Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 32(3); 2019 > Article
- Original Article Paratricipital Approach for AO/OTA Type C2 Intra-Articular Fracture of Distal Humerus
- Chul Hyung Lee, Doo Hun Sun, Deukhee Jung, Chung Han An
-
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma 2019;32(3):128-134.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.3.128
Published online: July 31, 2019
- 997 Views
- 8 Download
- 1 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
Abstract
PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to determine the outcomes of fixation of AO/OTA type C2 fractures among intra-articular fractures of the distal humerus using the paratricipital approach (side to side retraction of the triceps).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From June 2008 to January 2018, 12 patients underwent an open reduction and internal fixation with the paratricipital approach and were followed-up for more than 10 months after surgery. According to the AO/OTA classification, type C2 fractures were chosen among the intraarticular distal humerus fractures. An extended posterior incision was used over the olecranon in the prone position, preserving the insertion site of the triceps brachii muscle. The fracture site was exposed by retracting the muscle side-to side through a dissection of the medial and lateral intermuscular septum of the triceps brachii muscle. The therapeutic results were assessed by the anatomical reduction of the articular surface and integrity of the metaphyseal contour in postoperative simple radiographs, complications, such as neuropathy or non-union, and the Mayo elbow performance score (MEPS) were checked to estimate the functional outcome.
RESULTS
In the postoperative simple radiographs, no case showed more than 1 mm step-off and the disrupted contour of the distal humerus was recovered to normal alignment in most cases. The range of elbow joint motion in the last follow-up was 133.8° on average with a mean flexion contracture of 5.0°. The clinical results depending on the MEPS were excellent, except for two cases, which were good. Neuropathy of the ulnar nerve was observed in one patient, which was resolved after metal removal.
CONCLUSION
The paratricipital approach is useful technique in AO/OTA type C2 intra-articular distal humerus fractures that provides sufficient exposure of the surgical field, without injury to the triceps brachii muscle and postoperative complications associated with the trans-olecranon approach.
Published online Jul 24, 2019.
https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.3.128
Paratricipital Approach for AO/OTA Type C2 Intra-Articular Fracture of Distal Humerus
Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to determine the outcomes of fixation of AO/OTA type C2 fractures among intra-articular fractures of the distal humerus using the paratricipital approach (side to side retraction of the triceps).
Materials and Methods
From June 2008 to January 2018, 12 patients underwent an open reduction and internal fixation with the paratricipital approach and were followed-up for more than 10 months after surgery. According to the AO/OTA classification, type C2 fractures were chosen among the intraarticular distal humerus fractures. An extended posterior incision was used over the olecranon in the prone position, preserving the insertion site of the triceps brachii muscle. The fracture site was exposed by retracting the muscle side-to side through a dissection of the medial and lateral intermuscular septum of the triceps brachii muscle. The therapeutic results were assessed by the anatomical reduction of the articular surface and integrity of the metaphyseal contour in postoperative simple radiographs, complications, such as neuropathy or non-union, and the Mayo elbow performance score (MEPS) were checked to estimate the functional outcome.
Results
In the postoperative simple radiographs, no case showed more than 1 mm step-off and the disrupted contour of the distal humerus was recovered to normal alignment in most cases. The range of elbow joint motion in the last follow-up was 133.8° on average with a mean flexion contracture of 5.0°. The clinical results depending on the MEPS were excellent, except for two cases, which were good. Neuropathy of the ulnar nerve was observed in one patient, which was resolved after metal removal.
Conclusion
The paratricipital approach is useful technique in AO/OTA type C2 intra-articular distal humerus fractures that provides sufficient exposure of the surgical field, without injury to the triceps brachii muscle and postoperative complications associated with the trans-olecranon approach.
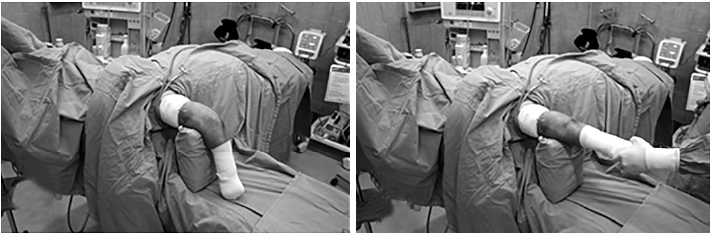
Fig. 1
Positioning for the paratricipital approach. The approach was used over the olecranon in the prone position. The pedestal was located on the distal portion of the upper arm and by supporting the fracture site of distal humerus, allowed the operators to flex and extend the elbow joint to acquire sufficient exposure of the surgical field.
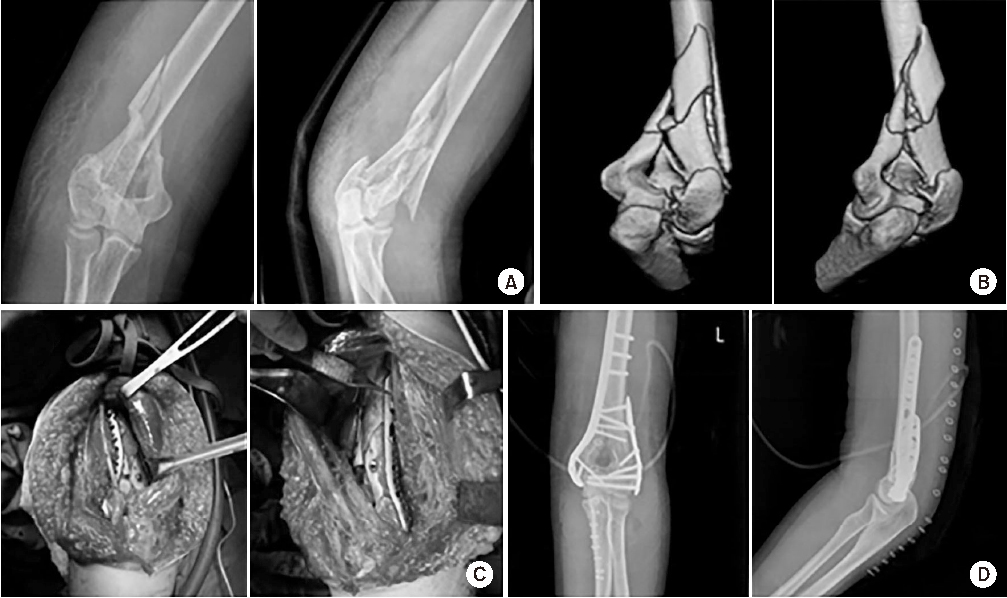
Fig. 2
A 58-year-old female slipped down and injured her elbow. (A, B) Anteroposterior X-ray and lateral X-ray and computed tomographies of a type C2 intra-articular fracture of the distal humerus. (C) Intraoperative photos of the paratricipital approach. (D) Postoperative anteroposterior and lateral X-rays of the patient fixed with a plate and screws and maintained anatomical reduction. The patient had an excellent result.
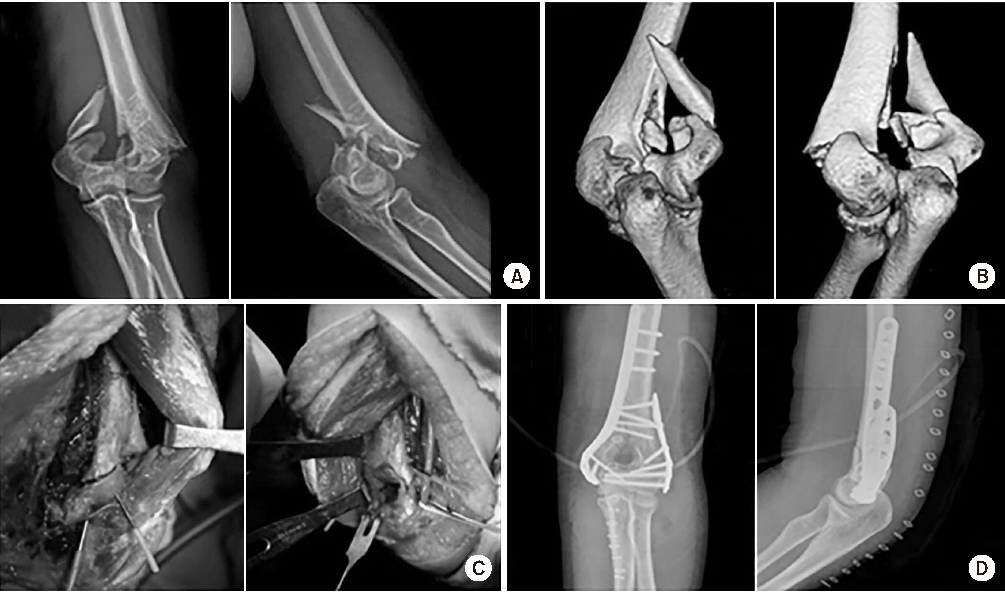
Fig. 3
A 39-year-old female fell on the ground and injured her elbow. (A, B) Anteroposterior X-ray and lateral X-ray and computed tomographies of a type C2 intra-articular fracture of the distal humerus. (C) Intraoperative photos of the paratricipital approach. (D) Postoperative anteroposterior and lateral X-rays of the patient fixed with a plate and screws and maintained anatomical reduction. The patient had an excellent result.
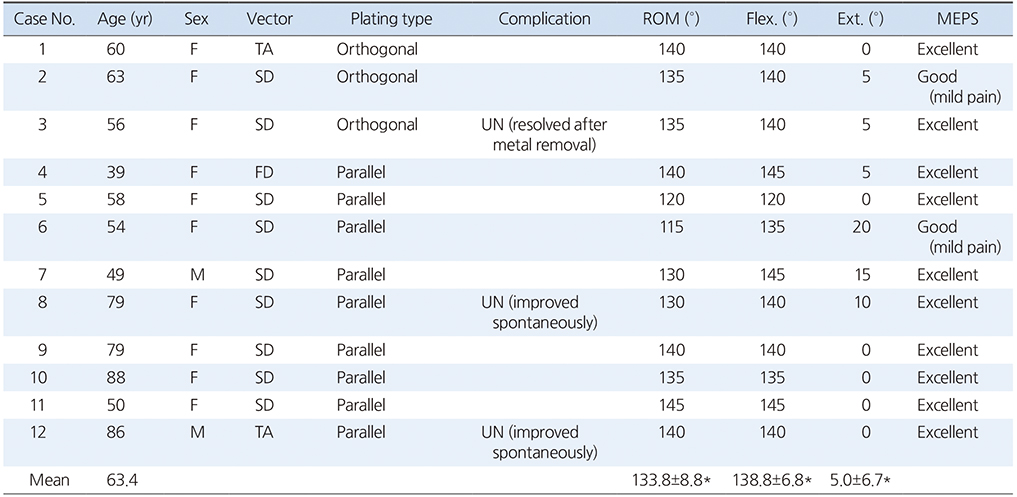
Table 1
Demographics and Clinical Results of Patients
Financial support:None.
Conflict of interests:None.
References
-
O'Driscoll SW. Parallel plate fixation of bicolumn distal humeral fractures. Instr Course Lect 2009;58:521–528.
-
-
O'Driscoll SW, Sanchez-Sotelo J, Torchia ME. Management of the smashed distal humerus. Orthop Clin North Am 2002;33:19–33. vii.
-

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS


 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite

