Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Comparative results of the femoral neck system versus the dynamic hip screw for stable femoral neck fractures in older adults in Korea: a retrospective cohort study
- Byung-Chan Choi, Byung-Woo Min, Kyung-Jae Lee, Jun-Sik Hong
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):203-211. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00276
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
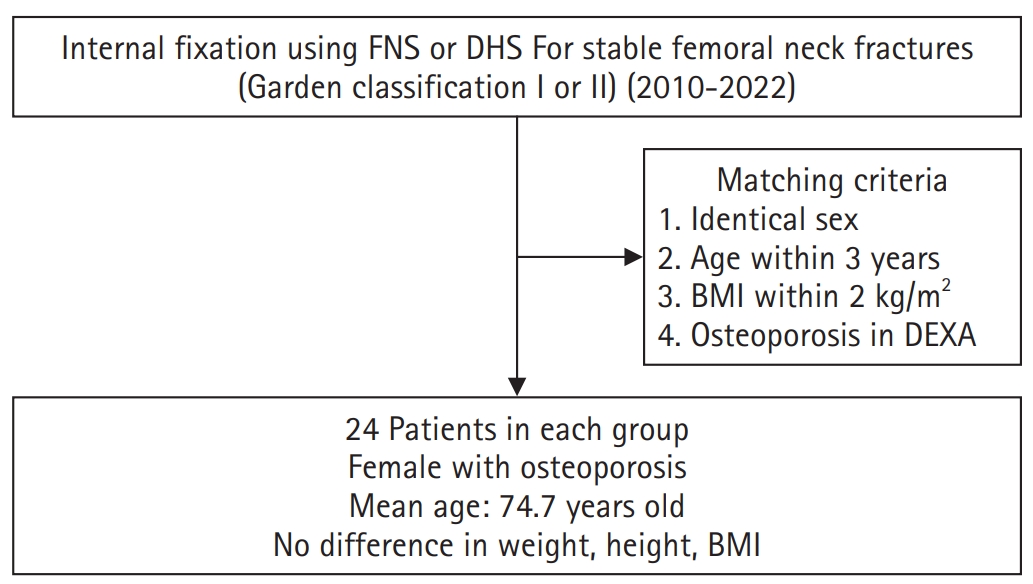
This study aimed to compare the clinical and radiological outcomes of the femoral neck system (FNS) and the dynamic hip screw (DHS) for the internal fixation of stable femoral neck fractures in older adults.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study included 48 matched older adult patients based on sex, age, BMI, and osteoporosis status, who had undergone internal fixation with either FNS or DHS for stable femoral neck fractures between January 2010 and December 2022. To minimize selection bias, a 1:1 case-control matching was performed based on sex, age, body mass index (BMI), and the presence of osteoporosis. A total of 48 patients (24 in each group) were included. We compared perioperative data (operation time, hemoglobin change, transfusion rate), functional outcomes using the Koval score, and radiological outcomes, including union rate, femoral neck shortening, and complication rates.
Results
The mean operation time was significantly shorter in the FNS group than in the DHS group (60.9 minutes vs. 70.8 minutes; P=0.007). There were no statistically significant differences between the two groups in the union rate (87.5% in FNS vs. 95.8% in DHS), femoral neck shortening, final Koval score distribution, or overall complication rates (12.5% in both groups).
Conclusions
For treating stable femoral neck fractures in older adults, the FNS demonstrated comparable clinical and radiological outcomes to the DHS, with the distinct advantage of a shorter operation time. While these findings suggest that the FNS is a promising and safe alternative that may reduce the surgical burden, definitive conclusions are precluded by the small sample size, warranting further research to corroborate these results. Level of evidence: IV.
- 336 View
- 10 Download

Review Articles
- Avulsion fractures around the hip joint and pelvis
- Won-Sik Choy, Yonghan Cha, Jung-Taek Kim, Jun-Il Yoo, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):53-62. Published online March 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Avulsion fractures occur when tendons or ligaments are subjected to forces greater than they can withstand at the apophysis or enthesis, regardless of fusion status. The pelvis and hip joint are vulnerable to these injuries due to the diverse muscular structures in these structures, which serve as origins for multiple muscles leading to the lower extremities. Pelvic avulsion fractures commonly affect young athletes, but can also occur in adults. The diagnosis typically involves assessing trauma history, a clinical examination, and radiographic imaging. If the diagnosis is unclear, additional tests such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging may assist in the diagnosis and provide useful information for treatment decisions. While most avulsion fractures respond well to conservative treatment, surgical intervention may be preferred in severe displacements, cases of significant retraction in active athletes, or when a faster recovery is necessary. Chronic or neglected injuries may lead to excessive osseous formation around the pelvis, causing impingement syndromes. Recognizing characteristic radiological findings based on pelvic anatomy helps to make an accurate diagnosis, as chronic injuries can mimic tumors or infectious conditions, necessitating a careful differential diagnosis.
- 5,227 View
- 88 Download

- Avulsion Fractures around the Hip Joint and Pelvis
- Ha-Yong Kim, Hajun Jang, Jung-Taek Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Jun-Il Yoo, Won-Sik Choy, Yonghan Cha
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(3):150-157. Published online July 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.3.150
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Avulsion fractures occur when tendons or ligaments are subjected to forces greater than they can withstand at the apophysis or enthesis, regardless of the fusion status. Given the diverse muscular structures around the pelvis and hip joint, which serve as origins for multiple muscles leading to the lower extremities, these areas are vulnerable to such injuries. Pelvic avulsion fractures commonly af-fect young athletes, but they can also occur in adults. Diagnosis typically involves assessing the trauma history, clinical examination, and radiographic imaging. In cases of unclear diagnosis, additional tests, such as computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, may assist in treatment decisions and diagnosis. Although most avulsion fractures respond well to conservative treatment, surgical interven-tion may be preferred in severe displacements, significant retraction in active athletes, or when a faster recovery is necessary. Chronic or neglected injuries may lead to excessive osseous formation around the pelvis, causing impingement syndromes. Recognizing the characteristic radiological findings based on the pelvic anatomy aids in accurate diagnosis because chronic injuries might mimic tumors or infectious conditions, necessitating a careful differential diagnosis.
- 1,108 View
- 34 Download

Original Articles
- Analysis of Missed Fractures by Bone Scan in Elderly Hip Fracture Patients with Osteoporosis
- Tae Hun Lee, Yeong Hyun Lee, Seo Won Kang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(3):144-149. Published online July 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.3.144
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The incidence of hip fractures is increasing due to an increase in elderly populations because elderly patients often have accompanying diseases, such as cognitive impairment or dementia, which may lead to missed fractures. Therefore, this study assessed the utility of bone scans in detecting missed fractures in elderly patients.
Materials and Methods
This study analyzed the data from 178 patients treated from January 2014 to March 2023. The inclusion criteria were patients who had hip fractures with osteoporosis over 70 years old. Bone scans were performed on average 10 days after injury. The rate and trend of missed fractures not detected in the initial diagnosis were determined based on sex, age, dementia status, and the presence of osteoporosis.
Results
Among the 178 hip fracture patients over 70 years old, 37 patients had a history of being diagnosed with dementia, and 141 patients had never been diagnosed. Missed fractures were confirmed in 49 cases (42 patients) (23.6%). The dementia group had 13 missed fractures, and the non-dementia group had 36 missed fractures, but there was no significant difference. Rib fractures were most common, followed by vertebral fractures.
Conclusion
Missed diagnoses of fractures were common among elderly hip fracture patients. A whole body bone scan appeared to be effective in detecting missed fractures. Therefore, identifying accompanying fractures through bone scans and delivering appropriate treatment can play an important role in postoperative rehabilitation.
- 510 View
- 8 Download

- Effect of Coincident Hip Fracture on Distal Radius Fracture in Patients Treated with a Volar Locking Plate: A Matched-Pair Analysis of Elderly Patients
- Hyoung-Seok Jung, Min-Su Chu, Jae-Sung Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(3):137-143. Published online July 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.3.137
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Although the incidence of simultaneous distal radius and hip fractures in older patients is minimal, patients with these coincident types of fractures exhibit unique features. This study analyzed the outcomes associated with operative treatment involving volar-locking plates in patients who sustained distal radius fractures and hip fractures and compared them with those in matched control patients who had undergone treatment for isolated distal radius fractures.
Materials and Methods
Between 2010 and 2015, 34 patients, who met the criteria for hip and distal radius fractures, were retrospectively reviewed. Thirty-four matched patients who underwent volarlocking plate fixation for isolated distal radius fractures during the same period were also reviewed. The clinical outcomes between the groups were compared using postoperative radiological parameters.
Results
The radiological assessment revealed a better radial length and inclination in the control group than in the study group at the final follow-up. In other words, patients with coincident hip fractures showed a higher tendency for loss of reduction. Despite the differences in radiological parameters, no significant differences in clinical outcomes were observed, except for grip strength.
Conclusion
Although volar-locking plating provides greater stabilization, a loss of reduction occurred in patients with coincident hip fractures.
- 606 View
- 8 Download

Review Article
- Osteoporotic Hip Fracture: How We Make Better Results?
- Byung-Chan Choi, Kyung-Jae Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(1):52-59. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.1.52
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The prevalence of osteoporosis and incidence of osteoporotic fractures is increasing gradually as life expectancy is prolonged and the aged population increases. Osteoporotic hip fractures (femoral neck fractures and femoral intertrochanteric fractures) have high mortality because the patients with these fractures are elderly and have several comorbidities. Thorough preparation and a multidisciplinary approach in the preoperative period are critical, and early surgery is recommended. There are also several principles to treat osteoporotic hip fractures and prevent fixation failures. Many studies have suggested various treatment methods for femoral neck fractures and femoral intertrochanteric fractures. Functional recovery treatment is essential based on the patient’s health and activity levels. Finally, aggressive management of osteoporosis and the prevention of falling is needed to treat osteoporotic hip fractures successfully.
- 448 View
- 21 Download

Original Article
- Cephalomedullary Nailing with an Additional Cannulated Screw Fixation in Basicervical Femur Fractures
- Keong-Hwan Kim, Woo Dong Nam, Yeon Sik Heo, Gu-Hee Jung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(1):22-29. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.1.22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study is to analyze the clinical results of patients with basicervical fracture undergoing cephalomedullary nailing (CMN) with an additional cannulated screw fixation compared to only performing CMN. We hypothesized that a difference may exist in the clinical outcomes if an ad-ditional screw is fixed with CMN compared to only performing CMN in basicervical fracture.
Materials and Methods
A total of 28 consecutive patients who underwent CMN for basicervical fracture were included. In 9 cases, only CMN was conducted, and in 19 cases, an additional cannulated screw fixation was performed with CMN. Bone union, sliding distance, reduction status, and fixation failure were evaluated by postoperative radiography, and ambulatory ability was evaluated by functional results. These findings were compared between a group of CMN and a group of CMN with an additional cannulated screw.
Results
There were 4 males and 24 females with a mean age of 84 years (range, 69–100 years). No significant difference was found in postoperative reduction, tip-apex distance, bone union, and walking function recovery after surgery between the two groups, but in the sliding distance of the lag screw, the CMN group demonstrated more sliding (6.2 mm [range, 2.5–13.4 mm] vs 3.5 mm [range, 0.1– 9.2 mm]; p=0.045). Among the two groups, only one case of fixation failure at the postoperative four months was observed in the CMN group (p=0.321), and hemiarthroplasty with nail construct removal was performed.
Conclusion
CMN with additional cannulated screw fixation is a safe and reliable surgical option in basicervical fracture. It provided favorable clinical outcomes and may be a good alternative for treating basicervical fracture.
- 708 View
- 11 Download

Review Article
- Hip Fractures in the Elderly: Perioperative Management and Prevention of Medical Complications
- Keong-Hwan Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(1):39-44. Published online January 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.1.39
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Elderly patients with hip fractures are at an increased risk of developing medical complications with higher mortality rates. Most patients require surgical treatment, and an early surgical intervention can reduce complications and lower mortality risk. A restrictive red blood cell transfusion strategy is usually applied, and the amount of transfusion can be reduced through medications such as tranexamic acid. Delirium can be prevented using non-pharmacological methods. In addition, it is necessary to prevent venous thromboembolism through mechanical or chemical prophylaxis. A multidisciplinary approach using the ERAS (Enhanced Recovery After Surgery) protocol and orthogeriatric care can help to reduce medical complications and mortality.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Treatment of Incompletely Displaced Femoral Neck Fractures Using Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced in Patients Older Than 50 Years of Age
Jee Young Lee, Gyu Min Kong
Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma.2025; 39(7): 352. CrossRef
- Treatment of Incompletely Displaced Femoral Neck Fractures Using Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced in Patients Older Than 50 Years of Age
- 941 View
- 30 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- Comparison of the Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of TFNA (Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced) and PFNA-II (Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation-II) Treatment in Elderly Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures
- Min Sung Kwon, Young Bok Kim, Gyu Min Kong
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(4):162-168. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.4.162
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Trochanteric fixation nail advanced (TFNA) was modified to compensate for the shortcomings of proximal femoral nail antirotation-II (PFNA-II). The clinical and radiological outcomes of surgeries us-ing the PFNA-II and TFNA for femoral intertrochanteric fractures were compared.
Materials and Methods
Eighty-two patients who underwent surgeries using PFNA-II or TFNA were analyzed. Only those who were followed up for more than a year were enrolled. Bone union, shortening of the femoral neck, and the tip–apex distance of the intramedullary nail were compared in the radiological findings. Clinical outcomes, including the frequency of complications and gait ability (Koval score), were also assessed.
Results
The mean follow-up periods were 22 and 19 months for the PFNA-II and TFNA groups, re-spectively. In the PFNA-II group, two cases of femoral head cut-out and one case of varus collapse were observed. In the TFNA group, only one case of femoral head cut-out was observed; however, there was no significant difference in the frequency of complications between the two groups (p=0.37). Ad-ditionally, both the shortening of the femoral neck and the decrease in gait ability after surgery showed relative improvement in the TFNA group compared to the PFNA-II group; however, there was no sig-nificant difference between the two groups.
Conclusion
The use of both TFNA and PFNA-II was associated with satisfactory outcomes. In patients who underwent surgeries using TFNA, the recovery of gait ability, frequency of complications, and short-ening of the femoral neck were not significantly different from PFNA-II, suggesting that both are suitable instrument choices for intertrochanteric fracture treatment. However, the clinical significance must be further assessed using a larger group of patients over a longer follow-up period in future studies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Treatment of Incompletely Displaced Femoral Neck Fractures Using Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced in Patients Older Than 50 Years of Age
Jee Young Lee, Gyu Min Kong
Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma.2025; 39(7): 352. CrossRef - Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures Treated with Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced and Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation-II: Correlation between Lateral Sliding of the Helical Blade and Lateral Trochanteric Pain
Sung Yoon Jung, Myoung Jin Lee, Lih Wang, Hyeon Jun Kim, Dong Hoon Sung, Jun Ha Park
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2024; 59(3): 208. CrossRef
- Treatment of Incompletely Displaced Femoral Neck Fractures Using Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced in Patients Older Than 50 Years of Age
- 2,189 View
- 30 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Benefits of a Demineralized Bone Matrix in Osteoporotic Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture Patients
- Se Jin Kim, Hong-Man Cho, Myung Cheol Jung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(4):151-161. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.4.151
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Osteoporosis causes various fixation failures in patients with intertrochanteric fractures. This study aimed to investigate the effect of a demineralized bone matrix (DBM) for cancellous or cortical bone defects on internal fixation in older osteoporotic patients with intertrochanteric fractures.
Materials and Methods
Among patients with intertrochanteric fractures who underwent surgical treatment from January 2016 to December 2021 at a facility, 171 patients were AO/OTA type 31-A1 and type 2 fractures which are considered relatively stable. The patients were grouped based on DBM use (Group A: DBM use, Group B: DBM non-use), and their clinical and radiology results were analyzed retrospectively. The patients were then subdivided into Group A-a and -b after removing factors that could cause treatment failures, such as the reduction status and location of the helical blade, and then further subdivided (Group A-a-1/2/3/4 and Group B-b-1/2/3/4) according to cancellous or cortical bone defects that could accompany intertrochanteric fractures. The time to full weight-bearing (FWB) and Harris hip score (HSS) 3 months after surgery in these subgroups were investigated.
Results
There was no significant difference in the clinical radiology results and complications between Group A and Group B. However, the time to FWB (p<0.001) and HSS (p=0.029) were significantly superior in Group A. In Group A-a with DBM use, after removing the risk factors for intertrochanteric fracture failure, the time to FWB (p=0.055) was close to the significance level, and HSS (p=0.036) was significantly superior. In Group A-a-1 (cancellous defect only) and Group A-a-3 (cancellous and cortical defect), the time to FWB (p=0.088, 0.052) was close to the significance level, and the HSS (p=0.039, 0.018) was significantly superior when DBM was used.
Conclusion
In patients with intertrochanteric fractures of AO/OTA type 31-A2.3 or less, if stable reduction and firm fixation are achieved, selective DBM use may help early recovery after surgery.
- 317 View
- 2 Download

- Mortality-Related Risk Factors in Total Hip Arthroplasty for Femoral Neck Fractures in Elderly Patients
- Jae Sung Suh, Hyung Gon Ryu, Young Ju Roh, Dae Won Shin
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(2):51-56. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.2.51
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Total hip arthroplasty (THA) using dual mobility components (DMC) is a reasonable surgical option for displaced femoral neck fractures in elderly patients, resulting in lower dislocation rates and improved stability. The purpose of this study was to investigate the clinical outcomes and risk factors responsible for mortality in elderly patients who were diagnosed with a displaced femoral neck fracture and had undergone DMC-THA.
Materials and Methods
Out of 147 cases of THA from December 2018 to June 2020, a total of 79 cases were enrolled in this study, with the following characteristics: (1) Garden stage III or IV, (2) over 75 years of age, and (3) over 1 year of follow-up. All the patients received DMC-THA surgery using the anterolateral approach.
Results
The mean follow-up period was 15.0±8.43 months and a total of one dislocation case was observed. The mortality rate was 17.7% (14/79), and it was especially higher in patients with a past medical history of malignancy (odds ratio [OR]=7.18, p=0.03) or a cognitive disorder such as dementia (OR=5.48, p=0.03). Preoperative low initial hemoglobin levels (OR=0.65, p=0.04) and low UCLA (Uni-versity of California at Los Angeles) score (OR=0.47, p=0.02) were also associated with mortality.
Conclusion
When considering THA as a treatment approach in elderly patients with a displaced femoral neck fracture, a high mortality rate is expected in patients with low preoperative hemoglobin levels or a history of malignancy or cognitive disorders. Hence, thorough monitoring and management should be undertaken before and after surgery.
- 289 View
- 24 Download

Case Reports
- Recurrent Treatment Failure in Vancouver Classification Type C Periprosthetic Fractures around a Well Fixed Short Femoral Stem
- Byeong Yeol Choi, Hong-Man Cho, Jiyeon Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(1):16-20. Published online January 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.1.16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A short femoral stem (type 1 cementless stem) is being increasingly used to perform total hip arthroplasty; however, various types of intra- or postoperative periprosthetic fractures have been reported in recent times. A 66-year-old woman with a history of bilateral total hip arthroplasties using a type 1B femoral stem was admitted 2 months post-operation for a Vancouver type C periprosthetic fracture. She underwent open reduction and internal fixation; however, we observed recurrent non-union and plate breakage at the same site. In this case report, we discuss the factors associated with treatment failure in patients with a Vancouver type C periprosthetic fracture following type 1 femoral stem im-plantation.
- 242 View
- 0 Download

- Injury of the Ascending Branch of the Lateral Femoral Circumflex Artery Caused by a Spike of the Displaced Lesser Trochanter in an Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture - A Case Report -
- Soon Ho Huh, Hong-Man Cho, Jiyeon Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2021;34(2):71-75. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2021.34.2.71
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Although vascular injuries associated with femoral intertrochanteric fractures have been reported infrequently, bleeding due to vascular injury can lead to severe complications that can be potentially life and limb-threatening. The authors report a case of an injury of the ascending branch of the lateral femoral convolutional artery in a patient who underwent surgical treatment for a femoral intertrochanteric fracture. Vascular injury occurred due to the sharp margin of displaced lesser trochanter five weeks after surgery. Percutaneous transcatheter embolization was done and improved without additional complications. Therefore, the surgeons need to be aware of possible associated vascular injuries caused by displaced lesser trochanter fragments in femoral intertrochanteric fractures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Delayed Deep Femoral Artery Injury Secondary to Migrated Lesser Trochanter Fragment After Intertrochanteric Fracture Fixation: A Case Report and Updated Literature Review
Slavko Čičak, Josip Kocur, Vedran Farkaš, Petra Čičak, Stjepan Ištvanić, Marko Lovrić, Marko Perić, Nenad Koruga, Tomislav Ištvanić
Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Vascular Complications Following Trans-Trochanteric Fracture: Case Report and Literature Review
Robert Bot, Adrian Tirla, Simona Daniela Cavalu
Reports.2025; 8(4): 191. CrossRef
- Delayed Deep Femoral Artery Injury Secondary to Migrated Lesser Trochanter Fragment After Intertrochanteric Fracture Fixation: A Case Report and Updated Literature Review
- 376 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

Original Articles
- Risk Factors for Subsequent Contralateral Hip Fracture following Osteoporotic Hip Fracture Surgery
- Kyung-Jae Lee, Jung-Hoon Choi, Hee-Uk Ye, Young-Hun Kim, Kyung-Hwan Lim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2021;34(2):51-56. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2021.34.2.51
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the risk factors contributing to subsequent hip fractures in patients with osteoporotic hip fractures.
Materials and Methods
Between March 2008 and February 2016, 68 patients sustained a subsequent contralateral hip fracture after surgery for a primary osteoporotic hip fracture (Study group). The patients were compared with 475 patients who had been followed up for a minimum of one year with a unilateral osteoporotic hip fracture (Control group). The demographic data, bone mineral density (BMD), osteoporosis medication, osteoporotic fracture history, comorbid disease, type of surgery, preoperative, postoperative ambulatory capacity, and postoperative delirium in the two groups were compared.
Results
The demographic data, BMD, osteoporosis medication history, comorbid disease, type of surgery, and postoperative delirium were similar in the two groups. At three months after the primary surgery, the poor ambulatory capacity was significantly higher in the study group than the control group (p<0.001).
Conclusion
The ambulatory capacity after primary surgery is an important risk factor in the occurrence of subsequent hip fractures after osteoporotic hip fracture. Cause analysis regarding the poor ambulatory capacity after surgery will be necessary, and the development of a functional recovery program and careful management of the walking ability recovery will be needed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Osteoporotic Hip Fracture: How We Make Better Results?
Byung-Chan Choi, Kyung-Jae Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2024; 37(1): 52. CrossRef
- Osteoporotic Hip Fracture: How We Make Better Results?
- 546 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Risk Factors Affecting the Early Complications of Femoral Head Fractures
- HoeJeong Chung, Jin-Woo Lee, Dong Woo Lee, Hoon-Sang Sohn
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(4):204-209. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.4.204
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study analyzed the prognostic factors in patients with femoral head fractures by comparing two groups with and without complications.
Materials and Methods
A retrospective study was performed on femoral head fracture patients who visited two different level-1 trauma centers from January 1, 2014 to June 30, 2018. Thirty-three patients with a follow-up period of more than one year were included. Early complications were defined as fair or poor in the Thompson–Epstein clinical evaluation criteria and grades 3 or 4 in the Kellgren– Lawrence classification within one year after the fracture. The patients were divided into two groups, with and without early complications. Statistical analysis was performed for the nominal variables with a Fisher’s exact test and continuous variables using a Mann–Whitney U test.
Results
Nine patients (27.3%) had early complications, and there were no significant differences according to age, sex, treatment method, combined fractures, Pipkin classification, and AO/OTA classification between the two groups.
Conclusion
The prognosis in femoral head fractures is difficult to predict. Therefore, the validation of existing classifications or a new classification is necessary.
- 352 View
- 1 Download

- Treatment of Proximal Femur Fracture with a Newly Designed Nail: Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced (TFNA)
- Jae Youn Yoon, Ji Wan Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(4):189-195. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.4.189
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study evaluated the clinical results and implant safety of a newly developed implant, Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced (TFNA; DePuy Synthes), in the treatment of proximal femur fractures.
Materials and Methods
This was a retrospective cohort study of 26 patients diagnosed with proximal femur fracture and treated surgically with TFNA. The patients’ demographic data, surgical data, radiologic findings, and functional outcomes, including complications, were evaluated.
Results
The mean age of the patients was 71.2 years (95% confidence interval [CI], 68.2-74.2); 65.4% were female. The mean Carlson comorbidity index score was 5.4, and the mean Koval grade before fracture was 2.1. Fracture classification included four cases of AO/OTA 31.A1, nine cases of A2, six cases of A3, and seven cases of 32A including six cases of atypical femoral fractures. The mean operating time was 53.3 minutes (95% CI, 43.6-63.1). There were no early postoperative complications, such as postoperative infection, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, or in-hospital death, except one case of pneumonia. The mean Koval score at the postoperative six-month follow-up was 2.9. EuroQol-5 Dimension (EQ-5D) increased from 0.05 to 0.54 after three months and 0.72 at six months postoperatively. Bone union was observed in all cases with a mean union time of 12.9 weeks. No implant failure occurred, and no cases required secondary revision surgery.
Conclusion
A new intramedullary nail system, TFNA, showed excellent outcomes and safety in the surgical treatment of proximal femur fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intermediate Length Cephalomedullary Nails in Proximal Femoral Fractures: Review of Indications and Outcomes
Daniel Scott Horwitz, Ahmed Nageeb Mahmoud, Michael Suk
Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.2025; 33(19): 1071. CrossRef - Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures Treated with Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced and Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation-II: Correlation between Lateral Sliding of the Helical Blade and Lateral Trochanteric Pain
Sung Yoon Jung, Myoung Jin Lee, Lih Wang, Hyeon Jun Kim, Dong Hoon Sung, Jun Ha Park
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2024; 59(3): 208. CrossRef - Prospective randomized multicenter noninferiority clinical trial evaluating the use of TFN-advancedTM proximal femoral nailing system (TFNA) for the treatment of proximal femur fracture in a Chinese population
Lidan Zhang, Zhijun Pan, Xiaohui Zheng, Qiugen Wang, Peifu Tang, Fang Zhou, Fan Liu, Bin Yu, Frankie K. L. Leung, Alex Wu, Suzanne Hughson, Zhuo Chen, Michael Blauth, Anthony Rosner, Charisse Sparks, Manyi Wang
European Journal of Trauma and Emergency Surgery.2023; 49(3): 1561. CrossRef - Risk of shortening in operatively treated proximal femur fractures with cephalomedullary nails with dynamically versus statically locked helical blades
Nathan Cherian, Lasun Oladeji, Cole Ohnoutka, Dan Touhey, Madeline Sauer, Kyle A. Schweser, Mauricio Kfuri, James L. Cook, Gregory J. Della Rocca, Brett D. Crist
Injury.2023; 54(2): 669. CrossRef - GS Hip Nail versus Affixus Hip Fracture Nail for the Intramedullary Nailing of Intertrochanteric Fractures
Seungcheol Kwon, Minjae Lee, Heeyeon Lee, Jihyo Hwang
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(21): 6720. CrossRef - Comparison of the Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of TFNA (Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced) and PFNA-II (Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation-II) Treatment in Elderly Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures
Min Sung Kwon, Young Bok Kim, Gyu Min Kong
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2022; 35(4): 162. CrossRef - Analysis of Clinical and Functional Outcomes according to the Blood Sugar Control Status at the Time of Ankle Fractures Resulting from Rotational Injuries
Jun Young Lee, Dong Seop Lim, Seung Hyun Lee, Seo Jin Park
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2022; 35(4): 135. CrossRef - Conventional versus helical blade screw insertion following the removal of the femoral head screw: a biomechanical evaluation using trochanteric gamma 3 locking nail versus PFN antirotation
Hong Man Cho, Kwang Min Park, Tae Gon Jung, Ji Yeon Park, Young Lee
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and Radiologic Outcome of Intertrochanteric Fracture Treatment Using TFNA (Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced)
Hyeon Joon Lee, Hyun Bai Choi, Ba Rom Kim, Seung Hwan Jo, Sang Hong Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2021; 34(3): 105. CrossRef
- Intermediate Length Cephalomedullary Nails in Proximal Femoral Fractures: Review of Indications and Outcomes
- 1,479 View
- 20 Download
- 9 Crossref

Review Articles
- Treatment of Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures after Hip Arthroplasty
- Jung Hoon Choi, Jong Hyuk Jeon, Kyung Jae Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(1):43-51. Published online January 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.1.43
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Although the incidence of postoperative periprosthetic femoral fractures after hip arthroplasty is expected to increase, these complex fractures are still challenging complications. To obtain optimal results for these fractures, thorough clinical and radiographic evaluation, precise classification, and understanding of modern management principles are mandatory. The Vancouver classification system is a simple, effective, and reproducible method for planning proper treatments of these injuries. The fractures associated with a stable femoral stem can be effectively treated with osteosynthesis, though periprosthetic femoral fractures associated with a loose stem require revision arthroplasty. We describe here the principles of proper treatment for the patients with periprosthetic femoral fractures as well as how to avoid complications.
- 993 View
- 6 Download

- Total Hip Arthroplasty after Acetabular Fracture: Acute Phase and Delayed Phase
- Hwan Hee Lee, Se Won Lee, Weon Yoo Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(4):232-239. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.4.232
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The incidence of acetabular fractures in the elderly has increased because of the increasing elderly population. To determine the treatment plan for acetabular fractures, the patient's age, gait ability, presence or absence of osteoporosis and osteoarthritis, underlying disease, and fracture pattern should be considered. The application of total hip arthroplasty for acetabular fractures with the proper indications can be expected to have a good prognosis. In this paper, the application of total hip arthroplasty as a treatment method for acetabular fractures is divided into acute and delayed phases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Korean Medicine Treatments for Pain Reduction in Patients with Hip Fracture : A Retrospective Observational Study
Nam Hoon Kim, Min Seok Oh
Journal of Physiology & Pathology in Korean Medicine.2020; 34(5): 263. CrossRef
- Effect of Korean Medicine Treatments for Pain Reduction in Patients with Hip Fracture : A Retrospective Observational Study
- 609 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Principles for Management of Periprosthetic Acetabular Fractures after Hip Arthroplasty
- Chan Woo Park, Hyoung Keun Oh, Woo Suk Lee, Youn Soo Park, Seung Jae Lim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(3):148-156. Published online July 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.3.148
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Periprosthetic acetabular fracture (PAF) is an uncommon complication following hip arthroplasty. However, as the number of people needing hip prostheses continues to rise, the absolute number of PAF is expected to increase as well. These fractures may occur either intraoperatively or postoperatively. Postoperative fractures can be caused by traumatic events or by pathologic conditions related to periacetabular osteolysis. The management of PAF usually depends on the degree of displacement and the stability of the acetabular component. While most of non-displaced fractures can be managed nonoperatively by protected weight bearing, displaced fractures with unstable implants require surgical intervention, which is often technically challenging. This review summarized the latest findings on the epidemiology, the diagnosis, the classification, and the treatment of PAF.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Treatment of Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures after Hip Arthroplasty
Jung-Hoon Choi, Jong-Hyuk Jeon, Kyung-Jae Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2020; 33(1): 43. CrossRef
- Treatment of Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures after Hip Arthroplasty
- 1,044 View
- 24 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- Treatment of the Proximal Femoral Fracture Using the New Design Cephalomedullary Nail: Prospective Outcomes Study
- Young Ho Roh, Joseph Rho, Kwang Woo Nam
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(1):35-42. Published online January 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.1.35
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The aim of this study is to investigate the clinical performance and safety of Zimmer® natural nail cephalomedullary nail (ZNN CM nail) in the treatment of proximal femur fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The following research was conducted as a prospective, non-comparative, single center outcome study. Upon providing written informed consent, enrolled patients' data were collected and analyzed. Postoperative follow-up visits were scheduled at 6 weeks, 3 months, 6 months, and 1 year. Follow-up evaluation included radiographic assessment, physical examination, and quality of life and adverse events reports.
RESULTS
Thirty-nine patients were available for evaluation at one year postoperative. The patients reported the mean EuroQol-5 Dimension score increased after surgery: from 0.4 points at discharge (n=49) to 0.6 points at 1-year post-surgery (n=39). The mean Harris hip score also increased after surgery: from 56.3 points at discharge (n=49) to 72.1 points at 1 year (n=12). Bone union was seen in 64% (n=16) in 6 months and 95% (n=37) in 1 year.
CONCLUSION
The results of this 1-year follow-up study affirmed the effectiveness and safety of the ZNN CM nail in the treatment of proximal femur fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical and Radiologic Outcome of Intertrochanteric Fracture Treatment Using TFNA (Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced)
Hyeon Joon Lee, Hyun Bai Choi, Ba Rom Kim, Seung Hwan Jo, Sang Hong Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2021; 34(3): 105. CrossRef - Treatment of Proximal Femur Fracture with a Newly Designed Nail: Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced (TFNA)
Jae Youn Yoon, Ji Wan Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2020; 33(4): 189. CrossRef
- Clinical and Radiologic Outcome of Intertrochanteric Fracture Treatment Using TFNA (Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced)
- 608 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Evaluation of the Wearing Characteristics of Hip Protectors Based on Draping Pattern Design and Body Shape in Korean Elderly People
- Eunjin Jeon, Heeeun Kim, Heecheon You, Seunghoon Lee, Giwook Kim, Sunjung Yoon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(4):180-185. Published online October 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.4.180
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to verify the new hip protector design with respect to the comfort and mobility. The new hip protector was developed based on a pattern of draping and body shape of Korean elderly individuals.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
An wearing characteristics evaluation was conducted on 101 elderly women wearing hip protector using a questionnaire of preference and ease of wearing. Hip protectors, with existing and newly developed belt and underwear types, which were previously preferred by the Korean elderly, were evaluated.
RESULTS
The newly developed belt type (65.0%) and newly developed underwear type (30.1%) hip protectors were preferred to the existing type (3.9%) and existing underwear type (1.0%) ones. The convenience of the newly developed belt type was greater than 4 out of 5 points (1 for strongly disagree and 5 for strongly agree) for all nine measures, including fit, allowance, mobility, pad placement, pad thickness, pad size, material, design, ease of dressing, and ease of undressing. The newly developed hip protectors showed less discomfort than the existing ones. In particular, the newly developed belt type and developed underwear type improved sitting convenience by 31.1% and 26.1%, respectively, compared with the existing ones.
CONCLUSION
The hip protectors developed in the present study is expected to provide better fit for the body shape of Korean elderly individuals and prevent hip fracture due to fall. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Evaluation of Fall Impact Protective Clothing for the Elderly Women
Jung Hyun Park, Jin Suk Lee, Jeong Ran Lee
Fashion & Textile Research Journal.2018; 20(5): 569. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of Fall Impact Protection Pad
Jung Hyun Park, Jin Suk Lee, Jeong Ran Lee
Fashion & Textile Research Journal.2018; 20(4): 422. CrossRef
- Development and Evaluation of Fall Impact Protective Clothing for the Elderly Women
- 538 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The Cause of Primary Reduction Failure in Hip Dislocation with or without Hip Fracture
- Hee Gon Park, Yong Eun Shin, Sung Hyun Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(1):9-15. Published online January 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.1.9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
A rapid and accurate reduction is important for hip dislocated patients to avoid various potential complications, including avascular necrosis of the femoral head. We analyzed hip dislocation cases, ones that particularly failed during the primary reduction trial.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Eighty-seven patients with hip dislocation, who visited the emergency department between January 2007 and September 2015, were retrospectively analyzed. Of them, 68 patients were successfully treated in the first closed reduction trial, and the remaining 19 patients were unsuccessful. Of the 19 unsuccessful first trial, 12 patients were successfully treated in the second closed reduction; however, in the remaining 7 patients, open reduction was performed in the operation room with general anesthesia. Every closed reduction was practiced by at least 2 orthopedic doctors, and open reduction was performed by a single senior author.
RESULTS
The rate of first reduction failure was higher, with statistical significance, in patients aged under 50 years, male gender, and those with combined around hip fractures, including femoral head and acetabular fracture (p<0.05). In particular, the presence of impacted fracture fragment in the hip joint and large size of the impacted fracture fragment was highly related to the failure of second closed reduction trial requiring open reduction. Conversely, the method of reduction, Thompson-Epstein classification, Pipkin classification were not related to the failure of closed reduction statistically (p>0.05).
CONCLUSION
To evaluate the patients with hip dislocation, realizing the type of dislocation, presence of accompanied fracture, location and size of fracture fragment, age, as well as gender of patients is important. If the fracture fragment is impacted in the hip joint and the size of the fragment is large, then the operative treatment is considered, rather than the repetitive trial of closed reduction by constraint. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Atypical and unclassifiable hip dislocation with capsule and labrum incarceration: a case report and review of the literature
Francis Zifa Pentèce Zengui, Moise Radam Ellah, Kevin Bienvenu Parfait Bouhelo-Pam, Arnauld Sledge Wilfrid Bilongo-Bouyou, Nevil Stève Ngona Gampio Mvili, Marius Monka
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2025; 135: 111879. CrossRef - Traumatic obturator dislocation of the hip joint: About 2 cases and review of the literature
Z.F. Zengui, O. El Adaoui, M. Fargouch, O. Adnane, Y. El Andaloussi, M. Fadili
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2022; 93: 106983. CrossRef
- Atypical and unclassifiable hip dislocation with capsule and labrum incarceration: a case report and review of the literature
- 611 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The Role of Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate Graft in the Dynamic Hip Screw Fixation of Unstable Intertrochanter Fracture
- Chul Ho Kim, Ji Wan Kim, Eic Ju Lim, Jae Suk Chang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(4):250-257. Published online October 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.4.250
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to introduce our method of stabilizing unstable intertrochanteric fractures by using the dynamic hip screw (DHS) with a beta-tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP) graft and to compare the outcomes of this procedure with those of the conventional DHS without β-TCP.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients who underwent surgery by using DHS between March 2002 and January 2016 were retrospectively reviewed for analysis of the outcomes. The inclusion criteria were: 1) age of 60 years and older; 2) low-energy fracture resulting from a fall from no greater than the standing height; 3) multifragmentary pertrochanteric fracture (AO classification 31-A2.2, 2.3); and 4) follow-up of over 3 months. We compared 29 patients (29 hips) who underwent surgery, using DHS without β-TCP, with 29 age-sex matched patients (29 hips) who underwent surgery using DHS with grafted β-TCP granules to empty the trochanter area after reaming. We investigated the fracture union rate, union time, and length of lag screw sliding.
RESULTS
Bone union was achieved in all cases. The mean union time was 7.0 weeks in the β-TCP group and 8 .8 weeks in the non-β-TCP group. The length of lag screw sliding was 3.6 mm in the β-TCP group and 5 .5 mm in the non-β-TCP group. There were no implant failure cases in both groups.
CONCLUSION
The β-TCP graft for reinforcement DHS acquired satisfactory clinical outcomes for treating unstable intertrochanteric fractures.
- 309 View
- 3 Download

- Surgical Treatment for Stable 2-Part Intertrochanteric Femur Fracture Using Dynamic Hip Screw with 2-Hole Side Plate in Elderly Patients
- Kyung Hoon Lee, Suk Ku Han, Seung Jae Chung, Jongho Noh, Kee Haeng Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(3):192-199. Published online July 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.3.192
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the postoperative outcomes of elderly patients with stable 2-part intertrochanteric femur fractures surgically treated using dynamic hip screw with 2-hole side plate.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From February 2008 to January 2014, 50 patients older than the age of 65 years, who had been followed-up for more than 6 months after the operation at The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital were enrolled. A clinical evaluation of the skin incision length, operating time, and ambulatory status, using Clawson's Ambulation Capacity Classification, was performed, and a radiologic evaluation of Fogagnolo reduction quality, tip-apex distance (TAD), Cleveland index, sliding extent of lag screws, time duration till bony union, and complications was also done.
RESULTS
The mean skin incision length was 9.8 cm (range, 8-13 cm), the mean operating time was 41.4 minutes (range, 30-60 minutes), and 32 patients recovered their ambulatory function. Forty-eight patients gained bony union, and the time lapsed till union was average 10.6 weeks (range, 8-16 weeks). The evaluation of postoperative radiologic images showed the following reduction statuses by the Fogagnolo classification: 46 cases of "Good", 3 cases of "Acceptable," and 1 case of "Poor." Moreover, the mean TAD was 18.9 mm (range, 9.0-24.9 mm). While 45 cases fit into the zone 5 of the Cleveland index, other 3 were within zone 8 and the other 2 were within zone 6. The mean sliding length of the lag screws were 4.9 mm (range, 0.1-19.4 mm). There were a case of nonunion and a case of periprosthetic infection with nonunion as complications.
CONCLUSION
Using dynamic hip screws with 2-hole side plate for stable 2-part intertrochanteric femur fractures in elderly patients showed satisfactory results with respect to the recovery of ambulatory functions and bony union.
- 334 View
- 0 Download

- Cognitive Impairment in Hip Fracture Patients without Underlying Neurologic Diseases: Risk Factors and Relationship to Early Functional Recovery: Preliminary Study
- Jae Yong Park, Yong Beom Lee, Kun Tae Park, Je Hyun Yoo, Narei Hong
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(1):34-41. Published online January 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.1.34
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - PURPOSE
The aim of this study is to examine the risk factors of cognitive impairment in elderly hip fracture patients with no underlying neurologic disease, and to determine its effect on functional recovery postoperatively.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From August 2012 to August 2013, 39 patients older than 65 years of age, who underwent hip fracture surgery and were followed-up for a minimum of 1 year at Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, were enrolled. All patients were assessed using Korean version of Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE-K) after admission. All patients were divided into cognitive normal group (MMSE-K> or =24) and cognitive impairment group (MMSE-K<24). WOMAC (Western Ontario and McMaster University) score and Harris hip score were used for assessment of functional recovery at 6-month follow-up.
RESULTS
Sixteen patients (41.0%) were classified as the cognitive impairment group. The number of underlying diseases was the only statistically different factor between the two groups. In the evaluation of functional outcome, the functional decline was less in the cognitive normal group. Risk factors for cognitive impairment in elderly hip fracture patients were old age, high body mass index, and the number of underlying diseases, particularly an endocrinologic disease like diabetes.
CONCLUSION
Cognitive impairment in elderly patients may have a negative effect on functional recovery after hip fracture surgery. Therefore, we recommend routine evaluation of cognitive function in elderly hip fracture patients even with no underlying neurologic disease.
- 340 View
- 1 Download

- The Clinical and Radiological Results of Vancouver Type B1 and C Periprosthetic Fractures
- Bo Ram Na, Taek Rim Yoon, Kyung Soon Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(1):26-33. Published online January 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.1.26
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the clinical and radiologic results of plate fixation in the Vancouver B1 and C periprosthetic femoral fracture (PFF).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty patients who had sustained a Vancouver type B1 and C periprosthetic fracture after hip arthroplasty (years 2002-2012) were identified. The mean age was 66.0 years (range, 43-85 years) and the mean follow-up duration of the group was 38 months (range, 12-102 months). The dynamic compression plate (DCP) group included 12 patients and the locking compression plate (LCP) group included eight patients. Harris hip score (HHS) and walking ability, knee joint range of motion (ROM) were compared before injury and last follow-up. Fracture union rate and period were compared.
RESULTS
The mean HHS score was 90.7 (64-96). There was no statistical difference between the two groups. At the last follow-up, knee joint ROM was 103.3degrees (105degrees-140degrees) in the DCP group and 118.4degrees (110degrees-140degrees) in the LCP group, showing good results in the LCP group (p=0.043). No significant difference in the fracture union rate and union periods was observed between the two groups.
CONCLUSION
A better result for the postoperative knee flexion exercise capacity was observed in the LCP group. Use of LCP plate fixation is a good option in management of Vancouver classification B1 and C PFF.
- 357 View
- 3 Download

- Assessment of Coronal Plane Malalignment Following Reduction of Trochanteric Fractures-Simple Intraoperative Guideline Using Greater Trochanter Orthogonal Line
- Young Cheol Yoon, Jong Keon Oh, Won Yong Shon, Han Ju Kim, Jae Woo Cho
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(1):1-11. Published online January 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
There is no consensus on a clear intraoperative guideline for judging the coronal plane alignment following reduction of trochanteric fractures. Complex angular measurements using fluoroscope monitors are tedious. Therefore the relation of the horizontal line from the tip of the greater trochanter (GT orthogonal) and femur head center (HC orthogonal) was studied to define this line as a criterion for predicting varus-valgus malalignment.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We studied this relation in 200 standing orthoradiograms which included 100 males and 100 females. The images were digitally analyzed using the picture archiving and communication system. GT orthogonal line and HC orthogonal line were evaluated. The distance of these lines was measured as trochanter center distance (TCD) and its correlation with angular parameters like neck shaft angle, medial proximal femoral angle with reference to anatomical axis (aMPFA) and lateral proximal femoral angle with reference to mechanical axis (mLPFA) were analyzed.
RESULTS
In all patients, the GT orthogonal line passed either at or above the center of the head. Overall mean of TCD was 7.22 mm, ranging from 0 to 17.57 mm. TCD was found to show strong correlation with angular parameters like aMPFA, mLPFA and neck shaft angle. TCD was less than one fourth of the corresponding head diameter in around 90%. Therefore following reduction of trochanteric fractures, the GT orthogonal line should pass through the superior juxta central quadrant of the femoral head.
CONCLUSION
This line can be represented by a guide wire with fluoroscopy during surgery. The GT orthogonal line can be used intraoperatively as a simplified tool for prediction of varus/valgus malalignment following the reduction of trochanteric fractures.
- 307 View
- 0 Download

- Result of Surgical Treatment for the Femoral Head Fracture
- Joon Soon Kang, Kyoung Ho Moon, Tong Joo Lee, Jong Hyuck Yang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(3):198-205. Published online July 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.3.198
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study analyzed the clinical and radiological long-term follow-up results of patients with femoral head fracture who received surgical treatments.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Retrospective evaluation was performed for 20 patients with femoral head fracture who received surgical treatments between December 1997 and May 2010. According to Pipkin's classification, there were five type I, six type II, one type III, and eight type IV fractures.
RESULTS
The average Merle d'Aubigne'-Postel score was 12.8 (12.80+/-3.53). According to surgical method, the score for the bony fragment excision group was 9.8 (9.83+/-2.79), and that for the open reduction and internal fixation group was 13.9 (13.92+/-3.07). Depending on Thompson-Epstein criteria, two patients were good, two were fair, and two were poor in the bony fragment excision group. Four patients were excellent, six were good, and three were poor in the open reduction and internal fixation group.
CONCLUSION
Bony fragment excision should be performed with caution in patients with femoral head fracture. Considering fragment size, location, and presence of acetabular fracture, better outcome can be expected using the open reduction and internal fixation method in comparison with excision.
- 416 View
- 2 Download

- Results of Use of Compression Hip Screw with Trochanter Stabilizing Plate for Reverse Oblique Intertrochanteric Fracture
- Byung Woo Min, Kyung Jae Lee, Gyo Wook Kim, Ki Cheor Bae, Si Wook Lee, Du Han Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(2):120-126. Published online April 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.2.120
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to analyze the use of a compression hip screw with a trochanter stabilizing plate for treatment of reverse oblique intertrochanteric fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed the results of 33 cases of reverse oblique intertrochanteric fracture treated with a compression hip screw with a trochanter stabilizing plate from January 2000 to December 2012 which were followed-up for more than one year. We evaluated postoperative bone union period, change of neck-shaft angle, sliding of hip screw, and other complications.
RESULTS
Of 33 patients, satisfactory reduction was achieved in 28 patients. Five patients had an unsatisfactory reduction, with two cases of excessive screw sliding, one of broken metal, one of varus deformity, and one of internal rotation deformity. We performed corrective osteotomy in varus and internal rotation deformity and partial hip replacement in a case of excessive screw sliding. Bone union was achieved in 29 patients, and the average bone union period was 19.2 weeks.
CONCLUSION
We consider that a compression hip screw with a trochanteric stabilized plate is a good option for treatment of reverse oblique intertrochanteric femoral fractures. However, adequate fracture reduction and ideal implant placement are a basic necessity for successful treatment.
- 588 View
- 5 Download

- The Character of Reverse Obliquity Intertrochanteric Fractures in Elderly Patients
- Ji Wan Kim, Jae Suk Chang, Jung Hwan Sung, Jung Jae Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(3):173-177. Published online July 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.3.173
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To discriminate the characteristics between reverse obliquity fractures in the elderly and that of young adults using three-dimensional computed tomography (3D CT).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Eighteen patients who had reverse obliquity intertrochanteric fractures were enrolled from January 2007 to March 2012. The fracture pattern was analyzed using the 3D CT. The area showing low density (bone defect) of trochanter and femoral neck region was measured. Patients were divided into two groups: Group I, less than 65 years old and Group 2, 65 years and over.
RESULTS
In all 9 cases of group 1, the proximal fragment had a 'V' shape with an average of 5.6 cm below the vastus ridge; however, the fracture of 8 cases (88.97%) in group 2 had a 'Lambda' shape of the distal fragment at the level of vastus ridge and an additional fracture line extending to the greater trochanter tip. The bone defect volume of the trochanter and femoral neck region was larger significantly in group 2 than in group 1.
CONCLUSION
Reverse obliquity intertrochanteric fracture in the elderly demonstrated a pattern of bursting fracture with 4 parts, which had different patterns from that of young patients. We believe that the larger volume of bone defects resulted in the difference of fracture patterns between the two groups. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comparison of Internal Fixation and Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty for the Treatment of Reverse Oblique Intertrochanteric Femoral Fractures in Elderly Patients
Bong-Ju Park, Hong-Man Cho, Woong-Bae Min
Hip & Pelvis.2015; 27(3): 152. CrossRef
- A Comparison of Internal Fixation and Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty for the Treatment of Reverse Oblique Intertrochanteric Femoral Fractures in Elderly Patients
- 505 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


