Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 30(3); 2017 > Article
-
Original Article
- Minimal Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis versus Conventional Open Plating in Simple Humeral Shaft Fracture (AO Type A, B1, B2)
-
Boseon Kim, M.D.
 , GwangChul Lee, M.D.
, GwangChul Lee, M.D. , Hyunwoong Jang, M.D.
, Hyunwoong Jang, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2017;30(3):124-130.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.3.124
Published online: July 21, 2017
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chosun University School of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea.
- Correspondence to: GwangChul Lee, M.D. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chosun University Hospital, 365 Pilmundae-ro, Dong-gu, Gwangju 61453, Korea. Tel: +82-62-220-3147, Fax: +82-62-226-3379, leekci@chosun.ac.kr
Copyright © 2017 The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 686 Views
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) by comparing the results between open plating and MIPO conducted by simple humeral shaft fractures.
-
Materials and Methods
- From September 2010 to February 2015, we evaluated humeral shaft fractures that 26 cases underwent MIPO and 41 cases underwent open plate fixation (OPEN). Operation time, amount of blood loss, and radiative exposure time were examined. Radiographically, bone union time and angulation were compared. At last, UCLA shoulder score and MEPI were used to compare the clinical results of shoulder and elbow and complications were examined.
-
Results
- The average operation time 82±23 minutes in MIPO, 119±20 minutes in OPEN (p=0.007) and amount of bleeding 238±67 ml in MIPO, 303±48 ml in OPEN (p=0.003), radiation exposure time 201±85 seconds in MIPO, 20±5 seconds in OPEN (p=0.000) were statistically significant. Bone union time and angulations, clinical results were not statistically significant. In Complication, iatrogenic radial nerve paralysis occurred 2 cases, nonunion occurred 1 case in MIPO. Nonunion and soft tissue infection occurred 2 cases each in OPEN.
-
Conclusion
- MIPO in simple humeral shaft fractures gave us radiologically and clinically satisfactory results, and may be useful by understanding the anatomical knowledge and using appropriate implants and skills.
- 1. Bae SW, Kim WJ, Song BY, Choi NH, Lee JH. Postoperative functional assessments in adult humerus shaft fractures-comparison among plates and screws, intramedullary nail and external fixator-. J Korean Soc Fract, 2001;14:228-235.Article
- 2. Bhandari M, Devereaux PJ, McKee MD, Schemitsch EH. Compression plating versus intramedullary nailing of humeral shaft fractures: a meta-analysis. Acta Orthop, 2006;77:279-284.ArticlePubMed
- 3. An Z, He X, Jiang C, Zhang C. Treatment of middle third humeral shaft fractures: minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis versus expandable nailing. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol, 2012;22:193-199.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 4. Changulani M, Jain UK, Keswani T. Comparison of the use of the humerus intramedullary nail and dynamic compression plate for the management of diaphyseal fractures of the humerus. A randomised controlled study. Int Orthop, 2007;31:391-395.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 5. Chiu FY, Chen CM, Lin CF, Lo WH, Huang YL, Chen TH. Closed humeral shaft fractures: a prospective evaluation of surgical treatment. J Trauma, 1997;43:947-951.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Dabezies EJ, Banta CJ 2nd, Murphy CP, d'Ambrosia RD. Plate fixation of the humeral shaft for acute fractures, with and without radial nerve injuries. J Orthop Trauma, 1992;6:10-13.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Bell MJ, Beauchamp CG, Kellam JK, McMurtry RY. The results of plating humeral shaft fractures in patients with multiple injuries. The Sunnybrook experience. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1985;67:293-296.ArticlePubMed
- 8. McCormack RG, Brien D, Buckley RE, McKee MD, Powell J, Schemitsch EH. Fixation of fractures of the shaft of the humerus by dynamic compression plate or intramedullary nail. A prospective, randomised trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2000;82:336-339.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Apivatthakakul T, Arpornchayanon O, Bavornratanavech S. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) of the humeral shaft fracture. Is it possible? A cadaveric study and preliminary report. Injury, 2005;36:530-538.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Jiang R, Luo CF, Zeng BF, Mei GH. Minimally invasive plating for complex humeral shaft fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, 2007;127:531-535.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 11. Babst R, Bavonratanavech S, Pesantez R. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. Switzerland: AO Foundati; 2012. p. 86-90.Article
- 12. Smith MV, Calfee RP, Baumgarten KM, Brophy RH, Wright RW. Upper extremity-specific measures of disability and outcomes in orthopaedic surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2012;94:277-285.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 13. Turchin DC, Beaton DE, Richards RR. Validity of observer-based aggregate scoring systems as descriptors of elbow pain, function, and disability. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1998;80:154-162.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Vander Griend R, Tomasin J, Ward EF. Open reduction and internal fixation of humeral shaft fractures. Results using AO plating techniques. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1986;68:430-433.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Apivatthakakul T, Phornphutkul C, Laohapoonrungsee A, Sirirungruangsarn Y. Less invasive plate osteosynthesis in humeral shaft fractures. Oper Orthop Traumatol, 2009;21:602-613.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 16. Ji F, Tong D, Tang H, et al. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) technique applied in the treatment of humeral shaft distal fractures through a lateral approach. Int Orthop, 2009;33:543-547.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 17. Livani B, Belangero WD. Bridging plate osteosynthesis of humeral shaft fractures. Injury, 2004;35:587-595.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Zhiquan A, Bingfang Z, Yeming W, Chi Z, Peiyan H. Minimally invasive plating osteosynthesis (MIPO) of middle and distal third humeral shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma, 2007;21:628-633.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Oh CW, Byun YS, Oh JK, et al. Plating of humeral shaft fractures: comparison of standard conventional plating versus minimally invasive plating. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res, 2012;98:54-60.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Lee HJ, Oh CW, Kim DH, Park KH. Minimally invasive anterior plating of humeral shaft fractures. J Korean Fract Soc, 2011;24:341-346.Article
- 21. Farragos AF, Schemitsch EH, McKee MD. Complications of intramedullary nailing for fractures of the humeral shaft: a review. J Orthop Trauma, 1999;13:258-267.ArticlePubMed
- 22. An Z, Zeng B, He X, Chen Q, Hu S. Plating osteosynthesis of mid-distal humeral shaft fractures: minimally invasive versus conventional open reduction technique. Int Orthop, 2010;34:131-135.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 23. Livani B, Belangero WD, Castro de. Fractures of the distal third of the humerus with palsy of the radial nerve: management using minimally-invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2006;88:1625-1628.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Kobayashi M, Watanabe Y, Matsushita T. Early full range of shoulder and elbow motion is possible after minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for humeral shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma, 2010;24:212-216.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
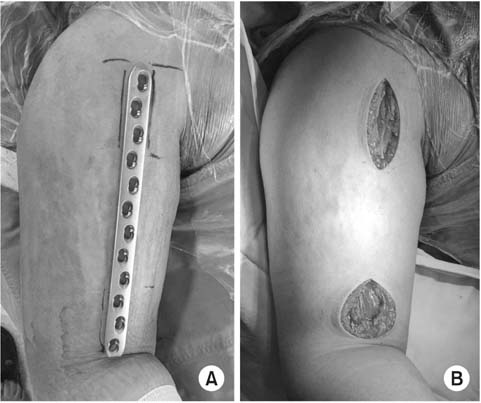
Incisional site design (A) with broad 5.0 LCP® and skin incision (B) for the minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis technique.
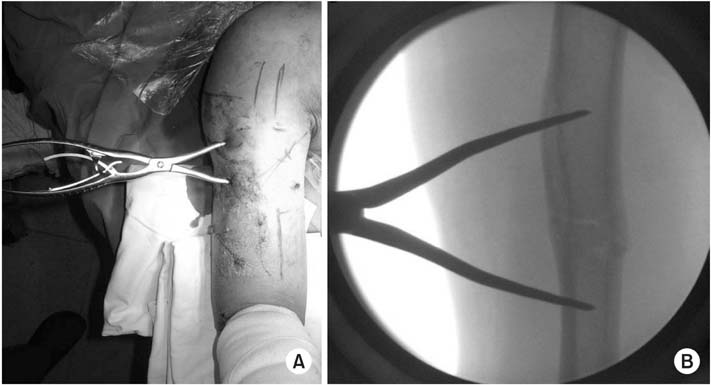
Clinical photo (A) and C-arm image (B) of closed reduction using modified pointed reduction forceps.
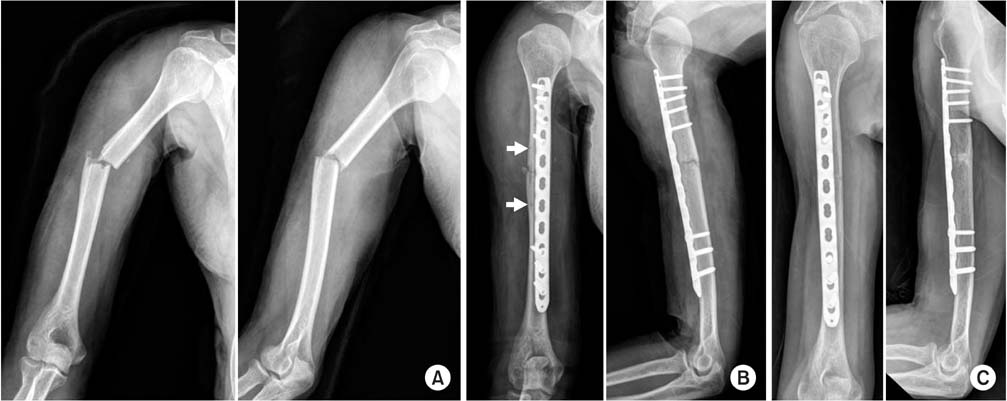
(A) Preoperative radiography of a 52-year-old male showing a right humeral fracture (AO/OTA type A3). (B) Postoperative radiography showing closed reduction and internal fixation with Metaphyseal Plate® using the minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis technique. There are two holes for reduction and compression using modified pointed reduction forceps (white arrows). (C) Radiography at three months after the operation showing radiologic union.
Patient Data of Humeral Fracture
Comparison of Results
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Outcomes of Arthroscopic Assisted Reduction and Percutaneous Fixation for Tongue-Type Sanders Type II Calcaneal Fractures
Jae Woo Park, Chul Hyun Park
Journal of Korean Foot and Ankle Society.2017; 21(4): 144. CrossRef
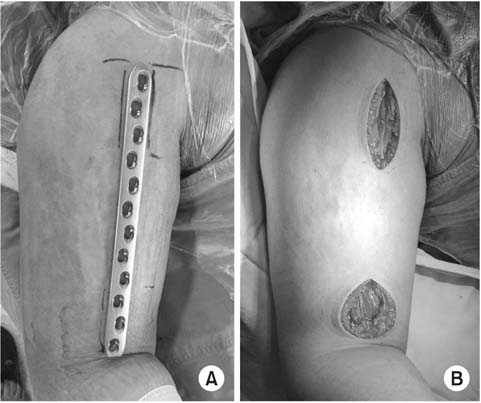
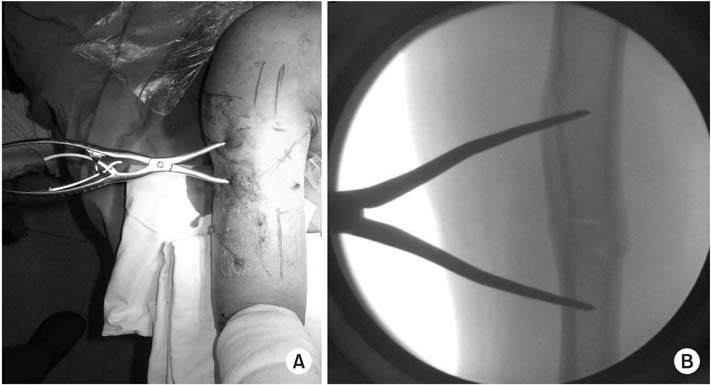
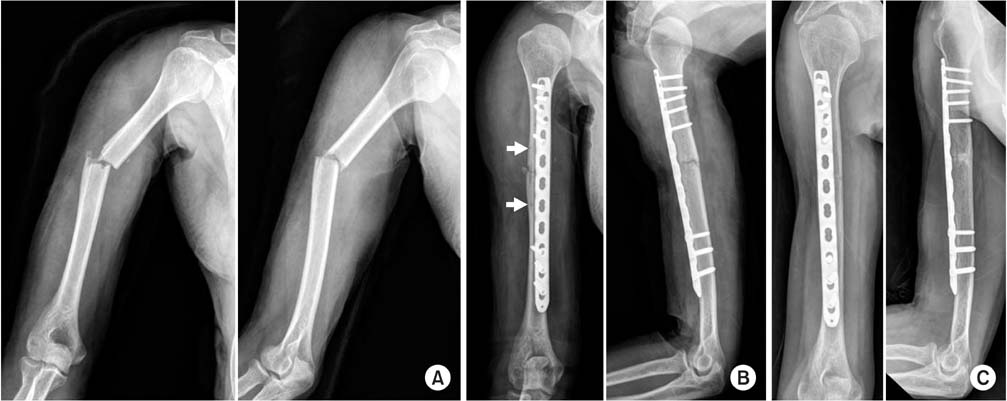
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Patient Data of Humeral Fracture
| Variable | MIPO group | OPEN group |
|---|---|---|
| No. of patient | 26 | 41 |
| Mean age (yr) | 50.2±18 | 43.0±18 |
| Sex | ||
| Male | 13 | 21 |
| Female | 13 | 20 |
| AO classification | ||
| A1 | 2 (7.7) | 3 (7.3) |
| A2 | 5 (19.2) | 7 (17.1) |
| A3 | 7 (26.9) | 5 (12.2) |
| B1 | 1 (3.8) | 11 (26.8) |
| B2 | 11 (42.3) | 15 (36.6) |
Values are presented as number only, mean±standard deviation, or number (%). The sum of the percentages does not equal 100% because of rounding. MIPO: minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis, OPEN: open plate fixation.
Comparison of Results
| Variable | MIPO group | OPEN group | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operation time (min) | 82.0±23 | 119.0±20 | 0.007 |
| Bleeding (ml) | 238.0±67 | 303.0±48 | 0.003 |
| Exposure to radiation (s) | 201.0±85 | 20.0±5 | 0.000 |
| Bone union (wk) | 17.2±9.4 | 17.0±3.6 | 0.226 |
| Angulation (°) | |||
| Varus | 6.0±2.1 | 1.0±1.5 | 0.114 |
| Anterior | 2.0±2.5 | 0.0±0.7 | |
| UCLA shoulder score | 34.1±10.7 | 33.7±12.9 | 0.156 |
| MEPI | 97.8±12.7 | 96.0±17.7 | 0.694 |
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation. p-values <0.05 were considered significant. MIPO: minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis, OPEN: open plate fixation, UCLA: University of California Los Angeles, MEPI: Mayo Elbow Performance Index.
Values are presented as number only, mean±standard deviation, or number (%). The sum of the percentages does not equal 100% because of rounding. MIPO: minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis, OPEN: open plate fixation.
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation. p-values <0.05 were considered significant. MIPO: minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis, OPEN: open plate fixation, UCLA: University of California Los Angeles, MEPI: Mayo Elbow Performance Index.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

