Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 28(1); 2015 > Article
-
Original Article
- Perioperative Blood Loss in Intramedullary Hip Screw for Intertrochanteric Fracture: Analysis of Risk Factors
- Jai Hyung Park, M.D., Ph.D., Hwa Jae Jung, M.D., Ph.D., Hun Kyu Shin, M.D., Ph.D., Eugene Kim, M.D., Ph.D., Se-Jin Park, M.D., Ph.D., Taeg Su Ko, M.D., Jong-Hyon Park, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2015;28(1):53-58.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.1.53
Published online: January 20, 2015
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kangbuk Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Jai Hyung Park, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kangbuk Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, 29 Saemunan-ro, Jongno-gu, Seoul 110-746, Korea. Tel: 82-2-2001-2168, Fax: 82-2-2001-2176, jaihyung.park@samsung.com
Copyright © 2015 The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 125 Views
- 0 Download
Abstract
-
Purpose
- We compared visible blood loss and calculated blood loss after intramedullary fixation in intertrochanteric fracture, and evaluated correlation between blood loss and its risk factors.
-
Materials and Methods
- A total of 256 patients who underwent closed reduction and intramedullary fixation in femoral intertrochanteric fracture between 2004 and 2013 were enrolled in this study. The total blood loss was calculated using the formula reported by Mercuiali and Brecher. We analyzed several factors, including fracture pattern (according to Evans classification), gender, age, body mass index (BMI), anesthesia method, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease, preoperative anemia, American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) score and use of antithrombotic agents.
-
Results
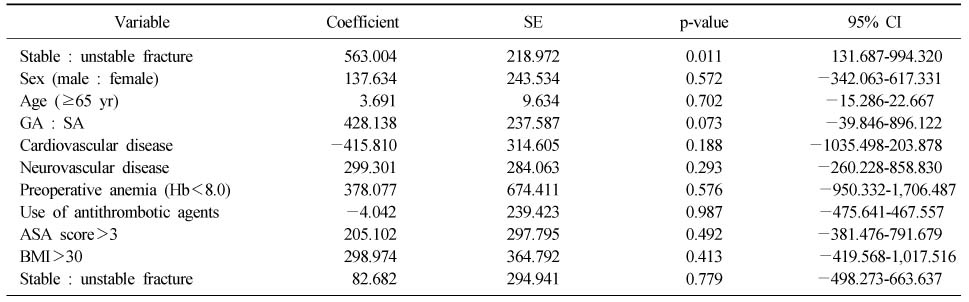
- Total calculated blood loss (2,100±1,632 ml) differed significantly from visible blood loss (564±319 ml). In addition, the blood loss of unstable fracture patient was 2,496±1,395 ml and multivariate analysis showed a significant relationship between blood loss and fracture pattern (p<0.01). However, other factors showed no statistically significant difference.
-
Conclusion
- Total calculated blood loss was much greater than visible blood loss. Patients with unstable intertrochanteric fracture should be treated with care in order to reduce blood loss.
- 1. Sehat KR, Evans RL, Newman JH. Hidden blood loss following hip and knee arthroplasty Correct management of blood loss should take hidden loss into account. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2004;86:561-565.
- 2. Good L, Peterson E, Lisander B. Tranexamic acid decreases external blood loss but not hidden blood loss in total knee replacement. Br J Anaesth, 2003;90:596-599.Article
- 3. Lemos MJ, Healy WL. Current concepts review: blood transfusion in orthopaedic operations. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1996;78:1260-1271.Article
- 4. Keating EM, Meding JB. Perioperative blood management practices in elective orthopaedic surgery. J Am Acad Orthop Surg, 2002;10:393-400.
- 5. Lemaire R. Strategies for blood management in orthopaedic and trauma surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2008;90:1128-1136.
- 6. Salido JA, Marín LA, Gómez LA, Zorrilla P, Martínez C. Preoperative hemoglobin levels and the need for transfusion after prosthetic hip and knee surgery: analysis of predictive factors. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2002;84:216-220.
- 7. Bell TH, Berta D, Ralley F, et al. Factors affecting perioperative blood loss and transfusion rates in primary total joint arthroplasty: a prospective analysis of 1642 patients. Can J Surg, 2009;52:295-301.
- 8. Walker RW, Rosson JR, Bland JM. Blood loss during primary total hip arthroplasty: use of preoperative measurements to predict the need for transfusion. Ann R Coll Surg Engl, 1997;79:438-440.
- 9. Rosencher N, Kerkkamp HE, Macheras G, et al. OSTHEO Investigation. Orthopedic Surgery Transfusion Hemoglobin European Overview (OSTHEO) study: blood management in elective knee and hip arthroplasty in Europe. Transfusion, 2003;43:459-469.
- 10. Slappendel R, Dirksen R, Weber EW, van der. An algorithm to reduce allogenic red blood cell transfusions for major orthopedic surgery. Acta Orthop Scand, 2003;74:569-575.
- 11. Bierbaum BE, Callaghan JJ, Galante JO, Rubash HE, Tooms RE, Welch RB. An analysis of blood management in patients having a total hip or knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1999;81:2-10.
- 12. Nam WD, Kim IY, Rhyu KH. Blood loss and transfusion in primary total hip arthroplasty. J Korean Hip Soc, 2006;18:1-5.
- 13. Mylod AG Jr, France MP, Muser DE, Parsons JR. Perioperative blood loss associated with total knee arthroplasty. A comparison of procedures performed with and without cementing. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1990;72:1010-1012.
- 14. Sharrock NE, Salvati EA. Hypotensive epidural anesthesia for total hip arthroplasty: a review. Acta Orthop Scand, 1996;67:91-107.
- 15. Juelsgaard P, Larsen UT, Sørensen JV, Madsen F, Søballe K. Hypotensive epidural anesthesia in total knee replacement without tourniquet: reduced blood loss and transfusion. Reg Anesth Pain Med, 2001;26:105-110.
- 16. McLaughlin JR, Lee KR. The outcome of total hip replacement in obese and non-obese patients at 10- to 18-years. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2006;88:1286-1292.
- 17. Stickles B, Phillips L, Brox WT, Owens B, Lanzer WL. Defining the relationship between obesity and total joint arthroplasty. Obes Res, 2001;9:219-223.
- 18. Chechik O, Thein R, Fichman G, Haim A, Tov TB, Steinberg EL. The effect of clopidogrel and aspirin on blood loss in hip fracture surgery. Injury, 2011;42:1277-1282.
- 19. Foss NB, Kehlet H. Hidden blood loss after surgery for hip fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2006;88:1053-1059.
- 20. Jensen JS. Classification of trochanteric fractures. Acta Orthop Scand, 1980;51:803-810.
- 21. Dimon JH, Hughston JC. Unstable intertrochanteric fractures of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1967;49:440-450.
REFERENCES
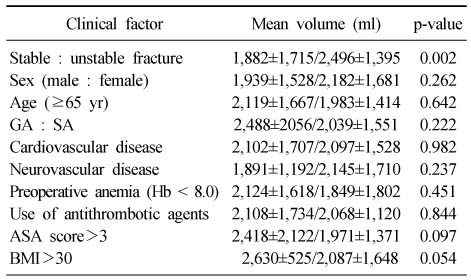
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

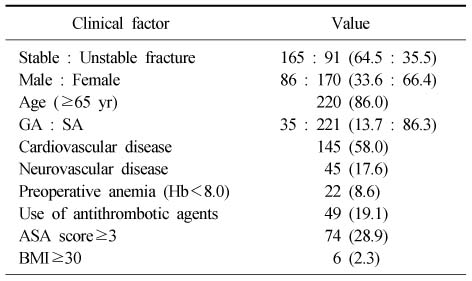
Characteristics of Studied Patients
Values are presented as number (%). GA: General anesthesia, SA: Spinal anesthesia, Hb: Hemoglobin, ASA: American Society of Anesthesiologists, BMI: Body mass index.
Predictor of Total Blood Loss in Patients Who Underwent Intramedullary Fixation for Intertrochanteric Fracture in Student T-test
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation. GA: General anesthesia, SA: Spinal anesthesia, Hb: Hemoglobin, ASA: American Society of Anesthesiologists, BMI: Body mass index.
Predictor of Total Blood Loss in Patients Underwent Intramedullary Fixation for Intertrochanteric Fracture in Multivariate Analysis
SE: Standard error, CI: Confidence interval, GA: General anesthesia, SA: Spinal anesthesia, Hb: Hemoglobin, ASA: American Society of Anesthesiologists, BMI: Body mass index.
Values are presented as number (%). GA: General anesthesia, SA: Spinal anesthesia, Hb: Hemoglobin, ASA: American Society of Anesthesiologists, BMI: Body mass index.
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation. GA: General anesthesia, SA: Spinal anesthesia, Hb: Hemoglobin, ASA: American Society of Anesthesiologists, BMI: Body mass index.
SE: Standard error, CI: Confidence interval, GA: General anesthesia, SA: Spinal anesthesia, Hb: Hemoglobin, ASA: American Society of Anesthesiologists, BMI: Body mass index.

 E-submission
E-submission KFS
KFS
 Cite
Cite

