Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Articles
- Fracture-related infections: a comprehensive review of diagnosis and prevention
- HoeJeong Chung, Hoon-Sang Sohn
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):86-95. Published online April 25, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00164
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fracture-related infections are challenging complications in orthopedic trauma that often require prolonged treatment and impose a significant healthcare burden. Accurate diagnosis and effective prevention strategies are essential for minimizing their occurrence. A recent international consensus has established standardized diagnostic criteria based on clinical, microbiological, radiological, and histopathological findings. Prevention is the top priority and involves a thorough preoperative risk assessment, along with glycemic control, nutritional optimization, and management of comorbidities, as well as intraoperative and postoperative measures such as appropriate antibiotic prophylaxis, surgical site antisepsis, and meticulous wound care. A multidisciplinary approach involving orthopedic surgeons, infectious disease specialists, and microbiologists is crucial for successfully reducing the burden of fracture-related infections.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Personalized Approaches to Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies in Periprosthetic Fracture-Related Infections (PFRIs): Case Series and Literature Review
Marianna Faggiani, Marco Zugnoni, Matteo Olivero, Salvatore Risitano, Giuseppe Malizia, Silvia Scabini, Marcello Capella, Stefano Artiaco, Simone Sanfilippo, Alessandro Massè
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2025; 15(12): 576. CrossRef - Pathogen-Specific Risk for Iterative Surgical Debridement in Orthopedic Infections: A Prospective Multicohort Analysis
Flamur Zendeli, Anna Jędrusik, Raymond O. Schaefer, David Albrecht, Michael Betz, Felix W. A. Waibel, Tanja Gröber, Nathalie Kühne, Sören Könneker, İlker Uçkay
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(24): 8750. CrossRef
- Personalized Approaches to Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies in Periprosthetic Fracture-Related Infections (PFRIs): Case Series and Literature Review
- 6,572 View
- 262 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Systematic Diagnosis and Treatment Principles for Acute Fracture-Related Infections
- Jeong-Seok Choi, Jun-Hyeok Kwon, Seong-Hyun Kang, Yun-Ki Ryu, Won-Seok Choi, Jong-Keon Oh, Jae-Woo Cho
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(4):148-161. Published online October 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.4.148
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
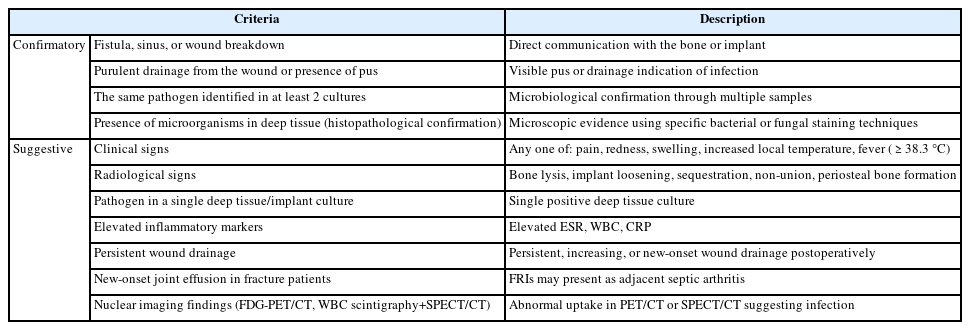
PDF - Acute fracture-related infection (FRI) is a common and serious complication of fracture treatment. The clinical symptoms of the patient and the results of the serological, radiological, and histopathologi-cal examinations can be divided into ‘Confirmatory’ criteria and ‘Suggestive’ criteria, allowing for the diagnosis of FRI. Treatment principles can be broadly categorized into (1) the DAIR (Debridement, Antimicrobial therapy, Implant Retention) method and (2) the staged reconstruction method. The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the time elapsed after infection, stability of the internal fixation device, reduction status, host physiology, and virulence of the pathogens. Thorough surgical debridement and irrigation, ensuring stability at the fracture site, reconstruction of bone defects, and appropriate soft tissue coverage, along with antibiotic therapy, are essential to suppress or eradicate the infection. The restoration of limb function should be promoted through proper soft tissue coverage and bone union at the fracture site.
- 788 View
- 15 Download

Original Article
- Minimal Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis versus Conventional Open Plating in Simple Humeral Shaft Fracture (AO Type A, B1, B2)
- Boseon Kim, GwangChul Lee, Hyunwoong Jang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(3):124-130. Published online July 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.3.124
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) by comparing the results between open plating and MIPO conducted by simple humeral shaft fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From September 2010 to February 2015, we evaluated humeral shaft fractures that 26 cases underwent MIPO and 41 cases underwent open plate fixation (OPEN). Operation time, amount of blood loss, and radiative exposure time were examined. Radiographically, bone union time and angulation were compared. At last, UCLA shoulder score and MEPI were used to compare the clinical results of shoulder and elbow and complications were examined.
RESULTS
The average operation time 82±23 minutes in MIPO, 119±20 minutes in OPEN (p=0.007) and amount of bleeding 238±67 ml in MIPO, 303±48 ml in OPEN (p=0.003), radiation exposure time 201±85 seconds in MIPO, 20±5 seconds in OPEN (p=0.000) were statistically significant. Bone union time and angulations, clinical results were not statistically significant. In Complication, iatrogenic radial nerve paralysis occurred 2 cases, nonunion occurred 1 case in MIPO. Nonunion and soft tissue infection occurred 2 cases each in OPEN.
CONCLUSION
MIPO in simple humeral shaft fractures gave us radiologically and clinically satisfactory results, and may be useful by understanding the anatomical knowledge and using appropriate implants and skills. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Outcomes of Arthroscopic Assisted Reduction and Percutaneous Fixation for Tongue-Type Sanders Type II Calcaneal Fractures
Jae Woo Park, Chul Hyun Park
Journal of Korean Foot and Ankle Society.2017; 21(4): 144. CrossRef
- Outcomes of Arthroscopic Assisted Reduction and Percutaneous Fixation for Tongue-Type Sanders Type II Calcaneal Fractures
- 785 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review Articles
- Treatment Strategy of Infected Nonunion
- Hyoung Keun Oh
- J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(1):52-62. Published online January 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.1.52
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The management of infected nonunion is based on a detailed evaluation of patients, the involved bone and soft tissues, stability of fixation, and type of bacterial pathogens. Preoperative surgical planning and strategies for each step is mandatory for the successful treatment of infected nonunion. The radical debridement of infected tissues, including the unstable implant, is one of the most important procedures. Adequate soft tissue coverage should be considered for the appropriate management of infection; a reconstructive procedure and stable skeletal stabilization by internal or external fixation is also necessary later. A restoration of bone defects and bony union can be accomplished with bone grafting, distraction osteogenesis, vascularized fibular grafting, and induced membrane technique.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Systematic Diagnosis and Treatment Principles for Acute Fracture-Related Infections
Jeong-Seok Choi, Jun-Hyeok Kwon, Seong-Hyun Kang, Yun-Ki Ryu, Won-Seok Choi, Jong-Keon Oh, Jae-Woo Cho
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2023; 36(4): 148. CrossRef - The Antibiotic Cement Coated Nail and Masquelet Technique for the Treatment of Infected Nonunion of Tibia with Bone Defect and Varus Deformity: A Case Report
Min Gu Jang, Jae Hwang Song, Dae Yeung Kim, Woo Jin Shin
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2022; 35(1): 26. CrossRef
- Systematic Diagnosis and Treatment Principles for Acute Fracture-Related Infections
- 1,536 View
- 31 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Scaphoid Fractures and Nonunion
- Jin Rok Oh
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(1):79-92. Published online January 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.1.79
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fracture of scaphoid is relatively common, and accurate and prompt diagnosis leads to bony union with good clinical outcome. However, it can be easily missed due to vague symptomatic complaints by patients, which in turn leads to negligence of a doctor in making the diagnosis or anatomical shape of scaphoid that causes minute fracture to be ignored while viewing simple radiography. When missed, nonunion of scaphoid gradually progresses to arthritic change in the wrist. Thus when fracture of the scaphoid is suspected, further evaluation should be initiated with care, and if the diagnosis is confirmed, a proper treatment plan must be set with assessment of stability of the fracture fragment. Internal fixation is usually proposed since solid fixation of the fracture provides early return to daily activity. When nonunion of the scaphoid is present, most patients can achieve bony union with avascular bone graft and internal fixation. However, if there is sclerotic change, large bone cyst or avascular necrosis of the fracture fragment, internal fixation with bone graft that includes vascular supply should be introduced in order to achieve bony union.
- 563 View
- 3 Download

Original Articles
- Perioperative Blood Loss in Intramedullary Hip Screw for Intertrochanteric Fracture: Analysis of Risk Factors
- Jai Hyung Park, Hwa Jae Jung, Hun Kyu Shin, Eugene Kim, Se Jin Park, Taeg Su Ko, Jong Hyon Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2015;28(1):53-58. Published online January 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.1.53
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
We compared visible blood loss and calculated blood loss after intramedullary fixation in intertrochanteric fracture, and evaluated correlation between blood loss and its risk factors.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 256 patients who underwent closed reduction and intramedullary fixation in femoral intertrochanteric fracture between 2004 and 2013 were enrolled in this study. The total blood loss was calculated using the formula reported by Mercuiali and Brecher. We analyzed several factors, including fracture pattern (according to Evans classification), gender, age, body mass index (BMI), anesthesia method, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease, preoperative anemia, American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) score and use of antithrombotic agents.
RESULTS
Total calculated blood loss (2,100+/-1,632 ml) differed significantly from visible blood loss (564+/-319 ml). In addition, the blood loss of unstable fracture patient was 2,496+/-1,395 ml and multivariate analysis showed a significant relationship between blood loss and fracture pattern (p<0.01). However, other factors showed no statistically significant difference.
CONCLUSION
Total calculated blood loss was much greater than visible blood loss. Patients with unstable intertrochanteric fracture should be treated with care in order to reduce blood loss.
- 452 View
- 0 Download

- Intrapelvic Anterior Plate Fixation for Crescent Fracture-Dislocation of Sacroiliac Joint
- Kwang Jun Oh, Jin Ho Choi
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(3):184-190. Published online July 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.3.184
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the radiological and clinical outcomes of intrapelvic anterior plate fixations for Day Classification Type II crescent fracture-dislocations of sacroiliac joints.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Ten patients who had undertaken the surgical treatment for the sacroiliac joint from 2006 to 2012 were enrolled in this study. All cases fell into Type II by Day Classification for sacroiliac joint injuries. For surgical treatments, the plate fixation through the intra-pelvic anterior approach was first performed for all cases and anterior ring fixation was performed in 4 cases with more severely displaced anterior pelvic ring injuries. Then, radiological and clinical evaluation was implemented.
RESULTS
The bone union was observed from all patients whom performed the surgical fixation. In the radiological results, 9 cases with the anatomic and nearly-anatomic reductions were observed. Out of the 10 cases which performed the rotational displacement analysis, there were 3 excellent cases, 6 good cases and 1 fair case. The 10 cases that performed the deformity index and vertical displacement analysis, less variations were observed in the anterior ring fixations after intra-pelvic anterior plate fixation group. According to the clinical results, 4 excellent cases, 3 good cases, and 3 moderate cases were observed.
CONCLUSION
In the Type II crescent fracture-dislocation of sacroiliac joint, the intrapelvic anterior plate fixation achieved satisfactory anatomical reductions, radiological stabilities and clinical results.
- 479 View
- 5 Download

- Clinical Results of Various Surgical Techniques for Isolated Fracture of Greater Tuberosity of Humerus
- Nam Su Cho, Seong Cheol Moon, Yong Girl Rhee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(2):133-139. Published online April 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.2.133
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To compare the clinical and radiologic outcomes of various surgical techniques for an isolated fracture of greater tuberosity of the humerus.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From February 2001 to December 2008, 31 patients, who underwent an operation for isolated greater tuberosity fracture and were followed up for more than 1 year, were enrolled in this study. The mean age at the time of operation was 49.3 years (range, 23-73 years). The operation methods included in this study were as follows: a transosseous suture using nonabsorbable suture material (16 cases), a fixation by cannulated screws (10 cases), tension band wiring (2 cases), bony fragment excision with rotator cuff repair (2 cases), and percutaneous pinning (1 case).
RESULTS
At the last follow-up, the average Constant score was 79.4 and Korean Shoulder Score (KSS) was 81.2. Among the various operation methods used in this study, the transosseous suture had the highest scores with 82.5 in Constant score and 89.3 in KSS. Bone union was achieved at average 10.3 weeks (range, 7-15 weeks), and there were 2 cases in which the reoperation was required due to internal fixation failure. Postoperative shoulder stiffness occurred in 3 cases, and all the cases were done with the deltopectoral approach.
CONCLUSION
Clinically and radiologically satisfactory results were obtained using various operation techniques for an isolated greater tuberosity fracture of the humerus. The transosseous suture showed relatively better results than the other methods used in this study. To achieve favorable clinical and radiologic results, it is important to select an appropriate surgical approach and fixation method according to the fracture site, degree of displacement, and size of fragment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biomechanical comparisons of hook plate and screw fixations in split-type greater tuberosity fractures of the humerus
Fa-Chuan Kuan, Kai-Lan Hsu, Chih-Kai Hong, Yueh Chen, Chen-Hao Chiang, Hao-Ming Chang, Wei-Ren Su
Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery.2022; 31(6): 1308. CrossRef
- Biomechanical comparisons of hook plate and screw fixations in split-type greater tuberosity fractures of the humerus
- 708 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Treatment of Non-union Distal Humerus Fractures after Operation
- Hyung Sik Kim, Ki Joon Jang, Yun Rak Choi, Il Hyun Koh, Ho Jung Kang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(4):310-316. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.4.310
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study is a retrospective analysis of patients who had undergone surgical treatment for non-union of distal humerus fracture. We evaluated them in terms of causes of injury, radiologic findings, and clinical outcomes such as prognosis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Seven consecutive radiologic patients who were confirmed to have nonunion of a distal humerus fracture underwent reoperations. These patients had already undergone operations for distal humerus fractures. This survey was held from 2005 to 2010. The average period up to diagnosis of non-union after the first operation was 7.4 months (4 to 16 months). The mean follow-up period was 24.6 months (12 to 65 months). Each patient was graded functionally according to the Mayo Elbow Performance Score and the Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand Score.
RESULTS
Osteosynthesis was performed by internal fixation with plates and screws and then a bone graft for non-union of the distal humerus fracture. The average range of motion within the elbow joints was found to be a flexion contracture of 18.8 degrees (0~30 degrees) and further flexion of 120.2 degrees (102~140 degrees). Among postoperative complications, three cases of medium-degree stiffness, two cases of medial column nonunion, and one case of dissociation of the internal fixator were reported.
CONCLUSION
Stable internal fixation for maintenance reduction status is essential after accurate initial anatomical reduction. We concluded that nonunion could be prevented by additional surgical treatment such as autogenous bone graft, if it is necessary. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Autogenous Inlay Bone Graft for Distal Humerus Nonunion with Metaphyseal Bone Defect: A Technical Note
Yong-Suk Lee, Dongmin Kim, Min-Sung Kang, Jong-Hwa Park, Sang-Uk Lee
Archives of Hand and Microsurgery.2020; 25(1): 39. CrossRef
- Autogenous Inlay Bone Graft for Distal Humerus Nonunion with Metaphyseal Bone Defect: A Technical Note
- 832 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Clinical Outcome of Surgical Treatment for Intra-articular Distal Humerus Fracture
- Myung Jin Lee, Hyeon Jun Kim, Sung Keun Sohn, Kyu Yeol Lee, Sung Soo Kim, Chul Hong Kim, Lib Wang, Hyun Woo Sung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2010;23(2):201-205. Published online April 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.2.201
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate functions of the elbow joint according to surgical approach, time to exercise, and type of fracture after surgical treatment for the intra-articular comminuted fracture of the distal humerus.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
27 patients with the intra-articular comminuted fractures of the distal humerus underwent surgery from March, 2000 to January, 2007. We investigated the surgical approach, time for union, time to exercise and age. We also evaluated postoperative functions of the elbow joint according to the flexion contracture, the range of motion and the Mayo elbow performance score.
RESULTS
The average follow-up period was 37 months and the average time for union was 14 weeks. The average range of flexion was 115 degrees, the average flexion contracture was 10 degrees, and the Mayo elbow performance score with average value of 85 point showed good clinical results. There were no statistically significant differences in functions of the elbow joint according to the operative method and age. However, patients with early postoperative exercise within 6 days showed statistically better outcomes than patients with postoperative exercise after 7 days. Type C1, 2 fractures showed statistically better results than the type C3 fracture.
CONCLUSION
Stable fixation and early exercise are required to prevent postoperative complications and restore functions of the elbow joint with an intra-articular comminuted fracture of the distal humerus. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surgical Treatment Using a Transolecranon Approach with a Dual Locking Plate for Unstable Intercondylar Fractures of the Humerus
Ji-Kang Park, Yong-Min Kim, Dong-Soo Kim, Eui-Sung Choi, Hyun-Chul Shon, Kyoung-Jin Park, Byung-Ki Cho
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2012; 25(2): 129. CrossRef
- Surgical Treatment Using a Transolecranon Approach with a Dual Locking Plate for Unstable Intercondylar Fractures of the Humerus
- 775 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Surgical Treatment of Pathologic Humeral Fracture
- Ho Jung Kang, Byoung Yoon Hwang, Jae Jeong Lee, Kyu Ho Shin, Soo Bong Hahn, Sung Jae Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2010;23(2):187-193. Published online April 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.2.187
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate and analyze the radiographic and clinical outcomes after the surgical treatments of pathologic humeral fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From October 1993 to September 2007, a retrospective investigation was conducted with a total of 13 patients who underwent operations for pathologic humeral fractures. The methods of surgical treatment were as follows-four cases of open reduction and internal fixation; eight cases of closed reduction and internal fixation with intramedullary nailing; and one of radical excision and hemiarthroplasty.
RESULTS
Of nine patients with metastatic bone lesions, three were diagnosed with primary cancer after the incidence of pathologic humeral fracture. The mean period between the diagnosis of primary cancer and pathologic fracture in the latter six cases was 36.7 (2~144) months and the mean survival period after the surgical treatments was 22.8 (12~35) weeks in all patients with bone metastasis. Fracture unions were noted in all four cases of primary humeral bone lesion but none in metastatic cases. Pain relief and functional recovery were noted in eleven patients of this study.
CONCLUSION
Satisfactory clinical outcomes with sustained pain relief and functional recovery were observed after the surgical treatments of pathologic humeral fracture. Benign bone lesions require more active and early treatments in order to facilitate the functional recovery of upper extremities and fracture union. With pathologic humeral fractures originated from metastasis, palliative treatments were preferred to fracture union method for planning long-term pain relief and functional recovery. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The application of a dual-lead locking screw could enhance the reduction and fixation stability of the proximal humerus fractures: a biomechanical evaluation
Eunju Lee, Hyeon Jang Jeong, Yeon Soo Lee, Joo Han Oh
Frontiers in Surgery.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Therapeutic Approach to Humeral Pathologic Fracture Caused by Benign Bone Tumor
Jeung Il Kim, Um Ji Kim, Nam Hoon Moon, Hui Taek Kim, Tae Young Ahn, In Sook Lee, You Seon Song, Kyung Un Choi
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2016; 51(6): 509. CrossRef
- The application of a dual-lead locking screw could enhance the reduction and fixation stability of the proximal humerus fractures: a biomechanical evaluation
- 855 View
- 7 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The Results of Surgical Treatment for Nonunion of Phalanges in the Hand
- Hee Dong Kim, Yoon Hong Kim, Yong Soo Choi, Heun Guyn Jung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2008;21(2):140-144. Published online April 30, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.2.140
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the results of internal fixation and autogenous bone graft for the phalangeal nonunion in the hand.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From Feb. 2000 until May 2006, thirteen cases that had been treated for non-union of phalanges in the hand were investigated retrospectively. Seven cases were treated with mini-plate fixation and autogenous cancellous graft and six cases with Kirschner wire fixation and autogenous cancellous graft. We analyzed bony union period radiographically and clinical results according to Belsky's score.
RESULTS
Thirteen cases obtained bony union. Seven cases of mini-plate fixation and bone graft, and six cases of K-wire fixation and bone graft achieved the bony union postoperatively on average 7.9 weeks and 6.3 weeks, respectively. Clinical results were "good" in four cases and "poor" in nine cases according to the Belsky's score. Only one of ten cases with associated injuries, such as tendon, nerve, arterial injuries and other finger fractures in the injured hand, had the good clinical result, but all three cases without associated injuries had the good one.
CONCLUSION
Internal fixation and autogenous bone graft can be a successful treatment of phalangeal nonunion. However, more careful choice of surgical treatment methods and preoperative explanation of poor post-operative results or complications should be made for phalangeal nonunion with associated injuries in the finger because of poor outcome in those cases.
- 630 View
- 4 Download

- The Surgical Outcomes for Isolated Greater Tuberosity Fracture of Proximal Humerus
- Eun Sun Moon, Myung Sun Kim, Young Jin Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(3):239-245. Published online July 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.3.239
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the adequate surgical methods and postoperative rehabilitation by analyzing the outcome of surgical treatment for isolated greater tuberosity fracture of proximal humerus.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Ten patients who allowed at least 1 year follow up after the surgical treatment of isolated greater tuberosity fractures were evaluated. Their mean age was 52.3 years (range, 28~67) and mean follow up duration was 23.8 months (range, 12~36). We choosed the different approaches and fixation methods according to size, location and presence of comminution of the fragment, and combined injury. The rehabilitation programs were indivisualized and we evaluated the clinical outcomes using UCLA and Constant scoring system.
RESULTS
According to the UCLA scoring system, 5 cases were excellent, 3 cases were satisfactory, and 2 cases were unsatisfactory. By the Constant scoring system, 8 cases were excellent and 2 cases were good. The average bony union time was 7.6 weeks (range, 6~8) except the 2 cases of revision surgery. Two cases were operated using cannulated screws alone, 3 cases using only nonabsorbable sutures and 5 cases using cannulated screws and nonabsorbable sutures. One out of two revision cases was developed from the negligence of preoperative shoulder anterior dislocation with rupture of subscapularis, and the other was caused by improper immobilization of the fracture site postoperatively.
CONCLUSION
Not only the adequate surgical approaches and the fixation methods according to the size and comminution of fragment, but also the identification of combined injuries were very important in the surgical treatment for the isolated greater tuberosity fracture. And we considered that the adequate postoperative rehabilitation and proper protection based on the intraoperative fixation stability play an important role for the better clinical and radiological outcomes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Features and Characteristics of Greater Tuberosity Fractures with or without Shoulder Dislocation
Dong-Wan Kim, Young-Jae Lim, Ki-Cheor Bae, Beom-Soo Kim, Yong-Ho Lee, Chul-Hyun Cho
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2018; 31(4): 139. CrossRef - The Surgical Outcomes of Isolated Greater Tuberosity Fractures of the Proximal Humerus Fixed with the Spring Plate
Dong-Ju Shin, Young-Soo Byun, Se-Ang Chang, Hee-Min Yun, Ho-Won Park, Jae-Young Park
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(3): 159. CrossRef
- Clinical Features and Characteristics of Greater Tuberosity Fractures with or without Shoulder Dislocation
- 691 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Surgical Treatment of Posterior Wall Fractures of the Acetabulum
- Young Soo Byun, Se Ang Chang, Young Ho Cho, Dae Hee Hwang, Sung Rak Lee, Sang Hee Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(2):123-128. Published online April 30, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.2.123
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the results of surgical treatment of posterior wall fractures of the acetabulum and to determine the factors affecting the results.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty-one posterior wall fractures were reviewed; 7 type A1-1, 19 type A1-2 and 5 type A1-3 by AO classification. Postoperatively, the accuracy of the reduction was evaluated. At the final follow-up, clinical and radiographic results were evaluated with medical records and radiographs. The factors affecting the results were determined.
RESULTS
The reduction was graded as anatomical in 22 patients, imperfect in seven and poor in two. The clinical result was excellent in 21 hips, good in six, fair in three and poor in one. The quality of the reduction was strongly associated with the clinical result. The radiographic result was excellent in 22 hips, good in five, fair in two and poor in two. The clinical result was related closely to the radiographic result. Complications were osteoarthritis in three patients, osteonecrosis of the femoral head in one, heterotopic ossification in one, penetration of a screw into the joint in one and iatrogenic sciatic nerve injury in one. The factors affecting the clinical results were fracture patterns, the surgeon's experience, the accuracy of the reduction and late complications.
CONCLUSION
In this present series of posterior wall fractures, as their prognosis depends on the severity of the injury and the accuracy of the reduction, satisfactory result can be obtained by anatomical reduction with thorough preoperative planning and the surgeon's experience.
- 476 View
- 3 Download

Case Report
- Surgical Treatment of the Myositis Ossificans in Supracondylar Fracture of the Humerus in Children: A Case Report
- Tai Seung Kim, Kee Cheol Park, Seung Pyo Seo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(4):482-485. Published online October 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.4.482
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- Supracondylar fracture of the humerus is a common injury in the pediatric patient. A less common complication is the development of myositis ossificans. Although frequently cited as a possible complication, there are few reported cases of this occurring in the pediatric patient. We present a case report of a 8 year old boy who developed myositis ossificans after a supracondylar fracture of the humerus. After one year of the injury, we could ascertained radiologically complete maturation of the mass which developed in front of the distal humerus and markedly made motion of the elbow joint limited. We could obtain further motion through the surgical resection and then physical therapy. Now, eleven months have lapsed since the mass was removed, the range of motion is almost normal, and the recurrence of myositis ossificans is not existed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recent Trends in Treatment of Supracondylar Fracture of Distal Humerus in Children
Soon Chul Lee, Jong Sup Shim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2012; 25(1): 82. CrossRef
- Recent Trends in Treatment of Supracondylar Fracture of Distal Humerus in Children
- 628 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- Surgical Treatment of Displaced Intra-articular Calcaneal Fractures: Minimum of 2-year Follow-up
- Myung Ho Kim, Hong Geun Jung, Joong Bae Seo, You Jin Kim, Je Wook Yu
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(2):201-207. Published online April 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.2.201
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the overall clinical features and postoperative functional results of the intra-articular calcaneal fractures at more than 2 years follow-up, and also to compare the results at postoperative 1 year with the results at more than 2-year follow-up.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study is based on 39 intra-articular calcaneal fractures (34 patients) that underwent surgical treatment from March 1997 to May 2002 with at least 2 years follow-up. The overall postoperative results were evaluated with Creighton-Nebraska functional scale. The comparison of results at postoperative 1 year was also performed with results at more than 2-year follow-up.
RESULTS
By Sanders classifications, there were 13 type II fractures (33.3%), 20 type III (51.3%), and 6 type IV fractures (15.4%). Average follow-up period was 35 months (range: 24~87 months) and at final follow-up of more than 2 years, Creighton-Nebraska score was average 76.0 (range: 30~100) which significantly improved from postoperative 1-year results of 67.1 (range: 22~95) (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
The clinical outcome at more than 2 years after surgical treatment of intra-articular calcaneal fractures was quite promising, which significantly improved compared to 1-year results. Therefore, we concluded that functional results of calcaneal fractures should be evaluated at least 2 years after the treatment.
- 313 View
- 0 Download

- Treatment of Bony Mallet Finger: Closed Reduction Using Extension Block K-wire
- Jae Yeol Choi, Hwa Jae Jung, Ho Jin Lee, Kyung Mo Son, Young Hun Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(4):362-367. Published online October 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.4.362
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To review the result of bony mallet finger treated with a closed reduction using extension block K-wire MATERIALS AND METHODS: Between January 2001 and November 2002, among the patients with bony mallet finger underwent closed reduction using extension block K-wire, we retrospectively reviewed 14 patients with 14 fractures who had a minimum follow-up of 12 months.
RESULTS
There were 10 men and 4 women, with an average follow-up for all cases 15.7 months (range, 12 months~18 months). According to Crawford's evaluation criteria, we obtained 7 excellent, 5 good, 2 fair. We obtained bony union in all patients, with no remained pain. The average ROM was 67 degrees at postoperative 12 months. Postoperative complications occurred in two cases, which were nail deformity and mild osteoarthritis at the distal interphalangeal joint. There was no pin site infection.
CONCLUSION
This technique is not only easier but also less invasive than other techniques for reduction of mallet finger. Also, it shows excellent result with lower complication rate. So, it seems a reliable treatment for bony mallet finger. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Osteoarthritis after Extension Block Technique for the Bony Mallet Finger
Sung Hoon Koh, Jung Hyun Park, Jin Soo Kim, Si Young Roh, Kyung Jin Lee, Dong Chul Lee
Archives of Hand and Microsurgery.2021; 26(4): 238. CrossRef - Comparison of Surgical Outcomes of Percutaneous K-Wire Fixation in Bony Mallet Fingers with Use of Towel Clip versus 18-Gauge Needle
Ho-Seung Jeon, Chan-Sam Moon, Seo-Goo Kang, Kyeong-Seop Song, Uk-Hyun Choi
Journal of the Korean Society for Surgery of the Hand.2013; 18(1): 1. CrossRef - Percutaneous Kirschner Wire Fixation of Acute Mallet Fractures Percutaneousely Reduced by Towel Clip
Chung Soo Han, Duke Whan Chung, Bi O Jeong, Hyun Chul Park, Jin Young Kim, Cheol Hee Park, Jin Sung Park
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(4): 283. CrossRef
- Osteoarthritis after Extension Block Technique for the Bony Mallet Finger
- 612 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Results of Surgical Treatment in Schatzker Type VI Tibial Plateau Fracture
- Kyung Jin Song, Kwang Bok Lee, Seung Jin Moon, Joo Hong Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(1):32-37. Published online January 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.1.32
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the factors influencing the results for the treatment of the Schatzker type VI tibial plateau fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty-two cases of the 21 patients in Schatzker type VI tibial plateau fractures were analyzed. Treatment results were analyzed according to the type of fracture (open vs closed), method of operative treatment, angulation more than 5 degree and status of infection. The functional results was evaluated by Hohl's functional criteria. Student t-test was used for the statistical analysis.
RESULTS
Functional outcome demonstrated 5 excellent, 8 good, 6 fair and 3 poor results. There was no significant difference in the treatment results between type of fracture, method of operative treatment and status of infection. Among 9 cases with angular deformity of more than 5 degree, 2 showed excellent or good result and 7 showed fair or poor result (p<0.05). There was no significant difference between rate of postoperative infection and the mean period of the clinical bone union (p=0.66).
CONCLUSION
Accurate anatomical reduction and rigid fixation is essential for the treatment of Schatzker type VI tibial plateau fractures for the prevention of the angular deformity. And early weight bearing exercise should be controlled for the prevention of loss of reduction and loss of alignment leading to angular deformity.
- 474 View
- 12 Download

- The Correlation between Surgical Timing and Perioperative Complications in the Treatment of Displaced Supracondylar Humeral Fractures of Children
- Soo Hong Han, Duck Yun Cho, Hyung Ku Yoon, Byung Soon Kim, Jae Hwa Kim, Hyung Kun Park, Se Hyen Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(2):278-283. Published online April 30, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.2.278
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
Even though emergent percutaneous pinning after closed reduction is the popularized treatment of the displaced type II and type III pediatric supracondylar fractures of the humerus, the timing of pinning still presents controversy. The purpose of this study is to suggest an appropriate surgical time without significant perioperative complications.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From April 1995 to January 2002, 179 consecutive patients who had undergone surgical treatment were selected. They were divided to 5 groups [A group: 8 hours or less following injury (24 cases), B group: from 9 to 16 hours (63 cases), C group: from17 hours to 24 hours (63 cases), D group: from 25 hours to 48 hours (18 cases), and E group: from 49 hours to 72 hours (11 cases)] and reviewed retrospectively to analyze perioperative complications and operation time.
RESULTS
There was no significant difference between each group with respect to surgical wound infection, iatrogenic ulnar nerve injury, VIC, operation time and the necessity of reoperation (p>0.05).
CONCLUSION
Within the parameters outlined in our study, we could not find the any meaningful correlation between surgical timing and occurrence of perioperative complications and also, we think that the timing of percutaneous pinning can be delayed to the time when a surgeon considers it appropriate.
- 398 View
- 0 Download

- Surgical Treatment for Fractures of the Talus
- Ho Rim Choi, Jang Geun Lee, Hun Hwi Choi, Sung Woo Choi
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(1):67-73. Published online January 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.1.67
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the clinical results and develope guidelines for surgical treatment of talus fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Among the 60 cases that were treated during March 1990 to November 2000, 34 cases were treated operatively and followed up for more than one year( range: 1 4.4 years ). They were analyzed retrospectively with questionnaire directly or by telephone interview, radiograms and medical records. Clinical results were evaluated by Hawkins 'scoring system.
RESULTS
25 out of 34 cases showed satisfactory results. Unisatisfactory results were seen in cases that we couldn 't achieve anatomical reduction due to severe communition, and also in case of delayed treatment due to associated trauma and soft tissue injury. Six out of 8 cases that showed no Hawkins 'sign developed avascular necrosis. However, satisfactory results were achieved through conservative treatment.
CONCLUSION
Satisfactory results could be achieved through early anatomical reduction and rigid internal fixation followed by aggressive rehabilitation. There was no differences in clinical results either by the surgical approach or method of internal fixation. Avascular necrosis was not essentially related to the clinical results.
- 593 View
- 2 Download

- Assessment of Surgical Treatment of Acetabular Fracture after Minimum Five-year Follow-up
- Do Hyun Moon, Jang Seok Choi, Ki Ju Park, Jong Min Yun
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(3):342-348. Published online July 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.3.342
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To review the clinical and radiographic results of operative treatment of acetabular fractures for which there were minimum five-year follow-up.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed 22 acetabular fracture cases that had been treated operatively from March 1993 to July 1996. Each of the patients had been followed for a minimum five-year. The radiographic results were classified by Matta 's criteria and the clinical results were analyzed according to d 'Aubigne and Postel 's criteria.
RESULTS
Satisfactory reduction were obtained in 18 hips (81.8%), 14 and 13 hips of which were included in good or excellent categories of roentgenographic and clinical results respectively. Overall radiographic results for 17 hips (77.3%) at the one-year follow-up and 14 hips (63.6%) at the minimum five-year follow-up were excellent or good. According to clinical criteria, 16 hips (72.7%) at the one-year follow-up and 13 hips (59.1%) at the minimum five-year follow-up were classified as excellent or good.
CONCLUSION
Folow-up roentgenographic and clinical results were good or excellent in satisfactory reduction group. Threrefore the accuracy of reduction is an important prognostic factor in acetabular fracture. The results were worse at the minimum five-year follow-up than at the one-year follow-up. Late-postoperative complication is expected to increase as time passes.
- 470 View
- 1 Download

- The Surgical Treatment of Distal Clavicle Fractures
- Eun Sun Moon, Jong Wook Jung, Gwang Cheul Jeong
- J Korean Soc Fract 2001;14(4):706-713. Published online October 31, 2001
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2001.14.4.706
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate and analyze the clinical and radiological result of surgical treatment for distal clavicular fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From Jan. 1995 to May. 2000, eighteen cases of distal clavicle fractures were treated operatively. Among them, fifteen cases with more than 12 months follow-up were analyzed retrospectively. In Neer classification, type I was 1 case and 14 cases were type II. We performed closed reduction in 4 cases and open reduction in 11 cases. We treated with Steinman pin in I case, K-wires in 6 cases and coracoclavicular screw(Bosworth technique) in 6 cases. One case was treated with coracoclavicular screw due to screw loosening which was used in primary operation. Another case was treated by internal fixation with plate and K-wire due to delayed union after conservative treatment of segmental fracture. Mean follow up period was 18 months(12~62 months). Clinical results was evaluated by Kona s criteria.
RESULTS
Radiological evidence of solid union was detected within 10 weeks in 13 cases. Clinical results were satisfactory in 13 cases (excellent in 10 cases and good in 3 cases). In K-wire fixation, all six cases were demonstrated excellent result. In coracoclavicular screw fixation, four of six cases were excellent, one was good and one was fair. Poor result was noted in one case of Steinmann pin fixation due to nonunion and limitation of range of motion. SUMMARY: Surgical treatment of distal claviclular fracture would obtain satisfactory clinical result with early range of motion exercise and reduce the complications such as nonunion and sustained pain.
- 344 View
- 2 Download

- Complications after Surgical Treatment in Fracture of The Neck of Humerus
- Ho Jung Kang, Sang Jin Shin, Dae Eui Lim, Eung Shick Kang
- J Korean Soc Fract 2001;14(1):91-98. Published online January 31, 2001
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2001.14.1.91
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The causes and risk factors of complications following operative treatment of fracuture of neck of humerus were analysis. MATERIALS & METHODS: From 1995 to 1998, 32 cases of fracture of neck of humerus on which operative treatment have been taken were reviewed. The average age was 48.3 years. There were 13 cases of two part fracture, 11 cases of three part fracture and 8 cases of four part fracture, with 4 cases associated with comminution. Closed reduction and pinning was performed in 11 cases. An external fixator was applied in 1 case. Other 18 cases underwent open reduction using various fixation method including 4 K-wires, 2 cannulated screws, 5 plates, 1 Ender nail and 6 tension band wirings combined with screws each. 2 cases were underwent hemiarthroplasty.
RESULTS
Thirteen patients (41%) had postoperative complications. There were 3 nonunion, 2 pin site infection, 2 inferior subluxation of humeral head, 3 impingement syndrome, 1 hardware failure, 1 avascular necrosis of humeral head and 1 glenoid rim erosion. The incidence of postoperative complication was high in ages older than 40 years and the four part and comminuted fractures. The insufficient fixation due to osteoporosis, incomplete reduction, surgical technique and use of inappropriate implant were considered as related causative factures.
CONCLUSION
The patient's age, the quality of bone, severity of fracture and methods of fixation are all important contributing factors for postoperative complications.
- 462 View
- 4 Download

- The Surgical Reconstruction of Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures
- Suck Woo Kim, Yung Khee Chung
- J Korean Soc Fract 2001;14(1):30-36. Published online January 31, 2001
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2001.14.1.30
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to analyze the surgical results of 11 patients who underwent posterior instrumentation and anterior interbody fusion using titanium mesh vertebral ring(MOSS) in osteoporotic vertebral fracture. MATERIAL AND METHODS: From May 1997 to July 1999, we checked plain radiographs every 3 months and evaluated the change of kyphotic angle, fusion rate, change of clinical, neurologic symptoms and complications of these patients.
RESULTS
There were only average 0.2 degree correction of preoperative kyphotic angle at last follow-up X-ray. However, we confirmed successful bony fusion at nine of eleven patients(82%) and ten of eleven patients(90.9%) got satisfactory clinical results. Four patients with neurologic symptoms have recovered from their original neurologic status. Only one patient reoperated her back because of displacement of surgical device used in previous operation.
CONCLUSION
Among the surgical treatment methods in osteoporotic vertebral fractures, posterior instrumentation and anterior interbody fusion using titanium mesh vertebral ring(MOSS) is recommended as one of the effective surgical methods in severe osteoporotic patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Kümmell's Disease Treated with Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: Minimum 1 Year Follow-Up
Jae Won Park, Jong-Hwa Park, Hong Jun Jeon, Jong Young Lee, Byung Moon Cho, Se-Hyuck Park
Korean Journal of Neurotrauma.2017; 13(2): 119. CrossRef - Peculiarities of Treatment of Patients with Complicated Compression Fractures of Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Vertebral Bodies on the Background of Osteoporosis
S T Vetrile, Aleksandr Alekseevich Kuleshov, L Yu Darchiya, S T Vetrile, A A Kuleshov, L Yu Darchiya
N.N. Priorov Journal of Traumatology and Orthopedics.2009; 16(2): 34. CrossRef - Delayed vertebral collapse with neurological deficits secondary to osteoporosis
K-T Kim, K-S Suk, J-M Kim, S-H Lee
International Orthopaedics.2003; 27(2): 65. CrossRef - Surgical Treatment of Kümmell Disease with Neurologic Deficits - Posterolateral Decompression and Posterior Reconstruction -
Ki-Tack Kim, Kyung-Soo Suk, Jin-Moon Kim
Journal of Korean Society of Spine Surgery.2001; 8(2): 136. CrossRef
- Kümmell's Disease Treated with Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: Minimum 1 Year Follow-Up
- 540 View
- 0 Download
- 4 Crossref

Case Report
- Osteopetrosis combined with Subtrochanteric Fracture of Femur: A Case Report
- Ok Gyun An, Jong Ho Jang, Young Kyu Lim
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(4):804-808. Published online October 31, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.4.804
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Osteopetrosis (Albers-Schonberg's disease, Marble bones, and chalk bones) is a rare genetic disorder in which the bony structure throughout the body becomes dense and brittle. Because of the fragility of the pathologic bone, fractures are common and insufficient development of the bone marrow, optic atrophy, deafness, and facial paralysis can be developed to complications. We report a case of 35-year-old female with the autosomal dominant form of osteopetrosis combined with subtrochanteric fracture of femur that underwent surgical treatment.
- 413 View
- 3 Download

Original Articles
- Reconstruction of Neglected Traumatic Radial Head Dislocation in Children
- Dong Yeon Lee, Tae Joon Cho, In Ho Choi, Chin Youb Chung, Young Jin Sohn
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(4):1024-1032. Published online October 31, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.4.1024
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the clinical result of surgical reconstruction of the old traumatic radial head dislocation in children, and to delineate the optimal surgical procedure for it.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fifteen cases of the old traumatic radial head dislocation were included in this study, which had surgical reconstruction at the age of 15 years or less. Preoperative and postoperative clinical symptom, range of joint motion, and radiologic findings were reviewed. Reconstructions were performed by combination of various procedures, and the advantages and disadvanges of each procedures were analyzed.
RESULTS
All the preoperative complaints were relieved by the operation. In twelve cases out of 15, the radial head reduction was well maintained. The reasons for the loss of reduction were non-union of ulnar osteotomy site, and the neglected angular deformity at the proximal radius. Although forearm pronation was decreased in most cases, they did not affect most of the daily activities except in cases where the radioulnar osseocartilaginous bridge were complicated.
CONCLUSION
Our results justify the surgical reconstruction of neglected traumatic radial head dislocations in children. Complete clearing of radiocapitellar joint, accurate bony realignment and rigid fixation, appropriate annular ligament reconstruction, and temporary fixation with transcapitellar pin may ensure satisfactory result.
- 452 View
- 8 Download

- The Surgical Treatment of displaced Acetabular Fracture
- Sang Hong Lee, Kyung Ho Kim, Pyong Ju
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(3):454-462. Published online July 31, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.3.454
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analysis clinical and radiological results of operative treatment of displaced acetabular fractures and establish the guideline for the operative treatment of displaced acetabular fracture with the analysis of the clinical and radiological results.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A clinical analysis was performed on 36 patients with displaced acetabular fractures who had been operated on and followed for minimum 1 year period from January 1993 to December 1998. Clinical outcome was analyzed clinically by Harris hip scoring system and radiologically by Matta's roentgenographic grading system.
RESULTS
According to Letournel's classification, we had 25 elementary fractures(69%) and 12 associated fracture(31%). Among the elementary fractures, the posterior wall fracture was the most common type(17 cases, 47%) and both column fracture was the most common type among associated fractures(5 cases, 11%). Surgical approaches were 22 Kocher-Langenbeck, 8 extended iliofemoral, 3 triradiate transtrochanteric, 3 ilioinguinal. The mean duration of follow up after the operation was 2.2 years (range, 1 to 7 years). Among thirty six patients who had followed up more than one year, the satisfactory results were achieved in 27 cases (75%) on clinical grade and 26 cases (72%) on radiographic grade. The complications were developed in 20 cases out of 36 cases including posttraumatic arthritis 7 cases, heterotopic ossification 4 cases.
CONCLUSION
In the majority of the displaced acetabular fractures, accurate open reduction and internal fixation was recommended. It seems that the satisfactory operative reduction of the fracture is the factor that correlates with a satisfactory clinical result according to our study. Therefore in the surgical treatment of the acetabuluar fractures, it is essential to achieve an anatomical reduction and firm fixation by fully understanding the pathologic anatomy and by choosing an appropriate approach and fixation device.
- 396 View
- 0 Download

- Closed Reduction and Percutaneous Pinning in Displaced Surgical Neck Fracture of the Proximal Humerus
- Ju Hong Lee, Gyu Hyung Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(2):406-413. Published online April 30, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.2.406
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
: to appreciate the effectiveness of th closed reduction and percutaneous pinning(CRPP) in reducible but unstable displaced surgical neck fracture of the humerus.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
: reviewed 30 patients(19 cases in CRPP and 11 cases in ORIF) with at least 1 year follow-up, comparing clinical union time, elapse time for surgery and clinical results using UCLA end-result scoring system in two froups and determining prognostic factors in CRPP.
RESULTS
: Clinical union was seen 8.4 weeks in CRPP and 11.2 weeks in ORIF. The difference between two groups in the clinical results was not significant. Lower UCLA score in CRPP correlated with the increment in age(p<0.05), but not with sex and metaphyseal comminution. Elapse time for surgery was taken average 38minutes in CRPP and average 95 minutes in ORIF. The postoperative complications in CRPP were 1 in nonunion, 4 in stiffness and 4 in pin loosening, most of them were occurred in female over sixty. SUMMARY : CRPP is a useful alternative and may be primarily applicable method in respect of comparable results to ORIF, minimal soft tissue damage and shorter surgical time. However, in cases of female with sixty or more, ORIF would be preferred because of poor bone quality, less compliant, and frequent joint stiffness.
- 463 View
- 0 Download

- Muller Type C Intercondylar Fractures of Femur : Comparative Analysis by Surgical Approach
- Hong Geun Jung, Myung Ho Kim, Moon Jib Yoo, Suk Joo Yoo, Sung Churl Lee, Jin Young Park, Sang Hyuk Min
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(1):64-73. Published online January 31, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.1.64
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to compare the functional results of Muller type C intercondylar fractures treated by 2 different surgical approaches : lateral and extensile approach.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study is based on 20 patients 21 knees of Muller type C intercondylar fractures. Two surgical approaches, i.e. 13 cases with lateral and 8 cases with extensile approach were used. The functional evaluation of results was done with criteria by Schatzker and Lambert. Excellent and good was grouped superior while fair and failure was grouped inferior.
RESULTS
Comparative analysis by surgical approach showed that among total 10 cases of C2 fractures, 6 cases(85.7%) of lateral approach and 2 cases(66.7%) of extensile approach were categorized in inferior group. Among the 8 cases in type C3 fractures, 3 cases treated surgically using the lateral approach showed fair and failure results and 3 cases(60%) of the remaining 5 cases using the extensile approach showed good results.
CONCLUSION
There was no significant result difference between lateral and extensile approach in type C2 fractures, but in C3 fracture, cases with extensile approach showed better results. Therefore the extensile approach should be recommended in C3 intercondylar fractures with intra-articular comminution.
- 320 View
- 1 Download

- A Comparision of conservative and Operative Treatmene in the Bony Mallet Finger
- Ik Su Choi, Su In Roh, Hong Ju Ha, Jin Goo Kang, Dae Yeon Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1999;12(4):1021-1026. Published online October 31, 1999
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1999.12.4.1021
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Mallet finger is a commom deformity caused by disruption of the extensor mechnism at the dorsal base of the distal phalanx. Patients can by managed by either conservative or operative treatment depending on some factors, such as the fracture type and interval from injury to medical treatment. However, whether to perform conservative or operative treatment is in debate. We conducted this study to compare the results of conservative and operative treatment of mallet finger caused by intra-articular fracture of the distal phalanx, with not mere than one third of the articular surface of the distal phalanx involved. From March 1994 to April 1999, we experienced 26 cases of bony mallet fingers. Following are the results. 1. The result by Kanies scale was satisfactory in 9 cases of 12 in conservative treatment(75%), and 10 cases of 14 in operative treatment(71%)(P>0.05). 2. The result was satisfactory in 8 cases of 10 in patients who were treated within 2 weeks(80%), and 4 cases of 7 in those treated after 4 weeks(57%)(P<0.05). 3. Conservative treatment was more cost effective, easier to perform compared to operative treatment. Thus, we suggest conservative treatment as the better treatment method for bony mallet finger with ont more than one third of the articular surface of the distal phalanx involved.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Extension pin block technique versus extension orthosis for acute bony mallet finger; a retrospective comparison
Gurkan Gumussuyu, Mehmet Melih Asoglu, Olcay Guler, Hasan May, Adil Turan, Ozkan Kose
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research.2021; 107(5): 102764. CrossRef
- Extension pin block technique versus extension orthosis for acute bony mallet finger; a retrospective comparison
- 554 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Operative Treatment of Acetabular Fracture
- Deuk Soo Hwang, Kwang Jin Rhee, Jun Young Yang, Jang Ik Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 1999;12(2):212-219. Published online April 30, 1999
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1999.12.2.212
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analysis clinical and radiological result of surgically treated acetabular fractures and to present appropriate surgical approach for fracture type. MATERIAL AND METHODS: A review of 51 surgically treated acetabular fractures, treated between April 1988 and October 1996, using single surgical exposures and combined surgical exposures was conducted. The classification was used Judet & Letournel,s classification and the surgical approach was applied Kocher-Langenbeck, Ilioinguinal, and Combined approach according to fracture aspect. The result was rated on a radiographic as well as a clinical result scale based on Matta,s.
RESULTS
The most common fracture was 14 posterior wall fracture and 7 transverse fracture. the surgical approach was applied Kocher-Langenbeck 29 cases, ilioinguinal 10 cases, and combined approach 8 cases, triradiate approach 2 cases and Extended iliofemoral approach 1 case. A satisfactory reduction was obtained in 87% of the cases (concentric, gap < 3mm). Clinical results were excellent in 28%, good in 54%, fair in 12%, and poor in 6%. Radiologic results at followup indicated 40% excellent results, 35% good results, 16% fair results, and 9% poor results. Postoperative complications appeared in 7 cases including posttraumatic arthritis 2 cases. Two patients later required total hip arthroplasty for avascular necrosis of femoral head and posttraumatic arthritis.
CONCLUSION
Ilioinguinal approach was good method for access to the anterior wall and column fracture, but in case of severe comminuted medial wall fracture company with anterior column, internal fixation is impossible. So, accurate assesment of the fracture pattern by careful radiologic analysis is essential. The posterosuperior dome fracture is important to anatomical reduction because of high risk of posttraumatic arthritis. In case of Transverse fracture, T-shape fracture, and both column, the more displaced column was reduced first, followed by opposite column after reduction identify by intraoperative radiography. We can be attained satisfactory reduction. Therefore, combined approach was good surgical method for this complex fracture.
- 346 View
- 0 Download

- Arthroscopically-Assisted Reduction and Fixation in Fractures of the Tibial Condyle
- Jung Su Hwang, Han Chul Kim, Yong Soon Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1999;12(1):90-97. Published online January 31, 1999
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1999.12.1.90
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fractures of the tibial condyle are characterized that often involve the articular surfaces and frequently associated with soft tissue injuries such as collateral ligament, cruciate ligament and menisci of the knee. The author analyzed 12 cases of tibial condyle fractures, which were surgically treated by reduction of depressed articular surface under assist of arthroscopy and then fixed with cannulated cancellous screws and accompanied by bone graft under the control of image intensifier in 9 cases of the 12 cases. The purpose of this study are (1) obtaining accurate reduction of the depressed articular surface, (2) preventing knee joint from the surgical wide dissection, (3) not only bony problems but also combined menisci and ligament injuries were diagnosis and management. We can obtain more anatomical reduction and excellent or good functional knee score since extensive exposure is avoided. There is no complication with regard to arthroscopic surgery and rapid recovery with reduced pain and early full ROM are obtained after follow-up study of a mean of 1 year.
- 346 View
- 0 Download

- Minimal Surgical Treatment of the Tibial Pilon Fracture
- Min Young Chung, Chang Woo Kim, Joon Kwon Jung, Eun Hwan Bae, Ho Keun Park, Seong Ho Park, Jang Won Hur
- J Korean Soc Fract 1999;12(1):113-118. Published online January 31, 1999
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1999.12.1.113
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The goals of the treatment of pilon fracture include to restore a normal anatomy and functional level of uninjured state. We analysed the clinical outcomes of the treatment of pilon fractures with calcaneal traction and percutaneous intramedullary nailing in the fibula (group A, 12 cases), or open reduction and internal fixation (group B, 11 cases) in 23 cases between April 1994 and March 1997. All of the patients were followed for at least one year (average, 18 months; range, 12 to 24 months). Fifteen patients were male (group A, 8; group B, 7), and eight were female (group A, 4; group B, 4). Falling-down injury is the most common cause and automobile accident is the second. According to the R.. uedi and Allg.. ower classification, type II fractures were most common. In the group A, two of the 12 fractures were type I, six were type II, and four were type III, and in the group B, two of the 11 fractures were type I, six were type II, and four were type III. According to the criteria of Mast and Teipner, in the group A, six were good result and six were fair, and in the group B, four were good, five were fair, and two were poor. A nonunion with wound infection and a malunion developed in the group B. The results in the group A were better than those in the group B in clinically, we propose the minimal surgical treatment is useful treatment option of pilon fracture.
- 316 View
- 0 Download

- Surgical Treatment of Femoral Nonunion
- Hyun Sik Gong, Hee Joong Kim, Han Soo Kim, Goo Hyun Baek, Sang Hoon Lee, Sang Rim Kim, Moon Sang Chung, Young Min Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1999;12(1):1-5. Published online January 31, 1999
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1999.12.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Femur is one of the most frequent sites of nonunion and femoral nonunion imposes many complications secondary to repeated surgical procedures and immobilizations. Many kinds of treatment options have been used and studied for comparison, but still the classical principle is rigid fixation, bone grafting, and adequate postoperative immobilization. In this study, the results of surgical treatment for femoral nonunion were analyzed. From July 1995 to August 1997, a total of 14 cases of femoral nonunion were treated surgically at the department of Orthopedic Surgery of the Seoul National University Hospital. All cases were treated by autogenous bone graft and internal fixation. For internal fixation, plate and screws were used in 10 cases and intramedullary nail in 3 cases and compression hip screw in 1 case. Postoperatively, hip spica cast was applied in 8 cases, cast brace in 2 cases and long leg splint in 1 case. In the other 3 cases, no additional support was adopted. In all cases, clinical union was achieved at postoperative 5 months in average. There was no significant complication except one case of marked limited motion in knee followed by hip spica cast.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cause and Treatment of the Nonunion of Femoral Shaft Fracture after Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing
Sung-Soo Kim, Sung-Keun Sohn, Chul-Hong Kim, Myung-Jin Lee, Lih Wang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2007; 20(2): 141. CrossRef
- Cause and Treatment of the Nonunion of Femoral Shaft Fracture after Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing
- 623 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Surgical Treatment for Displaced Talus Fracture-Dislocation
- Kwang Soon Song, Chul Hyung Kang, Seong Ryeol Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1998;11(4):906-911. Published online October 31, 1998
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1998.11.4.906
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Talus fracture is an uncommon fracture and frequently accompanied with serious complications such as avascular necrosis, nonunion and osteoarthritis. The purpose of this paper is to assess the effectiveness of open reduction and internal fixation in treatment of displaced talus fracture. Fourteen patients with severely displaced talus fracture-dislocation, classified as more severe than Hawkins type III and comminuted body fracture were evaluated. They were treated at Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center during the period of July 1989 to August 1996. The average period for follow up was 53 months, ranging from 18 months to 8 years. All patients were treated by open reduction and internal fixation using screws except 2 cases of severe talar body fractures, which were treated by Blair fusion. according to Hawkins scoring system. the end results were excellent only in 4 cases, good in 2, fair in 5, poor in 3. Avascular necrosis developed in 3 cases and traumatic arthritis in 5 cases. In conclusion, displaced talus fracture-dislocation had a high incidence of postoperative complications(57%) in spite of early sugical treatment. It is essential to consider about possible complications and sequelae before operation is performed.
- 404 View
- 0 Download

- The Acute surgical Treatment in Superior Peroneal Retinacular Injury in Ankle
- Suk Goo Han, Nam Yong Choi, In Tak Choo, Sung Jin Park, Young Mok Kang, In Ju Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 1998;11(3):605-610. Published online July 31, 1998
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1998.11.3.605
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The superior peroneal retinacular injury in ankle is often diagnosed as an ankle sprain and treated conservatively because of normal bony contour in type 1,2 injury according to Eckery's classification and small bony fragment with early union, evenly displaced in type 3. But its complications such as peroneal tendinitis and recurrent subluxation or dislocation of peroneal tendons sometimes develop late. Compared to peroneal tendinitis, the surgical treatment method for recurrent subluxation or dislocation of peroneal tendons is known superor to conservative method in results. And many reconstructive methods have been reported. In spite of their good results, harmfulness to normal structures, recurrences and technical difficulties may be a problem. So we perfomed 10 cases of acute surgical repair in superior peroneal retinacular injuries in ankle from March 1993 to February 1997 and prospectively analysed their clinical and radiological results with complications. Preoperative radiological diagnosis was done by plain films, peroneal tenography with computed tomography and also postperatively evaluated with plain films and peroneal tenography. 1. The most common cause of injury was sports(6 cases) including ski injury(4 cases) and average age of the patient was 29(17-56) years. 2. 4 cases of bony avulsion(type 3) were fixed with mini-screws and mean duration of bony union was 3.6 months. 3. The incidental subluxation or dislocation of peroneal tendons was not found intraoperatively and postoperatively. 4. All patients are able to participate in active exercise postoperatively except one patient who complains of lateral ankle discomfort due to peroneal tendinitis. In conclusion, acute surgical repair of superior peroneal retinacular injury in ankle is a recommended method to prevent it's complications such as peroneal retinacular injury in ankle is a recommended method to prevent it's complications such as peroneal tendinitis and subluxation or dislocation of peroneal tendons especially, in young and active patients.
- 333 View
- 0 Download

- Surgical Treatment of Acute acromioclavicular Dislocation
- Hyoun Oh Cho, Kyoung Duck Kwak, Byeung Yong Kim, su Min Sohn, Jin Kyoung Moon
- J Korean Soc Fract 1998;11(2):413-419. Published online April 30, 1998
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1998.11.2.413
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We have reviewed 40 patients of acute acromioclavicular dislocation all treated by several operative procedure from January 1990 to July 1996. After about 12 months follow up period, we analyzed the relationship between the type of operation and the clinical results. Several operative mothods were demonstrated till now, but 4 techniques or their combinations are commonly used. Those are fixation of acromioclavicular joint, fixation of coracoclavicular ligament, resection of distal end of clavicle and dynamic muscle transfer. Modified Phemister technique, modified phemister technique with coracoclavicular fixation and modified Bosworth technique were used with or without repairment of coracoclavicular ligament at our hospital. Modified Phemister technique showed less good results than those of other techniques especially when repair of the coracoclavicular ligamentwas not made, and the repair of the coracoclavicular ligaments or fixation of the coracoclavicular joint is an important factor affecting the final results.
- 363 View
- 0 Download

- Treatment of Acetabular Fractures -Comparison of Conservative Treatment and Surgical Treatment According to AO Comprehensive Classification-
- Chang Hyuk choi, Koing Woo Kwun, shin Kun Kim, Sang Wook Lee, seung Hee Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1998;11(2):288-295. Published online April 30, 1998
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1998.11.2.288
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Acetabular fracture is a severe injury associated with other body injuries. they result in permanent disability due to management difficulty and its complications such as traumatic arthritis, avascular necrosis of femoral head, etc.. In order to restore excellent function of hip joint, anatomic reduction and secure internal fixation followed by early mobilization are neccessary. We analysed 21 patients who were diagnosed as type A1 acetabular fracture from Jan. of 1991 to Dec. of 1996, and compared the functional results of conservative treatment method with that of surgical treatment method. The results were as follows. 1. Conservative management was done at 8 cases, and surgical management was done at 13 cases with open reduction and internal fixation. 2. The functional result by Goodwin criteria was all satisfactory in conservative reatment method and 12 cases(92%) in surgical treatment method. 3. Associated injuries were found in 18 cases, among them pelvic bone fracture was the most common fractured site and knee ligament injury was the most common soft tissue injury. 4. In the cases of larger acetabular fragment or in the presence of associated injury and instability after closed reduction, faster rehabilitation was achieved by starting early range of motion exercise and weight-bearing after surgical treatment than classical conservative treatment.
- 338 View
- 0 Download

- Operative Treatment of Intraarticular Fractures of the Distal Radius
- Chung Nam Kang, Jin Man Wang, Kwon Jae Roh, Jong Oh Kim, Dong Jun Kim, Jong Keon Oh, Han Cheon Bang
- J Korean Soc Fract 1998;11(1):56-62. Published online January 31, 1998
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1998.11.1.56
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Intraarticular fractures of the distal part of the radius comprise a distinct subgroup of fractures that are difficult to manage and are associated with a high frequency of complication and represent one of the greatest challenges to the orthopaedic surgeon. We reviewed 30 cases(28 patients) of intraarticular fractures of the distal radius treated surgically in orthopaedic department of Ewha medical center between January 1993 to May 1996 and analyzed the correlation between the clinical end results and radiographic parameters. The clinical end results were significantly worse when radia inclination didn't exceed 15, or radial length was less than 10mm or dorsal tilt exceeded 0. Ulna styloid fractre did adversely affect the clinical results. In our study 2mm articular step off did not show any difference in clinical results. But this is thought to be the result of relatively short period of follow up. Therefore we need to analyse this factor with long term follow up data.
- 360 View
- 0 Download

- Surgical Treatment of Tibial Plateau Fracture: Validity of Arthroscopy
- Shin Kang Cho, Jung Dae Oh, Young Sik Lee, Jin Tae Choi, Gyeong Hin Lim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1997;10(4):832-842. Published online October 31, 1997
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1997.10.4.832
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Twenty tibial plateau fractures were surgically treated by means of the double images of the arthroscopy and the image intensifier. The purpose of this attempt was (1) obtaining more anatomical reduction of articular margin, (2) preventing knee joint from the surgical dissection and (3) simultaneous diagnosis & management of the combined meniscus and ligament injuries. Three aims of this study are searching for (1) the indications of the arthroscopic surgery for the libial plateau fractures, (2) the techniques of the arthroscopic surgery for reduction and fixation and (3) the techniques for reducing the risk of the arthroscopic surgery. As a result, we can obtain more anatomical reduction and excellent or good functional knee score after follow-up study of a mean of 1 year and 9 months. There is no complication with regard to arthroscopic surgery. But anatomical reduction of the bicondyle fractures with severe articular and metaphyseal comminution was technically difficult. So, the other technique as if open reduction will be needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Arthroscopically-Assisted Reduction and Internal Fixation of Intra-Articular Fractures of the Lateral Tibial Plateau
Juhan Kim, Dong Hwi Kim, Jae-Hwan Lim, Hyunwoong Jang, Young Wook Kim
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2019; 54(3): 227. CrossRef - Treatment of Shatzker Type VI Tibia Plateau Fracture Using Lateral and Posteromedial Dual Incision Approach and Dual Plating
In-Jung Chae, Sang-Won Park, Soon-Hyuck Lee, Won Noh, Ho-Joong Kim, Seung-Beom Hahn
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(4): 252. CrossRef
- Arthroscopically-Assisted Reduction and Internal Fixation of Intra-Articular Fractures of the Lateral Tibial Plateau
- 668 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Surgical Treatment of Avulsion Fracture of the Fibular Head Associated with Lateral Instability of the Knee
- Min Young Chung, Won Suck Lee, Soo Myung Lee, Won Cheul Song, Chang Woo Kim, Kwang Min Jung
- J Korean Soc Fract 1997;10(3):597-603. Published online July 31, 1997
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1997.10.3.597
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Though avulsion fracture of the fibular head rarely occurs, it frequently associates with lateral compartment injury of the knee which resulls in lateral instability. Some authors preferred to internally fixing avulsion fracture of the fibular head to prevent and restore lateral instability of the knee. Our purpose was to suggest that lateral instability of the knee be restored by internal fixation of the fibular head in these cases. We reviewed 6 cases of avulsion fracture of the fibular head associated with lateral instability of the knee which were treated surgically from January, 1993 to December, 1994 with average 2-year-over follow-up. We evaluated each cases using the Knee Ligament Standard Evaluation Form proposed by International Knee Documentation Committee. The results were as follows. The average displacement of the fibular head was 8.4mm. The activity level and overall grade were A(normal) in 4 cases, B(nearly normal) in 1 case, D(severe abnormal) in 1 case. Lateral instability of the knee was satisfactorily restored by internal fixation of the fibular head and repair of ligamentous injuries in cases of avulsion fracture of the fibular head associated with lateral instability of the knee.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Establishment of Classification of Tibial Plateau Fracture Associated with Proximal Fibular Fracture
Zhan‐le Zheng, Yi‐yang Yu, Heng‐rui Chang, Huan Liu, Hui‐lin Zhou, Ying‐ze Zhang
Orthopaedic Surgery.2019; 11(1): 97. CrossRef
- Establishment of Classification of Tibial Plateau Fracture Associated with Proximal Fibular Fracture
- 589 View
- 7 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Surgical Treatment of the Pilon Fractures
- Jung Jae Kim, Jong Hi Park, Woo Shin Cho, Key Yong Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1997;10(3):492-500. Published online July 31, 1997
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1997.10.3.492
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The intraarticular fractures of the distal tibia. so-called pilon fractures have been difficult in management due to the severe comminution of articular surface and frequent soft tissue problems. So there have been many controversies in the method of treatment. Although historically the results of various type of treatment of these fractures have been less than optimal, there has been a recent trend that suggests success in the majority of cases through operative treatment following the principles outlined by the AO/ASIF group. Among the patients of pilon fracture admitted to our hospital from October 1989 to August 1995 who were treated by open reduction and internal fixation, 32 patients(34 cases) were included who could be follow up for more than 2 years. According to AO/ASIF classification, type B1 5 cases, type B2 7 cases, type B3 5 cases, type C1 3 cases, type C2 4 cases, type C3 10 cases. The authors analyaed the clinical and radiological results of tibial pilon fractures exclusively treated by internal fixation. The results as follow : 1. Among 34 cases, 12 cases(35.3%) were not associated with of fibula fracture. There was no stastical relationship between the severity of pilon fracture and the presence of flbula fracture. 2. Good results in fracture reduction was obtained at 26 cases(76.5%) and good functional reults was obtained at 26 cases(76.5%). 3. The most commom postoperative complication was infection combined with skin problem(6 cases), which were treated by antibiotics and flap surgery. 4. Anatomical reduction and stable internal fixation of articular surface, careful manipulation of soft tissues and early range of motion exercise yielded good results of surgical treatment of pilon fracture.
- 452 View
- 1 Download

- Operative Treatment of Forearm Fractures in Children
- Nam Gee Lee, Seung Ki Kim, Won Jong Bahk, Hyun Joon Song, Ban Chang
- J Korean Soc Fract 1997;10(1):195-202. Published online January 31, 1997
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1997.10.1.195
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Management of severe diaphyseal fracture of radius and ulna in children can be a challenging problem. Reduction and maintenance of the position of two mobile parallel bones is difficult because pronating and supinating muscles produce angulatory as well as rotational forces. Open reduction and internal fixation are generally accepted for adult forearm fractures, but controversy surrounds open reduction for children. What should be done for the irreducible fracture that will result in a malunion? Several authors advocate open reduction in children over 10 years of age rather than accept poor position. And others advocate open reduction regardless of age if closed reduction is unsatisfactory. We reviewed thirteen children between 6-14 years of age, who had irreducible fractures of diaphysis of forearm both bone, and who were treated with open reduction and internal fixation with plate for mid 1/3 fractures(4 cases) and open reduction and internal fixation with K-wires for distal 1/3 fractures(9 cases). The results were as follows; 1. 2 cases(15%) had limitation of pronation within 10 comparing with uninjured side. But 11 cases(85%) had equal movements on both sides. And the range of motions of the elbow and wrist are within normal limit. 2. More than 20 angulation for mid 1/3 fracture over 10 years of age, and more than 20 angulation or 20% displacement for distal 1/3 fracture over 6 years of age, it would be better to perform a surgical treatment if nonsurgical treatment was failed. 3. Immobilization periods were 5 weeks for plate fixation group and 6.9 weeks for K-wire fixatioin group. Bone union was occurred in all cases, at 9 weeks in plate fixation group and 8 weeks in K-wire fixation group. 4. Its better to fix with plate ofr promimal 2/3 fracture and K-wire for distal 1/3 fracture in case of operation. In conclusion, our results of open reduction and internal fixation were satisfactory if adequate alignment of fractures had not been achieved or maintained.
- 431 View
- 0 Download

- Impaction and Tension-Band Wiring Technique in Proximal Humerus Fractures Accompanying Severe Comminution of Surgical Neck
- Sung Il Bin, Sung Jin Cho, Key Yong Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1996;9(4):1054-1060. Published online October 31, 1996
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1996.9.4.1054
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Proximal humerus frartures occur most commonly in elderly people, especially with osteoporotic bone. But recently these fractures are also common in younger people due to the increased incidence of trafnc accidents or sports injuries. It is reported that displacement of major fracture fragments can be observed in about 20 percents of proximal humerus fractures and they need some form of surgical treatment. But when there is a sevfre comminution in the area of surgical neck which precludes anatomical reduction, it is almost impossible to obtain rigid fixation and to start an early motion. We reported ten cases of unstable proximal humerus fractures with severe comminution of surgical neck which preclude anatomical reduction and stable rxation and require impaction of the shaft fragment into the head and fixation with multiple pins and tension band wiring. After an arevage follow-up period of 30 months, we obtained the following results: 1. Nine cases out of 10 showed satisfactory results, excellent in 2 cases and good in 7 cases. But there was 1 case in poor. 2. In complications, 2 cases showed transient postoperative subluxation and 3 case showed moderate joint stiffness. But there was no avascular necrosis of humeral head.
- 382 View
- 1 Download

- The tibial condylar fractures treated by surgical method
- Hee Soo Kyung, Joo Chul Ihn, Chang Ho Park
- J Korean Soc Fract 1996;9(2):439-448. Published online April 30, 1996
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1996.9.2.439
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The treatment of the tibial piateau fractures has been under discussion for several decades, but no final answer has been reached. But many surgeons today believe that open reduction and internal fixation of commninuted, severly depressed, or displaced fractures are indicated The goal of the surgery is anatomic reduction of joint surface, rigid fixation, and early range of motion. This retrospective study evaluated 40 cases of tibial condylar fractures that treated surgically at the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Kyungpook National University Hospital from February, 1991 to August, 1995. The minimum follow up period was 13 months and average follow up period of the patients was 33 months. The obtained result were as follows: 1. There were forty patients treated by surgically, the mean age was forty-six, and thirty patients were male, ten patients were female., thirty-one patients involved in motor vehicle accidents. 2. The most common type of the fracture was SchatBker type II in 10 patients., the most common associated soft tissue injury was rupture of the ipsilateral medial collateral ligament. 3. The most common method of the treatment was minimal screw fixation and bone graft in 20 cases. 4. The thirty-one cases (77.5%) had satisfactory result according to the Blokkers criteria among 40 cases. There were 2 superficial infections and 1 deep infection for post operative complications. 5. We had good result by anatomical reduction of the articular surfaces and early knee motion and delayed weight bearing for the treatment of the displaced, comminuted tibial condylar fracture.
- 339 View
- 3 Download

- Result of 29 consecutive patients with the distal femiral fracture: Analysis of the result treated with AO DCS(dynamic condylar Screw) Supracondylar nail, May anatomical plate
- Weon Yoo Kim, Jin Hyung Sung, Chong Hoon Park, Jeong Soo Park, Jin Yong Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1996;9(1):68-75. Published online January 31, 1996
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1996.9.1.68
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Twenty-nine cases of the surgically treated distal femoral fracture were analyzed to compare internal fixatorw (AO DCS,Supracondylar nail, May anatomical plate),who were treated at Department of orthopaedic surgery, Taejon Saint Marys hospital from Jan. 1992 to Jun. 1994. The cases were classified according to AO classification and minmum 12 months(average:22.4 monthw) follow up. Following results were obtained: 1.Male was more common than female, age distrbution was between 16 and 77 years old(average 40.4), abd the most common cause of the fracture was traffic accident. 2.The most comon type C by AO classification(type A 11 cases, type B 1 case, type C 17 cases). 3.According to Schatzkers criteria in the clincal result, type A,B were better resykt than type C, and severe soft tissue damage, comminution and joint involvement lead to unsatisfactory results. 4.Supracondylar nail was inadequate implant due to inferior clinical result(1 excellent, 2 good and 3 poor). 5.DCS had more sateafactory result than other internal fixators(supracondylar nail, May anatomical plate). Based on the observations, the better results depend on the amount of initial trauma, early anatomical reduction, rigid internal fixation and exercise of the knee joint.
- 364 View
- 0 Download

- Treatment of A-C joint dislocation with cannulated screw fixation under local anesthesia
- Bu Hwan Kim, Jong In Yim, Deog Jeong Kang
- J Korean Soc Fract 1996;9(1):185-192. Published online January 31, 1996
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1996.9.1.185
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In 1941, Bosworth used noncannulated coracoclavicular lag screw to Oeat acute A-C joint dislocation. In 1989, Tsou fixed coracoclavicular joint with percutaneous cannulated screw under general anesthesia in the treatment of acute A-C joint complete dislocations. We tried to treat 10 cases of acute A-C joint dislocations with cannulated screw fixation of C-C joint under local anesthesia, so we report the results with review of literatures. The results were as follows 1. Results of treatment were good in 7 cases, fair in 2 cases, and poor in 1 case by Weaver and Dunn evaluation criteria. 2. The operations were done under local anesthesia, but in two cases operation ended under general anesthesia due to discomfort of the patients. 3. In skeletally thin patient, it was very difficult to make accurate hole and we experienced an iatrogenic fracture of clavicle and coracoid process. This technique is not recommendable in skeletally thin patient. 4. Operation took 42 minutes on average(from 30 minutes to 105 minutes) though it took more time in the early cases. 5. We had several complications in 3 patients. Misdirection of screw(1 case), screw loosening and pull out(1 case), subluxation of A-C joint after removal of screw(2 cases), and iatrogenic fracture of clavicle and coracoid process(1 case) but no case of metal breakage or infection.
- 407 View
- 0 Download

- The Surgical Treatment and Prognosis of the Talar Body Fracture
- Hyung Yeoun Choi, Jae Hyung Lee, Il Ho Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1995;8(4):864-869. Published online October 31, 1995
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1995.8.4.864
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fracture of the talus is infrequent injury when they occur, gut, the complications of the displaced fractures are frequent and resulting disabilities are severe that the importance of proper management is emphasized. Authors reviewed 18 cases of talus fracture (Hawkins classification type III and IV) treated at Department of orthopaedic surgery, Capital Armed force Gerneral Hospital from 1991 to 1994 to evaluate the result. The results were as follows; 1. Most common cause was fall down. 2. Associated injuries were fracture of the medial malleolus, calcaneus and Bursting fracture of spine. 3. The methods of treatment were open reduction and screw fixation in all cases. 4. Classification by Hawkins were Type III in 12 cases and Type IV in 6 cases. 5. Final clinical result by Hawkins criteria were good in 6 cases, fair in 7 cases and poor in 5 cases. 6. Complications were avascular necrosis in 7 cases, degenerative arthritis in 5 and nonunion in 3.
- 319 View
- 0 Download

- Surgical Treatment of Galezzi's Fracture in Adult
- In Suk Oh, Do Hyun Moon, Ju Moon Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1995;8(1):234-242. Published online January 31, 1995
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1995.8.1.234
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Galeazzi's fracture has been defined as a fracture of the distal part of the radial diaphysis that is associated with rupture of the capsule and ligaments of the distal radioulnar joint. This fracture is infrequent and shows the tendency to redisplacement after reduction due to various factors including strong muscles (the brachioradialis, the pronator quadratus, the thumb aHuctors and extensors) and the distal radioulnar joint instability. Because of these factors, the treatment of choice for Galeazzis fracture is open reduction and internal fuation. The authors reviewed the cases of 22 patients with GaleazBis fracture who had been treated surgically form January 1988 to December 1993. The results were as follows 1. There were 18 males and 4 females. The age range was from 19 to 54 years(average, 31 years). 2. The fracture occured mostly at the junction of the middle and distal third of the radial diaphysis in 13 cases(59%). 3. In 16 cases(73%), the fractures were closed and in 6 cases(27%), open. In 17 cases(78%), the fractures were simple and in 5 cases(22%), comminuted. 4. Radiograph signs of the distal radioulnar joint disruption was positive in 86% of the cases. 5. Operative treatment was performed in all cases. Operative treatment resulted in an excellent outcome in 11 cases(50%), a fair outcome in 7 cases(31%) and poor in 4 cases(17%). 6. Among 9 cases. complications were delayed union in 3 cases, subluxation of the distal radioulnar joint in 3 cases, superfical wound infection in 1 case, injury of sensory branch of radial nerve in 1 case and angulation(5 ↑)in 1 case.
- 285 View
- 1 Download

- Surigcal Treatment for Acute Acromioclayicular Joint Dislocation
- Nam Yong Choi, In Ju Lee, Moon Ku Choi, Young Chae Lee, Han Jin Kim, Chong Ook Shin
- J Korean Soc Fract 1995;8(1):188-192. Published online January 31, 1995
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1995.8.1.188
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Thirty-one patients who had a acromioclavicular joint dislocation that were treated by surgical operation, between January 1990 and December 1993 at St. Pauls & Holy Family hospital were analyzed. The results are as follows; 1. There were twenty-five males and six females. The mean age was 33 years, ranging from 17 to 52 years old. 2. Out of thirty-one cases, twenty-six had good to excellent functional results. 3. As regards complication, wire migration occurred in two cases, wire breakage in one case, screw loosening in one, and subluxation following wire or screw removal in four.
- 314 View
- 0 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


