Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 25(4); 2012 > Article
-
Original Article
- Alteration of the Patella Tendon Length after Intramedullary Nail in Tibial Shaft Fractures
- Dong-Eun Shin, M.D., Ki-Shik Nam, M.D., Jin-Young Bang, M.D., Ji-Hoon Chang, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2012;25(4):283-287.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.4.283
Published online: October 19, 2012
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Bundang CHA Hospital, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea.
*Nanoori Gangseo Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Ki-Shik Nam, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Bundang CHA Hospital, CHA University, 59, Yatap-ro, Bundang-gu, Seongnam 463-712, Korea. Tel: 82-31-780-5270, Fax: 82-31-703-3578, allthatineed@naver.com
Copyright © 2012 The Korean Fracture Society
- 521 Views
- 0 Download
Abstract
-
Purpose
- To compare and analyze length change of patella tendon after intramedullary nailing of tibial shaft fracture using transtendinous approach.
-
Materials and Methods
- Thirty-two cases were analyzed from December, 1999 to December, 2005. Insall Salvati ratios were estimated. Severity of initial trauma, duration of nail retension, knee function and pain on change of length of patellar tendon was evaluated.
-
Results
- Mean duration of nail retention was twenty-two months. The shortening of patella tendon was observed in 25 cases (p<0.001). The effect of AO type and the duration of nail retension on the decrease of Insall Salvati ratio was not significant (p>0.05, p=0.778). Lysholom score decrease to 89.5. There was no significant difference between the shortening of patellar tendon length and knee pain (p=0.058).
-
Conclusion
- After intramedullary nailing for closed tibia fracture, shortening of patellar tendon length is observed. That is irrelevant to the fracture type and the duration of nail retension. The shortening of patella tendon length may contribute to decreasing of knee function, but it was no significance of knee pain after intramedullary nailing.
- 1. Adam F, Pape D, Kohn D, Seil R. Length of the patellar tendon after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with patellar tendon autograft: a prospective clinical study using Roentgen stereometric analysis. Arthroscopy, 2002;18:859-864.
- 2. Court-Brown CM, Christie J, McQueen MM. Closed intramedullary tibial nailing. Its use in closed and type I open fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1990;72:605-611.PDF
- 3. Court-Brown CM, Gustilo T, Shaw AD. Knee pain after intramedullary tibial nailing: its incidence, etiology, and outcome. J Orthop Trauma, 1997;11:103-105.
- 4. Devitt AT, Coughlan KA, Ward T, et al. Patellofemoral contact forces and pressures during intramedullary tibial nailing. Int Orthop, 1998;22:92-96.PDF
- 5. Karladani AH, Granhed H, Kärrholm J, Styf J. The influence of fracture etiology and type on fracture healing: a review of 104 consecutive tibial shaft fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, 2001;121:325-328.PDF
- 6. Katsoulis E, Court-Brown C, Giannoudis PV. Incidence and aetiology of anterior knee pain after intramedullary nailing of the femur and tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2006;88:576-580.PDF
- 7. Keating JF, Orfaly R, O'Brien PJ. Knee pain after tibial nailing. J Orthop Trauma, 1997;11:10-13.
- 8. Kim DW, Roh KJ, Yoo WK, Chung IH. The morphometric study on cruciate and patellar ligaments in Korean Adults. J Korean Orthop Assoc, 1995;30:1210-1215.
- 9. Lee KW, Kang JW, Lee SH, Kim HY, Choy WS. Knee pain analysis after tibia intramedullary nailing. J Korean Soc Fract, 2001;14:278-284.
- 10. Lin CF, Wu JJ, Chen TS, Huang TF. Comparison of the Insall-Salvati ratio of the patella in patients with and without an ACL tear. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc, 2005;13:8-11.
- 11. Sanders R, Jersinovich I, Anglen J, DiPasquale T, Herscovici D Jr. The treatment of open tibial shaft fractures using an interlocked intramedullary nail without reaming. J Orthop Trauma, 1994;8:504-510.
- 12. Scuderi GR, Windsor RE, Insall JN. Observations on patellar height after proximal tibial osteotomy. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1989;71:245-248.
- 13. Shelbourne KD, Trumper RV. Preventing anterior knee pain after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Am J Sports Med, 1997;25:41-47.
- 14. Sohn SK, Kim KT, Cho KW. Anterior knee pain after tibia intramedullary nailing. J Korean Knee Soc, 1998;10:109-113.
- 15. Väistö O, Toivanen J, Paakkala T, Järvelä T, Kannus P, Järvinen M. Anterior knee pain after intramedullary nailing of a tibial shaft fracture: an ultrasound study of the patellar tendons of 36 patients. J Orthop Trauma, 2005;19:311-316.
- 16. Weale AE, Murray DW, Newman JH, Ackroyd CE. The length of the patellar tendon after unicompartmental and total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1999;81:790-795.
- 17. Westrich GH, Peters LE, Haas SB, Buly RL, Windsor RE. Patella height after high tibial osteotomy with internal fixation and early motion. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1998;(354):169-174.
- 18. Windsor RE, Insall JN, Vince KG. Technical considerations of total knee arthroplasty after proximal tibial osteotomy. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1988;70:547-555.
- 19. Yoon YS, Rah JH. Histologic changes in dog intra-articular patellar tendon transplants. J Korean Orthop Assoc, 1992;27:802-808.
REFERENCES
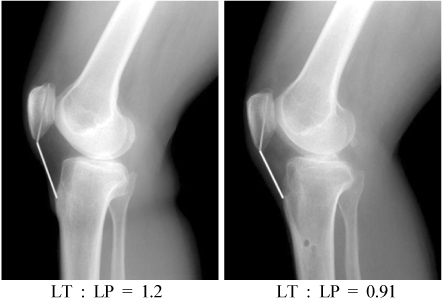
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

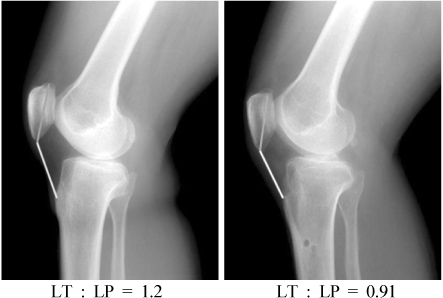
Fig. 1
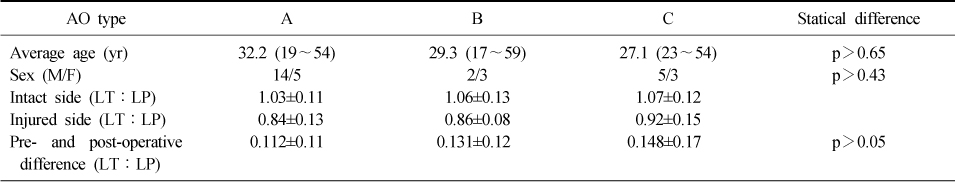
Difference in Insall-Salvati Ratio according to AO Classification
Values are presented as mean (range) or number or mean±standard deviation. M: Male, F: Female, LT: Length of patella tendon, LP: Length of patella.
Difference in Insall-Salvati Ratio according to Duration of Nail Retention
Values are presented as mean (range) or number or mean±standard deviation. M: Male, F: Female, LT: Length of patella tendon, LP: Length of patella.
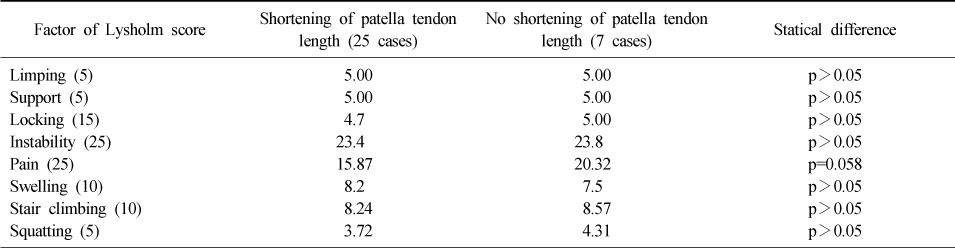
Relationship between Patellar Tendon Length Change and Knee Pain
Values are presented as mean (range) or number or mean±standard deviation. M: Male, F: Female, LT: Length of patella tendon, LP: Length of patella.
Values are presented as mean (range) or number or mean±standard deviation. M: Male, F: Female, LT: Length of patella tendon, LP: Length of patella.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 Cite
Cite

