Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 33(2); 2020 > Article
- Original Article Results of Single Small Incision Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis in the Treatment of the Distal Radius Fractures
- Young Sung Kim, Jong Pil Kim, Phil Hyun Chung, Ho Min Lee, Bo Sung Go
-
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma 2020;33(2):72-80.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.2.72
Published online: April 30, 2020

- 592 Views
- 8 Download
- 0 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
Abstract
Purpose
This study compared minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) using a single small skin incision and conventional open volar locking plate fixation (OP) for distal radius fracture to identify outcome difference.
Materials and Methods
Forty-three patients who underwent MIPO using a single small skin incision or OP for distal radius fractures were evaluated retrospectively. Of the patients, 21 were treated with MIPO using a single small skin incision and 22 with the OP method through the conventional volar approach. The postoperative radiographic results and clinical outcomes at the final follow-up in each group were compared.
Results
All patients achieved bone union in the MIPO and OP groups. No significant differences in the bone union time, alignment, range of motion, QuickDASH, or pain score were observed. On the other hand, the size of the incision was significant: 23 mm in the MIPO group and 55 mm in the OP group (p<0.001).
Conclusion
MIPO technique using a single small incision showed similar satisfactory radiographic and functional outcomes compared to conventional OP for distal radius fractures. The MIPO technique using a single small incision offered advantages, including cosmetic benefits and minimal soft tissue damage, is recommended, particularly in young women and high functional demand patients.
Published online Apr 28, 2020.
https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.2.72
Results of Single Small Incision Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis in the Treatment of the Distal Radius Fractures
 , M.D.,
Jong Pil Kim
, M.D.,
Jong Pil Kim , M.D.,
Phil Hyun Chung
, M.D.,
Phil Hyun Chung , M.D.,
Ho Min Lee
, M.D.,
Ho Min Lee , M.D.
and Bo Sung Go
, M.D.
and Bo Sung Go , M.D.
, M.D.
Abstract
Purpose
This study compared minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) using a single small skin incision and conventional open volar locking plate fixation (OP) for distal radius fracture to identify outcome difference.
Materials and Methods
Forty-three patients who underwent MIPO using a single small skin incision or OP for distal radius fractures were evaluated retrospectively. Of the patients, 21 were treated with MIPO using a single small skin incision and 22 with the OP method through the conventional volar approach. The postoperative radiographic results and clinical outcomes at the final follow-up in each group were compared.
Results
All patients achieved bone union in the MIPO and OP groups. No significant differences in the bone union time, alignment, range of motion, QuickDASH, or pain score were observed. On the other hand, the size of the incision was significant: 23 mm in the MIPO group and 55 mm in the OP group (p<0.001).
Conclusion
MIPO technique using a single small incision showed similar satisfactory radiographic and functional outcomes compared to conventional OP for distal radius fractures. The MIPO technique using a single small incision offered advantages, including cosmetic benefits and minimal soft tissue damage, is recommended, particularly in young women and high functional demand patients.
Fig. 1
A 20-mm sized skin incision is drawn over the flexor carpi radialis tendon just 2 cm proximal to the wrist flexor crease.
Fig. 2
(A) Intraoperative photo. (B) Fluoroscopic anteroposterior radiograph. A K-wire is used to temporarily hold the plate after sliding the plate under the pronator quadratus muscle belly.
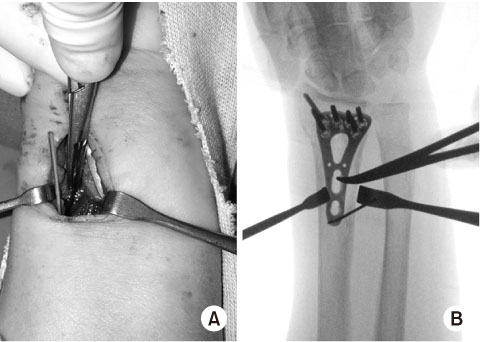
Fig. 3
(A) Intraoperative photo. (B) Fluoroscopic anteroposterior radiograph. The proximal diaphyseal plate hole is identified by C-arm fluoroscopy
Fig. 4
Proximal diaphyseal locking screw is inserted through the small slot of the pronator quadratus muscle belly.
Fig. 5
Plate anterior protrusion and plate-watershed distance were measured on the lateral wrist radiograph.
Table 1
Demographic Data of the Patients
Table 2
Radiological Results
Table 3
Clinical Outcomes
Financial support:None.
Conflict of interests:None.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS








 Cite
Cite

