Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 20(2); 2007 > Article
-
Original Article
- Operative Treatment of Displaced Intercondylar Fracture of the Distal Humerus with Reconstruction Plate
- Ryuh Sup Kim, M.D., Tong Joo Lee, M.D., Kyoung Ho Moon, M.D., Seung Rim Park, M.D., Moon Lee, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2007;20(2):172-177.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.2.172
Published online: June 14, 2016
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Tong Joo Lee, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inha University College of Medicine, 253, Yonghyeon-dong, Nam-gu, Incheon 402-751, Korea. Tel: 82-32-890-3664, Fax: 82-32-890-3099, TJLEE@inha.ac.kr
Copyright © The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved
- 444 Views
- 1 Download
Abstract
-
Purpose
- To evaluate the therapeutic effects of chevron olecranon osteotomy and bilateral reconstruction plate as operative treatment for distal humerus intercondylar fracture.
-
Materials and Methods
- Among patients operated for distal humerus intercondylar fracture in our hospital from June, 1997 to October, 2005, 26 patients were selected who could be followed-up for more than one year. The average follow-up period was 15 months. All olecranon osteotomies were chevron osteotomy and all fractures were treated with internal fixation using bilateral reconstruction plate. The ulnar nerve was checked in all cases. Three patients in which case the plate might irritate the ulnar nerve, received with ulnar nerve anterior transposition. Cassebaum's classification and Mayo elbow performance score were used to evaluate at three, six and twelve months.
-
Results
- Mean bone union period was 11.7 weeks. There were 9 excellent cases, 11 good cases, 4 fair cases and 2 poor cases. Mean flexion contracture was 11° and further flexion was 126° at last follow-up.
-
Conclusion
- Bilateral reconstruction plate internal fixation using chevron olecranon osteotomy showed strong fixation and good clinical results and it is possible for early rehabilitation treatment.
- 1. Aiken GK, Rorabeck CH. Distal humeral fractures in the adult. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1986;207:191-197.
- 2. Bryan RS, Morrey BF. Extensive posterior exposure of the elbow. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1982;166:188-192.
- 3. Caja VL, Moroni A, Vendemia V, Sabato C, Zinghi G. Surgical treatment of bicondylar fractures of the distal humerus. Injury, 1994;25:433-438.
- 4. Celli A, Arash A, Adams RA, Morrey BF. Triceps insufficiency following total elbow arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2005;87:1957-1964.
- 5. Fornasieri C, Staub C, Journe Y, Rumelhart C, Saragaglia D. Biomechanical comparative study of three type of osteosynthesis in the treatment of the supra and intercondylar fractures of the humerus in adult. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot, 1997;83:237-242.
- 6. Gabel GT, Hanson G, Bennett JB, Noble PC, Tullos HS. Intraarticular fracture of the distal humerus in the adult. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1987;216:99-108.
- 7. Gupta R. Intercondylar fractures of the distal humerus in adults. Injury, 1996;27:569-572.
- 8. Helfet DL, Hotchkiss RN. Internal fixation of the distal humerus: a biomechanical comparison of methods. J Orthop Trauma, 1990;4:260-264.
- 9. Helfet DL, Schmeling GJ. Bicondylar intraarticular fractures of the distal humerus in adults. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1993;292:26-36.
- 10. Henley MB. Intra-articular distal humeral fractures in adults. Orthop Clin North Am, 1987;18:11-23.
- 11. Henley MB, Bone LB, Parker B. Operative management of intra-articular fractures of the distal humerus. J Orthop Trauma, 1987;1:24-35.
- 12. Holdsworth BJ, Mossad MM. Fractures of the adult distal humerus. Elbow function after internal fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1990;72:362-365.PDF
- 13. Jacobson SR, Glisson RR, Urbaniak JR. Comparison of distal humerus fracture: a biomechanical study. J South Orthop Assoc, 1997;6:241-249.
- 14. John H, Rosso R, Neff U, Bodoky A, Regazzoni P, Harder F. Operative treatment of distal humeral fractures in the elderly. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1994;76:793-796.
- 15. Jupiter JB, Holzach P, Allgower M. Intercondylar fractures of the humerus. An operative approach. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1985;67:226-239.
- 16. Kang CN, Wang JM, Roh KJ, Yun YH, Cho DY. Multiple K-wires fixation of the intercondylar fracture of humerus in adults. J Korean Soc Fract, 1993;6:325-330.
- 17. Kim KY, Bin SI, Kim YJ. Surgical treatment of comminuted distal humerus intercondylar fracture in adult using transolecranon approach and AO method. J Korean Orthop Assoc, 1992;27:1060-1067.
- 18. Kinik H, Atalar H, Mergen E. Management of distal humerus fractures in adults. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, 1999;119:467-469.
- 19. Kundel K, Braun W, Wieberneit J, Ruter A. Intraarticular distal humerus fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1996;332:200-208.
- 20. Mohan N, Hunter JB, Colton CL. The posterolateral approach to the distal humerus for open reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the lateral condyle in children. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2000;82:643-645.
- 21. Moran MC. Modified lateral approach to the distal humerus for internal fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1997;340:190-197.
- 22. Muller ME, Allgower M, Schneider R, Willenegger H. Manual of internal fixation: techniques recommended by the AO group. 2nd ed. New York: Springer; 1979. p. 71-87.
- 23. Papaioannou N, Babis GC, Kalavritinos J, Pantazopoulos T. Operative treatment of type C intra-articular fractures of the distal humerus: the role of stability achieved at surgery on final outcome. Injury, 1995;26:169-173.
- 24. Park JY, Seo JB, Chun JY, Kim MH, Min SH, Lee JH. Treatment of intercondylar fracture of humerus with Y-plate. J Korean Fract Soc, 2006;19:443-448.
- 25. Ring D, Jupiter JB. Complex fractures of distal humerus and their complications. J Shoulder Elbow Surg, 1999;8:85-97.
- 26. Sander RA, Raney EM, Pipkin S. Operative treatment of the bicondylar intraarticular fractures of the distal humerus. Orthopedics, 1992;15:159-163.
- 27. Schemitsch EH, Tencer AF, Henly MB. Biomechaniclal evaluation of methods of internal fixation of the distal humerus. J Orthop Trauma, 1994;8:468-475.
- 28. Sodergard J, Sandelin J, Bostman O. Mechanical failures of internal fixation in T and Y fractures of the distal humerus. J Trauma, 1992;33:687-690.
- 29. Waddell JP, Hatch J, Richards R. Supracondylar fractures of the humerus: results of surgical treatment. J Trauma, 1988;28:1615-1621.
REFERENCES
Fig. 1
(B) Postoperative radiographs show bilateral reconstruction plate through chevron osteotomy of olecranon.
(C) At postoperative 1 year, the patient has excellent ROM of elbow from 0° to 150°

(A) Initial radiographs show AO/ASIF type C2 fracture of the distal humerus.

Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

Operative Treatment of Displaced Intercondylar Fracture of the Distal Humerus with Reconstruction Plate
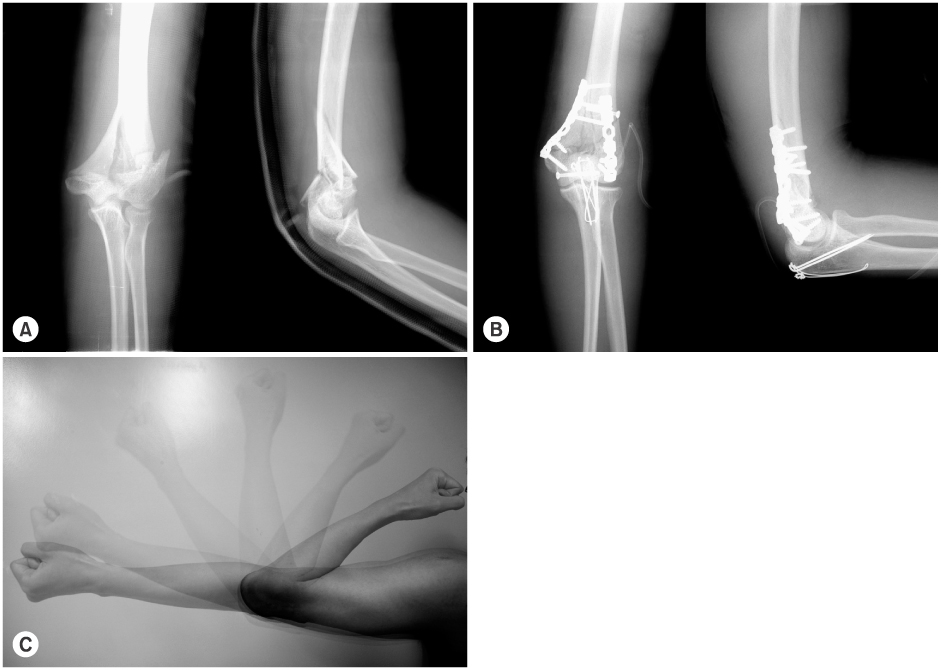
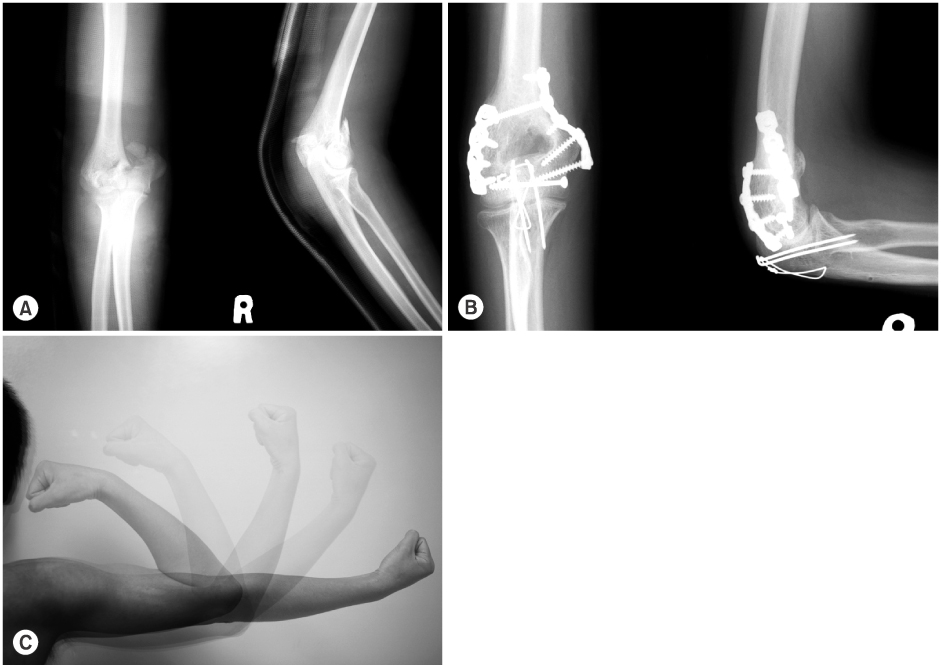
Fig. 1
(A) Initial radiographs show AO/ASIF type C2 fracture of the distal humerus.
(B) Postoperative radiographs show bilateral reconstruction plate through chevron osteotomy of olecranon.
(C) At postoperative 1 year, the patient has excellent ROM of elbow from 0° to 150°
Fig. 2
(A) Initial radiographs show AO/ASIF type C2 fracture.
(B) At postoperative 12 weeks, radiographs show complete bony union.
(C) At postoperative 13 months, ROM of elbow was 0°~135°.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Operative Treatment of Displaced Intercondylar Fracture of the Distal Humerus with Reconstruction Plate
Cassebaum's classification for elbow range of motion
Mayo elbow performance score
Classification: excellent>90, good: 75~89, fair: 60~74, poor<60.
Table 1
Cassebaum's classification for elbow range of motion
Table 2
Mayo elbow performance score
Classification: excellent>90, good: 75~89, fair: 60~74, poor<60.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS



 Cite
Cite

