Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 23(1); 2010 > Article
-
Original Article
- Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis Using a Lateral Plate in Distal Tibial Fracture
- Oog Jin Shon, M.D., Dae Sung Kim, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2010;23(1):42-49.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.1.42
Published online: January 31, 2010
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Oog Jin Shon, M.D. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yeungnam University Hospital, 317-1, Daemyeong-dong, Nam-gu, Daegu 705-717, Korea. Tel: 82-53-620-3645, Fax: 82-53-628-4020, min1913@hanmail.net
• Received: May 18, 2009 • Revised: August 12, 2009 • Accepted: October 25, 2009
Copyright © 2010 The Korean Fracture Society
- 721 Views
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- To evaluate the efficacy of minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) using a lateral plate (Zimmer, Periarticular Lateral Distal Tibial Plates, USA) in distal tibial fracture within 3 cm to plafond, associated with medial soft tissue damage.
-
Materials and Methods
- From January 2005 to December 2007, 15 patients with distal tibial fracture treated by MIPPO technique using a lateral plate were analyzed. The duration of follow-up was more than 1 year. We evaluated union time by simple X-ray, clinical results by IOWA ankle rating system, and complication.
-
Results
- The bone union was achieved in all cases at average 16.7 weeks. Evaluation of the ankle function test showed an average of 90.3 points, resulting in satisfactory. At the last follow-up, there was no non-union, angular deformity more than 5 degrees or infection.
-
Conclusion
- We concluded that MIPPO technique using a lateral plate is a efficient method for high functional recovery with good bone healing and low complication in distal tibial fracture within 3 cm to plafond, associated with medial soft tissue damage.
- 1. Anglen JO. Early outcome of hybrid external fixation for fracture of the distal tibia. J Orthop Trauma, 1999;13:92-97.
- 2. Asche G. Result of the treatment of femoral and tibial fractures following interlocking nailing and plate osteosynthesis. A comparative retrospective study. Zentralbl Chir, 1989;114:1146-1154.
- 3. Borg T, Larsson S, Lindsjo U. Minimally-invasive plating of distal tibia fractures: preliminary results in 21 patients. Injury, 2004;35:608-614.
- 4. Borrelli J Jr, Prickett W, Song E, Becker D, Ricci W. Extraosseous blood supply of the tibia and the effects of different plating techniques: a human cadaveric study. J Orthop Trauma, 2002;16:691-695.
- 5. Brumback RJ, McGarvey WC. Fractures of the tibial plafond. Orthop Clin North Am, 1995;26:273-285.
- 6. Fan CY, Chiang CC, Chuang TY, Chiu FY, Chen TH. Interlocking nails for displaced metaphyseal fractures of the distal tibia. Injury, 2005;36:669-674.
- 7. Hahn D, Bradbury N, Hartley R, Radford PJ. Intramedullary nail breakage in distal fractures of the tibia. Injury, 1996;27:323-327.
- 8. Helfet DL, Shonnard PY, Levine D, Borrelli J Jr. Minimally Invasive plate osteosynthesis of distal fractures of the tibia. Injury, 1997;28:A42-A47.
- 9. Helfet DL, Suk M. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis of fractures of the distal tibia. Instr Course Lect, 2004;53:471-475.
- 10. Holbrook JL, Swiontkowski MF, Sanders R. Treatment of open fractures of the tibial shaft: ender nailing versus external fixation. A randomized, prospective comparison. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1989;71:1231-1238.
- 11. Hong KD, Ha SS, Chung NS, Sim JC, Ahn SC. Lateral fixation of distal tibial metaphyseal fracture using minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis technique. J Korean Fract Soc, 2006;19:24-28.
- 12. Kim YM, Yang JH, Kim DK. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis using periarticular plate for distal tibial fractures. J Korean Fract Soc, 2007;20:315-322.
- 13. Krackhardt T, Dilger J, Flesch I, Höntzsch D, Eingartner C, Weise K. Fractures of the distal tibia treated with closed reduction and minimally invasive plating. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, 2005;125:87-94.PDF
- 14. Maffulli N, Toms AD, McMurtie A, Oliva F. Minimally-invasive plating of distal tibial fractures. Int Orthop, 2004;28:159-162.
- 15. Marsh JL, Bonar S, Nepola JV, Decoster TA, Hurwitz SR. Use of an articulated external fixator for fractures of the tibial plafond. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1995;77:1498-1509.
- 16. Marsh JL, Weigel DP, Dirschl DR. Tibial plafond fractures. How do these ankles function over time? J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2003;85:287-295.
- 17. Merchant TC, Dietz FR. Long-term follow-up after fractures of tibial and fibular shafts. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1989;71:599-606.
- 18. Oh CW, Kyung HS, Park IH, Kim PT, Ihn JC. Distal tibia metaphyseal fractures treated by percutaneous plate osteosynthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 2003;408:286-291.
- 19. Pai V, Coulter G, Pai V. Minimally invasive plate fixation of the tibia. Int Orthop, 2007;31:491-496.PDF
- 20. Puno RM, Teynor JT, Nagano J, Gustilo RB. Critical analysis of result of 201 tibial shaft fracture. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1986;212:113-121.
- 21. Redfern DJ, Syed SU, Davies SJ. Fractures of the distal tibia: minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. Injury, 2004;35:615-620.
- 22. Robinson CM, McLauchlan GJ, McLean IP, Court-Brown CM. Distal metaphyseal fractures of the tibia with minimal involvement of the ankle. Classification and treatment by locked intramedullary nailing. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1995;77:781-787.PDF
- 23. Rüedi TP, Allgöwer M. The operative treatment of intra-articular fractures of the lower end of the tibia. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1979;138:105-110.
- 24. Saleh M, Shanahan MD, Fern ED. Intra-articular fractures of the distal tibia: surgical management by limited internal fixation and articulated distraction. Injury, 1993;24:37-40.
- 25. Shepherd LE, Costigan WM, Gardocki RJ, Ghiassi AD, Patzakis MJ, Stevanovic MV. Local or free muscle flaps and unreamed interlocked nails for open tibial fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1998;350:90-96.
- 26. Yoo SH, Ahn SJ, Song MH, Kim BH, Lee MS, Park JH. The comparison of MIPPO vs open plate fixation in the treatment of the distal tibia fracture. J Korean Fract Soc, 2006;19:29-33.
- 27. Wolinsky P, Lee M. The distal approach for anterolateral plate fixation of the tibia: an anatomic study. J Orthop Trauma, 2008;22:404-407.
REFERENCES
Fig. 1
(A) The initial film shows a comminuted fracture of the distal tibia with medial open wound.
(B) Lateral plate was inserted anterolaterally through mini skin incision.
(C) The location and size of plate was verified by C-arm.
(D) Postoperative radiograph shows satisfactory position of plate and screws.
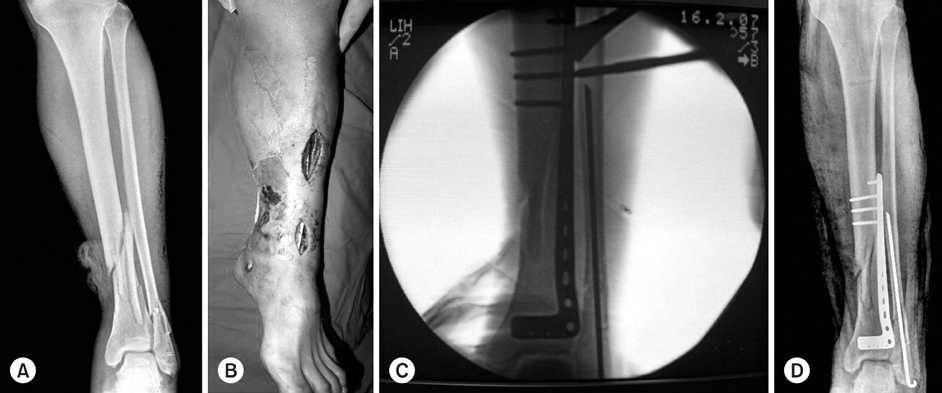

Fig. 2
(A) A 64 year old man sustained a right distal tibial fracture (AO/OTA type 43, A3) with medial open wound after traffic accident.
(B) First, lateral malleolar fracture was fixed using MIPPO technique, and bridge external fixator was applied.
(C) After 3 weeks, lateral plate fixation of distal tibia using MIPPO technique was performed, and postoperative radiograph at 1 year after the injury shows solid bony union and satisfactory alignment.
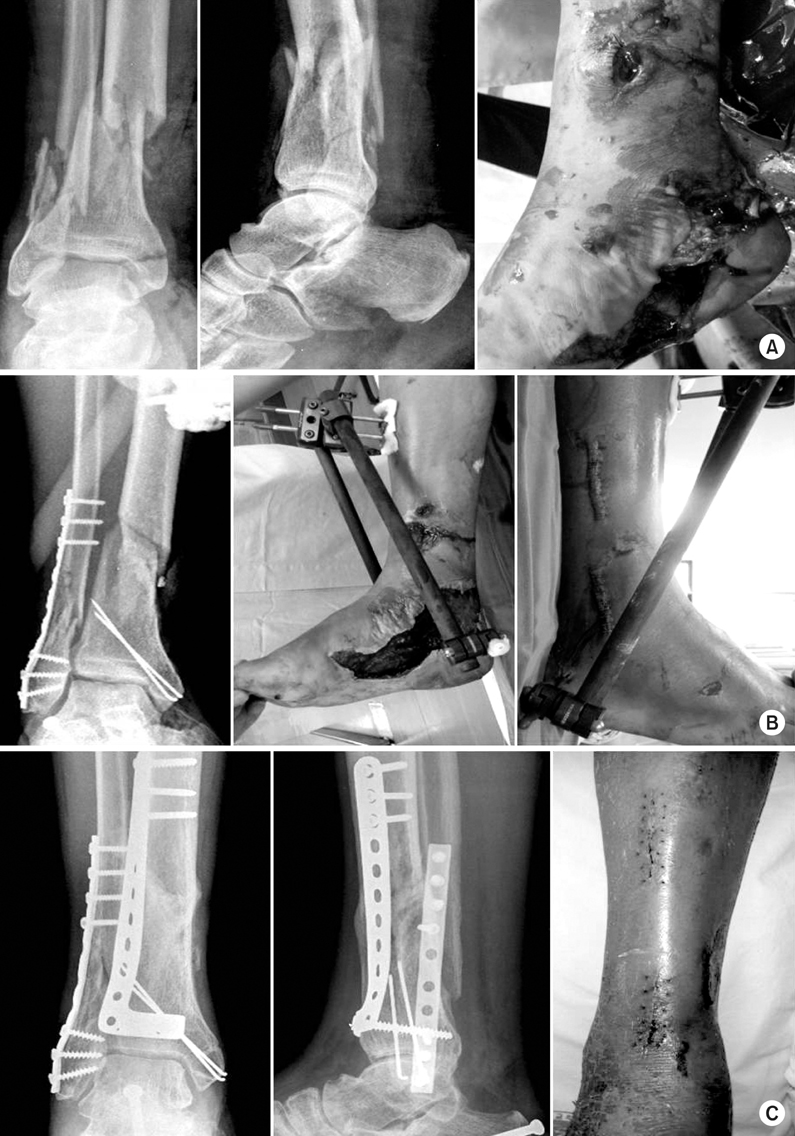

Fig. 3
(A) A 38 year old man sustained an intraarticular fracture of right distal tibia (AO/OTA type 43, C1) after traffic accident.
(B) Medial open wound was showed.
(C) First, lateral malleolar and tibial intraarticular fracture were fixed, and bridge external fixator was applied.
(D) After 1 week, lateral plate fixation of distal tibia using MIPPO technique was performed, and postoperative radiograph shows satisfactory alignment.
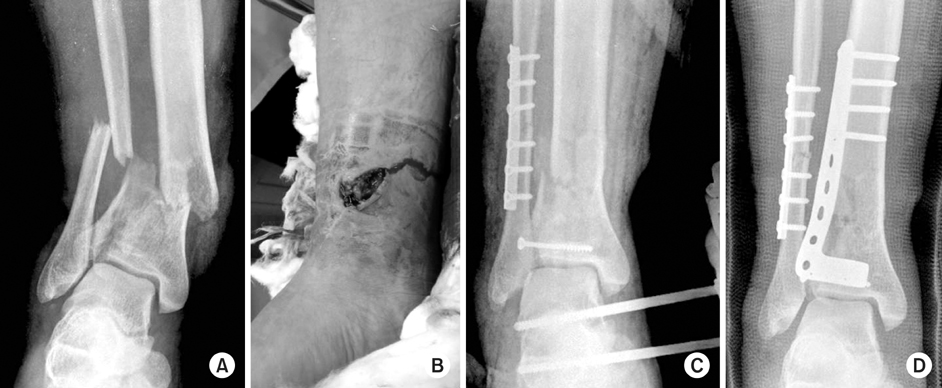

Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Anatomically Percutaneous Wiring Reduction in Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Distal Tibial Fractures
Young-Mo Kim, Chan Kang, Deuk-Soo Hwang, Yong-Bum Joo, Woo-Yong Lee, Jung-Mo Hwang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(3): 230. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Osteosynthesis with Locking Compression Plate for Distal Tibia Fractures
Sung-Kyu Kim, Keun-Bae Lee, Keun-Young Lim, Eun-Sun Moon
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(1): 33. CrossRef
Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis Using a Lateral Plate in Distal Tibial Fracture
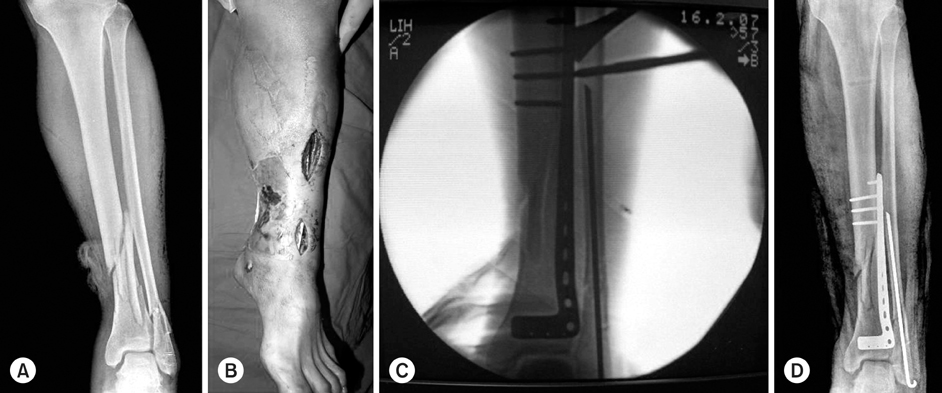
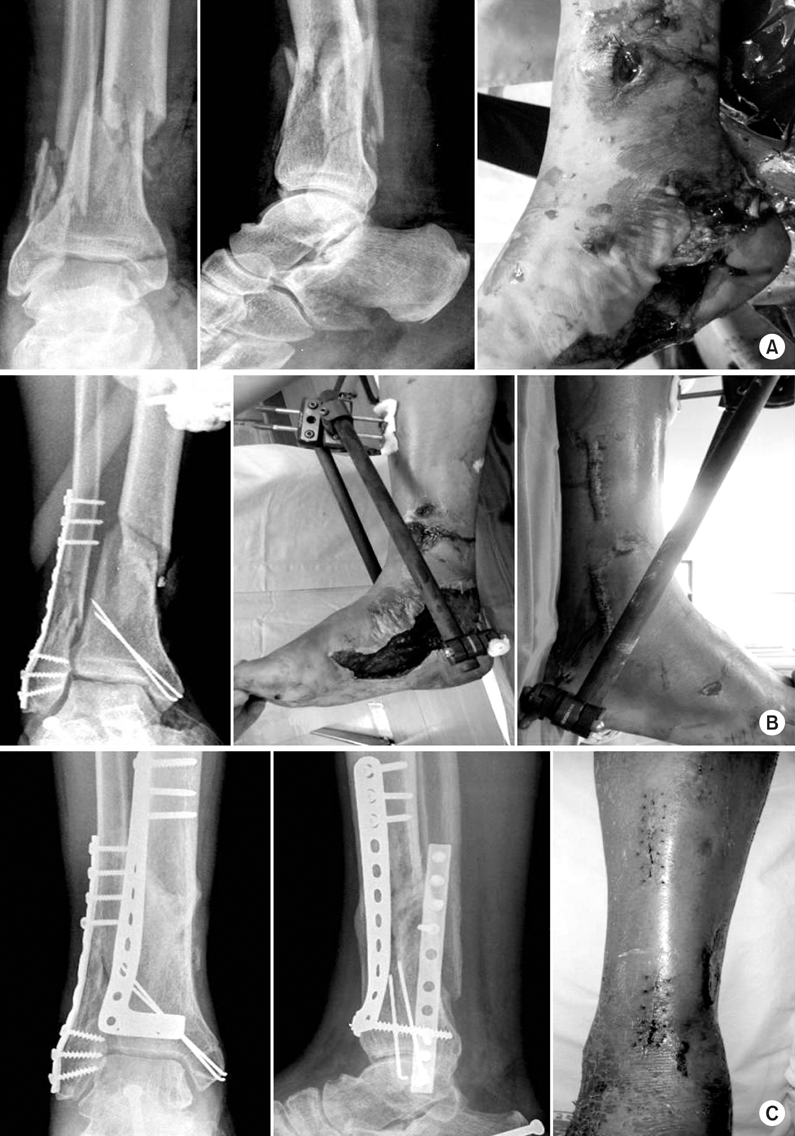
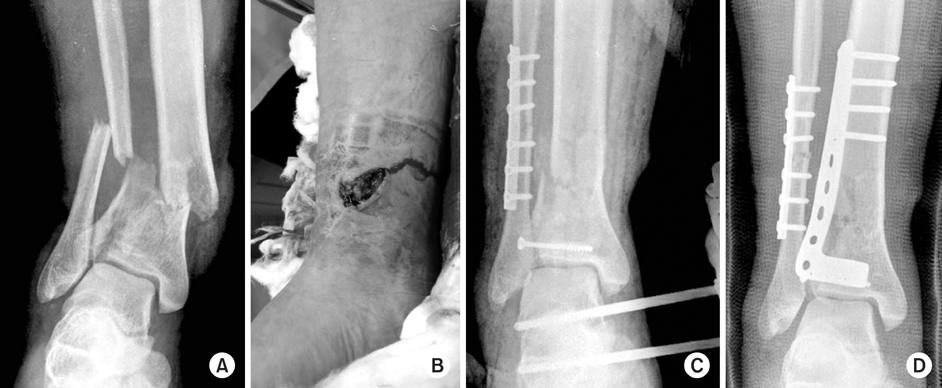
Fig. 1
(A) The initial film shows a comminuted fracture of the distal tibia with medial open wound.
(B) Lateral plate was inserted anterolaterally through mini skin incision.
(C) The location and size of plate was verified by C-arm.
(D) Postoperative radiograph shows satisfactory position of plate and screws.
Fig. 2
(A) A 64 year old man sustained a right distal tibial fracture (AO/OTA type 43, A3) with medial open wound after traffic accident.
(B) First, lateral malleolar fracture was fixed using MIPPO technique, and bridge external fixator was applied.
(C) After 3 weeks, lateral plate fixation of distal tibia using MIPPO technique was performed, and postoperative radiograph at 1 year after the injury shows solid bony union and satisfactory alignment.
Fig. 3
(A) A 38 year old man sustained an intraarticular fracture of right distal tibia (AO/OTA type 43, C1) after traffic accident.
(B) Medial open wound was showed.
(C) First, lateral malleolar and tibial intraarticular fracture were fixed, and bridge external fixator was applied.
(D) After 1 week, lateral plate fixation of distal tibia using MIPPO technique was performed, and postoperative radiograph shows satisfactory alignment.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis Using a Lateral Plate in Distal Tibial Fracture
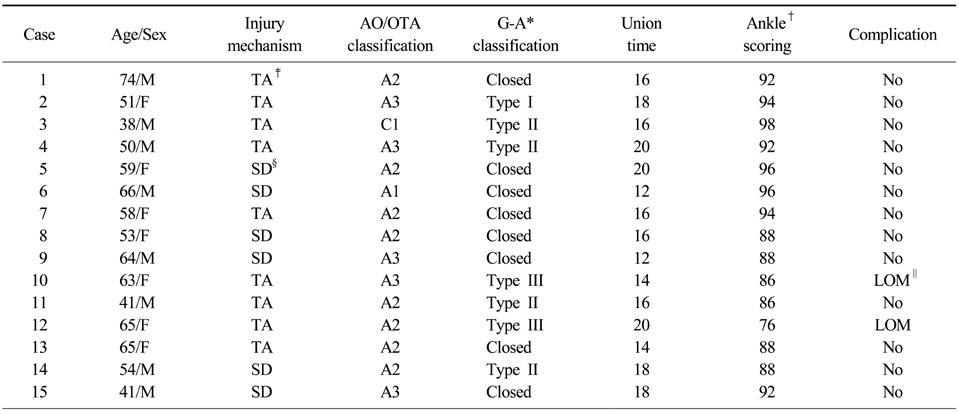
Patient data
*G-A: Gustillo-Anderson classification, †Ankle scoring: IOWA ankle rating system, ‡TA: Traffic accident, §SD: Slip down, ∥LOM: Limitation of motion.
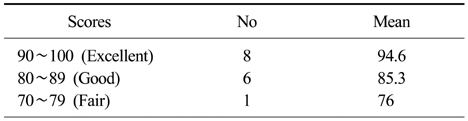
IOWA ankle rating system
Table 1
Patient data
*G-A: Gustillo-Anderson classification, †Ankle scoring: IOWA ankle rating system, ‡TA: Traffic accident, §SD: Slip down, ∥LOM: Limitation of motion.
Table 2
IOWA ankle rating system

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

