Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 30(4); 2017 > Article
-
Original Article
- Clinical Features and Outcomes of Pelvic Insufficiency Fractures
-
Yong Min Seo, M.D.
 , Young Chang Kim, M.D., Ph.D.
, Young Chang Kim, M.D., Ph.D. , Ji Wan Kim, M.D., Ph.D.
, Ji Wan Kim, M.D., Ph.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2017;30(4):186-191.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.4.186
Published online: October 25, 2017
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- Correspondence to: Ji Wan Kim, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, 875 Haeundaero, Haeundae-gu, Busan 48108, Korea. Tel: +82-51-797-0668, Fax: +82-51-797-0669, bakpaker@hanmail.net
Copyright © 2017 The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 560 Views
- 1 Download
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to investigate the radiological and epidemiological characteristics, as well as the clinical course of pelvic insufficiency fractures in the elderly population.
-
Materials and Methods
- At a Haeundae Paik Hospital, we retrospectively reviewed patients with pelvic insufficiency fractures between March 2010 and May 2017. The demographic data of patients were analyzed, and bone mineral density and bone turnover markers were evaluated to estimate the metabolic status of the bone. The radiological characteristics were evaluated by comparing the simple x-ray images with the computed tomography images, and the types of fractures were classified via computed tomography images. For clinical course evaluation, we investigated comorbid complications, and compared the walking ability scale before and 6 months after the fracture.
-
Results
- A total of 42 patients were included, with an average age of 76.5 years. All were female except one case. In 5 cases where the initial medical examination was from another institution, the fracture was not found in 3 cases. All cases received conservative treatment. After the diagnosis of pelvic bone fracture using a simple x-ray imaging, additional fractures were found in 81.0% of the study population using a computed tomography. Initiation of gait occurred at an average of 2.8 weeks, and every case except 1 (97.6%) fully recovered their gait ability.
-
Conclusion
- We concluded that there was a limitation with diagnosing pelvic insufficiency fracture using only a simple x-ray imaging technique. In general, cases in this study showed conservative treatment yielded favorable clinical outcome with relatively less critical complications.
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea(NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education(2017R1D1A3B03035185).
None.
- 1. World Health Organization. Guidelines for preclinical evaluation and clinical trials in osteoporosis. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1998.
- 2. Dell R, Greene D, Schelkun SR, Williams K. Osteoporosis disease management: the role of the orthopaedic surgeon. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2008;90:Suppl 4. 188-194.
- 3. Lin JT, Lane JM. Osteoporosis: a review. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 2004;(425):126-134.
- 4. Rowe SM, Yoon TR, Ryang DH. An epidemiological study of hip fracture in Honam, Korea. Int Orthop, 1993;17:139-143.PDF
- 5. Carretta E, Bochicchio V, Rucci P, Fabbri G, Laus M, Fantini MP. Hip fracture: effectiveness of early surgery to prevent 30-day mortality. Int Orthop, 2011;35:419-424.PDF
- 6. Khan MA, Hossain FS, Ahmed I, Muthukumar N, Mohsen A. Predictors of early mortality after hip fracture surgery. Int Orthop, 2013;37:2119-2124.PDF
- 7. Saracen A, Kotwica Z. Treatment of multiple osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures by percutaneous cement augmentation. Int Orthop, 2014;38:2309-2312.PDF
- 8. O'Connor TJ, Cole PA. Pelvic insufficiency fractures. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil, 2014;5:178-190.PDF
- 9. Moon SW, Lee DH, Kim YC, Kim YB, Lee SJ, Kim JW. Parathyroid hormone 1-34(teriparatide) treatment in pelvic insufficiency fractures: a report of two cases. J Bone Metab, 2012;19:147-151.
- 10. Taillandier J, Langue F, Alemanni M, Taillandier-Heriche E. Mortality and functional outcomes of pelvic insufficiency fractures in older patients. Joint Bone Spine, 2003;70:287-289.
- 11. Yoo JI, Ha YC, Ryu HJ, et al. Teriparatide treatment in elderly patients with sacral insufficiency fracture. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2017;102:560-565.
- 12. Bergström U, Björnstig U, Stenlund H, Jonsson H, Svensson O. Fracture mechanisms and fracture pattern in men and women aged 50 years and older: a study of a 12-year population-based injury register, Umeå, Sweden. Osteoporos Int, 2008;19:1267-1273.PDF
- 13. Holick MF. Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med, 2007;357:266-281.
- 14. Rommens PM, Hofmann A. Comprehensive classification of fragility fractures of the pelvic ring: recommendations for surgical treatment. Injury, 2013;44:1733-1744.
- 15. Finiels H, Finiels PJ, Jacquot JM, Strubel D. Fractures of the sacrum caused by bone insufficiency. Meta-analysis of 508 cases. Presse Med, 1997;26:1568-1573.
- 16. Babayev M, Lachmann E, Nagler W. The controversy surrounding sacral insufficiency fractures: to ambulate or not to ambulate? Am J Phys Med Rehabil, 2000;79:404-409.
- 17. Rommens PM, Ossendorf C, Pairon P, Dietz SO, Wagner D, Hofmann A. Clinical pathways for fragility fractures of the pelvic ring: personal experience and review of the literature. J Orthop Sci, 2015;20:1-11.
- 18. Cabarrus MC, Ambekar A, Lu Y, Link TM. MRI and CT of insufficiency fractures of the pelvis and the proximal femur. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2008;191:995-1001.
- 19. Lapina O, Tiškevičius S. Sacral insufficiency fracture after pelvic radiotherapy: a diagnostic challenge for a radiologist. Medicina (Kaunas), 2014;50:249-254.
- 20. Chen CK, Liang HL, Lai PH, et al. Imaging diagnosis of insufficiency fracture of the sacrum. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi (Taipei), 1999;62:591-597.
- 21. Fujii M, Abe K, Hayashi K, et al. Honda sign and variants in patients suspected of having a sacral insufficiency fracture. Clin Nucl Med, 2005;30:165-169.
- 22. Gotis-Graham I, McGuigan L, Diamond T, et al. Sacral insufficiency fractures in the elderly. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1994;76:882-886.PDF
- 23. Krestan CR, Nemec U, Nemec S. Imaging of insufficiency fractures. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol, 2011;15:198-207.
- 24. Koval KJ, Aharonoff GB, Schwartz MC, et al. Pubic rami fracture: a benign pelvic injury? J Orthop Trauma, 1997;11:7-9.
- 25. Young Y, Brant L, German P, Kenzora J, Magaziner J. A longitudinal examination of functional recovery among older people with subcapital hip fractures. J Am Geriatr Soc, 1997;45:288-294.
- 26. Peichl P, Holzer LA, Maier R, Holzer G. Parathyroid hormone 1-84 accelerates fracture-healing in pubic bones of elderly osteoporotic women. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2011;93:1583-1587.
REFERENCES
(A) Initial pelvis Anteroposterior image of an 86-year-old female showing a non-displaced fracture at the right inferior ramus (arrow). (B) Outlet view showing right inferior ramus fracture (arrow). (C) Inlet view showing no definite posterior ring disruption. (D) Computed tomography images revealing both sacral alar fractures.

AO/OTA Classification of Pelvic Fracture
| AO/OTA classification | Number of case (%) |
|---|---|
| A2 | 13 (31.0) |
| B2 | 15 (35.7) |
| B3 | 8 (19.0) |
| C1 | 4 (9.5) |
| C2 | 2 (4.8) |
| Total | 42 (100) |
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

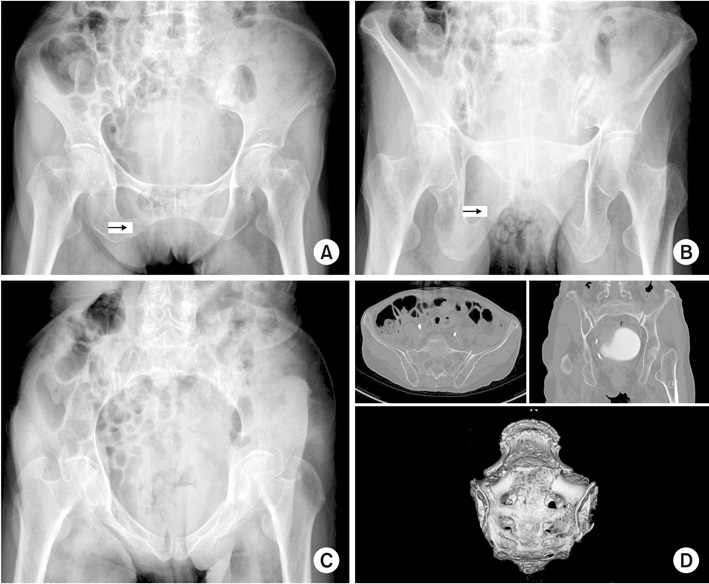
Fig. 1
AO/OTA Classification of Pelvic Fracture
| AO/OTA classification | Number of case (%) |
|---|---|
| A2 | 13 (31.0) |
| B2 | 15 (35.7) |
| B3 | 8 (19.0) |
| C1 | 4 (9.5) |
| C2 | 2 (4.8) |
| Total | 42 (100) |
Rommens Classification of Fragility Fractures of the Pelvic Ring
| Rommens classification | Number of case (%) |
|---|---|
| Ia | 9 (21.4) |
| Ib2 | 4 (9.5) |
| IIa | 1 (2.4) |
| IIb | 18 (42.9) |
| IIc | 7 (16.7) |
| IIIa | 2 (4.8) |
| IIIb | 1 (2.4) |
| IIIc | 0 |
| IV | 0 |
| Total | 42 (100) |
The sum of the percentages does not equal 100% because of rounding.
Walking Ability
| Post-injury 6 months walking ability | Number of case (%) |
|---|---|
| Independent walking | 21 (50.0) |
| Walking with an assistant device | 19 (45.2) |
| Requiring a wheelchair | 2 (4.8) |
| Bedridden | 0 |
| Recovery rate of ambulation to pre-injury levels | 41 (97.6) |
The sum of the percentages does not equal 100% because of rounding.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

