Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse articles > Previous issues
Review Articles
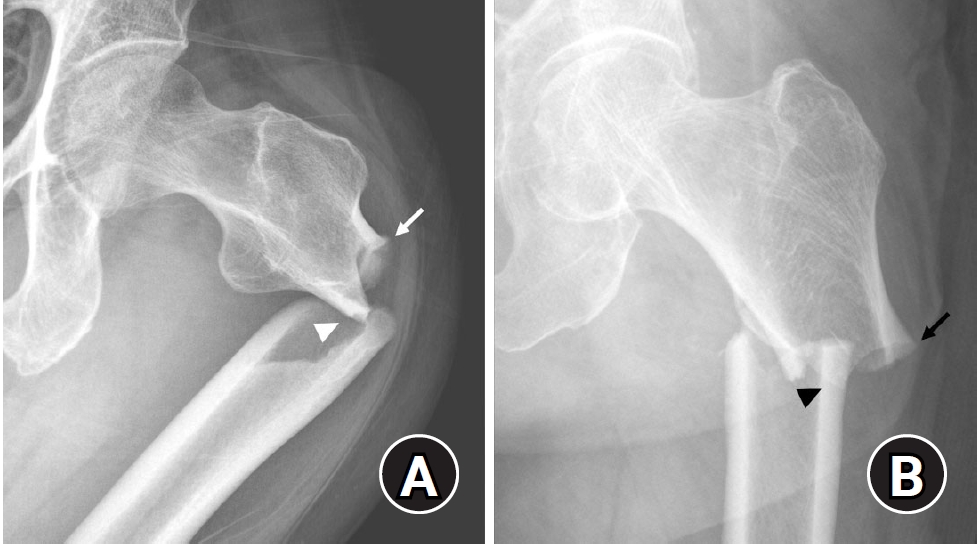
- Atypical femoral fractures: an update
- Won-Tae Cho, Jeong-Hyun Koh, Seungyeob Sakong, Jung-Taek Kim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):41-52. Published online March 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00031
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This narrative review provides an up-to-date overview of atypical femoral fractures (AFFs), emphasizing diagnostic criteria, epidemiology, pathophysiology, risk factors, and evaluation with screening strategies. AFFs are rare but significant complications associated with prolonged bisphosphonate (BP) therapy for osteoporosis. Although the pathogenesis of AFFs has not been fully elucidated, its primary mechanism is thought to involve impaired bone remodeling, leading to unhealed microfractures that progress to stress fractures under repetitive loading. AFFs can occur in various regions of the femur, influenced by femoral geometry and the lower limb axis. Other risk factors include prolonged steroid use, arthroplasty, genetic predispositions, and metabolic bone disorders. The diagnosis of AFFs is based on criteria established by the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. Key radiographic features include lateral cortical transverse fracture lines and localized cortical thickening, typically with minimal or no comminution on the medial cortex. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry for screening tests and magnetic resonance imaging as an advanced imaging modality enable the early detection of incomplete fractures. This multi-modal approach facilitates the prompt identification of prodromal cortical changes, reducing the risk of complete fractures in high-risk populations, particularly patients undergoing prolonged BP therapy. Level of Evidence: V
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Atypical Femur Fractures Without Bisphosphonate Exposure (AFFwB): A Retrospective Report of 21 Cases
Lorenzo Lucchetta, Carmelinda Ruggiero, Samuele Berardi, Alice Franceschi, Michele Bisaccia, Giuseppe Rinonapoli
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 15(1): 25. CrossRef
- Atypical Femur Fractures Without Bisphosphonate Exposure (AFFwB): A Retrospective Report of 21 Cases
- 13,385 View
- 379 Download
- 1 Crossref

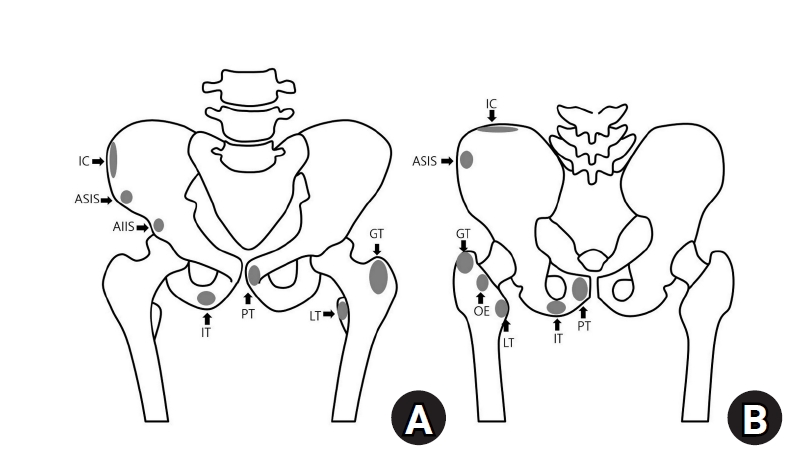
- Avulsion fractures around the hip joint and pelvis
- Won-Sik Choy, Yonghan Cha, Jung-Taek Kim, Jun-Il Yoo, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):53-62. Published online March 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Avulsion fractures occur when tendons or ligaments are subjected to forces greater than they can withstand at the apophysis or enthesis, regardless of fusion status. The pelvis and hip joint are vulnerable to these injuries due to the diverse muscular structures in these structures, which serve as origins for multiple muscles leading to the lower extremities. Pelvic avulsion fractures commonly affect young athletes, but can also occur in adults. The diagnosis typically involves assessing trauma history, a clinical examination, and radiographic imaging. If the diagnosis is unclear, additional tests such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging may assist in the diagnosis and provide useful information for treatment decisions. While most avulsion fractures respond well to conservative treatment, surgical intervention may be preferred in severe displacements, cases of significant retraction in active athletes, or when a faster recovery is necessary. Chronic or neglected injuries may lead to excessive osseous formation around the pelvis, causing impingement syndromes. Recognizing characteristic radiological findings based on pelvic anatomy helps to make an accurate diagnosis, as chronic injuries can mimic tumors or infectious conditions, necessitating a careful differential diagnosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Avulsion Fracture of the Lesser Trochanter and the Use of Conservative Treatment
Dawid Bartosik, Bartlomiej Cwikla, Anna Kowalczyk, Michalina Loson-Kawalec, Anna Palka-Szymaniec, Bartosz Starzynski, Alina Keska, Jakub Szkuta, Klaudia Wojcik
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Avulsion Fracture of the Lesser Trochanter and the Use of Conservative Treatment
- 8,287 View
- 126 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Treatment of avulsion fractures around the knee
- Jeong-Hyun Koh, Hyung Keun Song, Won-Tae Cho, Seungyeob Sakong, Sumin Lim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):63-73. Published online March 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00073

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Avulsion fractures of the knee occur when tensile forces cause a bone fragment to separate at the site of soft tissue attachment. These injuries, which frequently affect adolescent athletes, can involve the cruciate and collateral ligaments, arcuate complex, iliotibial band, and patellar and quadriceps tendons. Radiographs aid in the initial diagnosis, while computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging facilitate a comprehensive evaluation of injury severity and concomitant damage. Specific avulsion fracture types include: anterior cruciate ligament avulsions (tibial site, Meyers and McKeever classification), posterior cruciate ligament avulsions (tibial attachment, Griffith's classification), Segond fractures (anterolateral complex injury), iliotibial band avulsions, medial collateral ligament avulsions (reverse Segond, Stieda fractures), arcuate complex avulsions ("arcuate sign"), medial patellofemoral avulsions (patellar dislocations), and patellar/quadriceps tendon avulsions. The treatment depends on the fracture location, displacement, and associated injuries. Non-displaced fractures can be managed conservatively, while displaced fractures or those with instability require surgical reduction and fixation. Prompt recognition and appropriate intervention prevent complications such as deformity, nonunion, malunion, and residual instability. This review provides an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management of knee avulsion fractures to guide clinical decision-making.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lateral marginal fractures of the patella and patellofemoral pain
Jae-Ang Sim, Chul-Ho Kim, Ji Wan Kim
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(3): 152. CrossRef
- Lateral marginal fractures of the patella and patellofemoral pain
- 16,869 View
- 184 Download
- 1 Crossref

- How to obtain the desired results from distal tibial nailing based on anatomy, biomechanics, and reduction techniques
- Jungtae Ahn, Se-Lin Jeong, Gu-Hee Jung
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):74-85. Published online March 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00024

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Distal tibial metaphyseal fractures are commonly caused by high-energy injuries in young men and osteoporosis in older women. These fractures should be clearly distinguished from high-energy pilon fractures. Although the optimal surgical intervention methods for distal tibial metaphyseal fractures remain uncertain and challenging, surgical treatments for nonarticular distal tibia fractures can be broadly divided into two types: plate fixation and intramedullary nail (IMN) fixation. Once functional reduction is achieved using an appropriate technique, distal tibial nailing might be slightly superior to plate fixation in reducing postoperative complications. Thus, the surgical strategy should focus on functional realignment and proceed in the following sequence: (1) restoring the original tibial length, regardless of whether fibular fixation is to be done; (2) making the optimal entry point through an anteroposterior (AP) projection based on the overlapping point between the fibular tip and lateral plateau margin; (3) placing Kirschner wires (Ø2.4 mm) as blocking pins (in the AP orientation for coronal control and in the mediolateral [ML] orientation for sagittal control) as close to the upper locking hole as possible without causing further comminution on the concave aspect of the short fragment; and (4) making the the distal fixation construct with at least two ML and one AP interlocking screw or two ML interlocking screws and blocking screws. After the IMN is adequately locked, blocking pins (Ø2.4 mm) need to be replaced by a 3.5 mm screw.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Foot Width on Patient-Reported Outcomes Assessed by 3-Dimensional Foot Morphometry in Hallux Valgus
Jungtae Ahn, Dae-Cheol Nam, Gu-Hee Jung
Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery.2025; 17(6): 1062. CrossRef
- Impact of Foot Width on Patient-Reported Outcomes Assessed by 3-Dimensional Foot Morphometry in Hallux Valgus
- 2,712 View
- 52 Download
- 1 Crossref

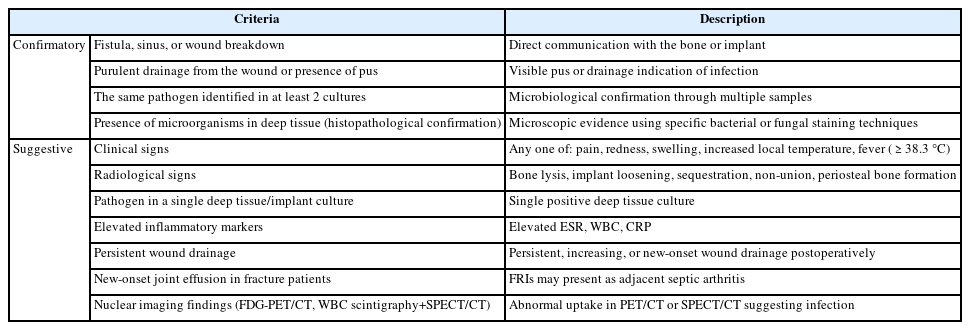
- Fracture-related infections: a comprehensive review of diagnosis and prevention
- HoeJeong Chung, Hoon-Sang Sohn
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):86-95. Published online April 25, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00164
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fracture-related infections are challenging complications in orthopedic trauma that often require prolonged treatment and impose a significant healthcare burden. Accurate diagnosis and effective prevention strategies are essential for minimizing their occurrence. A recent international consensus has established standardized diagnostic criteria based on clinical, microbiological, radiological, and histopathological findings. Prevention is the top priority and involves a thorough preoperative risk assessment, along with glycemic control, nutritional optimization, and management of comorbidities, as well as intraoperative and postoperative measures such as appropriate antibiotic prophylaxis, surgical site antisepsis, and meticulous wound care. A multidisciplinary approach involving orthopedic surgeons, infectious disease specialists, and microbiologists is crucial for successfully reducing the burden of fracture-related infections.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Personalized Approaches to Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies in Periprosthetic Fracture-Related Infections (PFRIs): Case Series and Literature Review
Marianna Faggiani, Marco Zugnoni, Matteo Olivero, Salvatore Risitano, Giuseppe Malizia, Silvia Scabini, Marcello Capella, Stefano Artiaco, Simone Sanfilippo, Alessandro Massè
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2025; 15(12): 576. CrossRef - Pathogen-Specific Risk for Iterative Surgical Debridement in Orthopedic Infections: A Prospective Multicohort Analysis
Flamur Zendeli, Anna Jędrusik, Raymond O. Schaefer, David Albrecht, Michael Betz, Felix W. A. Waibel, Tanja Gröber, Nathalie Kühne, Sören Könneker, İlker Uçkay
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(24): 8750. CrossRef
- Personalized Approaches to Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies in Periprosthetic Fracture-Related Infections (PFRIs): Case Series and Literature Review
- 6,290 View
- 239 Download
- 2 Crossref

Original Articles
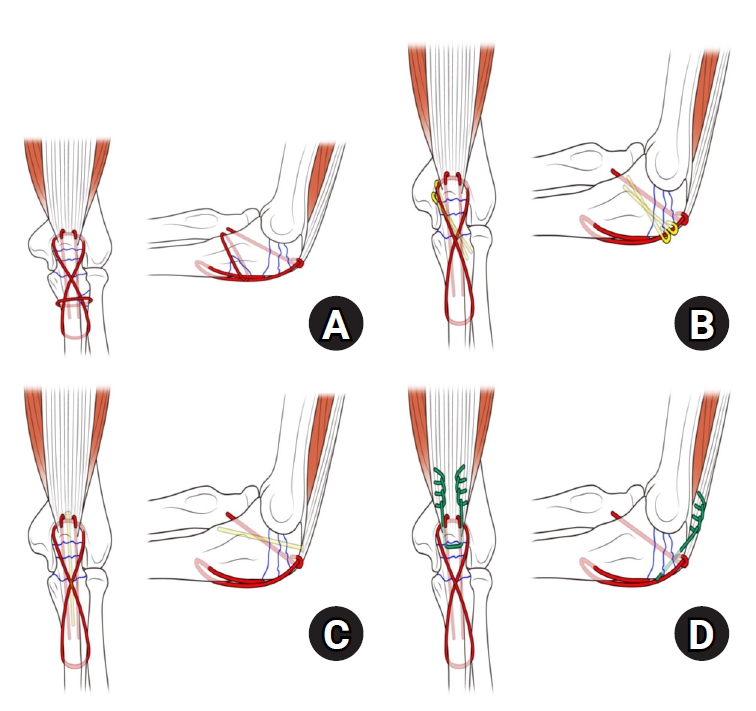
- Comparison of outcomes of reinforced tension band wiring and precontoured plate and screw fixation in the management of Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures
- Hyun Goo Kang, Tong Joo Lee, Samuel Jaeyoon Won
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):96-101. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00059
- Correction in: J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):168
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures are characterized by significant displacement and comminution, presenting a challenge in selecting the appropriate fixation technique. This study compared the clinical and radiographic outcomes, complications, and reoperation rates of reinforced tension band wiring (TBW) and precontoured plate and screw fixation (PF) in the surgical treatment of Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures.
Methods
This retrospective review analyzed 24 patients diagnosed with Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures, who were treated between 2005 and 2023. Of these, 11 patients underwent reinforced TBW, and 13 received precontoured PF. Clinical outcomes were assessed using Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH) scores and the Mayo Elbow Performance Score (MEPS). Radiographic outcomes focused on fracture union. Operative times, complication rates, and reoperation rates were compared between the groups.
Results
Both the reinforced TBW and PF groups achieved satisfactory clinical outcomes, with no significant between-group differences in DASH and MEPS scores (P>0.05). Radiographic union was achieved in all patients. The reinforced TBW group demonstrated a significantly shorter operative time than the PF group (93.6±7.4 min vs. 132.3±13.7 min; P<0.001). Complication rates were similar between the two groups (reinforced TBW, 38.4%; PF, 36.3%), but hardware-related irritation occurred more frequently in the reinforced TBW group. Reoperations were required in 15.8% of the reinforced TBW group due to hardware irritation, whereas no reoperations were necessary in the PF group.
Conclusions
Reinforced TBW and PF are both effective surgical options for managing Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures, yielding comparable clinical and radiographic outcomes. While reinforced TBW offers shorter operative times and lower costs, PF is associated with fewer hardware-related complications. Further prospective studies are needed to optimize treatment strategies for these complex fractures. Level of Evidence: Level III. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Are posterior olecranon locking plates a problem for patients after fracture healing because of prominence?
Reva Qiu, Mallika Makkar, Richard Buckley
Injury.2025; 56(11): 112769. CrossRef
- Are posterior olecranon locking plates a problem for patients after fracture healing because of prominence?
- 2,165 View
- 51 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Reverse V step-cut osteotomy for the correction of cubitus varus in adults: a retrospective study
- Jinyoung Bang, Hyung Jun Koo
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):102-108. Published online April 25, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00045
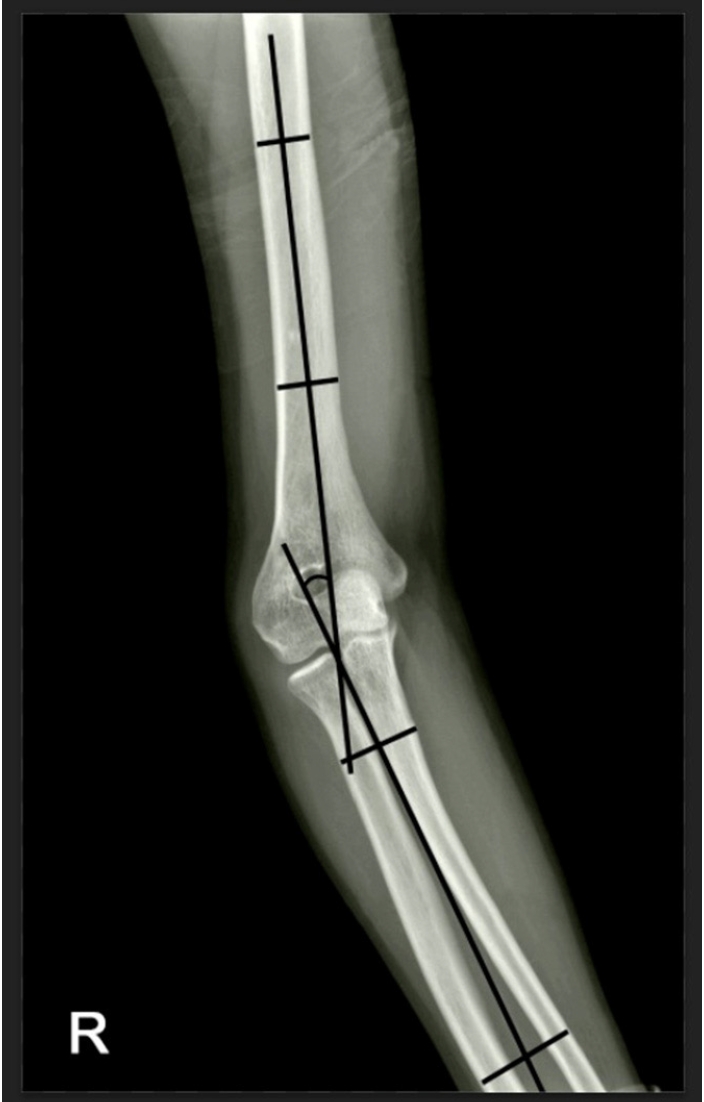
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Cubitus varus deformity in adults most commonly occurs as a late complication resulting from malunion of distal humeral fractures sustained during childhood. This deformity can cause cosmetic problems and anatomical deformities that hinder normal sports activities and potentially lead to long-term complications. Although various surgical techniques exist for correcting cubitus varus, this study investigated the clinical and functional outcomes of reverse V step-cut osteotomy.
Methods
In total, 15 patients underwent surgical treatment with reverse V step-cut osteotomy between 2012 and 2023. The mean age of the patients at the time of surgery was 46.3 years (range, 20–65 years). The preoperative carrying angle was ‒11.09° of varus, which was corrected to +12.81° of valgus postoperatively. The mean preoperative lateral prominence index (LPI) was ‒10.03, and the mean postoperative LPI improved to ‒4.48. A comparison to the unaffected side showed a P-value of 0.978, indicating similarity.
Results
Preoperatively, eight patients exhibited signs of posterolateral rotatory instability, and among them, three underwent concomitant lateral ulnar collateral ligament reconstruction. Seven patients reported ulnar nerve symptoms, and all underwent concurrent ulnar nerve release. Postoperatively, improvements in elbow pain, instability, and ulnar nerve symptoms were observed. One patient required reoperation due to malunion and insufficient correction, but no other complications were noted.
Conclusions
These outcomes demonstrate that reverse V step-cut osteotomy can be an effective treatment method for cubitus varus deformity in adults. Level of evidence: IV.
- 1,747 View
- 51 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS



 First
First Prev
Prev


