Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 32(3); 2019 > Article
- Review Article Anterior Approach for the Acetabular Fractures
- Jae Youn Yoon, Jae Woo Cho, Ji Wan Kim
-
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma 2019;32(3):157-164.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.3.157
Published online: July 31, 2019

2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.

- 1,243 Views
- 21 Download
- 1 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
Abstract
In the surgical treatment of acetabular fractures, the anterior approach is used widely for anterior column fractures with or without posterior column fractures. This paper reviews the anterior approach for the anatomical reduction and rigid fixation of acetabular fractures: traditional ilioinguinal approach, modified Stoppa approach, and new Pararectal approach.
Published online Jul 24, 2019.
https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.3.157
Anterior Approach for the Acetabular Fractures
Abstract
In the surgical treatment of acetabular fractures, the anterior approach is used widely for anterior column fractures with or without posterior column fractures. This paper reviews the anterior approach for the anatomical reduction and rigid fixation of acetabular fractures: traditional ilioinguinal approach, modified Stoppa approach, and new Pararectal approach.
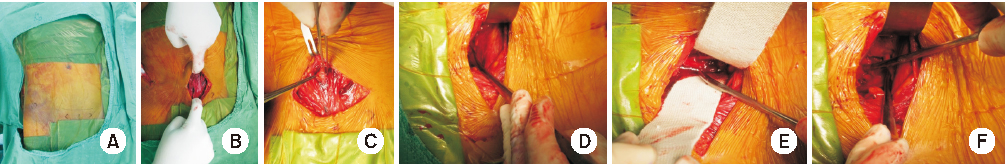
Fig. 1
Ilioinguinal approach. (A) Skin incision from the symphysis pubis to the iliac crest. (B) Incision of the inguinal ligament. (C) Iliopectineal fascia. (D) Exposure of the lateral window (white arrow: lateral femoral cutaneous nerve, black arrow: iliopectineal fascia). (E) Exposure of the ilium and anterior sacroiliac joint through the lateral window. (F) Three windows (1: lateral window, 2: middle window, 3: medial window, m: lacuna musculorum, v: lacuna vasorum, s: spermatic cord).
Fig. 2
Modified Stoppa approach. (A) Skin incision-like Pfannelstiel incision; 10 cm transverse incision 2 cm above the symphysis pubis. (B) Subcutaneous dissection. (C) Incision of the fascia (linea alba) of the rectus abdominis. (D) Deep blunt dissection along the superior pubic ramus. (E) Identification of the obturator nerve. (F) Exposure of the quadrilateral surface.
Fig. 3
Modified Stoppa approach for a bilateral pelvis ring injury and right acetabular fracture. (A) Initial pelvis X-ray showing the right acetabular anterior column fracture with the right sacral alar fracture and left pubic fracture. (B, C) Three-dimensional reconstruction images. (D) Postoperative pelvis anteroposterior.
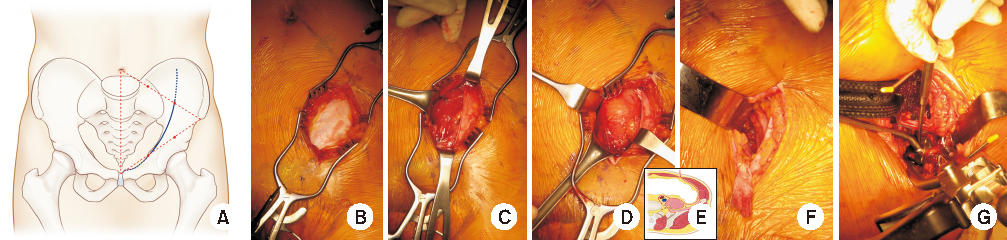
Fig. 4
Pararectal approach. (A) Skin incision. (B) Exposure of the deep fascia. (C) Incision of the rectus sheath. (D) Exposure of the lateral border of the rectus abdominis and retroperitoneal fat. (E) Schematic diagrams of the approach for the retroperitoneal space. (F) Exposure of the anterior column. (G) Reduction of the anterior and posterior column with a Collinear clamp.
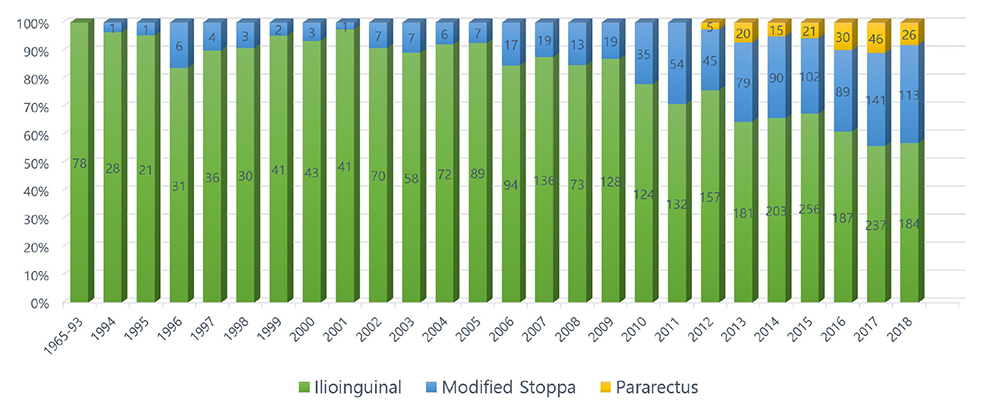
Fig. 5
Number of journals published worldwide related to each anterior pelvic approach in acetabular fractures.
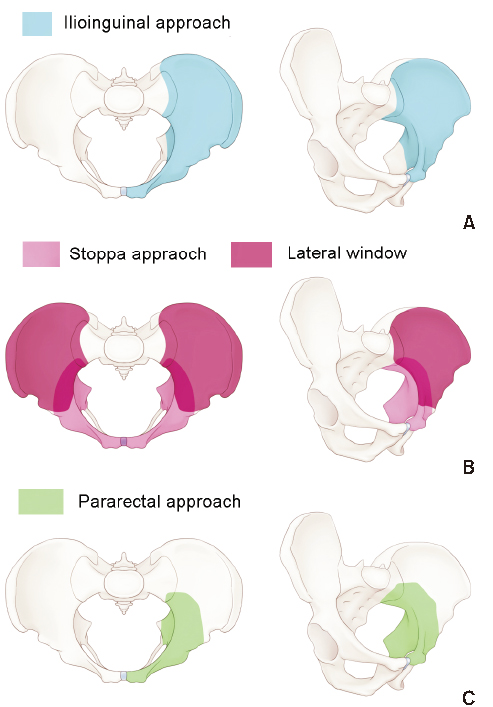
Fig. 6
Illustrated images on the range of surgical exposure, according to the type of anterior pelvic approach. (A) Ilioinguinal approach. (B) Modified Stoppa approach. (C) Pararectal approach.
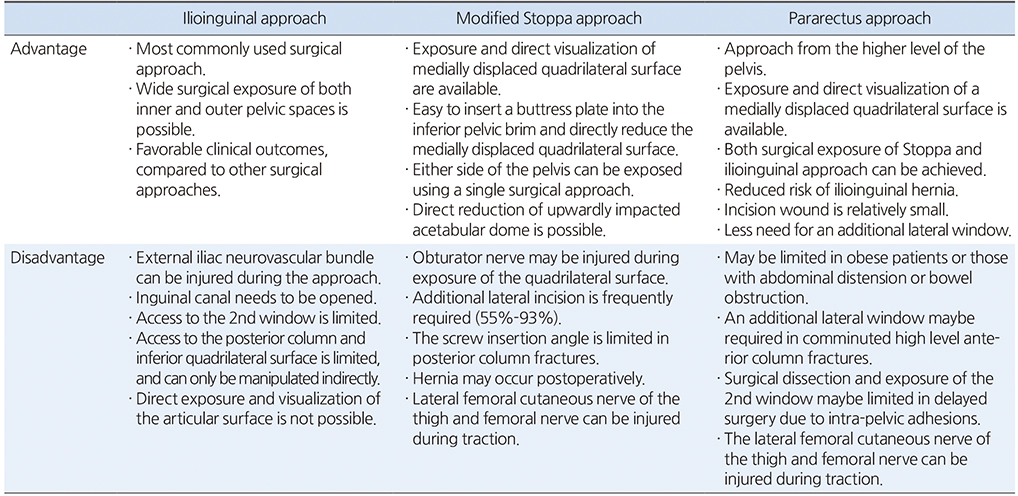
Table 1
Comparison of the Anterior Approach
Financial support:None.
Conflict of interests:None.
References
-
Märdian S, Schaser KD, Hinz P, Wittenberg S, Haas NP, Schwabe P. Fixation of acetabular fractures via the ilioinguinal versus pararectus approach: a direct comparison. Bone Joint J 2015;97:1271–1278.
-

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS




 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite

