Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 20(2); 2007 > Article
-
Original Article
- Result of Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing for Humeral Shaft Fracture Evaluation of Post-operative Shoulder Function
- Seung Rim Park, M.D., Tong Joo Lee, M.D., Ryuh Sub Kim, M.D., Kyoung Ho Moon, M.D., Dong Seok You, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2007;20(2):166-171.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.2.166
Published online: June 14, 2016
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Tong Joo Lee, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inha University College of Medicine, 253, Yonghyeon-dong, Nam-gu, Incheon 402-751, Korea. Tel: 82-32-890-3664, Fax: 82-32-890-3047, TJLEE@inha.ac.kr
Copyright © The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved
- 541 Views
- 0 Download
- 4 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- To evaluate the post-operative functional reduction of the shoulder joint and the impacting factors to post-operative shoulder joint function in interlocking IM nailing treatment of humeral shaft fracture.
-
Materials and Methods
- From April 1999 to August 2004, 35 patients (35 cases) whom admitted to hospital for humeral shaft fracture and treated using interlocking intramedullary nail were followed up for more than 1 year. 1 year post-operative shoulder joint function were evaluated using American Shoulder Elbow Surgery Scale (ASES). Pre-operative shoulder joint pain, radiologically degenerative change and extent of nail protrusion were evaluated, and each factor was correlated with function of the shoulder joint.
-
Results
- 33 cases out of 35 cases showed union and average union period was 12 weeks. Complications consisted of 2 cases of nonunion, 1 case of infection, 1 case of loosening of distal fixing screw, 1 case of radial nerve palsy and 1 case of axillary nerve palsy. Shoulder joint function 3 months after operation : mean ASES score 78.2, 12 months after operation : mean ASES score 89.6. Pre-operative shoulder joint pain and nail protrusion showed to be statistically related to shoulder joint function.
-
Conclusion
- If the operation leaves no protrusion of intramedullary nail, it can be concluded to be relatively safe and effective.
- 1. Bae SW, Kim WJ, Song BY, Choi NH, Lee JH. Postoperative functional assessments in adult humerus shaft fractures-comparison among plates and screws, intramedullary nail and external fixator. J Korean Soc Fract, 2001;14:228-235.Article
- 2. Bell MJ, Beauchamp CG, Kellam JK, McMurtry RY. The results of plating humeral shaft fractures in patients with multiple injuries. The Sunnybrook experience. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1985;67:293-296.ArticlePDF
- 3. Brumback RJ, Bosse MJ, Poka A, Burgess AR. Intramedullary stabilization of humeral shaft fractures in patients with multiple trauma. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1986;68:960-970.Article
- 4. Chapman JR, Henley MB, Agel J, Benca PJ. Randomized prospective study of humeral shaft fracture fixation: intramedullary nails versus plates. J Orthop Trauma, 2000;14:162-166.Article
- 5. Crates J, Whittle AP. Antegrade interlocking nailing of acute humeral shaft fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1998;350:40-50.Article
- 6. Habernek H, Orthner E. A locking nail for fractures of the humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1991;73:651-653.ArticlePDF
- 7. Hems TE, Bhullar TP. Interlocking nailing of humeral shaft fractures: the Oxford experience 1991 to 1994. Injury, 1996;27:485-489.
- 8. Hunter SG. The closed treatment of fractures of the humeral shaft. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1982;164:192-198.Article
- 9. Ikpeme JO. Intramedullary interlocking nailing for humeral fractures: experiences with the Russell-Taylor humeral nail. Injury, 1994;25:447-455.Article
- 10. Ingman AM, Waters DA. Locked intramedullary nailing of humeral shaft fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1994;76:23-29.
- 11. Matsen FA 3rd, Ziegler DW, DeBartolo SE. Patient self-assessment of health status and function in glenohumeral degenerative joint disease. J Shoulder Elbow Surg, 1995;4:345-351.
- 12. McCormack RG, Brien D, Buckley RE, Mckee MD, Powell J, Schemitsch EH. Fixation of fractures of the shaft of the humerus by dynamic compression plate or intramedullary nail. A prospective, randomized trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2000;82:336-339.
- 13. Modabber MR, Jupiter JB. Operative management of diaphyseal fracture of the humerus. Plate versus nail. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1998;347:93-104.
- 14. Richards RR, An KN, Bigliani LU, et al. A standardized method for the assessment of shoulder function. J Shoulder Elbow Surg, 1994;3:347-352.Article
- 15. Riemer BL, Butterfield SL, D'Ambrosia R, Kellam J. Seidel intramedullary nailing of humeral diaphyseal fractures: a preliminary report. Orthopedics, 1991;14:239-246.
- 16. Robert VG, John T, Frazier W. Open reduction and internal fixation of humeral shaft fractures. J Bone joint Surg Am, 1986;68:430-433.
- 17. Robinson CM, Bell KM, Court-Brown CM, McQueen MM. Locked nailing of humeral shaft fractures. Experience in Edinburgh over a two-year period. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1992;74:558-562.
- 18. Rommens PM, Verbruggen J, Broos PL. Retrograde locked nailing of humeral shaft fractures. A review of 39 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1995;77:84-89.
- 19. Rupp RE, Chrissos Mg, Ebraheim NA. The risk of neurovascular injury with distal locking screws of humeral intramedullary nails. Orthopedics, 1996;19:593-595.
- 20. Shin HD, Rhee KJ, Kim KC, Song HS. Operative treatment of traumatic humeral shaft fracture. Comparision of interlocking IM nailing and plate fixation by posterior approach. J Korean Fract Soc, 2005;18:93-99.
- 21. Stern PJ, Mattingly DA, Pomeroy DL, Zenni EJ Jr, Kreig JK. Intramedullary fixation of humeral shaft fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1984;66:639-646.
- 22. Varley GW, Radford P. Locked intramedullary nailing of the humerus The Nottingham experience of the seidel nail. J Bone Joint Surg Br, Suppl I. 1993;75:34-39.
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Comparison of the Result of the Intramedullary Nail Fixation and Plate Fixation in Humeral Shaft Fracture with Butterfly Fragments
Duk-Hwan Kho, Hyeung-June Kim, Byoung-Min Kim, Hyun-Ryong Hwang
The Korean Journal of Sports Medicine.2016; 34(2): 120. CrossRef - Plain Radiograph Analysis of the Distal Humerus Posterior Bowing That May Affect Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing for Humerus Shaft Fracture
Jaekwang Yum, Kyunghwan Boo, Minkyu Sung, Jiseok Jang
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2015; 50(1): 31. CrossRef - Clinical and Radiographical Follow-up for Residual Displacement of Fracture Fragments after Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing in Humeral Shaft Fractures
Jae-Kwang Yum, Dong-Ju Lim, Eui-Yub Jung, Su-Een Sohn
The Journal of the Korean Shoulder and Elbow Society.2013; 16(2): 107. CrossRef - Surgical Treatment of Pathologic Humeral Fracture
Ho Jung Kang, Byoung Yoon Hwang, Jae Jeong Lee, Kyu Ho Shin, Soo Bong Hahn, Sung Jae Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(2): 187. CrossRef
Result of Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing for Humeral Shaft Fracture Evaluation of Post-operative Shoulder Function
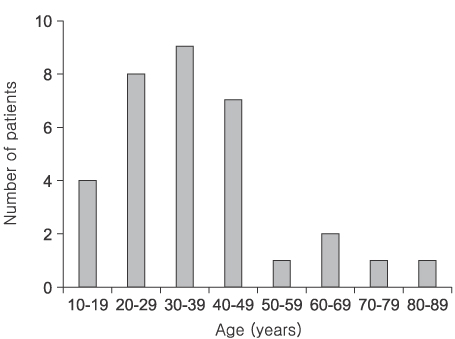
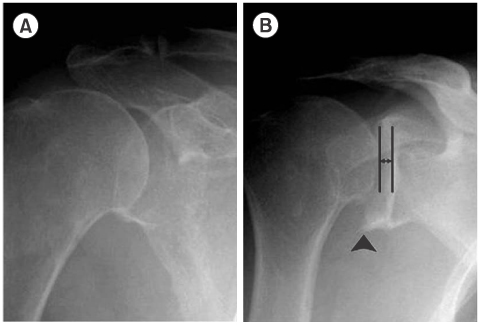
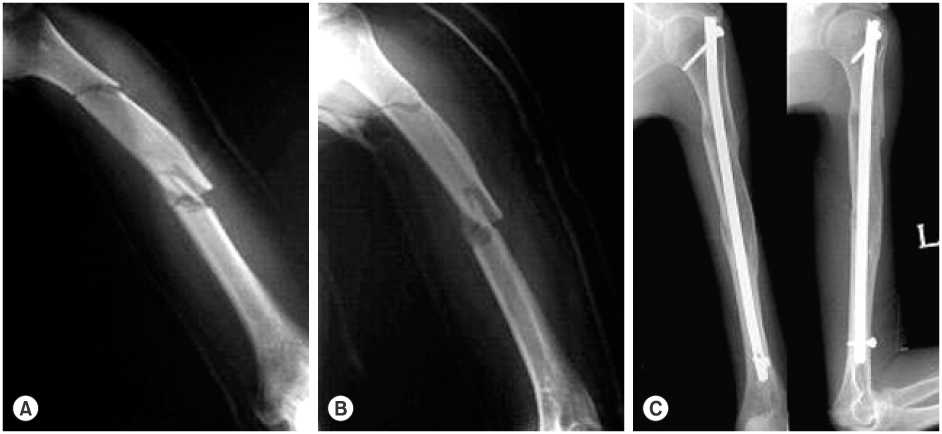
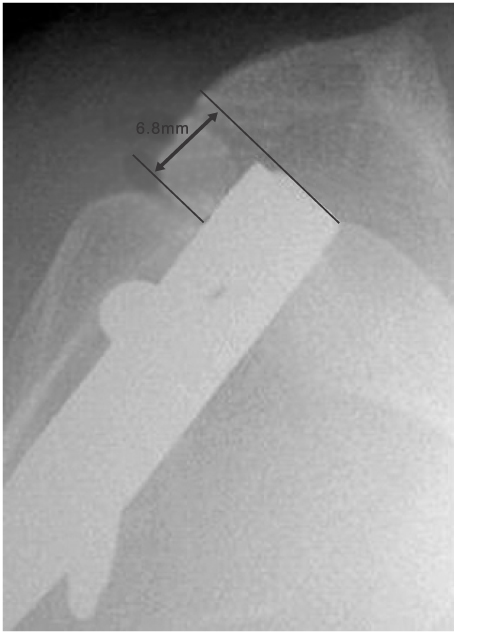
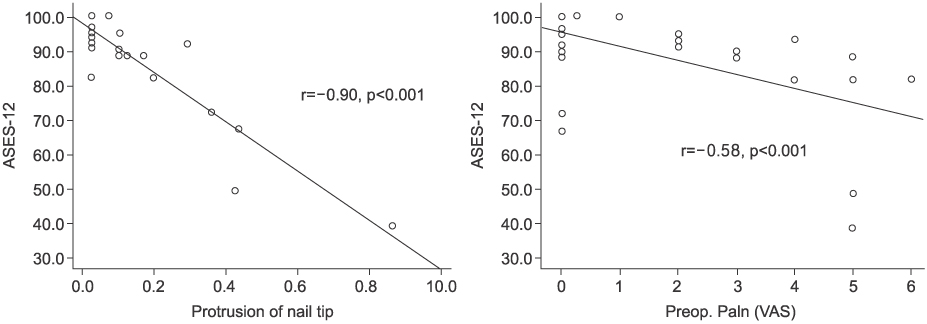
Fig. 1
Distribution of patient for age.
Fig. 2
(A) shows a sclerotic articular surface, (B) shows a narrowing articular space and degenerative osteophyte (arrow head).
Fig. 3
Acute segmental fracture of humeral shaft (A), (B) and union state in 1 year follow up after operation (C).
Fig. 4
Protrusion of nail tip is measured through the widest distant from humeral head to nail tip.
Fig. 5
Correlation of ASES and protrusion of nail tip, ASES and preoperative pain score.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Result of Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing for Humeral Shaft Fracture Evaluation of Post-operative Shoulder Function

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS





 Cite
Cite

