Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Correlation of bone mineral density with ankle fractures in older adults in Korea: a retrospective cohort study
- Seung Hyun Lee, Chae Hun Lee, Seo Jin Park, Jun Young Lee
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):186-192. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00150
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
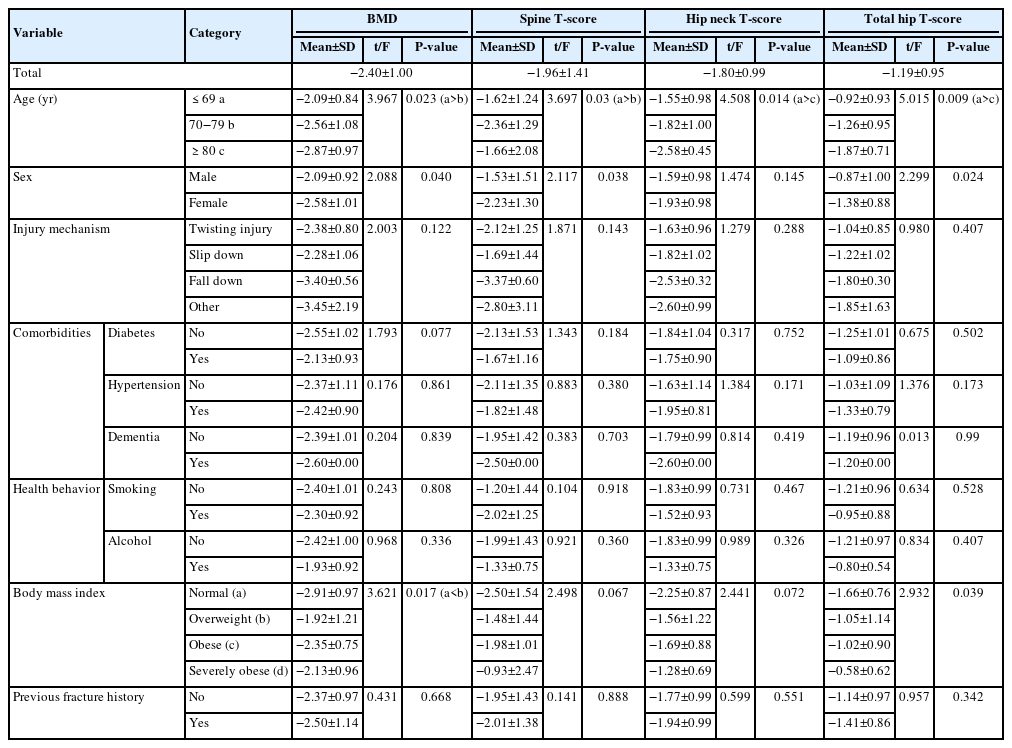
Bone mineral density (BMD) is well-documented in relation to fractures of the spine, hip, distal radius, and proximal humerus; however, its correlations with other fracture types are less established. This study aimed to analyze BMD and associated risk factors in older adults (≥65 years of age) with osteoporotic ankle fractures. These fractures involve low-energy trauma, resulting from falls from a standing height or lower, and occur from impacts which typically do not cause fractures in individuals with normal bone.
Methods
This retrospective study analyzed data from 1,411 patients diagnosed with ankle fractures admitted to Chosun University Hospital between February 2012 and April 2023. After applying inclusion criteria (age ≥65 years; low energy ankle fracture) and exclusion criteria (high energy trauma, open/multiple fractures, missing dual X-ray absorptiometry [DXA]), 73 of 1,411 patients were analyzed. Lumbar spine, femoral neck, and total hip T scores were obtained with a Horizon Wi DXA scanner, and associations with age, sex, mechanism of injury, comorbidities, smoking status, alcohol consumption, body mass index (BMI), and history of fractures were tested by ANOVA with Scheffe post hoc and Fisher exact tests.
Results
Lower BMD correlated significantly with older age, female sex, and lower BMI (P<0.05) in older adults with ankle fractures. No significant associations were observed for comorbidities (diabetes, hypertension, dementia), smoking, alcohol consumption, injury mechanism, or prior fractures.
Conclusion
These results indicate that older age, female, and lower BMI are linked to reduced BMD in ankle fracture patients over 65 years of age. Focused osteoporosis screening and management may therefore be most beneficial for older, low BMI women presenting with ankle fractures. Level of evidence: IV.
- 873 View
- 2,147,483,670 Download

- Analysis of Missed Fractures by Bone Scan in Elderly Hip Fracture Patients with Osteoporosis
- Tae Hun Lee, Yeong Hyun Lee, Seo Won Kang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(3):144-149. Published online July 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.3.144
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The incidence of hip fractures is increasing due to an increase in elderly populations because elderly patients often have accompanying diseases, such as cognitive impairment or dementia, which may lead to missed fractures. Therefore, this study assessed the utility of bone scans in detecting missed fractures in elderly patients.
Materials and Methods
This study analyzed the data from 178 patients treated from January 2014 to March 2023. The inclusion criteria were patients who had hip fractures with osteoporosis over 70 years old. Bone scans were performed on average 10 days after injury. The rate and trend of missed fractures not detected in the initial diagnosis were determined based on sex, age, dementia status, and the presence of osteoporosis.
Results
Among the 178 hip fracture patients over 70 years old, 37 patients had a history of being diagnosed with dementia, and 141 patients had never been diagnosed. Missed fractures were confirmed in 49 cases (42 patients) (23.6%). The dementia group had 13 missed fractures, and the non-dementia group had 36 missed fractures, but there was no significant difference. Rib fractures were most common, followed by vertebral fractures.
Conclusion
Missed diagnoses of fractures were common among elderly hip fracture patients. A whole body bone scan appeared to be effective in detecting missed fractures. Therefore, identifying accompanying fractures through bone scans and delivering appropriate treatment can play an important role in postoperative rehabilitation.
- 661 View
- 9 Download

Review Article
- Avulsion Fractures in the Ankle and Foot
- Gyeong Hoon Lim, Jae Won Kim, Sung Hyun Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(2):102-116. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.2.102
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - An avulsion fracture occurs when a muscle-tendon unit attached to a bone produces sufficient force to tear a fragment of the bone. If not treated properly, this injury can lead to deformity, nonunion, malunion, pain, and disability. Although avulsion fractures around the foot and ankle can occur anywhere there are tendon and ligament attachments, they are common in the anterior talofibular ligament, anterior-inferior tibiotalar ligament, calcaneal tuberosity, the base of the fifth metatarsal, and navicular bone. The optimal treatment for each fracture depends on the location and severity of the fracture. Conservative treatment involves limiting weight bearing for a period, splint immobilization, and using various orthoses. Surgical treatment is usually reserved for cases of severe displacement or when nonsurgical treatment has failed. The goals of surgery include reduction of the fracture fragment, prevention of nonunion or malunion and soft tissue injury, and early return to function. The decision for each treatment modality may depend on the patient demographics or preferences and the surgeon experience. This review summarizes previous and current views on the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of common avulsion fractures to guide the treatment and diagnosis.
- 2,028 View
- 47 Download

Original Articles
- Comparison of Surgical Outcomes for Lisfranc Joint Injuries: Dorsal Bridge Plating versus Transarticular Screw versus Combination
- Ba Rom Kim, Jun Young Lee, Sung Hun Yang, Seung Hyun Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(1):17-24. Published online January 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.1.17
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
In Lisfranc joint injury, the traditional treatment has been open reduction and internal fixation with a transarticular screw. Despite this, additional complications, such as damage to the articular surface and breakage of the screw, have been reported. Therefore, this study compared the clinical and radiological outcomes of dorsal bridge plating with those of transarticular screws and combination treatment in Lisfranc joint injury.
Materials and Methods
Among the 43 patients who underwent surgical treatment due to Lisfranc joint injury from June 2015 to March 2021, 40 cases followed for more than six months after surgery were analyzed, excluding three patients: one lost to follow-up, one had to amputate, and one expired. The radiological parameters were measured using the Wilppula classification in the last follow-up. The clinical outcomes were evaluated using the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) midfoot score.
Results
The AOFAS midfoot score, according to the surgical method, was significantly higher in the dorsal bridge plating (p=0.003). The radiological outcomes showed significantly better anatomical reduction when dorsal bridge plating was used (p=0.040). According to the Wilppula classification, the AOFAS midfoot score improved as the quality of anatomical reduction improved (p=0.018). Finally, the AOFAS midfoot score decreased as the number of column fixations increased (p=0.002). There were two complications: screw breakage in dorsal bridge plating and superficial skin necrosis in the combination treatment. Skin defects caused by necrosis improved after negative pressure wound therapy and split-thickness skin graft.
Conclusion
In treating Lisfranc joint injuries, open reduction and internal fixation by dorsal bridge plating can be an appropriate treatment option. Nevertheless, studies, such as long-term follow-up research, on complications, such as osteoarthritis, will be needed.
- 749 View
- 8 Download

- Analysis of Clinical and Functional Outcomes according to the Blood Sugar Control Status at the Time of Ankle Fractures Resulting from Rotational Injuries
- Jun Young Lee, Dong Seop Lim, Seung Hyun Lee, Seo Jin Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(4):135-141. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.4.135
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Patients with diabetes are known to have poor clinical outcomes due to the high incidence of complications after ankle joint fracture surgery. This study reports the clinical and functional outcomes based on glycemic control status among patients with ankle joint fractures who underwent surgical treatment.
Materials and Methods
Among patients who underwent surgical treatment due to ankle joint fractures from January 2015 to October 2019, 253 patients with a minimum follow-up of 12 months were identified. We divided them into 3 groups: 195 patients with no diabetes (Group A), 26 patients with well-controlled diabetes (Group B), and 32 patients with uncontrolled diabetes (Group C). In addition, patients with lateral, medial malleolar, bimalleolar, and trimalleolar fractures were identified using radi-ography. The functional outcome measures used for evaluation were the Revised Foot Function Index (FFI), Short Musculoskeletal Function Assessment (SMFA), and the Foot and Ankle Outcome Score (FAOS).
Results
Bone union at 3 months after surgery was high in Group A, showing significant differences compared to the other groups. There was a significant difference between the groups in the incidence of arthropathy and one or more complications. However, the FFI, SMFA, and FAOS did not show significant differences between the groups.
Conclusion
The incidence of complications was high in patients with uncontrolled diabetes compared to the patients with well-controlled diabetes and those with no diabetes. However, functional outcomes showed no significant difference.
- 659 View
- 6 Download

Review Article
- Current Treatment of Calcaneal Fractures and Dislocation
- Dae Jin Nam, Sung Hyun Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(2):74-82. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.2.74
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Calcaneal fractures are the most common fractures occurring in the tarsal bone. In the past, surgical treatments were not preferred because they were accompanied by severe comminution and soft tissue complications. In recent years, there have been great advancements in the treatment of calcaneal fractures owing to the development of new surgical techniques and instruments. However, a standard treatment method has not yet been established. In this review article, we summarize the latest information on the indications and treatment methods of calcaneal fractures.
- 523 View
- 15 Download

Case Report
- Major Limb Replantation of Lower Leg Amputation with Ipsilateral Distal Femoral Comminuted Fracture in Old Age: A Case Report
- Tae Young Ahn, Seung Joon Rhee, Sang Ho Kwak, Hyo Seok Jang, Sang Hyun Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(4):227-231. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.4.227
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The development of microsurgical techniques has also increased the success rate of replantation surgery. This paper reports the results of limb replantation performed on a lower extremity amputation that was associated with crush amputation and an ipsilateral comminuted fracture in and elderly patient. A 68-year-old female presented with a right distal tibia amputation due to a traffic accident. At that time, with a comminuted fracture in the distal femoral condyle, simple wound repair was recommended, but the caregivers strongly wanted replantation. Three years after surgery, normal walking was possible without a cane and the patient was satisfied with the function and aesthetics. What used to be contraindicated in limb replantation in the past are now indications due to the development of microsurgical techniques, surgical experience, and postoperative rehabilitation treatment. If the patient is willing to be treated, good results in contraindications can be obtained.
- 698 View
- 4 Download

Review Article
- Bone Substitutes and the Advancement for Enhancing Bone Healing
- Dong Hyun Lee, Ji Wan Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(2):102-109. Published online April 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.2.102
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - With an aging population and the development of surgical techniques, there is a growing demand for bone reconstruction in areas of trauma, arthroplasty, and spinal fusion Although autogenous bone grafting may be the best method for stimulating bone repair and regeneration, there are still problems and complications, including morbidity related to bone harvesting and limitation of harvest amount. Allogeneic bone grafts have a limited supply and risk of transmission of infectious diseases. Over the past several decades, the use of bone substitutes, such as calcium phosphate, has increased; however, they have limited indications. Biomedical research has suggested a possibility of stimulating the self-healing mechanism by locally transmitting the external growth factors or stimulating local production through a gene transfer. In this review, we evaluate recent advances, including bone graft, bone substitutes, and tissue engineering.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Calcium phosphate injection technique for treatment of distal radius fracture
Dae-Geun Kim, Byung Hoon Kwack
Medicine: Case Reports and Study Protocols.2021; 2(9): e0117. CrossRef - Experimental Study ofDohongsamul-tang(Taohongsiwu-tang) on Fracture Healing
Hyun Ju Ha, Min-Seok Oh
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2020; 30(2): 47. CrossRef
- Calcium phosphate injection technique for treatment of distal radius fracture
- 641 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

Case Report
- Iatrogenic Humeral Fracture during Reduction of Shoulder Dislocation: Two Cases Report
- Hyung Lae Cho, Hyoung Min Kim, Ki Bong Park, Tae Hyun Wang, Dong Hyun Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(1):50-54. Published online January 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.1.50
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Shoulder dislocation is the most common dislocation presenting to the emergency department. In old age, the attempt of closed reduction is made with caution in order to prevent iatrogenic fracture around the shoulder. We report two cases of iatrogenic fractures of humeral shaft and anatomical neck in female patients older than 70 years old, which occurred during the manual closed reduction. One patient was proved as first-time and the other was recurrent. In addition, the second case had a massive irreparable rotator cuff tear. Those patients were treated successfully with humeral nailing and reverse total shoulder arthroplasty, respectively.
- 403 View
- 4 Download

Original Article
- Ankle Fracture Associated with Tibia Shaft Fractures
- Ji Wan Kim, Hong Joon Choi, Dong Hyun Lee, Young Chang Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(2):136-143. Published online April 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.2.136
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the incidence of ankle injury in ipsilateral tibial shaft fractures and to assess the risk factors for ankle injury associated with tibial shaft fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sixty patients with tibial shaft fractures were enrolled in this retrospective study. The incidence and characteristics of ankle injury were evaluated, and fracture classification, fracture site, and fracture pattern of the tibial shaft fractures were analyzed for assessment of the risk factors for ankle injury combined with tibial shaft fractures.
RESULTS
Ankle injury occurred in 20 cases (33%). There were four cases of lateral malleolar fracture, four cases of posterior malleolar fracture, two cases of distal tibiofibular ligament avulsion fracture, and 10 cases of complex injury. Fourteen cases (70%) of 20 cases of ankle injury were diagnosed from x-ray films, and the other six cases were recognized in ankle computed tomography (CT). Ankle injury occurred in 45.1% of distal tibial shaft fractures and found in 41.4% of A type, but there was no statistical significance. Ankle injury was observed in 54% of cases of spiral pattern of tibial shaft fracture and the incidence was statistically higher than 19% of cases of non-spiral pattern tibial shaft fracture.
CONCLUSION
Ankle injury was observed in 33% of tibial shaft fractures; however, only 70% could be diagnosed by x-ray. Ankle injury occurred frequently in cases of spiral pattern of tibial shaft fracture, and evaluation of ankle injury with CT is recommended in these cases. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Usefulness of Computed Tomography on Distal Tibia Intra-Articular Fracture Associated with Spiral Tibia Shaft Fracture
Seong-Eun Byun, Sang-June Lee, Uk Kim, Young Rak Choi, Soo-Hong Han, Byong-Guk Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2016; 29(2): 114. CrossRef
- Usefulness of Computed Tomography on Distal Tibia Intra-Articular Fracture Associated with Spiral Tibia Shaft Fracture
- 790 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Report
- Heterotopic Ossification around Patellar Tendon Following Treatment of Patellar Fracture: A Case Report
- Sang Jin Lee, Ji Wan Kim, Dong Hyun Lee, Jae Young Lim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(1):73-76. Published online January 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.1.73
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Heterotopic ossification around the patellar tendon is known to be extremely rare. A 42-year-old man had a transverse fracture of the left patella. Open reduction and tension band wiring were performed. At four weeks, plain radiographs showed an extensive ossification around the patellar tendon and the patient presented limitation of flexion and pain in kneeling position. We just encouraged active and passive ranges of motion exercises and performed one manipulation under anesthesia. At the final follow-up (10 months post-operatively), he was able to flex his knee by 140 degrees. We present a case of heterotopic ossification around the patellar tendon with limitation of knee flexion that was successfully treated with nonoperative treatment.
- 625 View
- 1 Download

Original Articles
- Surgical Treatment of AO Type C Distal Femoral Fractures Using Locking Compression Plate (LCP-DF, Synthes(R))
- Kap Jung Kim, Sang Ki Lee, Won Sik Choy, Won Cho Kwon, Do Hyun Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2010;23(1):20-25. Published online January 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.1.20
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analyze the surgical results of AO type C distal femoral fractures using locking compression plate.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From February 2006 to June 2008, 14 patients 15 cases were included. Injury mechanisms, combined injuries, radiologic and clinical results and postoperative complications were analyzed.
RESULTS
The mean age was 59.6 (30~77) years. The mean follow up period was 25 (12~40) months. AO types were 3 of C1, 5 of C2 and 7 of C3. Injury mechanisms were 9 of traffic accident, 5 of slip down and 1 of fall from a height. Four cases were combined with other extremity injuries or fractures. The mean radiologic union was obtained at postoperative 15 (13~20) weeks. The mean Neer's functional score was 74.2 (58~97); 3 of excellent, 5 of satisfactory and 7 of unsatisfactory. Postoperative complications were 2 of infection and 1 of nonunion. There were no mechanical failures or fixation loss with locking compression plate at the final follow up.
CONCLUSION
Internal fixation using locking compression plate for AO type C distal femoral fractures provided excellent fixations. At the final follow up, the clinical results were variable. The affecting factors on the final results seemed to be joint congruencies after anatomical reduction and active rehabilitation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Functional outcome of distal femoral fractures treated with distal femoral locking compression plate: a cross-sectional study
Sandeep Kumar Kumar Deep, Varun Phogat, Sankar Debroy
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics.2025; 11(5): 1089. CrossRef - A STUDY OF SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF DISTAL FEMORAL FRACTURES BY DISTAL FEMORAL LOCKING COMPRESSION PLATE OSTEOSYNTHESIS
Dema Rajaiah, Yerukala Ramana, Kuppa Srinivas, Venkateswar Reddy S
Journal of Evidence Based Medicine and Healthcare.2016; 3(66): 3584. CrossRef
- Functional outcome of distal femoral fractures treated with distal femoral locking compression plate: a cross-sectional study
- 810 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Retrograde Intramedullary Nailing or the Treatment of Segmental Femoral Shaft Fracture Including Distal Part
- Jong Ho Yoon, Byung Woo Ahn, Chong Kwan Kim, Jin Woo Jin, Ji Hoon Lee, Hyun Ku Cho, Joo Hyun Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(3):145-151. Published online July 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.3.145
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the usefulness of the retrograde intramedullary nailing for the treatment of segmental femoral shaft fracture including distal part.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed 15 patients of segmental femoral fracture, who had treated with retrograde intramedullary nailing and followed-up more than 1 year from January 2003 to October 2007. There were 10 men, 5 women, and the mean age was 45 years old. There were associated fracture in 10 cases. We evaluate the time for union, non-union and malunion by radiologic finding and functional assessment by Sanders' criteria.
RESULTS
The mean time of union was 21 weeks. There was one delayed union in proximal fracture site. There was no shortening more than 1.5 cm, no angular deformity more than 10 degrees, no postoperative infection or instability. According to Sanders' criteria, there were excellent clinical results in 9 cases, good results in 5 cases and fair result in 1 case.
CONCLUSION
The retrograde intramedullary nailing can be a useful method for treatment of segmental femoral shaft fracture including distal part. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Risk Factors for Nonunion after Intramedullary Nailing of Femoral Shaft Fracture in Adult
Yong-Woon Shin, Yerl-Bo Sung, Jeong Yoon Choi, Minkyu Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(4): 313. CrossRef
- Analysis of Risk Factors for Nonunion after Intramedullary Nailing of Femoral Shaft Fracture in Adult
- 623 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review Article
- Volar Plating of Distal Radius Fractures
- Kwang Hyun Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2008;21(4):325-333. Published online October 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.4.325
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Volar plating seems to indicate that many surgeons believe it leads to superior results, and is attractive because of the ease of the operative approach and the soft tissue sleeve to protect digital and wrist tendons. And also it have a locking mechanism to produce the fixed angle device with a low profile and may be thought to be a new era in the surgical treatment of dorsally displaced distal radius fractures even in the face of comminuted or osteoporotic bone. Locked volar plating allows direct fracture reduction, stable fixation and provides stability enough to allow early mobilization and function. The results with volar locking or fixed angle fixation for the general treatment of unstable distal radius fractures in elderly patients has been favorable. Volar plating has fewer complications than external fixation and dorsal plating and allow for earlier return to function. The current indications, technical aspects, clinical results, and complications of the volar plating are being reviewed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ultrasonographic Assessment of the Pronator Quadratus Muscle after Surgical Treatment for Distal Radius Fractures
Dong Hyuk Choi, Hyun Kyun Chung, Ji Won Lee, Cheol Hwan Kim, Yong Soo Choi
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2017; 30(2): 69. CrossRef - The Fate of Pronator Quadratus Muscle after Volar Locking Plating of Unstable Distal Radius Fractures
Chae-Hyun Lim, Heun-Guyn Jung, Ju-Yeong Heo, Young-Jae Jang, Yong-Soo Choi
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2014; 27(3): 191. CrossRef - Comparison of Operative Management in Distal Radius Fractures Using 3.5 mm Versus 2.4 mm Volar Locking Compression Plates
Sung-Sik Ha, Tae-Ho Kim, Ki-Do Hong, Jae-Chun Sim, Jong Hyun Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(2): 156. CrossRef - Treatment for Unstable Distal Radius Fracture with Osteoporosis -Internal Fixation versus External Fixation-
Jin Rok Oh, Tae Yean Cho, Sung Min Kwan
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(1): 76. CrossRef - Short Term Results of Operative Management with 2.4 mm Volar Locking Compression Plates in Distal Radius Fractures
Ki-Chul Park, Chang-Hun Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(4): 264. CrossRef
- Ultrasonographic Assessment of the Pronator Quadratus Muscle after Surgical Treatment for Distal Radius Fractures
- 654 View
- 1 Download
- 5 Crossref

Original Article
- Contributing Factors of Radial Nerve Palsy Associated with Humeral Shaft Fracture
- Tae Soo Park, Joon Hwan Lee, Tai Seung Kim, Kwang Hyun Lee, Ki Chul Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2008;21(4):292-296. Published online October 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.4.292
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analyze related factors of radial nerve palsy in patients with humeral shaft fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed 107 paients with humeral shaft fracture between January 2000 and June 2007. Thirteen patients had radial nerve palsy after trauma and 9 patients after the operation. We analyzed contributing factors of radial nerve palsy associated with humeral shaft fracture including the cause of trauma, location and pattern of fracture, surgical approach and tourniquet application in cases of plate fixation, the exploration for the nerve and the time for operation.
RESULTS
The difference in the incidences of radial nerve palsy after trauma and operation was not significant according to the location and pattern of fracture. The tendency of higher rate of radial nerve palsy after trauma in oblique or comminuted fractures, and after operation in spiral fractures was observed. The operation using intramedullary nailing and radial nerve exploration significantly reduced the incidence of radial nerve palsy after operation (p=0.01 and p=0.02). Posterior approach in open reduction and plate fixation showed a tendency of lower incidence of radial nerve palsy after operation (p=0.78). In logistic regression analysis, radial nerve exploration was the only significant factor that reduced the possibility of radial nerve palsy after operation (17.27: odds ratio, p=0.02).
CONCLUSION
In humeral shaft fractures, we should take into consideration whether intramedullary nailing is possible or not. In cases of anterior or anterolateral approach of open reduction and plate fixation, radial nerve should be carefully inspected. In most cases, we recommend radial nerve exploration in order to minimize the possibility of radial nerve palsy after operation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Treatment of Radial Nerve Palsy Associated with Humeral Shaft Fracture
Soo-Hong Han, Jin-Woo Cho, Han-Seung Ryu
Archives of Hand and Microsurgery.2020; 25(1): 60. CrossRef - Associated Factors of Radial Nerve Palsy Combined with Humerus Shaft Fracture
Si-Wuk Lee, Chul-Hyun Cho, Ki-Choer Bae
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2014; 27(3): 185. CrossRef - Polarus Intramedullary Nail for Proximal Humeral and Humeral Shaft Fractures in Elderly Patients with Osteoporosis
Youn-Soo Hwang, Kwang-Yeol Kim, Hyung-Chun Kim, Su-Han Ahn, Dong-Eun Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2013; 26(1): 14. CrossRef
- Treatment of Radial Nerve Palsy Associated with Humeral Shaft Fracture
- 684 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref

Review Article
- Factors and Surgical Pitfalls Causing Nonunion
- Kwang Hyun Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2008;21(2):186-188. Published online April 30, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.2.186
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - No abstract available.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Short Term Results of Operative Management with 2.4 mm Volar Locking Compression Plates in Distal Radius Fractures
Ki-Chul Park, Chang-Hun Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(4): 264. CrossRef - Plate Fixation of AO Type C3 Fractures of the Distal Radius
Eun-Sun Moon, Myung-Sun Kim, Hyeong-Won Park, Min-Sun Choi
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(3): 172. CrossRef - Volar Plating of Distal Radius Fractures
Kwang-Hyun Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2008; 21(4): 325. CrossRef
- Short Term Results of Operative Management with 2.4 mm Volar Locking Compression Plates in Distal Radius Fractures
- 451 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref

Original Articles
- A Skeletal Traction on the Radiolucent Table in Closed Intramedullary nailing of Femoral Fracture
- Eun Woo Lee, Han Jun Lee, Kee Hyun Lee, Ho Sun Jin
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(3):244-249. Published online July 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.3.244
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the clinical results of femoral shaft fracture treated by Intramedullary (IM) nailing through skeletal traction compared with manual traction on a radiolucent table.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty cases with femoral shaft fracture treated with closed IM nailing from January 2000 to June 2002 were divided into two groups; fifteen fractures reduced by manual traction (Group A) and fifteen fractures reduced by skeletal traction (Group B) on a radiolucent table. The number of people participated in the operations, operation and radiation exposure time, and post-operative complications were evaluated.
RESULTS
The number of people participated in the operations was five in Group A and four in Group B. The average operation time was 116 minutes and 82 minutes (p<0.001). The radiation exposure time was 2.8 minutes and 1.2 minutes (p<0.001). However, there was no significant difference in the post-operative complications such as shortening or lengthening of bone between two groups.
CONCLUSION
There was no significant difference in the operative outcome between two groups. However, skeletal traction has positive effects of reducing the operation time, radiation exposure time, and number of people participating in the operations. Also, regarding the consistent traction power, skeletal traction is the better treatment modality in maintaining the alignment and length of femoral bone than manual traction.
- 428 View
- 2 Download

- The Clinical Results in Compression Plate Fixation with Autogenous Cancellous Bone Graft for Humerus Diaphyseal Nonunion
- Kwang Hyun Lee, Seong pil Lee, Hyung Jong Kim, Bong Geun Lee, Joo Hak Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(2):90-94. Published online April 30, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.2.90
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
A The purpose of this retrospective study was to evaluate the results of compression plating and autogenous iliac bone graft in the management of humeral diaphyseal nonunion.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty patients who underwent the surgical treatments between May. 1998 and May. 2002 were included in this study. Nine of them are males and the others are females. The average age of them, when they was on operation, was 45 years. The symptoms lasted 23 months on average. They have been followed up for 33 months at an average. Treatment of nonunion consisted of resecting the atrophic nonunion, shortening the bone, apposing bleeding diaphyseal surface. Rigid fixation was then achieved using a compression plate and autogenous bone graft.
RESULTS
Solid bony union was achieved in all patients. In one patient, the bone was not healed at the first operation of plating and autogenous bone graft, but achieved union after the use of intramedullary nailing. In another patient, because of infected nonunion, we achieved union after several surgical debridement and stabilization by internal fixation.
CONCLUSION
This study documents that compression plate fixation with autogenous cancellous bone graft is a viable option with predictable and satisfactory results for humerus diaphyseal nonunion.
- 420 View
- 0 Download

- Clinical Outcome of Surgical Treatment of Distal Humerus Intercondylar Fractures Through the Transolecranon Approach Combined with Anterior Transposition of the Ulnar Nerve
- Kwang Hyun Lee, Seong Pil Lee, Kyu Tae Hwang, Joo Hak Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(2):70-75. Published online April 30, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.2.70
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analyze the clinical outcomes of surgical treatment of distal humerus intercondylar fractures through the transolecranon approach combined with anterior transposition of the ulnar nerve.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Eight patients who had distal humerus intercondylar fractures were included in this study and underwent operative treatment through the transolecranon approach for sufficient operative field with anterior transposition of the ulnar nerve and fixed with reconstruction plate.
RESULTS
The results were evaluated using Riseborough and Radin rating criteria. Seven cases of eight cases were achieved good results with flexion contracture less than 30 degrees and forward flexion more than 115 degrees. However, one case was acheived poor result with 40 degrees of flexion contractue and 70 degrees of forward flexion. There were no the compressive ulnar neuropathy.
CONCLUSION
We found the transolecranon approach and anterior transposition of the ulnar nerve a viable option for surgical treatment of the distal humerus intercondylar fractures
- 402 View
- 0 Download

- A Clinical Study about Postoperative Wound Complications In Liver Cirrhotic Patients
- Seung Woo Suh, Seok Hyun Lee, Jun Kyu Moon, Young Jin Roh, Chang Woo Seok
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(4):577-584. Published online October 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.4.577
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study undertaken to evaluate the postoperative wound complications between Child class A liver cirrosis patients and Child class B liver cirrhosis patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In a retrospective study from 1998 to 2003, fifteen patients who underwent surgical intervention for fractures were evaluated the period of wound healing, hopital day, infection, wound complications (swelling, hematoma formation, wound discharge).
RESULTS
The cases of wound complication are 6/15 (40%), in which Child class A LC patients are two (14%), and Child class B LC patients are four (50%). The cases of wound Infection are 2/15 (13%), in which Child class A LC patient is one (14%), and Child class B LC patient is one (12.5%). The average of hospital day is 28 days.
CONCLUSION
The clinical results of postoperative complications is associated with Child classification, but the ralationship between postoperative wound infection and Child classification is not observed. We thought that careful wound management needs in liver cirrhosis patients.
- 346 View
- 0 Download

- Treatment of the Femoral Shaft FracturesUsing Unreamed Interlocking Intramedullary Nail
- Chang Wook Oh, Joo Chul Ihn, Poong Taek Kim, Shin Yoon Kim, Hee Soo Kyung, Chung Hyun Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(4):832-836. Published online October 31, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.4.832
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the usefulness of unreamed nailing inthe treatment of femoral shaft fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between March 1996 and June 1998, unreamed nailing with closed method was done for 74 patients with 82 femoral shaft fractures. The main indications for this treatment were multiple injury or isolated femoral fracture above Winquist type II. The influence of Winquist- Hansen classification, anatomical location, and open injury over bone union and the influence of injury severity score over general complication including fat embolism were investigated.
RESULTS
Primary union occurred in 76 cases(93%) with 6 cases of nonunion and 10(12%) of delayed union, and mean time to union was 27 weeks. In open fractures, the union time was delayed(32 weeks) rather than closed fracture. In Winquist classification, there was no stastical importance on time to union, but nonunion was most common in Winquist type IV. Anatomical location has no influence on time to union. In the view point of multiple injury, the group above 18 points(31 patients) in injury severity score had none of fat embolism, but the group below 18 points(43 patients) had 2 patients.
CONCLUSION
The treatment of femoral shaft fractures by unreamed nailing had longer time to union with higher rate of delayed union, and we think that the theoretical advantage of decreasing pulmonary complications is controversial.
- 326 View
- 0 Download

- Intramedullary pressure changes in reamed and unreamed nailing systems: an experimental study in cadaveric femoral bones
- Chang Wug Oh, Joo Chul Ihn, Poong Taek Kim, Il Hyung Park, Sung Jung Kim, Chung Hyun Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(3):631-637. Published online July 31, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.3.631
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study was designed to investigate whether intramedullary pressure is different in reamed compared with unreamed femoral nailing in cadeveric femoral bones. MATERIALS & METHODS: Eight pairs of fresh-frozen cadaveric femoral bones were studied. The diameter of isthmus was checked from 10mm to 14mm and the length of femur was checked from 35cm to 44cm. Intramedullary pressure was measured in the distal femoral shaft at the supracondylar region. Data were monitored in femoral nailing procedures. We utilized the AO universal nail(reamed) and AO unreamed femoral nail.
RESULTS
Intramedullary pressure increased in the reamed group to 423.8 mmHg(mean pressure) during reaming by starting reamer(9 mm) and in the unreamed group to 290 mmHg(mean pressure) during insertion of nails(p=0.001). In the unreamed groups, the next high intramedullary pressure is 136.6 mmHg during proximal reaming. A statistiscally significant difference in intramedullary pressure was found during the first reaming process in the reamed group compared with the proximal reaming process in the unreamed group(p=0.005).
CONCLUSION
The data indicate that the intramedullary pressure during unreamed nailing process is lower than reamed nailing process. So we can consider that the unreamed nailing in multiple fracture or pulmonary injured patients is a good modalities.
- 434 View
- 5 Download

- Treatment of comminuted distal humeral intercondylar fracture using transolecranon approach
- Kwang Hyun Lee, Myung Ryul Park, Jae Min Lee, Tae Hyoung Kweon
- J Korean Soc Fract 1999;12(4):981-987. Published online October 31, 1999
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1999.12.4.981
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fracture of the distal humerus is rare, so the surgeons experience is limited. This injuries represent a constellation of complex articular fractures and anatomic complexity of distal humerus makes surgical treatment, open reduction and internal fixation is difficult. We analyze the clinical result of immediate open reduction, rigid internal fixation, and early postoperative motion. From Nov. 1990 to Sep. 1997, the authors analyzed the clinical results of 5 cases those who underwent operative treatment using transolecranon approach, internal fixation with Y plate and early motion for comminuted distal humeral intercondylar fracture. ROM exercise was started at average 2.2 weeks postoperatively. 4 of 5 patients obtained satisfactory results by Riseborough and Radin rating criteria. One patient obtained poor result of 40 degree flexion contracture and 90 degree further flexion of elbow. Transolecranon approach makes the complete anatomic reduction of articular surface possible and the satisfactory results is associated with immediate, complete anatomic reduction and rigid fixation in conjuction with early postoperative motion.
- 306 View
- 0 Download

- Causative Factor for Cubitus Varus Deformity in Severely Displaced Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children : s Rotational Deformity of Distal Fragment Needed to be Acurately Reduced?
- Seung Woo Suh, Jeong Ho Park, Jong Gun Oh, Seung Ju Chun, Jeong Ro Yoon, Seok Hyun Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 1997;10(3):712-717. Published online July 31, 1997
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1997.10.3.712
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We reviewed retrospectively 53 cases of supracondylar fracture of humerus in children which were severely displaced(Gartland type III). All patients were treated with closed reduction and percutaneous pinning. Purpose of this study is to evaluate the residual effect of incompletely reduced fragment, especially of rotation of distal fragment(represented by fish-tail sign) on clinical relults. The quality of reduction was determined by carrying angle, varus tilting, existence of fish-tail sign and medial displacement. Of the 53 elbows, fish tail signs only presented in twelve cases(50.0%), medial tilting combined with fish tail in five(20.8%) and medial displacements in seven cases(29.2%). Final results by Flynn et al. were as follows; Excellent was in 40 cases(15.9%), Good in 6(11.3%), Fair in 1(1.8%), poor in 6(11.3%). Six cases of poor outcomes resulted from cubitus varus deformed elbow, of which cubitus varus deformity developed in 5 cases of medial tilted distal fragment, one developed in medially displaced fragment, and cases presented with fish tail sign(rotation of distal fragment) had no contribution to cubitus varus deformity yielding acceptable clinical results. In conclusion, even though the quantification of fish tail sign is needed, fish tail sign only presenting on fluorscopy might be acceptable in operative room.
- 356 View
- 0 Download

- Clinical Application of Gamma Nail
- Il Yong Choi, Kwang Hyun Lee, Chung Kyu Choi
- J Korean Soc Fract 1996;9(2):489-495. Published online April 30, 1996
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1996.9.2.489
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The Gamma nail combining the advantages of a sliding lag screw and the intramedullary femoral fixation is a advance in the treatment of trochanteric fractures. The Gamma nail is a new intramedullary device which has been applied in treatment of the trochanteric fractures with the benefits of closed technique such as low blood loss, low risk of infection, short operative time, short bone union period and early weight bearing and with the biomechanical advantages such as short lever arm and decreased bending moment. The implant can be used by the method of static or dynamic. Intraoperative compression of the fracture segments can be achieved by acting on the sliding lag screw and further compression is given by weight bearing. We studied 31 cases of patients who had the trochanteric fractures and treated opratively with Camma nail. The intertrochanteric fracture was 25 cases and subtrochanteric fracture was 6 cases. Intraoperative complication was encountered failure of distal locking in 1 case. Postoperative complications were encounted superior cutting-out in 3 cases. As results of postoperative ambulation, 4 cases were death, 4 cases were bedridden state, 4 cases were ambulation state within house, 19 cases were social activity respectively.
- 500 View
- 1 Download

Case Report
- Fracture of the Capitate with Velar Perilunate Dislocation: One case report
- Kwang Hyun Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 1995;8(4):908-913. Published online October 31, 1995
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1995.8.4.908
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fracture of the capitate is a rare form of carpal injuries. It can occur with perilunate dislocation. In that case, capitate fracture associated with scaphoid fracture is common enough that it has been called the scaphocapitate fracture(or syndrome). A rare case of a displaced fracture of the capitate and unusual locked volar perilunate dislocation without scaphoid fracture is described. This carpal injury was treated by closed reduction and percutaneous pinning with one K-wire and the result is now excellent. A possible explantation of the mechanism underlying this conditian is offered and the literature is reviewed.
- 969 View
- 2 Download

Original Articles
- Treatment by modified huntington fibula transference operation in fracture and non union of tibia diaphysis with extensive bone defect
- Chan Soo Park, Kang Hyun Lee, Myung Ku Kim, Geon Woo Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 1993;6(1):128-134. Published online May 31, 1993
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1993.6.1.128
- 493 View
- 0 Download

- A Clinical Study on Open Fracture of the Shaft of the Ulna and Radius in Adults
- Sung Joon Kim, Il Yong Choi, Kwang Hyun Lee, Do Gyoung Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 1992;5(2):309-318. Published online November 30, 1992
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1992.5.2.309
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We reviewed 55 cases of open fracture of the forearm bones had been treated by conservative treatment or open reduction and intramedullary nailing or internal fixation with dynamic compression plate and analyzed the results by wound management and methods of treatment.The results were obtained as follows ;1. In the type I,II and type III-A open fractures, primary closure of the wound was reliable method of treatment. 2. The non-union rate was 44% in the positive culture test and 14.8% in the negative culture test. 3. Immediate internal fixation with dynamic compression plate was reliable method in the treatment of the type I, II open fractures.
- 360 View
- 1 Download

- Report of four cases of fracture and dislocation of the hip with ipsilateral fracture of the femoral shaft
- Myung Ku Kim, Kang Hyun Lee, Chan Soo Park, Kyu Ho Sin, Ju Hyoung Kwon
- J Korean Soc Fract 1991;4(2):267-274. Published online November 30, 1991
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1991.4.2.267
- 419 View
- 0 Download

- Idiopathic Fever following Childrens femur Fractures
- Hong Jun Han, Hyun Lee, Sang Soo Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1990;3(2):280-283. Published online November 30, 1990
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1990.3.2.280
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Not infrequently, Orthopaedic surgeons notice that fever following childrens femur fractures does not coincide with the laboratory findings. The authors agree that knowledge of the frequency, time of onset, duration, and magnitude would be helpful in accessing the significance of fever in the postinjury period. The authors reviewed 65 childrens femur fractures without infection under the 15 years old from March 1984 to December 1989 and following observations were made. 1. Fever developed in 32 patients(49%), but only in 7 patients(11%) significant fever elevation was found. 2. The mean onset of fever was 4 days after trauma, and the mean duration was 3 days. 3. The rate of fever occurrence increased In accordance with age. 4. Fever was least common in patients having oblique fracture. 5. Associated injuries were found more commonly in the febrile group.
- 518 View
- 4 Download

- Open reduction and Internal Fixation of Calcaneus Fractures by Staples and Screws
- Myung Ku Kim, Soo Ill Kang, Kang Hyun Lee, Chan Soo Park, Jae Woo Ryuh
- J Korean Soc Fract 1990;3(1):22-33. Published online May 31, 1990
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1990.3.1.22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Clacaneal fractures involving subtalar joint can be associated with prolonged and severe disability. Many different methods have been tried for the treatment in order to search for better results. From October 1987 to October 1989, five cases of calcaneal fractures involving subtalar joint were treated by open reduction and internal fixation, and the results were as follows: 1. The causes of fractures of the calcaneus were fall from a height in all five cases. 2. The medial approach was used usually and, when the anatomical reduction was impossible by medial approach only, the lateral approach was combined. 3. The average Bohlers angle was 4.6 before reduction and 24.6 after open reduction. The Bohlers angle was increased to average 20 4. Satisfactory results were botained in all but one, who was not followed up for over 1 year. 5. The open reduction and internal fixation through the medial approach was valuable treatment method of the intraarticular calcaeal fracture.
- 363 View
- 1 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


