Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 22(4); 2009 > Article
-
Original Article
- Treatment of Ulnar Olecranon Fracture Using Acutrak Screw
- Hyungchun Kim, M.D., Kwangryul Kim, M.D., Moonsup Lim, M.D., Youngil Park, M.D., Inhwan Hwang, M.D., Jihoon Lee, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2009;22(4):270-275.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.4.270
Published online: October 30, 2009
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Wallace Memorial Baptist Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Hyungchun Kim, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Wallace Memorial Baptist Hospital, 374-75, Namsan-dong, Geumjung-gu, Busan 609-728, Korea. Tel: 82-51-580-1422, Fax: 82-51-583-2568, medifor@paran.com
• Received: October 7, 2008 • Revised: April 18, 2009 • Accepted: August 10, 2009
Copyright © 2009 The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 194 Views
- 1 Download
Abstract
-
Purpose
- To evaluate the clinical results of Acutrak screw fixation for ulnar olecranon fractures.
-
Materials and Methods
- We reviewed 15 cases of ulnar olecranon fractures which were treated with Acutrak screws from February 2003 to September 2007. Follow-up period is from 12 months to 42 months. We used Mayo classification. Radiologic results were analyzed according to step-off, gap, reduction loss, and functional results were analyzed according to pain and ROM. We analyzed union time, operation time, incision size and complications.
-
Results
- In functional results, there were 3 good cases out of 3 Mayo type IA, 8 good cases and 2 fair cases out of 10 type IIA, 1 fair case and 1 poor case out of 2 type IIB. In radiologic results, there was 1 case of reduction loss. Average union time was 9.4 weeks, average operation time was 24 minutes and average incision size was 1.8 cm.
-
Conclusion
- We conclude that Acutrak screw fixation can be a treatment option for olecranon fracture of Mayo type IA and IIA.
- 1. Adla DN, Kitsis C, Miles AW. Compression forces generated by Mini bone screws--a comparative study done on bone model. Injury, 2005;36:65-70.Article
- 2. Bryan RS. Fracture about the elbow in adults. Instr Course Lect, 1981;30:200-223.
- 3. Cabanela ME, Morrey BF. Fractures of the proximal ulna and olecranon. In: Morrey BF, editor. The elbow and its disorder. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co; 1993. p. 407-408.
- 4. Cho DY, Lee JM, Kim HC, Kim HJ. Clinical analysis of fractures around th elbow joint in adults. J Korean Soc Fract, 1995;8:430-438.Article
- 5. Conn J, Wade PA. Injuries of the elbow: a ten year review. J Trauma, 1961;1:248-268.
- 6. Daland EM. Fractures of the olecranon. J Bone Joint Surg, 1933;15:601-607.
- 7. Eriksson E, Sahlin O, Sandahl U. Late results of conservative and surgical treatment of fracture of the olecranon. Acta Chir Scand, 1957;113:153-166.
- 8. Gartsman GM, Sculco TP, Otis JC. Operative treatment of olecranon fractures. Excision or open reduction with internal fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1981;63:718-721.Article
- 9. Helm RH, Hornby R, Meller SW. The complications of surgical treatment of displaced fractures of the olecranon. Injury, 1987;18:48-50.Article
- 10. Hume MC, Wiss DA. Olecranon fractures. A clinical and radiologic comparison of tension band wiring and plate fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1992;285:229-235.
- 11. Muller ME, Allgower M, Schneider R, Willenegger H. Mannual of internal fixation. 3nd ed. Berin: Springer Verlag Co; 1991. p. 44-55. p. 460-461.
- 12. Murphy DF, Greene WB, Dameron TB Jr. Displaced olecranon fractures in adults. Clinical evaluation. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1987;224:215-223.Article
- 13. Park SW, Hur CY, Shim JH. Operative treatment of olecranon fracture. J Korean Soc Fract, 1994;7:58-64.Article
- 14. Watson-Jones R. Fractures and Joint Injuries. 6th ed. Churchill Livingstone Co; 1982. p. 650-655.
- 15. Wheeler DL, McLoughlin SW. Biomechanical assessment of compression screws. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1998;350:237-245.Article
REFERENCES
Fig. 1
(A) Initial radiographs show the intra-articular olecranon fracture of type IIA.
(B) Radiographs of postoperative 3 weeks show anatomical reduction with Acutrak screw.
(C) Radiographs of postoperative 7 months show complete union and good congruity of elbow joint after removal of Acutrak screw.
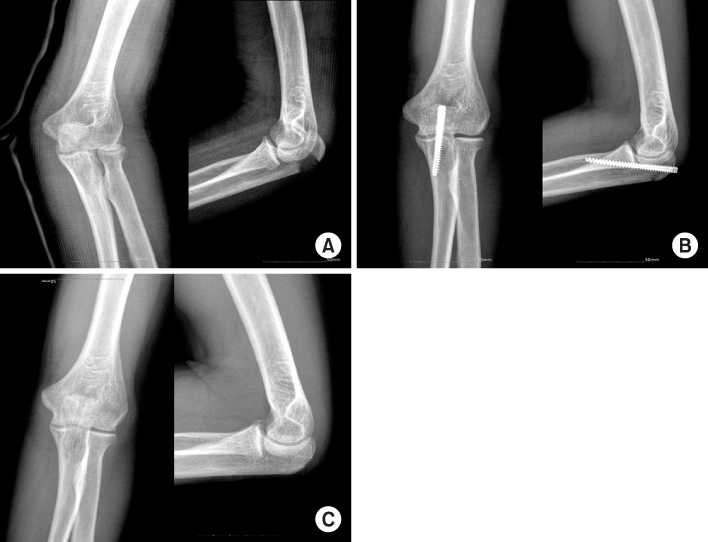

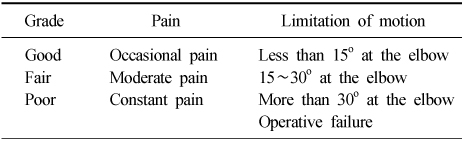
Fig. 2
(A) Radiographs show olecranon fracture of type IIA.
(B) These radiographs show internal fixation of olecranon fracture with 2 Acutrak screws postoperatively.
(C) Radiographs of postoperative 30 months show 2 Acutrak screws with good congruity of elbow.
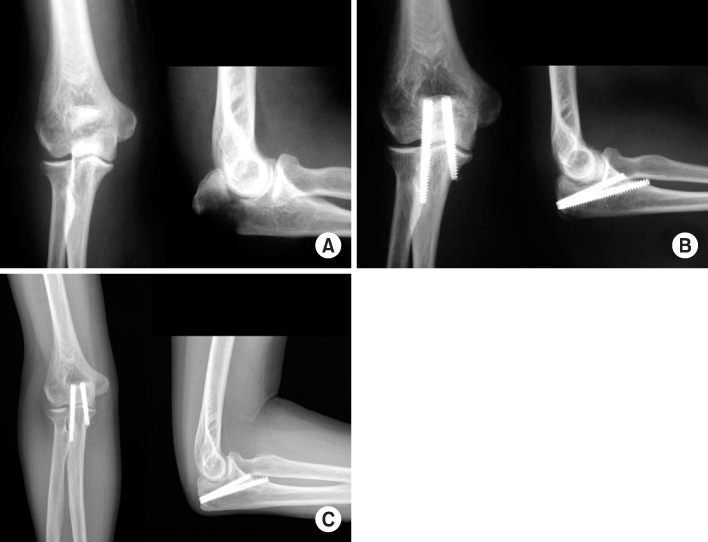

Fig. 3
(A) Initial radiographs show olecranon fracture of type IIB.
(B) Radiographs of postoperative 3 days show internal fixation of fracture with 2 Acutrak screws.
(C) On 26th day after operation, reduction loss is shown in these radiographs.
(D) After reduction loss, hardware removal and tension band wiring was done in these radiographs.
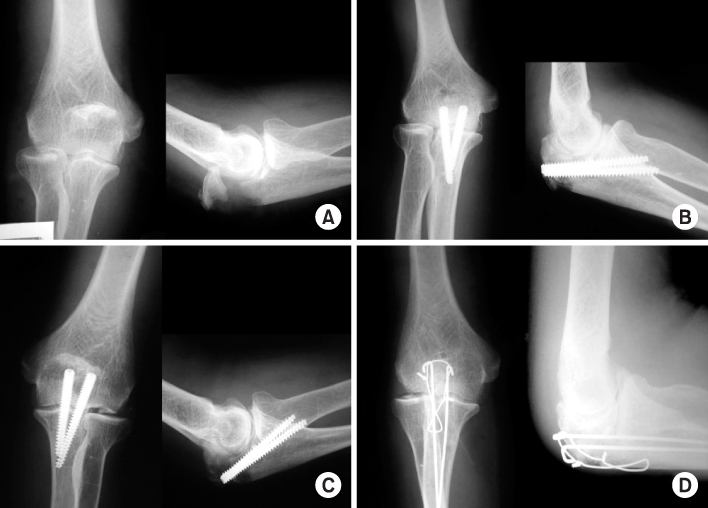

Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

Treatment of Ulnar Olecranon Fracture Using Acutrak Screw

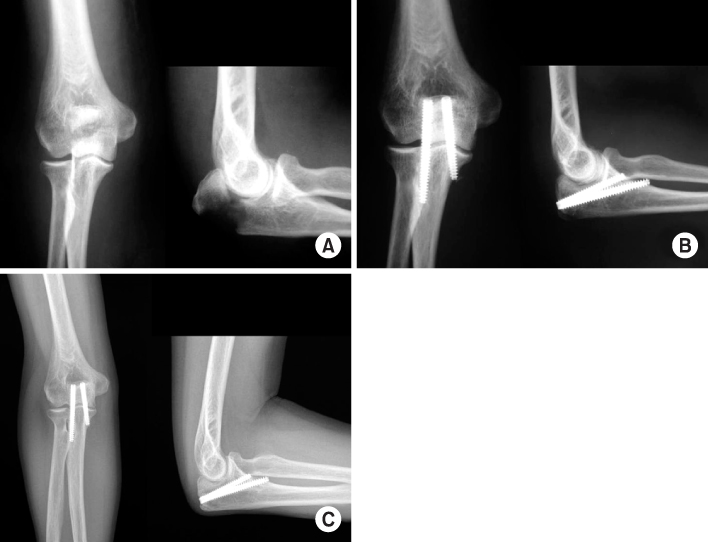
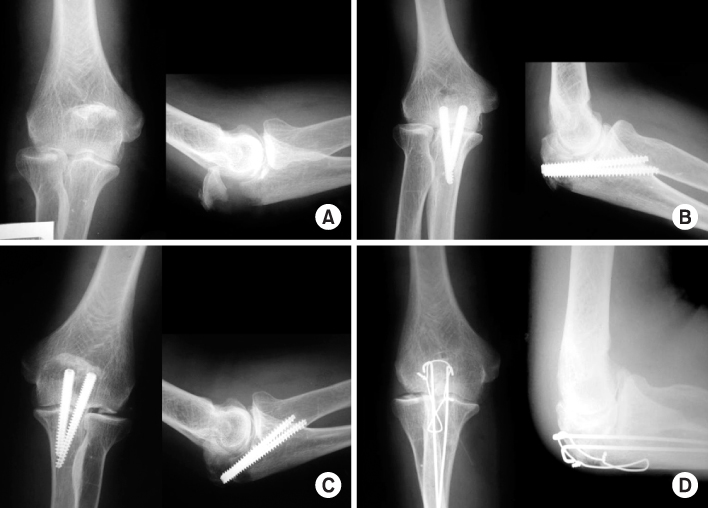
Fig. 1
(A) Initial radiographs show the intra-articular olecranon fracture of type IIA.
(B) Radiographs of postoperative 3 weeks show anatomical reduction with Acutrak screw.
(C) Radiographs of postoperative 7 months show complete union and good congruity of elbow joint after removal of Acutrak screw.
Fig. 2
(A) Radiographs show olecranon fracture of type IIA.
(B) These radiographs show internal fixation of olecranon fracture with 2 Acutrak screws postoperatively.
(C) Radiographs of postoperative 30 months show 2 Acutrak screws with good congruity of elbow.
Fig. 3
(A) Initial radiographs show olecranon fracture of type IIB.
(B) Radiographs of postoperative 3 days show internal fixation of fracture with 2 Acutrak screws.
(C) On 26th day after operation, reduction loss is shown in these radiographs.
(D) After reduction loss, hardware removal and tension band wiring was done in these radiographs.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Treatment of Ulnar Olecranon Fracture Using Acutrak Screw
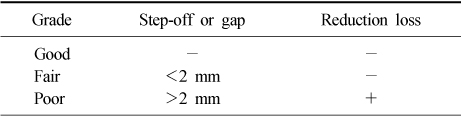
Table 1
Criteria for clinical evaluation9)
Table 2
Criteria for radiologic evaluation10,12)
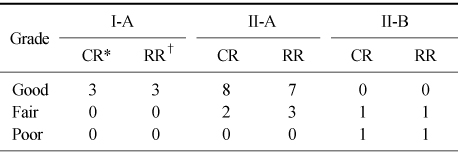
Table 3
Clinical and radiologic results
*CR: Clinical result, †RR: Radiologic result.
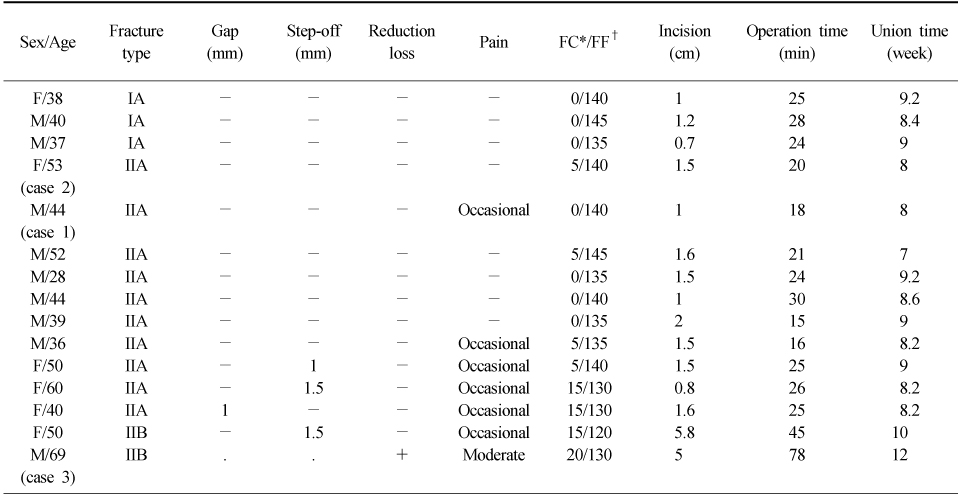
Table 4
Data of patients (postoperative follow-up)
*FC: Flexion contracture, †FF: Further flexion.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA
 Cite
Cite

