment of the Distal Tibia Fractures
- Ho Min Lee, Young Sung Kim, Jong Pil Kim, Phil Hyun Chung, Suk Kang, Kaung Suk Jo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(3):94-101. Published online July 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.3.94
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study compared the radiological and clinical results of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) and intramedullary nailing (IMN) of distal tibial fractures, which were classified as the simple intra-articular group and extra-articular group.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fifty patients with distal tibial fractures, who could be followed-up more than 12 months, were evaluated. Group A consisted of 19 patients treated with MIPO and group B consisted of 31 patients treated with IMN. The results of each group were analyzed by radiological and clinical assessments.
RESULTS
The mean operation times in groups A and B were 72.4 minutes and 65.7 minutes, respectively. The mean bone union times in groups A and B were 16.4 weeks and 15.7 weeks, respectively. The bone union rate in groups A and B were 100% and 93%, respectively. The ranges of ankle motion were similar in the two groups at the last follow-up. The mean American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society score was similar: 90.1 in group A and 90.5 in group B. The radiological and clinical results were similar in the intra and extra-articular groups. In groups A and B, two cases of posterior angulation and five cases of valgus deformity of more than 5° were encountered.
CONCLUSION
Both MIPO and IMN achieved satisfactory results in extra-articular AO type A and simple articular extension type C1 and C2 distal tibia fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intramedullary Nailing versus Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Distal Tibia Shaft Fractures: Retrospective Comparison of Functional and Cosmetic Outcomes
Kahyun Kim, In Hee Kim, Geon Jung Kim, SungJoon Lim, Ji Young Yoon, Jong Won Kim, Yong Min Kim
Journal of Korean Foot and Ankle Society.2023; 27(3): 93. CrossRef
- Intramedullary Nailing versus Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Distal Tibia Shaft Fractures: Retrospective Comparison of Functional and Cosmetic Outcomes
- 489 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A Comparison of the Results between Internal Fixation and External Fixation in AO C Type Distal Radius Fractures
- Yoon min Lee, Hwa Sung Lee, Seok Whan Song, Jae Hoon Choi, Jong Tae Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(3):87-93. Published online July 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.3.87
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the radiological and clinical results of plate fixation and external fixation with additional devices for treating distal radius fracture in AO type C subtypes, and propose a treatment method according to the subtypes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Two hundred and one AO type C distal radius fracture patients were retrospectively reviewed. Eighty-five patients in group 1 were treated with volar or dorsal plate, and 116 patients in group 2, were treated with external fixation with additional fixation devices. Clinical (range of mtion, Green and O'Brien's score) and radiological outcomes were evaluated.
RESULTS
At the 12-month follow-up, group 1 showed flexion of 64.4°, extension of 68.3°, ulnar deviation of 30.6°, radial deviation of 20.8°, supination of 76.1°, and pronation of 79.4° in average; group 2 showed flexion of 60.5°, extension of 66.9°, ulnar deviation of 25.5°, radial deviation of 18.6°, supination of 73.5°, and pronation of 75.0° in average. The mean Green and O'Brien score was 92.2 in group 1 and 88.6 in group 2. The radial height of group 1 and group 2 was 11.6/11.4 mm; radial inclination was 23.2°/22.5°; volar tilt was 11.6°/8.7°; and the ulnar displacement was 1.27/0.93 mm.
CONCLUSION
Judicious surgical techniques during device application and tips for postoperative management during external fixation can produce similar clinical results compared with internal fixation patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intra-articular fracture distal end radius external fixation versus locking volar radius plate: A comparative study
S.P.S Gill, Manish Raj, Santosh Singh, Ajay Rajpoot, Ankit Mittal, Nitin Yadav
Journal of Orthopedics, Traumatology and Rehabilitation.2019; 11(1): 31. CrossRef
- Intra-articular fracture distal end radius external fixation versus locking volar radius plate: A comparative study
- 494 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- How Difficult Is It to Surgically Treat AO-C Type Distal Humerus Fractures for Inexperienced Orthopedic Surgeons?
- Seong Ho Yoo, Suk Woong Kang, Moo Ho Song, Young Jun Kim, Hyuck Bae
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(2):45-49. Published online April 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.2.45
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
Twenty early surgical management cases of distal humerus type-C fractures were analyzed.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study analyzed 20 early patients, who received surgical management of distal humerus type-C fractures, and could be followed-ups for more than one year between March of 2013 and May of 2015. The operative time, bone union time, and elbow range of motion were analyzed. The Mayo's functional score was used to evaluate their postoperative function. The primary and secondary complications of each patient immediately after each of their surgery were also reviewed.
RESULTS
All patient groups achieved bone union within an average period of 16.4 weeks. Based on the Mayo functional score, 6, 10, and 4 patients scored excellent, good, and fair, respectively. The average range of motion was a flexion contracture of 14.5° with a follow-up improvement averaging 120.7°. Six patients received nine revision operations due to major and minor complications. Two patients received revision fixation from an inadequate fixating power, and another patient received an ulnar nerve transposition. Other complications included olecranon osteotomy site displacement, superficial operational site infection, and pin loosening.
CONCLUSION
Distal humerus fractures of the AO-C type can cause a range of complications and has a very high rate of revision due to its difficult nature of surgical manageability. Therefore, it is imperative for a surgeon to expect various complications beforehand and a careful approach to their postoperative rehabilitation is essential.
- 272 View
- 0 Download

- The Result of Using an Additional Mini-Locking Plate for Tibial Pilon Fractures
- Suenghwan Jo, Jun Young Lee, Boseon Kim, Kang Hyeon Ryu
- J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(2):75-82. Published online April 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.2.75
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
We evaluated the usefulness of an additional, 2.7 mm mini-locking plate for tibial pilon fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We studied 21 patients (14 males and 7 females), who were treated with a 2.7 mm mini-locking plate via the anterolateral approach for tibial pilon fractures between September 2012 and April 2014. The mean age was 43.85 years, and the mean follow-up period was 16.6 months. The radiologic outcomes were graded by the Burwell and Charnley modified system and clinical outcomes were evaluated by the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) ankle-hind foot score and visual analogue scale (VAS) score.
RESULTS
The mean union period was 14.3 weeks. At the final follow-up, radiologic results showed 16 excellent results, 4 fair results, and 1 poor result. The average VAS was 3.4 points; the average AOFAS score was 81.8 points. During the follow-up period, there were three cases of posttraumatic osteoarthritis and one case of superficial skin infection.
CONCLUSION
Additional anterolateral, 2.7 mm mini-locking plate may be a good treatment method to manage tibial pilon fractures.
- 502 View
- 4 Download

- A Comparison of Results between AO Hook Plate and TightRope for Acute Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation
- Yong Gun Kim, Ho Jae Lee, Dong Won Kim, Jinmyoung Dan
- J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(1):16-23. Published online January 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.1.16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of our study is to compare the radiographic and clinical outcomes with respect to acromioclavicular (AC) joint dislocation depending on the surgical method: Hook plate (HP) versus TightRope (TR).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between May 2009 and May 2012, 51 patients with Rockwood type III-V lesions received clinical and radiographic follow-up. Patients were divided into two groups according to the surgical methods (HP: n=32; TR: n=19). Radiological follow-up included comparative coracoclavicular distance (CCD) measurements as a percentage of the uninjured shoulder. For clinical follow-up, a standardized functional shoulder assessment with the Constant score, University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA) score, and Korea shoulder score (KSS) were carried out.
RESULTS
Comparing the functional results, no differences were observed between the two groups (Constant score: HP, 78.5; TP, 81.4; UCLA score: HP, 29.2; TP, 29.9; KSS: HP, 79.2; TP, 80.7). Time to restoration of the range of motion (ROM) above shoulder level was longer in the HP group than in the TR group. However, the ROM at 1 year postoperation and final follow-up revealed similar results between the two groups. The AC joints were well reduced in both groups, the CCD increased to 44.7% in the HP group and to 76.5% in the TR group at the final follow-up; however, no one was significantly superior to the others. Furthermore, there were 8 cases (25.0%) and 5 cases (26.3%) of AC joint arthritis in the HP group and TR group, respectively. However, the observed AC joint arthritis has a poor correlation between clinical symptom and radiological results in both groups.
CONCLUSION
Both HP and TR fixation could be a recommendable treatment option in acute unstable AC joint dislocation. Both groups showed excellent radiologic and functional results at the final visit. Moreover, there was no significant difference in statistics, except for the time to restoration of ROM above shoulder level. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Suture-Button Fixation Outperforms Hook Plate in Functional Outcomes After Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation
Murat Aşçı, Mete Gedikbaş
Bozok Tıp Dergisi.2025; 15(4): 477. CrossRef - Arthroscopic Treatment of Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocations
Du-Han Kim, Chul-Hyun Cho
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2023; 58(5): 384. CrossRef - Combination of Clavicular Hook Plate with Coracoacromial Ligament Transposition in Treatment of Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation
Aikebaier Tuxun, Ajimu Keremu, Pazila Aila, Maimaitiaili Abulikemu, Zengru Xie, Palati Ababokeli
Orthopaedic Surgery.2022; 14(3): 613. CrossRef
- Suture-Button Fixation Outperforms Hook Plate in Functional Outcomes After Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation
- 2,218 View
- 6 Download
- 3 Crossref

Case Report
- Medial Plating of Distal Femoral Fracture with Locking Compression Plate-Proximal Lateral Tibia: Cases' Report
- Se Ang Jang, Young Soo Byun, In Ho Han, Dongju Shin
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(3):206-212. Published online July 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.3.206
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Generally, lateral plating is used for a comminuted fracture of the distal femur. However, in some cases, it has been shown that using a medial plate is necessary to achieve better outcome. Nevertheless, there are no available anatomical plates that fit either the distal medial femoral condyle or fracture fixation, except for the relatively short plate developed for distal femoral osteotomy. We found that locking compression plate-proximal lateral tibia (LCP-PLT) fits anatomically well for the contour of the ipsilateral medial femoral condyle. Moreover, LCP-PLT has less risk of breaking the thread holes since it rarely needs to be bent. We report a plastic bone model study and two cases of distal femoral fractures fixed with medial plating using LCP-PLT.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A novel anatomical locked medial femoral condyle plate: a biomechanical study
M. A. Ozer, S. Keser, D. Barıs, O. Yazoglu
European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology.2024; 34(5): 2767. CrossRef - Medial plating of distal femur: which pre-contoured angular stable plate fits best?
Shaam Achudan, Rex Premchand Antony Xavier, Sze Ern Tan
European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology.2024; 34(6): 3297. CrossRef - Medial augmentation of distal femur fractures using the contralateral distal femur locking plate: A technical note
Jaime Andrés Leal
OTA International.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The missing piece of the trauma armoury-medial femoral condyle plate
Piyush Upadhyay, Farhan Syed, Darryl N Ramoutar, Jayne Ward
Injury.2022; 53(3): 1237. CrossRef - Surgical Tips and Tricks for Distal Femur Plating
Christopher Lee, Dane Brodke, Ajay Gurbani
Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.2021; 29(18): 770. CrossRef - Medial minimally invasive helical plate osteosynthesis of the distal femur – a new technique
G.M. Hohenberger, A.M. Schwarz, P. Grechenig, B. Clement, Mario Staresinic, Bore Bakota
Injury.2021; 52: S27. CrossRef - Feature-Based Design of Personalized Anatomical Plates for the Treatment of Femoral Fractures
Xiaozhong Chen, Zhijian Mao, Xi Jiang
IEEE Access.2021; 9: 43824. CrossRef
- A novel anatomical locked medial femoral condyle plate: a biomechanical study
- 1,410 View
- 66 Download
- 7 Crossref

Original Article
- Surgical Treatment for Stable 2-Part Intertrochanteric Femur Fracture Using Dynamic Hip Screw with 2-Hole Side Plate in Elderly Patients
- Kyung Hoon Lee, Suk Ku Han, Seung Jae Chung, Jongho Noh, Kee Haeng Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(3):192-199. Published online July 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.3.192
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the postoperative outcomes of elderly patients with stable 2-part intertrochanteric femur fractures surgically treated using dynamic hip screw with 2-hole side plate.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From February 2008 to January 2014, 50 patients older than the age of 65 years, who had been followed-up for more than 6 months after the operation at The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital were enrolled. A clinical evaluation of the skin incision length, operating time, and ambulatory status, using Clawson's Ambulation Capacity Classification, was performed, and a radiologic evaluation of Fogagnolo reduction quality, tip-apex distance (TAD), Cleveland index, sliding extent of lag screws, time duration till bony union, and complications was also done.
RESULTS
The mean skin incision length was 9.8 cm (range, 8-13 cm), the mean operating time was 41.4 minutes (range, 30-60 minutes), and 32 patients recovered their ambulatory function. Forty-eight patients gained bony union, and the time lapsed till union was average 10.6 weeks (range, 8-16 weeks). The evaluation of postoperative radiologic images showed the following reduction statuses by the Fogagnolo classification: 46 cases of "Good", 3 cases of "Acceptable," and 1 case of "Poor." Moreover, the mean TAD was 18.9 mm (range, 9.0-24.9 mm). While 45 cases fit into the zone 5 of the Cleveland index, other 3 were within zone 8 and the other 2 were within zone 6. The mean sliding length of the lag screws were 4.9 mm (range, 0.1-19.4 mm). There were a case of nonunion and a case of periprosthetic infection with nonunion as complications.
CONCLUSION
Using dynamic hip screws with 2-hole side plate for stable 2-part intertrochanteric femur fractures in elderly patients showed satisfactory results with respect to the recovery of ambulatory functions and bony union.
- 441 View
- 0 Download

Case Reports
- Medial and Lateral Dual Plate Fixation for Osteoporotic Proximal Humerus Comminuted Fracture: 2 Case Reports
- Sam Guk Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(1):61-67. Published online January 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.1.61
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Some proximal humeral fractures in elderly patients are accompanied by medial metaphyseal comminution and quality of the bone is so poor that head preserving osteosynthesis seems to be amenable. In cases of medial metaphyseal comminution, lateral locking compression plate (LCP) fixation also has a tendency to become a matter of screw cut out or loss of fixation. The author reports on successful treatment of two osteoporotic proximal humeral fractures combined with medial meta-physeal comminution, with application of additional direct medial supporting plate fixation. Medial plate fixations were added when the fractures were still unstable after the conventional lateral LCP fixation and anterior circumflex humeral arteries had been ruptured before. The fixations were stable enough to start exercise immediately after surgery. The inclinations of the humeral neck were not changed until the last follow-up and clinical results were satisfactory without humeral head osteonecrosis which was a concern.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dual-Plate Fixation for Proximal Humerus Fractures With Unstable Medial Column in Patients With Osteoporosis
Hyun-Gyu Seok, Sam-Guk Park
Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma.2023; 37(10): e387. CrossRef - The plate fixation strategy of complex proximal humeral fractures
Qi Sun, Xiaoming Wu, Lei Wang, Ming Cai
International Orthopaedics.2020; 44(9): 1785. CrossRef - Biomechanical evaluation of a novel dualplate fixation method for proximal humeral fractures without medial support
Yu He, Yaoshen Zhang, Yan Wang, Dongsheng Zhou, Fu Wang
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
- Dual-Plate Fixation for Proximal Humerus Fractures With Unstable Medial Column in Patients With Osteoporosis
- 663 View
- 7 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Periprosthetic Fracture after Hook Plate Fixation in Neer Type II Distal Clavicle Fracture: A Report of 3 Cases
- Kyung Yong Kim, Joon Yub Kim, Won Bok Lee, Myong Gon Jung, Jeong Hyun Yoo, Joo Hak Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(1):55-60. Published online January 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.1.55
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hook plate fixation is a treatment method for the displaced distal clavicle fracture with favorable results regarding bone union and shoulder function, however possible complications include impingement syndromes, subacrormial erosions, acromial fractures, and periprosthetic fractures. In this report, we observed 3 cases of periprosthetic fracture after hook plate fixation. All cases of periprosthetic fractures were initiated at the medial end screw holes. The causes of these periprosthetic fractures appeared to be the off centered fixation of medial end screws near the anterior or posterior cortex which were specific during operations with hook plates with more than 6 holes and the increased stress on the medial end screw by over-reduced or inferiorly reduced position of the distal end of the clavicle by the hook plate.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of a novel hybrid hook locking plate fixation method with the conventional AO hook plate fixation method for Neer type V distal clavicle fractures
Joongbae Seo, Kang Heo, Seong-Jun Kim, Jun-Kyom Kim, Hee-Jung Ham, Jaesung Yoo
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research.2020; 106(1): 67. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of a locking plate with an all-suture anchor versus hook plate fixation of Neer IIb distal clavicle fractures
Joong-Bae Seo, Kwon-young Kwak, Jae-Sung Yoo
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Locking Compression Plate Superior Anterior Clavicle Plate with Suture Augmentation and Hook Plate for Treatment of Distal Clavicle Fractures
Jun-Cheol Choi, Woo-Suk Song, Woo-Sung Kim, Jeong-Muk Kim, Chan-Woong Byun
Archives of Hand and Microsurgery.2017; 22(4): 247. CrossRef
- Comparison of a novel hybrid hook locking plate fixation method with the conventional AO hook plate fixation method for Neer type V distal clavicle fractures
- 642 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref

Original Articles
- The Clinical and Radiological Results of Vancouver Type B1 and C Periprosthetic Fractures
- Bo Ram Na, Taek Rim Yoon, Kyung Soon Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(1):26-33. Published online January 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.1.26
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the clinical and radiologic results of plate fixation in the Vancouver B1 and C periprosthetic femoral fracture (PFF).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty patients who had sustained a Vancouver type B1 and C periprosthetic fracture after hip arthroplasty (years 2002-2012) were identified. The mean age was 66.0 years (range, 43-85 years) and the mean follow-up duration of the group was 38 months (range, 12-102 months). The dynamic compression plate (DCP) group included 12 patients and the locking compression plate (LCP) group included eight patients. Harris hip score (HHS) and walking ability, knee joint range of motion (ROM) were compared before injury and last follow-up. Fracture union rate and period were compared.
RESULTS
The mean HHS score was 90.7 (64-96). There was no statistical difference between the two groups. At the last follow-up, knee joint ROM was 103.3degrees (105degrees-140degrees) in the DCP group and 118.4degrees (110degrees-140degrees) in the LCP group, showing good results in the LCP group (p=0.043). No significant difference in the fracture union rate and union periods was observed between the two groups.
CONCLUSION
A better result for the postoperative knee flexion exercise capacity was observed in the LCP group. Use of LCP plate fixation is a good option in management of Vancouver classification B1 and C PFF.
- 579 View
- 3 Download

- Usefulness of Spring Plate for Acetabular Posterior Wall Fracture Including Small Fragment
- Jeong Hoon Kang, Sang Hong Lee, Hyeon Jun Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(1):19-25. Published online January 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.1.19
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
We applied internal fixation using a spring plate against an acetabular posterior wall fracture including small fragments and then evaluated the clinical and radiological results and want to understand the usefulness of the spring plate.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fifteen patients in whom fixation was difficult using leg screws or a metal plate because of a small bone fragment, in patients with posterior wall acetabular fractures who presented in our hospital since August of 2011 to March of 2014 were enrolled. The mean age was 42.6 years (range 24-54 years) with relatively young patients, and they were followed-up for at least one year. We analyzed the rate of reduction after surgery using the classification of Matta in radiographs, and the classification of Borrelli in 3-dimensional computed tomography (CT) and clinical results were evaluated using the clinical grading system.
RESULTS
There were five cases of anatomical reduction, 9 cases of imperfect reduction, and 1 case of unsatisfactory reduction according to the classification of Matta. Except for one case during the follow-up period, the union of bone was successful without failure of fixation and the clinical results were 6 cases of excellence, 8 cases of good, and 1 case of failure. Articular displacement was also evaluated in postoperative CT scan according to Borrelli's criteria. The mean of gap and step off was 2.04 mm, 1.3 mm.
CONCLUSION
Use of leg screw fixation and so on in posterior wall fractures including a small fragment of the acetabular rim is not easy. However the method using spring plate fixation enables relatively accurate reduction and fixation for a small fragment and the clinical outcome showed satisfactory results. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biomechanical Comparison of Fixation Methods for Posterior Wall Fractures of the Acetabulum: Conventional Reconstruction Plate vs. Spring Plate vs. Variable Angle Locking Compression Plate
HoeJeong Chung, Hoon-Sang Sohn, Jong-Keon Oh, Sangho Lee, DooSup Kim
Medicina.2024; 60(6): 882. CrossRef
- Biomechanical Comparison of Fixation Methods for Posterior Wall Fractures of the Acetabulum: Conventional Reconstruction Plate vs. Spring Plate vs. Variable Angle Locking Compression Plate
- 628 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Result of Open Reduction and Mini-Plate Fixation for Displaced Talar Neck Fracture
- Woong Chae Na, Sang Hong Lee, Jun Young Lee, Sang Jun Lee, Boseon Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2015;28(4):215-222. Published online October 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.4.215
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
We evaluated the complications, radiological and clinical results after operative treatment using a mini-plate for fixation of displaced talar neck fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
There were 20 cases of displaced talar neck fractures from May 2006 to December 2011; we performed a retrospective chart review of 15 patients treated by open reduction and internal fixation using a mini-plate who had more than 2 years of follow-up. According to Hawkin's classification, there were 7 cases of type II fractures and 8 cases of type III fractures. During postoperative 12-16 weeks we checked magnetic resonance imaging. The assessment of clinical results was based on the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) ankle-hindfoot scale.
RESULTS
Mean union period was 11.6 weeks (10-15 weeks). Nonunion and malunion did not occur in all cases. The mean AOFAS score was 88.2 points (80-97 points). There were 5 cases of avascular necrosis. Of these, there were 3 cases of body collapse and 4 cases of post-traumatic arthritis. In the statistical analysis, there was no correlation between the elements including gender, Hawkin's classification and union rates and clinical results.
CONCLUSION
Mini-plate fixation of a displaced talar neck fracture is thought to be a good technique, with a low rate of malunion and also showed satisfactory results in radiological and clinical assessment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Outcome of Type 3 Talar Neck Fractures by Means of Medial Malleolar Osteotomy and Large Distractor
Sung Hae Park, Jun Young Lee, Jung Woo Lee
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2019; 54(1): 45. CrossRef - The Measurement of Normal Talus in Korean Cadaver
Dong-Jun Ha, Heui-Chul Gwak, Jeon-Gyo Kim, Jung-Han Kim, Chang-Rak Lee, Young-Jun Kim, Jeong-Han Lee, Byung-Ho Ha, Ui-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Foot and Ankle Society.2016; 20(4): 163. CrossRef
- Outcome of Type 3 Talar Neck Fractures by Means of Medial Malleolar Osteotomy and Large Distractor
- 568 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Treatment of the Communited Distal Radius Fracture Using Volar Locking Plate Fixation with Allogenic Cancellous Bone Graft in the Elderly
- Je Kang Hong, Chang Hyun Shin
- J Korean Fract Soc 2015;28(1):8-16. Published online January 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.1.8
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
We studied results of the communited distal radius fracture treated with allogenic cancellous bone graft and volar locking plate in the elderly.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We studied 29 cases of communited distal radius fracture treated with allogenic cancellous bone graft and volar locking plate from April 2009 to April 2013. Fracture was classified according to AO/OTA classification. Postoperative clinical evaluation was performed with measurement of wrist range of motion (ROM) at last follow-up, modified Mayo wrist scoring system (MMWS), and visual analogue pain scale (VAS). Radiologic evaluation was performed with measurement of radial length on immediate postoperation and last follow-up, radial inclination, volar tilt and ulnar variance checked at the last follow-up using Sarmiento criteria.
RESULTS
Using the MMWS, 13 cases were classified as 'good', 10 'fair', and 5 'normal'. The average wrist ROM was 88.5% for flexion, 92.2% for extension, 90.5% for adduction, and 94.0% for abduction. The average VAS was 1.7. On the last follow-up, average radius length, radial inclination and volar tilt did not show statistically significant improvement (p>0.05) compared to immediate post operation measurements, and according to Sarmiento criteria, 5 cases were classified as 'good', 14 'fair', and 7 'normal'.
CONCLUSION
Treatment of severe communited distal radius fracture accompanied by bone defect with volar locking plate and allogenic cancellous bone graft is a satisfying and effective treatment method in the elderly.
- 796 View
- 3 Download

Case Report
- Infected Nonunion of Clavicle Shaft after Operation: A Case Report
- Ho Su Jang, Suk Hwan Jang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2015;28(1):77-81. Published online January 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.1.77
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The infected nonunion of clavicle with bone defect is an uncommon complication following clavicle shaft fracture. There were a few reports regarding treatment of the infected nonunion after clavicle fracture. We report on a case of infected clavicle nonunion successfully treated with autologous bone graft and dual plate fixation.
- 666 View
- 3 Download

Original Articles
- Treatment of Olecranon Fractures with Proximal Ulna Comminution Using Locking Compression Plates
- Ki Do Hong, Tae Ho Kim, Jae Cheon Sim, Sung Sik Ha, Min Chul Sung, Jong Hyun Jeon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2015;28(1):59-64. Published online January 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.1.59
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the clinical results of locking compression plate (LCP) fixation for olecranon fractures with proximal ulna comminution.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We review 10 cases of olecranon fractures with proximal ulna comminution treated with LCPs from August 2011 to August 2013. Follow-up period was from 12 months to 18 months. Mean age was 63.1 years (35-84 years). According to the Mayo classification, there were eight type IIB, and two type IIIB fractures. We used Mayo classification. Clinical evaluation was performed based on radiographic union of olecranon and measurements of range of motion at last follow-up. Disability of the arm, shoulder and hand (DASH) score and Mayo elbow performance score (MEPS) were used for evaluation of functional recovery.
RESULTS
All patients had bone union. According to the MEPS, nine of ten patients had a good or excellent outcome. The mean DASH score was 18.6. All cases started postoperative range of motion (ROM) within 14 days. Elbow ROM was more than 110degrees in all cases except one. Mean radiological bony union time was 4.2 months (2.5-6.0 months) postoperatively. Complication was hardware irritation in three patients.
CONCLUSION
Internal fixation using LCP for olecranon fractures with proximal ulna comminution can be a good treatment option which obtains good clinical results and enables early ROM.
- 576 View
- 4 Download

- Treatment of Fractures of the Distal Radius Using Variable-Angle Volar Locking Plate
- Jae Cheon Sim, Sung Sik Ha, Ki Do Hong, Tae Ho Kim, Min Chul Sung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2015;28(1):46-52. Published online January 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.1.46
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate outcome of variable-angle volar locking plate for treatment of distal radius fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We retrospectively analyzed the results in 45 cases treated by variable-angle volar locking plate. We evaluated the clinical results according to the Mayo wrist performance scoring system and radiographic results.
RESULTS
All cases had bony union. The mean Mayo wrist performance scoring system was 84.8. Between preoperative and immediate postoperative radiographic measurement, the mean radial length improved from 8.4 to 11.8 mm, radial inclination from 14.2degrees to 22.4degrees, volar tilt from -4.5degrees to 9.6degrees, and intraarticular step-off from 1.8 to 0.3 mm (p<0.05). Between immediate postoperative and latest follow-up radiographic measurements, the mean loss of radial length measured 0.8 mm, radial inclination 0.4degrees, and volar tilt 0.9degrees (p>0.05). All cases showed bone union with no evidence of malunion, nonunion, or metal failure.
CONCLUSION
Treatment of distal radius fractures using variable angle volar locking plate showed satisfactory outcomes. It is a good option to obtain stable fixation without significant loss of reduction.
- 517 View
- 4 Download

- The Surgical Outcome of Unstable Distal Clavicle Fractures Treated with 2.4 mm Volar Distal Radius Locking Plate
- Suk Kyu Choo, Ji Ho Nam, Youngwoo Kim, Hyoung Keun Oh
- J Korean Fract Soc 2015;28(1):38-45. Published online January 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.1.38
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study evaluated the surgical outcomes of unstable distal clavicular fractures treated with a 2.4 mm volar distal radius locking plate.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From August 2009 to August 2012, 16 patients with distal clavicle fractures underwent surgical treatment. Mean age was 36 years (18-62 years) and mean follow-up period was 12.9 months (6-32 months). Two cases were Neer type I, six cases IIa, three cases IIb, three cases III, and two cases V. For the radiologic assessment, union time and metal failure were evaluated, and coracoidiologic assessment, union time and metal failure were evaluatethe acromioclavicular joint. The clinical results were evaluated by range of motion, postoperative complication, and University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA) score.
RESULTS
Mean time to fracture union was 7.4 weeks (6-14 weeks) in all cases. No statistical difference in coracoid-clavicle distance was observed between immediate post-operation group and contra-lateral group (p=0.6), but an increase of 2.1 mm was observed in the last follow up group compared with the contra-lateral group (p<0.01). The UCLA scoring system showed excellent results in 15 cases and good results in one case. Acromial-clavicle instability occurred in one case so that metal removal and distal clavicle resection were performed.
CONCLUSION
A 2.4 mm volar distal radius locking plate can provide rigid fixation through several screw fixation in the short distal fragment and lead to satisfactory clinical outcomes in unstable distal clavicular fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Estudo retrospectivo da placa anterior superior como tratamento para fraturas instáveis da clavícula distal (tipo 2 de Neer)
Syed Ibrahim, Jimmy Joseph Meleppuram
Revista Brasileira de Ortopedia.2018; 53(3): 306. CrossRef - Retrospective study of superior anterior plate as a treatment for unstable (Neer type 2) distal clavicle fractures
Syed Ibrahim, Jimmy Joseph Meleppuram
Revista Brasileira de Ortopedia (English Edition).2018; 53(3): 306. CrossRef
- Estudo retrospectivo da placa anterior superior como tratamento para fraturas instáveis da clavícula distal (tipo 2 de Neer)
- 620 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- A Retrospective Comparative Study of Internal Fixation with Reconstruction Plate Versus Anatomical Locking Compression Plate in Displaced Intercondylar Fractures of Humerus
- Tong Joo Lee, Young Tae Kim, Dae Gyu Kwon, Ju Yong Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(4):294-300. Published online October 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.4.294
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analyze the clinical result of a conventional reconstruction plate (CRP) fixation and locking compressive plate (LCP) fixation on the surgical treatment of an adult's displaced intercondylar fracture of humerus.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 40 patients enrolled in the study were treated between August 2002 and May 2012. Fixation with a CRP was performed in 20 patients (group A) and anatomical locking compression plate fixation was performed in 20 patients (group B). The clinical and functional evaluation was performed according to the Mayo elbow performance score and Cassebaum classification of elbow range of motion (ROM), disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand score.
RESULTS
The Mayo elbow functional evaluation scores, eight cases were excellent, 10 cases were good, and two cases were fair in group A, and 12 cases were excellent, seven cases good, and one case fair in group B; both groups showed satisfactory results. The durations of attaining 90 to 120 degrees of the ROM of joints postoperatively were 8.3 days on average (6 to 15 days) in group A and 5.5 days on average (5 to 9 days) in group B, demonstrating a significant difference between the two groups (p=0.04). Although the correlations of clinical results according to the difference of bone mineral densities (BMDs) were not statistically significant between the two groups (p=0.35), loss of fixation occurred due to loosening of screws in two patients with low BMDs in whose operations reconstruction plates were used.
CONCLUSION
The use of locking compressive plate on the surgical treatment of an diaplaced intercondylar fracture of humerus have a good clinical results because that permits early rehabilitation through good fixation and reduces the complications such as loosening of screws.
- 384 View
- 0 Download

- The Fate of Pronator Quadratus Muscle after Volar Locking Plating of Unstable Distal Radius Fractures
- Chae Hyun Lim, Heun Guyn Jung, Ju Yeong Heo, Young Jae Jang, Yong Soo Choi
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(3):191-197. Published online July 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.3.191
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the pronator quadrates muscle in patients who underwent internal fixation with a volar locking plate for unstable distal radius fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Forty patients who underwent internal fixation with a volar locking plate for unstable distal radius fracture were enrolled. We evaluated the clinical results according to the Mayo wrist score, the wrist range of motion, and the grip strength at the last follow-up. Using ultrasonography, muscle thickness of the pronator quadrates was compared between injured and uninjured arm.
RESULTS
Bone union was achieved in all cases. The mean Mayo wrist score was 82.79 points. The grip strength of the injured arm was decreased to 89.1% of the uninjured side. The decrease of pronation range of the injured wrist motions was significant (82.3degrees, p=0.004). There was significant atrophy of the pronator quadrates muscle on the injured side (injured side: 3.19 mm, uninjured side: 4.72 mm, p=0.001); and the decrement of muscle thickness in pronator quadrates showed an association with the Mayo wrist score (r=-0.35, p=0.042).
CONCLUSION
These results suggest that continuity of the muscle is maintained after use of the volar locking plating for unstable distal radius fractures with repair of pronator quadrates; however, there is atrophy of pronator quadrates muscle and limitation of pronation in the injured wrist.
- 425 View
- 0 Download

- Results of Use of Compression Hip Screw with Trochanter Stabilizing Plate for Reverse Oblique Intertrochanteric Fracture
- Byung Woo Min, Kyung Jae Lee, Gyo Wook Kim, Ki Cheor Bae, Si Wook Lee, Du Han Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(2):120-126. Published online April 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.2.120
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to analyze the use of a compression hip screw with a trochanter stabilizing plate for treatment of reverse oblique intertrochanteric fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed the results of 33 cases of reverse oblique intertrochanteric fracture treated with a compression hip screw with a trochanter stabilizing plate from January 2000 to December 2012 which were followed-up for more than one year. We evaluated postoperative bone union period, change of neck-shaft angle, sliding of hip screw, and other complications.
RESULTS
Of 33 patients, satisfactory reduction was achieved in 28 patients. Five patients had an unsatisfactory reduction, with two cases of excessive screw sliding, one of broken metal, one of varus deformity, and one of internal rotation deformity. We performed corrective osteotomy in varus and internal rotation deformity and partial hip replacement in a case of excessive screw sliding. Bone union was achieved in 29 patients, and the average bone union period was 19.2 weeks.
CONCLUSION
We consider that a compression hip screw with a trochanteric stabilized plate is a good option for treatment of reverse oblique intertrochanteric femoral fractures. However, adequate fracture reduction and ideal implant placement are a basic necessity for successful treatment.
- 756 View
- 6 Download

- Treatment of Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures Following Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Lih Wang, Kyu Yeol Lee, Chul Hong Kim, Myung Jin Lee, Min Soo Kang, Jin Soo Hwang, Sun Hyo Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(1):42-49. Published online January 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.1.42
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to compare the treatment results of fracture fixations by using two minimal invasive techniques for patients with periprosthetic femoral fractures following total knee arthroplasty.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed 36 patients (5 males, 31 females) of periprosthetic femoral fractures whom were treated surgically between January 2005 and January 2011. Mean patient age was 68.9 years (range, 43 to 81 years) old and the follow-up period averaged 41 months (range, 18 to 72 months). Nineteen patients were treated with minimal invasive locking plate fixations (group I) and 17 patients with retrograde intramedullary nailing (group II). Clinical and radiological outcomes in each group were comparatively analyzed.
RESULTS
Successful bone unions occurred in all patients and the mean time to bone union was 3.7 months in group I and 4.2 months in group II. There were no statistical differences between the two groups according to mean operative time and mean intraoperative blood loss. There were also no statistical differences between two groups according to clinical outcomes but the valgus deformity was apparent in group II and radiological outcomes revealed significant differences between the two groups.
CONCLUSION
For the treatment of periprosthetic femoral fractures after total knee arthroplasty, two minimal invasive techniques have shown good clinical results. However, the minimal invasive plate fixation showed better results in the radiological alignments. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Result of Treatment of Femoral Periprosthetic Fractures after Total Knee Arthroplasty
Jun-Beom Kim, In-Soo Song, Dong-Hyuk Sun, Hyun Choi
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2014; 49(6): 446. CrossRef
- The Result of Treatment of Femoral Periprosthetic Fractures after Total Knee Arthroplasty
- 815 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Clinical Assessment after the Volar Locking Plate Removal of Distal Radius Fracture
- Hee Chul Gwak, Joo Yong Kim, Gyu Min Kong, Jung Won Kim, Jae Yong Kwak, Dong Gyun Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(1):23-28. Published online January 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.1.23
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the clinical outcomes after removing the volar locking plate for distal radius fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed retrospectively the medical records of 34 patients, 36 cases after removing the plates among 150 patients, with 162 cases that underwent open reduction and internal fixation using the volar locking plate between January 2006 and May 2011. We performed preoperative and postoperative clinical assessments using the quick-disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand (Q-DASH), the visual analog scale (VAS) score, and the range of motion on wrist, grip and pinch power.
RESULTS
The major reason for plate removal was the time to remove the plate according to the fracture union and the patient's demand without other specific complaints (28 cases). The mean preoperative VAS score was 1.78 and the mean postoperative VAS score 1.81 (p=0.64). The mean preoperative Q-DASH score was 30.02 and the mean postoperative Q-DASH score 38.46 (p<0.001). The mean preoperative grip and pinch power were 18.14 kg and 7.67 kg. The mean postoperative grip and pinch power were 15.27 kg and 6.94 kg (p=0.23).
CONCLUSION
The removal of the volar locking plate for distal radius fracture should be decided by considering the patient's clinical and socioeconomic conditions carefully.
- 789 View
- 0 Download

Case Reports
- Rupture of the Extensor Pollicis Longus Tendon at the Proximal Screw of Volar Plate Fixation for Distal Radius Fracture: A Case Report
- Dong Ju Shin, Seung Oh Nam, Hun Sik Cho
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(4):338-342. Published online October 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.4.338
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - As volar plate fixation of distal radius fracture becomes more common, reports of ruptured extensor pollicis longus tendon by a protruding distal screw tip are also increasing steadily. Authors have experienced a rare case of ruptured extensor pollicis longus tendon at the prominent proximal screw of fixed volar plate for distal radius fracture, and we report it herein with a review of the literature.
- 503 View
- 1 Download

- Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Stabilization Using a Medial Locking Plate for Proximal Tibial Fractures: Technical Note
- Jae Ang Sim, Beom Koo Lee, Kwang Hui Kim, Yong Seuk Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(4):327-332. Published online October 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.4.327
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) is beneficial for proximal tibial fractures since these injuries are mostly caused by high energy traumas. The advantages of MIPO are minimization of soft tissue dissection and preservation of periosteal vascularization. Lateral plating has mostly developed as MIPO for proximal tibial fractures. We introduce minimal invasive percutaneous plate stabilization using a medial locking plate as alternative treatment for proximal tibial fractures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Korean Medicine Treatments in Patients with Proximal Tibia Fracture: A Retrospective Observational Study
Jung Min Lee, Eun-Jung Lee
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2020; 30(3): 141. CrossRef - Medial Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis in Proximal Tibial Comminuted Fractures
Jae-Ang Sim, Kwang-Hui Kim, Yong-Seuk Lee, Sang-Jin Lee, Beom-Koo Lee
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2014; 49(4): 278. CrossRef
- Effect of Korean Medicine Treatments in Patients with Proximal Tibia Fracture: A Retrospective Observational Study
- 764 View
- 22 Download
- 2 Crossref

Original Article
- The Comparison of Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis versus Open Plate Fixation in the Treatment of in the Distal Femur Fracture
- Seong Jun Ahn, Suk Woong Kang, Bu Hwan Kim, Moo Ho Song, Seong Ho Yoo, Kwan Taek Oh
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(4):314-320. Published online October 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.4.314
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the efficacy of surgical treatment through retrospective comparison of minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) vs open plate fixation in the treatment of the distal femur fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty-one patients with distal femur fractures from January 2002 to December 2010 were divided into two groups depending on the surgical method. Minimum follow up was 12 months. Group A consisted of 17 patients treated with MIPPO, and group B was comprised of 14 patients treated with open plate fixation. Clinical outcomes including operation time, transfusion rate, rehabilitation, range of motion, and interval change of postoperative C-reactive protein (CRP) were evaluated to assess postoperative inflammatory reaction, postoperative complications and clinical results with the use of Sanders criteria.
RESULTS
The operative time was 86/135 min and transfusion volume was 0.8/1.9 unit respectively. The postoperative 3-day and 7-day CRP were 7.4/1.5 mg% in group A and 10.3/2.4 mg% in group B, showing more minimal tissue injury and early recovery in group A. There were no significant differences in clinical results by Sanders criteria in both groups.
CONCLUSION
Both MIPPO and open plate fixation for the treatment of distal femur fractures showed comparably good results. However, the MIPPO technique is superior to group B in view of minimal tissue injury and operation time and was proven to lessen the transfusion rate. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Usefulness of Reduction and Internal Fixation Using a 2.4 mm Hand Plating System in Type AO 33-A3 Distal Femur Fracture: Technical Note
Bong-Ju Lee, Ja-Yeong Yoon, Seungha Woo
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2023; 36(1): 25. CrossRef
- Usefulness of Reduction and Internal Fixation Using a 2.4 mm Hand Plating System in Type AO 33-A3 Distal Femur Fracture: Technical Note
- 716 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


