Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Article
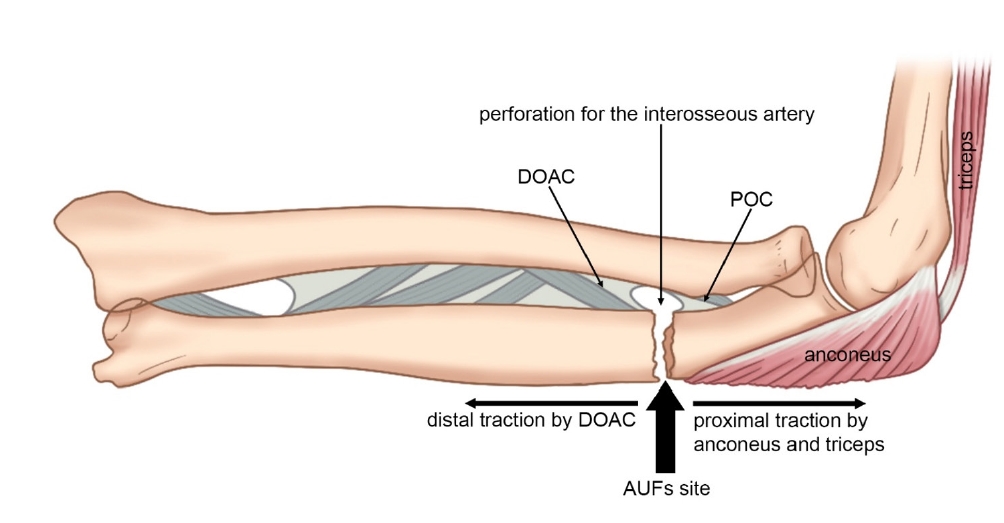
- Atypical ulnar fractures: a narrative review of current concepts and a case of bilateral surgical management
- Chi-Hoon Oh, Hyun Tak Kang, Jun-Ku Lee
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):124-132. Published online July 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00227
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Atypical ulnar fractures (AUFs) are rare complications that are often linked to long-term antiresorptive therapy. Although atypical femoral fractures are well-studied, AUFs lack standardized diagnostic and treatment protocols. This review summarizes current knowledge on AUFs, including their pathophysiology, diagnostic criteria, and management. A case of bilateral AUFs treated with two distinct osteosynthesis methods is presented, emphasizing the principles of biological healing and mechanical stabilization.
- 1,397 View
- 39 Download

Original Articles
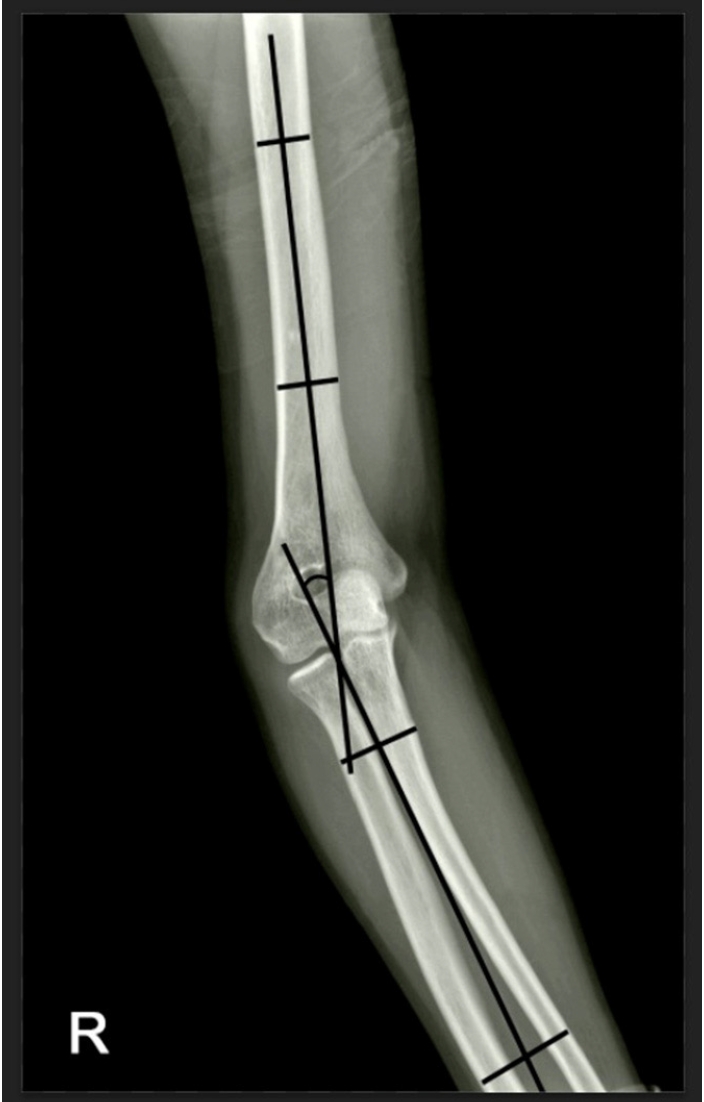
- Reverse V step-cut osteotomy for the correction of cubitus varus in adults: a retrospective study
- Jinyoung Bang, Hyung Jun Koo
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):102-108. Published online April 25, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00045
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Cubitus varus deformity in adults most commonly occurs as a late complication resulting from malunion of distal humeral fractures sustained during childhood. This deformity can cause cosmetic problems and anatomical deformities that hinder normal sports activities and potentially lead to long-term complications. Although various surgical techniques exist for correcting cubitus varus, this study investigated the clinical and functional outcomes of reverse V step-cut osteotomy.
Methods
In total, 15 patients underwent surgical treatment with reverse V step-cut osteotomy between 2012 and 2023. The mean age of the patients at the time of surgery was 46.3 years (range, 20–65 years). The preoperative carrying angle was ‒11.09° of varus, which was corrected to +12.81° of valgus postoperatively. The mean preoperative lateral prominence index (LPI) was ‒10.03, and the mean postoperative LPI improved to ‒4.48. A comparison to the unaffected side showed a P-value of 0.978, indicating similarity.
Results
Preoperatively, eight patients exhibited signs of posterolateral rotatory instability, and among them, three underwent concomitant lateral ulnar collateral ligament reconstruction. Seven patients reported ulnar nerve symptoms, and all underwent concurrent ulnar nerve release. Postoperatively, improvements in elbow pain, instability, and ulnar nerve symptoms were observed. One patient required reoperation due to malunion and insufficient correction, but no other complications were noted.
Conclusions
These outcomes demonstrate that reverse V step-cut osteotomy can be an effective treatment method for cubitus varus deformity in adults. Level of evidence: IV.
- 1,566 View
- 44 Download

- The clinical outcome of treating elderly distal radius fractures by long volar locking plate with the elimination of irreducible metaphyseal comminuted volar cortical fragments: a retrospective case series
- Soo Min Cha
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(1):13-22. Published online January 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00003

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
In severe comminuted metaphyseal distal radius fracture (DRF) of elderly patients, after maintaining only radiological parameters of the radius using long volar locking plates (VLPs), we inevitably eliminated a few volar cortical fragments of metaphysis. Here, we report the final radiological and clinical outcomes of our method. Methods: For the patients who were treated between 2014 and 2018, the demographic factors, the preoperative radiologic factors, area of the eliminated volar cortical fragment, and final radiologic parameter, were evaluated. Clinical outcomes and ranges of active motion were evaluated. Results: In total, 31 patients were included. The mean patient age was 77.3 years and the mean eliminated cortical area was 3.30 cm2. At the final follow-up, the mean volar tilt, radial inclination, articular step-off, and ulnar variance were 10.35°, 20.00°, 0.58 mm, and 0.71 mm, respectively. There were no definitive correlations between bone mineral density, fragment area, the largest cortical fragment diameter ratio and differences in final and immediate postoperative measurements of these radiological parameters, respectively. Visual analog scale and disabilities of the arm, shoulder, and hand (DASH) scores were satisfactory, and the mean arcs of flexion-extension and pronation-supination were 124.35° and 133.23°. Clinical outcomes were not significantly different according to the AO system category. Conclusions: For maintenance of radiological parameters of the radius, long VLPs are useful in older patients with DRFs who exhibit volar metaphyseal comminution, despite concurrent ulnar fractures. Inevitable elimination of irreducible free comminuted cortical fragments when filling the defect does not affect final radiological and clinical outcomes. Level of evidence: Level IV, case series.
- 1,100 View
- 40 Download

Review Article
- Pediatric around Elbow Fracture
- Taehun Kim, Jaeho Cho, Seungmin Chung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2021;34(1):44-49. Published online January 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2021.34.1.44
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study assessed the current concepts of pediatric elbow fractures. PubMed and Embase databases were searched for publications in English on elbow fractures. Papers believed to yield significant findings to this area were included in this review. The supracondyle of humerus, lateral condyle of the humerus, proximal radius, and proximal ulna fractures were included. Sixteen papers and textbooks were selected. Pediatric elbow fractures should be evaluated for combined injuries. Treatment should be done accurately for each fracture for the further growth of children.
- 421 View
- 10 Download

Case Reports
- Treatment of Atypical Ulnar Fracture Associated with Bisphosphonate Therapy - A Case Report -
- Dong-Soo Kim, Ji-Kang Park, Eui-Sung Choi, Ho-Seung Jeong, Seok-Hyun Hong, Byung-Hyun Ahn
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(2):101-104. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.2.101
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Bisphosphonates can cause atypical fractures when taken for a long time. Atypical fractures appear mainly as femoral subtrochanteric or shaft fractures. On the other hand, reports of atypical fractures in the proximal ulna are relatively rare, with a high proportion of nonunion cases. This paper reports a case of nonunion after fixation for atypical fractures of the proximal ulna.
- 428 View
- 2 Download

- Ulnar Insufficiency Fractures in Patients on Prolonged Bisphosphonate Therapy: A Case Report
- Kyu Min Kong, Yong Uk Kwon, Young Kyung Min, Doo Yeol Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(3):143-147. Published online July 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.3.143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Atypical fractures associated with prolonged bisphosphonate (BP) therapy rarely occur outside the femur, and the diagnostic criteria, appropriate treatment principles, and fixation methods for atypical ulnar fractures have not been established. The authors experienced the use of internal fixation with a metal plate and a new internal fixation method with an intramedullary nail in the treatment of an atypical ulnar fracture in a patient who had been on BP therapy for 10 to 20 years. This paper reports findings along with a review of the relevant literature.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Treatment of Atypical Ulnar Fracture Associated with Bisphosphonate Therapy: A Case Report
Dong-Soo Kim, Ji-Kang Park, Eui-Sung Choi, Ho-Seung Jeong, Seok-Hyun Hong, Byung-Hyun Ahn
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2020; 33(2): 101. CrossRef
- Treatment of Atypical Ulnar Fracture Associated with Bisphosphonate Therapy: A Case Report
- 724 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review Article
- Distal Humerus Fracture: How to Choose the Approach, Implant, Fixation and Rehabilitation
- Min Ho Lee, Young Ho Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(1):72-81. Published online January 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.1.72
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Distal humerus fractures require stable fixation and early joint motion, similar to other intra-articular fractures, but are difficult to treat adequately because of the anatomical complexity, severe comminution, and accompanying osteoporosis. In most cases, surgical treatment is performed using two supporting plates. Plate fixation can be divided into right angle plate fixation and parallel plate fixation. In addition, depending on the type of fracture, surgical procedures can be performed differently, and autologous bone grafting can be required in the case of severe bone loss. The elbow joint is vulnerable to stiffness, so it is important to start joint movement early after surgery. Postoperative complications, such as nonunion, ulnar nerve compression, and heterotopic ossification, can occur. Therefore, accurate and rigid fixation and meticulous manipulation of soft tissues are required during surgery.
- 1,965 View
- 93 Download

Original Article
- Surgical Outcomes of the Monteggia Type 2 Fracture Dislocation in Adults
- Sung Choi, Daegeun Jeong, Youngsoo Byun, Taehoe Gu, Sungsoo Ha, Dongju Shin
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(1):6-13. Published online January 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.1.6
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study examined clinical outcomes of Monteggia fracture type 2, which is the most common in adults with a high rate of accompanied injuries.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From June 2004 to November 2015, a retrospective study was performed on 12 patients diagnosed with Monteggia fracture type 2 with a follow-up period of at least 6 months after surgery. The clinical outcomes were evaluated using the Mayo elbow performance score (MEPS), and the existence of accompanied injures, radiological result, and complications were analyzed.
RESULTS
Posterior instability was confirmed in all patients and accompanied fractures were detected in 9 patients (75.0%) on the radial head, whereas 10 patients (83.3%) were found on the coronoid process. The average arc of motion was 107° (70°–130°) and the mean MEPS was 89 (45–100). Additional re-operation due to re-dislocation, radioulnar synostosis, elbow instability, ulna nonunion, and radial head nonunion were performed in 4 cases (33.3%).
CONCLUSION
The Monteggia fracture type 2 is more commonly associated with radial head fractures and coronoid process fractures rather than other types, which causes elbow instability. Because the rate of additional surgery due to complications is high, the treatment of Monteggia fracture type 2 requires careful assessments.
- 802 View
- 3 Download

Case Reports
- Transscaphoidal Dorsal Perilunar Dislocation Associated with Dislocation of Distal Radioulnar Joint: A Case Report
- Chul Hyung Kang, Chul Hyun Cho, Dong Wan Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(1):77-81. Published online January 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.1.77
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Dorsal perilunar dislocations are rare traumatic entities. Associated fractures such as carpal bones and radial styloid processes can occur. However, the dorsal perilunar dislocation associated with dislocation of distal radioulnar joint is extremely rare. The authors herein report the case of a 34-year-old man who was presented with transscaphoidal perilunar dislocation which is associated with dislocation of distal radioulnar joint.
- 309 View
- 0 Download

- Missed Variation of the Essex-Lopresti Injury Associated with Type-I Monteggia Equivalent Lesion: A Case Report
- Young Sung Kim, Phil Hyun Chung, Suk Kang, Ho Min Lee, Jong Pil Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(3):219-222. Published online July 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.3.219
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The authors report the case of a patient with the combination of a Type I Monteggia equivalent lesion and Essex-Lopresti injury. This combination of injury is very rare, and an associated distal radioulnar injury is often missed. We hope our experience illustrates the need to examine the wrist joint carefully and to be aware of the potential for distal radioulnar joint instability in all patients with type I Monteggia equivalent lesions.
- 364 View
- 0 Download

- The 'beta-wire Technique' for the Fixation of Ulnar Styloid Process Fracture: Surgical Technique
- Jee Hyoung Kim, Jin Hak Kim, Song Lee, Seung Jin Yang, Chang Wook Yoo, Tae Hwan Chun
- J Korean Fract Soc 2010;23(1):104-108. Published online January 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.1.104
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - For the fixation of ulnar styloid process fracture, we want to introduce the 'beta-wire technique', which is easy to learn and practice and thought to give a compressive force to the fracture site.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Korean Medicine Treatments for the Angular Deformity of Wrist Fracture with Disuse Osteopenia: A Case Report
Myung Jin Oh
Korean Journal of Acupuncture.2018; 35(4): 234. CrossRef
- Korean Medicine Treatments for the Angular Deformity of Wrist Fracture with Disuse Osteopenia: A Case Report
- 549 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Article
- Treatment of Ulnar Olecranon Fracture Using Acutrak Screw
- Hyungchun Kim, Kwangryul Kim, Moonsup Lim, Youngil Park, Inhwan Hwang, Jihoon Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(4):270-275. Published online October 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.4.270
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the clinical results of Acutrak screw fixation for ulnar olecranon fractures. MATERIALS AND METHODS: We reviewed 15 cases of ulnar olecranon fractures which were treated with Acutrak screws from February 2003 to September 2007. Follow-up period is from 12 months to 42 months. We used Mayo classification. Radiologic results were analyzed according to step-off, gap, reduction loss, and functional results were analyzed according to pain and ROM. We analyzed union time, operation time, incision size and complications. RESULTS: In functional results, there were 3 good cases out of 3 Mayo type IA, 8 good cases and 2 fair cases out of 10 type IIA, 1 fair case and 1 poor case out of 2 type IIB. In radiologic results, there was 1 case of reduction loss. Average union time was 9.4 weeks, average operation time was 24 minutes and average incision size was 1.8 cm. CONCLUSION: We conclude that Acutrak screw fixation can be a treatment option for olecranon fracture of Mayo type IA and IIA.
- 384 View
- 2 Download

Case Report
- Anterior Dislocation of Distal Radio-Ulnar Joint: A Case Report
- Shin Kun Kim, Sang Bong Ko, Seung Bum Chae
- J Korean Fract Soc 2008;21(1):66-69. Published online January 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.1.66
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - There are variable types in wrist joint injury. Most common case is simple distal radius fracture. And ulnar head dislocation associated with disruption of distal radioulnar ligament is unusual. Among thease injury types. volar dislocation of ulnar head in the distal radioulnar joint is not common and it is misdiagnosis frequently. So it needs to surgical operation frequently. The author reviews this injury with the relevant literature.
- 456 View
- 6 Download

Original Articles
- Distal Radioulnar Joint Injuries Associated with Intra-articular Fracture of Distal Radius
- Woo Sik Kim, Yong Sang Kim, Whan Yong Chung, Woo Suk Lee, Taek Soo Jeon, Seung Ryul Ryu
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(2):221-227. Published online April 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.2.221
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the significance of distal radioulnar joint injury which may affect the postoperative radiologic and clinical results of AO classification, type C distal radius fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From October 2000 to October 2005, 58 patients of AO classification, type C distal radius fracture, who had been treated with operative methods were studied. They are thirty-six men and twenty-two women. The average follow up period was 14 months. The patients were divided into five groups. In the first group (13 cases), there was no distal radioulnar joint injuries. In the second group (20 cases), there were ulnar styloid fractures. In the third group (11 cases), there were separation of distal radioulnar joint. In the fourth group (9 cases), there were ulnar styloid fractures with separation of distal radioulnar joint. In the fifth group (5 cases), there were displacement of ulna in sagittal plane. We measured the radial length, radial inclination and volar tilt in plain radiograph in each group and analyzed the results through Scheck's methods. To analyzed the clinical results, we used the Demerit Point System by Sarmiento.
RESULTS
There was no significant differences in radiologic and clinical results among the five groups.
CONCLUSION
According to compairing the radiologic results of each group which was suspicious of distal radioulnar joint injuries, in the intraarticular comminuted fractures of distal radius, the distal radioulnar joint injuries did not affect the results of treatment when anatomical reduction of distal radius was achieved. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Treatment of Distal Radioulnar Joint Injuries Associated with a Distal Radius Fracture
Ki-Bum Choi, Sung-Woo Huh, Seong-Eun Kim, Jung-Woo Lee, Seok-Whan Song, Seung-Koo Rhee
Journal of the Korean Society for Surgery of the Hand.2012; 17(4): 147. CrossRef
- Treatment of Distal Radioulnar Joint Injuries Associated with a Distal Radius Fracture
- 595 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Clinical Outcome of Surgical Treatment of Distal Humerus Intercondylar Fractures Through the Transolecranon Approach Combined with Anterior Transposition of the Ulnar Nerve
- Kwang Hyun Lee, Seong Pil Lee, Kyu Tae Hwang, Joo Hak Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(2):70-75. Published online April 30, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.2.70
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analyze the clinical outcomes of surgical treatment of distal humerus intercondylar fractures through the transolecranon approach combined with anterior transposition of the ulnar nerve.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Eight patients who had distal humerus intercondylar fractures were included in this study and underwent operative treatment through the transolecranon approach for sufficient operative field with anterior transposition of the ulnar nerve and fixed with reconstruction plate.
RESULTS
The results were evaluated using Riseborough and Radin rating criteria. Seven cases of eight cases were achieved good results with flexion contracture less than 30 degrees and forward flexion more than 115 degrees. However, one case was acheived poor result with 40 degrees of flexion contractue and 70 degrees of forward flexion. There were no the compressive ulnar neuropathy.
CONCLUSION
We found the transolecranon approach and anterior transposition of the ulnar nerve a viable option for surgical treatment of the distal humerus intercondylar fractures
- 349 View
- 0 Download

- The significance of distal radioulnar joint injury in distal radius fracture
- Jin Woo Kwon, Sung Ho Shin, Won Ho Jo, Dong Hyun Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(2):251-257. Published online April 30, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.2.251
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the effectiveness of operative treatment in distal radius fracture with distal radioulnar joint injury. MATERIAL AND METHOD: From January 1992 to January 2000, 66 cases of distal radius fracture with distal radioulnar joint injury who had been treated with conservative or operative methods were analyzed the final state of radius articular surface and distal radioulnar joint.
RESULT
In operatively treated cases(42 cases), the average of volar tilt was 3.74 degrees, ulnar inclination 21.9 degrees, radial length 9.74mm. In conservatively treated cases(24 cases), The average of volar tilt was 1.75 degrees, ulnar inclination 15.1 degrees, radial length 7.67mm. The state of distal radioulnar joints were as follows; In operatively treated cases, anatomical reduction 37(88%), joint widening 5, In conservatively treated cases, anatomical reduction 17(70%), joint widening or ulnar impingement syndrome 7.
CONCLUSION
In treatment of distal radius fracture with distal radioulnar injury, operative treatment is probably more effective in restoration of radius articular surface and distal radioulnar joint healing.
- 331 View
- 0 Download

Case Report
- Axial-Ulnar fracture-Dislocation of the Carpus : A Case Report
- Ho Rim Choi, Sang Seon Lee, Chi Won Lee, Sung Jun Han, Won Tae Choi
- J Korean Soc Fract 1999;12(4):1027-1030. Published online October 31, 1999
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1999.12.4.1027
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Axial dislocation of the carpus is a rare injury, and it usually is caused by crush mechanism in industrial fields. We experienced a case of axial-ulnar fracture-dislocation of the carpus which was treated by open reduction and internal fixation with K-wires and external rixator fixation.
- 401 View
- 0 Download

Original Articles
- Ulnar nerve palsy After Percutaneous Pinning in Childrens Supracondylar fracture
- Tai Seung Kim, Jay Rim Choi, Kuhn Sung Whang
- J Korean Soc Fract 1999;12(3):674-678. Published online July 31, 1999
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1999.12.3.674
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Many authors have described percutaneous pinning techniques as the treatment of choice for most supracondylar fractures. But little information is available concerning ulnar nerve injury resulting from pinning techniques. When the surgeon is faced with a postoperative ulnar nerve palsy, it can be the result of unrecognized preoperative palsy, manipulation during surgery, or damage to the nerve by one of the medial pin placements. The options for management include exploration, medial pin removal, or observation. We reviewed our hospital records on the 132 supracondylar elbow fractures that we treated in children from 1991 to 1998 There were 16 palsies found with normal preoperative and abnormal postoperative ulnar nerve function. Normal nerve function returned without exploration and early medial pin removal in all cases. We recommand that observation is the appropriate way to manage these postoperative ulnar nerve palsies in most cases.
- 289 View
- 0 Download

- Surgical Treament for Unstable Intra-articular Fracture of the Distal Radius with Rayhack's Transulnar Percutaneous Pinning Technique
- Eui Chan Jang, Ho Sung Ryu, Jae Sung Lee, Jung Nam Han
- J Korean Soc Fract 1999;12(2):422-428. Published online April 30, 1999
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1999.12.2.422
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - There has been many treatment modalities in the distal radius fracture. Although there is no doubt that external fixators have a role in the treatment of some highly displaced distal radius fractures, many unstable distal radius fractures may be treated adequately with far less complicated and intrusive percutaneous pinning technique. The purpose of this study was to evaluate indication and effectiveness of Rayhack's transulnar percutaneous pinning technique. Authors reviewed the unstable intra-articular fracture of the distal radius of 15 cases treated with Rayhack's transulnar percutaneous pinning technique between March 1994 and February 1997. At the final follow-up examination, the mean loss of radial length, radial inclination and volar tilt was respectively 0.4mm (3.9%), 2.0 (10.6%), 2.1 (14.7%). Posttraumatic arthritis was occurred in 1 case (11.1%) of less than 1mm residual articular step-off, 2 cases (40%) of more than 1mm and less than 3mm residual articular step-off, 1 case (100%) of more than 3mm residual articular step-off. Distal radioulnar joint synostosis by percutaneous pinning was not found. According to Demerit point rating system, excellent to good results were obtained in 73.3%. Authors suggest that Rayhack's pinning technique can be applied in terms of simple procedure, cost-effectiveness and functional outcome.
- 303 View
- 2 Download

- Tardy Ulnar Nerve Palsy Caused by Post-Traumatic Elbow deformities
- Seung koo Rhee, seok Whan Song, Hwa Sung Lee, Ho Tae Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1998;11(2):420-426. Published online April 30, 1998
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1998.11.2.420
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Thirty-five patients with tardy ulnar nerve palsy caused by cubitus valgus (33 cases0 and varus (2 cases) deformities were retrospectively studied. All patients had a history of old fracture on the distal humerus during childhood. The mean interval between the previous fractures and the onset of ulnar neuropathy was 19 years. The severity of nerve palsy was classified as McGowan's grade I in 24 patients, grade II in 8 patients, and grade III in 3 patients. The mean carrying angle was average 29 degrees in 33 cases with cubitus valgus and it was decreased to average 11 degrees postoperatively, but the angle was average -23 degrees preoperatively in 2 cases with cubitus varus and it was corrected to average 9 degrees postoperatively. the cause of palsy was analysed by mechanical stetching in 11 cases, compression by a fibrous band between the two heads of flexor carpi ulnaris in 8 cases, and diffuse fibrous adhesion around the ulnar tunnel in 5 cases. All patients was treated with supracondylar closing wedge osteotomy accompanied with anterior ulnar nerve transposition in 13 patients, corrective osteotomy only in 12 patients, and anterior ulnar nerve transposition only in 10 patients. Their end results were analysed as good in 24 cases, fair in 8 cases, and poor in 3 cases within average 6 months after the operations (4 to 13 months). The poor results was obtained in 3 cases out of 9 cases with corrective osteotomy group (33.3%). Conclusively, a tardy ulnar nerve palsy caused by post-traumatic elbow deformities should be corredcted with anterior ulnar nerve transposition with or without corrective closing wedge osteotomy but not by corrective osteotomy only, because of compressive neuropathy by diffuse fibrous adhesion or bands of two heads of FCU around the ulnar tunnel in elbow.
- 548 View
- 3 Download

- Fracture of the Distal Radius with Ulnar Nerve Palsy
- Chil Soo Kwon, Jong Kuk Ahn, Jin Hyok Kim, Yerl Bo Sung, Jin Ho Cho
- J Korean Soc Fract 1997;10(1):171-174. Published online January 31, 1997
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1997.10.1.171
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - There are several complications of distal radiug fracture such as median nerve injury, malunion nonunion, rupture of EPL, and ischemic contracture. Lesion of ulnar nerve as a complication of fracture of the distal radius are very rare. The authors report 1 case of the distal radius fracture with ulnar nerve palsy. The electromyography & nerve-conduction studies showed incomplete axonotmesis of ulnar nerve on 1 month following injury. A second electromyography & nerve-conduction study two months after injury showed complete recovery of nerve function.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ulnar Nerve Palsy Following Closed Fracture of the Distal Radius: A Report of 2 Cases
Chul-Hyun Cho, Chul-Hyung Kang, Jae-Hoon Jung
Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery.2010; 2(1): 55. CrossRef
- Ulnar Nerve Palsy Following Closed Fracture of the Distal Radius: A Report of 2 Cases
- 511 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Treatment for the Malunion of the Distal Radius
- Hyoun Oh Cho, Kyoung Duck Kwak, Sung Do Cho, Cheol Soo Ryoo, Woo Keun Jung
- J Korean Soc Fract 1996;9(2):290-294. Published online April 30, 1996
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1996.9.2.290
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Malunited fractures of the distal radius may result in adequate function of the wrist with absence of pain in elderly patients. However, posttraumatic dedormity in younger, active patients is less well toterated, especially in those engaged in heavy manual work or who require a normal range of motion of the wrist. surgical correction of the malunion of the distal radius should be considered for this group of patients. Operation for the malunited fractures of the distal radius was performed in ten cases during the periods between January, 1990 and December, 1993, who were followed for an average of 15 months.The procedures included radial osteotomy(RO) in four malunions of short duration, radial osteotomy with ulnar shortening (RO & US) in these malunions of long duration and ulnar shortening(US) in three cases. We reviewed these cases retrospectively with respect to the clinical findings(pain, grip strength, range of motion of the wrist) and radiograpic changes(volar tilt, radial articular inclination and radiul shortening). Symptoms(radioulnar or radiocarpal pain) were improved in all cases. By compairing with the opposite sides, resedual loss of grip strength was 35% in RO group, 40% in RO & US and 31% in & US group. Residual loss of motion in flexion and extension or in deviation was similar in all groups, whill loss in rotation was less in RO or RO & US group than in US group. Inclination of the radial articular surface (radial inclination and volar tilt) was restored up to the degree similar to the opposite wrist in RO or US group, while was not in US group. Radial length was restored up to the dgegrees similar to the opposite wrist in all groups. The overall results were good or very good in five among the seven cases of RO group(with or without ulnar shortening), while good only in one among the cases of US group.
- 354 View
- 2 Download

- Treatment of Fractures of Lateral Condyle of Humerus with Compliations
- Moon Sang Chung, Sung Churl Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 1995;8(3):659-666. Published online July 31, 1995
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1995.8.3.659
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fractures of the lateral condyle of the humerus are notorious for complications, most commonly nonunion with subsequent proximal migration of the ununited fragment, an increase in the carrying angle, and the tardy ulnar nerve palsy. In the past, the reconstructive surgery for complicated old fractures of the lateral condyle of the humerus had been hardly considered, but recently, attempts have been made to reconstruct the anatomy and function of the elbow joint. The authors have reviewed 21 cases of old fractures of the lateral condyle of the humerus, which had been treated at Seoul National University Hospital from April,1982 until March, 1990. For established nonunions of the lateral condyle fragment, better results were obtained from the procedure that includes osteosynthesis of the lateral condyle, attempting to restore the normal anatomy of the elbow joint. For tardy ulnar nerve palsies, better results were obtained from the procedure that includes medial epicondylectorny. Fractures of the lateral humeral condyle have many late problems in spite of treatment at the time of injury so early aggressive treatment is necessary. Even in cases with late problems, aggressive treatment should be done, too, as soon as possible.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- In SituLate Metaphyseal Osteosynthesis for the Fractures of the Lateral Humeral Condyle in Children
Kun Bo Park, Seung Whan Lee, Hyun Woo Kim, Hui Wan Park, Ki Seok Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2008; 21(2): 151. CrossRef
- In SituLate Metaphyseal Osteosynthesis for the Fractures of the Lateral Humeral Condyle in Children
- 587 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Report
- Treatment of Old Distal Radioulnar Dislocation: A Preliminary Report
- Kwon Ick Ha, Sung Ho Hahn, Min Young Chung, Bo Kyu Yung, Seung Rim Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 1990;3(1):10-15. Published online May 31, 1990
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1990.3.1.10
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Dislocations of the distal radioulnar joint without fracture are more common than would be expected from the literature and most of these injuries are not diagnosed when seen initially. Several chronic problems may befall the distal radioulnar joint-loss of forearm rotation, chronic pain and arthritis, and a great many surgical procedures have been devised to relieve them. Six patients were treated with resection of ulnar head (Darrach Operation)in 3 cases, ligamentous stabilization(Hui and Linscheid Operation)in 3 cases, and we found more satisfactory results in the latter.
- 365 View
- 0 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


