Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Three-dimensional computed tomography-based differentiation of engaged versus displaced intertrochanteric fractures using the anterior fracture line: a cross-sectional study from Korea
- Jae-Suk Chang, Jin Yeob Park, Sang-Ok Chun, Chul-Ho Kim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2026;39(1):30-37. Published online January 25, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00318
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
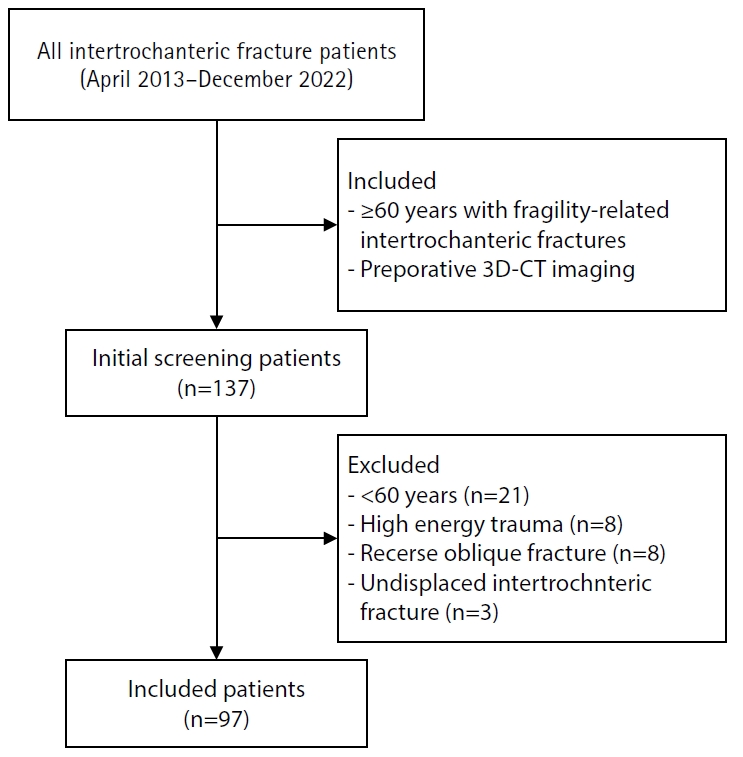
With the advent of an aging society, osteoporotic fractures—particularly hip fractures—are increasing, with a 1-year mortality rate of 17%. Achieving stable fixation that enables early ambulation is essential but remains challenging because complex intertrochanteric (IT) fracture patterns are often underestimated on plain radiographs. Using three-dimensional computed tomography (3D-CT), this study analyzed whether the anterior fracture line lies medial or lateral to the IT line and examined its relationship with displacement or distal medullary canal engagement, highlighting the potential influence of the joint capsule and capsular ligaments on fracture morphology and fixation stability.
Methods
A retrospective review was conducted on 96 osteoporotic IT fractures in patients aged ≥60 years treated between April 2013 and December 2022 at National Police Hospital and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. Fractures were classified as engaged, completely displaced, and partially displaced based on 3D-CT findings. The anterior fracture-line position (medial or lateral to the IT line) and the status of the lesser trochanter (LT) were evaluated. The chi-square or Fisher exact test was used for statistical comparisons.
Results
In total, 96 patients were analyzed. Of these, 49 cases (51.0%) were classified as engaged type, 27 cases (28.1%) as completely displaced type, and 20 cases (20.8%) as partially displaced type. When comparing fracture pattern with anterior fracture-line position, the completely displaced type showed a significantly higher proportion of lateral anterior fracture lines than the other two types (P<0.001). However, no significant association was identified between fracture pattern and LT displacement. When the anterior fracture-line position and LT displacement were evaluated together, only the engaged type demonstrated a possible association between a lateral anterior fracture line and LT displacement, though the statistical significance was weak (P=0.047).
Conclusions
Fracture lines lateral to the IT line were strongly associated with displacement in IT fractures; however, their relationship with LT involvement, reflecting iliopsoas tendon traction, was not clearly demonstrated. Although the factors contributing to the engaged-type fracture remain uncertain, the statistical association between fracture pattern and anterior fracture-line position suggests that capsular structures may play a stabilizing role in select fracture configurations. Further studies are needed to clarify these anatomical interactions. Level of evidence:
- 158 View
- 6 Download

Review Articles
- Treatment of Avulsion Fractures around the Knee
- Sumin Lim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(2):117-124. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.2.117
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Avulsion fractures are common in athletes and result from high-impact or sudden, forceful movements involving the separation of a bone fragment at the ligament or tendon attachment site. The key focus areas include the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments, medial collateral ligament, anterolateral complex, arcuate complex, medial patellofemoral ligament, patellar tendon, and quadriceps tendon. Diagnostic approaches combine radiography with advanced imaging techniques, such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, to elucidate the extent of injury and guide treatment decisions. Treatment ranges from conservative management for non-displaced fractures to surgical intervention for displaced fractures, with strategies customized based on the specific ligament involved and the nature of the fracture.
- 1,343 View
- 10 Download

- Checkrein Deformity after Fracture
- Jungtae Ahn, Gu-Hee Jung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(1):60-68. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.1.60
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Checkrein deformity has dynamic characteristics in which the degree of extension contracture of the metatarsophalangeal joint and flexion contracture of the interphalangeal joint change according to the movement of the ankle joint. Although the primary lesion is the flexor hallucis longus, several clinical features exist because of the accessory connection with the flexor tendon of other toes. After a physical diagnosis, a radiological examination should be performed to determine the cause and location of adhesion. Moreover, it is vital to determine if it is direct adhesion to the tendon tissue or muscle contracture due to ischemic muscle damage. Although there are no clear guidelines for surgical treatment, it can be divided broadly into two methods: soft tissue release and Z-plasty performed through direct access to the lesion site or indirect access through the tarsal tunnel or medial midfoot approach. Direct tendon tissue release surgery should be attempted if the tendon tissue is locally attached to the fracture callus or specific soft tissue. On the other hand, operation on the lesion site should be performed first if the checkrein deformity occurred due to an implant or bone fragments, followed by release surgery. If muscle contracture and movement are limited due to ischemic damage, surgery should be performed to remove adhesions and additional tendon connections around the flexor hallucis longus and digitorum longus by approaching through the tarsal canal and the medial side of the midfoot. The fixed contractures of the metatarsophalangeal and interphalangeal joints should be addressed if the limitations of tendon excursion are identified despite the release techniques.
- 1,444 View
- 29 Download

Case Reports
- Irreducible Ankle Fracture Dislocation due to Dislocated Tibialis Posterior Tendon - A Case Report -
- Seungyup Shin, Bum-Soo Kim, Ji-Won Lee, Euisun Yoon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(2):52-56. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.2.52
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - An irreducible ankle dislocation is a rare injury. The cause is a dislocation of the distal fibula anteriorly or posteriorly or the insertion of soft tissue, such as the deltoid ligament or posteromedial tendon. The tibialis posterior tendon can be dislocated through distal tibiofibular diastasis and prevent reduction of the ankle joint. The authors experienced anterolateral ankle fracture dislocation with a diastasis of the distal tibiofibular joint, and reduction was impossible because of impingement of the tibialis posterior tendon dislocated anteriorly through the distal tibiofibular diastasis. This paper reports the treatment of this injury.
- 594 View
- 13 Download

- Two-Year Follow-Up Results after Tendon Graft and Corrective Osteotomy for the Delayed Rupture of the 2nd-5th Flexor Tendons due to a Malunion of a Distal Radius Fracture - A Case Report -
- Jeung-Hwan Seo, Hyun-Gon Gwak, Jae Hoon Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(2):63-67. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.2.63
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The delayed rupture of the flexor tendons is a rare complication of malunited distal radius fractures after nonoperative management. The known cause of a flexor tendon rupture is attrition between the palmarly displaced ulnar head and the involved tendons. Sharp bony spurs on the volar side of the malunited distal radius can also cause flexor tendon rupture. About 30 cases have been reported in literature. There were only four case reports about the delayed rupture of the 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and 5th flexor tendons. In this case, we experienced flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor digitorum profundus tendon ruptures of the index, middle, ring, and little fingers, after 8 months following the malunion of a distal radius fracture. At two years follow-up after tendon graft and corrective osteotomy, the range of motion and motor weakness of the 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and 5th fingers improved.
- 466 View
- 2 Download

Review Article
- Tendon Healing: A Review of Basic Science and Current Progress
- Young Woo Kwon, Pei Wei Wang, Jun-Ku Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(4):227-237. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.4.227
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The tendon connects the muscles to the bones and transmits the loads generated by the muscles to the bones to move the joints, support the joints, and provide stability to the joints. Approximately 30% of patients complaining of musculoskeletal pain are associated with tendon disease, and approximately 50% of musculoskeletal injuries are caused by a tendon injury. Despite this frequent treatment of tendon damage, studies on the basic biology that provide scientific evidence for treatment, such as development, tendon injury, and healing, are still very limited. This review first summarizes the classification and composition of the tendon identified so far, the surrounding tissue, and the blood supply to the tendon. The limitations of the tendon recovery process after a tendon injury are also discussed. Finally, this review examines ways to improve tendon recovery and the biological approaches and tissue engineering that have been currently studied. In conclusion, innovative progress in promoting tendon healing has not been achieved despite the many advances in the basic structure of the tendon, and the cell and regulatory molecular factors involved in tendon recovery. Biological approaches and tissue engineering, which have become a recent issue, have shown many possibilities for the recovery of damaged cases, but further research will be needed until clinical application.
- 2,646 View
- 80 Download

Case Reports
- Irreducible Open Dorsal Dislocation of the Proximal Interphalangeal Joint: A Case Report
- Youn Tae Roh, Il Jung Park, Hyoung Min Kim, Jae Young Lee, Sung Lim You, Youn Soo Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2015;28(1):65-70. Published online January 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.1.65
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Dorsal dislocation of the proximal interphalangeal joint is a common injury in the orthopedic department. In most cases, the joint is reduced simply by closed manipulation. However, in rare cases, the joint is not reducible by closed manipulation, therefore, surgery is required. We report on a case of irreducible open dorsal dislocation of the proximal interphalangeal joint which was surgically treated. Because the flexor tendon interposed between the head of the proximal phalanx and the base of the middle phalanx, we could reduce the joint only after repositioning of the flexor tendon.
- 471 View
- 2 Download

- Peroneus Tendon Dislocation Associated with Fracture of Lateral Process of Talus: A Case Report
- Youn Soo Hwang, Sung Jun Jo, Kwang Yeol Kim, Hyung Chun Kim, Dong Seon Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(3):222-226. Published online July 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.3.222
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Traumatic peroneal tendon dislocation in association with fracture of the lateral process of the talus is a rare injury, which is difficult to diagnose. As a result, early detection is often delayed, which in turn leads to ankle pain and dysfunction. We treated a patient by open reduction and screw fixation in fracture of the lateral process of talus and primary repair of the superior peroneal retinaculum. We report this case with a brief review of the literature.
- 468 View
- 0 Download

- Rupture of the Extensor Pollicis Longus Tendon at the Proximal Screw of Volar Plate Fixation for Distal Radius Fracture: A Case Report
- Dong Ju Shin, Seung Oh Nam, Hun Sik Cho
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(4):338-342. Published online October 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.4.338
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - As volar plate fixation of distal radius fracture becomes more common, reports of ruptured extensor pollicis longus tendon by a protruding distal screw tip are also increasing steadily. Authors have experienced a rare case of ruptured extensor pollicis longus tendon at the prominent proximal screw of fixed volar plate for distal radius fracture, and we report it herein with a review of the literature.
- 536 View
- 1 Download

- Heterotopic Ossification around Patellar Tendon Following Treatment of Patellar Fracture: A Case Report
- Sang Jin Lee, Ji Wan Kim, Dong Hyun Lee, Jae Young Lim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(1):73-76. Published online January 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.1.73
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Heterotopic ossification around the patellar tendon is known to be extremely rare. A 42-year-old man had a transverse fracture of the left patella. Open reduction and tension band wiring were performed. At four weeks, plain radiographs showed an extensive ossification around the patellar tendon and the patient presented limitation of flexion and pain in kneeling position. We just encouraged active and passive ranges of motion exercises and performed one manipulation under anesthesia. At the final follow-up (10 months post-operatively), he was able to flex his knee by 140 degrees. We present a case of heterotopic ossification around the patellar tendon with limitation of knee flexion that was successfully treated with nonoperative treatment.
- 667 View
- 1 Download

- Interposition of Extensor Pollicis Longus Tendon in Smith's Fracture in a Child: A Case Report
- Seung Ju Jeon, Haeng Kee Noh, Do Yeon Kim, Sung Hoon Jung, Jun Beum Shin, Ho Seung Jeon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(1):65-68. Published online January 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.1.65
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Entrapment of the extensor pollicis longus tendon is reported rarely on Smith's fractures in children. In our case, a 15 year old boy with Smith's fracture received treatment of closed reduction at another hospital. When he visited our hospital, a wide gap at the fracture site was detected on radiograph and the thumb movement was limited. We have doubt the entrapment of the soft tissue, especially the tendon. We decided on open reduction. In the operation field, entrapment of the extensor pollicis longus tendon at the gap of the fracture site was found through dorsal approach. In addition, fracture treatment with K-wire fixation after reduction of extensonr pollicis longus tendon reduction was done. Therefore, we report this case with a review of the literatures.
- 425 View
- 0 Download

Original Article
- Alteration of the Patella Tendon Length after Intramedullary Nail in Tibial Shaft Fractures
- Dong Eun Shin, Ki Shik Nam, Jin Young Bang, Ji Hoon Chang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(4):283-287. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.4.283
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To compare and analyze length change of patella tendon after intramedullary nailing of tibial shaft fracture using transtendinous approach.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty-two cases were analyzed from December, 1999 to December, 2005. Insall Salvati ratios were estimated. Severity of initial trauma, duration of nail retension, knee function and pain on change of length of patellar tendon was evaluated.
RESULTS
Mean duration of nail retention was twenty-two months. The shortening of patella tendon was observed in 25 cases (p<0.001). The effect of AO type and the duration of nail retension on the decrease of Insall Salvati ratio was not significant (p>0.05, p=0.778). Lysholom score decrease to 89.5. There was no significant difference between the shortening of patellar tendon length and knee pain (p=0.058).
CONCLUSION
After intramedullary nailing for closed tibia fracture, shortening of patellar tendon length is observed. That is irrelevant to the fracture type and the duration of nail retension. The shortening of patella tendon length may contribute to decreasing of knee function, but it was no significance of knee pain after intramedullary nailing.
- 521 View
- 0 Download

Case Reports
- Checkrein Deformity by Incarcerated Posterior Tibial Tendon and Displaced Flexor Hallucis Longus Tendon following Ankle Dislocation: A Case Report
- Su Young Bae, Hyung Jin Chung, Man Young Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2011;24(3):271-276. Published online July 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.3.271
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We report a case of 20 year-old man who had unusual equinus and checkrein deformity following dislocation of his right ankle joint. He had been treated with distal tibiofibular screw fixation and external fixation. After removal of external fixator, he had suffered from progressive deformity of foot and ankle. Widening of distal tibiofibular joint and medial clear space was found on radiograph and it was revealed that posterior tibial tendon had been dislocated and incarcerated into the distal tibiofibular joint on MRI. We corrected the deformity with excision of incarcerated posterior tibial tendon, adhesiolysis and lengthening of flexor hallucis longus tendon, reconstruction of deltoid ligament and flexor digitorum longus tendon transfer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Management of Checkrein Deformity
Min Gyu Kyung, Yun Jae Cho, Dong Yeon Lee
Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery.2024; 16(1): 1. CrossRef - A Neglected Extensor Hallucis Longus Tendon Rupture Caused by Arthritic Adhesion
Sung Hun Won, Sung Hwan Kim, Young Koo Lee, Dong-Il Chun, Byung-Ryul Lee, Woo-Jong Kim
Medicina.2023; 59(6): 1069. CrossRef - The Checkrein Deformity of Extensor Hallucis Longus Tendon and Extensor Retinaculum Syndrome with Deep Peroneal Nerve Entrapment after Triplane Fracture: A Case Report
Hyungon Gwak, Jungtae Ahn, Jae Hoon Lee
Journal of Korean Foot and Ankle Society.2021; 25(3): 145. CrossRef - Checkrein Deformity Due to Flexor Digitorum Longus Adhesion after Comminuted Calcaneus Fracture: A Case Report
Jin Su Kim, Han Sang Lee, Ki Won Young, Keun Woo Lee, Hun Ki Cho, Sang Young Lee
Journal of Korean Foot and Ankle Society.2015; 19(1): 35. CrossRef
- Management of Checkrein Deformity
- 624 View
- 0 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Flexor Pollicis Longus Tendon Rupture as a Complication of a Closed Distal Radius Fracture: A Case Report
- Do Young Kim, Eun Min Seo, Woo Dong Nam, Seung Jae Park, Sang Soo Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2011;24(2):191-194. Published online April 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.2.191
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - There are few reported cases of flexor pollicis longus tendon (FPL) rupture complicating a closed distal radius fracture. We report a case of FPL tendon rupture complicating a closed distal radius fracture. A 24-year-old male presented with a severe right wrist pain. He had a closed distal radius fracture that was treated by closed manual reduction. Three days later, he complained forearm pain and limitation of thumb motion. The physical examination revealed loss of active interphalangeal joint flexion of thumb. He was taken to the operating room. Intraoperatively, the FPL was found to be discontinuous at the level of the radius fracture site. The FPL was repaired by a modified Kessler technique, and the fracture was repaired with a volar plate. Clinicians must be cautious in possibility of tendon injury complicating a closed distal radius fracture and assessing patients with distal radius fracture following closed reduction.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Acute Rupture of Flexor Tendons as a Complication of Distal Radius Fracture
Youn Moo Heo, Sang Bum Kim, Kwang Kyoun Kim, Doo Hyun Kim, Won Keun Park
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2015; 50(1): 60. CrossRef
- Acute Rupture of Flexor Tendons as a Complication of Distal Radius Fracture
- 764 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Stiff Knee by Entrapment of Quadriceps Femoris Tendon at Fracture Site in Paediatric Distal Femur Shaft Fracture
- Suk Kang, Jong Pil Kim, Chung Soo Hwang, Phil Hyun Chung, Young Sung Kim, Sang Ho Lee, Jin Wook Chung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(4):339-344. Published online October 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.4.339
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The complications following paediatric femur fracture are leg length discrepancy, angulation deformity, rotational deformity, ischemic limb. But, stiff knee is rarely expressed after trauma like paediatric femur fracture. We report a case of stiff knee due to entrapment of quadriceps femoris tendon at displaced fracture site after conservative treatment by Russel traction and hip spica cast in paediatric femur fracture. We treated successfully by resection of distal end of proximal segment of femur and release of quadriceps femoris tendon for flexion contracture of the knee.
- 379 View
- 0 Download

- Attritional Flexor Tendon Ruptures after Malunited Distal Radial Fracture: A Case Report
- Jin Ho Cho, Hyoung Keun Oh
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(1):93-95. Published online January 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.1.93
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- Ruptures of extensor pollicis longus tendon after distal radial fractures are well-known. However, delayed flexor tendon rupture of finger as a complication of the fracture are less common. We report the case of delayed rupture of flexor digitorum profundus tendon to middle and ring fingers and flexor digitorum superficialis to ring finger in 72 year old female patient. She was treated by free tendon graft with palmaris longus tendon. After 1 year follow-up, range of motion and flexion power were recovered to nearly normal.
- 407 View
- 0 Download

- Fracture of the Os Peroneum with Rupture of the Peroneus Longus Tendon: A Case Report
- Yong Hoon Kim, Keun Woo Kim, Hak Jin Min, Eui Seong Yoon, Hee Oh Kim, Jae Seong Suh
- J Korean Soc Fract 2001;14(4):685-688. Published online October 31, 2001
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2001.14.4.685
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Os peroneum is one of the normal sesamoids in the foot and it can be insertion of peroneus longus tendon. We report a case of as peroneum fracture with complete tear of peroneus longus tendon. This case was finally diagnosed in operation and treated by suture with peroneus brevis tendon and short leg cast.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome Presenting as Lateral Plantar Foot Pain
Seon Jeong Oh, Young Hoon Kim, Sun Ki Kim, Min-Wook Kim
Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine.2012; 36(1): 163. CrossRef
- Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome Presenting as Lateral Plantar Foot Pain
- 624 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- The Acute surgical Treatment in Superior Peroneal Retinacular Injury in Ankle
- Suk Goo Han, Nam Yong Choi, In Tak Choo, Sung Jin Park, Young Mok Kang, In Ju Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 1998;11(3):605-610. Published online July 31, 1998
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1998.11.3.605
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The superior peroneal retinacular injury in ankle is often diagnosed as an ankle sprain and treated conservatively because of normal bony contour in type 1,2 injury according to Eckery's classification and small bony fragment with early union, evenly displaced in type 3. But its complications such as peroneal tendinitis and recurrent subluxation or dislocation of peroneal tendons sometimes develop late. Compared to peroneal tendinitis, the surgical treatment method for recurrent subluxation or dislocation of peroneal tendons is known superor to conservative method in results. And many reconstructive methods have been reported. In spite of their good results, harmfulness to normal structures, recurrences and technical difficulties may be a problem. So we perfomed 10 cases of acute surgical repair in superior peroneal retinacular injuries in ankle from March 1993 to February 1997 and prospectively analysed their clinical and radiological results with complications. Preoperative radiological diagnosis was done by plain films, peroneal tenography with computed tomography and also postperatively evaluated with plain films and peroneal tenography. 1. The most common cause of injury was sports(6 cases) including ski injury(4 cases) and average age of the patient was 29(17-56) years. 2. 4 cases of bony avulsion(type 3) were fixed with mini-screws and mean duration of bony union was 3.6 months. 3. The incidental subluxation or dislocation of peroneal tendons was not found intraoperatively and postoperatively. 4. All patients are able to participate in active exercise postoperatively except one patient who complains of lateral ankle discomfort due to peroneal tendinitis. In conclusion, acute surgical repair of superior peroneal retinacular injury in ankle is a recommended method to prevent it's complications such as peroneal retinacular injury in ankle is a recommended method to prevent it's complications such as peroneal tendinitis and subluxation or dislocation of peroneal tendons especially, in young and active patients.
- 347 View
- 0 Download

- Attritional Rupture of the Flexor Tendons after Malunion of Distal Radial Fracture : Report of One Case
- Jae Do Kang, Kwang Yul Kim, Sang Hun Ko, Hyung Chun Kim, Kyeong Chil Jung, Moon Sub Yim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1997;10(4):929-933. Published online October 31, 1997
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1997.10.4.929
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - There are a few of reports of delayed rupture of flexor tendon around the wrist and hand by attrition. Only 4 cases of delayed flexor tendon rupture of finger except rupture of flexor pollicis longus after Cellos fracture were reported until now. Several causes of the delayed rupture of the tendon around the wrist and hand were reported by many authors. Cellos fracture is one of the cause of the attritional rupture. But the frequency of the attritonal rupture of the flexor tendon was only one-third of the extensor tendons. Furthermore, flexor tendons of the finger were less commonly affected than that of the thumb by their anatomical features. We would like to report a very rare case of delayed rupture of flexor digitorum profundus on 73 year old male patient by attrition on the bony spur which was formed by malunion of distal radial fracture about 10 years ago. They were treated by direct repair for ring finger and free tendon graft with flexor digitorum sublimis of middle finger for little finger. After 1 year follow up, range of motion and flexion power were recovered to nearly normal.
- 373 View
- 0 Download

Case Report
- Traumatic Rupture of the Extensor Pollicis Longus Tendon Associated with Smiths Fracture: A case report
- Keun Woo Kim, Yeng Boon Kim, Pil Gu Yi, Rak Jin Min, Ui Seoung Yoon, Yeng Ryeog Kang
- J Korean Soc Fract 1994;7(2):279-283. Published online November 30, 1994
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1994.7.2.279
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - As a complication of Smiths fracture, traumatic entrapment and closed rupture of the extensor pollicis longus tendon may occur rarely at the fracture site and cause loss of thumb extenion. Traumatic entrapment of the extensor pollicis longus tendon in Smiths fracture which was anatomic barrier of successful closed reduction was first described by Hunt in 1969. Since then, several authors reported another few cases. The mechanism of tendon rupture in Smiths fracture is thought that the sharp dorsal edge of the proximal fragment may tear the stretched muscular tendon unit during extreme wrist flexion. We experienced a case of traumatic rupture of the extensor pollicis longus tendon associated with a closed Smiths fracture and report this case with our treatment method.
- 347 View
- 1 Download

Original Article
- Bilateral traumatic didlocation of the tibialis posterior tendons a case report
- Jin Young Kim, Chan Hee Park, Jong Who Kang, Jong Hun Park
- J Korean Soc Fract 1992;5(1):157-160. Published online May 31, 1992
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1992.5.1.157
- 434 View
- 0 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


