Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Three-dimensional computed tomography-based differentiation of engaged versus displaced intertrochanteric fractures using the anterior fracture line: a cross-sectional study from Korea
- Jae-Suk Chang, Jin Yeob Park, Sang-Ok Chun, Chul-Ho Kim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2026;39(1):30-37. Published online January 25, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00318
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
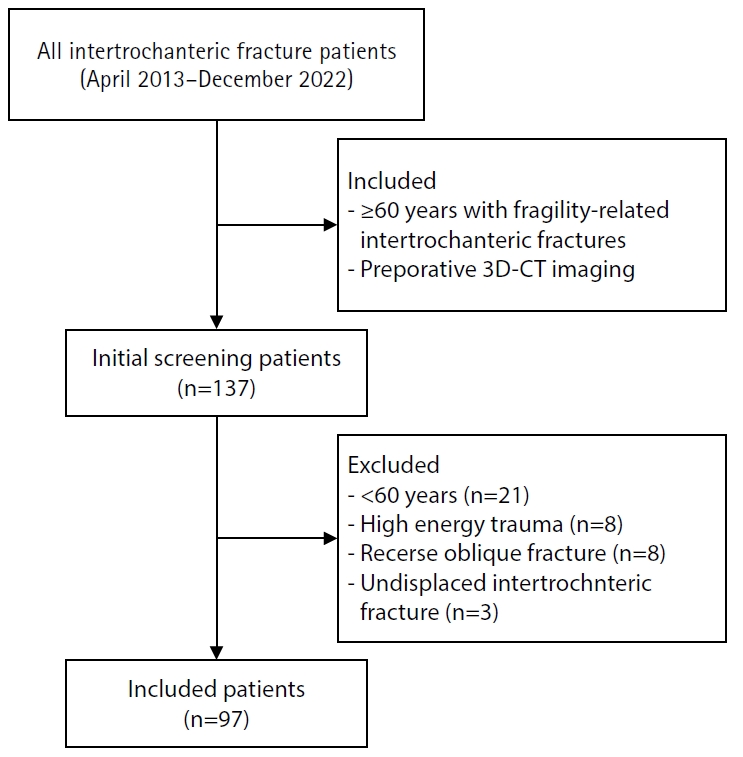
With the advent of an aging society, osteoporotic fractures—particularly hip fractures—are increasing, with a 1-year mortality rate of 17%. Achieving stable fixation that enables early ambulation is essential but remains challenging because complex intertrochanteric (IT) fracture patterns are often underestimated on plain radiographs. Using three-dimensional computed tomography (3D-CT), this study analyzed whether the anterior fracture line lies medial or lateral to the IT line and examined its relationship with displacement or distal medullary canal engagement, highlighting the potential influence of the joint capsule and capsular ligaments on fracture morphology and fixation stability.
Methods
A retrospective review was conducted on 96 osteoporotic IT fractures in patients aged ≥60 years treated between April 2013 and December 2022 at National Police Hospital and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. Fractures were classified as engaged, completely displaced, and partially displaced based on 3D-CT findings. The anterior fracture-line position (medial or lateral to the IT line) and the status of the lesser trochanter (LT) were evaluated. The chi-square or Fisher exact test was used for statistical comparisons.
Results
In total, 96 patients were analyzed. Of these, 49 cases (51.0%) were classified as engaged type, 27 cases (28.1%) as completely displaced type, and 20 cases (20.8%) as partially displaced type. When comparing fracture pattern with anterior fracture-line position, the completely displaced type showed a significantly higher proportion of lateral anterior fracture lines than the other two types (P<0.001). However, no significant association was identified between fracture pattern and LT displacement. When the anterior fracture-line position and LT displacement were evaluated together, only the engaged type demonstrated a possible association between a lateral anterior fracture line and LT displacement, though the statistical significance was weak (P=0.047).
Conclusions
Fracture lines lateral to the IT line were strongly associated with displacement in IT fractures; however, their relationship with LT involvement, reflecting iliopsoas tendon traction, was not clearly demonstrated. Although the factors contributing to the engaged-type fracture remain uncertain, the statistical association between fracture pattern and anterior fracture-line position suggests that capsular structures may play a stabilizing role in select fracture configurations. Further studies are needed to clarify these anatomical interactions. Level of evidence:
- 113 View
- 4 Download

- Analysis of Missed Fractures by Bone Scan in Elderly Hip Fracture Patients with Osteoporosis
- Tae Hun Lee, Yeong Hyun Lee, Seo Won Kang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(3):144-149. Published online July 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.3.144
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The incidence of hip fractures is increasing due to an increase in elderly populations because elderly patients often have accompanying diseases, such as cognitive impairment or dementia, which may lead to missed fractures. Therefore, this study assessed the utility of bone scans in detecting missed fractures in elderly patients.
Materials and Methods
This study analyzed the data from 178 patients treated from January 2014 to March 2023. The inclusion criteria were patients who had hip fractures with osteoporosis over 70 years old. Bone scans were performed on average 10 days after injury. The rate and trend of missed fractures not detected in the initial diagnosis were determined based on sex, age, dementia status, and the presence of osteoporosis.
Results
Among the 178 hip fracture patients over 70 years old, 37 patients had a history of being diagnosed with dementia, and 141 patients had never been diagnosed. Missed fractures were confirmed in 49 cases (42 patients) (23.6%). The dementia group had 13 missed fractures, and the non-dementia group had 36 missed fractures, but there was no significant difference. Rib fractures were most common, followed by vertebral fractures.
Conclusion
Missed diagnoses of fractures were common among elderly hip fracture patients. A whole body bone scan appeared to be effective in detecting missed fractures. Therefore, identifying accompanying fractures through bone scans and delivering appropriate treatment can play an important role in postoperative rehabilitation.
- 661 View
- 9 Download

- Effect of Coincident Hip Fracture on Distal Radius Fracture in Patients Treated with a Volar Locking Plate: A Matched-Pair Analysis of Elderly Patients
- Hyoung-Seok Jung, Min-Su Chu, Jae-Sung Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(3):137-143. Published online July 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.3.137
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Although the incidence of simultaneous distal radius and hip fractures in older patients is minimal, patients with these coincident types of fractures exhibit unique features. This study analyzed the outcomes associated with operative treatment involving volar-locking plates in patients who sustained distal radius fractures and hip fractures and compared them with those in matched control patients who had undergone treatment for isolated distal radius fractures.
Materials and Methods
Between 2010 and 2015, 34 patients, who met the criteria for hip and distal radius fractures, were retrospectively reviewed. Thirty-four matched patients who underwent volarlocking plate fixation for isolated distal radius fractures during the same period were also reviewed. The clinical outcomes between the groups were compared using postoperative radiological parameters.
Results
The radiological assessment revealed a better radial length and inclination in the control group than in the study group at the final follow-up. In other words, patients with coincident hip fractures showed a higher tendency for loss of reduction. Despite the differences in radiological parameters, no significant differences in clinical outcomes were observed, except for grip strength.
Conclusion
Although volar-locking plating provides greater stabilization, a loss of reduction occurred in patients with coincident hip fractures.
- 873 View
- 9 Download

Review Article
- Osteoporotic Hip Fracture: How We Make Better Results?
- Byung-Chan Choi, Kyung-Jae Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(1):52-59. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.1.52
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The prevalence of osteoporosis and incidence of osteoporotic fractures is increasing gradually as life expectancy is prolonged and the aged population increases. Osteoporotic hip fractures (femoral neck fractures and femoral intertrochanteric fractures) have high mortality because the patients with these fractures are elderly and have several comorbidities. Thorough preparation and a multidisciplinary approach in the preoperative period are critical, and early surgery is recommended. There are also several principles to treat osteoporotic hip fractures and prevent fixation failures. Many studies have suggested various treatment methods for femoral neck fractures and femoral intertrochanteric fractures. Functional recovery treatment is essential based on the patient’s health and activity levels. Finally, aggressive management of osteoporosis and the prevention of falling is needed to treat osteoporotic hip fractures successfully.
- 630 View
- 24 Download

Original Article
- Cephalomedullary Nailing with an Additional Cannulated Screw Fixation in Basicervical Femur Fractures
- Keong-Hwan Kim, Woo Dong Nam, Yeon Sik Heo, Gu-Hee Jung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(1):22-29. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.1.22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study is to analyze the clinical results of patients with basicervical fracture undergoing cephalomedullary nailing (CMN) with an additional cannulated screw fixation compared to only performing CMN. We hypothesized that a difference may exist in the clinical outcomes if an ad-ditional screw is fixed with CMN compared to only performing CMN in basicervical fracture.
Materials and Methods
A total of 28 consecutive patients who underwent CMN for basicervical fracture were included. In 9 cases, only CMN was conducted, and in 19 cases, an additional cannulated screw fixation was performed with CMN. Bone union, sliding distance, reduction status, and fixation failure were evaluated by postoperative radiography, and ambulatory ability was evaluated by functional results. These findings were compared between a group of CMN and a group of CMN with an additional cannulated screw.
Results
There were 4 males and 24 females with a mean age of 84 years (range, 69–100 years). No significant difference was found in postoperative reduction, tip-apex distance, bone union, and walking function recovery after surgery between the two groups, but in the sliding distance of the lag screw, the CMN group demonstrated more sliding (6.2 mm [range, 2.5–13.4 mm] vs 3.5 mm [range, 0.1– 9.2 mm]; p=0.045). Among the two groups, only one case of fixation failure at the postoperative four months was observed in the CMN group (p=0.321), and hemiarthroplasty with nail construct removal was performed.
Conclusion
CMN with additional cannulated screw fixation is a safe and reliable surgical option in basicervical fracture. It provided favorable clinical outcomes and may be a good alternative for treating basicervical fracture.
- 1,203 View
- 14 Download

Review Article
- Hip Fractures in the Elderly: Perioperative Management and Prevention of Medical Complications
- Keong-Hwan Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(1):39-44. Published online January 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.1.39
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Elderly patients with hip fractures are at an increased risk of developing medical complications with higher mortality rates. Most patients require surgical treatment, and an early surgical intervention can reduce complications and lower mortality risk. A restrictive red blood cell transfusion strategy is usually applied, and the amount of transfusion can be reduced through medications such as tranexamic acid. Delirium can be prevented using non-pharmacological methods. In addition, it is necessary to prevent venous thromboembolism through mechanical or chemical prophylaxis. A multidisciplinary approach using the ERAS (Enhanced Recovery After Surgery) protocol and orthogeriatric care can help to reduce medical complications and mortality.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Treatment of Incompletely Displaced Femoral Neck Fractures Using Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced in Patients Older Than 50 Years of Age
Jee Young Lee, Gyu Min Kong
Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma.2025; 39(7): 352. CrossRef - Comparison of Operation Time, Vital Signs, Bleeding Tendency, and Recovery Time Based on Anesthesia Methods in Patients Undergoing Hip Fracture Surgery
Je Bog Yoo, Woo Young In, Chang Ok Pyo, Jeung Hee Kwon, Min Ji Lee, Kwang Hee Kim, Kyoung Ok Kim, Mi Yu
Journal of PeriAnesthesia Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Treatment of Incompletely Displaced Femoral Neck Fractures Using Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced in Patients Older Than 50 Years of Age
- 1,390 View
- 40 Download
- 2 Crossref

Original Articles
- Comparison of the Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of TFNA (Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced) and PFNA-II (Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation-II) Treatment in Elderly Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures
- Min Sung Kwon, Young Bok Kim, Gyu Min Kong
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(4):162-168. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.4.162
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Trochanteric fixation nail advanced (TFNA) was modified to compensate for the shortcomings of proximal femoral nail antirotation-II (PFNA-II). The clinical and radiological outcomes of surgeries us-ing the PFNA-II and TFNA for femoral intertrochanteric fractures were compared.
Materials and Methods
Eighty-two patients who underwent surgeries using PFNA-II or TFNA were analyzed. Only those who were followed up for more than a year were enrolled. Bone union, shortening of the femoral neck, and the tip–apex distance of the intramedullary nail were compared in the radiological findings. Clinical outcomes, including the frequency of complications and gait ability (Koval score), were also assessed.
Results
The mean follow-up periods were 22 and 19 months for the PFNA-II and TFNA groups, re-spectively. In the PFNA-II group, two cases of femoral head cut-out and one case of varus collapse were observed. In the TFNA group, only one case of femoral head cut-out was observed; however, there was no significant difference in the frequency of complications between the two groups (p=0.37). Ad-ditionally, both the shortening of the femoral neck and the decrease in gait ability after surgery showed relative improvement in the TFNA group compared to the PFNA-II group; however, there was no sig-nificant difference between the two groups.
Conclusion
The use of both TFNA and PFNA-II was associated with satisfactory outcomes. In patients who underwent surgeries using TFNA, the recovery of gait ability, frequency of complications, and short-ening of the femoral neck were not significantly different from PFNA-II, suggesting that both are suitable instrument choices for intertrochanteric fracture treatment. However, the clinical significance must be further assessed using a larger group of patients over a longer follow-up period in future studies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Treatment of Incompletely Displaced Femoral Neck Fractures Using Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced in Patients Older Than 50 Years of Age
Jee Young Lee, Gyu Min Kong
Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma.2025; 39(7): 352. CrossRef - Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures Treated with Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced and Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation-II: Correlation between Lateral Sliding of the Helical Blade and Lateral Trochanteric Pain
Sung Yoon Jung, Myoung Jin Lee, Lih Wang, Hyeon Jun Kim, Dong Hoon Sung, Jun Ha Park
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2024; 59(3): 208. CrossRef
- Treatment of Incompletely Displaced Femoral Neck Fractures Using Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced in Patients Older Than 50 Years of Age
- 3,553 View
- 53 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Benefits of a Demineralized Bone Matrix in Osteoporotic Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture Patients
- Se Jin Kim, Hong-Man Cho, Myung Cheol Jung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(4):151-161. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.4.151
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Osteoporosis causes various fixation failures in patients with intertrochanteric fractures. This study aimed to investigate the effect of a demineralized bone matrix (DBM) for cancellous or cortical bone defects on internal fixation in older osteoporotic patients with intertrochanteric fractures.
Materials and Methods
Among patients with intertrochanteric fractures who underwent surgical treatment from January 2016 to December 2021 at a facility, 171 patients were AO/OTA type 31-A1 and type 2 fractures which are considered relatively stable. The patients were grouped based on DBM use (Group A: DBM use, Group B: DBM non-use), and their clinical and radiology results were analyzed retrospectively. The patients were then subdivided into Group A-a and -b after removing factors that could cause treatment failures, such as the reduction status and location of the helical blade, and then further subdivided (Group A-a-1/2/3/4 and Group B-b-1/2/3/4) according to cancellous or cortical bone defects that could accompany intertrochanteric fractures. The time to full weight-bearing (FWB) and Harris hip score (HSS) 3 months after surgery in these subgroups were investigated.
Results
There was no significant difference in the clinical radiology results and complications between Group A and Group B. However, the time to FWB (p<0.001) and HSS (p=0.029) were significantly superior in Group A. In Group A-a with DBM use, after removing the risk factors for intertrochanteric fracture failure, the time to FWB (p=0.055) was close to the significance level, and HSS (p=0.036) was significantly superior. In Group A-a-1 (cancellous defect only) and Group A-a-3 (cancellous and cortical defect), the time to FWB (p=0.088, 0.052) was close to the significance level, and the HSS (p=0.039, 0.018) was significantly superior when DBM was used.
Conclusion
In patients with intertrochanteric fractures of AO/OTA type 31-A2.3 or less, if stable reduction and firm fixation are achieved, selective DBM use may help early recovery after surgery.
- 453 View
- 2 Download

Case Report
- Injury of the Ascending Branch of the Lateral Femoral Circumflex Artery Caused by a Spike of the Displaced Lesser Trochanter in an Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture - A Case Report -
- Soon Ho Huh, Hong-Man Cho, Jiyeon Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2021;34(2):71-75. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2021.34.2.71
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Although vascular injuries associated with femoral intertrochanteric fractures have been reported infrequently, bleeding due to vascular injury can lead to severe complications that can be potentially life and limb-threatening. The authors report a case of an injury of the ascending branch of the lateral femoral convolutional artery in a patient who underwent surgical treatment for a femoral intertrochanteric fracture. Vascular injury occurred due to the sharp margin of displaced lesser trochanter five weeks after surgery. Percutaneous transcatheter embolization was done and improved without additional complications. Therefore, the surgeons need to be aware of possible associated vascular injuries caused by displaced lesser trochanter fragments in femoral intertrochanteric fractures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Delayed Deep Femoral Artery Injury Secondary to Migrated Lesser Trochanter Fragment After Intertrochanteric Fracture Fixation: A Case Report and Updated Literature Review
Slavko Čičak, Josip Kocur, Vedran Farkaš, Petra Čičak, Stjepan Ištvanić, Marko Lovrić, Marko Perić, Nenad Koruga, Tomislav Ištvanić
Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Vascular Complications Following Trans-Trochanteric Fracture: Case Report and Literature Review
Robert Bot, Adrian Tirla, Simona Daniela Cavalu
Reports.2025; 8(4): 191. CrossRef
- Delayed Deep Femoral Artery Injury Secondary to Migrated Lesser Trochanter Fragment After Intertrochanteric Fracture Fixation: A Case Report and Updated Literature Review
- 595 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref

Original Articles
- Treatment of Proximal Femur Fracture with a Newly Designed Nail: Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced (TFNA)
- Jae Youn Yoon, Ji Wan Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(4):189-195. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.4.189
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study evaluated the clinical results and implant safety of a newly developed implant, Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced (TFNA; DePuy Synthes), in the treatment of proximal femur fractures.
Materials and Methods
This was a retrospective cohort study of 26 patients diagnosed with proximal femur fracture and treated surgically with TFNA. The patients’ demographic data, surgical data, radiologic findings, and functional outcomes, including complications, were evaluated.
Results
The mean age of the patients was 71.2 years (95% confidence interval [CI], 68.2-74.2); 65.4% were female. The mean Carlson comorbidity index score was 5.4, and the mean Koval grade before fracture was 2.1. Fracture classification included four cases of AO/OTA 31.A1, nine cases of A2, six cases of A3, and seven cases of 32A including six cases of atypical femoral fractures. The mean operating time was 53.3 minutes (95% CI, 43.6-63.1). There were no early postoperative complications, such as postoperative infection, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, or in-hospital death, except one case of pneumonia. The mean Koval score at the postoperative six-month follow-up was 2.9. EuroQol-5 Dimension (EQ-5D) increased from 0.05 to 0.54 after three months and 0.72 at six months postoperatively. Bone union was observed in all cases with a mean union time of 12.9 weeks. No implant failure occurred, and no cases required secondary revision surgery.
Conclusion
A new intramedullary nail system, TFNA, showed excellent outcomes and safety in the surgical treatment of proximal femur fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intermediate Length Cephalomedullary Nails in Proximal Femoral Fractures: Review of Indications and Outcomes
Daniel Scott Horwitz, Ahmed Nageeb Mahmoud, Michael Suk
Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.2025; 33(19): 1071. CrossRef - Outcomes of Intertrochanteric Fracture Fixation Using the Trochanteric Fixation Nail Advanced (TFNA): A Retrospective Analysis
Ramprasad Jasti, Prithvi Mohandas, Mahesh K Ragavan, Sunil D Magadam, Umesh Kannadasan
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures Treated with Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced and Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation-II: Correlation between Lateral Sliding of the Helical Blade and Lateral Trochanteric Pain
Sung Yoon Jung, Myoung Jin Lee, Lih Wang, Hyeon Jun Kim, Dong Hoon Sung, Jun Ha Park
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2024; 59(3): 208. CrossRef - Prospective randomized multicenter noninferiority clinical trial evaluating the use of TFN-advancedTM proximal femoral nailing system (TFNA) for the treatment of proximal femur fracture in a Chinese population
Lidan Zhang, Zhijun Pan, Xiaohui Zheng, Qiugen Wang, Peifu Tang, Fang Zhou, Fan Liu, Bin Yu, Frankie K. L. Leung, Alex Wu, Suzanne Hughson, Zhuo Chen, Michael Blauth, Anthony Rosner, Charisse Sparks, Manyi Wang
European Journal of Trauma and Emergency Surgery.2023; 49(3): 1561. CrossRef - Risk of shortening in operatively treated proximal femur fractures with cephalomedullary nails with dynamically versus statically locked helical blades
Nathan Cherian, Lasun Oladeji, Cole Ohnoutka, Dan Touhey, Madeline Sauer, Kyle A. Schweser, Mauricio Kfuri, James L. Cook, Gregory J. Della Rocca, Brett D. Crist
Injury.2023; 54(2): 669. CrossRef - GS Hip Nail versus Affixus Hip Fracture Nail for the Intramedullary Nailing of Intertrochanteric Fractures
Seungcheol Kwon, Minjae Lee, Heeyeon Lee, Jihyo Hwang
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(21): 6720. CrossRef - Comparison of the Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of TFNA (Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced) and PFNA-II (Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation-II) Treatment in Elderly Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures
Min Sung Kwon, Young Bok Kim, Gyu Min Kong
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2022; 35(4): 162. CrossRef - Analysis of Clinical and Functional Outcomes according to the Blood Sugar Control Status at the Time of Ankle Fractures Resulting from Rotational Injuries
Jun Young Lee, Dong Seop Lim, Seung Hyun Lee, Seo Jin Park
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2022; 35(4): 135. CrossRef - Conventional versus helical blade screw insertion following the removal of the femoral head screw: a biomechanical evaluation using trochanteric gamma 3 locking nail versus PFN antirotation
Hong Man Cho, Kwang Min Park, Tae Gon Jung, Ji Yeon Park, Young Lee
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and Radiologic Outcome of Intertrochanteric Fracture Treatment Using TFNA (Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced)
Hyeon Joon Lee, Hyun Bai Choi, Ba Rom Kim, Seung Hwan Jo, Sang Hong Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2021; 34(3): 105. CrossRef
- Intermediate Length Cephalomedullary Nails in Proximal Femoral Fractures: Review of Indications and Outcomes
- 2,399 View
- 23 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Treatment of the Proximal Femoral Fracture Using the New Design Cephalomedullary Nail: Prospective Outcomes Study
- Young Ho Roh, Joseph Rho, Kwang Woo Nam
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(1):35-42. Published online January 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.1.35
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The aim of this study is to investigate the clinical performance and safety of Zimmer® natural nail cephalomedullary nail (ZNN CM nail) in the treatment of proximal femur fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The following research was conducted as a prospective, non-comparative, single center outcome study. Upon providing written informed consent, enrolled patients' data were collected and analyzed. Postoperative follow-up visits were scheduled at 6 weeks, 3 months, 6 months, and 1 year. Follow-up evaluation included radiographic assessment, physical examination, and quality of life and adverse events reports.
RESULTS
Thirty-nine patients were available for evaluation at one year postoperative. The patients reported the mean EuroQol-5 Dimension score increased after surgery: from 0.4 points at discharge (n=49) to 0.6 points at 1-year post-surgery (n=39). The mean Harris hip score also increased after surgery: from 56.3 points at discharge (n=49) to 72.1 points at 1 year (n=12). Bone union was seen in 64% (n=16) in 6 months and 95% (n=37) in 1 year.
CONCLUSION
The results of this 1-year follow-up study affirmed the effectiveness and safety of the ZNN CM nail in the treatment of proximal femur fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical and Radiologic Outcome of Intertrochanteric Fracture Treatment Using TFNA (Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced)
Hyeon Joon Lee, Hyun Bai Choi, Ba Rom Kim, Seung Hwan Jo, Sang Hong Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2021; 34(3): 105. CrossRef - Treatment of Proximal Femur Fracture with a Newly Designed Nail: Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced (TFNA)
Jae Youn Yoon, Ji Wan Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2020; 33(4): 189. CrossRef
- Clinical and Radiologic Outcome of Intertrochanteric Fracture Treatment Using TFNA (Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced)
- 868 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Evaluation of the Wearing Characteristics of Hip Protectors Based on Draping Pattern Design and Body Shape in Korean Elderly People
- Eunjin Jeon, Heeeun Kim, Heecheon You, Seunghoon Lee, Giwook Kim, Sunjung Yoon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(4):180-185. Published online October 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.4.180
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to verify the new hip protector design with respect to the comfort and mobility. The new hip protector was developed based on a pattern of draping and body shape of Korean elderly individuals.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
An wearing characteristics evaluation was conducted on 101 elderly women wearing hip protector using a questionnaire of preference and ease of wearing. Hip protectors, with existing and newly developed belt and underwear types, which were previously preferred by the Korean elderly, were evaluated.
RESULTS
The newly developed belt type (65.0%) and newly developed underwear type (30.1%) hip protectors were preferred to the existing type (3.9%) and existing underwear type (1.0%) ones. The convenience of the newly developed belt type was greater than 4 out of 5 points (1 for strongly disagree and 5 for strongly agree) for all nine measures, including fit, allowance, mobility, pad placement, pad thickness, pad size, material, design, ease of dressing, and ease of undressing. The newly developed hip protectors showed less discomfort than the existing ones. In particular, the newly developed belt type and developed underwear type improved sitting convenience by 31.1% and 26.1%, respectively, compared with the existing ones.
CONCLUSION
The hip protectors developed in the present study is expected to provide better fit for the body shape of Korean elderly individuals and prevent hip fracture due to fall. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Evaluation of Fall Impact Protective Clothing for the Elderly Women
Jung Hyun Park, Jin Suk Lee, Jeong Ran Lee
Fashion & Textile Research Journal.2018; 20(5): 569. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of Fall Impact Protection Pad
Jung Hyun Park, Jin Suk Lee, Jeong Ran Lee
Fashion & Textile Research Journal.2018; 20(4): 422. CrossRef
- Development and Evaluation of Fall Impact Protective Clothing for the Elderly Women
- 726 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Cognitive Impairment in Hip Fracture Patients without Underlying Neurologic Diseases: Risk Factors and Relationship to Early Functional Recovery: Preliminary Study
- Jae Yong Park, Yong Beom Lee, Kun Tae Park, Je Hyun Yoo, Narei Hong
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(1):34-41. Published online January 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.1.34
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - PURPOSE
The aim of this study is to examine the risk factors of cognitive impairment in elderly hip fracture patients with no underlying neurologic disease, and to determine its effect on functional recovery postoperatively.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From August 2012 to August 2013, 39 patients older than 65 years of age, who underwent hip fracture surgery and were followed-up for a minimum of 1 year at Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, were enrolled. All patients were assessed using Korean version of Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE-K) after admission. All patients were divided into cognitive normal group (MMSE-K> or =24) and cognitive impairment group (MMSE-K<24). WOMAC (Western Ontario and McMaster University) score and Harris hip score were used for assessment of functional recovery at 6-month follow-up.
RESULTS
Sixteen patients (41.0%) were classified as the cognitive impairment group. The number of underlying diseases was the only statistically different factor between the two groups. In the evaluation of functional outcome, the functional decline was less in the cognitive normal group. Risk factors for cognitive impairment in elderly hip fracture patients were old age, high body mass index, and the number of underlying diseases, particularly an endocrinologic disease like diabetes.
CONCLUSION
Cognitive impairment in elderly patients may have a negative effect on functional recovery after hip fracture surgery. Therefore, we recommend routine evaluation of cognitive function in elderly hip fracture patients even with no underlying neurologic disease.
- 492 View
- 1 Download

- Assessment of Coronal Plane Malalignment Following Reduction of Trochanteric Fractures-Simple Intraoperative Guideline Using Greater Trochanter Orthogonal Line
- Young Cheol Yoon, Jong Keon Oh, Won Yong Shon, Han Ju Kim, Jae Woo Cho
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(1):1-11. Published online January 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
There is no consensus on a clear intraoperative guideline for judging the coronal plane alignment following reduction of trochanteric fractures. Complex angular measurements using fluoroscope monitors are tedious. Therefore the relation of the horizontal line from the tip of the greater trochanter (GT orthogonal) and femur head center (HC orthogonal) was studied to define this line as a criterion for predicting varus-valgus malalignment.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We studied this relation in 200 standing orthoradiograms which included 100 males and 100 females. The images were digitally analyzed using the picture archiving and communication system. GT orthogonal line and HC orthogonal line were evaluated. The distance of these lines was measured as trochanter center distance (TCD) and its correlation with angular parameters like neck shaft angle, medial proximal femoral angle with reference to anatomical axis (aMPFA) and lateral proximal femoral angle with reference to mechanical axis (mLPFA) were analyzed.
RESULTS
In all patients, the GT orthogonal line passed either at or above the center of the head. Overall mean of TCD was 7.22 mm, ranging from 0 to 17.57 mm. TCD was found to show strong correlation with angular parameters like aMPFA, mLPFA and neck shaft angle. TCD was less than one fourth of the corresponding head diameter in around 90%. Therefore following reduction of trochanteric fractures, the GT orthogonal line should pass through the superior juxta central quadrant of the femoral head.
CONCLUSION
This line can be represented by a guide wire with fluoroscopy during surgery. The GT orthogonal line can be used intraoperatively as a simplified tool for prediction of varus/valgus malalignment following the reduction of trochanteric fractures.
- 439 View
- 2 Download

- The Character of Reverse Obliquity Intertrochanteric Fractures in Elderly Patients
- Ji Wan Kim, Jae Suk Chang, Jung Hwan Sung, Jung Jae Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(3):173-177. Published online July 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.3.173
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To discriminate the characteristics between reverse obliquity fractures in the elderly and that of young adults using three-dimensional computed tomography (3D CT).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Eighteen patients who had reverse obliquity intertrochanteric fractures were enrolled from January 2007 to March 2012. The fracture pattern was analyzed using the 3D CT. The area showing low density (bone defect) of trochanter and femoral neck region was measured. Patients were divided into two groups: Group I, less than 65 years old and Group 2, 65 years and over.
RESULTS
In all 9 cases of group 1, the proximal fragment had a 'V' shape with an average of 5.6 cm below the vastus ridge; however, the fracture of 8 cases (88.97%) in group 2 had a 'Lambda' shape of the distal fragment at the level of vastus ridge and an additional fracture line extending to the greater trochanter tip. The bone defect volume of the trochanter and femoral neck region was larger significantly in group 2 than in group 1.
CONCLUSION
Reverse obliquity intertrochanteric fracture in the elderly demonstrated a pattern of bursting fracture with 4 parts, which had different patterns from that of young patients. We believe that the larger volume of bone defects resulted in the difference of fracture patterns between the two groups. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comparison of Internal Fixation and Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty for the Treatment of Reverse Oblique Intertrochanteric Femoral Fractures in Elderly Patients
Bong-Ju Park, Hong-Man Cho, Woong-Bae Min
Hip & Pelvis.2015; 27(3): 152. CrossRef
- A Comparison of Internal Fixation and Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty for the Treatment of Reverse Oblique Intertrochanteric Femoral Fractures in Elderly Patients
- 772 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Analysis of the Factors Involved in Failed Fixation in Elderly Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture
- Joon Soon Kang, Ryuh Sup Kim, Bom Soo Kim, Young Tae Kim, Seung Hyun Hong
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(4):263-268. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.4.263
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analyze the causes of internal fixation failure in elderly intertrochanteric femoral fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We retrospectively analyzed 93 intertrochanteric femoral fractures that were treated by internal fixation. The follow-up period was at least 24 months. The mean age was 73 years. We analyzed the classification of the fracture, screw position, reduction state of the fracture, and neck-shaft angle.
RESULTS
Internal fixation failure occurred in 12 cases (12.9%). The causes of internal fixation failure were one case (1.0%) of head perforation, 7 cases (7.5%) of excessive slippage of a screw, and 4 cases (4.3%) of varus deformity. Significant factors infixation failure were displacement of the posterolateral fragment more than 8 mm in anteroposterior radiograph, anterior displacement of a fragment, or more than 20-degree angulation in lateral radiography. Thirty-three cases had a screw in the middle position and 4 of these cases (12.1%) had fixation failure. Notably, 14 cases had a screw in the posteromedial position and 6 of these cases had fixation failure (42.8%).
CONCLUSION
Accurate reduction of the posteromedial fragment is essential in unstable intertrochanteric fracture and anterior displacement or angulation should be avoided to prevent fixation failure. The tip apex distance of the screw and central location of the screw in the femoral head is also an important factor.
- 460 View
- 0 Download

Case Report
- Simultaneous Bilateral Proximal Femoral Fracture associated with Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizure: A Case Report
- Sang Hoo Lee, Kyeong Seop Song, Seung Joo Jeon, Seong Hwan Hong
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(1):69-72. Published online January 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.1.69
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Simultaneous bilateral proximal femoral fractures are extremely rare, and a few have been reported in and outside the country. It may have various causes, and most cases were associated with major trauma, repetitive minor trauma, seizure, parathyroid or renal dysfunction, and anti-epileptic medications. We experienced a case of simultaneous bilateral proximal femoral fractures after generalized tonic-clonic seizure in a 70-year-old female. Herein, we report it with a review of the literature.
- 455 View
- 0 Download

Original Articles
- Usefulness of the Cementless Stem for the Treatment of Hip Fracture in Elderly Patients with Osteoporosis: Comparative Analysis between Cementless Stem and Cemented Stem
- Joon Soon Kang, Kyoung Ho Moon, Rhu Seop Kim, Sang Ho Lee, Jong Min Choi
- J Korean Fract Soc 2011;24(1):16-22. Published online January 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.1.16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
We evaluated the usefulness of the cementless stem in treating hip fracture patients older than 70.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We studied elderly osteoporotic hip fractures in the neck and intertrochanter area who had received hip arthroplasty with over 2 years of follow up period. Among those, we analyzed the clinical and radiological results of hip arthroplasty with cemented stem (group 1) and hip arthroplasty with cementless stem (group 2). Each group was consists of fifty hips.
RESULTS
The mean age at surgery was 75 years and mean follow-up period was 40 months (minimum 24 months). The admission period was 28.68+/-8.8 days for group 1 and 28.05+/-8.7 days for group 2 (p>0.05) and the average operation time was 87+/-21.2 minutes, and 80+/-17 minutes (p>0.05) and the total blood loss was 611+/-141.3 cc and 557+/-120.5 cc (p>0.05) respectively. There was no statistically significant difference in all aspects. One case of pulmonary embolism occurred in group 1. Stem loosening was not observed in both groups at the last follow-up radiologic study.
CONCLUSION
The hip arthroplasty with cementless stem for the osteoporotic hip fractures showed a competent results clinically and radiologically in short term follow up as compared with the cemented stem.
- 442 View
- 0 Download

- TFCC Injury Associated with the Triquetral Dorsal Chip Fracture
- Seoung Joon Lee, Jin Ho Hwang, Min Seok Kang, Jong Woong Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(3):179-184. Published online July 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.3.179
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the usefulness of wrist arthroscopic examination in patient with persistent pain after the triquetral dorsal chip fracture and also to determine its relationship with TFCC injury in the triquetral dorsal chip fracture patient manifesting persistent pain.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study is based on six cases presenting persistent pain in the ulnar aspect after the triqeutral posterior cord fracture that were treated conservatively. Wrist arthroscopy was carried out for all six cases. All were preoperatively and postoperatively evaluated using VAS pain scale, grip power, ulnar grind test, Kleinman shearing test and lunotriquetral ballottment test.
RESULTS
Preoperatively, ulnar grind test yielded positive results in all six cases, Kleiman shearing test proved positive in three cases and lunotriquetral ballottment test yielded positive result in one case. In the arthroscopic findings, synovitis and TFCC injury were detected in all cases, and based on Palmer classification of TFCC injury, type IA was determined in five cases and type ID in one case. Arthroscopic TFCC partial resection and synovectomy were carried out. VAS pain scale improved from an average 8 points preoperatively to 3 points postoperatively. The difference of grip power between the normal and the other side improved from average of 15 lb preoperatively to 5 lb postoperatively. Based on postoperatively physical examination at 6 weeks, all cases yielded negative results in the ulnar grind test and Kleiman shearing test.
CONCLUSION
We think that TFCC injury is one of the causes of persistent pain after triquetral dorsal chip fracture. We recommend an arthroscopic TFCC partial resection as a valuable treatment option.
- 762 View
- 4 Download

- The Usefulness of Hip to Thigh Ratio as an Anthropometric Indicator for the Incidence of Hip Fracture
- Jin Park, Kyu Hyun Yang, Seong Hwan Moon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(1):1-5. Published online January 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To compare anthropometric indicators around the hip between osteoporotic fracture group and control group.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty patients for osteoporotic hip fracture and the same number of patients for spine fracture who admitted our institute from November 2006 to March 2007 were matched with control patients without osteoporotic fracture. The waist circumference (WC), hip circumference (HC), thigh circumference (TC), and height were measured. From these measurements, waist to hip ratio (WHR), waist to thigh ratio (WTR), hip to thigh ratio (HTR), waist to height ratio (WHtR), hip to height ratio (HHtR), and thigh to height ratio (THtR) were calculated. All these indicators were compared between hip fracture and control group, and between spine fracture and control group.
RESULTS
Comparison between spine fracture and control group showed that the WC, WHR, WHtR were statistically significant, but all indicators failed to show accuracy in the ROC analysis. Comparison between hip fracture and control group demonstrated the TC, WTR, HTR, WHtR, HHtR, THtR were statistically significant. However, only the HTR showed fair accuracy in the ROC analysis. The area under the curve (AUC) of the HTR was 0.75 (95% confidence interval, 0.62 to 0.87) (p=0.001).
CONCLUSION
The HTR was fairly accurate in predicting the incidence of hip fracture compared with any other anthropometric indicators. Therefore, we can consider that the HTR has clinical usefulness.
- 626 View
- 1 Download

- Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty Using Calcar Replacement Stem for Hip Fractures in the Elderly
- Duk Hwan Kho, Ki Hwan Kim, Hyeung June Kim, Dong Heon Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2008;21(3):232-239. Published online July 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.3.232
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the results of bipolar hemiarthroplasty using calcar replacement stem for hip fractures in elderly patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between March 1995 and March 2005, the clinical records on 68 cases more than 75 years old who underwent the bipolar hemiarthroplasty using calcar replacement stem and followed minimum 2 years were reviewed. We evaluated the results by modified Harris hip score, walking ability, activity of daily living, complications, osteoporosis and radiologic findings.
RESULTS
The mean postoperative modified Harris hip score was 88.3 (69~95) in femoral neck fractures and 83.5 (63~91) in femoral intertrochanteric fractures. Walking ability was recovered in 82.3% (56 cases) and activity of daily living was achived in 82.3% (56 cases). Complications were thigh pain, infection, femoral stem subsidence, stress shield, dislocation.
CONCLUSION
We consider bipolar hemiarthroplasty using calcar replacement stem for unstable hip fractures in elderly patients with severe osteoporosis is the useful treatment in view of the stable and rigid fixation, early ambulation and the low rate of complications, even if the operation is technically very difficult. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty With a Calcar Stem for the Management of a Failed Proximal Femoral Nail Anti-rotation Asia (PFNA2) in a Case of Geriatric Unstable Intertrochanteric Femur Fracture
Mukesh O Phalak, Tushar Chaudhari, Ajinkya K Chaudhari
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Bipolar Hemarthroplasty Using Cementless Conical Stem for Treatment of Dorr Type B and C Femoral Neck Fracture
Jeong Hoon Kang, Sang Hong Lee, Sung Jung
Hip & Pelvis.2015; 27(4): 232. CrossRef - Assessment of the Clinical Features of Bilateral Sequential Hip Fractures in the Elderly
Duk-Hwan Kho, Ju-Yong Shin, Hyeung-June Kim, Dong-Heon Kim
The Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2009; 44(3): 369. CrossRef - Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty for Femoral Basicervical Fractures in the Elderly
Duk-Hwan Kho, Ki-Hwan Kim, Hyeung-Jun Kim, Dong-Heon Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(4): 239. CrossRef
- Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty With a Calcar Stem for the Management of a Failed Proximal Femoral Nail Anti-rotation Asia (PFNA2) in a Case of Geriatric Unstable Intertrochanteric Femur Fracture
- 1,355 View
- 27 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Risk Factors of Postoperative Delirium in Elderly Patients with Hip Fractures
- Ki Hwan Kim, Duk Hwan Kho, Ju Yong Shin, Jin Yong Choi, Eung Sik Kim, Dong Heon Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2008;21(3):189-194. Published online July 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.3.189
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To find out the relationship between various risk factors and post-operative delirium in elderly patients with hip fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Out of 135 patients older than 65 years old who underwent the surgery for hip fracture in our department, between the periods of March 2003 to March 2005, 14 patients (10.4%) developed post-operative delirium and 121 patients (89.6%) did not. We studied risk factors of post-operative delirium in two groups.
RESULTS
In chi-square test between delirium group and non-delirium group, the patients were more likely to develop post-operative delirium if they had previous episodes of delirium, abnormal cognitive function, low walking ability before admission, high dependency on ADL (Activities of Daily Living), other medical accompanying diseases, history of dementia, post-operative hypoxia, post-operative electrolyte imbalance, low post-operative hemoglobin and hematocrit, low post-operative albumin and were older than 75 years old (p<0.05). Sex, type of fracture, anesthesia and the time between admission and operation did not show much difference between the two groups.
CONCLUSION
The risk factors of postoperative delirium in elderly patients with hip fracture have a tendency to be multifactorial. Therefore, we conclude that being prepared by thorough understanding of the risk factors and their relationships will help prevent post-operative delirium and result in good postoperative prognosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Increased Serum Neuropeptide Galanin Level Is a Predictor of Cognitive Dysfunction in Patients with Hip Fracture
Zichao Xue, Ke Zhang, Biao Luo, Long Fan, Ruizhe Zhao, Guangliang Hu, Yuzhen Xu
Disease Markers.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Sleep Disturbance Strongly Related to the Development of Postoperative Delirium in Proximal Femoral Fracture Patients Aged 60 or Older
Myung-Rae Cho, Suk-Kyoon Song, Cheol-Hwan Ryu
Hip & Pelvis.2020; 32(2): 93. CrossRef - Incidence and Associated Factors of Delirium after Orthopedic Surgery
Si-Wook Lee, Chul-Hyun Cho, Ki-Cheor Bae, Kyung-Jae Lee, Eun-Seok Son, Sang-Hyun Um
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2019; 54(2): 157. CrossRef - Relationship between Delirium and Clinical Prognosis among Older Patients underwent Femur Fracture Surgery
Jae-Lan Shim, Seon-Young Hwang
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(2): 649. CrossRef - Relationship between Knowledge, Stress, and Nursing Performance about Care for Delirium in Geriatric Hospital Nurses
Eun-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Clinical Health Science.2016; 4(2): 593. CrossRef - The effects of a tailored intensive care unit delirium prevention protocol: A randomized controlled trial
Kyoung-Ja Moon, Sun-Mi Lee
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2015; 52(9): 1423. CrossRef - Is Delirium an Unrecognized Threat to Patient Safety in Korean Intensive Care Units?
Kyoung-Ja Moon, Jinshi Piao, Yinji Jin, Sun-Mi Lee
Journal of Nursing Care Quality.2014; 29(1): 91. CrossRef - The Effects of Delirium Care Training Program for Nurses in Hospital Nursing Units
Moonja Kim, Haejung Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(5): 489. CrossRef - Knowledge, Performance and Stress about Care for Delirium in Orthopedic Hospital Nurses
Mi Young Kim, Young Eun
Journal of muscle and joint health.2013; 20(1): 72. CrossRef - The Experience of Delirium Care and Clinical Feasibility of the CAM-ICU in a Korean ICU
Joo-Hee Jung, Jung-Hye Lim, Eun-Jung Kim, Hyo-Chan An, Min-Kyung Kang, Jin Lee, Yu-Kyung Min, Eun-Zoo Park, Xiang-Hwa Song, Hye-Ryoung Kim, Sun-Mi Lee
Clinical Nursing Research.2013; 22(1): 95. CrossRef - Development and validation of the Korean Nursing Delirium Scale
Kyoung-Nam Kim, Cheol-Ho Kim, Kwang-Il Kim, Hyun-Jung Yoo, Si-Young Park, Yeon-Hwan Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(3): 414. CrossRef - Influencing Factors of the Incidence of Delirium in Elderly Patients with Arthroplasty
Young-Whee Lee, Hye-Bin Im, Eun-Jeong Jeong, Hee-Sun Ma
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(4): 348. CrossRef - Delirium After Spinal Surgery in Korean Population
Jin Kyu Lee, Ye-Soo Park
Spine.2010; 35(18): 1729. CrossRef - The Incidence and Related Factors of Delirium in Elderly Patients with Hip Fracture after Surgery
Bo-Kyung Sohn, Yerl-Bo Sung, Eun-Jin Park, Dong-Woo Lee
Journal of the Korean Geriatrics Society.2010; 14(3): 162. CrossRef
- Increased Serum Neuropeptide Galanin Level Is a Predictor of Cognitive Dysfunction in Patients with Hip Fracture
- 1,978 View
- 5 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Treatment of the Hip Fracture in Elderly Patients with Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA)
- Ki Hwan Kim, Duk Hwan Kho, Ju Yong Shin, Dong Heon Kim, Jun Hyuck Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(2):122-127. Published online April 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.2.122
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the results of the treatment of the hip fractures in elderly hemiplegic CVA patients with disuse osteoporosis. Hemiplegic CVA patients have much difficulties in rehabilitation such as walking, daily activity of living and so forth.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The clinical records on thirty-four CVA patients who had undergone the treatment in hip fracture and followed more than 12 months of period between March 1998 and March 2004 were retrospectively reviewed. The treatment methods were 22 cases of bipolar hemiarthroplasty, 6 cases of compression hip screw, 3 cases of ender nail, 3 cases of multiple cannulated screw. We compared the groups underwent bipolar hemiarthroplasty (Group I), internal fixation (Group II), fracture in ipsilateral (Group A), fracture in contralateral (Group B). We evaluated the results by modified Harris hip score, walker ambulation time, walking ability and activity of daily living.
RESULTS
The mean postoperative modified Harris hip score was decreased in Group I (11.7 points), Group II (9.6 points), Group A (10.0 points), Group B (12.3 points). Recovery of preoperative walking ability was achieved in total 21 cases (62%) that 7 cases (58%) were observed in Group I, 14 cases (64%) in Group II, 18 cases (67%) in Group A and 3 cases (43%) in Group B. Basic activity of daily living was possible in 18 cases (53%).
CONCLUSION
Hemiplegic CVA patients with hip fracture have much difficulties in rehabilitation. However, with appropriate treatment and confident positive attitude for rehabilitations of the patients, doctors and family members, we can expect more reliable results close to the pre-injury status in terms of walking ability and activity of daily living.
- 343 View
- 0 Download

- Postoperative Mortality Rate of Hip Fracture in Elderly Patients
- Duk Hwan Kho, Ki Hwan Kim, Ju Yong Shin, Jun Hyuck Lee, Dong Heon Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(2):117-121. Published online April 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.2.117
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the rate of mortality for the elderly patients after treatment of hip fractures and analyze the associated risk factors which might affect their mortality rate.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
About the clinical records on 305 patients who had undergone the treatment in hip fractures, we evaluated the mortality rate of the total number of 248 patients whose age between 70 and 103 who were followed more than 12 months of period between March 1994 and March 2003. The mean age was 81.3 years. The composition of each female and male were 176 and 72 cases respectively. 99 cases were femoral neck fractures, and 149 cases were femoral intertrochanteric fractures. The operation included bipolar hemiarthroplasty and internal fixation using multiple cannulated screws, compression hip screws and Ender nails. We compared and analyzed the relating factors for the mortality rate.
RESULTS
The mean postoperative mortality rate was 14.1% (35 cases). The highest mortality rate showed for the postoperative 3 months which was 57.1% (20 cases), between 4 and 6 months was 25.7% (9 cases), and 17.1% (6 cases) were presented for 7 and 12 months. The postoperative mortality rate within 1 year was affected by underlying diseases, ASA (American society of Anesthesiologists) and cemented bipolar hemiarthroplasty. but, there were no significant difference of the other factors such as the age, gender, osteoporosis and delayed operation.
CONCLUSION
The variable factors which affect the mortality rate of the hip fractures in the elderly patients whose age over 70 were mostly determined by underlying diseases, ASA grade, and cemented bipolar hemiarthroplasty. Further study should be necessary for the factors influencing on the mortality rate. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Finite element modeling and simulation of hip joints in elderly women: for development of protective clothing against fracture
Jinhee Park, Yun Ja Nam
International Journal of Clothing Science and Technology.2020; 32(5): 661. CrossRef - Anesthetic considerations for surgical treatment of geriatric hip fracture
Dong Kyu Lee, Seunguk Bang, Sangseok Lee
Anesthesia and Pain Medicine.2019; 14(1): 8. CrossRef - The Influence of Stroke on Postoperative Prognosis of Femoral Intertrochanteric Fractures
Youn Soo Hwang, Kyu Pill Moon, Kyung Taek Kim, Won Seok Park, Joon Yeon Song, Jeong Hoon Chae
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2016; 51(4): 273. CrossRef - Analysis of the Risk Factors and Clinical Outcomes of Femoral Intertrochanteric Fractures in Patients over 65 Years Old
Chul Hong Kim, Kyu Yeol Lee, Sung Soo Kim, Myung Jin Lee, Lih Wang, Hyeon Jun Kim, Jung Mo Kang
Hip & Pelvis.2013; 25(2): 127. CrossRef - Postoperative Mortality and the Associated Factors in Elderly Patients with Hip Fracture
You-Sung Suh, Yong-Beom Kim, Hyung-Suk Choi, Hong-Kee Yoon, Gi-Won Seo, Byung-Ill Lee
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2012; 47(6): 445. CrossRef - Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Complications Following Hip Surgery
Kuen Tak Suh, Seung Joon Rhee, Jung Sub Lee, Jeung Il Kim
Hip & Pelvis.2012; 24(2): 71. CrossRef - Current Recommendations for Laboratory Testing and Use of Bone Turnover Markers in Management of Osteoporosis
Jehoon Lee, Samuel Vasikaran
Annals of Laboratory Medicine.2012; 32(2): 105. CrossRef - The Daily Life Functions of Elderly Peritrochanteric Fracture Patients after Surgical Treatment
Dae Moo Shim, Tae Kyun Kim, Jong Yun Kim, Duk Hwa Choi, Joung Suk Lee, Seong In Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2012; 25(1): 8. CrossRef - One-Year Mortality Rate of Patients over 65 Years Old with a Hip Fracture
Phil Hyun Chung, Suk Kang, Jong Pil Kim, Young Sung Kim, Ho Min Lee, Young Hwa Choi
Hip & Pelvis.2011; 23(2): 137. CrossRef - Usefulness of the Cementless Stem for the Treatment of Hip Fracture in Elderly Patients with Osteoporosis - Comparative Analysis between Cementless Stem and Cemented Stem -
Joon Soon Kang, Kyoung Ho Moon, Rhu Seop Kim, Sang Ho Lee, Jong Min Choi
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(1): 16. CrossRef - Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty for Hip Fractures in Patients Aged over 90 Years - The Factors Influencing the Postoperative Mortality -
Jun-Dong Chang, Je-Hyun Yoo, Sang-Soo Lee, Tae-Young Kim, Kyu-Hak Jung, Yong-Kuk Kim
Hip & Pelvis.2010; 22(4): 283. CrossRef - Determination of an Applicable FRAX Model in Korean Women
Dong-Yun Lee, Seung-Jae Lim, Young-Wan Moon, Yong-Ki Min, DooSeok Choi, Byung-Koo Yoon, Youn-Soo Park
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2010; 25(11): 1657. CrossRef - Postoperative Mortality and the Associated Factors for Senile Hip Fracture Patients
Dong-Soo Kim, Hyun-Chul Shon, Yong-Min Kim, Eui-Sung Choi, Kyoung-Jin Park, Se-Hyuk Im
The Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2008; 43(4): 488. CrossRef
- Finite element modeling and simulation of hip joints in elderly women: for development of protective clothing against fracture
- 726 View
- 0 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Treatment of Fractures of the Hip in Children
- Do Hyun Moon, Jang Seok Choi, Jong Hun Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(3):283-286. Published online July 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.3.283
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the result of early anatomical reduction and internal fixation of hip fracture in children.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From January 1996 to July 2002, 21 cases (mean, 9 years) of hip fracture were available for follow-up more than 1 year. We performed early anatomical reduction and internal fixation within 24 hours as possible. Fractures were classified according to the 4 types described by Delbet. The results were analyzed according to the functional results by Ratliff and the incidence of complication.
RESULTS
There were no type I, 7 type II, 10 type III and 4 type IV fractures. Avascular necrosis of femoral head in 2 cases (type II, III). Functional result was 18 Good, 1 Fair and 2 Poor.
CONCLUSION
Fractures of the hip in children have been associated with a very high rate of serious complications, but our treatment by early anatomical reduction and interal fixation reduced rates of complication and had good functional result.
- 380 View
- 2 Download

- Morbidity and Mortality of Bilateral Hip Fractures in Elderly Patients
- Suk Ku Han, Nam Yong Choi, Seong Jin Park, Seong Keun Lee, Chan Woong Moon
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(4):788-794. Published online October 31, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.4.788
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to estimate the morbidity and mortality rate of bilateral hip fractures in elderly patients compared to that in unilateral hip fractures and to evaluate it's related risk factors.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty-two cases of bilateral hip fractures in patients who were older than 70 years with at least two year follow-up were included in our study. We analysed the risk factors of bilateral hip fractures by comparing with age, sex and diagnosis matched 22 cases of ipsilateral hip fractures including onset of secondary fracture, injury mechanism and the rate of morbidity and mortality, respectively.
RESULTS
The onset of secondary fracture and death were mostly within 1 year after operation for the first hip fracture. Comorbidity of cardiovascular, neurologic, urologic or history of previous fracture and decreased ambulation ability were related with the occurrence of bilateral hip fractures. The rate of morbidity and mortality of bilateral hip fractures were about two- fold than that of ipsilateral hip fractures. High mortality rate was noted in patients who had operation delay from injury. But no significant relationship between nutrition, body weight or bone mineral density and the development of secondary hip fractures.
CONCLUSION
To prevent the occurence of bilateral hip fractures which had more serious results than that of ipsilateral hip fractures, more aggressive rehabilitation to improve walking ability and appropriate environmental circumstances to avoid falls were important, especially in older patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessment of the Clinical Features of Bilateral Sequential Hip Fractures in the Elderly
Duk-Hwan Kho, Ju-Yong Shin, Hyeung-June Kim, Dong-Heon Kim
The Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2009; 44(3): 369. CrossRef
- Assessment of the Clinical Features of Bilateral Sequential Hip Fractures in the Elderly
- 669 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Treatment of the Hip fracture in the Dementia Patients
- Ui Seoung Yoon, Keun Woo Kim, Yong Hoon Kim, Hak Jin Min, Kook Hyoung Cho, Sang Lim Kim, Hyong Tack Choi
- J Korean Soc Fract 1999;12(4):767-772. Published online October 31, 1999
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1999.12.4.767
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
: The goal of treatment in elderly patients with hip fractures is restoration of function to preoperative ambulatory statuf as early as possible. The dementia patients who live in the asylum for the old need longer rehabilitation program for restoration of function, especially walking ability. The authors compare the modalities of the treatment for the hip fracture in the view point of walking ability.
MATERIALS and METHODS
: The twenty-eight dementia patients were operated due to hip fracture. Femur neck fractures were 7 cases, and femur intertrochanteric fractures were 21 cases. The authors analyze these patient on the recovery of walking ability. One patient who died immediately after operation was excluded in thil study. The patients were divided into two groups. Of 27 patients, 13 patients were treated with osteosynthesis(Group I), and remaining 14 patients were treated with hemidrthroplasy(Group II).
RESULTS
Fixation loss was treated with hemiarthroplasty in two case of osteosynthesis. The dislocation was treated with open reduction in one cafe of hemiarthioplasty. In the group I, the walking abilities were significantly different between the preoperative(3.85) and the postoperative at 2 weeks(2.46), at 2 months(2.73) and at the final follow-up(2.55)(P<0.05). In the group II, the walking abilities were not significantly different between the preoperative (2.57) and the postoperative at 2 weeks(2.14), at 2 months(2.36) and at the final follow- up(2.29)(P>0.05).
CONCLUSION
: Although there is no difference between two groups in final walking ability, The group treated with endoprosthesis showed earlier recovery of safting ability. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- CORR Insights®: What Are the Risk Factors for Dislocation of Hip Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty Through the Anterolateral Approach? A Nested Case-control Study
Eckart Mayr
Clinical Orthopaedics & Related Research.2016; 474(12): 2630. CrossRef - Risk Factors Associated with Dislocation after Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty in Elderly Patients with Femoral Neck Fracture
Yeesuk Kim, Joon-Kuk Kim, Il-Han Joo, Kyu-Tae Hwang, Young-Ho Kim
Hip & Pelvis.2016; 28(2): 104. CrossRef
- CORR Insights®: What Are the Risk Factors for Dislocation of Hip Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty Through the Anterolateral Approach? A Nested Case-control Study
- 527 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Mortality Rate in Older Patients Who Have a Hip Fracture
- Joo Chul Ihn, Poog Taek Kim, Il Hyung Park, Shin Yoon Kim, Chang Wug Oh, Jae Hyung Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1997;10(1):1-7. Published online January 31, 1997
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1997.10.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The significant risk to life associated with the hip fracture has long been recognized, and the reports of poor prognosis are well known with wide range of mortality rates. We retrospectively studied 164 patients(older than 60 years) who had a hip fracture to determine the effects of the age, treatment methods, pre-existing medical condition, operative delay after injury, type of fracture, and others on patient mortality. The summarized results were as follows ; 1. One hundred twenty three patients survived and forty one patients died(overall mortality rate; 25.0%). 2. Twenty one patients died within one year(one-year mortality rate, 12.8%). 3. Mortality was related to age of patient at injury, ASA classification, absense or presence of operative treatment, operation-related complication, which were statistically ignificant (P<0.05). 4. The operative delay after injury did not influence mortality, but we think that it is not signifcant because this study was done retrospectively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of the Risk Factors and Clinical Outcomes of Femoral Intertrochanteric Fractures in Patients over 65 Years Old
Chul Hong Kim, Kyu Yeol Lee, Sung Soo Kim, Myung Jin Lee, Lih Wang, Hyeon Jun Kim, Jung Mo Kang
Hip & Pelvis.2013; 25(2): 127. CrossRef - The Analysis of Postoperative Mortality after Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty for Hip Fractures in the Elderly
Dukhwan Kho, Kyoungmo Nam, Sunghak Oh, Hyeungjune Kim
Hip & Pelvis.2013; 25(4): 267. CrossRef - Postoperative Mortality and the Associated Factors in Elderly Patients with Hip Fracture
You-Sung Suh, Yong-Beom Kim, Hyung-Suk Choi, Hong-Kee Yoon, Gi-Won Seo, Byung-Ill Lee
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2012; 47(6): 445. CrossRef - One-Year Mortality Rate of Patients over 65 Years Old with a Hip Fracture
Phil Hyun Chung, Suk Kang, Jong Pil Kim, Young Sung Kim, Ho Min Lee, Young Hwa Choi
Hip & Pelvis.2011; 23(2): 137. CrossRef - Postoperative Mortality and the Associated Factors for Senile Hip Fracture Patients
Dong-Soo Kim, Hyun-Chul Shon, Yong-Min Kim, Eui-Sung Choi, Kyoung-Jin Park, Se-Hyuk Im
The Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2008; 43(4): 488. CrossRef
- Analysis of the Risk Factors and Clinical Outcomes of Femoral Intertrochanteric Fractures in Patients over 65 Years Old
- 604 View
- 1 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Epidemiology of Senile Fractures of the Proximal femur, 1983-1992
- Chang Ju Lee, Won Ho Cho, Ho Guen Jang, Soo Jung Choi, Jong Oh Ha
- J Korean Soc Fract 1994;7(2):331-340. Published online November 30, 1994
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1994.7.2.331
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The risk of fracture of the proximal femur is high for individuals with metabolic bone disease, or with low bone mass associated with advanced age. The menopause is generally believed to be an important factor in bone loss in women. In these group, even minor trauma(low energy injury) may result in fractures, while much greater force is needed to produce a fracture in people with higher bone mass. This study is aimed at ascertaining the age, sex and type-specific incidences in the hip fracture, the difference of frequency between the neck and trochanteric fracture and the change in the averse age of the hip fracture patient. All patient from this hospital with a diagnosis of fracture of the neck and trochanteric region of the femur during the period 1983 to 1992 were reviewed for this study. Patients with fracture resulting from metastatic lesions were excluded. The original medical records were reviewed for each patient, data were entered on protocol disinged for the study. The data included basic demographic informations such as patients age and sex, type of fracture of the femur neck or trochanter, type of the low/high energy injury, immediate cause of accidents, presence of the cormorbid diseases, and safety factors inducing fall accidents in home or outside. During the years 1983-1992, a total 240 patients with fractures of the proximal femur were identified from the operating recordings. Among them, data of 201 patients could be entered on protocol through the retrieved records. 1. Of 201 patients, 65 years or older are 117. 39 are men and 78 are women, 103 are low energy injury and 14 are high,57 are sustained by fractures on the neck of the femur and 60 are sustained on the trochanter. 2. Mean age of the 117 patients over 65 years old is 76 years. Those of men and women are equaly 76 years old. 3. Of 57 patients sustained with the fractures on the neck of the femur, their mean age is 71 years. Men are 18 patients, their mean age is 76 years. Women are 39 patients, their mean age is 75 years. 4. Of 60 patients sustained with the fractures on the trochanter of the femur, mean age is 76 years. Men are 22 patients, their mean age is 75 years. Women are 38 patients, their mean age is 77 years. 5. The cormorbid common diseases are the hypertension, cataract, diabetes mellitus(DM), celebre-vascular accidents(CVA), pulmonary tuberculosis, asthma, chronic obstrutive polmonary disease(COPD), mitral insuficiency(Ml), chronic heart failure(CHF), and chronic renal failure(CRF) in order of.
- 270 View
- 0 Download

- Treatment of hip fracture in elderly over sixty a comparison studybetween the internal fixation and arthroplasty
- Sung Kwan Hwang, Yong Seok Choi
- J Korean Soc Fract 1992;5(1):121-128. Published online May 31, 1992
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1992.5.1.121
- 404 View
- 0 Download

- Problems in the use of Compression Hip Screw in the Treatment of Hip Fractures
- Myung Sang Moon, In Ju Lee, Nam Yong Choi, Dong Soo Choi
- J Korean Soc Fract 1990;3(1):96-102. Published online May 31, 1990
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1990.3.1.96
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Though compression hip screw system has many advantages over the other fixation devices in the treatment of hip fractures, surgeons were frequently encountered by the intraoperative and postoperative complications leading to poor result. In reviewing out series of hip fractures treated with this device, between January 1983 and December 1988, serious complications developed in 5 cases, Additionally, three cases who were referred to our hospital during the same period were included in this study. The authors analyzed these 8cases, and found that the complications could have been prevented in using compression hip screw system for the treatment of hip fractures. The purpose of this paper is to re-emphasize the importance of 1) strict application of indication, 2) familiarity with surgical technique and handing instruments, 3) radiologic examination during surgery, 4) good postoperative care.
- 442 View
- 0 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


