Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 21(3); 2008 > Article
-
Original Article
- Risk Factors of Postoperative Delirium in Elderly Patients with Hip Fractures
- Ki-Hwan Kim, M.D., Duk-Hwan Kho, M.D., Ju-Yong Shin, M.D., Jin-Yong Choi, M.D., Eung-Sik Kim, M.D., Dong-Heon Kim, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2008;21(3):189-194.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.3.189
Published online: July 31, 2008
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Konkuk University Chungju Hospital, College of Medicine, Konkuk University, Chungju, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Dong-Heon Kim, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Konkuk University Chungju Hospital, College of Medicine, Konkuk University, 620-5, Gyohyeon 2-dong, Chungju 380-704, Korea. Tel: 82-43-840-8250, Fax: 82-43-844-7300, patella13@naver.com
Copyright © 2008 The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 1,501 Views
- 4 Download
- 14 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- To find out the relationship between various risk factors and post-operative delirium in elderly patients with hip fractures.
-
Materials and Methods
- Out of 135 patients older than 65 years old who underwent the surgery for hip fracture in our department, between the periods of March 2003 to March 2005, 14 patients (10.4%) developed post-operative delirium and 121 patients (89.6%) did not. We studied risk factors of post-operative delirium in two groups.
-
Results
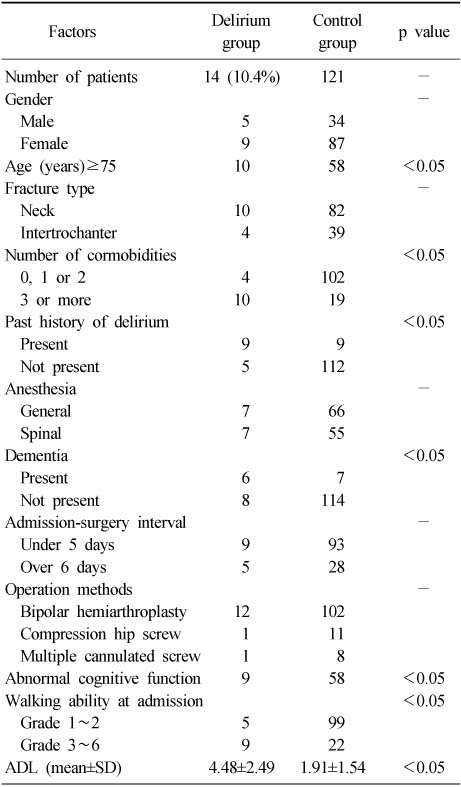
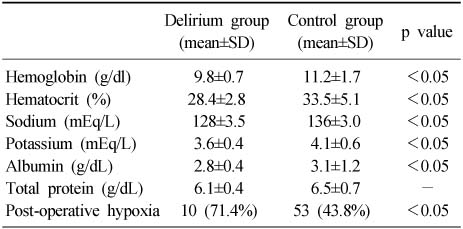
- In chi-square test between delirium group and non-delirium group, the patients were more likely to develop post-operative delirium if they had previous episodes of delirium, abnormal cognitive function, low walking ability before admission, high dependency on ADL (Activities of Daily Living), other medical accompanying diseases, history of dementia, post-operative hypoxia, post-operative electrolyte imbalance, low post-operative hemoglobin and hematocrit, low post-operative albumin and were older than 75 years old (p<0.05). Sex, type of fracture, anesthesia and the time between admission and operation did not show much difference between the two groups.
-
Conclusion
- The risk factors of postoperative delirium in elderly patients with hip fracture have a tendency to be multifactorial. Therefore, we conclude that being prepared by thorough understanding of the risk factors and their relationships will help prevent post-operative delirium and result in good postoperative prognosis.
- 1. Bedford PD. Adverse cerebral effects of anesthesia on old people. Lancet, 1955;269:259-263.
- 2. Berggren D, Gustafson Y, Eriksson B, et al. Postoperative confusion after anesthesia in elderly patients with femoral neck fractures. Anesth Analg, 1987;66:497-504.Article
- 3. Brännström B, Gustafson Y, Norberg A, Winblad B. Problems of basic nursing care in acutely confused and non-confused patients. Scand J Caring Sci, 1989;3:27-34.
- 4. Campion EW, Jette AM, Cleary PD, Harris BA. Hip fracture: a prospective study of hospital course, complications, and costs. J Gen Intern Med, 1987;2:78-82.
- 5. Clayer M, Bruckner J. Occult hypoxia after femoral neck fracture and elective hip surgery. Clin Orthp Relat Res, 2000;(370):265-271.Article
- 6. Edelstein DM, Aharonoff GB, Karp A, Capla EL, Zuckerman JD, Koval KJ. Effect of postoperative delirium on outcome after hip fracture. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 2004;422:195-200.Article
- 7. Edlund A, Lundström M, Brännström B, Bucht G, Gustafson Y. Delirium before and after operation for femoral neck fracture. J Am Geriatr Soc, 2001;49:1335-1340.Article
- 8. Francis J, Martin D, Kapoor WN. A prospective study of delirium in the hospitalized elderly. JAMA, 1990;263:1097-1101.Article
- 9. Gustafson Y, Berggren D, Brännström B, et al. Acute confusional states in elderly patients treated for femoral neck fracture. J Am Geriatr Soc, 1988;36:525-530.Article
- 10. Gustafson Y, Brännström B, Berggren D, et al. A geriatric-anesthesiologic program to reduce confusional states in the elderly patients treated for femoral neck fractures. J Am Geriatr Soc, 1991;39:655-662.
- 11. Gustafson Y, Brännström B, Norberg A, Bucht G, Winblad B. Underdiagnosis and poor documentation of acute confusional states in elderly hip fracture patients. J Am Geriatr Soc, 1991;39:760-765.Article
- 12. Inouye SK, Charpentier PA. Precipitating factors for delirium in hospitalized elderly persons. Predictive model and interrelationship with baseline vulnerability. JAMA, 1996;275:852-857.Article
- 13. Inouye SK, Rushing JT, Foreman MD, Palmer RM, Pompei P. Does delirium contribute to poor hospital outcomes? A three-site epidemiological study. J Gen Intern Med, 1998;13:234-242.Article
- 14. Inouye SK, van Dyck CH, Alessi CA, Balkin S, Siegal AP, Horwitz RI. Clarifying confusion: the confusion assessment method. A new method for detection of delirium. Ann Intern Med, 1990;113:941-948.ArticlePDF
- 15. Jitapunkul S, Pillay I, Ebrahim S. Delirium in newly admitted elderly patients: a prospective study. Q J Med, 1992;83:307-314.
- 16. Kagansky N, Rimon E, Naor S, Dvornikov E, Cojocaru L, Levy S. Low incidence of delirium in very old patients after surgery for hip fractures. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry, 2004;12:306-314.Article
- 17. Kawaguchi Y, Kasanori M, Ishihara H, et al. Postoperative delirium in spine surgery. Spine J, 2006;6:164-169.Article
- 18. Levkoff SE, Evans DA, Liptzin B, et al. Delirium. The occurrence and persistence of symptoms among elderly hospitalized patients. Arch Intern Med, 1992;152:334-340.Article
- 19. Lipowski ZJ. Delirium: acute confusional state. New York: Oxford University Press; 1990. p. 442-478.
- 20. Lundström M, Edlund A, Bucht G, Karlsson S, Gustafson Y. Dementia after delirium in patients with femoral neck fractures. J Am Geriatr Soc, 2003;51:1002-1006.Article
- 21. Marcantonio ER, Flacker JM, Wright RJ, Resnick NM. Reducing delirium after hip fracture: a randomized trial. J Am Geriatr Soc, 2001;49:516-522.Article
- 22. Marcantonio ER, Goldman L, Orav EJ, Cook EF, Lee TH. The association of intraoperative factors with the development of postoperative delirium. Am J Med, 1998;105:380-384.Article
- 23. Mullen JO, Mullen NL. Hip fracture mortality. A prospective, multifactorial study to predict and minimize death risk. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1992;280:214-222.
- 24. O'Brien LA, Grisso JA, Maislin G, Chiu GY, Evans L. Hospitalised elders. Risk of confusion with hip fracture. J Gerontol Nurs, 1993;19:25-31.Article
- 25. Ochs M. Surgical management of the hip in the elderly patient. Clin Geriatr Med, 1990;6:571-587.
- 26. O'Keeffe ST, Ni Chonchubhair A. Postoperative delirium in the elderly. Br J Anaesth, 1994;73:673-687.Article
- 27. Olofsson B, Lundström M, Borssen B, Nyberg L, Gustafson Y. Delirium is associated with poor rehabilitation outcome in elderly patients treated for femoral neck fractures. Scand J Caring Sci, 2005;19:119-127.Article
- 28. Potter JF. The older orthopaedic patient: general considerations. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 2004;425:44-49.
- 29. Robertson BD, Robertson TJ. Postoperative delirium after hip fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2006;88:2060-2068.Article
- 30. Rockwood K, Cosway S, Carver D, Jarrett P, Standnyk K, Fish J. The risk of dementia and death after delirium. Age Ageing, 1999;28:551-556.Article
- 31. Rogers MP, Liang MH, Daltroy LH, et al. Delirium after elective orthpedic surgery: risk factors and natural history. Int J Psychiatry Med, 1989;19:109-121.ArticlePDF
- 32. Schuurmans MJ, Duursma SA, Shortridge-Bagget LM, Clevers GJ, Pel-Little R. Elderly patients with a hip fracture: the risk for delirium. Appl Nurs Res, 2003;16:75-84.Article
- 33. Seymour DG, Pringle R. Post-operative complications in the elderly surgical patient. Gerontology, 1983;29:262-270.ArticlePDF
- 34. Williams-Russo P, Urquhart BL, Sharrock NE, Charlson ME. Postoperative delirium: predictors and prognosis in elderly orthopedic patients. J Am Geriatr Soc, 1992;40:759-767.Article
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Increased Serum Neuropeptide Galanin Level Is a Predictor of Cognitive Dysfunction in Patients with Hip Fracture
Zichao Xue, Ke Zhang, Biao Luo, Long Fan, Ruizhe Zhao, Guangliang Hu, Yuzhen Xu
Disease Markers.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Sleep Disturbance Strongly Related to the Development of Postoperative Delirium in Proximal Femoral Fracture Patients Aged 60 or Older
Myung-Rae Cho, Suk-Kyoon Song, Cheol-Hwan Ryu
Hip & Pelvis.2020; 32(2): 93. CrossRef - Incidence and Associated Factors of Delirium after Orthopedic Surgery
Si-Wook Lee, Chul-Hyun Cho, Ki-Cheor Bae, Kyung-Jae Lee, Eun-Seok Son, Sang-Hyun Um
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2019; 54(2): 157. CrossRef - Relationship between Delirium and Clinical Prognosis among Older Patients underwent Femur Fracture Surgery
Jae-Lan Shim, Seon-Young Hwang
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(2): 649. CrossRef - Relationship between Knowledge, Stress, and Nursing Performance about Care for Delirium in Geriatric Hospital Nurses
Eun-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Clinical Health Science.2016; 4(2): 593. CrossRef - The effects of a tailored intensive care unit delirium prevention protocol: A randomized controlled trial
Kyoung-Ja Moon, Sun-Mi Lee
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2015; 52(9): 1423. CrossRef - Is Delirium an Unrecognized Threat to Patient Safety in Korean Intensive Care Units?
Kyoung-Ja Moon, Jinshi Piao, Yinji Jin, Sun-Mi Lee
Journal of Nursing Care Quality.2014; 29(1): 91. CrossRef - The Effects of Delirium Care Training Program for Nurses in Hospital Nursing Units
Moonja Kim, Haejung Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(5): 489. CrossRef - Knowledge, Performance and Stress about Care for Delirium in Orthopedic Hospital Nurses
Mi Young Kim, Young Eun
Journal of muscle and joint health.2013; 20(1): 72. CrossRef - The Experience of Delirium Care and Clinical Feasibility of the CAM-ICU in a Korean ICU
Joo-Hee Jung, Jung-Hye Lim, Eun-Jung Kim, Hyo-Chan An, Min-Kyung Kang, Jin Lee, Yu-Kyung Min, Eun-Zoo Park, Xiang-Hwa Song, Hye-Ryoung Kim, Sun-Mi Lee
Clinical Nursing Research.2013; 22(1): 95. CrossRef - Development and validation of the Korean Nursing Delirium Scale
Kyoung-Nam Kim, Cheol-Ho Kim, Kwang-Il Kim, Hyun-Jung Yoo, Si-Young Park, Yeon-Hwan Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(3): 414. CrossRef - Influencing Factors of the Incidence of Delirium in Elderly Patients with Arthroplasty
Young-Whee Lee, Hye-Bin Im, Eun-Jeong Jeong, Hee-Sun Ma
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(4): 348. CrossRef - Delirium After Spinal Surgery in Korean Population
Jin Kyu Lee, Ye-Soo Park
Spine.2010; 35(18): 1729. CrossRef - The Incidence and Related Factors of Delirium in Elderly Patients with Hip Fracture after Surgery
Bo-Kyung Sohn, Yerl-Bo Sung, Eun-Jin Park, Dong-Woo Lee
Journal of the Korean Geriatrics Society.2010; 14(3): 162. CrossRef
Risk Factors of Postoperative Delirium in Elderly Patients with Hip Fractures
Risk Factors of Postoperative Delirium in Elderly Patients with Hip Fractures
Classification of walk ability
Comparision of various factors between the post-operative delirium and the control group
Comparision of post-operative laboratory data between the post-operative delirium and the control group
Table 1
Classification of walk ability
Table 2
Comparision of various factors between the post-operative delirium and the control group
Table 3
Comparision of post-operative laboratory data between the post-operative delirium and the control group

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 Cite
Cite

