Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Lateral marginal fractures of the patella and patellofemoral pain
- Jae-Ang Sim, Chul-Ho Kim, Ji Wan Kim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):152-159. Published online July 22, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00171
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
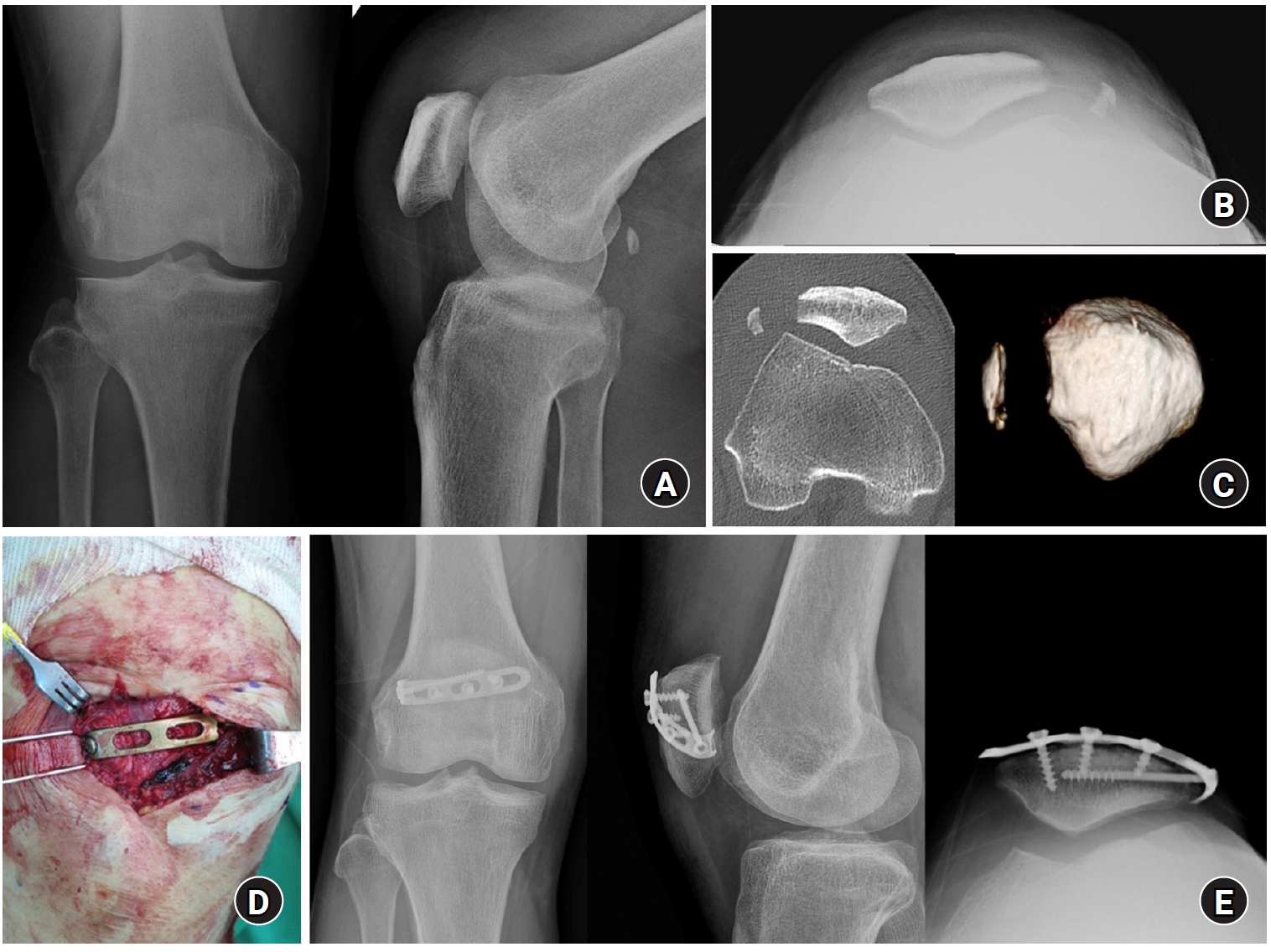
This study investigated the characteristics of lateral marginal fractures of the patella and evaluated the clinical outcomes.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed all patients with lateral marginal fractures of the patella, defined as a vertical fracture line within 15 mm of the lateral patellar border, from 2008 to 2020. In total, 41 patients were included. Patient characteristics, radiologic findings, and clinical outcomes, including the Lysholm score at 1 year postoperation, were evaluated.
Results
The injury mechanisms were direct in 34 cases and indirect in seven. Furthermore, 85% of patients had a skyline view of the patella at the initial visit, and one medial subluxation of the patella was found. Forty of the 41 patients underwent surgery. Anatomical and nonanatomical (>1-mm displacement or excision) reductions were carried out in 36 cases (88%) and five cases (12%), respectively. The average Lysholm score was 89.1 (range, 67–99). The nonanatomical reduction group had a poorer functional score (79.8 vs. 90.4; P=0.010). Lateral patellar compression syndrome occurred in two patients with nonanatomical reduction.
Conclusions
Lateral marginal fractures of the patella affected patellofemoral stability. Anatomical reduction showed good functional outcomes, while nonanatomical reduction was associated with patellofemoral stability and pain. Therefore, surgeons should perform anatomical reduction with any appropriate fixation method. Level of Evidence: IV
- 1,259 View
- 26 Download

- Reverse V step-cut osteotomy for the correction of cubitus varus in adults: a retrospective study
- Jinyoung Bang, Hyung Jun Koo
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):102-108. Published online April 25, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00045
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
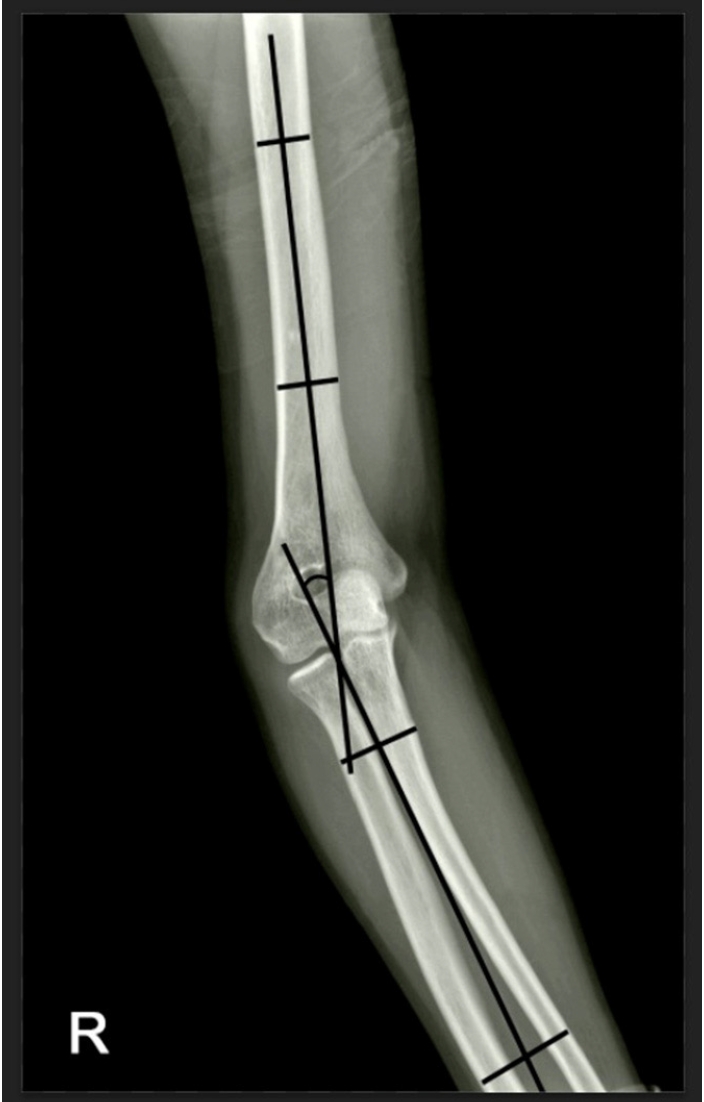
Cubitus varus deformity in adults most commonly occurs as a late complication resulting from malunion of distal humeral fractures sustained during childhood. This deformity can cause cosmetic problems and anatomical deformities that hinder normal sports activities and potentially lead to long-term complications. Although various surgical techniques exist for correcting cubitus varus, this study investigated the clinical and functional outcomes of reverse V step-cut osteotomy.
Methods
In total, 15 patients underwent surgical treatment with reverse V step-cut osteotomy between 2012 and 2023. The mean age of the patients at the time of surgery was 46.3 years (range, 20–65 years). The preoperative carrying angle was ‒11.09° of varus, which was corrected to +12.81° of valgus postoperatively. The mean preoperative lateral prominence index (LPI) was ‒10.03, and the mean postoperative LPI improved to ‒4.48. A comparison to the unaffected side showed a P-value of 0.978, indicating similarity.
Results
Preoperatively, eight patients exhibited signs of posterolateral rotatory instability, and among them, three underwent concomitant lateral ulnar collateral ligament reconstruction. Seven patients reported ulnar nerve symptoms, and all underwent concurrent ulnar nerve release. Postoperatively, improvements in elbow pain, instability, and ulnar nerve symptoms were observed. One patient required reoperation due to malunion and insufficient correction, but no other complications were noted.
Conclusions
These outcomes demonstrate that reverse V step-cut osteotomy can be an effective treatment method for cubitus varus deformity in adults. Level of evidence: IV.
- 1,881 View
- 54 Download

Review Article
- Avulsion Fractures in the Ankle and Foot
- Gyeong Hoon Lim, Jae Won Kim, Sung Hyun Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(2):102-116. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.2.102
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - An avulsion fracture occurs when a muscle-tendon unit attached to a bone produces sufficient force to tear a fragment of the bone. If not treated properly, this injury can lead to deformity, nonunion, malunion, pain, and disability. Although avulsion fractures around the foot and ankle can occur anywhere there are tendon and ligament attachments, they are common in the anterior talofibular ligament, anterior-inferior tibiotalar ligament, calcaneal tuberosity, the base of the fifth metatarsal, and navicular bone. The optimal treatment for each fracture depends on the location and severity of the fracture. Conservative treatment involves limiting weight bearing for a period, splint immobilization, and using various orthoses. Surgical treatment is usually reserved for cases of severe displacement or when nonsurgical treatment has failed. The goals of surgery include reduction of the fracture fragment, prevention of nonunion or malunion and soft tissue injury, and early return to function. The decision for each treatment modality may depend on the patient demographics or preferences and the surgeon experience. This review summarizes previous and current views on the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of common avulsion fractures to guide the treatment and diagnosis.
- 2,028 View
- 47 Download

Original Articles
- Prediction of Syndesmotic Instability according to the Lateral Malleolus Fracture Pattern in Supination-External Rotation Type Ankle Fractures: Short Oblique versus Long Oblique Fracture
- Chan-Jin Park, Min-Su Lee, Keun-Bae Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(1):39-45. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.1.39
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined whether preoperative radiological evaluations can predict syndesmotic instability according to the lateral malleolus fracture pattern in supination-external rotation-type ankle fractures.
Materials and Methods
This study enrolled 132 patients (132 ankles) with supination-external rotation stage 3 and 4 ankle fractures. Three-dimensional computed tomography was used for the morphological classification of the lateral malleolus fractures. A long oblique fracture was defined when the posterior cortical bone height of the fracture was 4.5 cm or more from the plafond of the distal tibial articular surface. A short oblique fracture was defined when the height was less than 4.5 cm. The demographic characteristics and syndesmotic instability of the two groups were evaluated.
Results
Short oblique fractures were confirmed in 102 cases, and long oblique fractures were confirmed in 30 cases. Long oblique fractures occurred at a statistically significantly higher incidence in younger ages and among males compared to short oblique fractures. Syndesmotic instability was more common in long oblique fractures.
Conclusion
In supination-external rotation-type ankle fractures, syndesmotic instability was observed in approximately 13%. Specifically, when the fracture pattern of the lateral malleolus is long oblique, the incidence of syndesmotic instability is approximately three times higher than in short oblique fractures. Therefore, meticulous evaluations of the lateral malleolus fracture pattern and establishing an appropriate treatment plan before surgery are crucial. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship of lateral malleolar fracture patterns to posterior malleolar fracture morphology in supination-external rotation ankle fractures in Korea: a retrospective cohort stduy
Jong-Eun Kim, Chan-Jin Park, Jun-Young Lee, Keun-Bae Lee, Gun-Woo Lee
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(4): 212. CrossRef
- Relationship of lateral malleolar fracture patterns to posterior malleolar fracture morphology in supination-external rotation ankle fractures in Korea: a retrospective cohort stduy
- 619 View
- 10 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of Additional Medial Locking Plate Fixation and Autogenous Bone Graft for Distal Femur Nonunion after Lateral Locking Plate Fixation
- Ho Min Lee, Jong Pil Kim, In Hwa Baek, Han Sol Moon, Sun Kyo Nam
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(1):30-38. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.1.30
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the outcomes of additional medial locking plate fixation and autogenous bone grafting in the treatment of nonunions that occurred after initial fixation for distal femoral fractures using lateral locking plates.
Materials and Methods
The study involved eleven patients who initially underwent minimally invasive lateral locking plate fixation for distal femoral fractures between January 2008 and December 2020. The initial procedure was followed by additional medial locking plate fixation and autogenous bone grafting for clinically and radiographically confirmed nonunions, while leaving the stable lateral locking plate in situ. A clinical evaluation of the bone union time, knee joint range of motion, visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores, presence of postoperative complications, and functional evaluations using the lower extremity functional scale (LEFS) were performed.
Results
In all cases, bone union was achieved in an average of 6.1 months after the secondary surgery. The range of knee joint motion, weight-bearing ability, and VAS and LEFS scores improved at the final follow-up compared to the preoperative conditions. All patients could walk without walking assistive devices and did not experience pain at the fracture site. On the other hand, three patients complained of pain in the lateral knee joint caused by irritation by the lateral locking plate; hence, lateral hardware removal was performed. One patient complained of mild paresthesia at the anteromedial incision site. Severe complications, such as deep infection or metal failure, were not observed.
Conclusion
For nonunion with stable lateral locking plates after minimally invasive lateral locking plate fixation of distal femur fractures, additional medial locking plate fixation and autogenous bone grafting, while leaving the lateral locking plate intact, can achieve successful bone union.
- 382 View
- 5 Download

- Posterior Anti-Glide Plating for Supination External Rotation Type Lateral Malleolar Fractures: Clinical Comparison of Locking versus Non-Locking One-Third Semi-Tubular Plate Fixation
- Jun Young Lee, Yong Jin Cho, Dong Hyuk Cha, Hyun Bai Choi, Jung Ho Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(2):57-62. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.2.57
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate and compare the clinical and radiological outcomes between locking plates and non-locking plates using posterior anti-glide plating for supination external rotation type lateral malleolar fractures.
Materials and Methods
A total of 50 patients who underwent internal fixation of posterior anti-glide plating due to lateral malleolar fractures, classified as supination-external rotation (SER) as per the Lauge-Hansen classification system, at our hospital from January 2017 to November 2018 were retro-spectively evaluated. Patients were divided into two groups: 1/3 semi-tubular locking plate (24 patients) and 1/3 semi-tubular non-locking plate (26 patients). A radiographic assessment was performed after surgery to evaluate the time of bone union. The American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) ankle-hindfoot functional score was measured after the surgery to evaluate the clinical outcomes.
Results
The two groups showed similar distributions in sex, age, height, body mass index, fracture pattern, and mean follow-up period. Complete bone union was obtained in all cases and the mean bone union time was 13.00±3.38 weeks in Group 1 and 12.92±3.26 weeks in Group 2 (p=0.87). The mean AOFAS score at 24 weeks was 95.66±2.86 in Group 1 and 95.84±2.79 in Group 2 (p=0.82). The mean AOFAS score at 48 weeks was 97.25±3.54 in Group 1 and 96.57±3.07 in Group 2 (p=0.47). Two cases of complications were observed in the non-locking plate group.
Conclusion
For the treatment of Lauge-Hansen SER type lateral malleolar fracture, internal fixation us-ing locking 1/3 semi-tubular plate and non-locking 1/3 semi-tubular plate are both favorable fixation methods.
- 347 View
- 2 Download

Review Articles
- Treatment of Ankle Fracture and Dislocation
- Chan Kang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(1):38-49. Published online January 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.1.38
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ankle fractures are the most common type of foot and ankle fracture injury. Several types of fractures occur in the ankle structures (medial malleolus, lateral malleolus, posterior malleolus, and Chaput’s tubercle) with various mechanisms and extent of fracture force. Moreover, fractures can be accompanied by other injuries, such as distal tibiofibular syndesmotic injury, medial deltoid ligament rupture, and lateral ligament complex rupture. Ankle dislocation can be accompanied when an injury is caused by a greater fracture force. Non-surgical treatments or combined surgeries may be performed depending on the mechanism and fracture type. Generally, a stable fracture maintaining anatomical reduction is treated conservatively, but surgical treatment is performed when this is not the case. Furthermore, surgeries for stable fractures can be offered when the patients demand early weight bearing due to their occupation, age, and performance state. Restoring the ankle mortise in its anatomical shape before the injury and starting early rehabilitation for functional recovery simultaneously until a union is achieved is important. Traumatic arthritis can occur if the treatment focuses only on fractures and neglects ligament injuries, such as distal tibiofibular syndesmotic injury and medial deltoid ligament rupture. Shortening, angular deformation, and rotational deformation of the fibular promote the progression of traumatic ankle arthritis in the long term, which may further cause chronic ankle pain. An overlooked displaced posterior malleolus fracture also causes traumatic arthritis through anteroposterior instability of the ankle joint.
- 974 View
- 46 Download

- Pediatric around Elbow Fracture
- Taehun Kim, Jaeho Cho, Seungmin Chung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2021;34(1):44-49. Published online January 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2021.34.1.44
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study assessed the current concepts of pediatric elbow fractures. PubMed and Embase databases were searched for publications in English on elbow fractures. Papers believed to yield significant findings to this area were included in this review. The supracondyle of humerus, lateral condyle of the humerus, proximal radius, and proximal ulna fractures were included. Sixteen papers and textbooks were selected. Pediatric elbow fractures should be evaluated for combined injuries. Treatment should be done accurately for each fracture for the further growth of children.
- 480 View
- 11 Download

Original Articles
- Comparison of the Clinical and Radiographic Results between 125° and 130° Caput-Collum-Diaphyseal Angle Proximal Femoral Nail Anti-Rotation II in Patients with Intertrochanteric Fracture
- Soo Jae Yim, Yong Bok Park, Hyun Kwon Kim, Sin Hyung Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(4):210-216. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.4.210
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study compared the clinical and radiographic results of two proximal femoral nail antirotation II (PFNA-II) angled by 125° and 130° in patients with intertrochanteric fractures.
Materials and Methods
From March in 2015 to September in 2016, 65 patients who underwent a closed reduction and internal fixation with PFNA-II for a femoral intertrochanteric fracture were evaluated retrospectively. The minimum follow-up period was two years. Of those, 30 and 35 patients underwent 125° angled PFNA-II and 130° angled PFNA-II, respectively. The clinical performance was evaluated using the Harris hip score, WOMAC (Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthrtis Index), and UCLA (University of California Los Angeles) score. Radiographic analyses were performed using standardized anteroposterior and lateral radiographs to assess the implant position and quality of reduction. The blade length, distance between the blade tip and the tip of the greater trochanter, and distance between the blade tip and the most lateral protrusion point of the greater trochanter in the two groups were measured and compared.
Results
The clinical results, including the Harris hip score, WOMAC, and UCLA, were similar in the two groups at the last follow-up postoperatively. In the radiography evaluation, the implant position, quality of reduction, and the blade length were similar in the two groups. The distances between the blade tip and the tip of the greater trochanter were 52.60±3.53 mm and 58.07±5.54 mm in the 125° angled PFNA-II and 130° angled PFNA-II groups, respectively. The distance between the blade tip and the most lateral protrusion point of greater trochanter were 16.48±2.54 mm and 21.19±4.43 mm in the 125° angled PFNA-II and 130° angled PFNA-II groups, respectively. The differences were significant (p=0.031, p=0.012).
Conclusion
The operation with the 125° angled PFNA-II showed a more superior and lateral position of the blade than that with the 130° angled PFNA-II. Nevertheless, lateral thigh pain can occur when the blade is positioned superolaterally.
- 588 View
- 2 Download

- Three-Dimensional Analysis of the Morphological Features in the Femur of Atypical Fracture and Practical Implications of Intramedullary Nailing
- Yong Uk Kwon, Kyung-Jae Lee, Joo Young Choi, Gu-Hee Jung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(2):87-95. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.2.87
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study analyzed the morphological features of the contralateral femur without an atypical fracture by constructing a three-dimensional model with an actual size medullary canal.
Materials and Methods
Lateral and anterior bowing of the shaft were measured for 21 models, and the shape of the medullary canal was analyzed. To eliminate the projection error, the anteroposterior (AP) femur was rotated internally to the extent that the centerline of the head and neck, which is the ideal position of cephalomedullary nail screw, was neutral, and the lateral femur matched the medial and lateral condyle exactly.
Results
The lateral bowing and anterior bowing was an average of 5.5° (range, 2.8°-10.7°; standard deviation [SD], 2.4°) and 13.1° (range, 6.2°-21.4°; SD, 3.2°), respectively. In the area where lateral bowing increased, the lateral cortex became thicker, and the medullary canal was straightened. On the lateral femur, the anterior angle was increased significantly, and the diameter of curvature averaged 1,370.2 mm (range, 896-1,996 mm; SD, 249.5 mm).
Conclusion
Even if the anterolateral bowing increases in the atypical femur, the medullary canal tends to be straightened in the AP direction. So, it might be considered as a reference to the modification of an intramedullary nail to increase the conformity.
- 475 View
- 5 Download

- Treatment of Isolated Lateral Malleolar Fractures Using Locking Compression Plate Fixation and Tension Band Wiring Fixation
- Woojin Shin, Seondo Kim, Jiyeon Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(1):16-21. Published online January 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.1.16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to compare the clinical and radiological outcomes of locking compression plate (LCP)-screw fixation and tension band wiring (TBW) fixation in isolated lateral malleolar fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From May 2016 to August 2018, 52 patients with isolated lateral malleolar fracture were retrospectively reviewed. They were divided into 30 cases of the LCP fixation group (Group I) and 22 cases of the TBW fixation group (Group II). The clinical and radiological results of those groups were compared. Pearson chi-square tests and independent t-tests were used in the statistical analysis.
RESULTS
The mean length of the surgical incision was 8.3 cm in Group I and 4.9 cm in Group II. Radiological union was obtained at a mean of 8.4 weeks in both groups. The mean American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society score was 90 (range, 85–97) and 92 (range, 85–100) in Groups I and II, respectively, at the last follow up.
CONCLUSION
Both the LCP-screw and TBW techniques revealed excellent results in isolated lateral malleolar fractures. The tension band technique may be a fine alternative method of fixation in the treatment of isolated lateral malleolar fracture.
- 999 View
- 8 Download

Case Report
- Major Limb Replantation of Lower Leg Amputation with Ipsilateral Distal Femoral Comminuted Fracture in Old Age: A Case Report
- Tae Young Ahn, Seung Joon Rhee, Sang Ho Kwak, Hyo Seok Jang, Sang Hyun Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(4):227-231. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.4.227
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The development of microsurgical techniques has also increased the success rate of replantation surgery. This paper reports the results of limb replantation performed on a lower extremity amputation that was associated with crush amputation and an ipsilateral comminuted fracture in and elderly patient. A 68-year-old female presented with a right distal tibia amputation due to a traffic accident. At that time, with a comminuted fracture in the distal femoral condyle, simple wound repair was recommended, but the caregivers strongly wanted replantation. Three years after surgery, normal walking was possible without a cane and the patient was satisfied with the function and aesthetics. What used to be contraindicated in limb replantation in the past are now indications due to the development of microsurgical techniques, surgical experience, and postoperative rehabilitation treatment. If the patient is willing to be treated, good results in contraindications can be obtained.
- 698 View
- 4 Download

Original Article
- Surgical Treatment for Displaced Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures in Elderly Patients: Comparison of the Minimally Invasive Approach and Extensile Lateral Approach
- Hong Ki Park, Jae Yoon Ko, Seung Kwan Lee, Jong Min Baik
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(3):135-142. Published online July 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.3.135
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
As the functional demands for activities in elderly patients are increasing according to their life extension, the need for surgical treatment is also increasing in elderly patients with displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures. In addition to the extensile lateral approach (ELA), which is a surgical procedure that showed good results on intra-articular calcaneal fractures, the minimally invasive approach (MIA) also showed an outstanding result. This study compared the radiological and clinical results of intraarticular calcaneus fractures in elderly patients in two groups: ELA and MIA.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty patients aged over 65 years with intra-articular calcaneus fractures, who could be followed-up more than 14 months, were included in this study. Thirteen patients of the MIA group and 17 patients of the ELA group were analyzed retrospectively using radiological and clinical assessments.
RESULTS
No significant difference in union time, posterior facet reduction accuracy, subtalar osteoarthritis frequency, Bohler angle, calcaneal width, American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society score, visual analogue scale score, 36-item short form survey, and foot function index was observed between the two groups. The p-value of the average height of the calcaneus correction, average length of calcaneal correction, and average loss of correction length were <0.001, 0.005, and 0.015, respectively. The incidence of complications, including soft tissue necrosis and bone infection, were 23.1% in the ELA group and none in the MIA group.
CONCLUSION
The clinical outcomes were similar in the two groups. The degree of reduction of fracture showed a better result in the MIA group than the ELA group. Furthermore, there were no complications in the MIA group, whereas the ELA group showed some complications. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of ‘Blocking Kirschner Wire Technique’ in Displaced Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures via the Extended Sinus Tarsi Approach
Jeong-Kil Lee, Chan Kang, Sang-Bum Kim, Gi-Soo Lee, Jung-Mo Hwang, Byung-Kuk An
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2021; 56(3): 224. CrossRef
- Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of ‘Blocking Kirschner Wire Technique’ in Displaced Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures via the Extended Sinus Tarsi Approach
- 890 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review Articles
- Locked Plating in Elderly Patients with Distal Femur Fracture: How to Avoid Complications?
- Chul Young Jang, Je Hyun Yoo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(2):112-119. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.2.112
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Distal femur fractures in elderly patients with osteoporosis are complicated because poor bone quality makes screw purchase and fixation less secure, presenting many clinical challenges to the orthopedic surgeon. Minimally invasive locked plating using an angularly stable locking compression plate has become an integral tool for achieving secure fixation in osteoporotic distal femur fractures with improved biomechanical performance. On the other hand, complications, such as implant failure and periplate fracture, have still occurred. This paper describes the principles of internal fixation in minimally invasive lateral locked plating in elderly patients with osteoporotic distal femur fractures as well as how to avoid complications.
- 922 View
- 13 Download

- New Injury Mechanism and Treatment Algorithm of Posterior Elbow Dislocation
- In Hyeok Rhyou
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(1):61-71. Published online January 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.1.61
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Although the concept of a single elbow dislocation mechanism, in which all dislocations start from the lateral side of the elbow joint and progress to the medial side, has never been able to explain the various conflicting experimental and clinical observations thus far, new studies and proposals for a valid mechanism have not been reported. The new proposal for posteromedial and posterolateral dislocation of the elbow joint according to the authors' study and the new treatment algorithm based on this new study can explain the various clinical and experimental results that have been difficult to explain, and provide a reasonable approach to the treatment of elbow dislocations.
- 1,619 View
- 14 Download

Original Article
- Prediction of Concomitant Lateral Meniscus Injury with a Tibia Plateau Fracture Based on Computed Tomography Assessment
- Wonchul Choi, Yunseong Choi, Go Tak Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(4):132-138. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.4.132
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study examined whether any fracture pattern shown in computed tomography (CT) scan is associated with the presence of lateral meniscus (LM) injury in a tibia plateau fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fifty-three tibia plateau fractures with both preoperative CT and magnetic resonance imagings (MRI) available were reviewed. The patient demographics, including age, sex, body mass index, and energy level of injury were recorded. The fracture type according to the Schatzker classification, patterns including the lateral plateau depression (LPD), lateral plateau widening (LPW), fracture fragment location, and the number of columns involved were assessed from the CT scans. The presence of a LM injury was determined from the MRI. The differences in the factors between the patients with (Group 1) and without (Group 2) LM injuries were compared and the correlation between the factors and the presence of LM injury was analyzed.
RESULTS
The LM was injured in 23 cases (Group 1, 43.4%) and intact in 30 cases (Group 2, 56.6%). The LPD in Group 1 (average, 8.2 mm; range, 3.0–20.0 mm) and Group 2 (average, 3.8 mm; range, 1.4–12.1 mm) was significantly different (p < 0.001). The difference in LPW of Group 1 (average, 6.9 mm; range, 1.2–15.3 mm) and Group 2 (average, 4.8 mm; range, 1.4–9.4 mm) was not significant (p=0.097). The other fracture patterns or demographics were similar between in the two groups. Regression analysis revealed that an increased LPD (p=0.003, odds ratio [OR]=2.12) and LPW (p=0.048, OR=1.23) were significantly related to the presence of a LM tear.
CONCLUSION
LPD and LPW measured from the CT scans were associated with an increased risk of concomitant LM injury in tibia plateau fractures. If such fracture patterns exist, concomitant LM injury should be considered and an MRI may be beneficial for an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The value of magnetic resonance imaging in the preoperative diagnosis of tibial plateau fractures: a systematic literature review
Gregoire Thürig, Alexander Korthaus, Karl-Heinz Frosch, Matthias Krause
European Journal of Trauma and Emergency Surgery.2023; 49(2): 661. CrossRef
- The value of magnetic resonance imaging in the preoperative diagnosis of tibial plateau fractures: a systematic literature review
- 528 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Report
- Medial Plating of Distal Femoral Fracture with Locking Compression Plate-Proximal Lateral Tibia: Cases' Report
- Se Ang Jang, Young Soo Byun, In Ho Han, Dongju Shin
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(3):206-212. Published online July 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.3.206
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Generally, lateral plating is used for a comminuted fracture of the distal femur. However, in some cases, it has been shown that using a medial plate is necessary to achieve better outcome. Nevertheless, there are no available anatomical plates that fit either the distal medial femoral condyle or fracture fixation, except for the relatively short plate developed for distal femoral osteotomy. We found that locking compression plate-proximal lateral tibia (LCP-PLT) fits anatomically well for the contour of the ipsilateral medial femoral condyle. Moreover, LCP-PLT has less risk of breaking the thread holes since it rarely needs to be bent. We report a plastic bone model study and two cases of distal femoral fractures fixed with medial plating using LCP-PLT.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A novel anatomical locked medial femoral condyle plate: a biomechanical study
M. A. Ozer, S. Keser, D. Barıs, O. Yazoglu
European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology.2024; 34(5): 2767. CrossRef - Medial plating of distal femur: which pre-contoured angular stable plate fits best?
Shaam Achudan, Rex Premchand Antony Xavier, Sze Ern Tan
European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology.2024; 34(6): 3297. CrossRef - Medial augmentation of distal femur fractures using the contralateral distal femur locking plate: A technical note
Jaime Andrés Leal
OTA International.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The missing piece of the trauma armoury-medial femoral condyle plate
Piyush Upadhyay, Farhan Syed, Darryl N Ramoutar, Jayne Ward
Injury.2022; 53(3): 1237. CrossRef - Surgical Tips and Tricks for Distal Femur Plating
Christopher Lee, Dane Brodke, Ajay Gurbani
Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.2021; 29(18): 770. CrossRef - Medial minimally invasive helical plate osteosynthesis of the distal femur – a new technique
G.M. Hohenberger, A.M. Schwarz, P. Grechenig, B. Clement, Mario Staresinic, Bore Bakota
Injury.2021; 52: S27. CrossRef - Feature-Based Design of Personalized Anatomical Plates for the Treatment of Femoral Fractures
Xiaozhong Chen, Zhijian Mao, Xi Jiang
IEEE Access.2021; 9: 43824. CrossRef
- A novel anatomical locked medial femoral condyle plate: a biomechanical study
- 1,485 View
- 74 Download
- 7 Crossref

Original Articles
- Comparison of Treatment Methods in Gartland Type III Pediatric Supracondylar Humeral Fracture: Lateral Entry Pin versus Crossed-Pin Technique
- Young Hoon Jo, Tai Seung Kim, Dong Yun Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2015;28(3):186-193. Published online July 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.3.186
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to compare the results of the lateral entry pin technique and the crossed pin technique in treatment of Gartland type III humerus supracondylar fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Seventeen patients (group I) underwent surgery using the lateral entry pin technique, and 33 patients (group II) underwent surgery using the crossed pin technique for Gartland type III humerus supracondylar fracture in Hanyang University Seoul Hospital between January 2011 and January 2014. Maintenance of reduction was compared between the 2 surgical techniques by measuring changes in Baumann angle and lateral humerocapitellar angle after surgery and after pin removal in groups I and II. In addition, the final carrying angle and level of loss of functional movement were measured for comparison of clinical results between the 2 groups. Occurrence of ulnar nerve palsy in the 2 groups was also examined.
RESULTS
The mean Baumann angle and lateral humerocapitellar angle changes were 3.3degrees and 3.7 in group I and 3.1degrees and 3.4degrees in group II, respectively. No statistically significant differences were found between the 2 groups. Clinical results showed that the changes in the final carrying angle and range of motion were 2.9degrees and 2.6degrees in group I and 2.6degrees and 3.0degrees in group II, respectively, indicating no significant differences between the 2 groups. In terms of nerve damage, 1 patient in group II had temporary iatrogenic ulnar nerve palsy.
CONCLUSION
The lateral entry pin technique may be regarded as an appropriate treatment that reduces the risk of iatrogenic ulnar nerve palsy and provides satisfactory results in Gartland type III humerus supracondylar fracture patients.
- 778 View
- 2 Download

- Analysis of Risk Factors for the Posterolateral Articular Depression and Status of Posterolateral Fragment in Lateral Condylar and Bicondylar Tibial Plateau Fractures with Joint Depression
- Jung Yun Choi, Yong Woon Shin, Beom Jung Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(4):241-247. Published online October 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.4.241
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate risk factors of posterolateral articular depression and characteristics of the posterolateral fragment in lateral condylar and bicondylar tibial plateau fractures with joint depression.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed 48 patients of Schatzker type II and type V (type II 34, type V 14) and evaluated risk factors of posterolateral articular depression according to the posterolateral fragment, fibular fracture, and Schatzker classification. We evaluated the position of articular depression and anterolateral fracture line of the posterolateral fragment and measured anterior to posterior lengths of the posterolateral fragment.
RESULTS
Posterolateral articular depression was found in 20 of 34 cases (59%) with coexisting posterolateral fragment and in 16 of 21 cases (76%) with coexisting fibular fracture. There was a significant difference in the occurrence of posterolateral articular depression with the existence of the posterolateral fragment and fibular fracture (p<0.001). Multivariate regression analysis revealed that fibular fracture increased the occurrence of posterolateral articular depression (odds ratio 24.5, 95% confidence interval 2.2-267.2). Fifty-seven percentage of the anterolateral fracture line of the posterolateral fragment existed posterior to the anterior margin of the fibular head.
CONCLUSION
This study showed that fibular fracture affects posterolateral articular depression in Schatzker type II and V tibial plateau fractures. Selecting a fixation device and performing fracture reduction requires a careful consideration since the anterolateral fracture line of the posterolateral fragment exists posterior to the anterior margin of the fibular head. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Current Concepts in Management of Tibia Plateau Fracture
Sang Hak Lee, Kang-Il Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2014; 27(3): 245. CrossRef
- Current Concepts in Management of Tibia Plateau Fracture
- 678 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Reports
- Surgical Management of Comminuted Avulsion Fracture of the Proximal Fibula with Lateral Collateral Ligament Injury: Technical Note
- Jong Min Kim, Byeong Mun Park, Sang Hoo Lee, Seung Ju Jeon, Jun Beum Shin, Kyeong Seop Song
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(1):77-80. Published online January 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.1.77
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Anteromedial force to the knee in an extended position can cause an avulsion fracture of the proximal fibula with combined injuries to the posterolateral ligaments. Avulsion fractures of the proximal fibula are rare and current management of these fractures is based on few descriptions in literature. Various surgical methods of fixation for these fractures have been reported, but there is still no standard treatment modality. Anatomic reduction of these fractures is technically difficult, and failure of reduction may cause posterolateral instability, secondary arthritis and other complications. We present our experience with two such cases of comminuted avulsion fractures of the proximal fibular with posterolateral ligament ruptures surgically fixated with a locking compression hook plate and non absorbable sutures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fixation of fibular head avulsion fractures with the proximal tibiofibular screw: Technique guide and clinical experience
Ryan A. Paul, Shu Yang Hu, Ananya Pathak, Ryan Khan, Daniel B. Whelan
Trauma Case Reports.2025; 57: 101175. CrossRef - Treatment of avulsion fractures around the knee
Jeong-Hyun Koh, Hyung Keun Song, Won-Tae Cho, Seungyeob Sakong, Sumin Lim
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(2): 63. CrossRef - Treatment of Avulsion Fractures around the Knee
Sumin Lim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2024; 37(2): 117. CrossRef
- Fixation of fibular head avulsion fractures with the proximal tibiofibular screw: Technique guide and clinical experience
- 1,247 View
- 27 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Repeated Metal Breakage in a Femoral Shaft Fracture with Lateral Bowing: A Case Report
- Dong Soo Kim, Yong Min Kim, Eui Sung Choi, Hyun Chul Shon, Kyoung Jin Park, Byung Ki Cho, Ji Kang Park, Hyun Cheol Lee, Kyung Ho Hong
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(2):136-141. Published online April 30, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.2.136
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fractures of the femoral shaft with marked bowing face some obstacles in fixation of the fracture such as difficulty in insertion of the intramedullary nail (IM nail) or exact contouring plate. Locking compression plates (LCP) are an option to manage this problem. However, we experienced consecutive breakage of LCP twice and IM nail once in an 80-year-old female. Finally, union of the fracture was achieved after fixation of the IM nail and additional plate together. Fractures of the femur shaft with marked bowing are thought to have different biomechanical properties; therefore, we present this case with a review of the literature.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative analysis of operation time and intraoperative fluoroscopy time in intramedullary and extramedullary fixation of trochanteric fractures
Milan Mitkovic, Sasa Milenkovic, Ivan Micic, Predrag Stojiljkovic, Igor Kostic, Milorad Mitkovic
Vojnosanitetski pregled.2022; 79(2): 177. CrossRef - Pre-operative planning for fracture fixation using locking plates: device configuration and other considerations
Alisdair R. MacLeod, Pankaj Pankaj
Injury.2018; 49: S12. CrossRef - Letter: Repeated Metal Breakage in a Femoral Shaft Fracture with Lateral Bowing - A Case Report -
Hae Seok Koh
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2012; 25(3): 240. CrossRef
- Comparative analysis of operation time and intraoperative fluoroscopy time in intramedullary and extramedullary fixation of trochanteric fractures
- 591 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Treatment of a 3rd Lumbar Vertebra Translational Injury Combined with Incomplete Cauda Equina Syndrome in Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Case Report
- Jin Wan Kim, Young Chul Ko, Chul Young Jung, Il Soo Eun, Young June Kim, Chang Kyu Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(1):77-81. Published online January 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.1.77
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ankylosing spondylitis is a rheumatic disease in which mainly the spinal and sacroiliac joints are affected. Patients with ankylosing spondylitis are at significant risk for spinal fracture when exposed to even minor trauma. Most spinal fractures with ankylosing spondylitis occur in the cervical spine, whereas spinal fractures in thoracic or lumbar spine are rare, especially in the lower lumbar spine. Furthermore, neurologic symptoms in cases of lower lumbar spine fracture are rarer than in cases of cervical and thoracic spinal fracture. We have experienced a case of translation injury of the 3rd lumbar vertebra accompanied by incomplete cauda equine syndrome in ankylosing spondylitis and the authors gained good clinical results with surgical treatment. We have reported here on this case and have included a review of the relevant literature.
- 468 View
- 1 Download

- Combined Ipsilateral Fracture and Dislocation of Hip, Knee and Foot Joints: A Case Report
- Hyoung Soo Kim, Ju Hak Kim, Sang Joon Park, Jae Won Hyung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(1):73-76. Published online January 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.1.73
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Although clinical cases of ipsilateral knee and hip joint dislocation have been reported, there are no reports of simultaneous ipsilateral hip, knee, and foot dislocations. We report here a case of a patient who had ipsilateral hip, knee, and foot joint dislocations, and review the relevant literature.
- 498 View
- 3 Download

Original Article
- Treatment of the Trimalleolar Fracture Using Posterolateral Approach: Minimum 2-year Follow Up Results
- Gwang Chul Lee, Jun Young Lee, Sang Ho Ha, Jae Won You, Sang Hong Lee, Hong Moon Sohn, Ki Young Nam, Kwang Hyo Seo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2011;24(4):328-334. Published online October 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.4.328
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analyze the long term follow up results of treatment with posterolateral approach and to investigate its usefulness in the patients of trimalleolar fracture with posterior fragment which is above 25% of articular involvement.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
There were 34 cases of trimalleolar fracture in our hospital from May 2004 to April 2008. We investigated 20 patients who underwent operation with the posterolateral approach and over-2 years follow up cases. The mean follow up period was 34 (24~58) months. Preoperative posterior malleolar fragment involved above 25% of articular surface in all cases and displaced more than 2 mm in 11 cases. We analyzed the radiologic type of posterior malleolar fragments and evaluated the function and pain through AOFAS score and complications.
RESULTS
All cases showed primary union at mean 13.1 weeks. The complications are that partial ankylosis result of soft tissue contracture is seen in 2 cases (10%) and post-traumatic arthritis is seen in 1 cases (5%) and 17 cases (85%) of all patients are showed excellent AOFAS score.
CONCLUSION
The posterolateral approach is a valuable method because that it enables us to easily reduction and internal fixation of the posterior malleolus and lateral malleolus at one time and the results are satisfied for a long time follow up. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Outcomes of Immediate Operative Treatment of Ankle Trimalleolar Open Fractures
Jun-Young Lee, Yong-Jin Cho, Sin-Wook Kang, Yung-Min Cho, Hyun-Bai Choi
Journal of Korean Foot and Ankle Society.2020; 24(1): 25. CrossRef
- Outcomes of Immediate Operative Treatment of Ankle Trimalleolar Open Fractures
- 663 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Report
- Lateral Positioning for Proximal Femoral Nailing of the Intertrochanteric Fracture: Surgical Technique
- Kwan Hee Lee, Hoon Jeong, Jong Kyoung Ha, Yong Ju Kim, Won Hee Jang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2011;24(1):79-82. Published online January 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.1.79
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures, most of intramedullary nailings are performed on a fracture table in supine position. In supine position, however, soft tissue mass of the patients and drapes make it difficult to access to the piriformis fossa and to straighten the trajectory of reamer and nail insertion. To resolve these problems, we have treated twenty intertrochanteric fractures in lateral position on the general operation table with IM nail. Adjustment of the position of lag screw in femoral head was done with the technique that overlaps the shadows of the femoral head, nail and targeting guide in the lateral view. Because the entire injured limb can be moved readily, it was easy to reduce fracture and to convert to open procedure. In cases likely that the fracture table is unavailable in which patients are obese, have short stature or are amputated, and that open procedure is strongly likelihood, lateral position will be helpful technique in the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures with IM nail.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Outcomes of Internal Fixation with Compression Hip Screws in Lateral Decubitus Position for Treatment of Femoral Intertrochanteric Fractures
Cheon-Gon Park, Taek-Rim Yoon, Kyung-Soon Park
Hip & Pelvis.2018; 30(4): 254. CrossRef - The Effects of Sa-Am Spleen-tonifying Acupuncture on Radial Pulse in Healthy Human Subjects
Kwang Sik Yoon, Hyun Lee
The Acupuncture.2013; 30(4): 1. CrossRef
- Outcomes of Internal Fixation with Compression Hip Screws in Lateral Decubitus Position for Treatment of Femoral Intertrochanteric Fractures
- 1,201 View
- 31 Download
- 2 Crossref

Original Article
- The Surgical Outcomes of Clavicle Lateral End Fractures Fixed with the Oblique T Locking Compession Plate
- Seung Oh Nam, Young Soo Byun, Dong Ju Shin, Jung Hoon Shin, Chung Yeol Lee, Tae Gyun Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2011;24(1):41-47. Published online January 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.1.41
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the surgical outcomes of the clavicle lateral end fracture fixed with an oblique T locking compression plate (LCP).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fourteen clavicle lateral end fractures were fixed with the oblique T-LCP and followed up for at least 1 year after the surgery. Thirteen cases were unstable Neer type II fractures and one case was nonunion of the Neer type I fracture. The mean age was 46 years of age (range, 26~70). In ten cases, augmenting sutures with the absorbable suture material were placed in the coraco-clavicular ligament and around the plate and the clavicle to improve the stability of fracture fixation. Autogenous iliac bone graft was done in four cases. The clinical outcomes were evaluated by using UCLA scoring system and KSS (Korean Shoulder Score).
RESULTS
The mean UCLA score was 33.5 and the mean KSS was 94.9. Average time of bone union was 11.9 weeks (range, 6~28), including 1 case with a delayed union. There was no complication such as loss of fixation or nonunion.
CONCLUSION
Fixation with the oblique T-LCP is a good option providing reliable functional results in clavicle lateral end fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Results of Hook Plate Fixation of Unstable Distal Clavicle Fractures
Hoon-Sang Sohn, Byung Chul Jo
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(4): 335. CrossRef
- Results of Hook Plate Fixation of Unstable Distal Clavicle Fractures
- 616 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Report
- Operative Treatment of Bilateral Tibial Tuberosity Fractures in Adolescent: A Case Report
- Hong Kyun Kim, Jung Han Yoo, Yong Wook Park, Jin Soo Park, Kyu Cheol Noh, Kook Jin Chung, Keun Jong Jang, Ji Hyo Hwang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2010;23(3):317-320. Published online July 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.3.317
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Bilateral avulsion fractures of the tibial tubercles are extremely rare. There is no case report about this in Korean literature. We present simultaneous bilateral tibial tuberosity fractures in 14-year-old adolescent male fell on the ground during running. These fractures were managed by open reduction and screw fixation. We gained complete union and removed metal after 6 months. Functional results were excellent 6 month after surgical treatment.
- 408 View
- 1 Download

Original Article
- Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis Using a Lateral Plate in Distal Tibial Fracture
- Oog Jin Shon, Dae Sung Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2010;23(1):42-49. Published online January 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.1.42
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the efficacy of minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) using a lateral plate (Zimmer, Periarticular Lateral Distal Tibial Plates, USA) in distal tibial fracture within 3 cm to plafond, associated with medial soft tissue damage.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From January 2005 to December 2007, 15 patients with distal tibial fracture treated by MIPPO technique using a lateral plate were analyzed. The duration of follow-up was more than 1 year. We evaluated union time by simple X-ray, clinical results by IOWA ankle rating system, and complication.
RESULTS
The bone union was achieved in all cases at average 16.7 weeks. Evaluation of the ankle function test showed an average of 90.3 points, resulting in satisfactory. At the last follow-up, there was no non-union, angular deformity more than 5 degrees or infection.
CONCLUSION
We concluded that MIPPO technique using a lateral plate is a efficient method for high functional recovery with good bone healing and low complication in distal tibial fracture within 3 cm to plafond, associated with medial soft tissue damage. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Anatomically Percutaneous Wiring Reduction in Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Distal Tibial Fractures
Young-Mo Kim, Chan Kang, Deuk-Soo Hwang, Yong-Bum Joo, Woo-Yong Lee, Jung-Mo Hwang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(3): 230. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Osteosynthesis with Locking Compression Plate for Distal Tibia Fractures
Sung-Kyu Kim, Keun-Bae Lee, Keun-Young Lim, Eun-Sun Moon
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(1): 33. CrossRef
- Anatomically Percutaneous Wiring Reduction in Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Distal Tibial Fractures
- 722 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

Case Report
- Bilateral Malunion and Distal Radioulnar Joint Dislocation after Operative Treatment of Bilateral Galeazzi Fractures in Child: A Case Report
- Sang Jin Cheon, Dong Joon Kang, Nam Hoon Moon, Seung Han Cha, He Myung Cho
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(4):292-296. Published online October 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.4.292
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Galeazzi fractures in child is rare and seldom necessary of operative treatment because the result of conservative treatment is good. We present the patient who was a 11-year-old male and fell onto his both hands during a hundred-meter dash. His diagnosis was bilateral Galeazzi fractures and limited open reduction and internal fixation with Kirschner pins was initial treatment at local hospital. After 4 weeks postoperatively, Kirschner pins were removed and rehabilitating exercise was started. After 4 months postoperatively, he was transferred to our hospital due to malunion with severe angular deformities and distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ) dislocation. He was treated with corrective osteotomy. Thus, as in this case, we suggest more careful treatment and observation if conservative method of Galeazzi fracture in child is chosen and consider operative method as treatment according to age and pattern of fracture.
- 580 View
- 1 Download

Original Article
- The Surgical Treatment of Distal Femur Medial Condyle Fracture Using Lateral Anatomical Plate of Opposite Side through Medial Approach
- Sung Sik Ha, Jae Chun Sim, Ki Do Hong, Jae Young Kim, Kwang Hee Park, Yoon Ho Choi
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(4):246-251. Published online October 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.4.246
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate clinical and radiological results of surgical treatment of distal femur medial condyle fracture using lateral anatomical plate of opposite side through medial approach. MATERIALS AND METHODS: This study reviewed the results of 9 cases of distal femur medial condyle fracture treated with lateral anatomical plate of opposite side through medial approach from December 2005 to June 2007, after a follow up of more than 12 months. There were 2 males and 7 females with a mean age of 63.1 (57~72) years. The clinical results were evaluated using the Schatzker's criteria, and the radiographic results were evaluated using the bone union time. RESULTS: Using the Schatzker's criteria, 7 cases of the 9 patients (78%) showed exellent results. The mean time for bone union was 13.4 (11~15) weeks. There were 3 cases of pain on full weight bearing same as previous operative state by degenerative osteoarthritis. There weren't complications as joint stiffness, infection, varus & rotational deformity, malunion, nonunion, and metal failure. CONCLUSION: Plate fixation using medial approach provides the proper anatomical reduction and stronger fixation, and outcome good results. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Medial Plating of Distal Femoral Fracture with Locking Compression Plate-Proximal Lateral Tibia: Cases' Report
Se-Ang Jang, Young-Soo Byun, In-Ho Han, Dongju Shin
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2016; 29(3): 206. CrossRef
- Medial Plating of Distal Femoral Fracture with Locking Compression Plate-Proximal Lateral Tibia: Cases' Report
- 1,339 View
- 21 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Reports
- Ipsilateral Femoral Segmental and Tibial Fractures : A Case Report
- Oog Jin Sohn, Chul Hyun Park, Sang Keun Bae
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(3):193-196. Published online July 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.3.193
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The ipsilateral femoral segmental and tibial fractures seldom occur such as traffic accidents needed high energy mechanisms. For these fractures, surgical stabilization and early mobilization of joint produce can be the best clinical outcomes. We have experienced a case of ipsilateral femoral segmental and tibial fracture and gained good clinical results with surgical treatment. We have reported here on this case and included a review of the relevant literature.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Outcome after Treatment of Tibia Segmental Fracture with Intramedullary Nailing and Minimal Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis
Jun Young Lee, Hyung Seok Park, Dong Hyuk Cha
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2020; 33(3): 142. CrossRef
- Clinical Outcome after Treatment of Tibia Segmental Fracture with Intramedullary Nailing and Minimal Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis
- 810 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Bilateral PCL Avulsion Fracture from Tibial Attatchment Site in a 16-years-old Male : A Case Report
- Hee Gon Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(3):189-192. Published online July 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.3.189
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture is occurred by high energy trauma, usually in motor vehicle accident or sports injury. Bilateral posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture is not yet reported in Korea. Authors report a case of bilateral posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture in 16-years-old man treated with anatomical reduction and internal fixation with a review of literature.
- 375 View
- 1 Download

- Irreducible Dislocation of the Interphalangeal Joint of the Great Toe with Lateral Collateral Ligament Entrapment: A Case Report
- Duke Whan Chung, Bi O Jeong
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(2):110-113. Published online April 30, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.2.110
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Dislocations of the interphalangeal joint of the great toe that are irreducible are very rare. Invagination of the plantar plate or the sesamoid bone into the IP joint, which prevents reduction. To our knowledge, however, dislocations of the IP joint of the great toe that were irreducible because of lateral collateral ligament entrapment, not invagination of the plantar plate or the sesamoid bone, have not been reported by any English literature. We report a 29-year-old ballet dancer who sustained an irreducible dislocation of the interphalangeal joint of the great toe owing to lateral collateral ligament entrapment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Open Reduction of a Dislocation of the Interphalangeal Joint of the Great Toe Neglected for 6 Weeks
Jae Kwang Kim, Rag-Gyu Kim
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2011; 46(5): 426. CrossRef
- Open Reduction of a Dislocation of the Interphalangeal Joint of the Great Toe Neglected for 6 Weeks
- 958 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Article
- A Comparison of Extensile Lateral Approach and Sinus Tarsi Approach for the Sanders Type II Calcaneal Fracture
- Jeong Seok Moon, Woo Chun Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(1):13-18. Published online January 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.1.13
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To compare the clinical results between the extensile lateral approach and sinus tarsi approach in the open reduction of the Sanders type II calcaneal fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From July 2002 to Februry 2007, thirty two patients having thirty three calcaneal fractures of Sanders type II were managed with open reduction and internal fixation using the extensile lateral approach or sinus tarsi approach. The mean age of 19 patients using extensile lateral approach was 43.3 years. The mean age of 13 patients using sinus tarsi approach was 46.3 years. Clinical outcome, radiographic parameters, and postoperative complications were compared between both groups.
RESULTS
There was no difference between two groups associated with patients demographs. The mean AOFAS score and VAS between both groups were not different (p=0.716, p=0.774). The mean Bohler's angle and Gissane's angle between both groups were not different (p=0.343, p=0.357). Two cases of sural nerve injury, one malunion, and one deep infection were occurred in the group of extensile lateral approach. However, patients using sinus tarsi approach had no postoperative complications.
CONCLUSION
The clinical results of sinus tarsi approach may be comparable with those of extensile lateral approach, with the advantages of reduced risk of postoperative complications. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Extensile Lateral Approach to the Calcaneus
Rohan Bhimani, Kush C. Shah, Rishin J. Kadakia
Techniques in Foot & Ankle Surgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Extensile lateral versus sinus tarsi approach for calcaneal fractures
Chuangang Peng, Baoming Yuan, Wenlai Guo, Na Li, Heng Tian
Medicine.2021; 100(31): e26717. CrossRef - Lateral Extensile Approach Versus Minimal Incision Approach for Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Displaced Intra-articular Calcaneal Fractures: A Meta-analysis
Andrea Seat, Christopher Seat
The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery.2020; 59(2): 356. CrossRef - Surgical Treatment of Calcaneal Fractures of Sanders Type II and III by A Minimally Invasive Technique with 6.5 mm Cancellous Screw
Yong Seung Oh, Kyung Ho Lee, Jung Ho Kim, Myoung Jin Lee
Journal of Korean Foot and Ankle Society.2019; 23(3): 116. CrossRef - A systematic review and meta-analysis of the sinus tarsi and extended lateral approach in the operative treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures
Tomasz L. Nosewicz, Siem A. Dingemans, Manouk Backes, Jan S.K. Luitse, J. Carel Goslings, Tim Schepers
Foot and Ankle Surgery.2019; 25(5): 580. CrossRef - Meta‐analysis of two surgical approaches for calcaneal fractures: sinus tarsi versus extensile lateral approach
Fei Zhang, Hongtao Tian, Shilun Li, Bo Liu, Tianhua Dong, Yanbin Zhu, Yingze Zhang
ANZ Journal of Surgery.2017; 87(3): 126. CrossRef - Usefulness of Treatment with 6.5 mm Cancellous Screw and Steinmann Pin Fixation for Calcaneal Joint Depression Fracture
Gi-Soo Lee, Chan Kang, Deuk-Soo Hwang, Chang-Kyun Noh, Gi-Young Lee
Journal of Korean Foot and Ankle Society.2015; 19(1): 11. CrossRef - Open reduction and internal fixation with conventional plate via L-shaped lateral approach versus internal fixation with percutaneous plate via a sinus tarsi approach for calcaneal fractures – A randomized controlled trial
Shengli Xia, Yaogang Lu, Huizhong Wang, Zuming Wu, Ziping Wang
International Journal of Surgery.2014; 12(5): 475. CrossRef - Intra-articular Calcaneal Fractures Treated with Open Reduction and Internal Fixation -A Comparative Study between Groups with and without Bone Graft-
Hong Moon Sohn, Sang Ho Ha, Jun Young Lee, Sung Hwan Jo, Hoon Yang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(2): 180. CrossRef
- The Extensile Lateral Approach to the Calcaneus
- 937 View
- 6 Download
- 9 Crossref

Case Report
- Lateral Dislocation of the First Metatarsophalangeal Joint: A Case Report
- Yeong Sik Yun, Young Mo Kim, Kyung Cheon Kim, Pil Sung Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2008;21(4):312-315. Published online October 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.4.312
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Dislocation of the metatarsophalangeal joint is rare due to the stability of the ligaments and soft tissue surrounding the joint. The authors have experienced lateral dislocation of the first metatarsophalangeal joint, which required surgery, accompanied by complete injuries of medial collateral ligament and capsule, contributing to medial stability, differing from posterior dislocation with intersesamoid complex rupture, with a review of the relevant literature and previous reported cases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Unusual Combination of Injuries Involving Lateral Dislocation of the First and Fifth Metatarsophalangeal Joints Along With Fractures of the Other Toes on the Same Foot: A Report of a Rare Case
Mohamed Jiddi, Georges F Bassil, Zied Missaoui
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Dislocation of the first metatarsophalangeal joint concomitant with Lisfranc joint dislocation in a 45-year-old man
Kanoko Mizumoto, Tadashi Kimura, Makoto Kubota, Mitsuru Saito
BMJ Case Reports.2021; 14(6): e243004. CrossRef - Rare Lateral Dislocation of the First Metatarsophalangeal Joint: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Amir Reza Vosoughi, Pascal F. Rippstein
The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery.2017; 56(2): 375. CrossRef
- An Unusual Combination of Injuries Involving Lateral Dislocation of the First and Fifth Metatarsophalangeal Joints Along With Fractures of the Other Toes on the Same Foot: A Report of a Rare Case
- 820 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref

Original Articles
- Anterolateral Thigh Island Flap
- Jae Hoon Lee, Il Hoen Choi
- J Korean Fract Soc 2008;21(3):207-212. Published online July 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.3.207
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To present the author's experience using the anterolateral thigh island flap for reconstruction of soft tissue defects around the hip and perineum.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Proximal based anterolateral thigh island flaps were performed to reconstruct the soft tissue defects at the perineum (3 patients) and the greater trochanter of the hip (one patient) in 4 patients. All patients were male. Mean age was 43 years (range, 32 to 50 years) and mean follow-up was 8 months (range, 6 to 13 months). The causes of the defects were traffic accident in 2 cases, necrotizing fasciitis 1 case, and pressure sore 1 case. Average size of the flap was 14x9 cm. Fasciocutaneous flaps were performed in 3 patients and musculocutaneous flap was performed in one patient.
RESULTS
All flaps were survived. There were no necrosis of the flaps. One flap presented venous congestion after surgery, which resolved with the decompression of the pedicle. Reconstruction with the anterolateral thigh island flap resulted in no recurrence of the infection or ulcer and good esthetic contour.
CONCLUSION
The anterolateral thigh island flap is a reliable flap for reconstruction around the perineum and hip joint.
- 510 View
- 0 Download

- In Situ Late Metaphyseal Osteosynthesis for the Fractures of the Lateral Humeral Condyle in Children
- Kun Bo Park, Seung Whan Lee, Hyun Woo Kim, Hui Wan Park, Ki Seok Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2008;21(2):151-156. Published online April 30, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.2.151
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the efficacy of the in situ late osteosynthesis for slightly displaced fractures of the lateral humeral condyle.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From 2000 to 2004, 12 patients (8 boys and 4 girls) were managed with in situ late osteosynthesis for fractures of the lateral humeral condyle. The average age at the time of operation was 6 years 1 month (1 year 7 months~9 years 1 month), and the mean amount of fragment displacement was 3.3 mm (2.0~4.5 mm). The operative procedure included curettage and in situ fixation of the fragment RESULTS: Bony union was achieved in all cases after avg. 48 months (33~73 months) follow-up assessment. According to the score system of Dhillon et al, 7 patients had excellent, 3 had good, 2 had fair results. None of the patients developed avascular necrosis or premature closure of the epiphysis.
CONCLUSION
We suggest that in situ fixation is an effective method for the late treatment of slightly displaced fracture of the lateral humeral condyle.
- 453 View
- 0 Download

Case Report
- Traumatic Bilateral Anterior Hip Dislocation: A Case Report
- Sung Taek Jung, Hyun Jong Kim, Myung Sun Kim, Young Jin Kim, Sang Kwan Cho
- J Korean Fract Soc 2008;21(1):62-65. Published online January 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.1.62
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Traumatic anterior dislocation of the hip is an uncommon injury, accounting for less than 10% of all reported cases of traumatic hip dislocation. Especially, there are no known report in our country so far. We are reporting a case of a 81 year old man who sustained bilateral anterior hip dislocation after pedestrian traffic accident, and treated by closed reduction and skeletal traction at our institute.
- 355 View
- 2 Download

Original Article
- Surgical Fixation with Biodegradable Plate for the Treatment of Ankle Fractures
- Jae Young Cho, Jin Whan Kim, Sang Eun Kim, Kyung Chil Jung, Seung Hyun Choi
- J Korean Fract Soc 2008;21(1):31-36. Published online January 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.1.31
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this article is to show the efficacy of a biodegradable plate for treating lateral malleolar fractures in the ankle joint.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The 20 patients who underwent an open reduction and internal fixation for lateral malleolar fractures in the ankle joint from February, 2006 to February, 2007 in our hospital were enrolled into the study. The average age of the patients was 49.7 years and the average follow-up period was 5.6 months. The cases were analyzed by radiological bone union time and clinical results according to the criteria of Meyer et al.
RESULTS
Average radiological bone union time was 10.5 weeks. The clinical result was excellent in 19 cases (95%), good in 1 case (5%). There was one case of minimal displacement less than 1 mm, associated with anterior distal tibio-fibular ligament avulsion fracture.
CONCLUSION
For proper patients, a biodegradable plate is an effecttive alternative implant for stabilizing lateral malleolar fractures in the ankle joint, because there is no requirement for subsequent removal and slow resorption in vivo. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Delayed Foreign-body Reaction of Ankle Fracture Treated with a Biodegradable Plate and Screws - A Case Report -
Chul-Hyun Park, Dae-Hyun Song, Jae Ho Cho
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2012; 25(2): 142. CrossRef
- Delayed Foreign-body Reaction of Ankle Fracture Treated with a Biodegradable Plate and Screws - A Case Report -
- 704 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Report
- Traumatic Simultaneous Bilateral Hip Dislocation in the Elderly Patient: A Case Report
- Koing Woo Keon, Sang Bong Ko
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(4):335-338. Published online October 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.4.335
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Traumatic simultaneous bilateral hip dislocation is reported rarely, but the most of them are limited in young patients. The authors managed the elderly patients whose both hip was dislocated traumatically, simultaneously and who didn't have any other underlying disease and other associated fracture - femur, hip joint and pelvis, with a review of the relevant literature.
- 403 View
- 1 Download

Original Article
- Comparison of Operative Methods between Retrograde and Antegrade Nailing for Ipsilateral Femoral Shaft and Neck Fracture
- Chang Wug Oh, Jong Keon Oh, Woo Kie Min, Shin Yoon Kim, Seung Hoon Baek, Byung Chul Park, Hyung Soo Ahn, Tae Gong Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(2):135-140. Published online April 30, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.2.135
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To compare retrospectively the antegrade and retrograde nailing in the management of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty-two patients (thirty-three injuries) were included in this study. Mean age of patients was 38 years-old in the antegrade nailing group (16 injuries) and 44 years-old in the retrograde nailing group (17 injuries). We compared the union of fractures and complications between two groups, and investigated the influencing factors.
RESULTS
Femoral shaft fracture was united in 10 cases (63%) of antegrade group and 12 cases (71%) of retrograde group, at 28.2 and 27.3 weeks respectively. Nonunion was more prevalent in Winquist-Hansen III and IV (5 in antegrade nailing, 3 in retrograde nailing) than I and II. Femoral neck fracture was united with 1 case of nonunion in each group. Nonunion developed from Garden stage IV, but fractures of Garden stage I and II united regardless of methods.
CONCLUSION
In ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures, the kinds of methods did not affect the results of shaft fractures. Minimally displaced neck fractures also were not influenced by kinds of methods, but retrograde nailing may have a benefit in fixing the displaced neck fractures -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surgical management of bifocal femoral fractures: a systematic review and pooled analysis of treatment with a single implant versus double implants
J. D. Cnossen, Esther M. M. Van Lieshout, Michael H. J. Verhofstad
Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery.2023; 143(10): 6229. CrossRef - Retrograde Intramedullary Nailing or the Treatment of Segmental Femoral Shaft Fracture Including Distal Part
Jong-Ho Yoon, Byung-Woo Ahn, Chong-Kwan Kim, Jin-Woo Jin, Ji-Hoon Lee, Hyun-Ku Cho, Joo-Hyun Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(3): 145. CrossRef - The Treatment of IM Nailing of Femoral Shaft Fracture: Piriformis Fossa versus Trochanteric Entry Portal
Hyun Kook Youn, Oog Jin Shon, Dong Sung Han
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2008; 21(3): 200. CrossRef
- Surgical management of bifocal femoral fractures: a systematic review and pooled analysis of treatment with a single implant versus double implants
- 714 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Crossref

Case Report
- Old Atlantoaxial Rotary Subluxation Associated with High-riding Vertebral Arteries: Arthrodesis Using C1 Lateral Mass Screws and C2 Laminar Screws: A Case Report
- Kyeong Hwan Kim, Jin Sup Yeom, Kun Woo Park, Soon Woo Hong, Bong Soon Chang, Choon Ki Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(1):90-93. Published online January 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.1.90
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To the best of our knowledge, there has been no domestic report on posterior atlantoaxial fusion with segmental screw fixation using C2 laminar screws and C1 lateral mass screws for atlantoaxial subluxation. We report the result of this operation performed in a patient with old atlantoaxial rotary subluxation who required posterior fusion. We chose this technique in this patient because wire fixation was not suitable due to osteoporosis, and transarticular screw fixation and use of C2 pedicle screws were not feasible due to the peculiar bony anatomy of the axis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Indirect Decompression using Segmental Screw Fixation for Cervical Myelopathy Caused by C1-2 Subluxation - Technical Note -
Yoon Jong Kim, Kyeong Hwan Kim, Jong Hwa Won, Hak Jin Min, Ui Seong Yoon, Jin Sup Yeom
The Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2007; 42(6): 815. CrossRef
- Indirect Decompression using Segmental Screw Fixation for Cervical Myelopathy Caused by C1-2 Subluxation - Technical Note -
- 667 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- Lateral Condylar Fracture of the Humerus in Children: An Epidemiological Analysis of 158 Cases
- Chul Hyun Cho, Kwang Soon Song, Sung Won Sohn, Ki Chul Bae, Jung Hoon Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(4):466-470. Published online October 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.4.466
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To analyze the correlation of various factors by examining the epidemiology of lateral condylar fracture of the humerus which is the second most fracture among elbow fractures in children.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Of 158 cases treated for lateral condylar fracture of the humerus in children from April 1996 to March 2006, their age and sex distribution, the seasonal frequency, etiology, type of fracture, method of treatment, etc. were analyzed retrospectively.
RESULTS
Boys were 113 cases, girls were 45 cases, and the mean age was 5.4 years. Regarding the seasonal occurrence, spring 43 cases, summer 44 cases, autumn 48 cases, and winter 23 cases had occurred. It occurred preferentially during the season when outdoor activity was most active. As its etiology, the accident in a playground was 39 cases, sports activity was 32 cases, traffic accident was 17 cases, slipping accident at home was 15 cases, falling accident at home was 14 cases, slip while playing with friends was 6 cases, a missing step while walking on stairs was 6 cases, fall from a height more than 2 floors was 4 cases, and the cases with unknown cause were 25 cases. According to the Jakob stage, the stage I was 42 cases, the stage II 77 cases, and the stage III was 39 cases. As treatment, cast immobilization was performed in 34 cases, closed reduction and percutaneous K-wire fixation was performed in 68 cases, and open reduction and K-wire fixation was performed in 56 cases. The prevalent causalities were play devices, accident during sports activity, and traffic accident, and in such cases, the displacement of fracture was severe and thus surgical treatments were performed in many cases (94%).
CONCLUSION
It is thought that during the season when outdoor action is active, particularly, for kindergarten children or the lower grade primary school children, safety education is required to prevent the fracture by play devices, sports activity and traffic accident. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Pattern of Occurrence of Fractures in Children and Adolescents and Its Managements Based on the Database of the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service
Yong-Wook Kwon, Soon-Hyuck Lee, Hyun-Woo Kim, Jin-Ho Hwang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2014; 27(4): 308. CrossRef
- The Pattern of Occurrence of Fractures in Children and Adolescents and Its Managements Based on the Database of the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service
- 575 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Treatment of Displaced Supracondylar Fracture of the Humerus in Children
- Soon Hyuck Lee, Sang Won Park, Woong Kyo Jeong, Dae Hee Lee, Soon Yong Yoo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(4):460-465. Published online October 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.4.460
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the radiological and clinical outcomes after operative treatment of displaced supracondylar fractures in children with lateral K-wire fixation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
69 displaced supracondylar fractures treated by closed reduction and percutaneous lateral K-wire fixation were included in this study. Carrying angle and range of motion were measured and graded by the Flynn criteria. To assess the accuracy of the reduction, Baumann angle and lateral humerocapital angles were compared to the contralateral side, and to evaluate the stability of fixation both measurements were taken immediately postoperatively and after K-wire removal.
RESULTS
55 cases (80%) were categorized as excellent and 12 cases (17%) as good. There were no significant statistical differences in Baumann angle and lateral humerocapital angle between postoperative and K-wire removal. Although there were 9 cases that showed differences in Baumann angle and 32 cases in lateral humerocapital angle of more than 10 degrees compared to the opposite side at the immediate postoperative radiograph, 9 cases showed satisfactory clinical results.
CONCLUSION
Closed reduction and lateral K-wire fixation is considered as an acceptable modality of the treatment of displaced supracondylar fractures in children, and clinical outcome is more closely correlated with carrying angle and stability of fracture site rather than rotational deformity or hyperextension of fragment measured radiographically.
- 334 View
- 0 Download

- Comparison of Open Fixation and Closed Percutaneous Pinning in Jakob Stage II Lateral Condylar Fractures of Children
- Eui Sung Choi, Dong Soo Kim, Hyun Chul Shon, Yong Min Kim, Kyoung Jin Park, Jun Mo Jeon, Gee Kang Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(2):277-282. Published online April 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.2.277
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare the results of open fixation and closed percutaneous pinning in managing Jakob stage II lateral condylar fractures of children's elbow.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Since Febuary 2000, We operated 21 children with Jakob stage II lateral condylar fractures of elbow. Eleven of the 21 were treated with closed percutaneous pinning, open fixation was done to the other 10 children. Each patient was evaluated about range of motion, carrying angle, scar satisfaction and radiologic findings for comparison between closed pinning and open fixation groups.
RESULTS
Open fixation group showed 3.8 degrees decrease of elbow motion while closed pinning group showed no significant decrease. Carrying angle and radiologic findings were not different between the two groups. Open fixation group expressed dissatisfaction to their scars (average 5.2 cm) whereas all the patients of closed pinning group were satisfied with their functional and cosmetic outcomes.
CONCLUSION
In managing Jakob stage II lateral condyle fractures of children's elbow, closed percutaneous pinning was thought to be superior to open fixation because of the same functional outcome and much better cosmetic results.
- 355 View
- 0 Download

- Lateral Plate Fixation of Distal Tibial Metaphyseal Fracture Using Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis Technique
- Ki Do Hong, Sung Sik Ha, Nam Sik Chung, Jae Cheon Sim, Sang Cheon Ahn
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(1):24-28. Published online January 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.1.24
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the efficiency of lateral plate fixation using minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) technique as a treatment of distal tibial metaphyseal fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Among the patient who were treated from March, 2002 to September, 2004, the cases of twenty patients with distal tibial metaphyseal fracture treated by lateral plate fixation using MIPO technique who were able to be followed up for at least one-year period were reviewed in this study. According to AO/OTA classification, five were type A1, twelve cases were type A2 and other three cases were type A3, and among them two cases were open fracture type I according to the Gustillo-Anderson classification. Radiologic studies and clinical assessment described by Daniel et al and complication following the treatment were evaluated.
RESULTS
At a mean of 16.4 weeks (range 11 to 23), all fractures united without secondary procedures. According to clinical assessment, all cases had good and excellent result, and there were no complications.
CONCLUSION
The lateral plate fixation using MIPO technique of distal tibial metaphyseal fracture is an efficient method of treatment with high functional recovery rate which minimize soft tissue damage, decreases the risk of infection and incidence of nonunion at the same time as the classic MIPO technique does, and it is a useful alternative method when there is a anteromedial soft tissue damage. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Fractures of Distal Tibia
Tae Hun Kim, So Hak Chung
Kosin Medical Journal.2014; 29(1): 23. CrossRef - Staged Protocol in Treatment of Open Distal Tibia Fracture: Using Lateral MIPO
Oog Jin Sohn, Dong Hwa Kang
Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery.2011; 3(1): 69. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis Using a Lateral Plate in Distal Tibial Fracture
Oog Jin Shon, Dae Sung Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(1): 42. CrossRef
- Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Fractures of Distal Tibia
- 588 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref

Case Report
- Bilateral Femoral Neck Fractures in a Young Adult: A Case Report
- Eea Sub Chung, Jae Kyu Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(4):478-480. Published online October 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.4.478
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ipsilateral femur shaft and neck fractures are occurred by high energy trauma, usually in motor vehicle accidents or fall from a height. Simultaneous Ipsilateral femur shaft and neck fractures and contralateral femur neck fracture are not yet reported in Korea. Authors report a case of simultaneous bilateral femoral neck fractures combined with a ipsilateral femoral shaft fracture in a young adult treated with anatomical reduction, internal fixation and vascularized bone graft with a review of the literature.
- 386 View
- 2 Download

Original Articles
- Internal Fixation of Clavicle Lateral and Fracture with Mini T-plate
- Byung Woo Ahn, Jong Ho Yoon, Chong Kwan Kim, Sung Won Chung, Young Il Kwan, Young Ho Lee, Chan Wan Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(4):410-414. Published online October 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.4.410
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the effectiveness of a mini T-plate fixation in clavicle lateral end fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed eleven cases of calvicle lateral end fracture which were treated with open reduction and internal fixion with mini T-plate from May 2000 to December 2004. The follow up period was 12 months minimum. The radiologic result, pain and shoulder function were evaluated by the ASES shoulder score.
RESULTS
All cases showed satisfactory results. Seven cases (63%) were excellent, and four (37%) cases were good. There were no fair or poor results. All cases showed radiologic union by the fifteenth week. No complications such as metal breakage, limited motion, infections were seen.
CONCLUSION
This study demonstrates that using a mini T-plate fixation which is easy and induces no injury of acromiocalvicular joint, contributes to provide stable fixation in clavicle lateral end fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Tension Band Wiring for Distal Clavicle Fracture: Radiologic Analysis and Clinical Outcome
Seong Cheol Moon, Chul Hee Lee, Jong Hoon Baek, Nam Su Cho, Yong Girl Rhee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2014; 27(2): 127. CrossRef - The Surgical Outcomes of Clavicle Lateral End Fractures Fixed with the Oblique T Locking Compession Plate
Seung-Oh Nam, Young-Soo Byun, Dong-Ju Shin, Jung-Hoon Shin, Chung-Yeol Lee, Tae-Gyun Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(1): 41. CrossRef - Comparison of Results of Tension Band Wire and Hook Plate in the Treatment of Unstable Fractures of the Distal Clavicle
Chul-Hyun Park, Oog-Jin Shon, Jae-Sung Seo
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(1): 55. CrossRef
- Tension Band Wiring for Distal Clavicle Fracture: Radiologic Analysis and Clinical Outcome
- 525 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Treatment using Reduction of Lateral and Posterior Displacement in Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures of the Elderly
- Jae Ang Sim, Jang Seok Choi, Do Hyun Moon, Seung Jun Ahn
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(4):390-393. Published online October 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.4.390
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the advantages of reduction of lateral and posterior displacement in unstable intertrochanteric fractures of the elderly.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From January, 1997 to December, 2001, we reviewed 23 cases of unstable intertrochanteric fractures in the elderly, which underwent by reduction of lateral and posterior displacement. Using the device of internal fixation is dynamic compression hip screw (DHS), the follow up period was minimally 12 months (mean 16 months). We estimated the clinical results, the radiologic results and complications.
RESULTS
The satisfactory results was regarded as walking with walking frame and 21 cases (91.3%) showed satisfactory results. The average period of radiologic union was 18 weeks. The average sliding of lag screw was 5.3 mm and the average changes of femoral neck-shaft angle was 2.6 degree. As for the complications, 2 cases showed superficial infection and 2 cases showed pain over trochanteric area.
CONCLUSION
In the unstable intertrochanteric fractures of the elderly, treatment with reduction of lateral and posterior displacement can be considered one of reduction technique. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unstable Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture Treated with Mini-incision Reduction Technique and Intramedullary Nail
Oog Jin Shon, Dae Sung Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(1): 13. CrossRef
- Unstable Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture Treated with Mini-incision Reduction Technique and Intramedullary Nail
- 625 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Clinical Distribution of Bilateral Non-contemporary Hip Fractures in Elderly Patients
- Hyung Ku Yoon, Duck Yun Cho, Dong Eun Shin, Sang Jun Song, Jong Hyun Kim, Byung Ho Yoon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(4):375-378. Published online October 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.4.375
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the clinical distribution of bilateral non-contemporary hip fractures regarding to fractures type, risk factors and fractures interval in elderly patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
24 bilateral non-contemporary cases among 621 hip fractures from Sep. 1997 to Dec. 2004 were evaluated regarding to gender, age, incidence, Singh index, causes, interval, fracture pattern, operative methods and underlying diseases between the two fractures retrospectively.
RESULTS
The distribution is as follows: males to females (5:19), incidence (3.86%), mean age (76.9 years and 78.9 years), average Singh index 2.5 degree (2~4) and 2.1 degree (1~3) respectively. 21 cases (87.5%) in both fractures suffered from minor slips and 19 cases (79.1%) occured within 3 years of the first fracture and 17 (68.1%) cases were same type fractures. Bipolar hemiarthroplasty was performed in 12 cases. All but one patient had underlying cardiovascular diseases and CVA sequales.
CONCLUSION
To prevent the bilateral non-contemporary hip fractures, surgeons must bear in mind that osteoporosis treatment, control of underlying cardiovascular diseases and CVA sequales, and the effective rehabilitation is very important. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Does the Time of Postoperative Bisphosphonate Administration Affect the Bone Union in Osteoporotic Intertrochanteric Fracture of Femur?
Yoon Je Cho, Young Soo Chun, Kee Hyung Rhyu, Joon Soon Kang, Gwang Young Jung, Jun Hee Lee
Hip & Pelvis.2015; 27(4): 258. CrossRef - Sequential Hip Fractures in Elderly Osteoporotic Patients
Soojae Yim, Yuseok Seo, Sanghyok Lee, Joonghyun Ahn
Hip & Pelvis.2012; 24(4): 309. CrossRef - Effect of Intravenous Administration of Bisphosphonate for Patients Operatively Treated for Osteoporotic Hip Fracture
Sang Hong Lee, Woong Chae Na, Yi Kyu Park
Hip & Pelvis.2012; 24(2): 133. CrossRef
- Does the Time of Postoperative Bisphosphonate Administration Affect the Bone Union in Osteoporotic Intertrochanteric Fracture of Femur?
- 559 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


