Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 34(2); 2021 > Article
- Case Report Injury of the Ascending Branch of the Lateral Femoral Circumflex Artery Caused by a Spike of the Displaced Lesser Trochanter in an Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture - A Case Report -
- Soon Ho Huh, Hong-Man Cho, Jiyeon Park
-
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma 2021;34(2):71-75.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2021.34.2.71
Published online: April 30, 2021
2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Gwangju Veterans Hospital, Gwangju, Korea
- 561 Views
- 2 Download
- 2 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
Abstract
Although vascular injuries associated with femoral intertrochanteric fractures have been reported infrequently, bleeding due to vascular injury can lead to severe complications that can be potentially life and limb-threatening. The authors report a case of an injury of the ascending branch of the lateral femoral convolutional artery in a patient who underwent surgical treatment for a femoral intertrochanteric fracture. Vascular injury occurred due to the sharp margin of displaced lesser trochanter five weeks after surgery. Percutaneous transcatheter embolization was done and improved without additional complications. Therefore, the surgeons need to be aware of possible associated vascular injuries caused by displaced lesser trochanter fragments in femoral intertrochanteric fractures.
Published online Apr 23, 2021.
https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2021.34.2.71
Injury of the Ascending Branch of the Lateral Femoral Circumflex Artery Caused by a Spike of the Displaced Lesser Trochanter in an Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture: A Case Report
Abstract
Although vascular injuries associated with femoral intertrochanteric fractures have been reported infrequently, bleeding due to vascular injury can lead to severe complications that can be potentially life and limb-threatening. The authors report a case of an injury of the ascending branch of the lateral femoral convolutional artery in a patient who underwent surgical treatment for a femoral intertrochanteric fracture. Vascular injury occurred due to the sharp margin of displaced lesser trochanter five weeks after surgery. Percutaneous transcatheter embolization was done and improved without additional complications. Therefore, the surgeons need to be aware of possible associated vascular injuries caused by displaced lesser trochanter fragments in femoral intertrochanteric fractures.
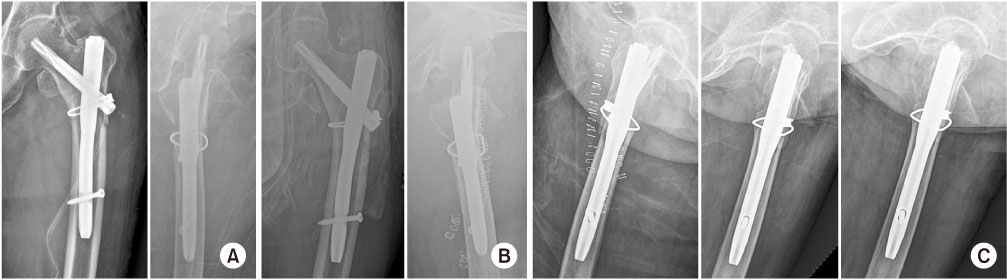
Fig. 1
(A) Simple radiograph of left femur anteroposterior (AP) and lateral showed the reduction state of intertrochanter femoral fracture with proximal femoral nail anti-rotation (PFNA) with drain insertion state and anterior and superior migration of lesser trochanter with sharp inferior margin. (B) Postoperative simple radiograph of the left femur AP and lateral showed a reduction of an intertrochanteric femoral fracture with the PFNA. (C) Follow-up postoperative radiograph until discharge showed gradual migration of the lesser trochanter superior and anterior compared to the right after surgery.
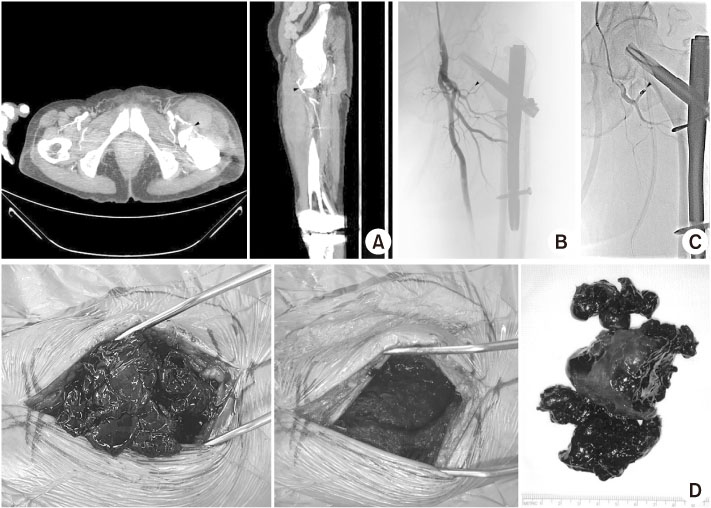
Fig. 2
(A) Computed tomographic angiography showed a massive hematoma near the branch of lateral circumflex femoral artery irritated by the sharp inferior margin of the lesser trochanter that was displaced superior and anterior (arrowheads). (B) Percutaneous transcatheter angiogram showed cutting of the ascending branch of the lateral circumflex femoral artery because of the sharp inferior margin of the displaced lesser trochanter (arrowhead). (C) After superselection of the bleeding artery using a microcatheter and guidewire, embolization of the bleeding artery was done using micro-coil (3.2 mm, 1×; 4.2 mm, 1×) (arrowhead). No extravasation of the left deep femoral artery was observed in the post-embolization angiogram. (D) Surgical evacuation of the hematoma near the vastus lateralis and intermedius was done under spinal anesthesia.
Financial support:None.
Conflict of interests:None.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS


 Cite
Cite

