Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Does the Operator’s Experience Affect the Occurrence of Complications after Distal Radius Fracture Volar Locking Plate Fixation? A Comparative Study of the First Four Years and Thereafter
- Kee-Bum Hong, Chi-Hoon Oh, Chae Kwang Lim, Sungwoo Lee, Soo-Hong Han, Jun-Ku Lee
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2024;37(4):175-183. Published online October 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2024.37.4.175
- Correction in: J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(1):40
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The management of distal radius fractures (DRFs) has evolved with the introduction of volar locking plate (VLP) fixation, offering stable fixation and better outcomes. Nevertheless, the impact of the surgeon’s experience on the complication rates in VLP fixation remains to be determined, particularly for less-experienced surgeons. This study compared the complication rates during the initial four years and subsequent two years of a hand surgeon’s practice of VLP fixation for DRFs.
Materials and Methods
The data between March 2016 and December 2022 were analyzed retrospectively under the Institutional Review Board approval. A single surgeon performed all VLP fixation surgeries after finishing regular hand surgery training, with the first four years representing the less experienced phase (Group 1) and the following two years indicating the experienced phase (Group 2). The patients’ characteristics, operation-related factors, and postoperative complications, including tendon injuries, nerve-related complications, fixation and instrument-related issues, osteosynthesis-related problems, and infections, were compared. In addition, the authors compared the data with a large multicenter study conducted by experienced hand surgeons.
Results
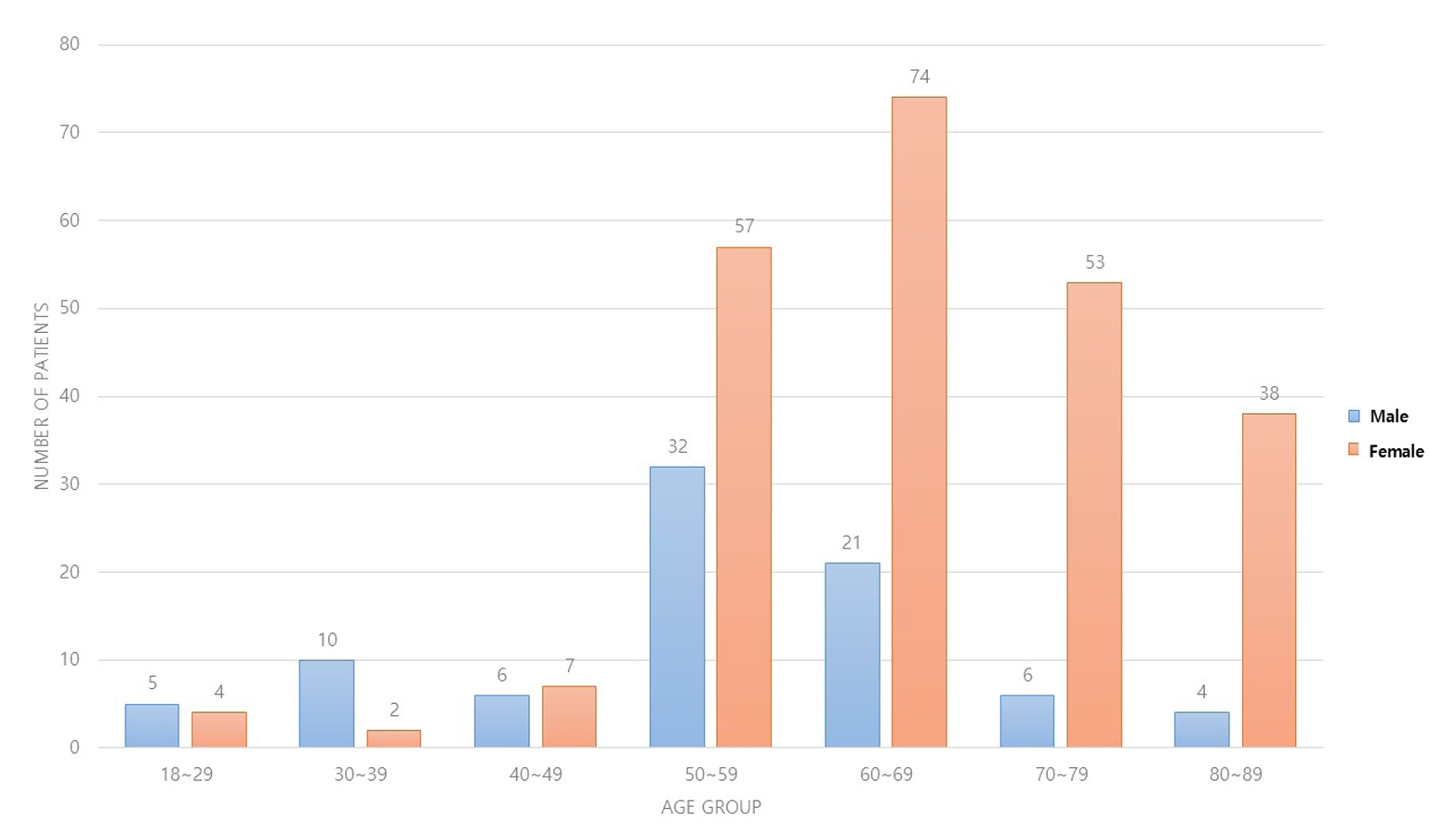
Three hundred and nineteen patients (321 wrists) were included. The mean age was 63.3 years, and 26.3% were male and 73.7% were female. The operation time was 53.7±14.5 minutes and 74.4±26.5 minutes in groups 1 and 2, respectively, which was statistically significantly shorter (p<0.001). The complication rates between the two groups were similar, except for the higher implant removal rates in Group 1. A comparison with a previous multicenter study revealed higher reduction losses and carpal tunnel syndrome in this study, but the overall complication rate was low.
Conclusion
In DRF management, when the operating surgeon has completed an accredited training course, VLP fixation is a good treatment method that can be performed effectively even by less experienced surgeons with low complication rates. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Author correction: “Does the operator's experience affect the occurrence of complications after distal radius fracture volar locking plate fixation? A comparative study of the first four years and thereafter”
Kee-Bum Hong, Chi-Hoon Oh, Chae Kwang Lim, Sungwoo Lee, Soo-Hong Han, Jun-Ku Lee
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(1): 40. CrossRef - Characteristics of patients with distal radius fracture requiring arthroscopic foveal repair after bone union
Min Jung Park, Cheungsoo Ha, Hyun Tak Kang, Yong Hyun Yoon, Jun-Ku Lee, Soo-Hong Han
Arthroscopy and Orthopedic Sports Medicine.2025; 12(2): 70. CrossRef
- Author correction: “Does the operator's experience affect the occurrence of complications after distal radius fracture volar locking plate fixation? A comparative study of the first four years and thereafter”
- 2,269 View
- 52 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Posterior Anti-Glide Plating for Supination External Rotation Type Lateral Malleolar Fractures: Clinical Comparison of Locking versus Non-Locking One-Third Semi-Tubular Plate Fixation
- Jun Young Lee, Yong Jin Cho, Dong Hyuk Cha, Hyun Bai Choi, Jung Ho Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(2):57-62. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.2.57
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate and compare the clinical and radiological outcomes between locking plates and non-locking plates using posterior anti-glide plating for supination external rotation type lateral malleolar fractures.
Materials and Methods
A total of 50 patients who underwent internal fixation of posterior anti-glide plating due to lateral malleolar fractures, classified as supination-external rotation (SER) as per the Lauge-Hansen classification system, at our hospital from January 2017 to November 2018 were retro-spectively evaluated. Patients were divided into two groups: 1/3 semi-tubular locking plate (24 patients) and 1/3 semi-tubular non-locking plate (26 patients). A radiographic assessment was performed after surgery to evaluate the time of bone union. The American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) ankle-hindfoot functional score was measured after the surgery to evaluate the clinical outcomes.
Results
The two groups showed similar distributions in sex, age, height, body mass index, fracture pattern, and mean follow-up period. Complete bone union was obtained in all cases and the mean bone union time was 13.00±3.38 weeks in Group 1 and 12.92±3.26 weeks in Group 2 (p=0.87). The mean AOFAS score at 24 weeks was 95.66±2.86 in Group 1 and 95.84±2.79 in Group 2 (p=0.82). The mean AOFAS score at 48 weeks was 97.25±3.54 in Group 1 and 96.57±3.07 in Group 2 (p=0.47). Two cases of complications were observed in the non-locking plate group.
Conclusion
For the treatment of Lauge-Hansen SER type lateral malleolar fracture, internal fixation us-ing locking 1/3 semi-tubular plate and non-locking 1/3 semi-tubular plate are both favorable fixation methods.
- 276 View
- 2 Download

- Results of Single Small Incision Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis in the Treatment of the Distal Radius Fractures
- Young Sung Kim, Jong Pil Kim, Phil Hyun Chung, Ho Min Lee, Bo Sung Go
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(2):72-80. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.2.72
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study compared minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) using a single small skin incision and conventional open volar locking plate fixation (OP) for distal radius fracture to identify outcome difference.
Materials and Methods
Forty-three patients who underwent MIPO using a single small skin incision or OP for distal radius fractures were evaluated retrospectively. Of the patients, 21 were treated with MIPO using a single small skin incision and 22 with the OP method through the conventional volar approach. The postoperative radiographic results and clinical outcomes at the final follow-up in each group were compared.
Results
All patients achieved bone union in the MIPO and OP groups. No significant differences in the bone union time, alignment, range of motion, QuickDASH, or pain score were observed. On the other hand, the size of the incision was significant: 23 mm in the MIPO group and 55 mm in the OP group (p<0.001).
Conclusion
MIPO technique using a single small incision showed similar satisfactory radiographic and functional outcomes compared to conventional OP for distal radius fractures. The MIPO technique using a single small incision offered advantages, including cosmetic benefits and minimal soft tissue damage, is recommended, particularly in young women and high functional demand patients.
- 545 View
- 5 Download

Review Article
- Locked Plating in Elderly Patients with Distal Femur Fracture: How to Avoid Complications?
- Chul Young Jang, Je Hyun Yoo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(2):112-119. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.2.112
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Distal femur fractures in elderly patients with osteoporosis are complicated because poor bone quality makes screw purchase and fixation less secure, presenting many clinical challenges to the orthopedic surgeon. Minimally invasive locked plating using an angularly stable locking compression plate has become an integral tool for achieving secure fixation in osteoporotic distal femur fractures with improved biomechanical performance. On the other hand, complications, such as implant failure and periplate fracture, have still occurred. This paper describes the principles of internal fixation in minimally invasive lateral locked plating in elderly patients with osteoporotic distal femur fractures as well as how to avoid complications.
- 712 View
- 9 Download

Original Articles
- Results after Less Invasive Locking Plating in Intra-Articular Fractures of the Distal Femur
- Sung Hyun Kim, Sung Hyun Yoon, Hee Gon Park, Jae Uk Jung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(1):14-20. Published online January 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.1.14
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to determine the clinical outcomes after a less invasive locking plating technique in intra-articular fractures of the distal femur.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This was a retrospective 19 case series of patients with distal femoral intraarticular fractures treated with a less invasive locking plating technique in a single center (Dankook University Hospital) from June 2010 to April 2016. Nineteen patients (11 males and 8 females) with a mean age of 55.9 years were enrolled. The functional outcomes were evaluated using the visual analogue scale (VAS), range of knee joint motion (flexion & extension), and Knee Society score. The radiology outcomes were evaluated with parameters measured in a plain radiograph (deviation angle of alignment axis on coronal and sagittal plane, mechanical lateral distal femur angle).
RESULTS
The mean follow-up period was 26.4 months (range, 12–72 months) and the mean duration to union was 15.94 weeks (range, 11–28 weeks). The mean VAS was 1.36 (range, 0–8) and the range of motion of the knee joint was extension 4.73° (range, 0°–30°) and flexion 107.36° (range, 60°–135°). The mean Knee Society score was 85.47 (range, 47–100). The mean deviation angle of the coronal alignment axis was 4.07° (range, 1.3°–8.8°), the mean deviation angle of the sagittal alignment axis was 3.23° (range, 0.7°–7.0°), and the mechanical lateral femoral angle was 87.75° (range, 82.8°–95.5°). Six patients had traumatic osteoarthritis at the final follow-up.
CONCLUSION
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the clinical and radiologic outcomes of intraarticular fractures of the distal femur in patients who underwent an anatomical reduction through an open reduction, and converted to an extra-articular fracture with rigid internal fixation. The results were relatively satisfactory.
- 449 View
- 2 Download

- Posterior Dual Plating for Distal Shaft Fractures of the Humerus
- Chul Hyun Cho, Kwang Yeung Jeong, Beom Soo Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(3):117-123. Published online July 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.3.117
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the results and efficacy of posterior dual plating for distal shaft fractures of the humerus.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We retrospectively analyzed 12 patients, who underwent open reduction and internal fixation using posterior dual plating for distal shaft fractures of the humerus, between July 2007 and July 2015, with at least 6 months of follow-up. After locating the radial nerve without dissection via posterior triceps splitting, the fracture was stabilized using a short 3.5 mm locking compression plate. Then additional fixation, using a long 3.5 mm locking compression plate, was performed. The clinical outcomes were assessed in accordance with the Mayo Elbow Performance Index (MEPI) scoring system, and the radiological outcomes were assessed using serial plain radiographs.
RESULTS
Eleven patients (91.7%) had bony union, and the mean union period was 13.9 weeks. In one patient, delayed union was treated by autogenous iliac bone graft at 8 months after surgery, which resulted in bony union. The mean MEPI score was 95.8, and the clinical outcomes were excellent in 9 patients and good in 3 patients. Postoperative complications included 1 elbow stiffness by heterotopic ossification and 1 temporary radial nerve palsy. One patient with temporary radial nerve palsy was completely recovered within the first 4 days after surgery.
CONCLUSION
Posterior dual plating for distal shaft fractures of the humerus revealed satisfactory clinical and radiological outcomes. It can be a useful alternative to provide stable fixation without the need for a dissection of the radial nerve.
- 591 View
- 15 Download

Case Reports
- Medial Plating of Distal Femoral Fracture with Locking Compression Plate-Proximal Lateral Tibia: Cases' Report
- Se Ang Jang, Young Soo Byun, In Ho Han, Dongju Shin
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(3):206-212. Published online July 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.3.206
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Generally, lateral plating is used for a comminuted fracture of the distal femur. However, in some cases, it has been shown that using a medial plate is necessary to achieve better outcome. Nevertheless, there are no available anatomical plates that fit either the distal medial femoral condyle or fracture fixation, except for the relatively short plate developed for distal femoral osteotomy. We found that locking compression plate-proximal lateral tibia (LCP-PLT) fits anatomically well for the contour of the ipsilateral medial femoral condyle. Moreover, LCP-PLT has less risk of breaking the thread holes since it rarely needs to be bent. We report a plastic bone model study and two cases of distal femoral fractures fixed with medial plating using LCP-PLT.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A novel anatomical locked medial femoral condyle plate: a biomechanical study
M. A. Ozer, S. Keser, D. Barıs, O. Yazoglu
European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology.2024; 34(5): 2767. CrossRef - Medial plating of distal femur: which pre-contoured angular stable plate fits best?
Shaam Achudan, Rex Premchand Antony Xavier, Sze Ern Tan
European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology.2024; 34(6): 3297. CrossRef - Medial augmentation of distal femur fractures using the contralateral distal femur locking plate: A technical note
Jaime Andrés Leal
OTA International.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The missing piece of the trauma armoury-medial femoral condyle plate
Piyush Upadhyay, Farhan Syed, Darryl N Ramoutar, Jayne Ward
Injury.2022; 53(3): 1237. CrossRef - Surgical Tips and Tricks for Distal Femur Plating
Christopher Lee, Dane Brodke, Ajay Gurbani
Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.2021; 29(18): 770. CrossRef - Medial minimally invasive helical plate osteosynthesis of the distal femur – a new technique
G.M. Hohenberger, A.M. Schwarz, P. Grechenig, B. Clement, Mario Staresinic, Bore Bakota
Injury.2021; 52: S27. CrossRef - Feature-Based Design of Personalized Anatomical Plates for the Treatment of Femoral Fractures
Xiaozhong Chen, Zhijian Mao, Xi Jiang
IEEE Access.2021; 9: 43824. CrossRef
- A novel anatomical locked medial femoral condyle plate: a biomechanical study
- 1,154 View
- 59 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Tension Band Plating for a Stress Fracture of the Anterior Tibial Cortex in a Basketball Player: A Case Report
- Chul Hyun Park, Woo Chun Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(4):323-326. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.4.323
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Stress fractures of the anterior tibial cortex are prone to complete fracture because these stress fractures occur on the tension side of the bone. Recently, surgical treatments are preferred in high-performance athletes requiring rapid return to sports. We report our experience of a case in which stress fracture of the anterior tibial cortex was treated using anterior tension band plating in a male athlete and successful bony union and rapid return to sports were achieved.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Stress fractures of the tibia
Jung Min Park, Ki Sun Sung
Arthroscopy and Orthopedic Sports Medicine.2015; 2(2): 95. CrossRef
- Stress fractures of the tibia
- 557 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- Operative Treatment of Distal Humeral Comminuted Fractures with Orthogonal Plating
- Joong Bae Seo, Jae Sung Yoo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2011;24(3):243-248. Published online July 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.3.243
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analyze the results of operative treatment for Comminuted Fracture of Distal Humerus with Transolecranon approach and Orthogonal plating.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The subjects were 22 patients with Comminuted fracture of humerus who were treated with Orthogonal plating. Patient's age, sex, type of fracture, surgical approach, method of fixation, time of operation, time of bony union, complication, range of motion were investigated, and Function of elbow was evaluated by functional evaluation of Riseborough and Radin, Mayo Elbow Performance Score (MEPS).
RESULTS
Age, sex, injuried arm, operation time were not related to postoperative result. Type C2 fractures showed better results in function and range of motion (ROM) than type C3 fractures. Also early rehabilitation was important to functional recovery and ROM. The postoperative ROM was average 110. Good were 16 cases, fair were 6 cases in functional evaluation of Riseborough and Radin. Excellent were 13 cases, good were 8 cases, fair was 1 case in MEPS.
CONCLUSION
Operative treatment with Transolecranon approach and Orthogonal plating showed favorable result on its function. Intraarticular comminution and early rehabilitation were closely related to postoperative function of elbow.
- 577 View
- 1 Download

- Treatment of Shatzker Type VI Tibia Plateau Fracture Using Lateral and Posteromedial Dual Incision Approach and Dual Plating
- In Jung Chae, Sang Won Park, Soon Hyuck Lee, Won Noh, Ho Joong Kim, Seung Beom Hahn
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(4):252-258. Published online October 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.4.252
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the radiologic and clinical results of treatment of the Shatzker type 6 tibia plateau fracture using the lateral and posteromedial dual incision approach and dual plating. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Twelve cases in eleven patients of Shatzker type 6 tibia plateau fracture which has been treated using the lateral and posteromedial dual incision approach and dual plating were analyzed with an average follow-up of 16 months. Times to union, alignment and reduction loss on radiograph and postoperative clinical outcome with checking the range of motion of the knee joint, Knee Society Score and UCLA activity scale were analyzed and evaluated. RESULTS: In all cases, bony union was obtained in an average fifteen weeks after the operation, and there was no reduction loss. The arc of motion of the knee joint at the latest follow-up was 132 degrees on average. Average of Knee Society Score was 85 and UCLA activity scale was decreased from 9.6 points preoperatively to 5.7 points postoperatively. CONCLUSION: The treatment of Shatzker type 6 tibia plateau fracture using the lateral and posteromedial dual approach and dual plating have shown clinically preferable results of excellent recovery of joint motion and good knee society score by early range of motion exercise after firm fixation. However, it was high energy injury, so the sports activity of patients was significantly decreased. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Staged Treatment of Bicondylar Tibial Plateau Fracture (Schatzker Type V or VI) Using Temporary External Fixator: Correlation between Clinical and Radiological Outcomes
Seung Min Ryu, Han Seok Yang, Oog Jin Shon
Knee Surgery and Related Research.2018; 30(3): 261. CrossRef - Medial Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis in Proximal Tibial Comminuted Fractures
Jae-Ang Sim, Kwang-Hui Kim, Yong-Seuk Lee, Sang-Jin Lee, Beom-Koo Lee
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2014; 49(4): 278. CrossRef - Current Concepts in Management of Tibia Plateau Fracture
Sang Hak Lee, Kang-Il Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2014; 27(3): 245. CrossRef
- Staged Treatment of Bicondylar Tibial Plateau Fracture (Schatzker Type V or VI) Using Temporary External Fixator: Correlation between Clinical and Radiological Outcomes
- 642 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Double Plating of Proximal Tibial Fractures Using Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Osteosynthesis Technique
- Chang Wug Oh, Jong Keon Oh, In Ho Jeon, Hee Soo Kyung, Il Hyung Park, Byung Chul Park, Woo Kie Min, Ji Ho Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(3):250-255. Published online July 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.3.250
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
To evaluate the results and its efficacy of double plating for proximal tibial fractures using minimally invasive percutaneous osteosynthesis (MIPO) technique. MATERIAL & METHODS: Twenty-three fractures, followed-up more than 1 year, were included in this retrospective study. There were 18 men and 5 women, and the mean age was 53.5 years-old. According to the AO-OTA classification, five were 41A, 13 were 41C, and 5 were 42. There were four open fractures (grade I- three, grade III A-one case). The plates were fixed on the medial and lateral sides of tibia with MIPO technique. Functional and radiographic results were evaluated by the modified Rasmussen system.
RESULTS
All fractures healed without bone graft, and the mean period for fracture healing was 19.3 weeks (range, 10~32 weeks). All other patients had excellent or good clinical or radiological results, except for two patients of a fair clinical result after a combined injury. Complications included one case of shortening (1 cm) and two cases of mal-alignments (varus less than 10 degrees). There was one case of superficial infection, but no patient showed deep infection.
CONCLUSION
Double plating using MIPO technique can provide favorable results in the treatment of proximal tibial fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Medial Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis in Proximal Tibial Comminuted Fractures
Jae-Ang Sim, Kwang-Hui Kim, Yong-Seuk Lee, Sang-Jin Lee, Beom-Koo Lee
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2014; 49(4): 278. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Proximal Tibial Shaft Fracture
Young-Soo Byun, Ki-Chul Park, Hyun-Jong Bong, Chang-Hoon Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(1): 23. CrossRef - Treatment of Proximal Tibia Fractures Using LCP by MIPO Technique
Sang-Ho Ha, Dong-Hui Kim, Jun-Young Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(1): 34. CrossRef - Staged Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis of Proximal Tibial Fracture
Joon-Woo Kim, Chang-Wug Oh, Jong-Keon Oh, Hee-Soo Kyung, Woo-Kie Min, Byung-Chul Park, Kyung-Hoon Kim, Hee-Joon Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(1): 6. CrossRef
- Medial Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis in Proximal Tibial Comminuted Fractures
- 495 View
- 7 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Treatment of Fractures of the Distal Radius using Locking Compression Plate
- Jae Cheon Sim, Nam Sik Chung, Ki Do Hong, Sung Sik Ha, Ji Hoon Kang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(2):100-104. Published online April 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.2.100
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the usefulness of locking compression plate (LCP) and volar plating through anterior approach for distal radius fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We retrospectively analysed that 15 distal radius fracture, which would not be reduced by closed reduction or too comminuated to maintain reduction or articular surface inconguency, were treated by open reduction through anterior approach and volar plating using LCP. The results were evaluated by preoperative and postoperative radiographs. Functional results were analysed using the Modified Mayo Wrist Scoring System.
RESULTS
All cases achieved anatomical articular surface reduction postoperatively. In terms of radiologic analysis, mean radial length (9.0 mm vs. 11.8 mm), radial inclination (14.7degrees vs. 20.9degrees ), volar tilt (-6.3degrees vs. 8.3degrees ) and articular step-off (1.4 mm vs. 0.3 mm) were improved. The average Modified Wrist Score was 89. Nonunion or malunion was not occurred.
CONCLUSION
Open reduction through anterior approach and volar plating using LCP is a useful method that provides excellent results with few complications in the treatment of fracture of the distal radius. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Periprosthetic Fracture after Locked Plating in the Osteoporotic Long Bone Fracture
Ki-Chul Park, Hong-Sik Kim, Jeong-Han Oh
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2012; 47(3): 222. CrossRef - 2.4 mm Volar Locking Compression Plate for Treatment of Unstable Distal Radius Fractures
Sung-Jin Kim, Chul-Hyun Cho
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(2): 151. CrossRef - Treatment of Femur Supracondylar Fracture with Locking Compression Plate
Seong Ho Bae, Seung Han Cha, Jeung Tak Suh
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(3): 282. CrossRef - Comparison of Outcomes for Unstable Distal Radius Intraarticular Fractures - T-locking Compression Plate versus External Fixator -
Chul-Hyun Cho, Su-Won Jung, Sung-Won Sohn, Chul Hyung Kang, Ki-Cheor Bae, Kyung-Jae Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2008; 21(1): 51. CrossRef - Basic Principle of the Locking Compression Plate
Keun Bae Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2008; 21(3): 261. CrossRef - Volar T-Locking Compression Plate for Treatment of Unstable Distal Radius Fractures
Chul Hyun Cho, Ki Choer Bae, Doo Hyun Kwon
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2008; 21(3): 220. CrossRef
- Periprosthetic Fracture after Locked Plating in the Osteoporotic Long Bone Fracture
- 524 View
- 1 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Stabilization of Proximal Tibial Fractures
- Chang Wug Oh, Jong Keon Oh, In Ho Jeon, Hee Soo Kyung, Il Hyung Park, Joo Chul Ihn, Yeon Ki Woo, Ho Sung Jung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(3):224-229. Published online July 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.3.224
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
Despite of various treatment methods, proximal tibial fractures are common injuries that may be associated with poor outcomes and high rates of complications. To improve this, percutaneous plating technique was performed in the proximal tibial fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty-four proximal tibial fractures (AO 41A; 5, AO 41C; 12, AO 42; 7) were treated by percutaneous plating with either or both sides without bone graft. One was open fracture.
RESULTS
All fractures were healed. The average time for fracture healing was 16.5 weeks (range, 8~24 weeks). Complications included a 1cm shortened case and two mal-alignments; a 6 degree valgus case and 5 degree varus case. There was one case of superficial infection, which healed after plate removal. But, there was no deep infection. Results were evaluated by modified Rasmussen score system, all patients had excellent or good result.
CONCLUSION
Minimally invasive percutaneous plating technique can provide favorable results in the treatment of proximal tibial fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- MINIMALLY INVASIVE OSTEOSYNTHESIS WITH PLATE OR NAIL FOR META-DIAPHYSEAL TIBIAL FRACTURES - WHAT IS BETTER?
B. Makelov
Trakia Journal of Sciences.2023; 21(4): 357. CrossRef - Medial Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis in Proximal Tibial Comminuted Fractures
Jae-Ang Sim, Kwang-Hui Kim, Yong-Seuk Lee, Sang-Jin Lee, Beom-Koo Lee
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2014; 49(4): 278. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Stabilization Using a Medial Locking Plate for Proximal Tibial Fractures - Technical Note -
Jae Ang Sim, Beom Koo Lee, Kwang Hui Kim, Yong Seuk Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2013; 26(4): 327. CrossRef - Clinical Outcomes of Locking Compression Plate Fixation through Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis in the Treatment of Distal Tibia Fracture
Jae-Sung Yoo, Hyun-Woo Park
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2012; 25(2): 117. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Proximal Tibial Shaft Fracture
Young-Soo Byun, Ki-Chul Park, Hyun-Jong Bong, Chang-Hoon Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(1): 23. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for the Upper Extremity Fracture Using a Lumbar Spreader - Surgical Technique -
Gu-Hee Jung, Chyul-Hyun Cho, Jae-Do Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(1): 83. CrossRef - Management of Fractures of Distal Tibia by Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis through an Anterior Approach
Gu-Hee Jung, Jae-Do Kim, Jae-Ho Jang, Sung-Keun Heo, Dong-won Lee
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2010; 45(6): 473. CrossRef - The Comparison of Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis and Intramedullary Nailing in the Treatment of the Proximal and Distal Tibia Fracture
Joon Soon Kang, Seung Rim Park, Sang Rim Kim, Yong Geun Park, Jae Ho Jung, Sung Wook Choi
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(2): 172. CrossRef - Staged Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis of Proximal Tibial Fracture
Joon-Woo Kim, Chang-Wug Oh, Jong-Keon Oh, Hee-Soo Kyung, Woo-Kie Min, Byung-Chul Park, Kyung-Hoon Kim, Hee-Joon Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(1): 6. CrossRef - Proximal Tibia Fracture: Plating
Ki-Chul Park
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(3): 206. CrossRef
- MINIMALLY INVASIVE OSTEOSYNTHESIS WITH PLATE OR NAIL FOR META-DIAPHYSEAL TIBIAL FRACTURES - WHAT IS BETTER?
- 433 View
- 2 Download
- 10 Crossref

- The Clinical Results in Compression Plate Fixation with Autogenous Cancellous Bone Graft for Humerus Diaphyseal Nonunion
- Kwang Hyun Lee, Seong pil Lee, Hyung Jong Kim, Bong Geun Lee, Joo Hak Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(2):90-94. Published online April 30, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.2.90
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
A The purpose of this retrospective study was to evaluate the results of compression plating and autogenous iliac bone graft in the management of humeral diaphyseal nonunion.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty patients who underwent the surgical treatments between May. 1998 and May. 2002 were included in this study. Nine of them are males and the others are females. The average age of them, when they was on operation, was 45 years. The symptoms lasted 23 months on average. They have been followed up for 33 months at an average. Treatment of nonunion consisted of resecting the atrophic nonunion, shortening the bone, apposing bleeding diaphyseal surface. Rigid fixation was then achieved using a compression plate and autogenous bone graft.
RESULTS
Solid bony union was achieved in all patients. In one patient, the bone was not healed at the first operation of plating and autogenous bone graft, but achieved union after the use of intramedullary nailing. In another patient, because of infected nonunion, we achieved union after several surgical debridement and stabilization by internal fixation.
CONCLUSION
This study documents that compression plate fixation with autogenous cancellous bone graft is a viable option with predictable and satisfactory results for humerus diaphyseal nonunion.
- 359 View
- 0 Download

- Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Distal Femoral Fractures
- Sung Jung Kim, Chang Wug Oh, In Ho Jeon, Hee Soo Kim, Byung Chul Park, Hee Soo Kyung, Joo Chul Ihn, Ho Sung Jung
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(4):474-481. Published online October 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.4.474
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
We retrospectively reviewed the outcomes and advantages of minimal invasive plating osteosynthesis (MIPO) technique as a new treatment of distal femoral fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sixteen supracondylar femoral fractures (15 patients) were treated by MIPO technique and evaluated radiologically and functionally after minimal 1 year follow-up (average; 22 months, range; 13~42 months). There were 9 women and 6 men with a mean age of 46 years old (range 35 to 64 years). Seven fractures were extended into knee joints (AO/OTA type C), and 9 were extraarticular (AO/OTA type A). Five cases were open fractures (type I; 2, type II; 3) according to the Gustilo-Anderson classification. After minimal lateral parapatellar incision and accurate reduction of intra-articular fractures, the supracondylar fractures were fixed by percuatneous plating method without exposure of fracture area. Neer scoring was used for functional evaluation of knee.
RESULT
At a mean of 17 weeks (range 14 to 22), most fractures united without secondary procedures. One case of nonunion had the procedure of bone graft, but there were no other complications including shortening over 1 cm, mal-alignment over 10 degrees, or deep infections. All the cases had good or excellent knee function, and the average range of knee motion was 120.6 degrees.
CONCLUSION
MIPO technique is a worthwhile method of managing distal femoral fractures with good unions and functional recovery. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Comparison of Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis versus Open Plate Fixation in the Treatment of in the Distal Femur Fracture
Seong-Jun Ahn, Suk-Woong Kang, Bu-Hwan Kim, Moo-Ho Song, Seong-Ho Yoo, Kwan-Taek Oh
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2013; 26(4): 314. CrossRef - Treatment of Distal Femur Fracture with Minimally Invasive Locking Compression Plate Osteosynthesis
Ki-Chul Park, Kyu-Sung Chung, Joon-Ki Moon
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2012; 25(1): 13. CrossRef - Axial Malalignment after Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis in Distal Femur Fractures with Metaphyseal Comminution
Jae-Ho Jang, Gu-Hee Jung, Jae-Do Kim, Cheung-Kue Kim
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2011; 46(4): 326. CrossRef - Surgical Treatment of AO Type C Distal Femoral Fractures Using Locking Compression Plate (LCP-DF, Synthes®)
Kap-Jung Kim, Sang Ki Lee, Won-Sik Choy, Won-Cho Kwon, Do Hyun Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(1): 20. CrossRef - What is an Ideal Treatment?
Chang-Wug Oh
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2008; 21(4): 347. CrossRef
- The Comparison of Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis versus Open Plate Fixation in the Treatment of in the Distal Femur Fracture
- 497 View
- 0 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Anterior Approach and Volar T-plate fixation of Distal Radius Fracture
- Woo Sung Choi, Weon Yoo Kim, Dong Won Choi, Yun Hack Shin, Jin Young Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(2):244-252. Published online April 30, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.2.244
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analyze the radiologic and clinical results of open reduction and volar plating through anterior approach for distal radius fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We retrospectively analysed that 19 distal radius fracture, which would not be reduced by closed reduction or too comminuted to maintain reduction or articular surface incongruency, were treated by open reduction and volar plating through anterior approach. The results were evaluated by preoperative and immediate postoperative radiographics and clinical results were analysed using Green and O'Brien scoring system at final follow up.
RESULTS
All cases achieved anatomical articular surface reduction postoperatively. In terms of radiologic analysis, mean radial length (8.8 mm +/-4.8 mm vs. 11 mm +/-3 mm), radial inclination (15 degrees+/-5.7 degreesvs. 20degrees+/-5degrees), volar tilt (-11 degrees+/-13 degrees vs. 7 degrees+/-4 degrees) and ulnar plus variant (4 mm+/-3 mm vs. 0 mm+/-1 mm) were improved. The clinical evaluation revealed 9 excellent cases, 7 good cases, 2 fair cases and 1 poor case. The reduction loss and flexor pollicis longus rupture was occurred in one patient, who had severely displaced comminute fracture in initial injury.
CONCLUSION
Using volar plating, authors gain good radiologic and clinical results. But, additional external fixation is recommended to prevent further collapse in severly comminuted fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Is dorsal cortex drilling necessary for distal radius fractures treated with a volar locking plate? A comparative study of near-cortex-only and far-cortex drilling
Chul Hong Kim, Sung Yoon Jung, Hyeon Jun Kim, Si-Hyun Park
Journal of Trauma and Injury.2025; 38(3): 248. CrossRef - Treatment of Fractures of the Distal Radius Using Variable-Angle Volar Locking Plate
Jae-Cheon Sim, Sung-Sik Ha, Ki-Do Hong, Tae-Ho Kim, Min-Chul Sung
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2015; 28(1): 46. CrossRef
- Is dorsal cortex drilling necessary for distal radius fractures treated with a volar locking plate? A comparative study of near-cortex-only and far-cortex drilling
- 423 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Treatment of Distal Clavicle Fractures with Coracoclavicular ligament Injury
- Nam Yong Choi, Suk Ku Han, Seong Jin Park, Ki Ho Na, Young Hun Kim, Hyun Seok Somg, Yong Jin Kwon
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(1):21-27. Published online January 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.1.21
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the radiological and clinical results of the treatment of distal clavicular fractures with coracoclavicular ligament injury by coracoclavicular fixation with plating or repair of coracoclavicular ligament.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sixteen cases with minimum six months of follow-up were included in our study. Male was twelve and average age was 43(28-80). Ten cases of Craig type 2 were treated with coracoclavicular screw fixation with plating. Six cases of Craig type 5 were treated with coracoclavicular screw fixation with repair of coracoclavicular ligament. The radiologic assessment including coracoclavicular distance and union time and the clinical assessment including range of motion and degree of pain were evaluated.
RESULTS
Fifteen cases were united, but one case developed osteomyelitis and nonunion. Full range of motion was achieved in fifteen cases at last follow-up. Average coraco- clavicular distance compared to contralateral site in AP view was 2.1 mm increase in patients with plate fixation and 1.3 mm increase in patients with ligament repair. Average union time was 14.3 weeks and little differenece was noted between two groups(P>0.05).
CONCLUSION
Coracoclavicular screw fixation with plating or repair of coracoclavicular ligament were a useful method to treat distal clavicular fractures combined with coracoclavicular ligament injury.
- 368 View
- 3 Download

- Augmentative Plate Fixation for Femoral Nonunion after Intramedullary Nailing
- Hyoun Oh Cho, Kyoung Duck Kwak, Jong Jin Kim, Soo Min Sohn, Cheol Ho Kang, Hong Ju Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(4):825-831. Published online October 31, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.4.825
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The purpose of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of augmentative plate fixation for the femoral nonunion after intramedullary nailing. We reviewed eleven femoral nonunion after intramedullary nailing, which were treated with augmentative plate internal fixation. All cases were initially managed with interlocking intramedullary nailing. Five were hypervascular and six were avascular. Leaving the intramedullay nail in situ, an augmentative plate fixation was applied to the fracture site to counter the rotational instability. A simultaneous bone grafting was performed in six avascular nonunion to repair the bony defect. The union time was 8.2 months in average( 7.8 months in hypervascular and 8.5 months in avascular). In conclusion, augmentative plating leaving the intramedullary nail in situ is an useful alternative for the treatment of femoral nonunion after intramedullary nailing. The technique is simple and does not require any special instruments. It facilitates an early weight bearing and gives a quick recovery from nonunion.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Comparison of LC-DCP versus LCP Fixation in the Plate Augmentation for the Nonunion of Femur Shaft Fractures after Intramedullary Nail Fixation
Se Dong Kim, Oog Jin Sohn, Byung Hoon Kwack
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2008; 21(2): 117. CrossRef
- The Comparison of LC-DCP versus LCP Fixation in the Plate Augmentation for the Nonunion of Femur Shaft Fractures after Intramedullary Nail Fixation
- 424 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Double-Plating in the Comminuted Supracondylar Fracture of the Distal Femur
- Taek Rim Yoon, Sung Taek Jung, Hyoung Yeon Seo
- J Korean Soc Fract 1997;10(4):778-784. Published online October 31, 1997
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1997.10.4.778
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Supracondylar fracture of femur is not well suited to internal fixation. A wide canal, a thin cortex, comminution and compound wound make open reduction more difficult. Especially, type C2 and C3 on AO classification is problematic. The cases of nine patients who had type C2 or C3 fracture including three open fractures and deficient medial-cortical buttress were reviewed. Stable fixation was achieved with the lateral condylar buttress plate. Additional stabilization with a medial plate and bone graft from the iliac crest was applied in all nine patients. At an average duration of follow-up nineteen months(range from twelve to forty-eight months), all of the fracture had healed. Evaluation of the functional outcome revealed two excellent, three good and four fair results. In three patient, less than 90 degree of flexion of the knee was present and in six, the arc of flexion was limited to between 90 and 110 degrees. One patient had two centimeter shortening, one had medial screw loosening which need not additional fixation. The results of our study suggest that, for the treatment of patients who have a difficult fracture in whom stable fixation of the distal part of the femur cannot be achieved with a condylar buttress plate because of medial cortical communition, a short distal condylar fragment, or loss of metaphyseal bone, double-plating is indicated.
- 241 View
- 3 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


