Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Article
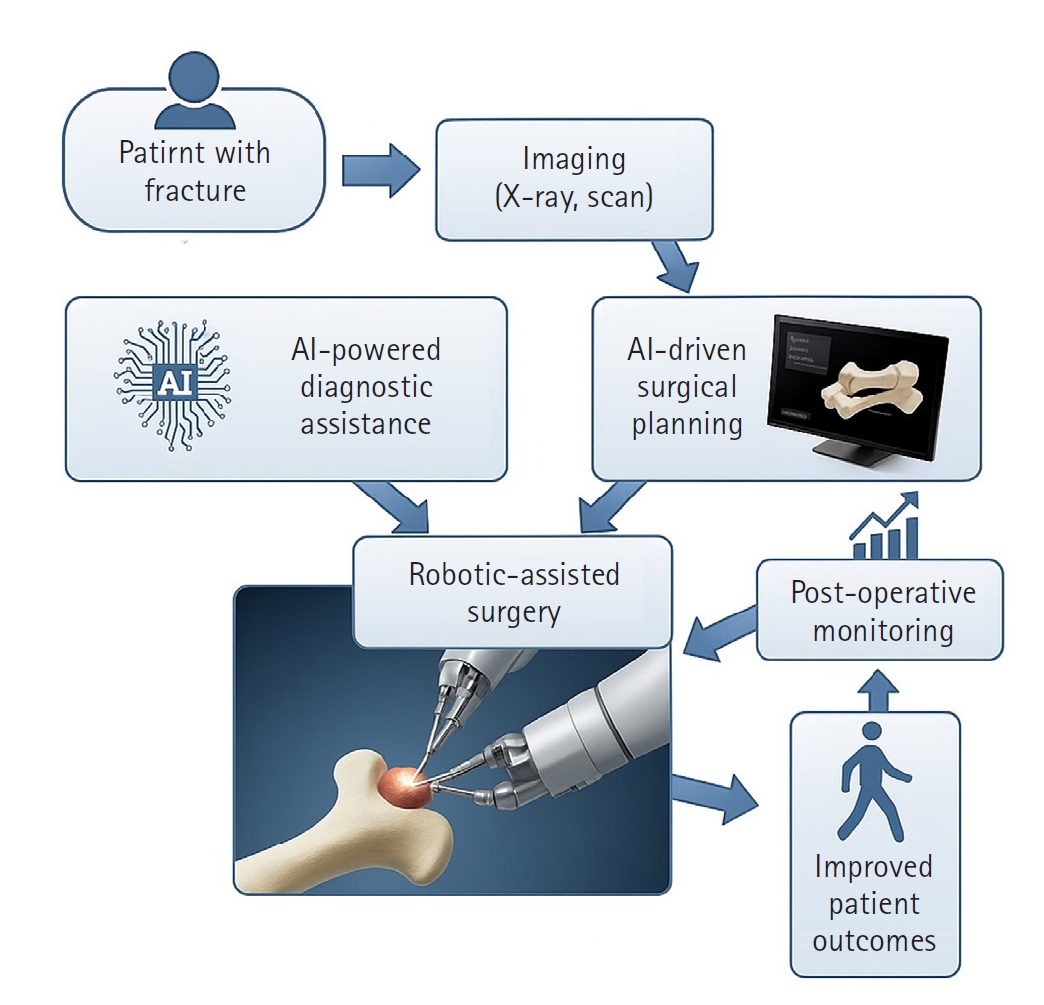
- Innovative applications of artificial intelligence in orthopedics focusing on fracture and trauma treatment: a narrative review
- Chul-Ho Kim, Ji Wan Kim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):178-185. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00283
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Artificial intelligence (AI) is bringing about transformative changes in orthopedic surgery, with its potential being particularly prominent in the field of fracture and trauma treatment. This review explores the current applications and future prospects of AI-driven surgical planning and simulation, robot and image-based navigation surgery, and image-assisted diagnostic technologies. Robotic assistance in orthopedic surgery, which was initially applied to improve accuracy in component implantation for knee and hip arthroplasty and to achieve high precision in spinal screw placement, has recently expanded its use to include accurate, minimally invasive reduction of pelvic fractures. In diagnostics, AI aids in the early prediction and classification of ambiguous fractures in various anatomical regions—for example, detecting shoulder or hip fractures, identifying incomplete atypical femur fractures, and classifying femoral neck fractures—through X-ray image analysis. This improves diagnostic accuracy and reduces medical costs. However, significant challenges remain, including high initial costs, steep learning curves, a lack of long-term studies, data bias, and ethical concerns. Continued research, interdisciplinary collaboration, and policy support are crucial for the widespread adoption of these technologies.
- 80 View
- 0 Download

Original Articles
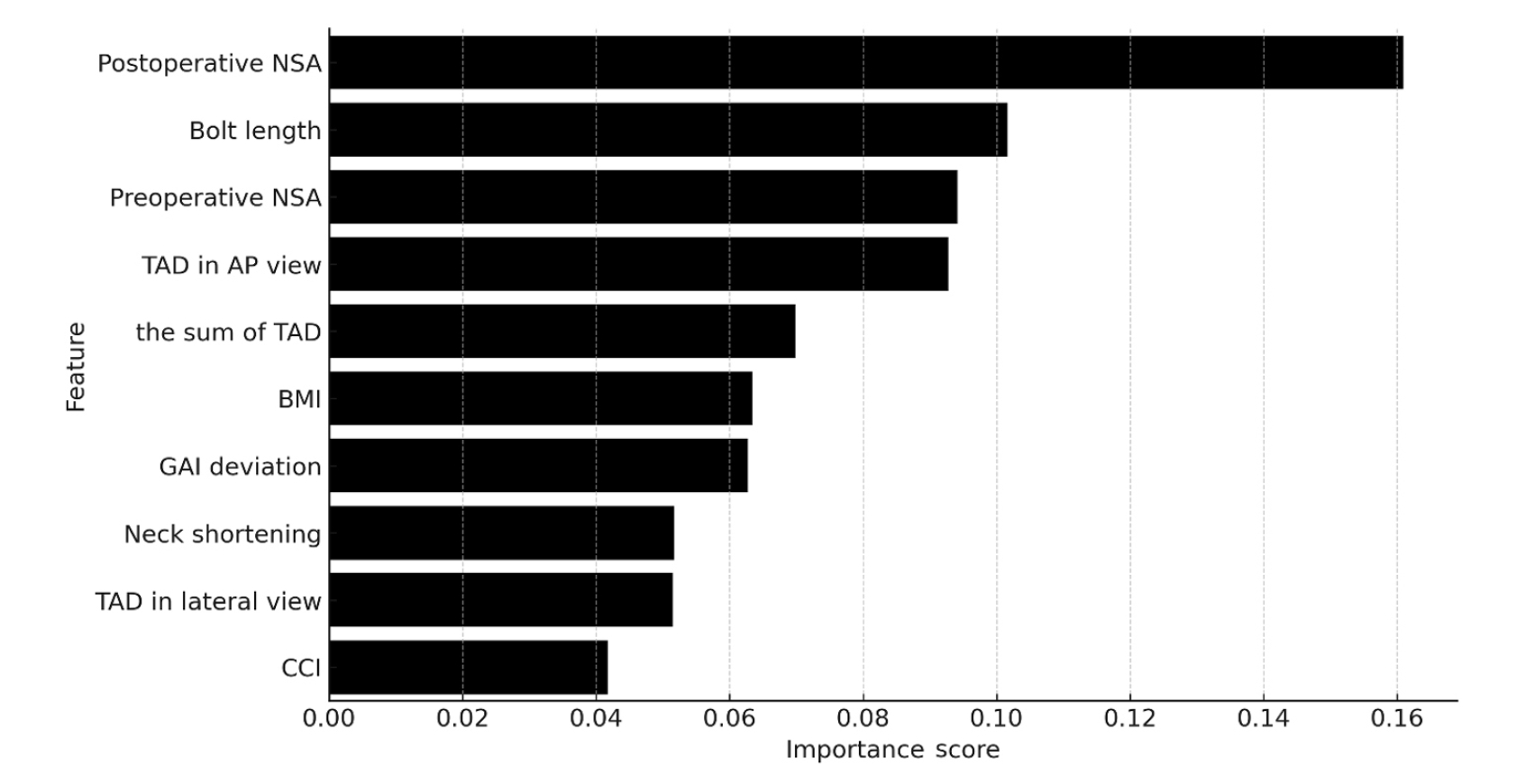
- Risk factors of surgical complications after use of the femoral neck system: a random forest analysis
- Chul-Ho Kim, Hyun-Chul Shon, Han Soul Kim, Ji Wan Kim, Eic Ju Lim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):160-167. Published online July 23, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00157
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The femoral neck system (FNS), a novel fixation device for managing femoral neck fractures (FNFs), has gained popularity in recent years. However, analyses of the surgical complications and reoperation risks associated with the use of FNS remain limited.
Methods
This retrospective observational study analyzed 57 patients who had undergone FNS fixation for FNF at two university hospitals between July 2019 and February 2024. Demographic, perioperative, and outcome variables, including age, sex, fracture classification (Garden, Pauwels, and AO), implant characteristics, tip-apex distance (TAD), neck shortening, and neck-shaft alignment, were analyzed. In addition to univariate analysis, a machine learning analysis was conducted using a random forest classifier with stratified sampling (80% training, 20% testing). The accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and area under the receiver’s operating curve were calculated to assess model performance.
Results
Ten patients experienced osteonecrosis of the femoral head (n=6), implant cut-out or penetration (n=3), and peri-implant fracture (n=1). Univariate analysis revealed that the TAD in the complication group was significantly shorter than that in the control group (12.1 vs. 16.7 mm; P=0.012). Additionally, neck shortening in the complication group was greater than that in the control group (4.9 vs. 2.3 mm; P=0.011). The random forest model achieved an accuracy of 83.3% and identified postoperative neck-shaft angle (NSA) as the most important predictor of complications (feature importance, 0.161), followed by bolt length (0.102) and preoperative NSA (0.094).
Conclusions
Risk factor analysis conducted using a random forest model identified postoperative NSA as the most important feature associated with postoperative complications following FNS. Therefore, care should be taken to normalize the postoperative NSA during FNF surgery. Level of Evidence: III.
- 576 View
- 25 Download

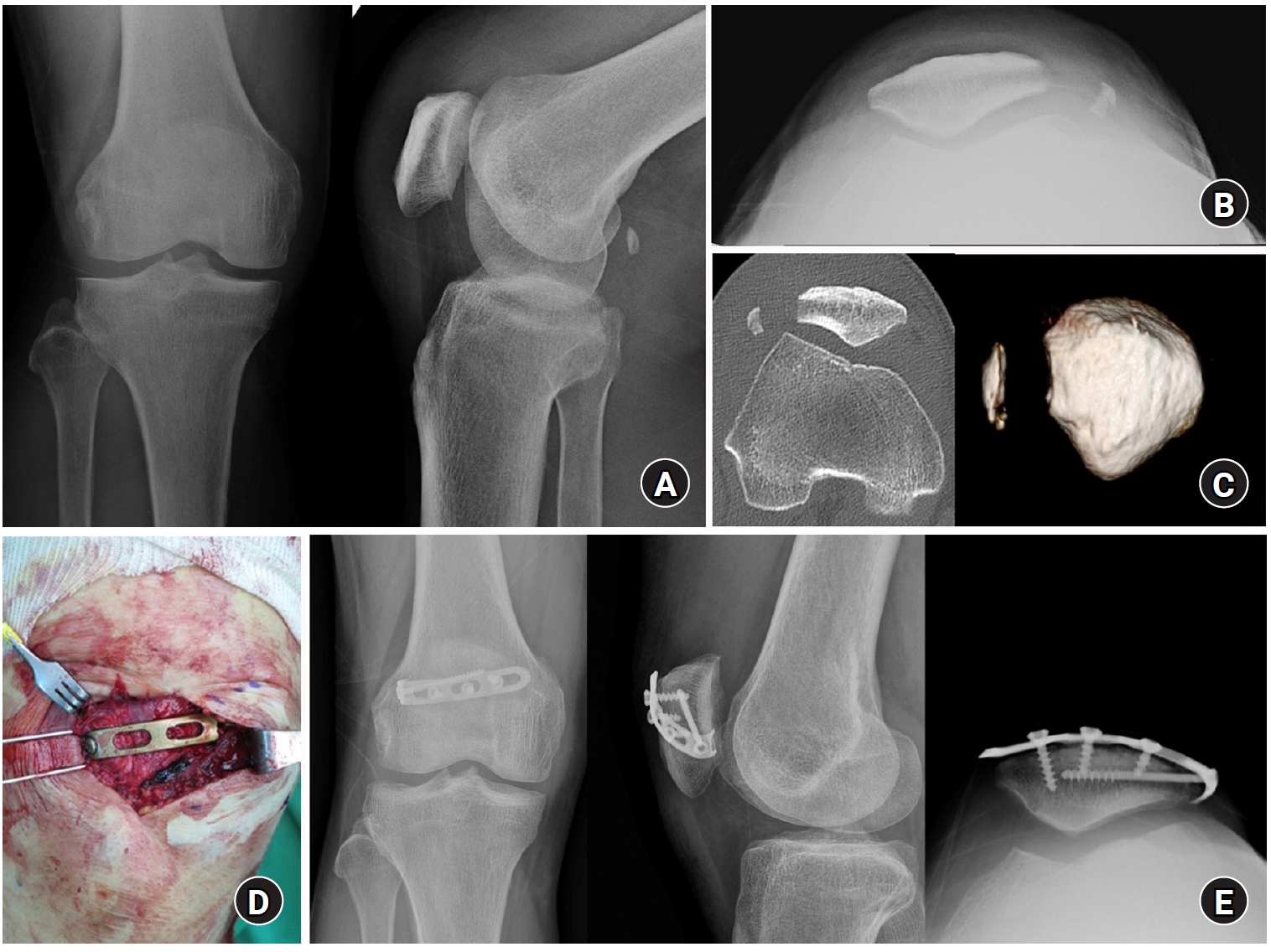
- Lateral marginal fractures of the patella and patellofemoral pain
- Jae-Ang Sim, Chul-Ho Kim, Ji Wan Kim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):152-159. Published online July 22, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00171
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This study investigated the characteristics of lateral marginal fractures of the patella and evaluated the clinical outcomes.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed all patients with lateral marginal fractures of the patella, defined as a vertical fracture line within 15 mm of the lateral patellar border, from 2008 to 2020. In total, 41 patients were included. Patient characteristics, radiologic findings, and clinical outcomes, including the Lysholm score at 1 year postoperation, were evaluated.
Results
The injury mechanisms were direct in 34 cases and indirect in seven. Furthermore, 85% of patients had a skyline view of the patella at the initial visit, and one medial subluxation of the patella was found. Forty of the 41 patients underwent surgery. Anatomical and nonanatomical (>1-mm displacement or excision) reductions were carried out in 36 cases (88%) and five cases (12%), respectively. The average Lysholm score was 89.1 (range, 67–99). The nonanatomical reduction group had a poorer functional score (79.8 vs. 90.4; P=0.010). Lateral patellar compression syndrome occurred in two patients with nonanatomical reduction.
Conclusions
Lateral marginal fractures of the patella affected patellofemoral stability. Anatomical reduction showed good functional outcomes, while nonanatomical reduction was associated with patellofemoral stability and pain. Therefore, surgeons should perform anatomical reduction with any appropriate fixation method. Level of Evidence: IV
- 608 View
- 17 Download

- Treatment of Proximal Femur Fracture with a Newly Designed Nail: Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced (TFNA)
- Jae Youn Yoon, Ji Wan Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(4):189-195. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.4.189
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study evaluated the clinical results and implant safety of a newly developed implant, Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced (TFNA; DePuy Synthes), in the treatment of proximal femur fractures.
Materials and Methods
This was a retrospective cohort study of 26 patients diagnosed with proximal femur fracture and treated surgically with TFNA. The patients’ demographic data, surgical data, radiologic findings, and functional outcomes, including complications, were evaluated.
Results
The mean age of the patients was 71.2 years (95% confidence interval [CI], 68.2-74.2); 65.4% were female. The mean Carlson comorbidity index score was 5.4, and the mean Koval grade before fracture was 2.1. Fracture classification included four cases of AO/OTA 31.A1, nine cases of A2, six cases of A3, and seven cases of 32A including six cases of atypical femoral fractures. The mean operating time was 53.3 minutes (95% CI, 43.6-63.1). There were no early postoperative complications, such as postoperative infection, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, or in-hospital death, except one case of pneumonia. The mean Koval score at the postoperative six-month follow-up was 2.9. EuroQol-5 Dimension (EQ-5D) increased from 0.05 to 0.54 after three months and 0.72 at six months postoperatively. Bone union was observed in all cases with a mean union time of 12.9 weeks. No implant failure occurred, and no cases required secondary revision surgery.
Conclusion
A new intramedullary nail system, TFNA, showed excellent outcomes and safety in the surgical treatment of proximal femur fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intermediate Length Cephalomedullary Nails in Proximal Femoral Fractures: Review of Indications and Outcomes
Daniel Scott Horwitz, Ahmed Nageeb Mahmoud, Michael Suk
Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.2025; 33(19): 1071. CrossRef - Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures Treated with Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced and Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation-II: Correlation between Lateral Sliding of the Helical Blade and Lateral Trochanteric Pain
Sung Yoon Jung, Myoung Jin Lee, Lih Wang, Hyeon Jun Kim, Dong Hoon Sung, Jun Ha Park
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2024; 59(3): 208. CrossRef - Prospective randomized multicenter noninferiority clinical trial evaluating the use of TFN-advancedTM proximal femoral nailing system (TFNA) for the treatment of proximal femur fracture in a Chinese population
Lidan Zhang, Zhijun Pan, Xiaohui Zheng, Qiugen Wang, Peifu Tang, Fang Zhou, Fan Liu, Bin Yu, Frankie K. L. Leung, Alex Wu, Suzanne Hughson, Zhuo Chen, Michael Blauth, Anthony Rosner, Charisse Sparks, Manyi Wang
European Journal of Trauma and Emergency Surgery.2023; 49(3): 1561. CrossRef - Risk of shortening in operatively treated proximal femur fractures with cephalomedullary nails with dynamically versus statically locked helical blades
Nathan Cherian, Lasun Oladeji, Cole Ohnoutka, Dan Touhey, Madeline Sauer, Kyle A. Schweser, Mauricio Kfuri, James L. Cook, Gregory J. Della Rocca, Brett D. Crist
Injury.2023; 54(2): 669. CrossRef - GS Hip Nail versus Affixus Hip Fracture Nail for the Intramedullary Nailing of Intertrochanteric Fractures
Seungcheol Kwon, Minjae Lee, Heeyeon Lee, Jihyo Hwang
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(21): 6720. CrossRef - Comparison of the Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of TFNA (Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced) and PFNA-II (Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation-II) Treatment in Elderly Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures
Min Sung Kwon, Young Bok Kim, Gyu Min Kong
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2022; 35(4): 162. CrossRef - Analysis of Clinical and Functional Outcomes according to the Blood Sugar Control Status at the Time of Ankle Fractures Resulting from Rotational Injuries
Jun Young Lee, Dong Seop Lim, Seung Hyun Lee, Seo Jin Park
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2022; 35(4): 135. CrossRef - Conventional versus helical blade screw insertion following the removal of the femoral head screw: a biomechanical evaluation using trochanteric gamma 3 locking nail versus PFN antirotation
Hong Man Cho, Kwang Min Park, Tae Gon Jung, Ji Yeon Park, Young Lee
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and Radiologic Outcome of Intertrochanteric Fracture Treatment Using TFNA (Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced)
Hyeon Joon Lee, Hyun Bai Choi, Ba Rom Kim, Seung Hwan Jo, Sang Hong Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2021; 34(3): 105. CrossRef
- Intermediate Length Cephalomedullary Nails in Proximal Femoral Fractures: Review of Indications and Outcomes
- 1,338 View
- 19 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Usefulness of Sonication in Implant-Related Infection
- Jae Hyeon Seo, Mi Na Kim, Ji Wan Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(2):81-86. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.2.81
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study determined whether the sonication of explants could improve the detection of bacteria and influence the optimal antibiotics treatment.
Materials and Methods
This retrospective study included the patients who underwent implant removal surgery followed by sonication culture as well as tissue culture in order to diagnose implant-related infection. A total of 37 consecutive patients with 41 cases were included. The patients’ demographic data, use of preoperative antibiotics, type of implants, change of antibiotics following the culture results, and recurrence of infection were all reviewed.
Results
Among 41 cases, 20 cases met the diagnostic requirements for implant-related infection as defined by musculoskeletal infection society criteria, while the other 21 cases had explant sonication to exclude indolent infection or residual infection. The latter showed negative results on the both explant cultures and tissue cultures. Among the 20 cases that met the requirements for implant-related infection, 19 cases (95.0%) were identified by any cultures. Of the 19 cases with positive culture results, 2 cases (10.5%) showed positive results only on sonication cultures, and one case (5.3%) showed positive results only on tissue culture. In 1 case of culture negative implant-related infection, a drain sinus was present preoperatively, but the cultures were negative according to both methods. The culture results made postoperative antibiotics change in 12 cases among the 19 culture (+) cases. Antibiotics changes were based on the tissue culture in 2 cases, 2 cases were based on the sonication culture, and the remaining 8 cases were based on both cultures.
Conclusion
The sonication culture improved the diagnosis of implant-related infection combined with conventional tissue culture and helped to determine administering the proper antibiotics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Systematic Diagnosis and Treatment Principles for Acute Fracture-Related Infections
Jeong-Seok Choi, Jun-Hyeok Kwon, Seong-Hyun Kang, Yun-Ki Ryu, Won-Seok Choi, Jong-Keon Oh, Jae-Woo Cho
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2023; 36(4): 148. CrossRef
- Systematic Diagnosis and Treatment Principles for Acute Fracture-Related Infections
- 565 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review Article
- Anterior Approach for the Acetabular Fractures
- Jae Youn Yoon, Jae Woo Cho, Ji Wan Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(3):157-164. Published online July 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.3.157
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In the surgical treatment of acetabular fractures, the anterior approach is used widely for anterior column fractures with or without posterior column fractures. This paper reviews the anterior approach for the anatomical reduction and rigid fixation of acetabular fractures: traditional ilioinguinal approach, modified Stoppa approach, and new Pararectal approach.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adhesion of External Iliac Vessels Found in a Modified Stoppa Approach to Acetabular Fracture in a Patient with a History of Previous Abdominal Surgery
Seong-Tae Kim, Seungyup Shin, Hohyoung Lee, Seong Man Jeon
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2022; 57(1): 68. CrossRef
- Adhesion of External Iliac Vessels Found in a Modified Stoppa Approach to Acetabular Fracture in a Patient with a History of Previous Abdominal Surgery
- 851 View
- 17 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Article
- Clinical Features and Outcomes of Pelvic Insufficiency Fractures
- Yong Min Seo, Young Chang Kim, Ji Wan Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(4):186-191. Published online October 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.4.186
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to investigate the radiological and epidemiological characteristics, as well as the clinical course of pelvic insufficiency fractures in the elderly population.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
At a Haeundae Paik Hospital, we retrospectively reviewed patients with pelvic insufficiency fractures between March 2010 and May 2017. The demographic data of patients were analyzed, and bone mineral density and bone turnover markers were evaluated to estimate the metabolic status of the bone. The radiological characteristics were evaluated by comparing the simple x-ray images with the computed tomography images, and the types of fractures were classified via computed tomography images. For clinical course evaluation, we investigated comorbid complications, and compared the walking ability scale before and 6 months after the fracture.
RESULTS
A total of 42 patients were included, with an average age of 76.5 years. All were female except one case. In 5 cases where the initial medical examination was from another institution, the fracture was not found in 3 cases. All cases received conservative treatment. After the diagnosis of pelvic bone fracture using a simple x-ray imaging, additional fractures were found in 81.0% of the study population using a computed tomography. Initiation of gait occurred at an average of 2.8 weeks, and every case except 1 (97.6%) fully recovered their gait ability.
CONCLUSION
We concluded that there was a limitation with diagnosing pelvic insufficiency fracture using only a simple x-ray imaging technique. In general, cases in this study showed conservative treatment yielded favorable clinical outcome with relatively less critical complications.
- 353 View
- 1 Download

Case Report
- Reduction Technique of Dome Impaction Using the Modified Stoppa Approach: A Technical Note
- Ji Wan Kim, Yong Min Seo, Hyo Seok Jang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(3):131-136. Published online July 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.3.131
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In elderly acetabular fractures, central dislocation of the femoral head and impacted superior dome of the acetabulum is common. Unreduced dome impaction can lead to degenerative arthritis and results in poor results. Herein, we present a case of operative reduction and fixation performed via the modified Stoppa approach in acetabular fracture with superior dome impaction.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surgical outcomes of acetabular fracture of elderly patients with superomedial dome impaction
Eic Ju Lim, Hyun-Chul Shon, Jae-Young Yang, Joosuk Ahn, Jung Jae Kim, Ji Wan Kim
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Anterior Approach for the Acetabular Fractures
Jae Youn Yoon, Jae-Woo Cho, Ji Wan Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2019; 32(3): 157. CrossRef
- Surgical outcomes of acetabular fracture of elderly patients with superomedial dome impaction
- 504 View
- 7 Download
- 2 Crossref

Review Article
- Bone Substitutes and the Advancement for Enhancing Bone Healing
- Dong Hyun Lee, Ji Wan Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(2):102-109. Published online April 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.2.102
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - With an aging population and the development of surgical techniques, there is a growing demand for bone reconstruction in areas of trauma, arthroplasty, and spinal fusion Although autogenous bone grafting may be the best method for stimulating bone repair and regeneration, there are still problems and complications, including morbidity related to bone harvesting and limitation of harvest amount. Allogeneic bone grafts have a limited supply and risk of transmission of infectious diseases. Over the past several decades, the use of bone substitutes, such as calcium phosphate, has increased; however, they have limited indications. Biomedical research has suggested a possibility of stimulating the self-healing mechanism by locally transmitting the external growth factors or stimulating local production through a gene transfer. In this review, we evaluate recent advances, including bone graft, bone substitutes, and tissue engineering.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Calcium phosphate injection technique for treatment of distal radius fracture
Dae-Geun Kim, Byung Hoon Kwack
Medicine: Case Reports and Study Protocols.2021; 2(9): e0117. CrossRef - Experimental Study ofDohongsamul-tang(Taohongsiwu-tang) on Fracture Healing
Hyun Ju Ha, Min-Seok Oh
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2020; 30(2): 47. CrossRef
- Calcium phosphate injection technique for treatment of distal radius fracture
- 410 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

Original Articles
- The Role of Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate Graft in the Dynamic Hip Screw Fixation of Unstable Intertrochanter Fracture
- Chul Ho Kim, Ji Wan Kim, Eic Ju Lim, Jae Suk Chang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(4):250-257. Published online October 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.4.250
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to introduce our method of stabilizing unstable intertrochanteric fractures by using the dynamic hip screw (DHS) with a beta-tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP) graft and to compare the outcomes of this procedure with those of the conventional DHS without β-TCP.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients who underwent surgery by using DHS between March 2002 and January 2016 were retrospectively reviewed for analysis of the outcomes. The inclusion criteria were: 1) age of 60 years and older; 2) low-energy fracture resulting from a fall from no greater than the standing height; 3) multifragmentary pertrochanteric fracture (AO classification 31-A2.2, 2.3); and 4) follow-up of over 3 months. We compared 29 patients (29 hips) who underwent surgery, using DHS without β-TCP, with 29 age-sex matched patients (29 hips) who underwent surgery using DHS with grafted β-TCP granules to empty the trochanter area after reaming. We investigated the fracture union rate, union time, and length of lag screw sliding.
RESULTS
Bone union was achieved in all cases. The mean union time was 7.0 weeks in the β-TCP group and 8 .8 weeks in the non-β-TCP group. The length of lag screw sliding was 3.6 mm in the β-TCP group and 5 .5 mm in the non-β-TCP group. There were no implant failure cases in both groups.
CONCLUSION
The β-TCP graft for reinforcement DHS acquired satisfactory clinical outcomes for treating unstable intertrochanteric fractures.
- 274 View
- 2 Download

- Clinical Outcomes of Fasciotomy for Acute Compartment Syndrome
- Ji Yong Park, Young Chang Kim, Ji Wan Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2015;28(4):223-229. Published online October 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.4.223
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate clinical outcomes and complications after fasciotomy in acute compartment syndrome.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Seventeen cases diagnosed as compartment syndrome and underwent fasciotomy from January 2011 to February 2015 were evaluated retrospectively. We investigated the causes and regions of acute compartment syndrome, the methods of wound management, the necessity of skin graft, and the complications including amputation and infection.
RESULTS
According to the causes of acute compartment syndrome, there were 7 fractures, 1 traumatic hematoma, 6 reperfusion injury, and 3 rhabdomyolysis. The regions of acute compartment syndrome were 3 cases of thigh, 10 cases of leg, and 3 cases of foot. One case had acute compartment syndrome involving thigh, leg, and foot. Of 17 cases, 3 cases died due to reperfusion injury and one case with severe necrosis of soft tissues underwent amputation. Among the 13 cases excluding 4 cases with death or amputation, 3 cases underwent split thickness skin graft. Shoelace technique and/or vacuum-assisted closure (VAC) was used for 9 cases, and wound closure without skin graft was achieved in all except one case, while 2 cases required skin graft among 4 cases without shoelace technique or VAC. There were 2 cases of infection.
CONCLUSION
Acute compartment syndrome caused by reperfusion injury had poor outcomes. Shoelace technique and/or VAC were useful for management of wound after fasciotomy.
- 303 View
- 1 Download

- Modified Stoppa Approach in Acetabular Fractures
- Ji Wan Kim, Young Chang Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(4):274-280. Published online October 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.4.274
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the clinical results of modified Stoppa approach in acetabular fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twelve patients who underwent surgery using the modified Stoppa approach for acetabular fractures were enrolled. There were 10 cases of isolated acetabular fracture, two cases of acetabular fracture combined with pelvic ring injury. There were two cases of anterior column fracture, nine cases of both column fracture, and one case of T-type fracture according to Letournel classification. The clinical outcomes were evaluated from Harris hip score (HHS) at postoperative one year and complications. The radiologic result was evaluated according to Matta criteria; anatomical, imperfect, and poor.
RESULTS
According to the radiological results, there were eight cases of anatomical, three cases of imperfect, and one case of poor reduction. The average HHS was 82.5 and 10 patients had excellent or good results. The other two patients had poor results due to lumbosacral plexopathy and poor reduction, respectively. The complication included one case of incomplete sciatic nerve palsy, which was recovered at postoperative three months.
CONCLUSION
Internal fixation of acetabular fractures using the modified Stoppa approach had satisfactory clinical and radiological outcomes. The modified Stoppa approach can be a useful option for acetabular fractures with appropriate indication and anatomical information. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adhesion of External Iliac Vessels Found in a Modified Stoppa Approach to Acetabular Fracture in a Patient with a History of Previous Abdominal Surgery
Seong-Tae Kim, Seungyup Shin, Hohyoung Lee, Seong Man Jeon
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2022; 57(1): 68. CrossRef - Anterior Approach for the Acetabular Fractures
Jae Youn Yoon, Jae-Woo Cho, Ji Wan Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2019; 32(3): 157. CrossRef - Reduction Technique of Dome Impaction Using the Modified Stoppa Approach: A Technical Note
Ji Wan Kim, Yong Min Seo, Hyo-Seok Jang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2017; 30(3): 131. CrossRef - Biological fixation of pelvic ring and acetabular fractures: a pilot study with anatomical validation
Abdelfattah Mohamed Fathy Saoud, Ahmed Mohamed Sallam, Ahmed Mohamed Morsey
Current Orthopaedic Practice.2017; 28(3): 303. CrossRef - Cerclage Clamping Using Cerclage Passer for Reduction of Anterior and Posterior Column Fracture
Ki Chul Park, Hyun Joong Cho, Hun Chul Kim, Kyung-Sik Min, Hae Won Jeong
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2016; 51(6): 486. CrossRef
- Adhesion of External Iliac Vessels Found in a Modified Stoppa Approach to Acetabular Fracture in a Patient with a History of Previous Abdominal Surgery
- 635 View
- 9 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Ankle Fracture Associated with Tibia Shaft Fractures
- Ji Wan Kim, Hong Joon Choi, Dong Hyun Lee, Young Chang Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(2):136-143. Published online April 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.2.136
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the incidence of ankle injury in ipsilateral tibial shaft fractures and to assess the risk factors for ankle injury associated with tibial shaft fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sixty patients with tibial shaft fractures were enrolled in this retrospective study. The incidence and characteristics of ankle injury were evaluated, and fracture classification, fracture site, and fracture pattern of the tibial shaft fractures were analyzed for assessment of the risk factors for ankle injury combined with tibial shaft fractures.
RESULTS
Ankle injury occurred in 20 cases (33%). There were four cases of lateral malleolar fracture, four cases of posterior malleolar fracture, two cases of distal tibiofibular ligament avulsion fracture, and 10 cases of complex injury. Fourteen cases (70%) of 20 cases of ankle injury were diagnosed from x-ray films, and the other six cases were recognized in ankle computed tomography (CT). Ankle injury occurred in 45.1% of distal tibial shaft fractures and found in 41.4% of A type, but there was no statistical significance. Ankle injury was observed in 54% of cases of spiral pattern of tibial shaft fracture and the incidence was statistically higher than 19% of cases of non-spiral pattern tibial shaft fracture.
CONCLUSION
Ankle injury was observed in 33% of tibial shaft fractures; however, only 70% could be diagnosed by x-ray. Ankle injury occurred frequently in cases of spiral pattern of tibial shaft fracture, and evaluation of ankle injury with CT is recommended in these cases. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Usefulness of Computed Tomography on Distal Tibia Intra-Articular Fracture Associated with Spiral Tibia Shaft Fracture
Seong-Eun Byun, Sang-June Lee, Uk Kim, Young Rak Choi, Soo-Hong Han, Byong-Guk Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2016; 29(2): 114. CrossRef
- Usefulness of Computed Tomography on Distal Tibia Intra-Articular Fracture Associated with Spiral Tibia Shaft Fracture
- 496 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Neurologic Injury within Pelvic Ring Injuries
- Ji Wan Kim, Dong Hoon Baek, Jae Hyun Kim, Young Chang Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(1):17-22. Published online January 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.1.17
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the incidence of neurologic injury in pelvic ring injuries and to assess the risk factors for neurologic injury related to pelvic fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sixty-two patients with the pelvic ring injury were enrolled in the study from March 2010 to May 2013. When the neurologic injury was suspected clinically, the electro-diagnostic tests were performed. Combined injuries, fracture types, and longitudinal displacements were examined for correlations with the neurologic injury.
RESULTS
There were 7 cases of AO/OTA type A, 37 cases of type B, and 18 cases of type C. Among them, 25 patients (40%) had combined spine fractures, and the average of longitudinal displacement was 7 mm (1-50 mm). Of the 62 patients, 13 (21%) had neurologic injury related with pelvic fractures; 5 with lumbosacral plexus injury, 5 with L5 or S1 nerve injury, 2 with obturator nerve injury, and 1 case of lateral femoral cutaneous nerve injury. There were no relationships between the neurologic injuries and fracture types (p=0.192), but the longitudinal displacements of posterior ring and combined spine fractures were related to the neurologic injury within pelvic ring injury (p=0.006, p=0.048).
CONCLUSION
The incidence of neurologic injury in pelvis fracture was 21%. In this study, the longitudinal displacements of posterior ring and combined spine fractures were risk factors for neurological injury in pelvic ring injury. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surgical Outcome of Posterior Pelvic Fixation Using S1, S2 Screws in Vertically Unstable Pelvic Ring Injury
Kwang Hee Yeo, Nam Hoon Moon, Jae Min Ahn, Jae Yoon Jeong, Jae Hoon Jang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2018; 31(1): 9. CrossRef
- Surgical Outcome of Posterior Pelvic Fixation Using S1, S2 Screws in Vertically Unstable Pelvic Ring Injury
- 359 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review Article
- Hip Arthroplasty in Intertrochanteric Fractures: Is It Acceptable Treatment?
- Young Chang Kim, Ji Wan Kim, Jae Young Lim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(1):105-112. Published online January 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.1.105
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - No abstract available.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Primary Cementless Hip Arthroplasty in Unstable Intertrochanteric Femur Fracture in Elderlys: Short-term Results
Su-Hyun Cho, Hyung Lae Cho, Hong Cho
Hip & Pelvis.2014; 26(3): 157. CrossRef
- Primary Cementless Hip Arthroplasty in Unstable Intertrochanteric Femur Fracture in Elderlys: Short-term Results
- 837 View
- 7 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Article
- The Character of Reverse Obliquity Intertrochanteric Fractures in Elderly Patients
- Ji Wan Kim, Jae Suk Chang, Jung Hwan Sung, Jung Jae Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(3):173-177. Published online July 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.3.173
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To discriminate the characteristics between reverse obliquity fractures in the elderly and that of young adults using three-dimensional computed tomography (3D CT).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Eighteen patients who had reverse obliquity intertrochanteric fractures were enrolled from January 2007 to March 2012. The fracture pattern was analyzed using the 3D CT. The area showing low density (bone defect) of trochanter and femoral neck region was measured. Patients were divided into two groups: Group I, less than 65 years old and Group 2, 65 years and over.
RESULTS
In all 9 cases of group 1, the proximal fragment had a 'V' shape with an average of 5.6 cm below the vastus ridge; however, the fracture of 8 cases (88.97%) in group 2 had a 'Lambda' shape of the distal fragment at the level of vastus ridge and an additional fracture line extending to the greater trochanter tip. The bone defect volume of the trochanter and femoral neck region was larger significantly in group 2 than in group 1.
CONCLUSION
Reverse obliquity intertrochanteric fracture in the elderly demonstrated a pattern of bursting fracture with 4 parts, which had different patterns from that of young patients. We believe that the larger volume of bone defects resulted in the difference of fracture patterns between the two groups. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comparison of Internal Fixation and Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty for the Treatment of Reverse Oblique Intertrochanteric Femoral Fractures in Elderly Patients
Bong-Ju Park, Hong-Man Cho, Woong-Bae Min
Hip & Pelvis.2015; 27(3): 152. CrossRef
- A Comparison of Internal Fixation and Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty for the Treatment of Reverse Oblique Intertrochanteric Femoral Fractures in Elderly Patients
- 479 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review Article
- Updated Basic Principles of Internal Fixation of Fracture
- Oog Jin Shon, Ji Wan Kim, Beom Jung Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(1):81-91. Published online January 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.1.81
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - No abstract available.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Review of Domestic and International Clinical Research Trends on Pharmacopuncture Treatment for Fractures
Hea Sun Chun
Journal of Physiology & Pathology in Korean Medicine.2023; 37(6): 185. CrossRef - Comparison of Greater Trochanter Versus Piriformis Entry Nail for Treatment of Femur Shaft Fracture
Jong-Hee Lee, Jong-Hoon Park, Si-Yeong Park, Seong-Cheol Park, Seung-Beom Han
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2014; 27(4): 287. CrossRef
- A Review of Domestic and International Clinical Research Trends on Pharmacopuncture Treatment for Fractures
- 1,229 View
- 34 Download
- 2 Crossref

Case Report
- Heterotopic Ossification around Patellar Tendon Following Treatment of Patellar Fracture: A Case Report
- Sang Jin Lee, Ji Wan Kim, Dong Hyun Lee, Jae Young Lim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(1):73-76. Published online January 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.1.73
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Heterotopic ossification around the patellar tendon is known to be extremely rare. A 42-year-old man had a transverse fracture of the left patella. Open reduction and tension band wiring were performed. At four weeks, plain radiographs showed an extensive ossification around the patellar tendon and the patient presented limitation of flexion and pain in kneeling position. We just encouraged active and passive ranges of motion exercises and performed one manipulation under anesthesia. At the final follow-up (10 months post-operatively), he was able to flex his knee by 140 degrees. We present a case of heterotopic ossification around the patellar tendon with limitation of knee flexion that was successfully treated with nonoperative treatment.
- 334 View
- 0 Download

Original Articles
- Anatomical Study of Symphysis Pubis Using 3 Dimensional Computed Tomography in Koreans
- Ji Wan Kim, Jung Min Park, Jae Suk Chang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(1):32-36. Published online January 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.1.32
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To acquire anatomical data for the normal pelvic bone structure using three-dimensional computed tomography (3D CT) and to propose the most appropriate angle and screw length for safe screw insertion during symphysis pubis plating.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We performed 3D CT analysis in 52 patients who required plating and selected a medial and lateral insertion point between the symphysis pubis and the pubic tubercle. Using a three-dimensional medical image analysis program, we evaluated the appropriate screw length, sagittal angle, and oblique angle at each point in this cohort.
RESULTS
At the medial point, the sagittal angle was determined to be 49.1degrees with an average screw length of 49.4 mm. At the lateral point, we calculated an average screw length of 49.1 mm, oblique angle of 23.2degrees, and sagittal angle of 45.7degrees. The screw length was longer in men than in women (4.6 mm and 7.3 mm, respectively) at the medial and lateral point.
CONCLUSION
At the symphysis pubis diastasis, we can insert the screw caudally at 49degrees with a minimal length of 37 mm at the medial point. We can insert the screw caudally at 46degrees, medially at 23degrees, with a minimal 34 mm length at the lateral point.
- 308 View
- 1 Download

- The Incidence of Venous Thromboembolism in Trauma Patients with Pelvic or Acetabular Fracture
- Ji Wan Kim, Hyun Wook Chung, Young Chang Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(4):250-256. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.4.250
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the incidence of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in trauma patients with pelvic or acetabular fracture and determine high risk factors.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty-three patients who had a pelvic or acetabular fracture were enrolled between March 2011 and February 2012. All patients had mechanical and chemical prophylaxis and underwent deep vein thrombosis (DVT) computed tomography around 2 weeks after injury for evaluation of VTE. The relationships between VTE and each of sex, age, body mass index, injury severity score, intensive care unit stay, transfusion, operation time, coagulopathy, and associated injury were analyzed.
RESULTS
A total of 8 patients developed VTE (34.8%), of which 5 had DVT, 2 had pulmonary embolism (PE), and one had both DVT and PE. The group with a VTE risk score of 14 or more had a significantly higher incidence of VTE.
CONCLUSION
Careful attention is needed in management of patients with pelvic or acetabular fracture. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Knowledge, Health Belief, and Preventive Behavioral Intention related to Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) of the Patients with Lower Limb Musculoskeletal System Disorders
Hye Jin Yang, Hee-Young Kang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(4): 531. CrossRef
- Knowledge, Health Belief, and Preventive Behavioral Intention related to Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) of the Patients with Lower Limb Musculoskeletal System Disorders
- 555 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Reports
- Bowel Entrapment by Fragments of Acetabular Fracture: A Case Report
- Ji Wan Kim, Jung Jae Kim, Suk Kyung Hong, Kyu Hyuk Kyung, Jin Hee Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2010;23(4):373-376. Published online October 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.4.373
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Abdominal injuries are common in patients with pelvic or acetabular fracture. However intestinal entrapment or perforation caused by fragments of a pelvic or acetabular fracture is rare and to date there has been no report of this occurring in Korea so far. As it is difficult to diagnose intestinal entrapment caused by fragments of pelvic or acetabular fracture, the entrapment therefore results in intestinal perforation, sepsis, and a high mortality rate in the absence of early detection. We present a case of intestinal entrapment and perforation caused by fragments of acetabular fracture as well as a literature review.
- 241 View
- 0 Download

- Bursting Fracture of the Proximal Femur during Insertion of Unreamed Femoral Nail for Femur Shaft Fracture: A Case Report
- Ji Wan Kim, Seong Eun Byun, Won Hyuk Oh, Jung Jae Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2010;23(2):227-231. Published online April 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.2.227
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - When treating femur shaft fracture in adults, undreamed nail can be an option in order to avoid systemic complications. To appropriately insert unreamed intramedullary nail, an accurate entry point and sufficient reaming of the entry portal is essential. The intramedullary canal of the proximal femur must be reamed over than the diameter of the proximal end of the nail. If the proximal reaming is not sufficient, complications such as bursting fracture of proximal femur can occur. We present two cases of bursting fracture of proximal femur following insertion of undreamed intramedullary nail as well as a literature review.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk Factors Associated with Intraoperative Iatrogenic Fracture in Patients Undergoing Intramedullary Nailing for Atypical Femoral Fractures with Marked Anterior and Lateral Bowing
Yong Bum Joo, Yoo Sun Jeon, Woo Yong Lee, Hyung Jin Chung
Medicina.2023; 59(4): 735. CrossRef - Results of Intramedullary Nailing of Femoral Shaft Fracture - Trochanteric Entry Portal (Sirus Nail) versus Piriformis Entry Portal (M/DN Nail) -
Sang Ho Ha, Woong-Hee Kim, Gwang Chul Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2014; 27(1): 50. CrossRef - Iatrogenic Femur Proximal Shaft Fracture during Nailing Using Lateral Entry Portal on Femur Shaft Fracture
Hong Moon Sohn, Gwang Chul Lee, Chae Won Lim
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2014; 49(4): 272. CrossRef
- Risk Factors Associated with Intraoperative Iatrogenic Fracture in Patients Undergoing Intramedullary Nailing for Atypical Femoral Fractures with Marked Anterior and Lateral Bowing
- 584 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref

Review Article
- Subtrochanteric Fracture: Intramedullary Nailing
- Jung Jae Kim, Ji Wan Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(2):114-122. Published online April 30, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.2.114
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - No abstract available.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Extra-capsular proximal femoral fractures: a cohort comparison of union and complication rates after ballistic versus blunt trauma
Jordan Cook Serotte, Kevin Chen, Julia Nascimben, Jason Strelzow
European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevention of inaccurate targeting of proximal screws during reconstruction femoral nailing
Ji Wan Kim, Derly O. Cuellar, Jiandong Hao, Benoit Herbert, Cyril Mauffrey
European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology.2016; 26(4): 391. CrossRef - Treatment of Femur Subtrochanteric Fracture Using the Intramedullary Long Nail; Comparison of Closed Reduction and Minimal Open Reduction
Sang Joon Lee, Sang Hong Lee, Sang Soo Park, Hyung Seok Park
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2015; 50(1): 18. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Time to Bony Union of Femoral Subtrochanteric Fractures Treated with Intramedullary Devices
Jung-Yoon Choi, Yerl-Bo Sung, Jin-Hee Yoo, Sung-Jae Chung
Hip & Pelvis.2014; 26(2): 107. CrossRef - Fixation of the Femoral Subtrochanteric Fracture with Minimally Invasive Reduction Techniques
Chul-Hyun Park, Chul-Wung Ha, Sang-Jin Park, Min-Su Ko, Oog-Jin Shon
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2013; 26(2): 112. CrossRef - The Treatment of Subtrochanteric Fracture with Cephallomedually Nail -Minimal Incision and Lowman Clamp Assisted Reduction-
Jang Seok Choi, Do Hyun Moon, Young Tae Noh
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(4): 301. CrossRef
- Extra-capsular proximal femoral fractures: a cohort comparison of union and complication rates after ballistic versus blunt trauma
- 660 View
- 16 Download
- 6 Crossref


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


