Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Computational simulation of coracoclavicular screw insertion through the superior distal clavicular plate for clinical applications in Korean cadavers
- Hyung-Lae Cho, Ji Han Choi, Se-Lin Jeong, Gu-Hee Jung
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):143-151. Published online July 22, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00122
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
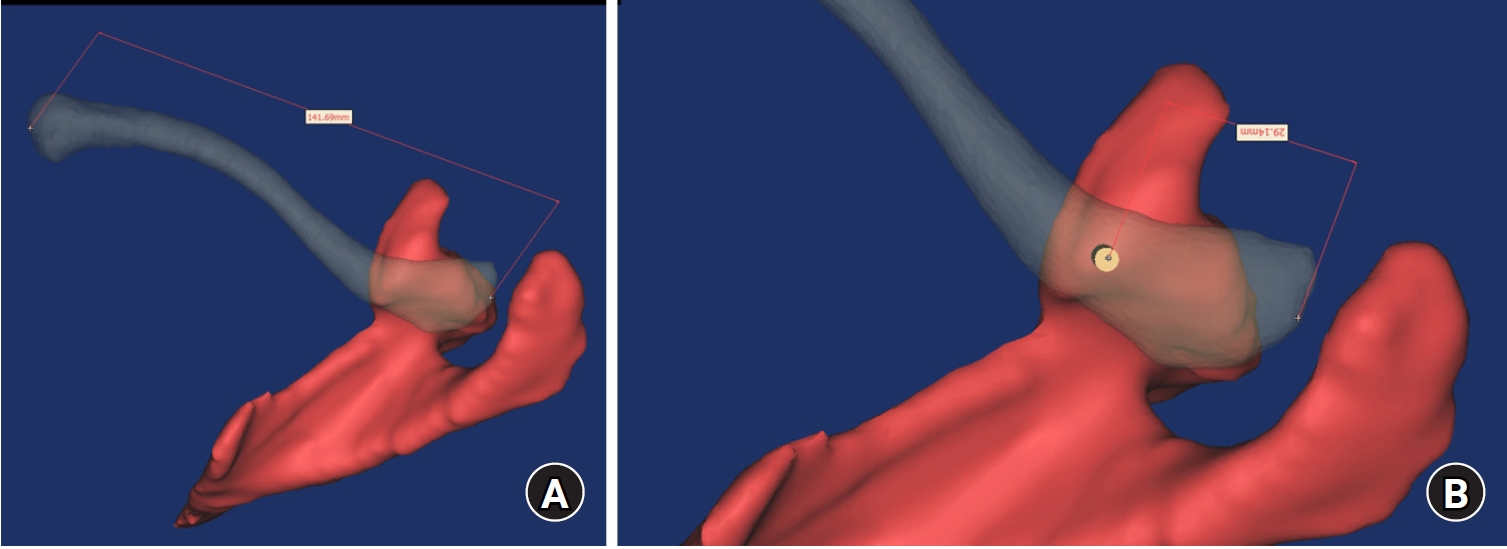
The study was conducted to determine the practical area for inserting the coracoclavicular (CC) screw through the plate by analyzing three-dimensional (3D) shoulder models featuring virtually implanted, actual-size plates and screws.
Methods
Ninety cadaveric shoulders (41 males and 49 females) underwent continuous 1.0-mm slice computed tomography scans. The data were imported into image-processing software to generate a 3D shoulder model, including the scapula and clavicle. The overlapping area between the clavicle and the horizontal portion of the coracoid process (horizontal portion_CP) was analyzed in the cranial view. A curved pelvic recon plate was virtually placed on the upper surface of the distal clavicle, and an actual-size (3.5 mm) CC screw was inserted through the plate.
Results
The distal clavicle directly overlapped with the horizontal portion_CP in the vertical direction. The overlapping area was sufficient to place the 3.5 mm and 4.5 mm-sized screws. In all shoulder models, the CC screw could be inserted through the plate into the vertical direction, with an average length of 35.5 mm (range, 26.2–62.5 mm; standard deviation, 1.2 mm). In 87 models, the CC screw was inserted through the third hole from the lateral end of the plate. Two models were inserted through the second hole, and one model through the fourth hole.
Conclusions
The upper surface of the clavicle has sufficient overlapping area to place CC screws through the plate in the vertical direction in the corresponding hole. Supplemental CC screw fixation through the plate can be performed without additional or special equipment. Level of evidence: IV
- 400 View
- 16 Download

Review Article
- How to obtain the desired results from distal tibial nailing based on anatomy, biomechanics, and reduction techniques
- Jungtae Ahn, Se-Lin Jeong, Gu-Hee Jung
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):74-85. Published online March 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00024

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Distal tibial metaphyseal fractures are commonly caused by high-energy injuries in young men and osteoporosis in older women. These fractures should be clearly distinguished from high-energy pilon fractures. Although the optimal surgical intervention methods for distal tibial metaphyseal fractures remain uncertain and challenging, surgical treatments for nonarticular distal tibia fractures can be broadly divided into two types: plate fixation and intramedullary nail (IMN) fixation. Once functional reduction is achieved using an appropriate technique, distal tibial nailing might be slightly superior to plate fixation in reducing postoperative complications. Thus, the surgical strategy should focus on functional realignment and proceed in the following sequence: (1) restoring the original tibial length, regardless of whether fibular fixation is to be done; (2) making the optimal entry point through an anteroposterior (AP) projection based on the overlapping point between the fibular tip and lateral plateau margin; (3) placing Kirschner wires (Ø2.4 mm) as blocking pins (in the AP orientation for coronal control and in the mediolateral [ML] orientation for sagittal control) as close to the upper locking hole as possible without causing further comminution on the concave aspect of the short fragment; and (4) making the the distal fixation construct with at least two ML and one AP interlocking screw or two ML interlocking screws and blocking screws. After the IMN is adequately locked, blocking pins (Ø2.4 mm) need to be replaced by a 3.5 mm screw.
- 1,654 View
- 38 Download

Original Articles
- The clinical outcome of treating elderly distal radius fractures by long volar locking plate with the elimination of irreducible metaphyseal comminuted volar cortical fragments: a retrospective case series
- Soo Min Cha
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(1):13-22. Published online January 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00003

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
In severe comminuted metaphyseal distal radius fracture (DRF) of elderly patients, after maintaining only radiological parameters of the radius using long volar locking plates (VLPs), we inevitably eliminated a few volar cortical fragments of metaphysis. Here, we report the final radiological and clinical outcomes of our method. Methods: For the patients who were treated between 2014 and 2018, the demographic factors, the preoperative radiologic factors, area of the eliminated volar cortical fragment, and final radiologic parameter, were evaluated. Clinical outcomes and ranges of active motion were evaluated. Results: In total, 31 patients were included. The mean patient age was 77.3 years and the mean eliminated cortical area was 3.30 cm2. At the final follow-up, the mean volar tilt, radial inclination, articular step-off, and ulnar variance were 10.35°, 20.00°, 0.58 mm, and 0.71 mm, respectively. There were no definitive correlations between bone mineral density, fragment area, the largest cortical fragment diameter ratio and differences in final and immediate postoperative measurements of these radiological parameters, respectively. Visual analog scale and disabilities of the arm, shoulder, and hand (DASH) scores were satisfactory, and the mean arcs of flexion-extension and pronation-supination were 124.35° and 133.23°. Clinical outcomes were not significantly different according to the AO system category. Conclusions: For maintenance of radiological parameters of the radius, long VLPs are useful in older patients with DRFs who exhibit volar metaphyseal comminution, despite concurrent ulnar fractures. Inevitable elimination of irreducible free comminuted cortical fragments when filling the defect does not affect final radiological and clinical outcomes. Level of evidence: Level IV, case series.
- 853 View
- 36 Download

- Does the Operator’s Experience Affect the Occurrence of Complications after Distal Radius Fracture Volar Locking Plate Fixation? A Comparative Study of the First Four Years and Thereafter
- Kee-Bum Hong, Chi-Hoon Oh, Chae Kwang Lim, Sungwoo Lee, Soo-Hong Han, Jun-Ku Lee
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2024;37(4):175-183. Published online October 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2024.37.4.175
- Correction in: J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(1):40
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
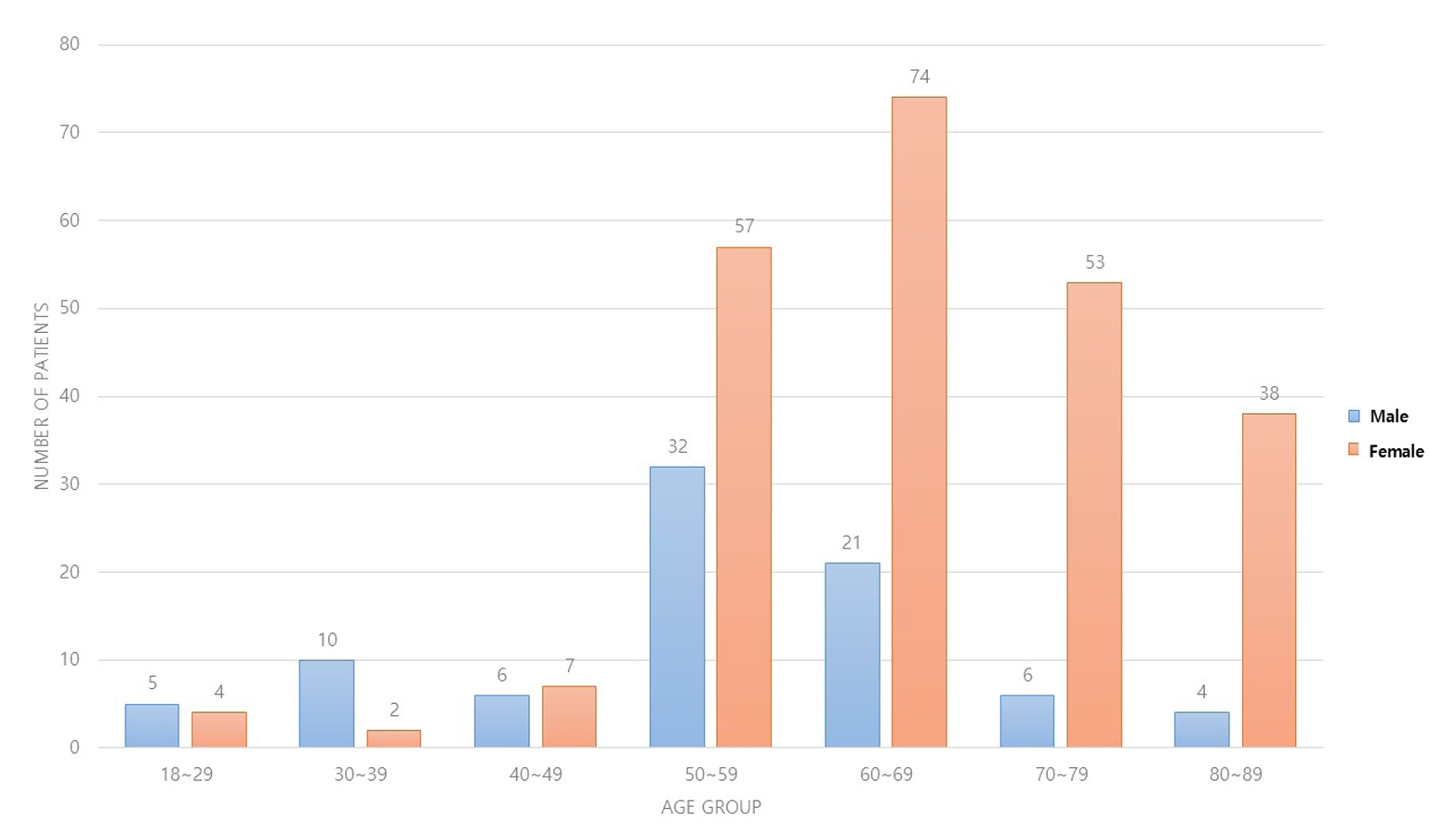
The management of distal radius fractures (DRFs) has evolved with the introduction of volar locking plate (VLP) fixation, offering stable fixation and better outcomes. Nevertheless, the impact of the surgeon’s experience on the complication rates in VLP fixation remains to be determined, particularly for less-experienced surgeons. This study compared the complication rates during the initial four years and subsequent two years of a hand surgeon’s practice of VLP fixation for DRFs.
Materials and Methods
The data between March 2016 and December 2022 were analyzed retrospectively under the Institutional Review Board approval. A single surgeon performed all VLP fixation surgeries after finishing regular hand surgery training, with the first four years representing the less experienced phase (Group 1) and the following two years indicating the experienced phase (Group 2). The patients’ characteristics, operation-related factors, and postoperative complications, including tendon injuries, nerve-related complications, fixation and instrument-related issues, osteosynthesis-related problems, and infections, were compared. In addition, the authors compared the data with a large multicenter study conducted by experienced hand surgeons.
Results
Three hundred and nineteen patients (321 wrists) were included. The mean age was 63.3 years, and 26.3% were male and 73.7% were female. The operation time was 53.7±14.5 minutes and 74.4±26.5 minutes in groups 1 and 2, respectively, which was statistically significantly shorter (p<0.001). The complication rates between the two groups were similar, except for the higher implant removal rates in Group 1. A comparison with a previous multicenter study revealed higher reduction losses and carpal tunnel syndrome in this study, but the overall complication rate was low.
Conclusion
In DRF management, when the operating surgeon has completed an accredited training course, VLP fixation is a good treatment method that can be performed effectively even by less experienced surgeons with low complication rates. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Author correction: “Does the operator's experience affect the occurrence of complications after distal radius fracture volar locking plate fixation? A comparative study of the first four years and thereafter”
Kee-Bum Hong, Chi-Hoon Oh, Chae Kwang Lim, Sungwoo Lee, Soo-Hong Han, Jun-Ku Lee
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(1): 40. CrossRef
- Author correction: “Does the operator's experience affect the occurrence of complications after distal radius fracture volar locking plate fixation? A comparative study of the first four years and thereafter”
- 1,835 View
- 51 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Comparison of Results between Minimally Invasive Plate Fixation and Antegrade Intramedullary Nailing of Recon-Type in Low-Energy Injury Distal Femoral Shaft Fractures
- Hong Moon Sohn, Gwangchul Lee, Ba Rom Kim, Jung Soo Oh
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(2):87-94. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.2.87
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study compared the outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis and antegrade intramedullary nailing for low-energy fracture of the distal femoral shaft.
Materials and Methods
A study was conducted on 30 patients who underwent surgery for low-energy fractures of the distal femoral shaft between January 2016 and April 2022. The study compared 15patients who underwent minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (Group P) with 15 patients who underwent recon-type antegrade intramedullary nailing (Group N). We evaluated intraoperative blood loss, operative time, C-arm exposure time, bone density, final union status, anatomical reduction, and clinical evaluation. The complications were also examined, and statistical analysis was conducted to compare the two groups.
Results
The blood loss, surgery time, and C-arm time were similar in the two groups. The radiographic assessments and clinical evaluations were also similar in the two groups. The clinical results showed no difference between the groups. Group N had one case of nonunion and one case of delayed union, while Group P had one case of nonunion and one case of peri-prosthetic fracture.
Conclusion
Antegrade intramedullary nailing of the recon-type demonstrated comparable results to minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. Hence, antegrade intramedullary nailing of the recon-type, which enhances stability by fixing the entire femur and providing additional fixation in the distal portion, is deemed appropriate for treating distal femoral shaft fractures.
- 547 View
- 10 Download

- Biomechanical Investigation to Establish Stable Fixation Strategies for Distal Tibial Fractures in Various Situations: Finite Element Analysis Studies
- Sung Hun Yang, Jun Young Lee, Gu-Hee Jung, Hyoung Tae Kim, Ba Woo Ko
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(2):71-81. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.2.71
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the structural and mechanical stability as well as the clinical significance of various fixation constructs for distal tibial fractures using finite element analysis.
Materials and Methods
Fracture models with 20 mm and 120 mm defects were produced, and implants of an intramedullary nail and anatomical plate model were applied. An axial load of 800 N with 60% distribution in the medial compartment and 40% in the lateral compartment was applied and analyzed using Ansys ® software.
Results
In the intramedullary nail model, the maximum von Mises stress occurred at the primary lag screw hole and adjacent medial cortex, while in the plate model, it occurred at the locking holes around the fracture. The maximum shear stress on the bone and metal implant in the fracture model with a 20 mm defect was highest in the plate assembly model, and in the fracture model with a 120 mm defect, it was highest in the two-lag screw assembly model.
Conclusion
Based on an analysis of the maximum shear stress distribution, securing the fixation strength of the primary lag screw hole is crucial, and the assembly model of the intramedullary nail with two lag screws and a blocking screw applied was the model that best withstood the optimal load. Securing the locking hole directly above the fracture is believed to provide the maximum fixation strength because the maximum pressure in the plate model is concentrated in the proximal locking hole and the surrounding cortex. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How to obtain the desired results from distal tibial nailing based on anatomy, biomechanics, and reduction techniques
Jungtae Ahn, Se-Lin Jeong, Gu-Hee Jung
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(2): 74. CrossRef
- How to obtain the desired results from distal tibial nailing based on anatomy, biomechanics, and reduction techniques
- 746 View
- 16 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of Additional Medial Locking Plate Fixation and Autogenous Bone Graft for Distal Femur Nonunion after Lateral Locking Plate Fixation
- Ho Min Lee, Jong Pil Kim, In Hwa Baek, Han Sol Moon, Sun Kyo Nam
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(1):30-38. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.1.30
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the outcomes of additional medial locking plate fixation and autogenous bone grafting in the treatment of nonunions that occurred after initial fixation for distal femoral fractures using lateral locking plates.
Materials and Methods
The study involved eleven patients who initially underwent minimally invasive lateral locking plate fixation for distal femoral fractures between January 2008 and December 2020. The initial procedure was followed by additional medial locking plate fixation and autogenous bone grafting for clinically and radiographically confirmed nonunions, while leaving the stable lateral locking plate in situ. A clinical evaluation of the bone union time, knee joint range of motion, visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores, presence of postoperative complications, and functional evaluations using the lower extremity functional scale (LEFS) were performed.
Results
In all cases, bone union was achieved in an average of 6.1 months after the secondary surgery. The range of knee joint motion, weight-bearing ability, and VAS and LEFS scores improved at the final follow-up compared to the preoperative conditions. All patients could walk without walking assistive devices and did not experience pain at the fracture site. On the other hand, three patients complained of pain in the lateral knee joint caused by irritation by the lateral locking plate; hence, lateral hardware removal was performed. One patient complained of mild paresthesia at the anteromedial incision site. Severe complications, such as deep infection or metal failure, were not observed.
Conclusion
For nonunion with stable lateral locking plates after minimally invasive lateral locking plate fixation of distal femur fractures, additional medial locking plate fixation and autogenous bone grafting, while leaving the lateral locking plate intact, can achieve successful bone union.
- 265 View
- 4 Download

- Bone Union Time of Simple Distal Femur Fractures in the Elderly according to Fracture Gap after Treated with Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis
- Young Ho Cho, Sangwoo Kim, Jaewook Koo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(4):133-138. Published online October 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.4.133
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the difference in bone union time according to the fracture gap after minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) for simple distal femoral fractures in elderly patients.
Materials and Methods
From January 2010 to December 2019, patients aged 60 years or older who underwent surgical treatment for distal femoral fractures due to a low-energy injury were investigated retrospectively. Forty patients were enrolled in the study. The patients were divided into two groups according to the fracture gap after reduction: no more than 2 mm (Group A) and more than 2 mm (Group B) in the anteroposterior and lateral plane. The demographic, operation time, presence or absence of cerclage wiring, plate screw density, plate span ratio, plate length, bone union period, non-union, and complications were evaluated.
Results
No statistical differences in operation time, cerclage wiring, plate screw density, plate span ratio, and plate length were observed between the two groups, and the bone union was achieved in all patients without complication. The bone union period was 17.24±1.48 weeks in Group A and 24.53± 5.20 weeks in Group B, which was statistically significant (p<0.001).
Conclusion
The bone union time in treating geriatric simple distal femur fractures using the MIPO tech-nique was significantly shorter in the 2 mm or less fracture gap than in the greater than 2 mm group.
- 563 View
- 2 Download

- Demographic and Radiographic Parameters as Predictors of Reduction Loss after Conservative Treatment of Distal Radius Fractures in Adults
- Kyu Jin Kim, Dae Won Shin, Seong Kee Shin
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(2):45-51. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.2.45
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the demographic and radiological risk factors for later reduction loss of distal radius fractures treated conservatively. Materials and Methods This study enrolled patients treated for distal radius fractures between January 2017 and December 2019. Seventy-eight patients were included in the analysis and divided into two groups. The patients who showed minimal reduction loss within an acceptable radiologic angle after initial manual reduction were classified as Group A. The patients who showed reduction loss out of an acceptable radiologic angle and finally malunited or converted to surgical treatments were classified as Group B. The patient’s age and bone marrow density were used as demographic data. The initial X-ray images were evaluated to determine the fracture type. Various radiological parameters were measured. Results The 78-patient study cohort consisted of nine men and 69 women with a mean age of 67 years. Forty-eight cases were sorted into Group A, and 30 cases into Group B. On logistic regression analysis, the age of 80 or older was a risk factor for later fracture displacement among the demographic factors (p=0.037, odds ratio=4.937). Among the radiographic factors, the presence of distal ulnar fracture and dorsal cortical comminution were disclosed as risk factors of later displacement (p=0.049, 0.003, odds ratio=3.429, 7.196). Conclusion When conservative management for distal radius fracture is decided in patients more than 80 years of age or accompanied by a distal ulnar fracture or with dorsal cortical comminution, the possibility of later displacement of the distal radius should be considered.
- 380 View
- 1 Download

Technical Note
- Usefulness of Reduction and Internal Fixation Using a 2.4 mm Hand Plating System in Type AO 33-A3 Distal Femur Fracture - Technical Note -
- Bong-Ju Lee, Ja-Yeong Yoon, Seungha Woo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(1):25-28. Published online January 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.1.25
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Open reduction in an AO 33-A3 class distal femur transverse and comminuted fracture is often difficult due to frequent reduction loss during surgery, leading to longer operative time and increased blood loss intra-operation. In this study, the authors report a case in which the use of an offset grid plate (OsteoMed, USA) using 2.4 mm HPS (hand plating system) eased the process of fracture reduction and achieved a stable internal fixation, ultimately leading to successful osteosynthesis. The authors experienced no need for temporary fixation devices such as K-wires or screws, which are otherwise required to stabilize the reduction. The fracture reduction was stable throughout the primary fixation of the fracture using a locking plate and screws. The authors report that the advantage of the HPS plate is fitting into the cortical contour and providing stable maintenance of fracture reduction intra-operation, which would be beneficial in certain distal femoral fracture patterns.
- 394 View
- 7 Download

Original Article
- Distal Femur Fractures Treated with Distal Femoral Locking Plate Fixation: A Retrospective Study of One Year Mortality and Risk Factors
- Kwang-Hwan Jung, Yoon-Seok Youm, Seung-Hyun Jung, Jae-Min Oh, Ki Bong Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(1):10-16. Published online January 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.1.10
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the one-year mortality after locking plate fixation for distal femur fractures and the risk factors related to death.
Materials and Methods
From July 2011 to June 2020, 128 patients who underwent locking plate fixation for distal femur fractures were analyzed retrospectively. Epidemiologic information of the patients, characteristics related to fracture and surgery, and death were investigated. The risk factors related to death were investigated using Cox analysis, and a subgroup analysis was also performed based on the age of 65 years.
Results
The one-year mortality rate after locking plate fixation for distal femur fractures was 3.9%, and the mortality rates in patients younger than 65 years and older than 65 years were 0% and 6.7%, respectively. There were no significant risk factors related to death in the total population. On the other hand, in patients aged 65 years or older, however, high-energy fracture and high comorbidity index increased the risk of death after surgery by 6.9-fold and 1.9-fold, respectively.
Conclusion
The one-year mortality rate for the total patients was 3.9%, but the mortality rate for patients over 65 years of age increased to 6.7%. High-energy fractures and high comorbidity index were risk factors related to death after surgery for distal femur fractures in patients aged 65 years or older.
- 365 View
- 1 Download

Review Article
- Pediatric Fractures around the Wrist
- Gihun Kim, Kun-Bo Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2021;34(2):80-86. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2021.34.2.80
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fractures around the wrist are the third most common fracture among all pediatric fractures. Furthermore, distal radius fractures, a type of wrist fracture, are the most common fractures in children. Understanding pediatric fractures around the wrist is very important considering their prevalence. There is a specific belief that pediatric fractures can heal easily because of remodeling, but not all fractures can heal without proper treatment. Complications such as growth problems, nonunion can occur if the fracture is not treated properly. This paper reviewed recent articles about distal radius fractures, Galeazzi-equivalent fractures, and carpal bone fractures, including scaphoid fractures in children and adolescents. Successful treatment can be achieved without complications when an accurate diagnosis and proper non-surgical or surgical treatment are performed based on this article.
- 976 View
- 21 Download

Original Articles
- Primary Open Reduction and Plate Fixation in Open Comminuted Intra-Articular Distal Radius Fracture
- Jun-Ku Lee, Soonchul Lee, Weon Min Cho, Minkyu Kil, Soo-Hong Han
- J Korean Fract Soc 2021;34(1):16-22. Published online January 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2021.34.1.16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
There are no standard surgical treatments for open distal radius fractures (DRFs), and the fracture fixator is chosen by the surgeon’s own experience. This study compared the outcomes of open reduction and volar locking plating (OR VLP) between closed and open AO-OTA type C3 DRFs. Materials and Methods: Patient data were retrospectively collected between January 2010 and December 2018. Only patients aged >18 years with AO-OTA C3 DRFs were included. After further exclusion, the patients with DRFs were divided into two groups: 13 patients with open DRFs in Group 1 and 203 patients with closed DRFs in Group 2. Data on the patient characteristics and treatment-related factors were further investigated. For the radiological evaluation, the radial height, volar height, and volar titling were measured based on the final plain radiography, and the union time was measured. The wrist range of motion (ROM), pain visual analogue scale score, and modified Mayo wrist score for function were measured at the final outpatient follow-up. Finally, the complications associated with OR VLP fixa-tion were investigated. Results: In the demographic comparison, the patients with open fractures were older (mean age, 62years) than those with closed fractures (mean age, 57 years), without a statistically significant differ-ence. The patients with open DRFs had longer antibiotic therapy and hospital stay durations. Although they presented a higher radial inclination, with statistical significance, the clinical implication was low with a mean difference of 3°. No significant differences were observed for the remaining radiological parameters, wrist ROM, and functional scores. An open DRF did not increase the complication rates,including deep infection. Conclusion: Depending on the expertise of the operating surgeon, the primary OR VLP fixation in open intra-articular comminuted DRF did not increase the incidence of deep infections and yielded similar outcomes to a closed intra-articular comminuted DRF.
- 619 View
- 10 Download

- Results of Intramedullary Nailing for Distal Metaphyseal Intra-Articular Fractures of Tibia
- Jun Young Lee, Yongjin Cho, Hyung Seok Park, Se Woong Jang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(4):196-203. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.4.196
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the results of internal fixation using an intramedullary nail in the treatment of distal metaphyseal fractures involving the articular surface.
Materials and Methods
From November 2009 to November 2018, distal tibia fractures involving the articular surface were treated with intramedullary nailing only for fractures corresponding to AO type 43 B and 43 C1, twenty-four cases were studied retrospectively. The tibial alignment was measured preoperatively and postoperatively, and the bone union time and nonunion were assessed. In addition, the clinical evaluation of ankle joint function was assessed using the Olerud and Molander ankle score (OMAS).
Results
Complete bone union was obtained in all cases, and the mean union time was 17.7±1.87 weeks (range, 15-20 weeks). The average preoperative coronal alignment was 6.4°±1.0° (range, 5.2°-8.4°), and sagittal alignment was 2.7°±0.6° (range, 1.9°-3.8°). The average postoperative coronal alignment was 2.5°±0.13° (range, 2.2°-2.6°) and sagittal alignment was 0.4°±0.25° (range, 0.09°-0.95°). There was no nonunion. The OMAS had an average of 85±7.9 points (range, 70-95 points).
Conclusion
In the treatment of distal metaphyseal fractures involving the articular surface, internal fixation using an intramedullary nail reduces complications and achieves satisfactory reduction and union. This method is considered an excellent treatment to obtain good clinical results.
- 342 View
- 4 Download

- Comparison of a Novel Box-Frame External Fixator and Conventional Delta-Frame External Fixator in the Staged Treatment of Distal Tibia Fractures
- Yong-Cheol Yoon, MinKyu Shin, Chang-Wug Oh, Jong-Keon Oh
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(3):125-133. Published online July 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.3.125
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Distal tibia fractures with severe soft-tissue edema or intra-articular fractures are treated by staged operations using external fixators. Definitive surgery that maintains ligamentotaxis has been difficult using existing fixators. This study introduced a novel ‘box-frame’ external fixator and evaluated its clinical usefulness.
Materials and Methods
This study included 45 patients (32 males, 13 females) diagnosed with distal tibia fractures who underwent staged operations between March 2012 and March 2016, with a follow-up of at least one year. The patients were divided into two groups. In one group, fixation was performed with a box-frame external fixator (Group A). In the other group, fixation was performed with a delta-frame external fixator (Group B). The following outcomes were evaluated: the time until definitive surgery, operative time of the definitive surgery, radiation exposure time, bone union, time to achieve bone union, postsurgical complications, American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society anklehindfoot score, and ankle range of motion.
Results
Compared to the delta-frame, the box-frame showed a statistically significant reduction in the mean radiation-exposure time and operative time during the definitive surgery by 58 seconds and 25 minutes, respectively. The differences in the time until definitive surgery, bone union, time to achieve bone union, postsurgical complications, and functional scores were not significant.
Conclusion
The box-frame external fixator can be a useful treatment method in the staged surgery of distal tibia fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Temporary Circular External Fixation for Spanning the Traumatized Ankle Joint
Nando Ferreira, Niel Bruwer, Adriaan Jansen van Rensburg, Ernest Muserere, Shao-Ting Jerry Tsang
JBJS Essential Surgical Techniques.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Temporary circular external fixation for spanning the traumatised ankle joint: A cohort comparison study
William D. Harrison, Franklin Fortuin, Matthieu Durand-Hill, Etienne Joubert, Nando Ferreira
Injury.2022; 53(10): 3525. CrossRef
- Temporary Circular External Fixation for Spanning the Traumatized Ankle Joint
- 1,365 View
- 10 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Results of Single Small Incision Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis in the Treatment of the Distal Radius Fractures
- Young Sung Kim, Jong Pil Kim, Phil Hyun Chung, Ho Min Lee, Bo Sung Go
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(2):72-80. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.2.72
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study compared minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) using a single small skin incision and conventional open volar locking plate fixation (OP) for distal radius fracture to identify outcome difference.
Materials and Methods
Forty-three patients who underwent MIPO using a single small skin incision or OP for distal radius fractures were evaluated retrospectively. Of the patients, 21 were treated with MIPO using a single small skin incision and 22 with the OP method through the conventional volar approach. The postoperative radiographic results and clinical outcomes at the final follow-up in each group were compared.
Results
All patients achieved bone union in the MIPO and OP groups. No significant differences in the bone union time, alignment, range of motion, QuickDASH, or pain score were observed. On the other hand, the size of the incision was significant: 23 mm in the MIPO group and 55 mm in the OP group (p<0.001).
Conclusion
MIPO technique using a single small incision showed similar satisfactory radiographic and functional outcomes compared to conventional OP for distal radius fractures. The MIPO technique using a single small incision offered advantages, including cosmetic benefits and minimal soft tissue damage, is recommended, particularly in young women and high functional demand patients.
- 461 View
- 4 Download

Case Report
- Tension Band Wiring Technique for Distal Radius Fracture with a Volar Articular Marginal Fragment: Technical Note
- Neunghan Jeon, Jong Keon Oh, Jae Woo Cho, Youngwoo Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(1):38-42. Published online January 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.1.38
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Most distal radius fractures are currently being treated with anterior plating using anatomical precontoured locking compression plates via the anterior approach. However, it is difficult to fix the volar articular marginal fragment because these anatomical plates should be placed proximally to the watershed line. There were just a few methods of fixation for this fragment on medical literature. Herein, we introduced a tension band wiring technique for fixation of a volar articular marginal fragment in the distal radius.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hook plate versus periarticular-type volar locking plate for distal radius fractures involving the volar lunate facet in Korea: a retrospective cohort study
Hyun-Jae Park, Joo-Hak Kim
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(4): 221. CrossRef
- Hook plate versus periarticular-type volar locking plate for distal radius fractures involving the volar lunate facet in Korea: a retrospective cohort study
- 526 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- Use of Miniplate for Severe Comminuted Metadiaphyseal Fractures of the Distal Radius
- Jong Ryoon Baek, Yong Cheol Yoon, Seung Hyun Baek
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(4):204-210. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.4.204
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study investigated the clinical and radiological outcomes of patients undergoing provisional fixation in conjunction with locking plate fixation. Miniplates were used as the reduction plates for the surgical treatment of severe comminuted metadiaphyseal fractures with an intra-articular fracture of the distal radius.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The radial length, radial inclination, volar tilt, and radial intra-articular step-off were measured preoperatively, postoperatively, and at one year after surgery in 12 patients (eight males, four females, mean age 55.4 years old). The patients underwent volar locking plate fixation with miniplate as a reduction plate for severe comminuted metadiaphyseal fractures with an intra-articular fracture of the distal radius. Clinical evaluations were conducted using the modified Mayo wrist score (MMWS).
RESULTS
Bone union was achieved in all cases. The mean MMWS was 81.8 points, including two excellent, three good, and seven fair cases. Radiological improvements were observed in the average radial length (preoperative, 6.4 mm; postoperative, 11.8 mm), average radial inclination (10.2° to 22.4°), average volar tilt (−4.5° to 10.6°), and average radial intra-articular step-off (4.8–0.8 mm) (all, p<0.05). Radiographic measurements obtained immediately after surgery and at the final follow-up revealed insignificant decreases in radial length (0.6 mm), radial inclination (0.4°), and volar tilt (0.9°) (all, p>0.05).
CONCLUSION
Miniplate fixation can be an effective treatment option as a reduction plate for the treatment of distal radial fractures, which is challenging to reduce and maintain due to severely comminuted metadiaphysis fractures with the intra-articular fracture.
- 512 View
- 2 Download

- Outcomes following Treatment of Geriatric Distal Femur Fractures with Analyzing Risk Factors for the Nonunion
- Soo young Jeong, Jae Ho Lee, Ki Chul Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(4):188-195. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.4.188
- Correction in: J Musculoskelet Trauma 2020;33(1):62
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
Many international journals have published studies on the results of distal femoral fractures in elderly people, but only a few studies have been conducted on the Korean population. The aim of this study was to determine the factors that are associated with the outcomes and prognosis of fixation of distal femur fractures using the minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) technique in elderly patients (age≥60) and to determine the risk factors related witht he occurrence of nonunion.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study is a retrospective study. From January 2008 to June 2018, distal femur fracture (AO/OTA 33) patients who underwent surgical treatment (MIPO) were analyzed. A total of 52 patients were included in the study after removing 121 patients that met with the exclusion criteria. Medical records, including surgical records, were reviewed to evaluate the patients' underlying disease, bone mineral density, the number of days delayed from surgery, complications and mortality. In addition, follow-up radiographs were used to determine bone union, delayed union and nonunion.
RESULTS
The average time to achieve bone union was 19.95 weeks, the rate of nonunion was 20.0% (10/50) and the overall mortality was 3.8% (2/52). There were no significant differences in the clinical and radiological results of those patients with or without periprosthetic fracture. On the univariate analysis, which compared the union group vs. the nonunion group, no factors were identified as significant risk factors for nonunion. On the multiple logistic regression analysis, medical history of cancer was identified as a significant risk factor for nonunion (p=0.045).
CONCLUSION
The rate of nonunion is high in the Korean population of elderly people suffering from distal femur fracture, but the mortality rate appears to be low. A medical history of cancer is a significant risk factor for nonunion. Further prospective studies are required to determine other associated factors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Clinical Outcomes for Femoral Neck System and Cannulated Compression Screws in the Treatment of Femoral Neck Fracture
Jae Kwang Hwang, KiWon Lee, Dong-Kyo Seo, Joo-Yul Bae, Myeong-Geun Song, Hansuk Choi
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2023; 36(3): 77. CrossRef
- Comparison of Clinical Outcomes for Femoral Neck System and Cannulated Compression Screws in the Treatment of Femoral Neck Fracture
- 765 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Paratricipital Approach for AO/OTA Type C2 Intra-Articular Fracture of Distal Humerus
- Chul Hyung Lee, Doo Hun Sun, Deukhee Jung, Chung Han An
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(3):128-134. Published online July 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.3.128
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to determine the outcomes of fixation of AO/OTA type C2 fractures among intra-articular fractures of the distal humerus using the paratricipital approach (side to side retraction of the triceps).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From June 2008 to January 2018, 12 patients underwent an open reduction and internal fixation with the paratricipital approach and were followed-up for more than 10 months after surgery. According to the AO/OTA classification, type C2 fractures were chosen among the intraarticular distal humerus fractures. An extended posterior incision was used over the olecranon in the prone position, preserving the insertion site of the triceps brachii muscle. The fracture site was exposed by retracting the muscle side-to side through a dissection of the medial and lateral intermuscular septum of the triceps brachii muscle. The therapeutic results were assessed by the anatomical reduction of the articular surface and integrity of the metaphyseal contour in postoperative simple radiographs, complications, such as neuropathy or non-union, and the Mayo elbow performance score (MEPS) were checked to estimate the functional outcome.
RESULTS
In the postoperative simple radiographs, no case showed more than 1 mm step-off and the disrupted contour of the distal humerus was recovered to normal alignment in most cases. The range of elbow joint motion in the last follow-up was 133.8° on average with a mean flexion contracture of 5.0°. The clinical results depending on the MEPS were excellent, except for two cases, which were good. Neuropathy of the ulnar nerve was observed in one patient, which was resolved after metal removal.
CONCLUSION
The paratricipital approach is useful technique in AO/OTA type C2 intra-articular distal humerus fractures that provides sufficient exposure of the surgical field, without injury to the triceps brachii muscle and postoperative complications associated with the trans-olecranon approach. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Short-Term Results After Intra-Articular Fractures of the Distal Humerus Treated by a Paratriceps Approach
Petar Petkov
Scripta Scientifica Medica.2025; 57(1): 48. CrossRef
- Short-Term Results After Intra-Articular Fractures of the Distal Humerus Treated by a Paratriceps Approach
- 667 View
- 7 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review Article
- Locked Plating in Elderly Patients with Distal Femur Fracture: How to Avoid Complications?
- Chul Young Jang, Je Hyun Yoo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(2):112-119. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.2.112
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Distal femur fractures in elderly patients with osteoporosis are complicated because poor bone quality makes screw purchase and fixation less secure, presenting many clinical challenges to the orthopedic surgeon. Minimally invasive locked plating using an angularly stable locking compression plate has become an integral tool for achieving secure fixation in osteoporotic distal femur fractures with improved biomechanical performance. On the other hand, complications, such as implant failure and periplate fracture, have still occurred. This paper describes the principles of internal fixation in minimally invasive lateral locked plating in elderly patients with osteoporotic distal femur fractures as well as how to avoid complications.
- 584 View
- 4 Download

Case Report
- Pseudoaneurysm of the Anterior Tibial Artery after Reduction with Pointed Bone Reduction Forceps on a Spiral Fracture of the Distal Tibia: A Case Report
- Hyunseung Yoo, Youngho Cho, Seongmun Hwang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(1):43-46. Published online January 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.1.43
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This paper reports a pseudoaneurysm of the anterior tibial artery after reduction with pointed bone reduction forceps on a spiral fracture of the distal tibia. Most reported injuries occurred at the proximal part of anterior tibial artery during drilling of the proximal tibia. To the best of the authors' knowledge, injury of the distal part of anterior tibial artery has never been reported. This paper describes a 54-year-old woman with a pseudoaneurysm of the anterior tibial artery clinically detected 11 weeks after the index surgery. This report highlights the need for surgeons to be aware of and careful about this complication during and after surgical intervention.
- 411 View
- 1 Download

Original Articles
- Results after Less Invasive Locking Plating in Intra-Articular Fractures of the Distal Femur
- Sung Hyun Kim, Sung Hyun Yoon, Hee Gon Park, Jae Uk Jung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(1):14-20. Published online January 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.1.14
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to determine the clinical outcomes after a less invasive locking plating technique in intra-articular fractures of the distal femur.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This was a retrospective 19 case series of patients with distal femoral intraarticular fractures treated with a less invasive locking plating technique in a single center (Dankook University Hospital) from June 2010 to April 2016. Nineteen patients (11 males and 8 females) with a mean age of 55.9 years were enrolled. The functional outcomes were evaluated using the visual analogue scale (VAS), range of knee joint motion (flexion & extension), and Knee Society score. The radiology outcomes were evaluated with parameters measured in a plain radiograph (deviation angle of alignment axis on coronal and sagittal plane, mechanical lateral distal femur angle).
RESULTS
The mean follow-up period was 26.4 months (range, 12–72 months) and the mean duration to union was 15.94 weeks (range, 11–28 weeks). The mean VAS was 1.36 (range, 0–8) and the range of motion of the knee joint was extension 4.73° (range, 0°–30°) and flexion 107.36° (range, 60°–135°). The mean Knee Society score was 85.47 (range, 47–100). The mean deviation angle of the coronal alignment axis was 4.07° (range, 1.3°–8.8°), the mean deviation angle of the sagittal alignment axis was 3.23° (range, 0.7°–7.0°), and the mechanical lateral femoral angle was 87.75° (range, 82.8°–95.5°). Six patients had traumatic osteoarthritis at the final follow-up.
CONCLUSION
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the clinical and radiologic outcomes of intraarticular fractures of the distal femur in patients who underwent an anatomical reduction through an open reduction, and converted to an extra-articular fracture with rigid internal fixation. The results were relatively satisfactory.
- 379 View
- 2 Download

- Comparative Analysis of Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis and Intramedullary Nailing in the Treatment of the Distal Tibia Fractures
- Ho Min Lee, Young Sung Kim, Jong Pil Kim, Phil Hyun Chung, Suk Kang, Kaung Suk Jo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(3):94-101. Published online July 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.3.94
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study compared the radiological and clinical results of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) and intramedullary nailing (IMN) of distal tibial fractures, which were classified as the simple intra-articular group and extra-articular group.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fifty patients with distal tibial fractures, who could be followed-up more than 12 months, were evaluated. Group A consisted of 19 patients treated with MIPO and group B consisted of 31 patients treated with IMN. The results of each group were analyzed by radiological and clinical assessments.
RESULTS
The mean operation times in groups A and B were 72.4 minutes and 65.7 minutes, respectively. The mean bone union times in groups A and B were 16.4 weeks and 15.7 weeks, respectively. The bone union rate in groups A and B were 100% and 93%, respectively. The ranges of ankle motion were similar in the two groups at the last follow-up. The mean American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society score was similar: 90.1 in group A and 90.5 in group B. The radiological and clinical results were similar in the intra and extra-articular groups. In groups A and B, two cases of posterior angulation and five cases of valgus deformity of more than 5° were encountered.
CONCLUSION
Both MIPO and IMN achieved satisfactory results in extra-articular AO type A and simple articular extension type C1 and C2 distal tibia fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intramedullary Nailing versus Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Distal Tibia Shaft Fractures: Retrospective Comparison of Functional and Cosmetic Outcomes
Kahyun Kim, In Hee Kim, Geon Jung Kim, SungJoon Lim, Ji Young Yoon, Jong Won Kim, Yong Min Kim
Journal of Korean Foot and Ankle Society.2023; 27(3): 93. CrossRef
- Intramedullary Nailing versus Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Distal Tibia Shaft Fractures: Retrospective Comparison of Functional and Cosmetic Outcomes
- 384 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A Comparison of the Results between Internal Fixation and External Fixation in AO C Type Distal Radius Fractures
- Yoon min Lee, Hwa Sung Lee, Seok Whan Song, Jae Hoon Choi, Jong Tae Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(3):87-93. Published online July 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.3.87
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the radiological and clinical results of plate fixation and external fixation with additional devices for treating distal radius fracture in AO type C subtypes, and propose a treatment method according to the subtypes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Two hundred and one AO type C distal radius fracture patients were retrospectively reviewed. Eighty-five patients in group 1 were treated with volar or dorsal plate, and 116 patients in group 2, were treated with external fixation with additional fixation devices. Clinical (range of mtion, Green and O'Brien's score) and radiological outcomes were evaluated.
RESULTS
At the 12-month follow-up, group 1 showed flexion of 64.4°, extension of 68.3°, ulnar deviation of 30.6°, radial deviation of 20.8°, supination of 76.1°, and pronation of 79.4° in average; group 2 showed flexion of 60.5°, extension of 66.9°, ulnar deviation of 25.5°, radial deviation of 18.6°, supination of 73.5°, and pronation of 75.0° in average. The mean Green and O'Brien score was 92.2 in group 1 and 88.6 in group 2. The radial height of group 1 and group 2 was 11.6/11.4 mm; radial inclination was 23.2°/22.5°; volar tilt was 11.6°/8.7°; and the ulnar displacement was 1.27/0.93 mm.
CONCLUSION
Judicious surgical techniques during device application and tips for postoperative management during external fixation can produce similar clinical results compared with internal fixation patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intra-articular fracture distal end radius external fixation versus locking volar radius plate: A comparative study
S.P.S Gill, Manish Raj, Santosh Singh, Ajay Rajpoot, Ankit Mittal, Nitin Yadav
Journal of Orthopedics, Traumatology and Rehabilitation.2019; 11(1): 31. CrossRef
- Intra-articular fracture distal end radius external fixation versus locking volar radius plate: A comparative study
- 345 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review Article
- Nonsurgical Treatment of a Distal Radius Fracture: When & How?
- Young Ho Shin, Jun O Yoon, Jae Kwang Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(2):71-78. Published online April 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.2.71
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Distal radius fractures are a common upper extremity fracture and a considerable number of patients have a stable fracture. In the treatment of distal radius fractures, there is considerable disagreement regarding the need for a strict anatomical restoration with operation in elderly patients. Therefore, nonsurgical treatment is a still important treatment option in distal radius fractures. The radiological parameters of before or after manual reduction are important for deciding whether to perform operation or not. The radiological parameters include dorsal angulation of the articular surface, radial shortening, extent of dorsal comminution, intra-articular displacement, concomitant ulnar metaphyseal fracture, shear fracture, and fracture-dislocation of the distal radio-ulnar joint. In addition, clinical situations of patients, including age, activity level, underline disease, and recovery level, which the patients wish should be considered, comprehensively. For the duration of a splint or cast, three to four weeks are recommended in impacted or minimally displaced fractures and five to six weeks in displaced fractures. After reduction of the displaced fractures, patients should undergo a radiologicical examination every week to check the redisplacement or deformity of the fracture site until two or three weeks post trauma. Arm elevation is important for controlling fracture site swelling and finger exercises, including metacarpophalangeal joint motion, are needed to prevent hand stiffness. Active range of motion exercise of the wrist should be initiated immediately after removing the splint or cast.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Clinical Effect of Complex Korean Medical Admission Treatment in Patients with Fractures of Distal Radius by Traffic Accident: 2 Cases Series Report
Gyu-cheol Choi, Ji-won Lee, Ji-Eun Bae, Dong-jin Kim, Jeong-su Hong, Da-hyun Kyung
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2021; 31(1): 187. CrossRef - The Clinical Effect of Rehabilitation Protocol for Distal Radius Fracture in Korean Medicine: A Report of 3 Cases
Won-Bae Ha, Ji-Hye Geum, Nak-Yong Koh, Jung-Han Lee
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2018; 28(3): 97. CrossRef
- The Clinical Effect of Complex Korean Medical Admission Treatment in Patients with Fractures of Distal Radius by Traffic Accident: 2 Cases Series Report
- 365 View
- 7 Download
- 2 Crossref

Original Articles
- Factors Affecting Posterior Angulation in Retrograde Intramedullary Nailing for Distal Femoral Fractures
- Hohyoung Lee, Ji Ho Jeong, Min Su Kim, Bum Soo Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(2):50-56. Published online April 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.2.50
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analyze the factors that cause a posterior angulatory deformity in the retrograde intramedullary nailing of distal femoral fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fifty-five patients with distal femur fractures who were treated with retrograde intramedullary nailing were enrolled in this study. They were followed-up for at least one year postoperatively. The posterior angulatory deformity was evaluated according to the fracture location, pattern, and insertion point and the insertion point was compared with the ideal point derived from the radiographs of 100 normal adults. The correlation between the posterior angulation and the entry point of the nail was analyzed.
RESULTS
The posterior angulation was similar in terms of the fracture location; a meaningful difference was noted among the fracture patterns (p=0.047). The posterior angulation was significantly greater when the entry point was located more posteriorly, accepting a malreduced state (p=0.012).
CONCLUSION
Posterior angulation was smaller in the transverse fracture and the posterior location of the entry point from the apex of the Blumensaat's line increased the posterior angulation.
- 239 View
- 6 Download

- How Difficult Is It to Surgically Treat AO-C Type Distal Humerus Fractures for Inexperienced Orthopedic Surgeons?
- Seong Ho Yoo, Suk Woong Kang, Moo Ho Song, Young Jun Kim, Hyuck Bae
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(2):45-49. Published online April 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.2.45
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
Twenty early surgical management cases of distal humerus type-C fractures were analyzed.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study analyzed 20 early patients, who received surgical management of distal humerus type-C fractures, and could be followed-ups for more than one year between March of 2013 and May of 2015. The operative time, bone union time, and elbow range of motion were analyzed. The Mayo's functional score was used to evaluate their postoperative function. The primary and secondary complications of each patient immediately after each of their surgery were also reviewed.
RESULTS
All patient groups achieved bone union within an average period of 16.4 weeks. Based on the Mayo functional score, 6, 10, and 4 patients scored excellent, good, and fair, respectively. The average range of motion was a flexion contracture of 14.5° with a follow-up improvement averaging 120.7°. Six patients received nine revision operations due to major and minor complications. Two patients received revision fixation from an inadequate fixating power, and another patient received an ulnar nerve transposition. Other complications included olecranon osteotomy site displacement, superficial operational site infection, and pin loosening.
CONCLUSION
Distal humerus fractures of the AO-C type can cause a range of complications and has a very high rate of revision due to its difficult nature of surgical manageability. Therefore, it is imperative for a surgeon to expect various complications beforehand and a careful approach to their postoperative rehabilitation is essential.
- 192 View
- 0 Download

- Anatomical Reduction with Brick-Work Technique in Comminuted Intraarticular Distal Radius Fractures
- Hyoung Min Kim, Hyung Lae Cho, Jong Woo Chae, Myung Ji Shin
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(1):1-8. Published online January 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study examined the clinical outcomes of comminuted intraarticular distal radius fractures treated by an anatomical reduction using a brick-work technique.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Seventeen patients with AO/OTA type 23-C3 distal radius fractures were enrolled in this study. An anatomical reduction of the articular surface was achieved using a brick-work technique through the dorsal approach and dorsal plates were used for fixation. The postoperative functional results were assessed with the range of motion of the wrist and the modified Mayo wrist score (MMWS). In addition, the radial length, radial inclination, volar tilt, and Lidstrom score were evaluated from the radiology results. The mean postoperative follow-up period was 13.6 months.
RESULTS
All patients showed bony union and the mean range of motion of the injured wrists was 94% (92% to 95%) of the uninjured side. The mean MMWS was 85.3, and the functional results were excellent in 12 patients, good in 4, and fair in one at the final follow-up. Based on the final radiographic measurements, the radial length, volar tilt, and radial inclination were 11.4 mm (10.0 to 13.5 mm), 6.6° (−1.8° to 9.2°), and 21.3° (20.1° to 25.7°), respectively. The radiologic results according to the Lidstrom score were excellent in 14 patients and good in three.
CONCLUSION
An anatomical reduction with the brick-work technique is relatively easy, results in a reproducible clinical outcome, and could be a safe and effective treatment option for severe comminuted intraarticular distal radius fractures that are not amenable to volar plate fixation.
- 229 View
- 1 Download

- Posterior Dual Plating for Distal Shaft Fractures of the Humerus
- Chul Hyun Cho, Kwang Yeung Jeong, Beom Soo Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(3):117-123. Published online July 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.3.117
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the results and efficacy of posterior dual plating for distal shaft fractures of the humerus.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We retrospectively analyzed 12 patients, who underwent open reduction and internal fixation using posterior dual plating for distal shaft fractures of the humerus, between July 2007 and July 2015, with at least 6 months of follow-up. After locating the radial nerve without dissection via posterior triceps splitting, the fracture was stabilized using a short 3.5 mm locking compression plate. Then additional fixation, using a long 3.5 mm locking compression plate, was performed. The clinical outcomes were assessed in accordance with the Mayo Elbow Performance Index (MEPI) scoring system, and the radiological outcomes were assessed using serial plain radiographs.
RESULTS
Eleven patients (91.7%) had bony union, and the mean union period was 13.9 weeks. In one patient, delayed union was treated by autogenous iliac bone graft at 8 months after surgery, which resulted in bony union. The mean MEPI score was 95.8, and the clinical outcomes were excellent in 9 patients and good in 3 patients. Postoperative complications included 1 elbow stiffness by heterotopic ossification and 1 temporary radial nerve palsy. One patient with temporary radial nerve palsy was completely recovered within the first 4 days after surgery.
CONCLUSION
Posterior dual plating for distal shaft fractures of the humerus revealed satisfactory clinical and radiological outcomes. It can be a useful alternative to provide stable fixation without the need for a dissection of the radial nerve.
- 473 View
- 9 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


