Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 24(3); 2011 > Article
-
Case Report
- Checkrein Deformity by Incarcerated Posterior Tibial Tendon and Displaced Flexor Hallucis Longus Tendon following Ankle Dislocation: A Case Report
- Su-Young Bae, M.D., Ph.D., Hyung-Jin Chung, M.D., Ph.D., Man-Young Kim, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2011;24(3):271-276.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.3.271
Published online: July 15, 2011
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Su-Young Bae, M.D., Ph.D. Foot & Ankle Center, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University, 761-1, Sanggye 6,7-dong, Nowon-gu, Seoul 139-707, Korea. Tel: 82-2-950-1399, 1032, Fax: 82-2-950-1398, sybae99@gmail.com
• Received: March 2, 2011 • Revised: April 8, 2011 • Accepted: April 28, 2011
Copyright © 2011 The Korean Fracture Society
- 595 Views
- 0 Download
- 4 Crossref
Abstract
- We report a case of 20 year-old man who had unusual equinus and checkrein deformity following dislocation of his right ankle joint. He had been treated with distal tibiofibular screw fixation and external fixation. After removal of external fixator, he had suffered from progressive deformity of foot and ankle. Widening of distal tibiofibular joint and medial clear space was found on radiograph and it was revealed that posterior tibial tendon had been dislocated and incarcerated into the distal tibiofibular joint on MRI. We corrected the deformity with excision of incarcerated posterior tibial tendon, adhesiolysis and lengthening of flexor hallucis longus tendon, reconstruction of deltoid ligament and flexor digitorum longus tendon transfer.
- 1. Carr JB. Complication of calcaneus fractures entrapment of the flexor hallucis longus: report of two cases. J Orthop Trauma, 1990;4:166-168.
- 2. De Zwart DF, Davidson JS. Rupture of the posterior tibial tendon associated with fractures of the ankle. A report of two cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1983;65:260-262.
- 3. Ermis MN, Yagmurlu MF, Kilinc AS, Karakas ES. Irreducible fracture dislocation of the ankle caused by tibialis posterior tendon interposition. J Foot Ankle Surg, 2010;49:166-171.
- 4. Feeney MS, Williams RL, Stephens MM. Selective lengthening of the proximal flexor tendon in the management of acquired claw toes. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2001;83:335-338.PDF
- 5. Jahss MH. Disorders of the foot and ankle, 1991;Vol. 2:2nd ed. Philadelphia, WB Saunders. 1471-1477.
- 6. Kwon H, Kim DW, Kim DJ, Sohn CS, Song JM, Rah SK. Checkrein deformity of the lesser toes following comminuted fracture of calcaneus: a case report. J Korean Soc Fract, 1998;11:806-810.
- 7. Lee HS, Kim JS, Park SS, Lee DH, Park JM, Wapner KL. Treatment of checkrein deformity of the hallux. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2008;90:1055-1058.PDF
- 8. Myerson M, Corrigan J. Treatment of posterior tibialis tendon dysfunction with flexor digitorum longus tendon transfer and calcaneal osteotomy. Orthopedics, 1996;19:383-388.
- 9. Sanhudo JA, Lompa PA. Checkrein deformity--flexor hallucis tethering: two case reports. Foot Ankle Int, 2002;23:799-800.PDF
REFERENCES
Fig. 2
(A) Anteroposterior view of right ankle shows widening of tibiofibular space and medial clear space.
(B) Lateral view shows equinus and flexion deformity of great toe.
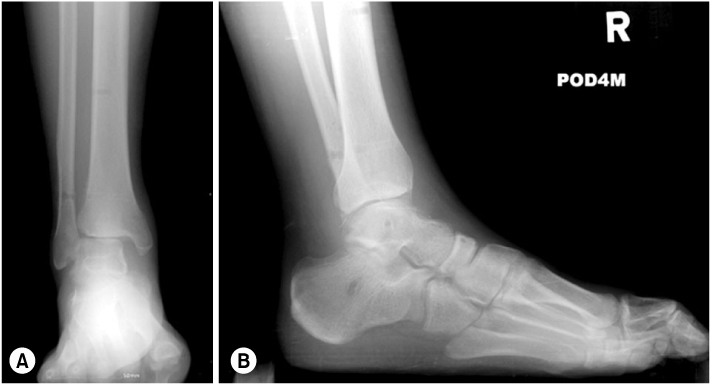

Fig. 3Immediate post-traumatic radiographs of other clinic show that talus was displaced into distal tibiofibular space.
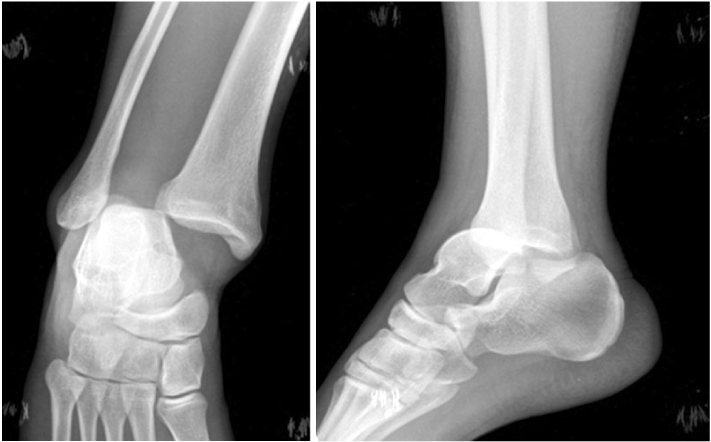

Fig. 4
(A) For initial treatment, open reduction and external fixation of ankle joint was done and a syndesmotic screw was inserted at other clinic.
(B) Follow-up X-ray with the external fixator removed 2 months later.
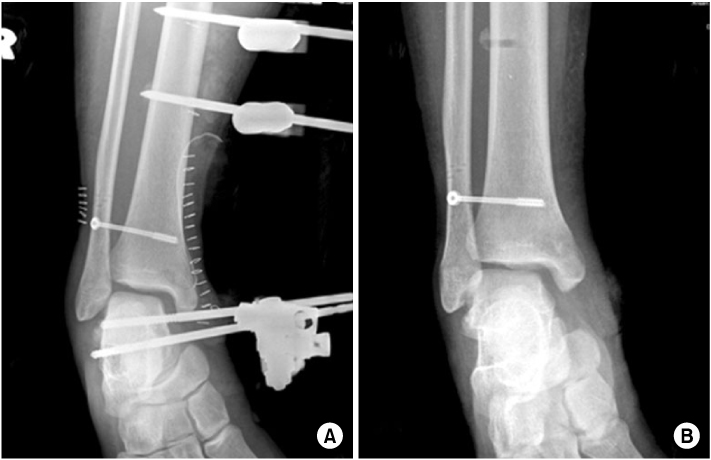

Fig. 5Ankle MRI shows incarceration of posterior tibial tendon into the fibular groove of distal tibia (white arrows) and displaced flexor hallucis longus tendon (black arrows).
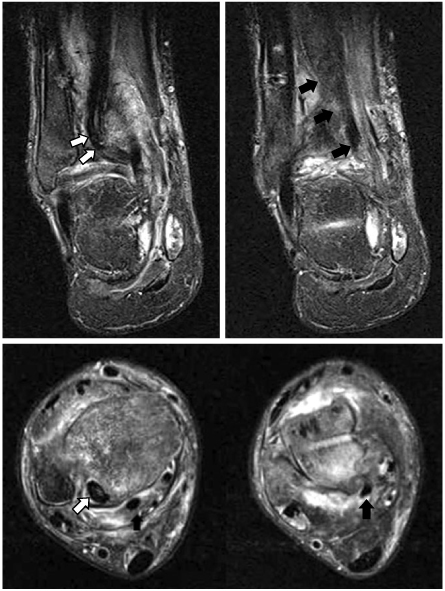

Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Management of Checkrein Deformity
Min Gyu Kyung, Yun Jae Cho, Dong Yeon Lee
Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery.2024; 16(1): 1. CrossRef - A Neglected Extensor Hallucis Longus Tendon Rupture Caused by Arthritic Adhesion
Sung Hun Won, Sung Hwan Kim, Young Koo Lee, Dong-Il Chun, Byung-Ryul Lee, Woo-Jong Kim
Medicina.2023; 59(6): 1069. CrossRef - The Checkrein Deformity of Extensor Hallucis Longus Tendon and Extensor Retinaculum Syndrome with Deep Peroneal Nerve Entrapment after Triplane Fracture: A Case Report
Hyungon Gwak, Jungtae Ahn, Jae Hoon Lee
Journal of Korean Foot and Ankle Society.2021; 25(3): 145. CrossRef - Checkrein Deformity Due to Flexor Digitorum Longus Adhesion after Comminuted Calcaneus Fracture: A Case Report
Jin Su Kim, Han Sang Lee, Ki Won Young, Keun Woo Lee, Hun Ki Cho, Sang Young Lee
Journal of Korean Foot and Ankle Society.2015; 19(1): 35. CrossRef
Checkrein Deformity by Incarcerated Posterior Tibial Tendon and Displaced Flexor Hallucis Longus Tendon following Ankle Dislocation: A Case Report
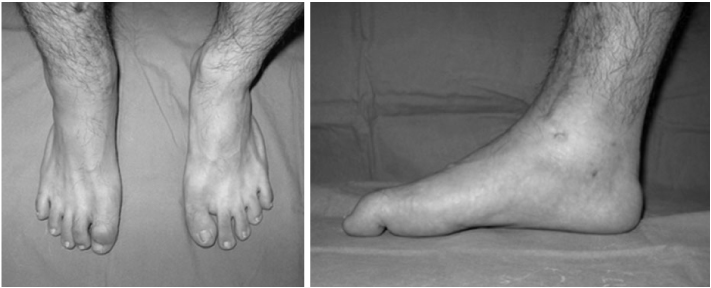
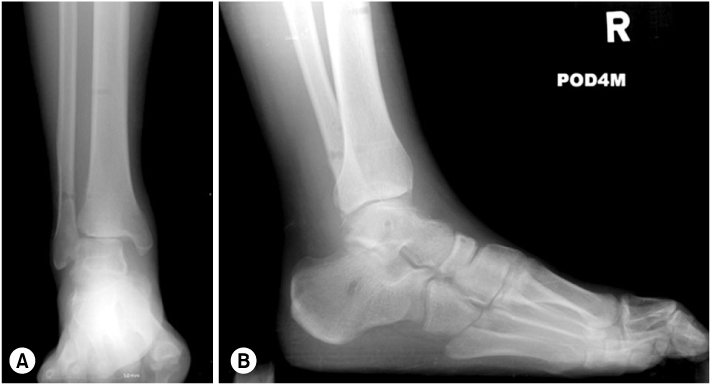
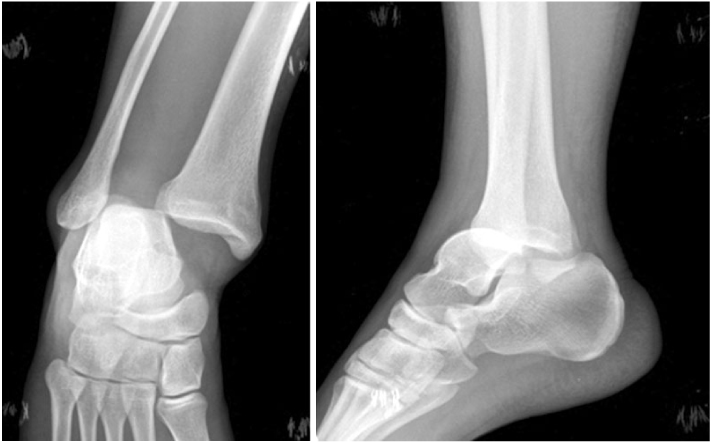
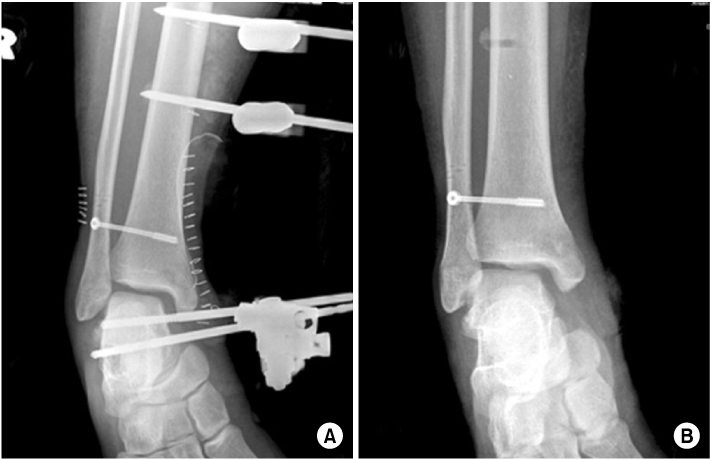
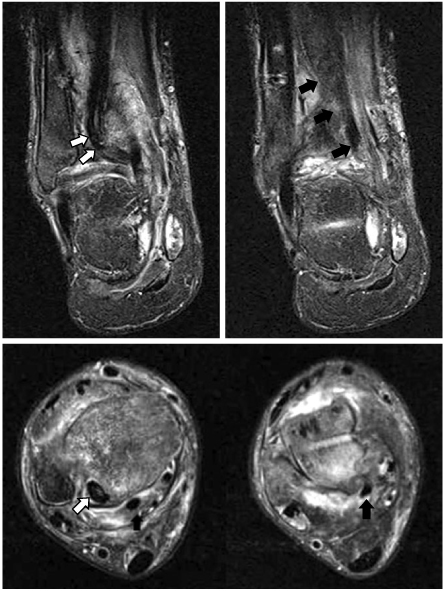
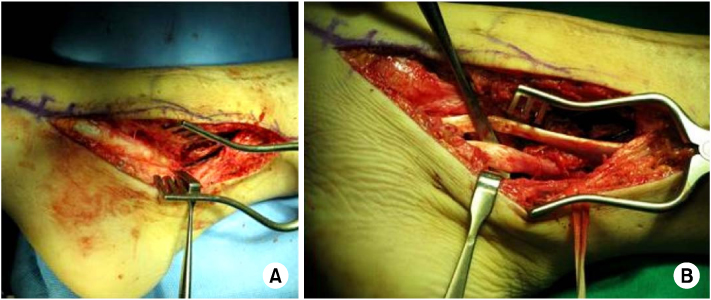
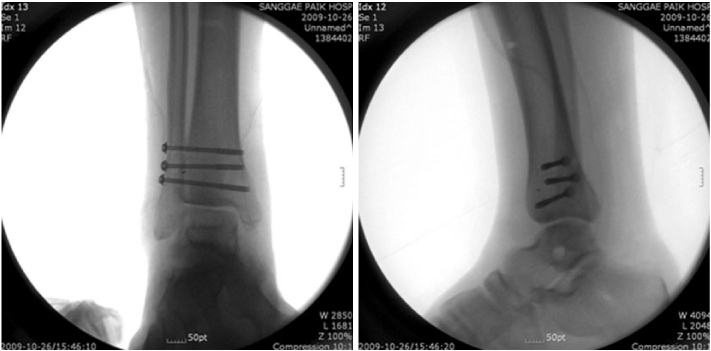
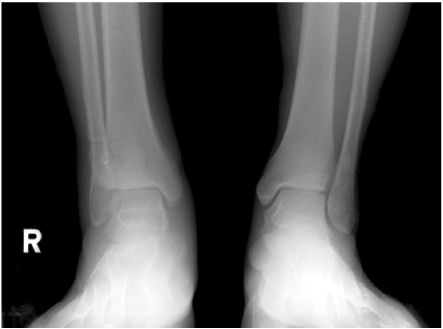
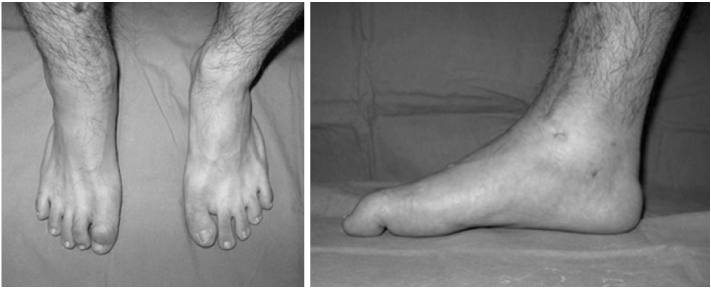
Fig. 1
Equinus of right ankle and flexion deformity of interphalangeal joint of great toe.
Fig. 2
(A) Anteroposterior view of right ankle shows widening of tibiofibular space and medial clear space.
(B) Lateral view shows equinus and flexion deformity of great toe.
Fig. 3
Immediate post-traumatic radiographs of other clinic show that talus was displaced into distal tibiofibular space.
Fig. 4
(A) For initial treatment, open reduction and external fixation of ankle joint was done and a syndesmotic screw was inserted at other clinic.
(B) Follow-up X-ray with the external fixator removed 2 months later.
Fig. 5
Ankle MRI shows incarceration of posterior tibial tendon into the fibular groove of distal tibia (white arrows) and displaced flexor hallucis longus tendon (black arrows).
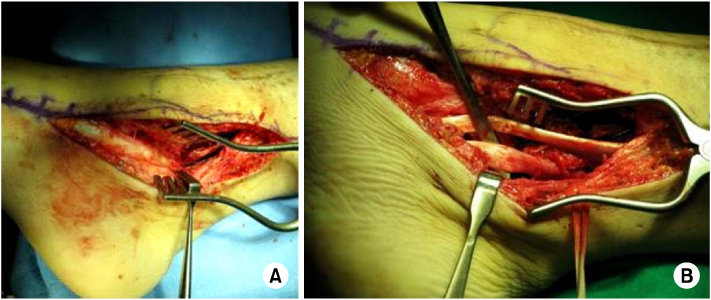
Fig. 6
(A) Posterior tibial tendon was displaced into the posterolateral aspect of the ankle joint.
(B) Continuity of flexor hallucis longus tendon was intact (freer under the tendon).
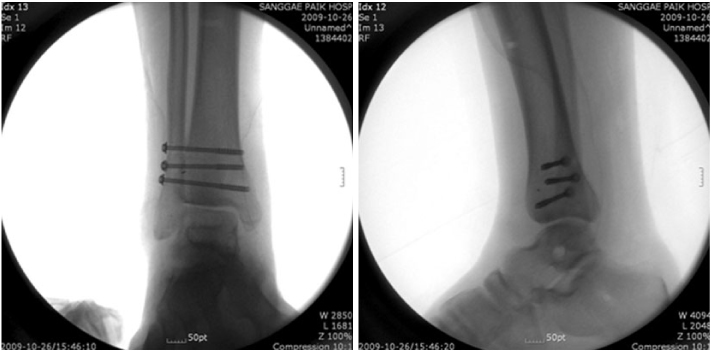
Fig. 7
Intra-operative ankle X-ray (AP and lateral views).
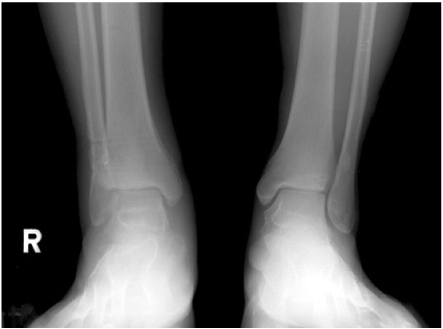
Fig. 8
Follow-up standing ankle radiograph.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Fig. 6
Fig. 7
Fig. 8
Checkrein Deformity by Incarcerated Posterior Tibial Tendon and Displaced Flexor Hallucis Longus Tendon following Ankle Dislocation: A Case Report

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

