Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Relationship of lateral malleolar fracture patterns to posterior malleolar fracture morphology in supination-external rotation ankle fractures in Korea: a retrospective cohort stduy
- Jong-Eun Kim, Chan-Jin Park, Jun-Young Lee, Keun-Bae Lee, Gun-Woo Lee
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):212-220. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00234
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
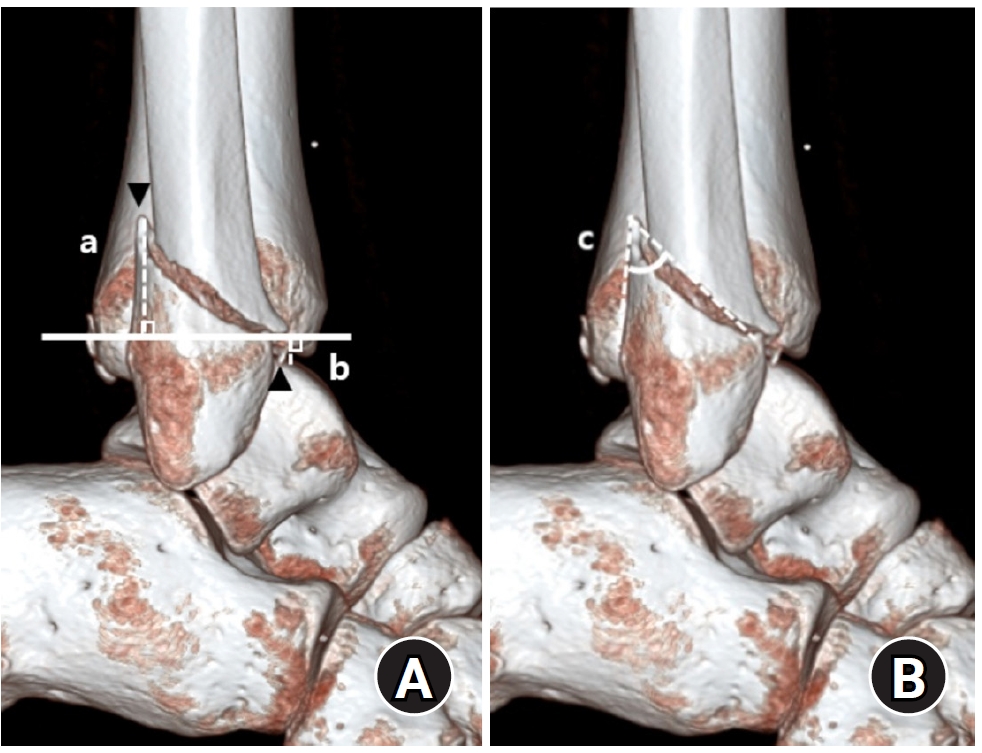
Posterior malleolar fractures frequently accompany rotational ankle fractures. However, the morphological relationship between lateral and posterior malleolar fractures in supination-external rotation (SER) ankle fractures remains unclear. This study aimed to classify lateral malleolar fracture patterns in SER type 3 and 4 ankle fractures and investigated their associations with posterior malleolar fracture morphology.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed 132 patients with SER type 3 or 4 ankle fractures and concurrent posterior malleolar fractures between January 2016 and December 2021. Lateral malleolar fractures were categorized as fibular fractures extending <4.5 cm proximal to the ankle joint (102 ankles) or fibular fractures extending ≥4.5 cm proximal to the ankle joint (30 ankles) based on posterior cortex height measured using three-dimensional computed tomography (3D-CT). Posterior malleolar fracture morphology was assessed using the Haraguchi and Bartonicek classifications. Quantitative parameters—including fracture height, angle, and articular involvement—were analyzed using 3D-CT imaging.
Results
Fibular fractures extending ≥4.5 cm proximal to the ankle joint were associated with a significantly higher frequency of Haraguchi type II and Bartonicek types 3 and 4 posterior malleolar fractures. This group also exhibited greater articular involvement (19.2% vs. 12.0%) and posterior cortical height (55.4 mm vs. 24.8 mm) compared to the <4.5 cm group (all P<0.001).
Conclusions
In SER type 3 and 4 ankle fractures, a fibular fracture extending ≥4.5 cm proximal to the ankle joint may be associated with posterior malleolar fractures exhibiting greater articular involvement and medial extension. Preoperative evaluation of the lateral malleolar fracture pattern may provide useful insights into posterior malleolar morphology and assist in surgical planning. However, these findings should be interpreted with caution due to inherent study limitations. Level of evidence: IV
- 89 View
- 1 Download

- Correlation of bone mineral density with ankle fractures in older adults in Korea: a retrospective cohort study
- Seung Hyun Lee, Chae Hun Lee, Seo Jin Park, Jun Young Lee
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):186-192. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00150
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Bone mineral density (BMD) is well-documented in relation to fractures of the spine, hip, distal radius, and proximal humerus; however, its correlations with other fracture types are less established. This study aimed to analyze BMD and associated risk factors in older adults (≥65 years of age) with osteoporotic ankle fractures. These fractures involve low-energy trauma, resulting from falls from a standing height or lower, and occur from impacts which typically do not cause fractures in individuals with normal bone.
Methods
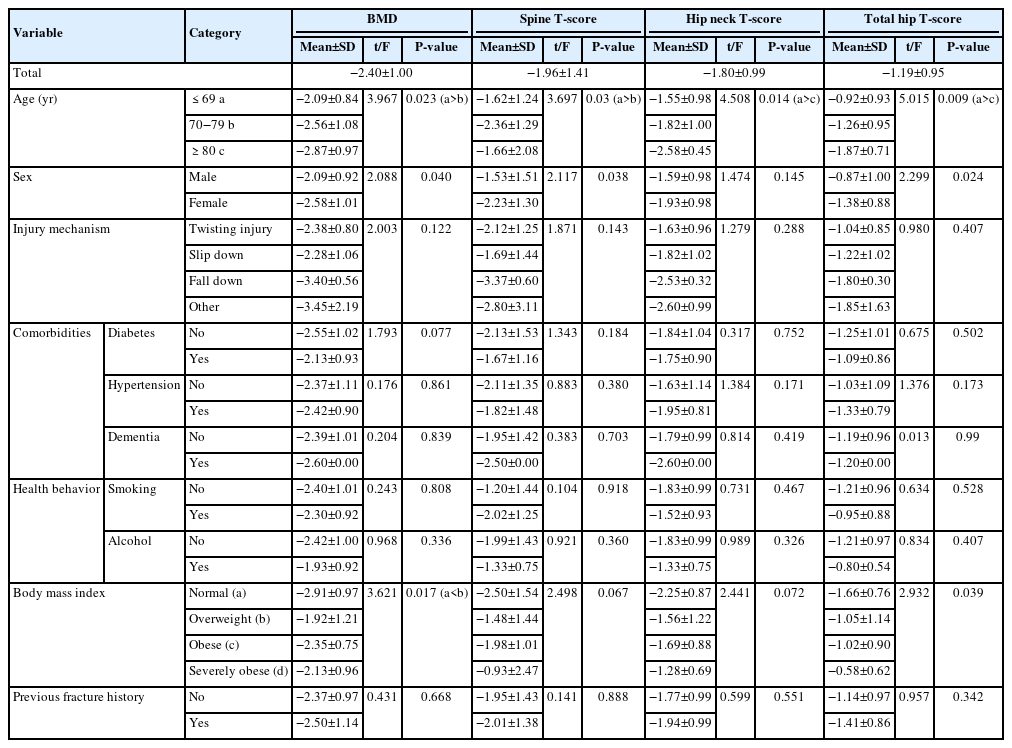
This retrospective study analyzed data from 1,411 patients diagnosed with ankle fractures admitted to Chosun University Hospital between February 2012 and April 2023. After applying inclusion criteria (age ≥65 years; low energy ankle fracture) and exclusion criteria (high energy trauma, open/multiple fractures, missing dual X-ray absorptiometry [DXA]), 73 of 1,411 patients were analyzed. Lumbar spine, femoral neck, and total hip T scores were obtained with a Horizon Wi DXA scanner, and associations with age, sex, mechanism of injury, comorbidities, smoking status, alcohol consumption, body mass index (BMI), and history of fractures were tested by ANOVA with Scheffe post hoc and Fisher exact tests.
Results
Lower BMD correlated significantly with older age, female sex, and lower BMI (P<0.05) in older adults with ankle fractures. No significant associations were observed for comorbidities (diabetes, hypertension, dementia), smoking, alcohol consumption, injury mechanism, or prior fractures.
Conclusion
These results indicate that older age, female, and lower BMI are linked to reduced BMD in ankle fracture patients over 65 years of age. Focused osteoporosis screening and management may therefore be most beneficial for older, low BMI women presenting with ankle fractures. Level of evidence: IV.
- 81 View
- 8 Download

- Risk factors for ankle fractures in older adults based on clinical components of the Fracture Risk Assessment (FRAX) tool and comorbidities in Korea: a retrospective case-control study
- Myeong Jun Song, Se Woong Jang, Jun Young Lee, Seojin Park
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):193-202. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Ankle fractures are common in older adults; however, their relationship with osteoporotic fractures remains unclear. This study aimed to evaluate potential risk factors for ankle fractures in older adults by analyzing individual clinical components of the Fracture Risk Assessment (FRAX) tool and comorbidities.
Methods
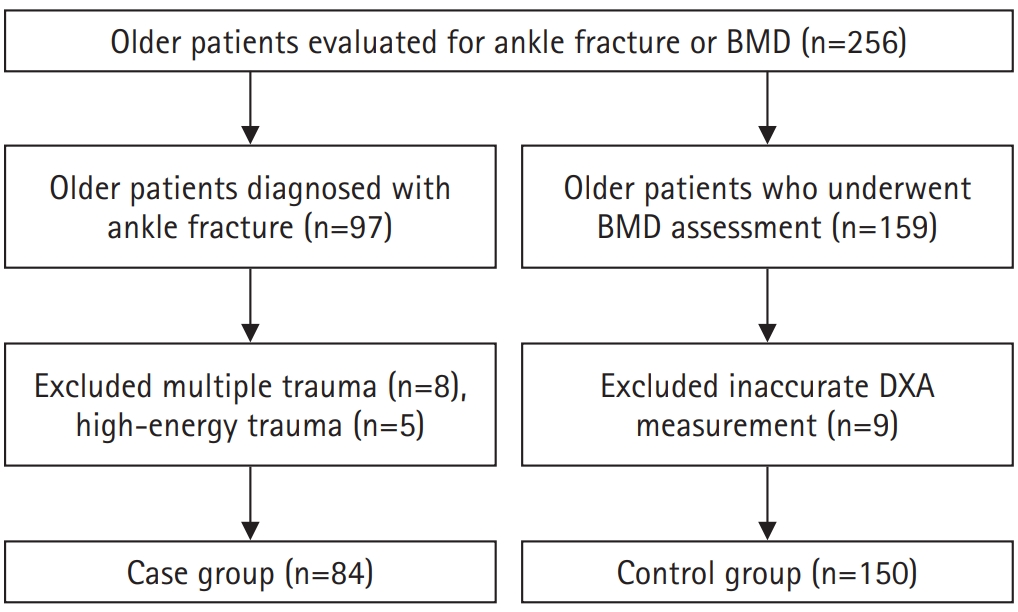
We conducted a retrospective case-control study including 84 patients aged ≥65 years with ankle fractures and 150 controls who underwent bone mineral density (BMD) testing without prior ankle fractures. The variables analyzed included age, sex, body mass index, smoking, alcohol consumption, prior fracture history, and comorbidities such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and dementia. BMD was measured at the spine, total hip, and femoral neck.
Results
Univariate analysis showed that alcohol consumption, diabetes mellitus, and total hip T-score categories were significantly associated with ankle fractures. In binary logistic regression, alcohol consumption remained significantly associated with higher ankle fracture risk (odds ratio [OR], 5.302; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.778–15.811; P=0.003), and both osteopenia and osteoporosis at the total hip were also associated with increased risk (OR, 3.260, P=0.049; OR, 3.561, P=0.031, respectively). Diabetes mellitus did not reach statistical significance in the adjusted model (P=0.074). Model fit was adequate (Hosmer-Lemeshow P=0.377), and post hoc power analysis confirmed sufficient sample size.
Conclusions
These findings suggest that lower total hip BMD and alcohol-related factors may be associated with ankle fracture risk in older adults. The FRAX score itself was not calculated; instead, this study focused on analyzing selected clinical components. Limitations include the retrospective design, lack of fall and medication data, and cross-sectional BMD assessment. Level of evidence: III.
- 84 View
- 7 Download

- Prediction of Syndesmotic Instability according to the Lateral Malleolus Fracture Pattern in Supination-External Rotation Type Ankle Fractures: Short Oblique versus Long Oblique Fracture
- Chan-Jin Park, Min-Su Lee, Keun-Bae Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(1):39-45. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.1.39
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined whether preoperative radiological evaluations can predict syndesmotic instability according to the lateral malleolus fracture pattern in supination-external rotation-type ankle fractures.
Materials and Methods
This study enrolled 132 patients (132 ankles) with supination-external rotation stage 3 and 4 ankle fractures. Three-dimensional computed tomography was used for the morphological classification of the lateral malleolus fractures. A long oblique fracture was defined when the posterior cortical bone height of the fracture was 4.5 cm or more from the plafond of the distal tibial articular surface. A short oblique fracture was defined when the height was less than 4.5 cm. The demographic characteristics and syndesmotic instability of the two groups were evaluated.
Results
Short oblique fractures were confirmed in 102 cases, and long oblique fractures were confirmed in 30 cases. Long oblique fractures occurred at a statistically significantly higher incidence in younger ages and among males compared to short oblique fractures. Syndesmotic instability was more common in long oblique fractures.
Conclusion
In supination-external rotation-type ankle fractures, syndesmotic instability was observed in approximately 13%. Specifically, when the fracture pattern of the lateral malleolus is long oblique, the incidence of syndesmotic instability is approximately three times higher than in short oblique fractures. Therefore, meticulous evaluations of the lateral malleolus fracture pattern and establishing an appropriate treatment plan before surgery are crucial. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship of lateral malleolar fracture patterns to posterior malleolar fracture morphology in supination-external rotation ankle fractures in Korea: a retrospective cohort stduy
Jong-Eun Kim, Chan-Jin Park, Jun-Young Lee, Keun-Bae Lee, Gun-Woo Lee
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(4): 212. CrossRef
- Relationship of lateral malleolar fracture patterns to posterior malleolar fracture morphology in supination-external rotation ankle fractures in Korea: a retrospective cohort stduy
- 362 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Analysis of Clinical and Functional Outcomes according to the Blood Sugar Control Status at the Time of Ankle Fractures Resulting from Rotational Injuries
- Jun Young Lee, Dong Seop Lim, Seung Hyun Lee, Seo Jin Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(4):135-141. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.4.135
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Patients with diabetes are known to have poor clinical outcomes due to the high incidence of complications after ankle joint fracture surgery. This study reports the clinical and functional outcomes based on glycemic control status among patients with ankle joint fractures who underwent surgical treatment.
Materials and Methods
Among patients who underwent surgical treatment due to ankle joint fractures from January 2015 to October 2019, 253 patients with a minimum follow-up of 12 months were identified. We divided them into 3 groups: 195 patients with no diabetes (Group A), 26 patients with well-controlled diabetes (Group B), and 32 patients with uncontrolled diabetes (Group C). In addition, patients with lateral, medial malleolar, bimalleolar, and trimalleolar fractures were identified using radi-ography. The functional outcome measures used for evaluation were the Revised Foot Function Index (FFI), Short Musculoskeletal Function Assessment (SMFA), and the Foot and Ankle Outcome Score (FAOS).
Results
Bone union at 3 months after surgery was high in Group A, showing significant differences compared to the other groups. There was a significant difference between the groups in the incidence of arthropathy and one or more complications. However, the FFI, SMFA, and FAOS did not show significant differences between the groups.
Conclusion
The incidence of complications was high in patients with uncontrolled diabetes compared to the patients with well-controlled diabetes and those with no diabetes. However, functional outcomes showed no significant difference.
- 500 View
- 5 Download

Case Reports
- Treatment of Neglected Proximal Interphalangeal Fracture Dislocation Using a Traction Device: A Case Report
- Yongun Cho, Jai Hyung Park, Se Jin Park, Ingyu Lee, Eugene Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(4):222-226. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.4.222
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This paper reports the use of a traction device for the treatment of neglected proximal interphalangeal fracture dislocations. A 44-year-old man with a fracture dislocation of a right ring finger proximal interphalangeal joint was admitted 17 days after the injury. Closed reduction and external fixation were performed using a dynamic traction device and C-arm under a brachial plexus block. Passive range of motion exercise was started after two weeks postoperatively and active range of motion exercise was started after three weeks. The traction device was removed after five weeks. No infection occurred during the traction period. No subluxation or displacement was observed on the X-ray taken two months postoperatively. The active range of motion of the proximal interphalangeal joint was 90°. The patient was satisfied with the functional result of the treatment with the traction device. The dynamic traction device is an effective treatment for neglected fracture dislocations of the proximal interphalangeal joint of a finger.
- 759 View
- 1 Download

- Bilateral Gluteal Necrosis and Deep Infection after Transarterial Embolization for Pelvic Ring Injury in Patient with Hemodynamic Instability: A Case Report
- Sung Jin Park, Chang Ho Jeon, Nam Hoon Moon, Yong Geon Park, Jae Hoon Jang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(1):56-60. Published online January 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.1.56
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Transarterial embolization is accepted as effective and safe for the acute management in hemodynamically unstable patients with pelvic ring injury. However, transarterial embolization has potential complications, such as gluteal muscle/skin necrosis, deep infection, surgical wound breakdown, and internal organ infarction, which are caused by blocked blood flow to surrounding tissues and organs, and many studies on the complications have been reported. Here, we report an experience of the management of gluteal necrosis and infection that occurred after transarterial embolization, with a review of the relevant literature.
- 467 View
- 0 Download

Original Articles
- Perioperative Blood Loss in Intramedullary Hip Screw for Intertrochanteric Fracture: Analysis of Risk Factors
- Jai Hyung Park, Hwa Jae Jung, Hun Kyu Shin, Eugene Kim, Se Jin Park, Taeg Su Ko, Jong Hyon Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2015;28(1):53-58. Published online January 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.1.53
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
We compared visible blood loss and calculated blood loss after intramedullary fixation in intertrochanteric fracture, and evaluated correlation between blood loss and its risk factors.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 256 patients who underwent closed reduction and intramedullary fixation in femoral intertrochanteric fracture between 2004 and 2013 were enrolled in this study. The total blood loss was calculated using the formula reported by Mercuiali and Brecher. We analyzed several factors, including fracture pattern (according to Evans classification), gender, age, body mass index (BMI), anesthesia method, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease, preoperative anemia, American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) score and use of antithrombotic agents.
RESULTS
Total calculated blood loss (2,100+/-1,632 ml) differed significantly from visible blood loss (564+/-319 ml). In addition, the blood loss of unstable fracture patient was 2,496+/-1,395 ml and multivariate analysis showed a significant relationship between blood loss and fracture pattern (p<0.01). However, other factors showed no statistically significant difference.
CONCLUSION
Total calculated blood loss was much greater than visible blood loss. Patients with unstable intertrochanteric fracture should be treated with care in order to reduce blood loss.
- 270 View
- 0 Download

- Fixation of the Femoral Subtrochanteric Fracture with Minimally Invasive Reduction Techniques
- Chul Hyun Park, Chul Wung Ha, Sang Jin Park, Min Su Ko, Oog Jin Shon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(2):112-117. Published online April 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.2.112
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the results of using minimally invasive reduction techniques in patients with femoral subtrochanteric fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We retrospectively analyzed 40 patients (41 cases) with subtrochanteric fracture who underwent using minimally invasive reduction techniques. The mean age was 61.4 years (15-89 years), and the mean follow-up period was 32.7 months (12-66 months). Clinical results were assessed using the Parker-Palmer mobility score and the Salvati-Wilson hip functional score. Radiographic results were evaluated using bone union time and femur neck-shaft angle.
RESULTS
No significant difference was observed in the pre- and postoperative Parker-Palmer mobility score. Salvati-Wilson hip functional score showed more than good grade in 37 cases (90%) at the last follow-up. Union was achieved in all 41 cases at an average of 22.5 weeks (18-30 weeks). The mean femoral neck-shaft angle immediately postoperatively was 128.8 degrees (120-140 degrees), and the mean difference versus contralateral sides was 2.5 degrees varus (-6-13 degrees).
CONCLUSION
Fixation of femoral subtrochanteric fracture using minimally invasive reduction techniques showed excellent clinical and radiographic results and low complication rate. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Yuhyangjeongtong-san on Fracture Healing in Rats
Ki-Tae Kim, Na-Young Jo
Journal of Korean Medicine.2019; 40(4): 61. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Time to Bony Union of Femoral Subtrochanteric Fractures Treated with Intramedullary Devices
Jung-Yoon Choi, Yerl-Bo Sung, Jin-Hee Yoo, Sung-Jae Chung
Hip & Pelvis.2014; 26(2): 107. CrossRef
- Effects of Yuhyangjeongtong-san on Fracture Healing in Rats
- 473 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Crossref

Case Report
- Repeated Metal Breakage in a Femoral Shaft Fracture with Lateral Bowing: A Case Report
- Dong Soo Kim, Yong Min Kim, Eui Sung Choi, Hyun Chul Shon, Kyoung Jin Park, Byung Ki Cho, Ji Kang Park, Hyun Cheol Lee, Kyung Ho Hong
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(2):136-141. Published online April 30, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.2.136
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fractures of the femoral shaft with marked bowing face some obstacles in fixation of the fracture such as difficulty in insertion of the intramedullary nail (IM nail) or exact contouring plate. Locking compression plates (LCP) are an option to manage this problem. However, we experienced consecutive breakage of LCP twice and IM nail once in an 80-year-old female. Finally, union of the fracture was achieved after fixation of the IM nail and additional plate together. Fractures of the femur shaft with marked bowing are thought to have different biomechanical properties; therefore, we present this case with a review of the literature.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative analysis of operation time and intraoperative fluoroscopy time in intramedullary and extramedullary fixation of trochanteric fractures
Milan Mitkovic, Sasa Milenkovic, Ivan Micic, Predrag Stojiljkovic, Igor Kostic, Milorad Mitkovic
Vojnosanitetski pregled.2022; 79(2): 177. CrossRef - Pre-operative planning for fracture fixation using locking plates: device configuration and other considerations
Alisdair R. MacLeod, Pankaj Pankaj
Injury.2018; 49: S12. CrossRef - Letter: Repeated Metal Breakage in a Femoral Shaft Fracture with Lateral Bowing - A Case Report -
Hae Seok Koh
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2012; 25(3): 240. CrossRef
- Comparative analysis of operation time and intraoperative fluoroscopy time in intramedullary and extramedullary fixation of trochanteric fractures
- 368 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Crossref

Original Articles
- Surgical Treatment Using a Transolecranon Approach with a Dual Locking Plate for Unstable Intercondylar Fractures of the Humerus
- Ji Kang Park, Yong Min Kim, Dong Soo Kim, Eui Sung Choi, Hyun Chul Shon, Kyoung Jin Park, Byung Ki Cho
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(2):129-135. Published online April 30, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.2.129
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the clinical outcomes of operative treatment using a transolecranon approach with a dual locking plate for unstable intercondylar fractures of the distal humerus.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Eighteen patients were followed for more than 1 year after surgical treatment for unstable intercondylar fractures of the humerus. Anterior transpositioning of the ulnar nerve and an early rehabilitation program to allow range of motion (ROM) exercise from postoperative week 1 were used for all cases. The clinical and functional evaluation was performed according to the Mayo Elbow Performance Index and Cassebaum's classification of ROM.
RESULTS
The range of elbow joint motion was a flexion contracture mean of 12.8 degrees to a further flexion mean of 119.3 degrees at the final follow-up. The Mayo Elbow Performance Index was an average of 88.5 points. Among the results, 6 were excellent, 9 good, 2 fair, and 1 poor. Therefore, 15 cases (83.3%) achieved satisfactory results. Fourteen cases (77.7%) achieved a satisfactory ROM according to Cassebaum's classification. All cases achieved bone union, and the interval to union was an average of 14.2 weeks.
CONCLUSION
Dual locking plate fixation through the transolecranon approach seems to be one of the effective treatment methods for unstable intercondylar fractures of the humerus because it enables the anatomical reduction and rigid fixation of articulation, and early rehabilitation exercise.
- 467 View
- 6 Download

- Arthroscopic Treatment of Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation Using TightRope(R): Preliminary Report
- Eui Sung Choi, Kyoung Jin Park, Yong Min Kim, Dong Soo Kim, Hyun Chul Shon, Byung Ki Cho, Ji Kang Park, Hyun Chul Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2010;23(3):310-316. Published online July 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.3.310
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the clinical and radiologic results of the arthroscopic treatment using TightRope(R) (Arthrex, Inc, Naples, FL) for management of acute acromioclavicular dislocation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twelve patients with acromioclavicular joint dislocation Rockwood type V are underwent the arthroscopic acromioclavicular joint reconstruction using TightRope(R) between March, 2008 and March, 2009. The average age was 40.4 years (range 25~63 years) and mean follow-up was 10 months (range 8~16 months). The shoulders were evaluated using parameters include radiologic measurements by comparing the clavicle posteroanterior and lateral radiographs with the contralateral one. Clinical evaluation was made for pain, function, and range of joint motion by Constant score and KSS (Korean Shoulder Score).
RESULTS
All twelve patients returned to their work without pain in 3 months after operation. The average Constant score and KSS score was 98.4 (range 97~100) and 97.8 (range 97~100) at the last follow-up. Because of technical error and indication error, two patients showed failures of TightRope(R) fixation on the coracoid side and the acromioclavicular joint was redislocated, so these cases were excluded. 10 patients were satisfied with functional results and cosmetic appearance.
CONCLUSION
Considering its less morbidity, less hospitalization, excellent cosmesis, early rehabilitation, this new technique offers an attractive alternative in acromioclavicular joint stabilization if the early technical error would be overcome. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Coracoclavicular Ligament Augmentation Using Tight-Rope®for Acute Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation - Preliminary Report -
Seok Hyun Kweon, Sang Su Choi, Seong In Lee, Jeong Woo Kim, Kwang Mee Kim
The Journal of the Korean Shoulder and Elbow Society.2013; 16(2): 115. CrossRef - Coracoclavicular Ligament Augmentation Using Endobutton for Unstable Distal Clavicle Fractures - Preliminary Report -
Chul-Hyun Cho, Gu-Hee Jung, Hong-Kwan Sin, Young-Kuk Lee, Jin-Hyun Park
The Journal of the Korean Shoulder and Elbow Society.2011; 14(1): 1. CrossRef
- Coracoclavicular Ligament Augmentation Using Tight-Rope®for Acute Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation - Preliminary Report -
- 412 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The Usefulness of Hip to Thigh Ratio as an Anthropometric Indicator for the Incidence of Hip Fracture
- Jin Park, Kyu Hyun Yang, Seong Hwan Moon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(1):1-5. Published online January 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To compare anthropometric indicators around the hip between osteoporotic fracture group and control group.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty patients for osteoporotic hip fracture and the same number of patients for spine fracture who admitted our institute from November 2006 to March 2007 were matched with control patients without osteoporotic fracture. The waist circumference (WC), hip circumference (HC), thigh circumference (TC), and height were measured. From these measurements, waist to hip ratio (WHR), waist to thigh ratio (WTR), hip to thigh ratio (HTR), waist to height ratio (WHtR), hip to height ratio (HHtR), and thigh to height ratio (THtR) were calculated. All these indicators were compared between hip fracture and control group, and between spine fracture and control group.
RESULTS
Comparison between spine fracture and control group showed that the WC, WHR, WHtR were statistically significant, but all indicators failed to show accuracy in the ROC analysis. Comparison between hip fracture and control group demonstrated the TC, WTR, HTR, WHtR, HHtR, THtR were statistically significant. However, only the HTR showed fair accuracy in the ROC analysis. The area under the curve (AUC) of the HTR was 0.75 (95% confidence interval, 0.62 to 0.87) (p=0.001).
CONCLUSION
The HTR was fairly accurate in predicting the incidence of hip fracture compared with any other anthropometric indicators. Therefore, we can consider that the HTR has clinical usefulness.
- 390 View
- 0 Download

- Comparison between Results of Internal Fixation and Hemiarthroplasty in Unstable Intertrochanter Fracture of Osteoporotic Bone
- Haw Jae Jung, Jae Yeol Choi, Hun Kyu Shin, Eugene Kim, Se Jin Park, Yong Taek Lee, Gwang Sin Kim, Jong Min Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(4):291-296. Published online October 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.4.291
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To perform comparative analysis between the results of internal fixation and hemiarthroplasty in unstable intertrochanteric fracture of osteoporotic bone.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From February 2003 to February 2006, 36 patients treated surgically for unstable intertrochanteric fractures were evaluated. The patient's age was older than 70 year old; the T-score of preoperative bone mineral density (BMD) was lower than -3.0; they were followed up for more than 1 year. The patient were divided into two groups. One group was treated with dynamic hip screw or proximal femoral nail (Group A, 23 cases), and the other group was treated with bipolar hemiarthroplasty (Group B, 13 cases). The two groups were compared in terms of hip joint function using Clawson classification and radiologically.
RESULTS
Nonunion and fixation failure happened in 6 cases (26%) of gruop A. However, all patients in group B showed stable maintenance of implant. Recovery of hip joint function was found in 13 cases (43%) of group A, whereas 12 cases (93%) of group B recovered.
CONCLUSION
Nonunion and failure of fixation happened more frequently in internal fixation than bipolar hemiarthroplasty, and the postoperative hip joint function was better in bipolar hemiarthroplasty than internal fixation. Therefore, bipolar hemiarthroplasty might be better operative treatment for unstable intertrochanteric fracture of osteoporotic bone. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Stability Score of the Intramedullary Nailed Intertrochanteric Fractures: Stability of Nailed Fracture and Postoperative Patient Mobilization
Sung-Rak Lee, Seong-Tae Kim, Min Geun Yoon, Myung-Sang Moon, Jee-Hyun Heo
Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery.2013; 5(1): 10. CrossRef - Analysis of the Factors Involved in Failed Fixation in Elderly Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture
Joon Soon Kang, Ryuh Sup Kim, Bom Soo Kim, Young Tae Kim, Seung Hyun Hong
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2012; 25(4): 263. CrossRef - Results of Osteoporotic Treatment Drug after Periarticular Fracture of Hip
Soo Jae Yim, Young Koo Lee, Cheong Kwan Kim, Hyun Seok Song, Hee Kyung Kang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(2): 167. CrossRef
- The Stability Score of the Intramedullary Nailed Intertrochanteric Fractures: Stability of Nailed Fracture and Postoperative Patient Mobilization
- 556 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Comparison of the Surgical Treatment Results of Avulsion Fracture of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament between Children and Adults
- Eun Kyoo Song, Sang Jin Park, Keun Bae Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(2):196-201. Published online April 30, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.2.196
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To compare the clinical and radiological results after surgical treatments of the avulsion fractures of ACL between children and adults.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
40 cases (18 cases of children, 22 cases of adults), who underwent surgical treatments after avulsion fractures of the ACL and followed up more than one year, were enrolled. Fractures were classified by modified Meyers & McKeever criteria. Range of motion, LK score, Lachman test, Pivot-Shift test, quadriceps muscle atropy and Telos® stress arthrometer were compared.
RESULTS
The types of fracture in children were categorized into 8 cases of type II, 10 cases of type III, and 2, 15, 5 cases of type II, III, IV each in adult group. Mean LK score showed significant difference between 99.3 points in children and 89.5 points in adults (p<0.05). In addition, accompanied injuries and the high degree of fracture leaded low LK score. However, there was no significant difference in range of motion, Lachman test and Pivot-Shift test. Anterior laxity by Telos® device showed an average of 2.0 mm in children, 2.5 mm in adults (p>0.05).
CONCLUSION
Children group showed better treatment results of avulsion fracture of ACL. Higher incidence of type II fractures and less combined injuries considered to be factors for better results.
- 295 View
- 0 Download

Case Report
- Simultaneous Dorsal Dislocation of Interphalangeal Joints in the Same Finger: Two Case Report
- Hyun Seok Song, Suk Ku Han, Sung Jin Park, Won Sik Nam, Hyuk Jae Yang, Nam Yong Choi
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(3):388-391. Published online July 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.3.388
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- We treated 2 cases of simultaneous dorsal dislocation of interphalangeal joints in the 5th finger. One case was injured by herperextension during basketball, and treated by open reduction and K-wire fixation. Another case was injured by industrial accident, and treated by splint for 1 week.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Double Dislocation of Interphalangeal Joints in a Single Digit - A Case Report -
Jai Hyung Park, Jeong Hyun Yoo, Joo Hak Kim, In Hyeok Lee
Journal of the Korean Society for Surgery of the Hand.2012; 17(4): 196. CrossRef
- Double Dislocation of Interphalangeal Joints in a Single Digit - A Case Report -
- 341 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Article
- Comparison of Open Fixation and Closed Percutaneous Pinning in Jakob Stage II Lateral Condylar Fractures of Children
- Eui Sung Choi, Dong Soo Kim, Hyun Chul Shon, Yong Min Kim, Kyoung Jin Park, Jun Mo Jeon, Gee Kang Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(2):277-282. Published online April 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.2.277
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare the results of open fixation and closed percutaneous pinning in managing Jakob stage II lateral condylar fractures of children's elbow.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Since Febuary 2000, We operated 21 children with Jakob stage II lateral condylar fractures of elbow. Eleven of the 21 were treated with closed percutaneous pinning, open fixation was done to the other 10 children. Each patient was evaluated about range of motion, carrying angle, scar satisfaction and radiologic findings for comparison between closed pinning and open fixation groups.
RESULTS
Open fixation group showed 3.8 degrees decrease of elbow motion while closed pinning group showed no significant decrease. Carrying angle and radiologic findings were not different between the two groups. Open fixation group expressed dissatisfaction to their scars (average 5.2 cm) whereas all the patients of closed pinning group were satisfied with their functional and cosmetic outcomes.
CONCLUSION
In managing Jakob stage II lateral condyle fractures of children's elbow, closed percutaneous pinning was thought to be superior to open fixation because of the same functional outcome and much better cosmetic results.
- 241 View
- 0 Download

Case Report
- Neglected Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation in a Crutch-walking Patient: A Case Report
- Yong Min Kim, Hyun Chul Shon, Dong Soo Kim, Eui Sung Choi, Kyung Jin Park, Se Hyuk Im
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(4):474-477. Published online October 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.4.474
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Traumatic posterior hip dislocation should be reduced emergently, but diagnosis could be delayed in a patient with head trauma or in developing countries. We have experienced neglected posterior hip dislocation for three months in a crutch-walking patient who had ipsilateral tibia fracture and alert mentality. Open reduction followed by six-weeks skeletal traction was performed. At one year follow-up, the reduced hip showed good range of motion with no evidence of avascular necrosis.
- 327 View
- 1 Download

Original Article
- Intramedullary Fixation in the Fracture of the Shaft of the Clavicle by Threaded Kirschner Wire
- Jae Kwang Yum, Se Jin Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(2):89-92. Published online April 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.2.89
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate and report the clinical result of the intramedullary fixation by threaded Kirschner wire in the clavicle shaft fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From May 2000 to April 2004, twenty patients who had the fracture of the shaft of the clavicle were treated by the intramedullary fixation with threaded Kirschner wire. Thirteen patients were followed up and the clinical and radiological results were analyzed.
RESULTS
All of the cases had satisfactory fracture union but there were four cases of skin irritation signs by the tip of threaded Kirschner wire. In one case, the Kirschner wire was bent at the fracture site with malunion. According to the clinical scoring system of Kang et al, eight cases were excellent and five cases were good.
CONCLUSION
Authors think that intramedullary fixation with threaded Kirschner wire in the fracture of the shaft of the clavicle is one of a good operative method because of small operative incision, easy operative method, satisfactory fracture union and easy removability of the implant.
- 251 View
- 2 Download

Case Report
- Fat Embolism in a Patient with Multiple Fractures of Cancellous Bones: A Case Report
- Eui Sung Choi, Yong Min Kim, Dong Soo Kim, Hyun Chul Shon, Kyung Jin Park, Jun Mo Jeon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(2):202-204. Published online April 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.2.202
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fat embolism is a rare complication of multiple long bone fracture or extensive soft tissue injury. The pathogenesis of fat embolism has been poorly understood and definite pathogenesis and treatment were not fully established. Respiratory failure associated with fat embolism is a major cause of death, but is usually self-limited, and is responsive to intensive treatment. We have experienced fat embolism in cancellous bone fracture which occurred in spine, distal radius and talus. Patient's fractures were treated with conservative management. The patient was recovered from fat embolism with supportive treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A case of fat embolism syndrome in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis patient
Kyung Hoon Kim, Ju Kyung Lee, Young Hun Choi, Woo Sun Kim, June Dong Park, Young Yull Koh, Dong In Suh
Allergy Asthma & Respiratory Disease.2013; 1(1): 94. CrossRef
- A case of fat embolism syndrome in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis patient
- 381 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Article
- Differences of Fracture Types and Associated Injuries in Thoracolumbar Fractures Caused by Fall from Height and by In-Car Accident
- Eui Sung Choi, Yong Min Kim, Dong Soo Kim, Kyung Jin Park, Kyeong Il Jeong, Yoon Moo Hur, Young Chan Cha, Jun Mo Jeon, Jong Won VKang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(2):176-180. Published online April 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.2.176
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the differences of associated factors in thoracolumbar fractures according to the mechanism of injury, level and type of the fracture, associated injuries were investigated for comparison between injuries by fall from height and by in-car accident injury.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Medical records and X-ray findings of 249 patients with fractures of thoracolumbar spine were reviewed retrospectively. Among them, 169 patients were injured by the two main causes. McAfee classification was adopted to determine the type of fracture. Associated injuries were classified as head and neck, chest and abdomen, pelvis, proximal and distal extremity, and neurologic deficit. Statistical analysis using Chi-square method was used for comparison between the two groups.
RESULTS
In overall patients, the most common cause of thoracolumbar fracture was fall from height (44.6%) followed by in-car accident (23.3%) and fall down (16.9%). In fall-from height gruoup, burst fracture was the most common (44.1%) while flexion-distraction injury was the most popular (39.7%) in in-car accident group (p=0.05). Comparison according to height of fall showed significant increase of multiple fractures (p=0.0326). Associated injuries of distal lower and upper extremities and pelvis were common in fall-from-height group, while injuries of head and neck, proximal part of upper extremity, chest and abdomen were common in in-car accident patients.
CONCLUSION
Type of fracture and distribution of associated injuries were significantly different between the two main causes of thoracolumbar injury, which seemed to be useful for understanding the mechanical events of injury and detecting associated injuries in each victim. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Injury Severity and Patterns of Accompanying Injury in Spinal Fracture
Hun Park, Kyung-Jin Song, Kwang-Bok Lee, Joo-Hyun Sim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2012; 25(3): 203. CrossRef - Differences in Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures by Falls from Height with Associated Foot and Ankle Fractures
Chung-Shik Shin, Eea-Sub Chung, Chang-Eon Yu, Byeong-Yeol Choi
Journal of Korean Society of Spine Surgery.2012; 19(2): 47. CrossRef
- Injury Severity and Patterns of Accompanying Injury in Spinal Fracture
- 460 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Crossref

Case Report
- Snapping Metacarpo-Phalangeal Joint after Depressed Fracture of Metacarpal Neck: Case Report
- Hyun Seok Song, Nam Yong Choi, Sung Jin Park, Suk Ku Han, Ki Ho Nah, Sang Il Seo, Do Sung Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(4):359-361. Published online October 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.4.359
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We report one case of snapping metacarpo-phalangeal joint after depressed fracture of metacarpal neck which could be diagnosed by exploration for the snapping during extension in spite of conservative treatments.
- 210 View
- 0 Download

Original Articles
- Bone & Soft Tissue Injuries Diagnosed by Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Thoracolumbar Fractures
- Yong Min Kim, Dong Soo Kim, Eui Seong Choi, Hyun Chul Shon, Kyoung Jin Park, Gi Seok Han, Jae Jung Jeong, Kyoung Il Jeong, Yung Sung Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(2):184-190. Published online April 30, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.2.184
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To assess diagnostic efficacy of the MRI in thoracolumbar fractures, especially in changes of bone and soft tissue which cannot be documented by other diagnostic tools.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Among 85 patients managed for thoracolumbar fractures between January 1997 and June 2003, MRI was performed in 30 patients to get more informations. Plain X-ray, CT and MRI of these cases were reviewed retrospectively by two orthopaedic spine surgeons and one radiologist to investigate the informations which only MRI could afford.
RESULTS
14 (46.7%) among 30 patients had occult fractures of vertebrae other than main fracture which had not been diagnosed as fractured. Besides 6 patients who showed distraction of posterior structure on plain X-ray, injury of posterior ligament complex was confirmed by MRI in 12(40%) patients. Additionally, MRI visualized other soft tissue injuries such as intramuscular and subcutaneous hematoma, changes of the spinal cord and intervertebral disc. In 16 among 30 patients, informations achieved from MRI were the most important factors in deciding treatment modality.
CONCLUSION
MRI seems to be efficient in visualizing not only soft tissue injury such as ligament but also occult fractures of additional vertebra in thoracolumbar fractures, therefore MRI seems to be an important diagnostic tool in decision of treatment modalities, especially in cases of uncertain stability. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Measurement Discrepancy of Sagittal Parameters between Plain Radiography and 3D Computed Tomography in Thoracolumbar and Lumbar Fractures
Dong-Soo Kim, Yong-Min Kim, Eui-Sung Choi, Hyun-Chul Shon, Kyoung-Jin Park, Byung-Ki Cho, Ji-Kang Park, Hyun-Cheol Lee
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2012; 47(3): 198. CrossRef - Relationship between Lamina Fractures and Dural Tear in Low Lumbar Burst Fractures
Ki-Chan An, Dae Hyun Park, Yong-Wook Kwon
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(3): 256. CrossRef
- Measurement Discrepancy of Sagittal Parameters between Plain Radiography and 3D Computed Tomography in Thoracolumbar and Lumbar Fractures
- 465 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Avulsion Fracture of Calcaneus in Diabetic Patients
- Sung Jin Park, Nam Yong Choi, In Tak Chu, Suk Ku Han, Ki Ho Nah, Hyun Seok Song, Jung Ho Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(2):173-176. Published online April 30, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.2.173
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Avulsion fracture of the calcaneal tuberosity is an uncommon injury. Usually it occurs from indirect trauma, and can be seen in old patients with osteoporosis or in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Follow-up studies showed fracture healing in most cases, but skeletal deformity may develop in some cases. Therefore we should do plain X-ray evaluations in diabetic patients with foot and ankle pain, even though there have been no definite trauma history. Four cases of calcaneus avulsion fracture were treated operatively in diabetic patients, and reported.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Avulsion Fracture of Calcaneal Apophysis in an Adolescent Gymnast : A Case Report
Youn Moo Heo, Whan Young Chung, Sang Bum Kim, Cheol Yong Park, Jin Woong Yi
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(4): 288. CrossRef
- Avulsion Fracture of Calcaneal Apophysis in an Adolescent Gymnast : A Case Report
- 374 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Treatment of Infected Nonunion of Long Bone Shaft: Comparison between Fixation by Antibiotic-cement Loaded Intramedullary Nailing and Fixation by Antibiotic-cement Loaded External Monofixator
- Ki Ho Nah, Seong Jin Park, Suk Ku Han, Hyun Suk Song, Nam Yong Choi
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(4):511-518. Published online October 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.4.511
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the surgical results between fixations by antibiotic-cement loaded intramedullary nailing and antibiotic-cement loaded external monofixator in the treatment of infected nonunion of long bone shaft with mild bone loss and shortening of less than 1 cm.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Among the 15 cases of infected nonunion of long bone shaft, 6 cases treated with fixation by antibiotic-cement coated intramedullary nailing and 3 cases treated with fixation by intramedullary nailing along with antibiotic-cement beads insertion were divided as group I (n=9), and other 6 cases treated with fixation by external monofixator along with antibiotic-cement beads insertion were divided as group II (n=6). There was no difference between the two groups in the degree of infection in the laboratory data and clinical feature and degree of bone loss and shortening. Male was in 7 and 5 patients, average age of the patients was 34.8 (26~53) and 37.2 (20~63) years old and average follow-up period was 15.9 (12~35) and 19.3 (15~41) months in group I and II respectively.
RESULTS
Among the nine cases of group I, 3 cases were newly convereted into fixation by antibiotic-cement coated intramedullary nailing at average 9.5 weeks. Radiologic union was gained at the average of 26 weeks from the time of initial nail fixation. Infection was responsive at 6.1 weeks by laboratoey data. Knee ROM of more than 100 degrees was gained in all case and average shortening was 9.2 mm in the last follow-up. And external rotation deformity of more than 5 degrees was noted in 1 case. Among the six cases of group II, radiologic union was gained at 14 weeks in 1 case without converting to internal fixation, and the other 5 cases were converted to antibiotic cement loaded intramedullary nailing at average 12.5 weeks because of delayed uinon or angulation deformity, and radiologic union was gained at average 44 weeks from the time of fixation by external fixator. Infection was responsive at 10.2 weeks by laboratoey data. Knee ROM of more than 100degrees was gained in 5 cases, and average shortening was 11.8 mm in the last follow-up.
CONCLUSION
In the treatment of infected nonunion of long bone shaft with mild bone loss and shortening of less than 1 cm, the fixation by intramedullary nailing with the use of antibiotic-cement prefers to the fixation by external monofixator with the use of antibiotic-cement in the velocity of union, control of infection, and in the clinical aspects such as alignment, early ambulation and joint stiffness.
- 277 View
- 0 Download

- Differential diagnosis and its treatment of gas forming infections
- Soo Bong Hahn, Ho Jung Kang, Jin Park
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(4):607-613. Published online October 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.4.607
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To establish the guidelines for the differential diagnosis and proper initial treatment of the gas forming infections through the review of literature and our clinical experiences.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The radiological findings, clinical course, gram stain, bacterial culture, predisposing factors and treatment of four cases of gas forming infections from January 1994 to August 2001, were retrospectively analyzed.
RESULTS
Three cases diagnosed presumptively as gas gangrene were improved through amputation or disarticulation and intravenous antibiotics. One case diagnosed presumptively as non-clostridial infection was expired due to sepsis in spite of incision, drainage and intravenous antibiotics. In the bacterial culture, two cases were non-clostridial infection, one case was not able to diagnose and one case was clostridial myonecrosis(gas gangrene) CONCLUSION: The gas forming infections are rare but life-threatening. When the proper initial treatment is delayed, the fatal complications may result. So, the presumptive diagnosis through gram stain, clinical course, radiological findings should be made as soon as possible, and according to which, the appropriate initial treatment, such as, surgical debridement, amputation, intravenous antibiotics must be started. The following treatments should be corrected by definitive diagnosis through the bacterial culture. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Salmonella gas-forming pyomyositis in an immunocompetent patient: a case report and review
Jee Young Lee, Gyu Min Kong
Journal of International Medical Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Type I, II Acute Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Low Extremity
Sang-Jun Song, In Seok Lee, Ju Hwan Chung
The Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2007; 42(5): 636. CrossRef
- Salmonella gas-forming pyomyositis in an immunocompetent patient: a case report and review
- 353 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Treatment of Distal Clavicle Fractures with Coracoclavicular ligament Injury
- Nam Yong Choi, Suk Ku Han, Seong Jin Park, Ki Ho Na, Young Hun Kim, Hyun Seok Somg, Yong Jin Kwon
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(1):21-27. Published online January 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.1.21
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the radiological and clinical results of the treatment of distal clavicular fractures with coracoclavicular ligament injury by coracoclavicular fixation with plating or repair of coracoclavicular ligament.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sixteen cases with minimum six months of follow-up were included in our study. Male was twelve and average age was 43(28-80). Ten cases of Craig type 2 were treated with coracoclavicular screw fixation with plating. Six cases of Craig type 5 were treated with coracoclavicular screw fixation with repair of coracoclavicular ligament. The radiologic assessment including coracoclavicular distance and union time and the clinical assessment including range of motion and degree of pain were evaluated.
RESULTS
Fifteen cases were united, but one case developed osteomyelitis and nonunion. Full range of motion was achieved in fifteen cases at last follow-up. Average coraco- clavicular distance compared to contralateral site in AP view was 2.1 mm increase in patients with plate fixation and 1.3 mm increase in patients with ligament repair. Average union time was 14.3 weeks and little differenece was noted between two groups(P>0.05).
CONCLUSION
Coracoclavicular screw fixation with plating or repair of coracoclavicular ligament were a useful method to treat distal clavicular fractures combined with coracoclavicular ligament injury.
- 284 View
- 2 Download

- Retrograde Flexible Intramedullary Nailing of Pediatric Femur Fractures
- Chang Wug Oh, Byung Chul Park, Hyung Jin Park
- J Korean Soc Fract 2001;14(2):272-277. Published online April 30, 2001
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2001.14.2.272
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study was designed to evaluate the clinical effectiveness including bone union, leg length discrepancy, after retrograde flexible intramedullary nailing for pediatric femoral fractures. MATERIAL AND METHOD: Nineteen cases (18 patients) with femur fracture at the age of 4 to 10 years (mean age 6.7) have been followed up over the minimum of one year. Under imaging intensifier, the fracture was temporarily reduced with manual traction, and 1 or 2 flexible nails were inserted at medial and lateral side of distal femur above the distal epiphysis. After two weeks of immobilization with long leg splint, joint motion was permitted. At 6-8 weeks, partial weight bearing was permitted, and at 10- 12 weeks, full weight bearing was permitted.
RESULTS
Time to radiologic union averaged 10.9 weeks. Limb length discrepancy ranged from 7mm of shortening to 6mm of overgrowth(mean ; 1.1mm of overgrowth), but there was no severe limb length discrepancy over 10mm. As another complications, there were one case of limited motion of knee joint and one case of broken nail.
CONCLUSION
We found that retrograde flexible intramedullary nailing is a safe, effective treatment for acute femoral shaft fractures in skeletally immature patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Treatment of Femoral Shaft Fracture with Interlocking Humeral Nail in Older Children and Adolescent
Kun-Bo Park, Hoon Park, Hyun-Woo Kim, Hui-Wan Park, Jae Young Roh
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(2): 206. CrossRef
- Treatment of Femoral Shaft Fracture with Interlocking Humeral Nail in Older Children and Adolescent
- 411 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Occult Fractures of the Subtalar Joint
- Chong Hyuk Choi, Seong Jin Park, DJ Ogilvie Harris
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(4):935-940. Published online October 31, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.4.935
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of the current study was to investigate the results of occult fractures in the subtalar joint which were detected in delay and to find out a way of early detection. The occult osteochondral fractures of the subtalar joint are known to be associated with dislocation and to have a poor prognosis. We treated ten patients who had the occult fractures that were not associated with dislocation. Nine fractures involved posterior facet with a displaced osteochondral fracture. Seven patients lost motion in the subtalar joint completely, and arthrodesis were performed. Three subtalar joints retained some motion and were treated with physiotherapy, which improved the movement and pain. The early detection of fracture was important for the prognosis. We note the "early warning"signs of the patients who have massive swelling without definite bone injury, and who had a failure to regain the subtalar motion after immobilization. The subtalar joint should be imaged with CT or MRI. At first, aggressive physiotherapy should be considered. Arthrodesis should be considered as a final option.
- 187 View
- 0 Download

- Morbidity and Mortality of Bilateral Hip Fractures in Elderly Patients
- Suk Ku Han, Nam Yong Choi, Seong Jin Park, Seong Keun Lee, Chan Woong Moon
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(4):788-794. Published online October 31, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.4.788
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to estimate the morbidity and mortality rate of bilateral hip fractures in elderly patients compared to that in unilateral hip fractures and to evaluate it's related risk factors.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty-two cases of bilateral hip fractures in patients who were older than 70 years with at least two year follow-up were included in our study. We analysed the risk factors of bilateral hip fractures by comparing with age, sex and diagnosis matched 22 cases of ipsilateral hip fractures including onset of secondary fracture, injury mechanism and the rate of morbidity and mortality, respectively.
RESULTS
The onset of secondary fracture and death were mostly within 1 year after operation for the first hip fracture. Comorbidity of cardiovascular, neurologic, urologic or history of previous fracture and decreased ambulation ability were related with the occurrence of bilateral hip fractures. The rate of morbidity and mortality of bilateral hip fractures were about two- fold than that of ipsilateral hip fractures. High mortality rate was noted in patients who had operation delay from injury. But no significant relationship between nutrition, body weight or bone mineral density and the development of secondary hip fractures.
CONCLUSION
To prevent the occurence of bilateral hip fractures which had more serious results than that of ipsilateral hip fractures, more aggressive rehabilitation to improve walking ability and appropriate environmental circumstances to avoid falls were important, especially in older patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessment of the Clinical Features of Bilateral Sequential Hip Fractures in the Elderly
Duk-Hwan Kho, Ju-Yong Shin, Hyeung-June Kim, Dong-Heon Kim
The Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2009; 44(3): 369. CrossRef
- Assessment of the Clinical Features of Bilateral Sequential Hip Fractures in the Elderly
- 450 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA

 First
First Prev
Prev


