Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Correction
- Author correction: “Comparison of outcomes of reinforced tension band wiring and precontoured plate and screw fixation in the management of Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures”
- Hyun Goo Kang, Tong Joo Lee, Samuel Jaeyoon Won
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):168-168. Published online July 22, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00059.e1
- Corrects: J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):96
- 201 View
- 10 Download

Original Articles
- Comparison of outcomes of reinforced tension band wiring and precontoured plate and screw fixation in the management of Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures
- Hyun Goo Kang, Tong Joo Lee, Samuel Jaeyoon Won
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):96-101. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00059
- Correction in: J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):168

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
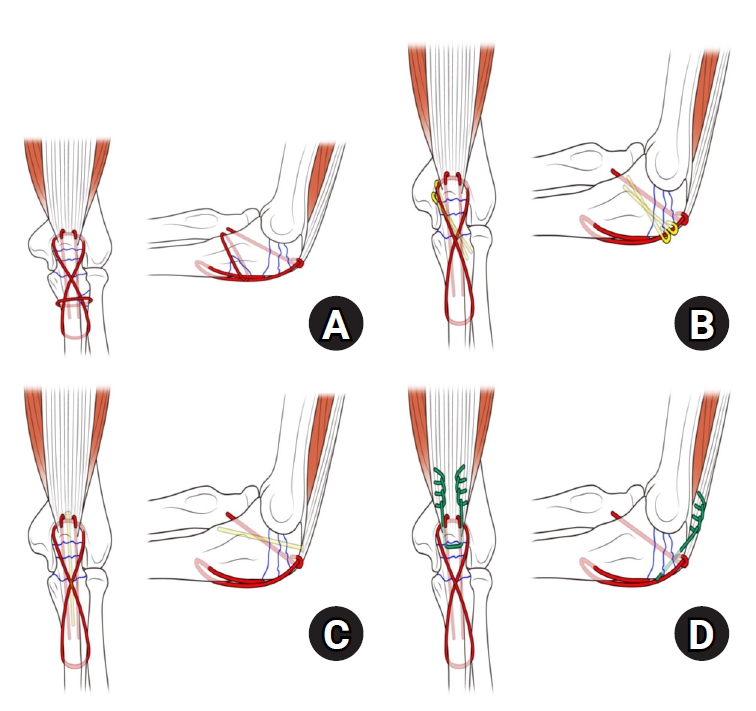
Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures are characterized by significant displacement and comminution, presenting a challenge in selecting the appropriate fixation technique. This study compared the clinical and radiographic outcomes, complications, and reoperation rates of reinforced tension band wiring (TBW) and precontoured plate and screw fixation (PF) in the surgical treatment of Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures.
Methods
This retrospective review analyzed 24 patients diagnosed with Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures, who were treated between 2005 and 2023. Of these, 11 patients underwent reinforced TBW, and 13 received precontoured PF. Clinical outcomes were assessed using Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH) scores and the Mayo Elbow Performance Score (MEPS). Radiographic outcomes focused on fracture union. Operative times, complication rates, and reoperation rates were compared between the groups.
Results
Both the reinforced TBW and PF groups achieved satisfactory clinical outcomes, with no significant between-group differences in DASH and MEPS scores (P>0.05). Radiographic union was achieved in all patients. The reinforced TBW group demonstrated a significantly shorter operative time than the PF group (93.6±7.4 min vs. 132.3±13.7 min; P<0.001). Complication rates were similar between the two groups (reinforced TBW, 38.4%; PF, 36.3%), but hardware-related irritation occurred more frequently in the reinforced TBW group. Reoperations were required in 15.8% of the reinforced TBW group due to hardware irritation, whereas no reoperations were necessary in the PF group.
Conclusions
Reinforced TBW and PF are both effective surgical options for managing Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures, yielding comparable clinical and radiographic outcomes. While reinforced TBW offers shorter operative times and lower costs, PF is associated with fewer hardware-related complications. Further prospective studies are needed to optimize treatment strategies for these complex fractures. Level of Evidence: Level III. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Are posterior olecranon locking plates a problem for patients after fracture healing because of prominence?
Reva Qiu, Mallika Makkar, Richard Buckley
Injury.2025; 56(11): 112769. CrossRef
- Are posterior olecranon locking plates a problem for patients after fracture healing because of prominence?
- 1,518 View
- 38 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Additional Hinged External Fixation in Complex Elbow Injury
- Tong Joo Lee, Taek Ho Hong, Nak Chul Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2015;28(3):169-177. Published online July 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.3.169
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the use of hinged external fixation in management of complex elbow injury.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed clinical outcomes in 10 patients with elbow dislocation and associated fractures of both the radial head and the coronoid process from January 2007 to December 2013. All ten patients were treated by hinged external fixation after open reduction and internal fixation. The indication for use of a hinged external fixator was persistent instability after fixation of the fractures. Early mobilization was started at 1 week (6.5 days) after surgery. The external fixator was removed at 6 weeks after surgery. Cassebaum classification and Mayo elbow performance score were used for clinical and functional evaluation. The follow-up period was at least 1 year.
RESULTS
At the last follow-up, the average further flexion was 127degrees, and the average flexion contracture was 16degrees. The average pronation was 83degrees and the average supination was 78degrees. By the Cassebaum classification after 1 year follow-up, patients were classified as 4 excellent, 4 good, and 2 poor. According to the Mayo elbow performance score, the average score was 87 points (65-100 points) with 3 excellent, 6 good, and 1 fair. Stability was restored in all patients at the last follow-up. There was no case of nonunion and the average union period was 11.5 weeks.
CONCLUSION
This study advocated the additional use of a hinged external fixator in the treatment of complex elbow instability, especially when fixation of fractures and repair of soft tissues were not sufficient. Providing adequate stability and allowing early motion, additional external fixation could improve the functional outcome.
- 317 View
- 1 Download

- A Retrospective Comparative Study of Internal Fixation with Reconstruction Plate Versus Anatomical Locking Compression Plate in Displaced Intercondylar Fractures of Humerus
- Tong Joo Lee, Young Tae Kim, Dae Gyu Kwon, Ju Yong Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(4):294-300. Published online October 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.4.294
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analyze the clinical result of a conventional reconstruction plate (CRP) fixation and locking compressive plate (LCP) fixation on the surgical treatment of an adult's displaced intercondylar fracture of humerus.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 40 patients enrolled in the study were treated between August 2002 and May 2012. Fixation with a CRP was performed in 20 patients (group A) and anatomical locking compression plate fixation was performed in 20 patients (group B). The clinical and functional evaluation was performed according to the Mayo elbow performance score and Cassebaum classification of elbow range of motion (ROM), disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand score.
RESULTS
The Mayo elbow functional evaluation scores, eight cases were excellent, 10 cases were good, and two cases were fair in group A, and 12 cases were excellent, seven cases good, and one case fair in group B; both groups showed satisfactory results. The durations of attaining 90 to 120 degrees of the ROM of joints postoperatively were 8.3 days on average (6 to 15 days) in group A and 5.5 days on average (5 to 9 days) in group B, demonstrating a significant difference between the two groups (p=0.04). Although the correlations of clinical results according to the difference of bone mineral densities (BMDs) were not statistically significant between the two groups (p=0.35), loss of fixation occurred due to loosening of screws in two patients with low BMDs in whose operations reconstruction plates were used.
CONCLUSION
The use of locking compressive plate on the surgical treatment of an diaplaced intercondylar fracture of humerus have a good clinical results because that permits early rehabilitation through good fixation and reduces the complications such as loosening of screws.
- 288 View
- 0 Download

- Result of Surgical Treatment for the Femoral Head Fracture
- Joon Soon Kang, Kyoung Ho Moon, Tong Joo Lee, Jong Hyuck Yang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(3):198-205. Published online July 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.3.198
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study analyzed the clinical and radiological long-term follow-up results of patients with femoral head fracture who received surgical treatments.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Retrospective evaluation was performed for 20 patients with femoral head fracture who received surgical treatments between December 1997 and May 2010. According to Pipkin's classification, there were five type I, six type II, one type III, and eight type IV fractures.
RESULTS
The average Merle d'Aubigne'-Postel score was 12.8 (12.80+/-3.53). According to surgical method, the score for the bony fragment excision group was 9.8 (9.83+/-2.79), and that for the open reduction and internal fixation group was 13.9 (13.92+/-3.07). Depending on Thompson-Epstein criteria, two patients were good, two were fair, and two were poor in the bony fragment excision group. Four patients were excellent, six were good, and three were poor in the open reduction and internal fixation group.
CONCLUSION
Bony fragment excision should be performed with caution in patients with femoral head fracture. Considering fragment size, location, and presence of acetabular fracture, better outcome can be expected using the open reduction and internal fixation method in comparison with excision.
- 416 View
- 2 Download

- Coracoclavicular Screw Fixation and Tension Band Wiring in Treatment of Distal Clavicle Fracture
- Dae Gyu Kwon, Tong Joo Lee, Kyung Ho Moon, Byoung Ki Shin, Min Su Woo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(1):1-7. Published online January 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to analyze the effectiveness of coracoclavicular screw fixation with tension band wiring in the treatment of displaced distal clavicle fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From October 2006 to December 2010, 18 patients with Neer type 2 displaced distal clavicle fracture were surgically treated. Fixation was performed, using coracoclavicular screw with tension band wiring. Radiographic and clinical evaluation was performed and the University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA) shoulder rating scale was employed for the assessment of shoulder joint function.
RESULTS
Osseous union was achieved approximately 9.5 weeks (8-11 weeks) in all patients. After the union, the screw and wire were removed under local anesthesia. All patients returned to the normal shoulder range of motion. Loosening of the screw was seen in two patients and breakage was seen in one patient. However, we could not observe the delayed union and complications, such as infection and refracture. All but one patient showed excellent results according to the UCLA shoulder score at one year after the operation.
CONCLUSION
Coracoclavicular screw fixation with tension band wiring in the treatment of displaced distal clavicle fractures is a clinically useful technique with good result and less complication.
- 401 View
- 1 Download

- Combined Anterolateral and Lateral Approaches in Treatment of Extra-articular Fracture of the Distal Humerus
- Dae Gyu Kwon, Kyoung Ho Moon, Suk In Na, Byung Ki Shin, Tong Joo Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(3):185-190. Published online July 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.3.185
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to analyze the clinical effectiveness of open reduction in the treatment of distal humeral fracture using a newly designed combined approach of anterolateral and lateral approaches to protect the radial nerve.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We investigated 24 consecutive cases of distal humeral fracture who received open reduction and internal fixation with a plate and screws with a minimum follow-up period of 1 year. We analyzed the patients' age, sex, fracture pattern, timing of the union, range of motion of the elbow joint, and complications. The Mayo elbow performance index (MEPI) was employed for the assessment of elbow joint function.
RESULTS
Clinical union was observed at 10.8 weeks (6~20 weeks) on average. Pre-operatively, there were 3 cases of incomplete radial nerve palsy. All of the cases recovered, and there was no additional radial nerve palsy due to surgery. According to the MEPI, 13 cases were "excellent" and 10 cases were "good" or better, comprising 95.83% of the cases. The range of motion at the elbow was 5.5 degrees (0~15 degrees) of extension, and 131.5 degrees (120~145 degrees) of flexion, suggesting no functional disability. The duration of return to work was 11.2 weeks (5~32 weeks) on average. There were no nonunion, malunion, or infection complications.
CONCLUSION
The combined anterolateral and lateral approach we designed is a clinically effective approach due to facilitation of protection of the radial nerve and attainment of adequate fixation space. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Posterior Dual Plating for Distal Shaft Fractures of the Humerus
Chul-Hyun Cho, Kwang-Yeung Jeong, Beom-Soo Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2017; 30(3): 117. CrossRef - Modified Combined Approach for Distal Humerus Shaft Fracture: Anterolateral and Lateral Bimodal Approach
Tong Joo Lee, Dae Gyu Kwon, Suk In Na, Seung Do Cha
Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery.2013; 5(3): 209. CrossRef
- Posterior Dual Plating for Distal Shaft Fractures of the Humerus
- 446 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

Case Report
- Osteochondral Autograft Using Head of Proximal Phalanx of Toe for Partial Osteochondral Defect of Proximal Interphalangeal Joint: A Case Report
- Tong Joo Lee, Kyung Ho Moon, Yoon Sang Jeon, Do Seung Kwon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2010;23(3):321-325. Published online July 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.3.321
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Osteochondral injury due to the trauma of the hand is relatively common. If the size of the osteochondral fracture fragment is large, open reduction and internal fixation are often feasible in treating these problems. However, arthroplasty using osteochondral graft is more preferred when the particle is small and articular surface is comminuted or fully defected. There are many reports of osteochondral graft using the costal osteochondral graft but the osteochondral graft using the interphalangeal joint of the toe is rarely reported. Thoroughly reviewed with relevant articles, this report presents a case of a 33 year old male who was successfully treated with osteochondral autograft using the proximal interphalangeal joint of the toe due to the traumatic osteochondral defect in the head of the second proximal phalanx.
- 260 View
- 2 Download

Original Articles
- Operative Treatment of Displaced Intercondylar Fracture of the Distal Humerus with Reconstruction Plate
- Ryuh Sup Kim, Tong Joo Lee, Kyoung Ho Moon, Seung Rim Park, Moon Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(2):172-177. Published online April 30, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.2.172
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the therapeutic effects of chevron olecranon osteotomy and bilateral reconstruction plate as operative treatment for distal humerus intercondylar fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Among patients operated for distal humerus intercondylar fracture in our hospital from June, 1997 to October, 2005, 26 patients were selected who could be followed-up for more than one year. The average follow-up period was 15 months. All olecranon osteotomies were chevron osteotomy and all fractures were treated with internal fixation using bilateral reconstruction plate. The ulnar nerve was checked in all cases. Three patients in which case the plate might irritate the ulnar nerve, received with ulnar nerve anterior transposition. Cassebaum's classification and Mayo elbow performance score were used to evaluate at three, six and twelve months.
RESULTS
Mean bone union period was 11.7 weeks. There were 9 excellent cases, 11 good cases, 4 fair cases and 2 poor cases. Mean flexion contracture was 11° and further flexion was 126° at last follow-up.
CONCLUSION
Bilateral reconstruction plate internal fixation using chevron olecranon osteotomy showed strong fixation and good clinical results and it is possible for early rehabilitation treatment.
- 302 View
- 1 Download

- Result of Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing for Humeral Shaft Fracture Evaluation of Post-operative Shoulder Function
- Seung Rim Park, Tong Joo Lee, Ryuh Sub Kim, Kyoung Ho Moon, Dong Seok You
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(2):166-171. Published online April 30, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.2.166
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the post-operative functional reduction of the shoulder joint and the impacting factors to post-operative shoulder joint function in interlocking IM nailing treatment of humeral shaft fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From April 1999 to August 2004, 35 patients (35 cases) whom admitted to hospital for humeral shaft fracture and treated using interlocking intramedullary nail were followed up for more than 1 year. 1 year post-operative shoulder joint function were evaluated using American Shoulder Elbow Surgery Scale (ASES). Pre-operative shoulder joint pain, radiologically degenerative change and extent of nail protrusion were evaluated, and each factor was correlated with function of the shoulder joint.
RESULTS
33 cases out of 35 cases showed union and average union period was 12 weeks. Complications consisted of 2 cases of nonunion, 1 case of infection, 1 case of loosening of distal fixing screw, 1 case of radial nerve palsy and 1 case of axillary nerve palsy. Shoulder joint function 3 months after operation : mean ASES score 78.2, 12 months after operation : mean ASES score 89.6. Pre-operative shoulder joint pain and nail protrusion showed to be statistically related to shoulder joint function.
CONCLUSION
If the operation leaves no protrusion of intramedullary nail, it can be concluded to be relatively safe and effective. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of the Result of the Intramedullary Nail Fixation and Plate Fixation in Humeral Shaft Fracture with Butterfly Fragments
Duk-Hwan Kho, Hyeung-June Kim, Byoung-Min Kim, Hyun-Ryong Hwang
The Korean Journal of Sports Medicine.2016; 34(2): 120. CrossRef - Plain Radiograph Analysis of the Distal Humerus Posterior Bowing That May Affect Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing for Humerus Shaft Fracture
Jaekwang Yum, Kyunghwan Boo, Minkyu Sung, Jiseok Jang
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2015; 50(1): 31. CrossRef - Clinical and Radiographical Follow-up for Residual Displacement of Fracture Fragments after Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing in Humeral Shaft Fractures
Jae-Kwang Yum, Dong-Ju Lim, Eui-Yub Jung, Su-Een Sohn
The Journal of the Korean Shoulder and Elbow Society.2013; 16(2): 107. CrossRef - Surgical Treatment of Pathologic Humeral Fracture
Ho Jung Kang, Byoung Yoon Hwang, Jae Jeong Lee, Kyu Ho Shin, Soo Bong Hahn, Sung Jae Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(2): 187. CrossRef
- Comparison of the Result of the Intramedullary Nail Fixation and Plate Fixation in Humeral Shaft Fracture with Butterfly Fragments
- 453 View
- 0 Download
- 4 Crossref


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


