Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Articles
- Current concepts and applications of bone graft substitutes in orthopedic surgery
- Jae Ho Cho, Hyung Keun Song
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):169-177. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00248

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Bone defects, which often arise from high-energy injuries, infections, tumor resections, or nonunions, represent a persistent challenge in orthopedic trauma surgery. Autologous bone grafting remains the gold standard due to its unique combination of osteogenic, osteoinductive, and osteoconductive properties. However, issues such as donor site morbidity, limited graft volume, and increased surgical time have driven the development of bone graft substitutes. These substitutes vary widely in origin, composition, biological activity, and mechanical characteristics, encompassing allografts, xenografts, synthetic materials, and biologically enhanced constructs. This review outlines the fundamental biological principles underlying bone regeneration—including osteogenesis, osteoinduction, and osteoconduction—and addresses additional key factors such as biocompatibility, biodegradability, and mechanical strength. Current bone graft materials are classified by biological origin and functional characteristics, with an emphasis on their use in trauma surgery. Particular attention is given to the clinical applications, indications, and limitations of allograft-based solutions (such as structural allografts and demineralized bone matrix), synthetic ceramics (including calcium phosphate and bioactive glass), and biologically enhanced options, such as recombinant growth factors and stem cell therapies. In trauma settings, graft selection must be tailored to the characteristics of the defect, mechanical demands, the biological environment, and patient-specific factors. Integration with surgical technique and fixation is crucial for optimizing outcomes. Although modern substitutes show promise, none fully replicate the complex biology of autografts. Looking ahead, emerging technologies such as 3D printing, nanotechnology, and smart biomaterials offer exciting possibilities but face translational challenges. This review aims to provide practicing orthopedic surgeons with a concise, evidence-based overview of bone substitute options and their roles in trauma care. By applying core biological principles and clinical judgment, surgeons can better navigate the expanding array of graft materials to improve outcomes for patients with complex skeletal defects.
- 2,381 View
- 48 Download

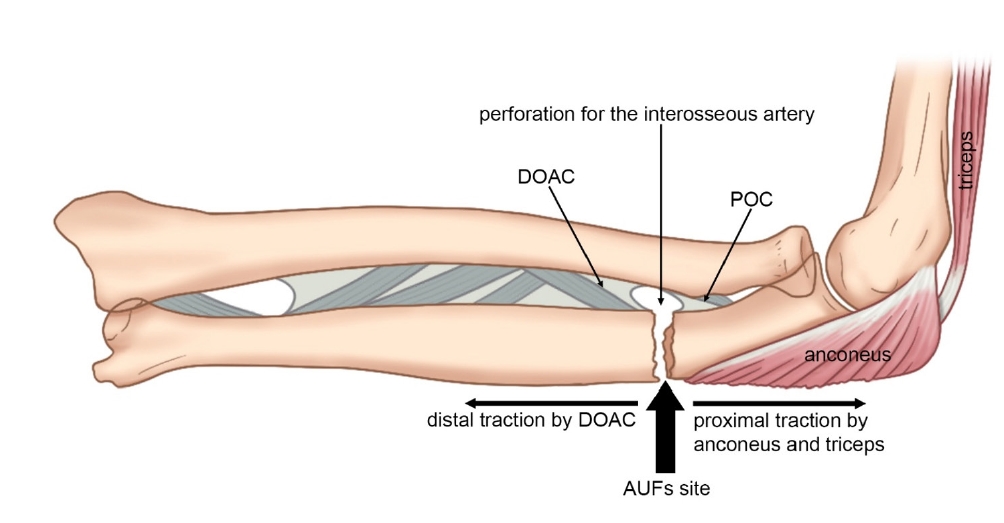
- Atypical ulnar fractures: a narrative review of current concepts and a case of bilateral surgical management
- Chi-Hoon Oh, Hyun Tak Kang, Jun-Ku Lee
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):124-132. Published online July 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00227
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Atypical ulnar fractures (AUFs) are rare complications that are often linked to long-term antiresorptive therapy. Although atypical femoral fractures are well-studied, AUFs lack standardized diagnostic and treatment protocols. This review summarizes current knowledge on AUFs, including their pathophysiology, diagnostic criteria, and management. A case of bilateral AUFs treated with two distinct osteosynthesis methods is presented, emphasizing the principles of biological healing and mechanical stabilization.
- 1,338 View
- 37 Download

Original Article
- Short-term Treatment Comparison of Teriparatide and Percutaneous Vertebroplasty in Patients with Acute Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures
- Joonoh Seo, Ki Youn Kwon, Bumseok Lee, Hoon-Sang Sohn
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(1):15-21. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.1.15
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study compared the 3-month treatment effects of teriparatide and percutaneous vertebroplasty for acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.
Materials and Methods
A retrospective study was conducted on 76 patients diagnosed with acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures from January 1, 2020 to December 31, 2022. The patients were divided into the teriparatide group and the percutaneous vertebroplasty+alendronate group. The visual analog scale (VAS), Oswestry disability index (ODI), and height of the vertebrae anterior wall were measured before treatment and at 1 and 3 months after treatment.
Results
Of the 76 patients, 42 were treated with teriparatide, and 34 were treated with percutaneous vertebroplasty. The symptoms improved in both groups, with a decrease in the VAS and ODI scores at 1 and 3 months after treatment, respectively. On the other hand, there was no significant difference in the VAS, ODI score, and anterior vertebral body height between the two groups before treatment and at 1 and 3 months after treatment.
Conclusion
In the treatment of acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures, conservative treatment using teriparatide showed similar short-term (3 months) treatment results to percutaneous vertebroplasty in terms of improvement in back pain and function and degree of reduction in anterior vertebral body height.
- 830 View
- 32 Download

Review Article
- Systematic Diagnosis and Treatment Principles for Acute Fracture-Related Infections
- Jeong-Seok Choi, Jun-Hyeok Kwon, Seong-Hyun Kang, Yun-Ki Ryu, Won-Seok Choi, Jong-Keon Oh, Jae-Woo Cho
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(4):148-161. Published online October 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.4.148
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Acute fracture-related infection (FRI) is a common and serious complication of fracture treatment. The clinical symptoms of the patient and the results of the serological, radiological, and histopathologi-cal examinations can be divided into ‘Confirmatory’ criteria and ‘Suggestive’ criteria, allowing for the diagnosis of FRI. Treatment principles can be broadly categorized into (1) the DAIR (Debridement, Antimicrobial therapy, Implant Retention) method and (2) the staged reconstruction method. The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the time elapsed after infection, stability of the internal fixation device, reduction status, host physiology, and virulence of the pathogens. Thorough surgical debridement and irrigation, ensuring stability at the fracture site, reconstruction of bone defects, and appropriate soft tissue coverage, along with antibiotic therapy, are essential to suppress or eradicate the infection. The restoration of limb function should be promoted through proper soft tissue coverage and bone union at the fracture site.
- 657 View
- 14 Download

Original Articles
- Comparison of a Novel Box-Frame External Fixator and Conventional Delta-Frame External Fixator in the Staged Treatment of Distal Tibia Fractures
- Yong-Cheol Yoon, MinKyu Shin, Chang-Wug Oh, Jong-Keon Oh
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(3):125-133. Published online July 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.3.125
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Distal tibia fractures with severe soft-tissue edema or intra-articular fractures are treated by staged operations using external fixators. Definitive surgery that maintains ligamentotaxis has been difficult using existing fixators. This study introduced a novel ‘box-frame’ external fixator and evaluated its clinical usefulness.
Materials and Methods
This study included 45 patients (32 males, 13 females) diagnosed with distal tibia fractures who underwent staged operations between March 2012 and March 2016, with a follow-up of at least one year. The patients were divided into two groups. In one group, fixation was performed with a box-frame external fixator (Group A). In the other group, fixation was performed with a delta-frame external fixator (Group B). The following outcomes were evaluated: the time until definitive surgery, operative time of the definitive surgery, radiation exposure time, bone union, time to achieve bone union, postsurgical complications, American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society anklehindfoot score, and ankle range of motion.
Results
Compared to the delta-frame, the box-frame showed a statistically significant reduction in the mean radiation-exposure time and operative time during the definitive surgery by 58 seconds and 25 minutes, respectively. The differences in the time until definitive surgery, bone union, time to achieve bone union, postsurgical complications, and functional scores were not significant.
Conclusion
The box-frame external fixator can be a useful treatment method in the staged surgery of distal tibia fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Temporary Circular External Fixation for Spanning the Traumatized Ankle Joint
Nando Ferreira, Niel Bruwer, Adriaan Jansen van Rensburg, Ernest Muserere, Shao-Ting Jerry Tsang
JBJS Essential Surgical Techniques.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Temporary circular external fixation for spanning the traumatised ankle joint: A cohort comparison study
William D. Harrison, Franklin Fortuin, Matthieu Durand-Hill, Etienne Joubert, Nando Ferreira
Injury.2022; 53(10): 3525. CrossRef
- Temporary Circular External Fixation for Spanning the Traumatized Ankle Joint
- 1,717 View
- 13 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Treatment of Isolated Lateral Malleolar Fractures Using Locking Compression Plate Fixation and Tension Band Wiring Fixation
- Woojin Shin, Seondo Kim, Jiyeon Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(1):16-21. Published online January 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.1.16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to compare the clinical and radiological outcomes of locking compression plate (LCP)-screw fixation and tension band wiring (TBW) fixation in isolated lateral malleolar fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From May 2016 to August 2018, 52 patients with isolated lateral malleolar fracture were retrospectively reviewed. They were divided into 30 cases of the LCP fixation group (Group I) and 22 cases of the TBW fixation group (Group II). The clinical and radiological results of those groups were compared. Pearson chi-square tests and independent t-tests were used in the statistical analysis.
RESULTS
The mean length of the surgical incision was 8.3 cm in Group I and 4.9 cm in Group II. Radiological union was obtained at a mean of 8.4 weeks in both groups. The mean American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society score was 90 (range, 85–97) and 92 (range, 85–100) in Groups I and II, respectively, at the last follow up.
CONCLUSION
Both the LCP-screw and TBW techniques revealed excellent results in isolated lateral malleolar fractures. The tension band technique may be a fine alternative method of fixation in the treatment of isolated lateral malleolar fracture.
- 820 View
- 7 Download

- Paratricipital Approach for AO/OTA Type C2 Intra-Articular Fracture of Distal Humerus
- Chul Hyung Lee, Doo Hun Sun, Deukhee Jung, Chung Han An
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(3):128-134. Published online July 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.3.128
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to determine the outcomes of fixation of AO/OTA type C2 fractures among intra-articular fractures of the distal humerus using the paratricipital approach (side to side retraction of the triceps).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From June 2008 to January 2018, 12 patients underwent an open reduction and internal fixation with the paratricipital approach and were followed-up for more than 10 months after surgery. According to the AO/OTA classification, type C2 fractures were chosen among the intraarticular distal humerus fractures. An extended posterior incision was used over the olecranon in the prone position, preserving the insertion site of the triceps brachii muscle. The fracture site was exposed by retracting the muscle side-to side through a dissection of the medial and lateral intermuscular septum of the triceps brachii muscle. The therapeutic results were assessed by the anatomical reduction of the articular surface and integrity of the metaphyseal contour in postoperative simple radiographs, complications, such as neuropathy or non-union, and the Mayo elbow performance score (MEPS) were checked to estimate the functional outcome.
RESULTS
In the postoperative simple radiographs, no case showed more than 1 mm step-off and the disrupted contour of the distal humerus was recovered to normal alignment in most cases. The range of elbow joint motion in the last follow-up was 133.8° on average with a mean flexion contracture of 5.0°. The clinical results depending on the MEPS were excellent, except for two cases, which were good. Neuropathy of the ulnar nerve was observed in one patient, which was resolved after metal removal.
CONCLUSION
The paratricipital approach is useful technique in AO/OTA type C2 intra-articular distal humerus fractures that provides sufficient exposure of the surgical field, without injury to the triceps brachii muscle and postoperative complications associated with the trans-olecranon approach. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Short-Term Results After Intra-Articular Fractures of the Distal Humerus Treated by a Paratriceps Approach
Petar Petkov
Scripta Scientifica Medica.2025; 57(1): 48. CrossRef
- Short-Term Results After Intra-Articular Fractures of the Distal Humerus Treated by a Paratriceps Approach
- 781 View
- 7 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Report
- Cortical Perforation Misidentified with Medial Condylar Fracture of Femur in Total Knee Arthroplasty: Case Report
- Seung Suk Seo, Sang Won Moon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(1):52-55. Published online January 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.1.52
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Intraoperative fracture in total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is a rare complication. However, when it happens, additional surgery to fix the fracture site is needed. Therefore, it is important to diagnose intraoperative fractures in TKA exactly. The authors experienced two cases of cortical perforation of medial femoral condyle misidentified as the fracture in TKA. Cortical perforation could be misdiagnosed as the fracture, which could lead to unnecessary surgery. This is the first report about cortical perforation in TKA. We report two cases of intraoperative cortical perforations and describe the radiological characteristics.
- 486 View
- 1 Download

Review Articles
- Atypical Femoral Fractures: What Do We Know about Them?
- Beom Seok Lee, Young Kyun Lee, Heejae Won, Hyungkook Kim, Kyung Hoi Koo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(4):159-164. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.4.159
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Recently, atypical femoral fractures (AFFs) have been found in patients who were prescribed bisphosphonate to prevent osteoporotic fractures. Although the occurrence of AFF is rare, there are some concerns, such as a higher risk of delayed or non-union of AFF. This paper reviews the treatment of AFF and suggests some considerations during surgery.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How to Improve Fracture Healing in Atypical Femoral Fractures
Sang-Jin Jeong, Chan-Woo Park, Seung-Jae Lim
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2024; 59(1): 9. CrossRef - Atypical Femoral Fracture Occurring at a Proximal Screw Insertion Site after Plate Removal in a Distal Femoral Fracture
Jin Woo Jin, Sung Jin Shin, Jong Min Jeon
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2024; 59(4): 314. CrossRef - Position Statement: Atypical Femoral Fracture from the Korean Society for Bone and Mineral Research in 2023
Jae-Hwi Nho, Byung-Woong Jang, Dong Woo Lee, Jae-Hyun Kim, Tae Kang Lim, Soo Min Cha, Dong-Kyo Seo, Yong-Geun Park, Dong-Geun Kang, Young-Kyun Lee, Yong-Chan Ha
Journal of Bone Metabolism.2023; 30(3): 209. CrossRef
- How to Improve Fracture Healing in Atypical Femoral Fractures
- 467 View
- 5 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Treatment Options of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures
- Yu Mi Kim, Tae Kyun Kim, Dae Moo Shim, Kyeong Hoon Lim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(3):114-121. Published online July 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.3.114
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This paper reviews previous studies on the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in elderly patients to determine what factors should be considered for successful treatment. In osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures, the primary treatment is conservative treatments. Other treatments include osteoporosis treatment, pain control, orthosis, and physical therapy. Recently, percutaneous catheterization or balloon plasty is performed for rapid pain recovery and early ambulation. Percutaneous catheterization or balloon posterior plasty is effective in reducing pain and improving the activity ability. Surgical treatment should be considered in cases of nonunion or osteonecrosis, dent, deformation, and spinal cord compression after conservative treatment has failed. In surgical treatment, posterior spinal fixation and vertebroplasty are more advantageous in terms of the amount of bleeding, operation time compared to the anterior approach, but the most appropriate method should be selected through the patient's condition and understanding of each surgical method.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Maigne Syndrome and Thoracolumbar Compression Fracture – An Overlooked Combination in Low Back Pain: A Case Report
Jae-Yong Shim, Myung-Hoon Shin
The Nerve.2025; 11(1): 21. CrossRef - Effects of Herbal Medicines on Bone Mineral Density Score in Osteoporosis or Osteopenia: Study Protocol for a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Su Min Hong, Eun Jung Lee
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2021; 31(2): 49. CrossRef -
Spinal Stability Evaluation According to the Change in the Spinal Fixation Segment Based on Finite Element Analysis
Cheol-Jeong Kim, Seung Min Son, Jin-Young Heo, Chi-Seung Lee
Journal of the Computational Structural Engineering Institute of Korea.2020; 33(3): 145. CrossRef
- Maigne Syndrome and Thoracolumbar Compression Fracture – An Overlooked Combination in Low Back Pain: A Case Report
- 542 View
- 7 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Nonsurgical Treatment of a Distal Radius Fracture: When & How?
- Young Ho Shin, Jun O Yoon, Jae Kwang Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(2):71-78. Published online April 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.2.71
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Distal radius fractures are a common upper extremity fracture and a considerable number of patients have a stable fracture. In the treatment of distal radius fractures, there is considerable disagreement regarding the need for a strict anatomical restoration with operation in elderly patients. Therefore, nonsurgical treatment is a still important treatment option in distal radius fractures. The radiological parameters of before or after manual reduction are important for deciding whether to perform operation or not. The radiological parameters include dorsal angulation of the articular surface, radial shortening, extent of dorsal comminution, intra-articular displacement, concomitant ulnar metaphyseal fracture, shear fracture, and fracture-dislocation of the distal radio-ulnar joint. In addition, clinical situations of patients, including age, activity level, underline disease, and recovery level, which the patients wish should be considered, comprehensively. For the duration of a splint or cast, three to four weeks are recommended in impacted or minimally displaced fractures and five to six weeks in displaced fractures. After reduction of the displaced fractures, patients should undergo a radiologicical examination every week to check the redisplacement or deformity of the fracture site until two or three weeks post trauma. Arm elevation is important for controlling fracture site swelling and finger exercises, including metacarpophalangeal joint motion, are needed to prevent hand stiffness. Active range of motion exercise of the wrist should be initiated immediately after removing the splint or cast.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Clinical Effect of Complex Korean Medical Admission Treatment in Patients with Fractures of Distal Radius by Traffic Accident: 2 Cases Series Report
Gyu-cheol Choi, Ji-won Lee, Ji-Eun Bae, Dong-jin Kim, Jeong-su Hong, Da-hyun Kyung
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2021; 31(1): 187. CrossRef - The Clinical Effect of Rehabilitation Protocol for Distal Radius Fracture in Korean Medicine: A Report of 3 Cases
Won-Bae Ha, Ji-Hye Geum, Nak-Yong Koh, Jung-Han Lee
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2018; 28(3): 97. CrossRef
- The Clinical Effect of Complex Korean Medical Admission Treatment in Patients with Fractures of Distal Radius by Traffic Accident: 2 Cases Series Report
- 432 View
- 7 Download
- 2 Crossref

Case Report
- Intrapelvic Penetration of Lag Screw in Proximal Femoral Nailing: A Case Report
- Jung Woo Lee, Hong Man Cho, Jae Woong Seo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(4):203-208. Published online October 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.4.203
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hip fractures are common among elderly individuals. Internal fixation with the intramedullary system has been widely used to treat intertrochanteric femur fractures. The Gamma 3 nail is a useful device for fixating trochanteric fractures of the proximal femur. We report a rare complication of medial pelvic penetration of the lag screw of a Gamma 3 nail two months after surgery. There was a complete separation between the nail body and lag screw, and the lag screw penetrated through the acetabulum into the pelvis. We report a case of unstable intertrochanteric fracture with intrapelvic penetration after surgical treatment with proximal femoral nailing and a case followed by fatal results.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Medial lag screw migration in an intramedullary nail combination
Zac Dragan, Ryan J Campbell, Terence R Moopanar
BMJ Case Reports.2025; 18(3): e262436. CrossRef - Endovascular assisted removal of intrapelvic lag screw after intramedullary proximal femoral nail: A case report and literature review
Zakaria Mousati, Mathias Van Den Broek, Joren Callaert, Jan Gielis, Kris Govaers
Trauma Case Reports.2023; 46: 100873. CrossRef - Intrapelvic migration of the lag screw in intramedullary nailing after intertrochanteric fracture fixation: A case report
Aymen Ben Fredj, Hedi Rbai, Fourat Farhat, Marouen Berriri
Clinical Case Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Intramedullary nailing confers an increased risk of medial migration compared to dynamic hip screw fixation in unstable intertrochanteric hip fractures
Gin Way LAW, Yoke Rung WONG, Antony GARDNER, Yau Hong NG
Injury.2021; 52(11): 3440. CrossRef - Medial migration in cephalomedullary nail fixation of pertrochanteric hip fractures
G. W. Law, Y. R. Wong, A. K-S. Yew, A. C. T. Choh, J. S. B. Koh, T. S. Howe
Bone & Joint Research.2019; 8(7): 313. CrossRef - Intrapelvic Migration of the Lag Screw with Wedge Wing from Dyna Locking Trochanteric Nail: A Case Report and Literature Review
Yong-Woo Kim, Weon-Yoo Kim, Kyong-Jun Kim, Se-Won Lee
Hip & Pelvis.2019; 31(2): 110. CrossRef
- Medial lag screw migration in an intramedullary nail combination
- 1,182 View
- 12 Download
- 6 Crossref

Original Articles
- Ultrasonographic Assessment of the Pronator Quadratus Muscle after Surgical Treatment for Distal Radius Fractures
- Dong Hyuk Choi, Hyun Kyun Chung, Ji Won Lee, Cheol Hwan Kim, Yong Soo Choi
- J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(2):69-74. Published online April 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.2.69
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study was to assess the morphological changes of the pronator quadratus (PQ) muscle using an ultrasonography in the volar locking plate fixation group and in the percutaneous K-wire fixation group for distal radius fracture, and to evaluate the impact on clinical outcomes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fifty-four patients who received surgical treatment for distal radius fracture were enrolled in this study. They were divided into two groups according to treatment modality: Group 1 included 34 patients who underwent internal fixation with volar locking plate and Group 2 included 20 patients with percutaneous K-wire fixation. Thickness of the PQ muscle was measured using an ultrasonography at the final follow-up. We evaluated the outcomes using the Mayo wrist score, wrist range of motion, and grip strength at the final follow-up.
RESULTS
Compared with the uninjured side, thickness of the PQ muscle showed 31.9% of mean atrophy in Group 1 and 11.4% in Group 2. The atrophy of PQ muscle was severe in Group 1 (p=0.01). However, there was no significant difference in the mean Mayo wrist score between the two groups (83.1±10.9 in Group 1 and 80.2±8.9 in Group 2, p=0.28), except a mild limitation of pronation in Group 1.
CONCLUSION
The healed PQ muscle from fracture itself after distal radius fracture revealed a morphological atrophy. Moreover, the volar locking plate resulted in greater atrophy of the PQ muscle, but there was no specific impact on clinical outcomes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Quantitative analysis of radial torsion angle according to location with CT scan
Eic Ju Lim, Seungyeob Sakong, Jeong Seok Choi, Wonseok Choi, Jong-Keon Oh, Jae-Woo Cho
Injury.2025; 56(10): 112634. CrossRef
- Quantitative analysis of radial torsion angle according to location with CT scan
- 578 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Fate of Pronator Quadratus Muscle after Volar Locking Plating of Unstable Distal Radius Fractures
- Chae Hyun Lim, Heun Guyn Jung, Ju Yeong Heo, Young Jae Jang, Yong Soo Choi
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(3):191-197. Published online July 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.3.191
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the pronator quadrates muscle in patients who underwent internal fixation with a volar locking plate for unstable distal radius fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Forty patients who underwent internal fixation with a volar locking plate for unstable distal radius fracture were enrolled. We evaluated the clinical results according to the Mayo wrist score, the wrist range of motion, and the grip strength at the last follow-up. Using ultrasonography, muscle thickness of the pronator quadrates was compared between injured and uninjured arm.
RESULTS
Bone union was achieved in all cases. The mean Mayo wrist score was 82.79 points. The grip strength of the injured arm was decreased to 89.1% of the uninjured side. The decrease of pronation range of the injured wrist motions was significant (82.3degrees, p=0.004). There was significant atrophy of the pronator quadrates muscle on the injured side (injured side: 3.19 mm, uninjured side: 4.72 mm, p=0.001); and the decrement of muscle thickness in pronator quadrates showed an association with the Mayo wrist score (r=-0.35, p=0.042).
CONCLUSION
These results suggest that continuity of the muscle is maintained after use of the volar locking plating for unstable distal radius fractures with repair of pronator quadrates; however, there is atrophy of pronator quadrates muscle and limitation of pronation in the injured wrist.
- 361 View
- 0 Download

- Morbidity and Mortality of the Elderly after Early Operation for Trochanteric Fractures
- Se Ang Jang, Young Ho Cho, Young Soo Byun, Ki Hong Park, Hyun Seong Yoo, Chul Jung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(3):199-204. Published online July 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.3.199
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To find out the effect of early closed reduction and internal fixation (within 24 hours after admission to hospital) on the morbidity and mortality in the elderly with intertrochanteric fractures of the femur.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Retrospectively, we analyzed 99 patients with intertrochanteric fracture of the femur who underwent surgery from January, 2009 to December, 2010. We reviewed 89 of the 99 patients and checked for early complications and reviewed the mortality rates 3 months, 6 months and 1 year after surgery. There were 24 males and 65 females. The average age was 79.8 years (61-99 years). According to the American Society of Anesthesiologists classification, 25 patients were class 1, 37 patients were class 2, 26 patients were class 3, and 1 patient was class 4. All patients were operated on by one surgeon, who was skilled in inserting intramedullary nail.
RESULTS
The average surgical time was 43 minutes and the average intraoperative blood loss was 165 ml. Sixteen patients experienced delirium but all of them recovered. One patient had pneumonia at one month after surgery. Pressure sores developed in one patient but improved with conservative treatment. Pulmonary thromboembolism developed in some patients one month after surgery. Three patients (3.4%) died within three months and one patient (1.1%) died between three and six months after surgery, but no patient died between six months and one year after surgery.
CONCLUSION
If patients are optimized for the operation, early internal fixation of trochanteric fracture in elderly patients after arrival at the hospital should be considered to reduce early complications and mortality. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- PREOPERATIVE NUTRITIONAL STATUS OF HIP FRACTURE PATIENTS: A PILOT STUDY IN 116 PATIENTS
Myung-Sang Moon, Min-Suk Park, Bong-Keun Park, Dong-Hyeon Kim, Min-Geun Yoon
Journal of Musculoskeletal Research.2017; 20(01): 1750002. CrossRef
- PREOPERATIVE NUTRITIONAL STATUS OF HIP FRACTURE PATIENTS: A PILOT STUDY IN 116 PATIENTS
- 540 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Intermittent Parathyroid Hormone Treatment for Stimulation of Callus Formation in Elderly Patients
- Hyung Keun Song, Sung Jun Kim, Jae Hoo Lee, Kyu Hyun Yang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(4):295-299. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.4.295
- Correction in: J Musculoskelet Trauma 2013;26(2):170
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of parathyroid hormone (PTH) on fracture healing in elderly patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We analyzed the radiologic results in 14 patients. Group I (n=7) was administrated intermittent PTH after surgical treatment and group II (n=7) was treated only with surgery. We checked the time of initial callus formation, bridging callus formation, and bone union through periodic follow-up radiographs by a radiologist who did not know the patient's information.
RESULTS
The mean time to initial callus formation was 6 weeks for group I, compared with 6.7 weeks for group II. The mean time to bridging callus formation was 15.9 weeks for group I, compared with 23.0 weeks for group II. The mean time to bone union was 28.7 weeks for group I, compared with 41.9 weeks for group II. The difference in the cumulative detection rate (CDR) of the initial callus formation of group I and II was not statistically significant (p=0.793). However, the CDR of the bridging callus formation and bone union for group I were higher than those of group II (p=0.008, p=0.001, respectively).
CONCLUSION
The intermittent PTH administration after surgical treatment and maximum possible preservation of the periosteum in elderly patients accelerates fracture healing. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Advances in Parathyroid Hormone-based medicines
Anne-Laure Bonnet, Lizaveta Aboishava, Michael Mannstadt
Journal of Bone and Mineral Research.2025; 40(11): 1195. CrossRef - Effects of Extracts from Cnidium officinale and Angelica sinensis on Bone Fusion in Mice with Femoral Fracture
Sang Woo Kim, Min-Seok Oh
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2024; 34(2): 1. CrossRef - Timing of osteoporosis therapies following fracture: the current status
Rajan Palui, Harsh Durgia, Jayaprakash Sahoo, Dukhabandhu Naik, Sadishkumar Kamalanathan
Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Postoperative Parathyroid Hormone Administration on Osteoporotic Intertrochanteric Fractures of Females
Hyun Cheol Oh, Ju Hyung Yoo, Joong Won Ha, Yung Park, Sang Hoon Park, Han Kook Yoon
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2020; 55(3): 237. CrossRef - The role of teriparatide in tuberosity healing after reverse shoulder arthroplasty in complex proximal humeral fragility fracture
Bancha Chernchujit, Renaldi Prasetia
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Bone Substitutes and the Advancement for Enhancing Bone Healing
Dong-Hyun Lee, Ji Wan Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2017; 30(2): 102. CrossRef - Current Role and Application of Teriparatide in Fracture Healing of Osteoporotic Patients: A Systematic Review
Sang-Min Kim, Kyung-Chung Kang, Ji Wan Kim, Seung-Jae Lim, Myung Hoon Hahn
Journal of Bone Metabolism.2017; 24(1): 65. CrossRef - The Effect of Teriparatide on Fracture Healing of Osteoporotic Patients: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Shenghan Lou, Houchen Lv, Guoqi Wang, Licheng Zhang, Ming Li, Zhirui Li, Lihai Zhang, Peifu Tang
BioMed Research International.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - A systematic review on the use of daily subcutaneous administration of teriparatide for treatment of patients with osteoporosis at high risk for fracture in Asia
J.F. Chen, K. H. Yang, Z.L. Zhang, H.C. Chang, Y. Chen, H. Sowa, S. Gürbüz
Osteoporosis International.2015; 26(1): 11. CrossRef
- Advances in Parathyroid Hormone-based medicines
- 567 View
- 8 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Analysis of Risk Factors for Nonunion after Intramedullary Nailing of Femoral Shaft Fracture in Adult
- Yong Woon Shin, Yerl Bo Sung, Jeong Yoon Choi, Minkyu Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2011;24(4):313-320. Published online October 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.4.313
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the union time and nonunion rate after intramedullary nailing of femoral shaft fracture in adult, we would like to analysis the operation techniques, comminution, contact surface and displacement.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed retrospectively 53 patients undergoing femoral intramedullary nailing at least 2 years postoperatively and analysised the union time and nonunion rate by operation techniques, comminution, contact surface and displacement. Patients were operated by either antegrade or retrograde intramedullary nailing.
RESULTS
There were no differences in nonunion rate, the duration of bony union between antegrade and retrograde intramedullary nail groups. Significant differences were found in the duration of bony union between the Winquist and Hansen type I, II and the type III, IV (p<0.05). There were significant differences in the duration of bony union among simple, comminuted, and segmental fracture groups (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
The union time is affected by not operation techniques and fracture displacement, but Winquist-Hansen classification and number of fracture fragments in intramedullary nailing of adult femoral shaft fracture. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Extra-capsular proximal femoral fractures: a cohort comparison of union and complication rates after ballistic versus blunt trauma
Jordan Cook Serotte, Kevin Chen, Julia Nascimben, Jason Strelzow
European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Affecting Time to Bony Union of Femoral Subtrochanteric Fractures Treated with Intramedullary Devices
Jung-Yoon Choi, Yerl-Bo Sung, Jin-Hee Yoo, Sung-Jae Chung
Hip & Pelvis.2014; 26(2): 107. CrossRef - Augmentative Locking Plate Fixation for the Treatment of Femoral Nonunion after Intramedullary Nailing
Ki-Chul Park, Chul-Woong Kim, Kyu-Tae Hwang, Ye-Soo Park
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2013; 26(4): 268. CrossRef
- Extra-capsular proximal femoral fractures: a cohort comparison of union and complication rates after ballistic versus blunt trauma
- 663 View
- 6 Download
- 3 Crossref

Case Reports
- Checkrein Deformity by Incarcerated Posterior Tibial Tendon and Displaced Flexor Hallucis Longus Tendon following Ankle Dislocation: A Case Report
- Su Young Bae, Hyung Jin Chung, Man Young Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2011;24(3):271-276. Published online July 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.3.271
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We report a case of 20 year-old man who had unusual equinus and checkrein deformity following dislocation of his right ankle joint. He had been treated with distal tibiofibular screw fixation and external fixation. After removal of external fixator, he had suffered from progressive deformity of foot and ankle. Widening of distal tibiofibular joint and medial clear space was found on radiograph and it was revealed that posterior tibial tendon had been dislocated and incarcerated into the distal tibiofibular joint on MRI. We corrected the deformity with excision of incarcerated posterior tibial tendon, adhesiolysis and lengthening of flexor hallucis longus tendon, reconstruction of deltoid ligament and flexor digitorum longus tendon transfer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Management of Checkrein Deformity
Min Gyu Kyung, Yun Jae Cho, Dong Yeon Lee
Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery.2024; 16(1): 1. CrossRef - A Neglected Extensor Hallucis Longus Tendon Rupture Caused by Arthritic Adhesion
Sung Hun Won, Sung Hwan Kim, Young Koo Lee, Dong-Il Chun, Byung-Ryul Lee, Woo-Jong Kim
Medicina.2023; 59(6): 1069. CrossRef - The Checkrein Deformity of Extensor Hallucis Longus Tendon and Extensor Retinaculum Syndrome with Deep Peroneal Nerve Entrapment after Triplane Fracture: A Case Report
Hyungon Gwak, Jungtae Ahn, Jae Hoon Lee
Journal of Korean Foot and Ankle Society.2021; 25(3): 145. CrossRef - Checkrein Deformity Due to Flexor Digitorum Longus Adhesion after Comminuted Calcaneus Fracture: A Case Report
Jin Su Kim, Han Sang Lee, Ki Won Young, Keun Woo Lee, Hun Ki Cho, Sang Young Lee
Journal of Korean Foot and Ankle Society.2015; 19(1): 35. CrossRef
- Management of Checkrein Deformity
- 490 View
- 0 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Bursting Fracture of the Proximal Femur during Insertion of Unreamed Femoral Nail for Femur Shaft Fracture: A Case Report
- Ji Wan Kim, Seong Eun Byun, Won Hyuk Oh, Jung Jae Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2010;23(2):227-231. Published online April 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.2.227
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - When treating femur shaft fracture in adults, undreamed nail can be an option in order to avoid systemic complications. To appropriately insert unreamed intramedullary nail, an accurate entry point and sufficient reaming of the entry portal is essential. The intramedullary canal of the proximal femur must be reamed over than the diameter of the proximal end of the nail. If the proximal reaming is not sufficient, complications such as bursting fracture of proximal femur can occur. We present two cases of bursting fracture of proximal femur following insertion of undreamed intramedullary nail as well as a literature review.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk Factors Associated with Intraoperative Iatrogenic Fracture in Patients Undergoing Intramedullary Nailing for Atypical Femoral Fractures with Marked Anterior and Lateral Bowing
Yong Bum Joo, Yoo Sun Jeon, Woo Yong Lee, Hyung Jin Chung
Medicina.2023; 59(4): 735. CrossRef - Results of Intramedullary Nailing of Femoral Shaft Fracture - Trochanteric Entry Portal (Sirus Nail) versus Piriformis Entry Portal (M/DN Nail) -
Sang Ho Ha, Woong-Hee Kim, Gwang Chul Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2014; 27(1): 50. CrossRef - Iatrogenic Femur Proximal Shaft Fracture during Nailing Using Lateral Entry Portal on Femur Shaft Fracture
Hong Moon Sohn, Gwang Chul Lee, Chae Won Lim
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2014; 49(4): 272. CrossRef
- Risk Factors Associated with Intraoperative Iatrogenic Fracture in Patients Undergoing Intramedullary Nailing for Atypical Femoral Fractures with Marked Anterior and Lateral Bowing
- 712 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref

Original Articles
- Risk Factors of Postoperative Delirium in Elderly Patients with Hip Fractures
- Ki Hwan Kim, Duk Hwan Kho, Ju Yong Shin, Jin Yong Choi, Eung Sik Kim, Dong Heon Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2008;21(3):189-194. Published online July 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.3.189
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To find out the relationship between various risk factors and post-operative delirium in elderly patients with hip fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Out of 135 patients older than 65 years old who underwent the surgery for hip fracture in our department, between the periods of March 2003 to March 2005, 14 patients (10.4%) developed post-operative delirium and 121 patients (89.6%) did not. We studied risk factors of post-operative delirium in two groups.
RESULTS
In chi-square test between delirium group and non-delirium group, the patients were more likely to develop post-operative delirium if they had previous episodes of delirium, abnormal cognitive function, low walking ability before admission, high dependency on ADL (Activities of Daily Living), other medical accompanying diseases, history of dementia, post-operative hypoxia, post-operative electrolyte imbalance, low post-operative hemoglobin and hematocrit, low post-operative albumin and were older than 75 years old (p<0.05). Sex, type of fracture, anesthesia and the time between admission and operation did not show much difference between the two groups.
CONCLUSION
The risk factors of postoperative delirium in elderly patients with hip fracture have a tendency to be multifactorial. Therefore, we conclude that being prepared by thorough understanding of the risk factors and their relationships will help prevent post-operative delirium and result in good postoperative prognosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Increased Serum Neuropeptide Galanin Level Is a Predictor of Cognitive Dysfunction in Patients with Hip Fracture
Zichao Xue, Ke Zhang, Biao Luo, Long Fan, Ruizhe Zhao, Guangliang Hu, Yuzhen Xu
Disease Markers.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Sleep Disturbance Strongly Related to the Development of Postoperative Delirium in Proximal Femoral Fracture Patients Aged 60 or Older
Myung-Rae Cho, Suk-Kyoon Song, Cheol-Hwan Ryu
Hip & Pelvis.2020; 32(2): 93. CrossRef - Incidence and Associated Factors of Delirium after Orthopedic Surgery
Si-Wook Lee, Chul-Hyun Cho, Ki-Cheor Bae, Kyung-Jae Lee, Eun-Seok Son, Sang-Hyun Um
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2019; 54(2): 157. CrossRef - Relationship between Delirium and Clinical Prognosis among Older Patients underwent Femur Fracture Surgery
Jae-Lan Shim, Seon-Young Hwang
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(2): 649. CrossRef - Relationship between Knowledge, Stress, and Nursing Performance about Care for Delirium in Geriatric Hospital Nurses
Eun-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Clinical Health Science.2016; 4(2): 593. CrossRef - The effects of a tailored intensive care unit delirium prevention protocol: A randomized controlled trial
Kyoung-Ja Moon, Sun-Mi Lee
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2015; 52(9): 1423. CrossRef - Is Delirium an Unrecognized Threat to Patient Safety in Korean Intensive Care Units?
Kyoung-Ja Moon, Jinshi Piao, Yinji Jin, Sun-Mi Lee
Journal of Nursing Care Quality.2014; 29(1): 91. CrossRef - The Effects of Delirium Care Training Program for Nurses in Hospital Nursing Units
Moonja Kim, Haejung Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(5): 489. CrossRef - Knowledge, Performance and Stress about Care for Delirium in Orthopedic Hospital Nurses
Mi Young Kim, Young Eun
Journal of muscle and joint health.2013; 20(1): 72. CrossRef - The Experience of Delirium Care and Clinical Feasibility of the CAM-ICU in a Korean ICU
Joo-Hee Jung, Jung-Hye Lim, Eun-Jung Kim, Hyo-Chan An, Min-Kyung Kang, Jin Lee, Yu-Kyung Min, Eun-Zoo Park, Xiang-Hwa Song, Hye-Ryoung Kim, Sun-Mi Lee
Clinical Nursing Research.2013; 22(1): 95. CrossRef - Development and validation of the Korean Nursing Delirium Scale
Kyoung-Nam Kim, Cheol-Ho Kim, Kwang-Il Kim, Hyun-Jung Yoo, Si-Young Park, Yeon-Hwan Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(3): 414. CrossRef - Influencing Factors of the Incidence of Delirium in Elderly Patients with Arthroplasty
Young-Whee Lee, Hye-Bin Im, Eun-Jeong Jeong, Hee-Sun Ma
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(4): 348. CrossRef - Delirium After Spinal Surgery in Korean Population
Jin Kyu Lee, Ye-Soo Park
Spine.2010; 35(18): 1729. CrossRef - The Incidence and Related Factors of Delirium in Elderly Patients with Hip Fracture after Surgery
Bo-Kyung Sohn, Yerl-Bo Sung, Eun-Jin Park, Dong-Woo Lee
Journal of the Korean Geriatrics Society.2010; 14(3): 162. CrossRef
- Increased Serum Neuropeptide Galanin Level Is a Predictor of Cognitive Dysfunction in Patients with Hip Fracture
- 1,503 View
- 4 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Factors Confluencing the Result of Percutaneous Balloon Kyphoplasty in Osteoporotic Thoracolumbar Compression Fracture
- Jung Hee Lee, Dae Woo Hwang, Jae Heung Shin, Woo Sung Hong, Ju Wan Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(1):76-82. Published online January 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.1.76
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
We are to find the method to objectify postoperative prognosis, analyzing the factors confluencing the result of kyphoplasty in osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture (OVCF).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Our study included 50 patients (55 vertebral bodies) who have undergone kyphoplasty from Sep. 2004 until Oct. 2005. We divided in the group according to bone mineral density (BMD), compression rate, recovery rate and cement leakage. We verified the significance of each group, using independent t-test, and ANOVA test among observers.
RESULTS
We performed kyphoplasty on 55 vertebral bodies, 12 cases with more than 0.4 g/cm2 in BMD (mean: 0.53 g/cm2) and their mean preoperative compression rate (CR), immediate postoperative recovery rate (RR-IPO), and recovery rate after 6 months (RR-6M) was each 30.58%, 12.35%P, 9.93%P. 15 cases under 0.4 g/cm2 (mean 0.31 g/cm2), and their CR, RR-IPO and RR-6M was 26.73%, 11.77%P, 5.26%P respectively. The p-value was 0.004. Another studies according to CR, RR-IPO and leakage of cement revealed the better results in the cases of the lower CR, the smaller reduction and abscecnce of cement leakage, but statistically insignificant (p=0.309, 0.069, 0.356).
CONCLUSION
Preoperative BMD was most important factor that confluencing postoperative radiological result in OVCF. Other factors were also thought to be confluencing factors, but statistically insignificant.. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cement Leakage into Disc after Kyphoplasty: Does It Increases the Risk of New Adjacent Vertebral Fractures?
Hoon-Sang Sohn, Seong-Kee Shin, Eun-Seok Seo, Kang-Seob Chang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(4): 361. CrossRef
- Cement Leakage into Disc after Kyphoplasty: Does It Increases the Risk of New Adjacent Vertebral Fractures?
- 500 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Comparison of Uniportal and Biportal Vertebroplasty in Bone Cement Distribution and Leakage
- Jae Hyup Lee, Kang Sup Yoon, Seung Baik Kang, Hyunchul Jo, Sang Ki Lee, Bong Soon Chang, Choon Ki Lee, Ji Ho Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(4):471-476. Published online October 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.4.471
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the differences of radiological outcomes of uniportal and biportal vertebroplasty in the point of bone cement distribution and leakage.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A retrospective study reviewing the period between May 2002 and January 2006 investigated 100 vertebrae which underwent vertebroplasty and followed for more than three months by uniportal approach (55 vertebrae, group 1) and biportal approach (45 vertebrae, group 2). The operative time, the amount of bone cement injected, anterior vertebral height restoration, kyphotic angle, bone cement distribution, and bone cement leakage were evaluated.
RESULTS
The amount of injected bone cement of group 1 (3.9 cc) was statistically smaller than that of group 2 (5.1 cc) (p=0.016). There were no significant differences in the operative time, anterior vertebral height restoration, kyphotic angle in both groups. The rate of bone cement distribution over 8 zones was significantly higher in group 2 than in group 1 (p=0.014). However, the rate of bone cement distribution over 7 zones and the rate of bone cement distributed on whole anterior vertebral body were not significantly different in both groups. The cement leakage was not also significantly different in both groups.
CONCLUSION
Although the amount of injected bone cement was smaller in uniportal vertebroplasty, the radiological results and cement leakage were similar to biportal vertebroplasty. These findings suggest that uniportal vertebroplasty can be the operative options in osteoporotic vertebral fracture.
- 282 View
- 0 Download

- Separation of the Symphysis Pubis during Childbirth
- Dong Ju Shin, Young Soo Byun, Se Ang Chang, Ok Rang Park, Shin Yoon Kim, Dae Hee Hwang, Sung Rak Lee, Dong Young Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(4):412-417. Published online October 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.4.412
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the clinical features and incidence of separation of the symphysis pubis during childbirth, and to evaluate the risk factors of the lesion and the outcome of treatment.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Seventy two cases of separation of symphysis pubis among 66,721 delivery between January 1992 and December 2004 was selected. The control group was composed of 498 cases without separation of symphysis pubis during childbirth. Several factors increasing the risk of this lesion were assessed using χ
- 280 View
- 0 Download

- Percutaneous Transphyseal Intramedullary K-wire Fixation for the Diaphyseal Forearm Fractures in Children
- Jung Hoei Ku, Young Chul Go, Man Jun Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(3):374-377. Published online July 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.3.374
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Although the standard treatment of diaphyseal forearm fractures in children is conservative treatment with closed reduction and cast immobilization, unstable or irreducible fractures are usually needed by surgical intervention. The aim of this article is to determine the efficacy of the percutaneous transphyseal intramedullary K-wires fixation for the forearm diaphyseal fractures in children.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In this retrospective study, we reviewed 18 cases of forearm diaphyseal fractures in children, which were treated with percutaneous transphyseal intramedullary nailing using K-wires from January 2001 to December 2004. We analyzed the period for radiologic bone union and the complications until the last follow-up.
RESULTS
The average period of follow-up was 15 months with mean age of 7.8 years. The average time to bone union was 6.2 weeks and nonunion, malunion, radio-ulnar synostosis and refracture were not found, just 2 local pin site infections were seen but healed by conservative treatment. Postoperative scar was small and the complications until the last follow-up were not found.
CONCLUSION
In the operative treatment of the forearm diaphyseal fractures in children, we think percutaneous transphyseal intramedullary K-wire fixation is one of the effective methods because of the minimal invasiveness, simplicity and easiness in removal.
- 366 View
- 0 Download

- Percutaneous Vertebroplasty in the Treatment of Osteoporotic Compression Fracture (99 Patients, 171 Vertebral Bodies)
- Chung Hwan Kim, Hyung Sun Ahn, Jae Kwang Hwang, Jung Suk Song, Eui Jung Bae
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(2):259-264. Published online April 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.2.259
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was designed to compare the clinical and radiologic outcome of the patients who underwent percutaneous vertebroplasty among the groups based on follow-up period and BMD.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 99 patients (171 vertebral bodies) underwent percutaneous vertebroplasty from January 2001 to September 2003. The patients were divided into 3 groups by follow-up periods, and also divided into 2 groups by BMD. We investigated the difference of radiologic and clinical effects among the groups. Radiologic findings was assessed as vertebral height restoration rate and rate of reduction loss by measurement of the height of vertebral body. The clinical outcomes were graded into 5. The statistical analysis was done using Chi-squire test and Independent-samples T test.
RESULTS
Among the groups divided by follow-up period, there was no statistically significant difference of clinical and radiologic results except the rate of reduction loss between group I and group III (p>0.05). Between the groups divided by BMD, there was no statistically significant difference of clinical and radiologic results.
CONCLUSION
Percutaneous vertebroplasty with bone cement for the osteoporotic compression fracture is an efficient procedure and considered as technique producing pleasurable clinical and radiologic results regardless of follow up-period and BMD.
- 362 View
- 0 Download

- Postoperative Mortality Rate of Hip Fracture in Elderly Patients
- Duk Hwan Kho, Ki Hwan Kim, Ju Yong Shin, Jun Hyuck Lee, Dong Heon Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(2):117-121. Published online April 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.2.117
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the rate of mortality for the elderly patients after treatment of hip fractures and analyze the associated risk factors which might affect their mortality rate.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
About the clinical records on 305 patients who had undergone the treatment in hip fractures, we evaluated the mortality rate of the total number of 248 patients whose age between 70 and 103 who were followed more than 12 months of period between March 1994 and March 2003. The mean age was 81.3 years. The composition of each female and male were 176 and 72 cases respectively. 99 cases were femoral neck fractures, and 149 cases were femoral intertrochanteric fractures. The operation included bipolar hemiarthroplasty and internal fixation using multiple cannulated screws, compression hip screws and Ender nails. We compared and analyzed the relating factors for the mortality rate.
RESULTS
The mean postoperative mortality rate was 14.1% (35 cases). The highest mortality rate showed for the postoperative 3 months which was 57.1% (20 cases), between 4 and 6 months was 25.7% (9 cases), and 17.1% (6 cases) were presented for 7 and 12 months. The postoperative mortality rate within 1 year was affected by underlying diseases, ASA (American society of Anesthesiologists) and cemented bipolar hemiarthroplasty. but, there were no significant difference of the other factors such as the age, gender, osteoporosis and delayed operation.
CONCLUSION
The variable factors which affect the mortality rate of the hip fractures in the elderly patients whose age over 70 were mostly determined by underlying diseases, ASA grade, and cemented bipolar hemiarthroplasty. Further study should be necessary for the factors influencing on the mortality rate. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Finite element modeling and simulation of hip joints in elderly women: for development of protective clothing against fracture
Jinhee Park, Yun Ja Nam
International Journal of Clothing Science and Technology.2020; 32(5): 661. CrossRef - Anesthetic considerations for surgical treatment of geriatric hip fracture
Dong Kyu Lee, Seunguk Bang, Sangseok Lee
Anesthesia and Pain Medicine.2019; 14(1): 8. CrossRef - The Influence of Stroke on Postoperative Prognosis of Femoral Intertrochanteric Fractures
Youn Soo Hwang, Kyu Pill Moon, Kyung Taek Kim, Won Seok Park, Joon Yeon Song, Jeong Hoon Chae
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2016; 51(4): 273. CrossRef - Analysis of the Risk Factors and Clinical Outcomes of Femoral Intertrochanteric Fractures in Patients over 65 Years Old
Chul Hong Kim, Kyu Yeol Lee, Sung Soo Kim, Myung Jin Lee, Lih Wang, Hyeon Jun Kim, Jung Mo Kang
Hip & Pelvis.2013; 25(2): 127. CrossRef - Postoperative Mortality and the Associated Factors in Elderly Patients with Hip Fracture
You-Sung Suh, Yong-Beom Kim, Hyung-Suk Choi, Hong-Kee Yoon, Gi-Won Seo, Byung-Ill Lee
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2012; 47(6): 445. CrossRef - Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Complications Following Hip Surgery
Kuen Tak Suh, Seung Joon Rhee, Jung Sub Lee, Jeung Il Kim
Hip & Pelvis.2012; 24(2): 71. CrossRef - Current Recommendations for Laboratory Testing and Use of Bone Turnover Markers in Management of Osteoporosis
Jehoon Lee, Samuel Vasikaran
Annals of Laboratory Medicine.2012; 32(2): 105. CrossRef - The Daily Life Functions of Elderly Peritrochanteric Fracture Patients after Surgical Treatment
Dae Moo Shim, Tae Kyun Kim, Jong Yun Kim, Duk Hwa Choi, Joung Suk Lee, Seong In Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2012; 25(1): 8. CrossRef - One-Year Mortality Rate of Patients over 65 Years Old with a Hip Fracture
Phil Hyun Chung, Suk Kang, Jong Pil Kim, Young Sung Kim, Ho Min Lee, Young Hwa Choi
Hip & Pelvis.2011; 23(2): 137. CrossRef - Usefulness of the Cementless Stem for the Treatment of Hip Fracture in Elderly Patients with Osteoporosis - Comparative Analysis between Cementless Stem and Cemented Stem -
Joon Soon Kang, Kyoung Ho Moon, Rhu Seop Kim, Sang Ho Lee, Jong Min Choi
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(1): 16. CrossRef - Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty for Hip Fractures in Patients Aged over 90 Years - The Factors Influencing the Postoperative Mortality -
Jun-Dong Chang, Je-Hyun Yoo, Sang-Soo Lee, Tae-Young Kim, Kyu-Hak Jung, Yong-Kuk Kim
Hip & Pelvis.2010; 22(4): 283. CrossRef - Determination of an Applicable FRAX Model in Korean Women
Dong-Yun Lee, Seung-Jae Lim, Young-Wan Moon, Yong-Ki Min, DooSeok Choi, Byung-Koo Yoon, Youn-Soo Park
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2010; 25(11): 1657. CrossRef - Postoperative Mortality and the Associated Factors for Senile Hip Fracture Patients
Dong-Soo Kim, Hyun-Chul Shon, Yong-Min Kim, Eui-Sung Choi, Kyoung-Jin Park, Se-Hyuk Im
The Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2008; 43(4): 488. CrossRef
- Finite element modeling and simulation of hip joints in elderly women: for development of protective clothing against fracture
- 605 View
- 0 Download
- 13 Crossref

Case Reports
- Multiple Fractures of Forearm Both Bones: A Case Report of 5 Separate Sites
- Bu Hwan Kim, Moo Ho Song, Seong Jun Ahn, Seong Ho Yoo, Min Soo Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(4):466-469. Published online October 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.4.466
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We have experienced multiple fractures of forearm both bones, which revealed the following fractures: comminuted fracture of olecranon, short oblique fracture of proximal ulnar shaft, transverse fracture of ulna mid-shaft, comminuted fracture of radial head, comminuted fracture of distal radius.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Treatment of a Segmental Ulnar Shaft Fracture and an Olecranon Fracture
Myoung Soo Kim, Kyu Pill Moon, Hyung Joon Cho, Jung Yun Bae, Kuen Tak Suh
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2010; 45(6): 496. CrossRef
- Treatment of a Segmental Ulnar Shaft Fracture and an Olecranon Fracture
- 412 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Intrathoracic Migration of K-wire after Fixation of Proximal Huemrus Fracture: Case Report
- Tae Jin Song, Joon Yeop Song, Sung Kon Kim, Jung Ho Park, Joon Ho Wang, Jong Woong Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(4):462-465. Published online October 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.4.462
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We report an unusual case of Kirschner wire migration from the proximal humerus into the thoracic cavity and diaphragm which induced pneumothorax and hemoperitoneum. An 81-year-old woman admitted to the emergency room due to sudden onset of dyspnea. X-rays showed pneumothorax and old proximal humerus fracture fixed with rush pins and K-wires. One of K-wires was seen on the diaphragm level at posterior gutter of chest wall. Through the abdomen, K-wire was removed from the diaphragm and a chest tube was inserted. The potential for K-wires to migrate must be recognized, and frequent postoperative radiographic studies have to be performed for the early detection of loosening and migration. It appears that if K-wires are used for fixation of proximal humerus, the lateral ends must be bent to prevent medial migration, and when the desired therapeutic goals have been achieved, these pins have to be susbsequently removed as soon as possible.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Spinal Canal Migration of a K-Wire Used for Fixation of a Distal Clavicular Fracture
Byung-Ill Lee, Yong-Beom Kim, Hyung-Suk Choi, Chang-Hyun Kim, Jung-Woo Ji
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2013; 48(3): 231. CrossRef - Early Intrathoracic Migration of K-wire Used for Fixation of Proximal Humerus Fracture
Sang Jin Cheon, Ji Min Lee
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2011; 46(2): 167. CrossRef
- Spinal Canal Migration of a K-Wire Used for Fixation of a Distal Clavicular Fracture
- 481 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Crossref

Original Articles
- Operative Treatment in Fracture-Dislocations of Carpometacarpal Joints
- Jae Yeol Choi, Hun Kyu Shin, Kyung Mo Son, Chun Suk Ko
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(4):443-451. Published online October 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.4.443
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To present our operative experiences with carpometacarpal (CMC) injuries, excluding thumb.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty four fracture and dislocations of CMC joint excluding thumb were reviewed retrospectively. Emphases were placed on injury mechanisms, anatomical location, times between diagnosis and surgery, treatment and complications.
RESULTS
The average age of patients was 31.5 years. 19 cases of axial loading by blow as an injury mechanism. The 5th CMC joint was found to be the most frequently involved single joint (18 cases of 34 cases). Dorsal dislocation of CMC joints was present in 12 cases. Comminution of the carpal or metacarpal bone was present in 18 cases. The average time to surgery was 6 days. Twenty-seven cases were operated upon by closed reduction and percutaneous pinning. Seven cases were treated by open reduction and internal fixation. In the last follow up period, a clinically full hand function was restored in 31 cases. Intermittent pain was present in 6 cases in which there was grip weakness in 4 cases and limitation of motion in 3 cases. However, all cases were able to activities of daily living.
CONCLUSION
We obtained good outcomes in CMC joint injuries through the accurate diagnosis and proper operative treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Study on Percutaneous Intramedullary Bioresorbable Pin Fixation for Fourth and Fifth Metacarpal Bone Fracture
Sang Hwan Lee, Sang Hun Kim, Eun Soo Park, Seung Min Nam, Ho Seong Shin
Journal of the Korean Society for Surgery of the Hand.2017; 22(2): 105. CrossRef - Percutaneous retrograde intramedullary single wire fixation for metacarpal shaft fracture of the little finger
Soo-Hong Han, Seung-Yong Rhee, Soon-Chul Lee, Seung-Chul Han, Yoon-Sik Cha
European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology.2013; 23(8): 883. CrossRef - Operative Treatment in the Delayed Diagnosed Fracture and Dislocation of Hamatometacarpal Joint
Suk Ha Lee, Jong Wong Park, Jin Il Kim, Seoung Joon Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(3): 249. CrossRef - Comparison of Early Fixation and Late Fusion of 4, 5th Carpometacarpal Joint in the Intra-Articular Fractures of 4th and 5th Metacarpal Base
Chang Ho Yi, Jin Rok Oh
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(1): 60. CrossRef - Percutaneous Retrograde Intramedullary Pin Fixation for Isolated Metacarpal Shaft Fracture of the Little Finger
Soo Hong Han, Hyung Ku Yoon, Dong Eun Shin, Seung Chul Han, Young Woong Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(4): 367. CrossRef - Operative Treatment of Trapezium Fractures
Ho Jung Kang, Nam Heon Seol, Man Seung Heo, Soo-Bong Hahn
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(4): 276. CrossRef - Fracture-Dislocation of the Carpometacarpal Joint with the Fracture of Hamate
Jin Woong Yi, Whan Young Chung, Woo Suk Lee, Cheol Yong Park, Youn Moo Heo
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2008; 21(4): 297. CrossRef
- Clinical Study on Percutaneous Intramedullary Bioresorbable Pin Fixation for Fourth and Fifth Metacarpal Bone Fracture
- 479 View
- 0 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Development and Accuracy Test of a Robot-arm Type Image-guided Surgery System for Percutaneous Screw Fixation of the Sacro-iliac Joint
- Jin Sup Yeom, Won Sik Choy, Hayong Kim, Jong Won Kang, Kwang Won Lee, Whoan Jeang Kim, Jae Hoon Ahn, Seong Kyu Park, Jong Hwa Won, Hyungmin Kim, Namkug Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(2):191-197. Published online April 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.2.191
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To develop a robot-arm type image-guided surgery system for percuatneous screw fixation of the sacro-iliac joint and to evaluate its accuracy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We have developed an image-guided surgery system using a three-dimensional digitizer (Microscribe 3-D G2, Immersion, USA) and a personal computer. The registration error and target localization error at fiducial registration were measured 30 times for each using a phantom made with plastic pelvic bone model (Sawbones, USA). Sixteen 6.5 mm cannulated screws were inserted into four plastic bone models, and the accuracy was evaluated.
RESULTS
The target localization error was 1.46+/-0.47 mm while the registration error was 0.73+/-0.23 mm. All of the 16 screws were inserted well across the sacro-iliac joint, and there was neither cortical breach nor collision between screws or washers.
CONCLUSION
The accuracy of the developed system was similar to that of optical tracker-based navigation systems, and its helpfulness and usefulness was proven with simulation surgery using plastic bone models.
- 326 View
- 0 Download

- Evaluation of Osseointegration in Titanium Alloy Cortical Screws with the Passage of Time
- Jae Hyup Lee, Bong Soon Chang, Choon Ki Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(4):401-407. Published online October 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.4.401
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the osseointegration of titanium alloy cortical screws with the passage of time.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fifty four titanium alloy cortical screws (24 mm in length, 3.5 mm in diameter) were implanted bilaterally in the tibial diaphysis of adult mongrel male dogs of similar size and weight (30 +/-5 kg). The insertion torques, radiographs, undecalcified histology, histomorphometric analysis and extraction torques were evaluated at 2, 4 and 8 weeks after surgery.
RESULTS
The extraction torque at 2 weeks (1.14+/-0.470 cN. m) was significantly lower than the insertion torque (1.76+/-0.609 cN. m) (p=0.0071), the extraction torque at 4 weeks (2.57+/-1.36 cN. m) was slightly improved and the extraction torque at 8 weeks (3.18+/-0.499 cN. m) was significantly higher than insertion torque (p=0.0005). Direct bony contact in the early phase was poor and intervening fibrous tissue was observed at the bone-screw interface. However, the fixation between the bone and the screws improved with time. The percentage of bone-screw contact at 8 weeks (33.1+/-18.5%) was higher than that of 2 weeks (22.4+/-12.9%), but not statistically significant.
CONCLUSION
Because of thermal injury or pressure necrosis, the fixation strength of titanium alloy cortical screws at 2 weeks after implantation is significantly lower than that at the insertion time. So, we should keep in mind the initial phase weakness of screw fixation when we allow the patients the range of motion exercise or weight bearing and the improvement of the initial phase fixation is very important in clinical results.
- 323 View
- 1 Download

- The Usefulness of Non-operative Treatment of Distal Radius Fracture in Elderly Patients
- Ki Ser Kang, Han Jun Lee, Sang Hak Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(4):345-349. Published online October 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.4.345
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To disclose the correlation between the functional and radiologic results of the treatment of distal radius fracture in elderly patients by non-operative versus operative treatment.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From January 1995 to December 2000, 36 patients, more than 60 years old with fractures of distal radius were treated and followed up for more than one year. We classified them using the Fernandez classification and evaluated functional and radiological results according to the subjective point system of Cole & Obletz and objective evaluation by Scheck.
RESULTS
In functional result, excellent to good results were obtained in 12 cases (71%) in the non-operative group and 14 cases (74%) in the operative group, there were no evidence of statistical difference between two groups (p>0.05). In radiographic results, mean radial inclination, loss of radial length and volar tilt were 13degree, 12.3 mm, 7.2degrees in the non-operative goup and 5.2degrees, 5.1 mm, 3.3degrees in the operative group on last follw-up radiographs, there were evidence of statistical difference between two groups (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
Operative treatment is radiographically better result in distal radius of elderly patients but functional satisfaction is not significantly related with radiographic result. When we decide the treatment of elderly patients, non-operative treatment can be useful method, considering with patient's age and activity status.
- 298 View
- 0 Download

- Operative Treatment of Proximal Tibial Plateau Fractures through Lateral Submeniscal Approach
- Hyug Su An, Se Ang Chang, Jun Woo Park, Jin Seok Lee, Hun Ho Bang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(3):237-242. Published online July 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.3.237
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was conducted to evaluate the clinical results of proximal tibial plateau fractures treated with open reduction and internal fixation through the lateral submeniscal approach and allowed early motion of the knee and to evaluate the effectiveness of the approach.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From January 1998 to December 2002, fifty four patients who underwent open reduction through the lateral submeniscal approach for proximal tibia plateau fracture and had a follow-up more than one year were included in this study. Clinical results were evaluated by postoperative radiographs taken at the last follow-up and Porter's assessment method.
RESULTS
Anatomical reduction was achieved under direct vision through the submeniscal approach in most of the cases in this study. The postoperative radiographs showed anatomical reduction in 32 cases (59%) and adequate reduction with displacement within 2 mm in 20 cases (37%). The clinical evaluation by Porter's assessment method revealed that 49 cases (91%) were acceptable results of excellent or good at the final follow-up CONCLUSION: This study indicates that open reduction and internal fixation through the lateral submeniscal approach can be a good option for proximal tibia plateau fractures because it allows accurate reduction of the articular fractures, which is confirmed directly during operation, identification and repair of associated soft tissue injuries are facilitated, sufficient bone graft and stable fixation of the articular fragments under direct vision allow early motion of the knee.
- 349 View
- 6 Download

- Reduction of Pediatric Forearm Diaphyseal Fractures by Pin Leverage Technique
- Soo Hong Han, Duck Yun Cho, Hyung Ku Yoon, Byung Soon Kim, Sung Hoon Kang, Tae Hyung Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(1):59-63. Published online January 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.1.59
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
Although the majority of children's forearm diaphyseal fractures may be treated conservatively with closed reduction and cast immobilization, unstable or irreducible fractures are usually treated by surgical management. Authors performed percutaneous pin leverage reduction technique for irreducible displaced diaphyseal fractures. The aim of this study is to determine the efficacy of pin leverage technique in pediatric forearm diaphyseal fractures MATERIALS AND METHODS: In this retrospective study, we reviewed 22 cases of forearm diaphyseal fractures reduced by percutaneous pin leverage technique between 1997 and 2002. We analyzed radiographs, operation time, hospital stay and immobilization period, range of motion, postoperative complications and functional results by Thomas.
RESULTS
Average length of follow up was 28 months with mean age of 10.5 years. All fractures in this series healed less than 2 degrees of diaphyseal angulation. Average operation time including anesthesia was 42 minutes and hospital stay was 4.6 days. Time to union was 49.6 days in average and range of motion and functional results were satisfactory in all cases except one case of congenital radioulnar synostosis. There was one case of superficial pin track infection as complication.
CONCLUSION
In operative treatment of children's diaphyseal fractures of forearm bones, percutaneous pin leverage reduction technique is a good alternative method prior to open reduction in case of difficult closed reduction. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pediatric Forearm Bone Fractures Treated with Flexible Intramedullary Nail
Suk Kyu Choo, Jin Hwan Kim, Hyung Keun Oh, Dong Hyun Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2007; 20(2): 190. CrossRef
- Pediatric Forearm Bone Fractures Treated with Flexible Intramedullary Nail
- 464 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Operative Treatment of Floating Shoulder
- Ho Jung Kang, Gun Bo Park, Dong Joon Shim, Soo Bong Hahn, Eung Shick Kang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(1):38-42. Published online January 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.1.38
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
Conservative treatment of displaced ipsilateral compound fractures of clavicle and scapula neck or gleonoid cavity, causing a floating shoulder, cannot expect satisfactory results in all of them. We reviewed 9 operative cases of floating shoulders and analyzed the results with review of literature.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Nine patients with floating shoulders were operated from July 1996 to August 2000 were reviewed. Patient's age was in average 38.3 years old. Associated injuries were 4 cases of rib fractures and 1 case of humerus shaft fracture. Other injuries included 3 hemothorax, 2 pneumothorax, 1 brachial plexus injury, and 1 ulnar nerve injury. Operation for both clavicle and scapula fracture was done in 6 cases, and surgery was done for only clavicle in 3 cases. Internal fixation for clavicle was done with 3.5 mm AO reconstruction plate in 4 cases and Dynamic Compression Plate in 5 cases.
RESULTS
Clinical results by Hardegger method showed 7 cases of excellent, 1 case of good, and 1 case of poor. Complications include 2 cases of limitation of motion of shoulder joint and one case of residual pain.
CONCLUSION
Floating Shoulder is caused by high-energy trauma, therefore initial assessment of associated injuries should be done carefully. In evaluating the articular surface of the glenoid and positions of the fracture fragment, CT evaluation is very useful in planning the surgical treatment. Clinical results after surgery can give satisfactory results.
- 477 View
- 2 Download

- The Results of Surgical Treatment of Acute Acromio-clavicular Separation, Type III
- Sung Ho Hahn, Bo Kyu Yang, Seung Rim Yi, Shun Wook Chung, Dong Ho Lee, Min Seok Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(2):235-243. Published online April 30, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.2.235
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to compare the Phemister technique with the modified Phemister technique for the patients with Rockwood type 3, acromio-clavicular separation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The 45 cases of 45 patients received surgical treatment for Rockwood type 3, acute acromio-clavicular separation in our hospital from Feb. 1992 to Aug. 2001 later with the follow-up study were selected as subjects. The average ages were 28.1 years old, male and female were 42, 3 persons, respectively. Physical examination and plain radiography were used for their diagnosis and the intervals between injury and surgical treatment were 7.8 days. In intraoperative finding, we performed Phemister technique in 15 cases according not to be able to repair coraco-clavicular ligament (group I), modified Phemister technique in 30 cases according to be able to repair that (group II). The average follow up period was 16.2 months, and the UCLA shoulder scoring system and the acromio-clavicular separation scoring system were used to obtain clinical results.
RESULTS
Only in Group II, the complication after surgery were associated with superficial infection in two cases and K-wire migration in one case. At last follow up, there were no pain and limitation of range of motion in all cases, and two cases in Group II were found to be subluxation in radiography. Clinical results revealed excellent was 93.3%, good was 6.7% in UCLA shoulder scoring system in both groups, and excellent was 90%, good was 10% for group II in acromio-clavicular separation scoring system.
CONCLUSION
The results are considered to be good with only Phemister technique in type 3, acute injury occurred in working ages.
- 336 View
- 0 Download

- A Comparative Study of Reamed and Unreamed Nail for Femoral Shaft Fracture's Treatment
- Hee gon Park, Myoung ho Kim, Mun jib Yoo, Woo sup Byun
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(2):169-176. Published online April 30, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.2.169
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The comparative analysis of clinical difference between the use of reamed nail and unreamed nail in treatment of femoral shaft fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In 105 patients with femoral shaft fracture who were treated with reamed nail or unreamed nail between June of 1997 and April of 2000, 95 patients who underwent more than a year of follow-up were selected. Winquist-Hansen criteria was applied for the classification of fracture. Based on the medical records and radiological examinations, conducted a retrospective, statistical analysis of the duration of operation, the amount of bleeding during operation, the first time of callus formation, union time, and complications.
RESULTS
The average duration of operation was 107 minutes for reamed nail group, and 94 minutes for unreamed nail group, and the difference was statistically significant (p<0.005). The amount of bleeding during the operation was 400 mL for reamed nail group and 250 mL for unreamed nail group, and the difference was statistically significant (p<0.001). There was no statistical difference in the first time of callus formation and union time between the two groups but, in general union time tend to be long in unreamed nail group.
CONCLUSION
In the treatment of femoral shaft fracture, the use of unreamed nail was shown to have an advantage over the use of reamed nail in terms of the duration of operation and the amount of bleeding. We recommend restrictive cases.
- 320 View
- 2 Download

- Development of a Computer-assisted Surgery System for Screw Fixation of the Sacro-iliac Joint
- Jin Sup Yeom, Won Sik Choy, Ha Yong Kim, Whoan Jeang Kim, Jong Won Kang, Yeongho Kim, Hyungmin Kim, Donghyun Seo, Seok Lee, Jae Bum Lee, Namkug Kim, Cheol Young Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(1):1-7. Published online January 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purposes of this study were to develop a computer-assisted surgery system for percutaneous screw fixation of the sacro-iliac joint and to evaluate its accuracy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We have developed a navigation system composed of an optical tracking device (Polaris, Northern Digital, Canada) and a personal computer. The registration error and target localization error at hybrid registration were measured using a phantom. The errors were measured 30 times for each. Sixteen 6.5 mm cannulated screws were inserted into four plastic bone models (Sawbones, USA), and the accuracy was evaluated.
RESULTS
The registration error was 0.76 +/-0.33 mm, and the target localization error was 1.43 +/-0.42 mm. All of the 16 screws were inserted well across the sacro-iliac joint, and there was neither penetration of the cortical bones nor collision between screws or washers.
CONCLUSION
The accuracy of the developed system was similar to existing ones, and its usefulness and helpfulness was proven with screw insertion into plastic bone models.
- 311 View
- 3 Download

- Impacted Cancellous Allograft and Quadratus Femoris Pedicle Bone Graft of Femoral Neck Fracture Nonunion
- Soo Jae Yim, Seung Han Woo
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(4):519-525. Published online October 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.4.519
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The aim of this study was attempted to evaluate the effects of impacted cancellous allograft and quadratus femoris pedicle bone graft in the management of nonunion of femur neck fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between March 1998 and April 1999, 5 patients, rating from 36 to 45 years of age, were treated with impacted cancellous allograft and quadratus femoris pedicle bone graft and all cases were nonunion with displaced transcervical fracture whose primary treatment had been done with closed reduction and multiple pinning. The duration of follow-up was from 36 months to 48 months and the mean follow-up period was 40 months. Clinical evaluation was done according to Lunceford functional results and radiologically bone union was evaluated by 3 monthly X-ray check.
RESULTS
After follow-up from 36 months to 48 months, all cases resulted in the bone union. Four cases, radiologically bone union was progressed during 14 weeks, and the other, obtained at 6 months. All cases, at 18 months, radiologically complete bone union was obtained. Clinical result was above fair results and no one complaints pain and instability.
CONCLUSION
For patients with nonunion of femoral neck fracture, impacted cancellous allograft and quadratus femoris pedicle bone graft was provide a good result of union.
- 280 View
- 1 Download

- The results of Operative Treatment in the Proximal Tibial Plateau Fracture
- Kyung Jin Song, Keun Ho Yang, Joo Hong Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(4):489-496. Published online October 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.4.489
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - INTRODUCTION: The purpose of this study was to analyze the results, prognosis and complications in the treatment of proximal tibia plateau fractures, and to suggest the guideline for the proper management in the difficult cases of tibial plateau fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We have analyzed 27 cases, which surgically treated during recent five years with average 36.6 months follow-up. Patients ranged in age from 24 to 83 years at the time of hospitalization, consisting of 19 males(70.4%) and 8 females(29.6%). The type of fracture by Schatzker classification revealed in type I 3 cases(11.1%), type II 1 case(3.7%), type III 0 case(0%), type IV 3 cases(11.1%), type V 1 case(3.7%) and type VI 19 cases(70.4%). The associated injury occurred in 22 cases(81.5%), most of them were ipsilateral fibular, ipsilateral femoral and radioulnar fractures. The results were evaluated by Blokker 's criteria.
RESULTS
Screw fixation was done in 4 cases(18%) and plate fixation in 23 cases(85.2%), and bone grafting was done in 10 cases(37.0%). There were 10 postoperative complications with 3 cases of knee ankyosis, 3 cases of angular deformity, 3 cases of infection, and 1 case of traumatic arthritis. According to Blokker 's criteria, 22 cases(81.5%) had satisfactory results.
CONCLUSIONS
Accurate anatomical reduction and rigid internal fixation of the proximal tibial plateau fracture enabled early motion and normalization of injured soft tissues, and also provided functional improvement of the knee.
- 309 View
- 2 Download

- The Evaluation of Clinical and Radiographic Prognostic Factors for the Surgically Treated Unstable Ankle Fractures
- Hong Geun Jung, Hee Kon Park, Moon Jib Yoo, Tai Won Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(2):216-225. Published online April 30, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.2.216
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to analyze the clinical and radiographic prognostic factors which may affect the postoperative clinical results of the unstable ankle fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study is based on 75 unstable ankle fractures treated by open reduction and internal fixation from May 1994 to August 2000, with a minimum follow-up period of 12 months(range : 13 months-7 years 3 months). The 75 patients were average 40.5 years old with male: female ratio of 52:23. Based on Lauge-Hansen classification, the supination-external rotation type was the most common with 42 (56.0%) cases. The clinical results was assessed by American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society(AOFAS) functional scale. The sex, age, side of injury, body weight, trauma-operation interval, operation time, cause of injury as the possible postoperative clinical prognostic factors and fracture type, anatomical reduction of fracture, preoperative medial clear space, postoperative medial clear space, talo-crural angle, talar tilt, tibio-fibular clear space, tibio-fibular overlap space as the possible radiographic prognostic factor were statistically analyzed RESULT: Postoperative AOFAS functional scale was average 81.0 points with 23(30.7%) cases excellent, 17(22.7%) good, 18(24.0%) fair and 17(22.7%) cases poor results. The age, the operation time(p<0.001) and the anatomical reduction of fracture(p<0.005) were found to be statistically significant factors affecting the prognosis. The other clinical and radiographic factors did not significantly affect the clinical results.
CONCLUSION
The surgically treated unstable ankle fractures in patients whose age was above 41 years old or operation time exceeding 90 minutes or unsatisfied anatomical reduction of fractures showed significantly poor clinical results. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Bone Mineral Density of Ankle Fracture Patients
Tae Hyung Kim, Jae Hyung Lee, Seung-Hwan Park
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2021; 56(4): 334. CrossRef
- Analysis of Bone Mineral Density of Ankle Fracture Patients
- 494 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Operative Treatment for AO Type C Supracondylar Fractures of the Distal Femur
- Ho Rim Choi, Joon Min Song, Hee Kwon, Youm Gyu Ko, Jang Geun Lee, Chang Hun Yoon
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(2):166-172. Published online April 30, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.2.166
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
Treatment of supracondylar fracture of the distal femur is challenging because of its characteristic anatomy and common occurrence of severe comminution. We evaluated the clinical results of 15 cases of AO type C supracondylar fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From December 1990 to November 1999, fifteen of 27 cases of AO type C supracondylar fracture of the distal femur were treated operatively. Mean follow-up period was one year and 5 months (range, 1 year-3 years and 3 months). The mean age of patients was 43.6 years. Eleven cases were treated by internal fixation and four cases by Ilizarov. Clinical results were evaluated by Schatzker and Lambert criteria.
RESULT
There were 5 excellent, 4 good, 1 fair and 1 poor results (81% satisfactory) in 11 cases treated by internal fixation and 1 excellent, 2 good, 1 fair results (75% satisfactory) in 4 cases treated by external fixation. COCLUSION: To get satisfactory results, AO type C supracondylar fracture of the distal femur need to be reduced anatomically and require rigid internal fixation. External fixation using Ilizarov can be an effective method of treatment in cases of open fracture and severe comminution with osteoporosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surgical Treatment of AO Type C Distal Femoral Fractures Using Locking Compression Plate (LCP-DF, Synthes®)
Kap-Jung Kim, Sang Ki Lee, Won-Sik Choy, Won-Cho Kwon, Do Hyun Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(1): 20. CrossRef
- Surgical Treatment of AO Type C Distal Femoral Fractures Using Locking Compression Plate (LCP-DF, Synthes®)
- 504 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Operative Treatment of Tibial Plateau Fractures - Analysis of the factors affecting to the clincal results
- Byeong Yeon Seong, Wan Soo Park, Sang Yul Shin, Yuen Ki Woo, Taek Geon Lee, Man Jae Park, Seung Ki Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(1):87-96. Published online January 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.1.87
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the relationship between variable factors and clinical results following the operative treatment of the tibial plateau fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The clinical and radiological analysis was performed on 29 cases of the tibial plateau fractures who had been treated with operative treatment and followed up for more than 1 year from January 1991 to December 1997. The analysis of clinical results was performed dividing into age, cause of injury, fracture type of Schatzker classification, associated soft tissue injury and method of operative treatment.
RESULTS
18 of 19 cases that were ranged of ages between 30 years and 59 years showed good clinical results as criteria of Blokker. Schatzker type II was noted 11 cases(37.9%) as most common. 13 of 14 cases of the type I,II and III, were showed good clinical results, compare to 10 of 15 cases of the type IV,Vand VI. 12 of 18 cases which were related with associated soft tissue injuries, were showed good clinical results.
CONCLUSION
We could expect good clinical results if early knee joint mobilization following open reduction and rigid internal fixation could be obtained. Factors affecting clinical results are age, type of fracture, associated soft tissue injuries. Bad clinical results were related with young age group under 30 and over 60, more than Schatzker classification type IV of high energy trauma and associated injury of anterior cruciated ligment or meniscus.
- 369 View
- 0 Download

- Operative Treatment of Open Tibial Fracture
- Kyung Jin Song, Sun Woong Jang
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(1):45-51. Published online January 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.1.45
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of the present study was to clarify the contributing factors, such as the method of fracture stabilization, type of internal fixation and the deep infection rate(DIR) in the treatment of open tibial fractures. MATERIAL AND METHODS: We made a retrospective study of these 87 open tibial fractures treated with various fixation method. Patients were divided into immediate internal fixation(IIF) group, delayed internal fixation(DIF) group and external fixation(EF) groups. Fixation methods, deep infection rate related with fixation devices and time to bone union were compared and anaylzed according to the Gustilo`s classification.
RESULTS
The mean time to union in open type I, II, IIIa, IIIb, and IIIc was 5.7 months, 8.6 months, 7.1 months, 9.7 months, and 18.0 month respectively. The mean time to union in group IIF, DIF1, DIF2 and EF was 7.2 months, 8.1 months 5.5 months, and 10.7 months and 13.1 months. The mean time to union of group using a interlocking IM nailing, plate and screws, and external fixator was 6.3 month, 6.9 months, and 10.6 months. SUMMARY: We concluded that there is an advantage of immediate internal fixation over external fixation in the prevention of infection and promotion of fracture healing in the treatment of open tibia fractures. Immediate internal fixation could be recommended for type I, II, IIIa and some cases of IIIb open tibia fracture.
- 352 View
- 1 Download

- Radiation Exposure from Fluoroscopy during Orthopaedic Surgical Procedures
- Su Young Bae, Jong Oh Kim, Jae Doo Yoo, Seong Yong Yoon, Jin Won Jang
- J Korean Soc Fract 2001;14(4):792-798. Published online October 31, 2001
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2001.14.4.792
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to evaluate the radiation dose administered in orthopedic operative procedures and to determine whether all operation room personnel must use the lead protector.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From March 2001 to May 2001, sixty six orthopedic operations were done with fluoroscopic intensifier(Series 9600TM, OEC Medical Systems Inc.). The accumulative exposure doses of operator, 1st assist, scrub nurse, circulating nurse and anesthesiologist were assessed by TLD(Thermo luminescence dosimeter) and compared with the dose limit set by the KINS(Korea Institute of Nuclear Safety). The exposure times and doses were evaluated in each cases and analyzed according to the each procedure. The exposure doses were assessed by the distance (Om, 0.5m, 1m, 2m) from the fluoroscopic generator.
RESULTS
Accumulative exposure doses(3 months) were checked 1.37mSv in operator, 1.73mSv in 1st assist, 0.17mSv in scrub nurse, 1.01mSv in circulating nurse, 0.01mSv in anesthesiologists and all doses were lower than dose limit set by the KINS(12.5mSv). Low exposure was checked in procedure of hand, ankle, cervical spine but high exposure was checked in IM nailing of femur(one way Anova with postHoc test, p<0.05). The exposure doses were decreased with the distance and exposure dose out of 1m was minimal.
CONCLUSION
Radiation is higher in IM nailing procedure but the total accumulative doses were safe especially in personnel who can fall apart from the operation field more than lm. So, we conclude that the lead protector is not essential to the all operation room personnel. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Radiation exposure and fluoroscopically-guided interventional procedures among orthopedic surgeons in South Korea
Seonghoon Kang, Eun Shil Cha, Ye Jin Bang, Teresa W. Na, Dalnim Lee, Sang Youn Song, Won Jin Lee
Journal of Occupational Medicine and Toxicology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Radiation exposure and fluoroscopically-guided interventional procedures among orthopedic surgeons in South Korea
- 530 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Cubitus Varus Resulted from Fracture-Separation of the Distal Humeral Epiphysis
- Sung Soo Kim, Sang Hwan Park, Kyoung Sik Hwang
- J Korean Soc Fract 2001;14(4):769-775. Published online October 31, 2001
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2001.14.4.769
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
We tried to find the cause of cubitus varus after treatment of fracture separation of the distal humeral epiphysis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed 13 cases of fracture-separation of the distal humeral epiphysis. Five cases were treated by open reduction and K-wire fixation, 8 cases were treated by closed reduction and K-wire fixation. Six cases of cubitus varus were evaluated.
RESULTS
With the average 27 months(14-96 months) of follow-up, six of 13 cases showed cubitus varus postoperatively and mean carrying angle was -6.7 degrees(range -3~-15 degrees). None of these cases showed the progression of deformity after then. Among the six cases, five cases were treated with closed reduction, and one case with open reduction. Average age of the cubitus varus cases was 31 months (14-60 months). Among the six cases, four cases were Salter-Hams type I and two cases were type II.
CONCLUSION
Incomplete reduction seems to be the cause of cubitus varus in fracture-separation of the distal humeral epiphysis, so the anatomical reduction is important to prevent the cubitus varus.
- 317 View
- 0 Download

- Operative treatment of fracture of medial epicondyle of humerus in children
- Ho Jung Kang, Yong Min Cheon, Kye Wook Song, Eung Shick Kang, Hui Wan Park
- J Korean Soc Fract 2001;14(4):762-768. Published online October 31, 2001
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2001.14.4.762
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
We investigated injury mechanism, clinical feature, treatment, and prognosis in fracture of medial epicondyle of humerus in children. MATERIAL AND METHOD: From April 1997 to April 2000, 10 fractures of medial epicondyle of humerus treated by operative method and followed up for minimum 12 months were analyzed retrospectively.
RESULTS
The injury mechanism includes slip down with elbow outstretched in 8 case, throwing ball in one case, arm wrestling in other one case. Ulnar nerve symptom at the distal region of fracture site was noted in one case. 2 cases had elbow dislocation at the time of trauma. Fractured fragment displaced more than 5mm in 9 cases and fractured fragment incarcerated in elbow joint in one case. Open reduction and internal fixation was done with medial approach. The mean period of cast immobilization was 6 weeks postoperatively and after removal of cast, gentle exercise of range of motion was started. After operation and postoperative follow up, in all case except one, the full range of motion of elbow joint was recovered and there were no Unar nerve symptom and valgus instability in affected elbow joint.
CONCLUSION
The indication of operation for fracture of medial epicondyle of humerus is controversial, yet. We had done open reduction and internal fixation for medial epicondyle of humerus only in case of displacement of fractured fragment more than 5mm and incarceration in elbow joint after manual reduction, ulnar nerve symptom. In 90 percents of all case, the result was satisfactory.
- 249 View
- 0 Download

- Operative treatment of Radial neck fractures in Children
- Ho Jung Kang, Jae Hoon Jun, Kye Wook Song, Soo Bong Hahn, Eung Shick Kang
- J Korean Soc Fract 2001;14(4):745-752. Published online October 31, 2001
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2001.14.4.745
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTS: Radial neck fractures are uncommon in children, and most cases were treated by conservative treatment or manual reduction. But if proximal fragment is angulated more than 30 degrees, and displaced more than 30%, operative treatment is needed. Operative treatment is also needed in cases of closed reduction failure or in type IV of Salter-Harris classification. If open reduction is not performed, limitation of motion, altered carrying angle and radiologic change occur. We retrospectively analyzed 12 patients who had operative treatment for radial neck fractures in children.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From April 1996 to December 1998, 12 patients with radial head fracture, were admitted to our hospital and were treated by operation. The average age of 9 years and 6 months (range 5 years 11 months to 14 years). Falling down was most common cause of injury. Seven cases were treated by open reduction and 5 cases by closed reduction. On open reduction group, 3 cases were fixed by Kirschner wire and 4 cases fixed by mini-screw. On closed reduction group, 3 cases were reduced percutaneously using steinmann pin, 1 case reduced using curet, and I case was fixed with Kirschner wire.
RESULTS
Ten cases were evaluated as good or excellent by criteria for judging results of radial neck fracture by Tibone and Stortz. Three cases had complication of heterotopic ossification, two cases had complication of limitation of motion. and one case had complication of pin loosening.
CONCLUSION
The operative treatment for radial neck fracture in children, improved the results of physical examination and roentgenographic evaluation. So operative treatment is needed for radial neck fracture in children which are more than 30 degrees angulation, more than 30% displacement and with displaced epiphyseal plate injury.
- 236 View
- 0 Download

- Complications after treatment of tibial Non fracture
- Ki Do Hong, Sung Sik Ha, Hyun Jong Cha
- J Korean Soc Fract 2001;14(4):668-676. Published online October 31, 2001
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2001.14.4.668
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
Aim of this study was to find the treatment and preventive method of the complication occurred after treatment of tibial pilon fracture. MATERIAL AND METHODS: 10 cases of complication, which has required the unplanned operative treatment among 25 cases of tibial pilon fracture from 1994 to 1999 were analyzed rertrospectively according to the Ruedi-Allgower classification, open or closed fracture, isolated or polytrauma , type of complication, type of procedure, primary or delayed wound closure.
RESULTS
There were 1 type I, 3 type II, and 6 type III Ruedi-Allgower fracture type, 3 open fracture, 7 isolated and 3 polytrauma. 6 required plastic surgery procedure such as pedicle flap or full thickness skin graft and 7 required orthpaedic procedure such as osteotomy, cancellous bone graft, metal removal and currettage, debridement of ankle.
CONCLUSION
The complications after treatment of tibial pilon fracture are classified to intraoperative, early and late postoperative complication. Intraoperative complication include penetration of the joint by screw and inadequate reconstitution of the articular surface which can be avoided by taking intraoperative roetgenograms, early complication include wound necrosis which can be minimized by good soft tissue technique, late complication include nonunion, joint stiffness and posttraumatic arthritis can be treated by osteotomy, cancellous bone graft and anatomic reduction with early motion.
- 294 View
- 0 Download

- The Result of Modified Bankart Operation with Suture Anchor in Traumatic Recurrent Anterior Dislocation of Shoulder Joint
- Kwang Suk Lee, Jung Dae Seo, Kwang Jun Oh, Seung Joon Lee, Seung Yong Wang
- J Korean Soc Fract 2001;14(3):484-490. Published online July 31, 2001
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2001.14.3.484
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the clinical result of modified Bankart operation repairing the Bankart lesion with capsular shifting using suture anchor in traumatic recurrent anterior dislocation of shoulder joint MATERIALS AND METHODS: All of the cases were treated with modified Bankart operation. The inferior and superior capsular flaps were advanced to the anterior aspect of glenoid neck and fixed with three suture anchors in 30 degrees abduction and external rotation of shoulder joint. Especially the inferior 1/3 capsular flap was sutured over the superior 2/3 capsular flap. We used the grading system of Rowe and Zarins as measuring function, pain, stability, range of motion of shoulder joint.
RESULT
The clinical results were excellent in 80%, good in 20%. The mean loss of motion at follow up study was 2% of flexion and 7% of external rotation.
CONCLUSION
This operative technique is useful in repairing the Bankart lesion and gaining adequate capsular tension. And the using of suture anchor could save the operation time. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Result of Early Active Range of Motion Exercise after Bankart Repair of Traumatic Anterior Instability
Haeng Kee Noh, Jong Woong Park, Jung Il Lee, Jung Ho Park
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2007; 20(1): 53. CrossRef
- Result of Early Active Range of Motion Exercise after Bankart Repair of Traumatic Anterior Instability
- 512 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


