Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 32(4); 2019 > Article
- Review Article Total Hip Arthroplasty after Acetabular Fracture: Acute Phase and Delayed Phase
- Hwan Hee Lee, Se Won Lee, Weon Yoo Kim
-
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma 2019;32(4):232-239.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.4.232
Published online: October 31, 2019
2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Yeouido St. Mary's Hospital, School of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 917 Views
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
Abstract
The incidence of acetabular fractures in the elderly has increased because of the increasing elderly population. To determine the treatment plan for acetabular fractures, the patient's age, gait ability, presence or absence of osteoporosis and osteoarthritis, underlying disease, and fracture pattern should be considered. The application of total hip arthroplasty for acetabular fractures with the proper indications can be expected to have a good prognosis. In this paper, the application of total hip arthroplasty as a treatment method for acetabular fractures is divided into acute and delayed phases.
Published online Oct 28, 2019.
https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.4.232
Total Hip Arthroplasty after Acetabular Fracture: Acute Phase and Delayed Phase
Abstract
The incidence of acetabular fractures in the elderly has increased because of the increasing elderly population. To determine the treatment plan for acetabular fractures, the patient's age, gait ability, presence or absence of osteoporosis and osteoarthritis, underlying disease, and fracture pattern should be considered. The application of total hip arthroplasty for acetabular fractures with the proper indications can be expected to have a good prognosis. In this paper, the application of total hip arthroplasty as a treatment method for acetabular fractures is divided into acute and delayed phases.
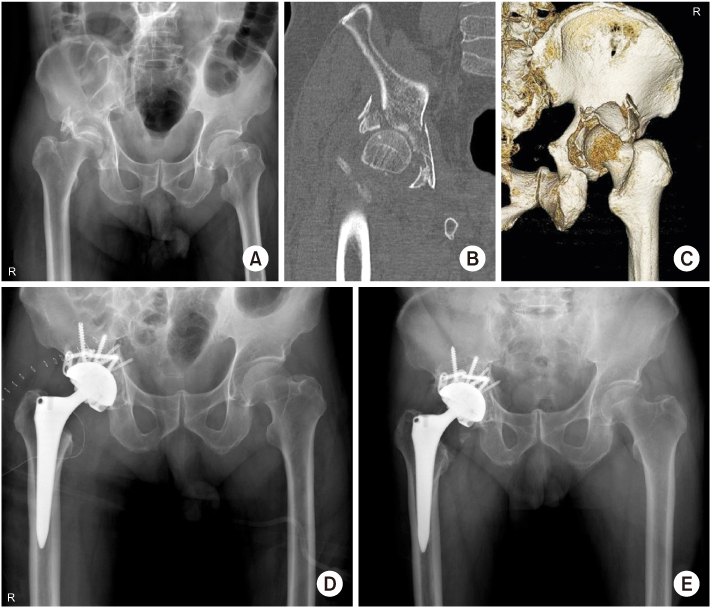
Fig. 1
(A) Preoperative anteroposterior radiograph of a 77-year-old male showed a posterior wall fracture with osteoporosis. (B, C) Computed tomography scan showed severe comminuted fracture of the posterior wall of the acetabulum and impaction of the femoral head. (D) Postoperative anteroposterior radiograph after internal fixation with total hip arthroplasty. (E) Four-year postoperative radiograph showed stable total hip component with bone union.
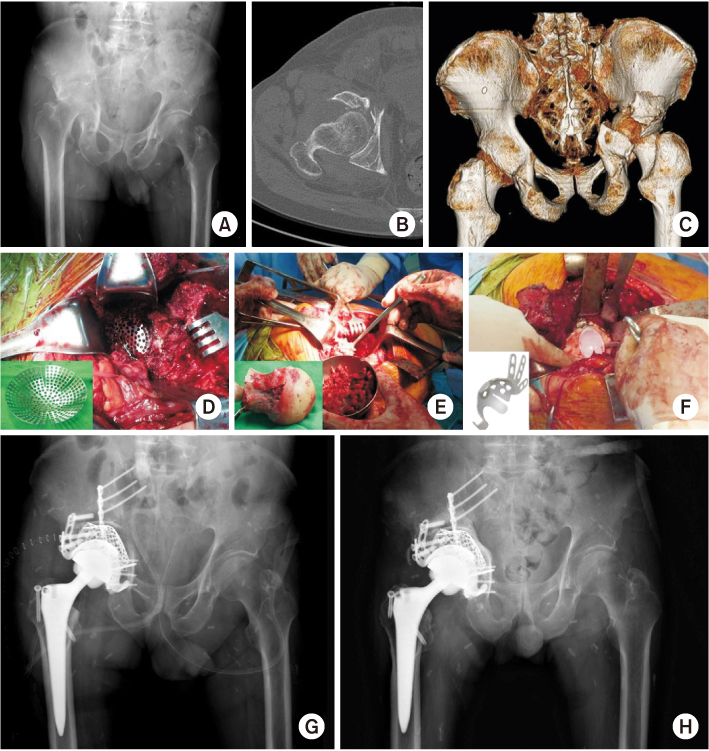
Fig. 2
(A) Preoperative anteroposterior radiograph of a 67-year-old male showed a transverse fracture with posterior wall fracture of the acetabulum and severe impaction. (B, C) Computed tomography showed a severe comminuted fracture of the posterior wall and protrusion of the femoral head. (D) The acetabular mesh plate was inserted into the acetabulum through the Kocher–Langenbeck approach. (E) Autogenous corticocancellous bone from the femoral head was grafted on a mesh plate to support the acetabular cup. (F) A liner was inserted after fixation of the cemented flanged acetabular cup. (G) Postoperative anteroposterior radiograph after internal fixation and total hip arthroplasty. (H) Three-year postoperative radiographs showed stable total hip arthroplasty.
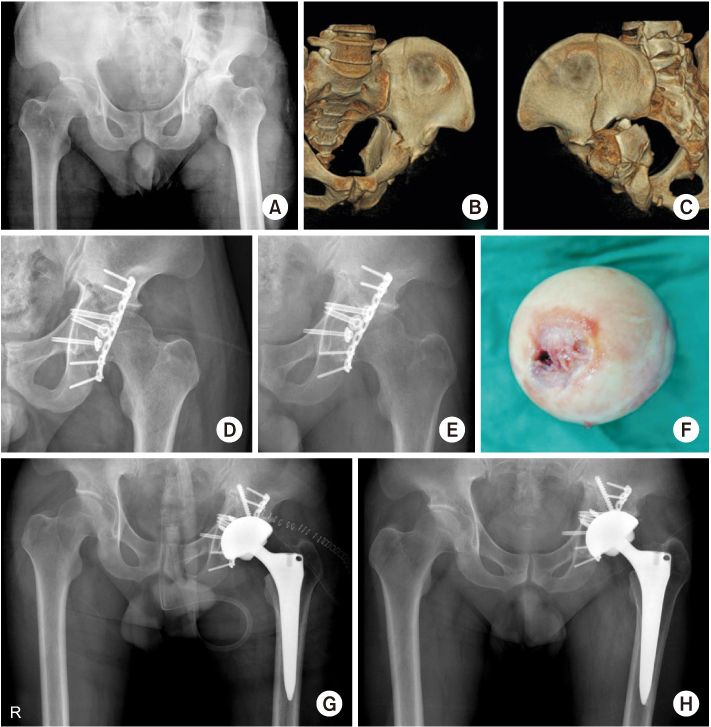
Fig. 3
(A) Preoperative anteroposterior radiograph of a 50-year-old male showed a transverse fracture with a posterior wall fracture of the acetabulum. (B, C) The three-dimensional reconstruction images showed the impaction of acetabulum and comminuted fragments. (D) Postoperative anteroposterior radiograph after internal fixation through the Kocher–Langenbeck approach. (E) Seven-month postoperative radiographs showed post-traumatic osteoarthritis on the left hip joint. (F) Intraoperatively, the resected femoral head showed denuded and destroyed articular cartilage. (G) Postoperative anteroposterior radiograph after total hip arthroplasty. (H) Five-year postoperative radiographs showed a stable total hip component with no complaint.
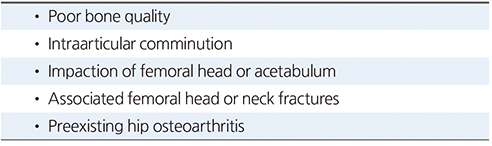
Table 1
Indications for Acute Total Hip Arthroplasty in Acetabular Fractures
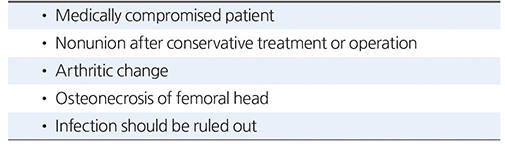
Table 2
Indications for Delayed Total Hip Arthroplasty in Acetabular Fractures
Financial support:None.
Conflict of interests:None.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS


 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite

