Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Articles
- Current concepts and applications of bone graft substitutes in orthopedic surgery
- Jae Ho Cho, Hyung Keun Song
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):169-177. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00248

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Bone defects, which often arise from high-energy injuries, infections, tumor resections, or nonunions, represent a persistent challenge in orthopedic trauma surgery. Autologous bone grafting remains the gold standard due to its unique combination of osteogenic, osteoinductive, and osteoconductive properties. However, issues such as donor site morbidity, limited graft volume, and increased surgical time have driven the development of bone graft substitutes. These substitutes vary widely in origin, composition, biological activity, and mechanical characteristics, encompassing allografts, xenografts, synthetic materials, and biologically enhanced constructs. This review outlines the fundamental biological principles underlying bone regeneration—including osteogenesis, osteoinduction, and osteoconduction—and addresses additional key factors such as biocompatibility, biodegradability, and mechanical strength. Current bone graft materials are classified by biological origin and functional characteristics, with an emphasis on their use in trauma surgery. Particular attention is given to the clinical applications, indications, and limitations of allograft-based solutions (such as structural allografts and demineralized bone matrix), synthetic ceramics (including calcium phosphate and bioactive glass), and biologically enhanced options, such as recombinant growth factors and stem cell therapies. In trauma settings, graft selection must be tailored to the characteristics of the defect, mechanical demands, the biological environment, and patient-specific factors. Integration with surgical technique and fixation is crucial for optimizing outcomes. Although modern substitutes show promise, none fully replicate the complex biology of autografts. Looking ahead, emerging technologies such as 3D printing, nanotechnology, and smart biomaterials offer exciting possibilities but face translational challenges. This review aims to provide practicing orthopedic surgeons with a concise, evidence-based overview of bone substitute options and their roles in trauma care. By applying core biological principles and clinical judgment, surgeons can better navigate the expanding array of graft materials to improve outcomes for patients with complex skeletal defects.
- 3,871 View
- 82 Download

- Treatment of avulsion fractures around the knee
- Jeong-Hyun Koh, Hyung Keun Song, Won-Tae Cho, Seungyeob Sakong, Sumin Lim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):63-73. Published online March 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00073

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Avulsion fractures of the knee occur when tensile forces cause a bone fragment to separate at the site of soft tissue attachment. These injuries, which frequently affect adolescent athletes, can involve the cruciate and collateral ligaments, arcuate complex, iliotibial band, and patellar and quadriceps tendons. Radiographs aid in the initial diagnosis, while computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging facilitate a comprehensive evaluation of injury severity and concomitant damage. Specific avulsion fracture types include: anterior cruciate ligament avulsions (tibial site, Meyers and McKeever classification), posterior cruciate ligament avulsions (tibial attachment, Griffith's classification), Segond fractures (anterolateral complex injury), iliotibial band avulsions, medial collateral ligament avulsions (reverse Segond, Stieda fractures), arcuate complex avulsions ("arcuate sign"), medial patellofemoral avulsions (patellar dislocations), and patellar/quadriceps tendon avulsions. The treatment depends on the fracture location, displacement, and associated injuries. Non-displaced fractures can be managed conservatively, while displaced fractures or those with instability require surgical reduction and fixation. Prompt recognition and appropriate intervention prevent complications such as deformity, nonunion, malunion, and residual instability. This review provides an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management of knee avulsion fractures to guide clinical decision-making.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lateral marginal fractures of the patella and patellofemoral pain
Jae-Ang Sim, Chul-Ho Kim, Ji Wan Kim
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(3): 152. CrossRef
- Lateral marginal fractures of the patella and patellofemoral pain
- 16,897 View
- 185 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Article
- Acute Compartment Syndrome of Thigh: Ten-Year Experiences from a Level I Trauma Center
- Hyung Keun Song, Won-Tae Cho, Wan-Sun Choi, Seung-Yeob Sakong, Sumin Im
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2024;37(4):171-174. Published online October 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2024.37.4.171
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
To assess the demographics, injury mechanisms, treatments, and outcomes of traumatic acute compartment syndrome in the thigh.
Materials and Methods
Patients diagnosed with thigh compartment syndrome were analyzed retrospectively at the authors’ level I trauma center from March 2012 to February 2022. Data were collected from medical and radiological records, focusing on demographics, injury details, treatment timelines, and clinical outcomes.
Results
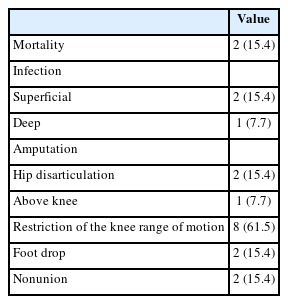
The cohort included 13 patients (11 males and 2 females) with a mean age of 46 years. Injuries primarily resulted from falls (6 patients) and vehicle accidents (5 patients). Fractures were noted in 11 patients, with seven involving the lower extremities and seven having open fractures; three of these were severe enough to be classified as Gustilo–Anderson type IIIc with associated femoral artery injuries. Time from the injury to fasciotomy ranged from within six hours to more than 24 hours. Fasciotomies were mainly single-sided (10 patients), targeting primarily the anterior compartments, and bilateral in three cases. Wound closures were performed using delayed primary closure (four patients) and partial- thickness skin grafts (five patients). Two patients died from multi-organ failure; other complications included infections (three patients), amputations (three patients), and long-term disabilities like drop foot (two patients), sensory deficits, joint stiffness (eight patients), and fracture non-unions requiring additional surgery (two patients).
Conclusion
Thigh-compartment syndrome, though infrequent, poses significant risks of mortality and chronic disability. This underscores the importance of prompt diagnosis and intervention.
- 1,759 View
- 52 Download

Review Article
- Bone Substitutes: From Basic to Current Update
- Jong Seong Han, Hyung Keun Song
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(4):238-244. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.4.238
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Bone substitutes are being used increasingly in bony surgery as more than two million bone grafts are performed worldwide per year. Autobone grafts represent the gold standard for bone grafting, but morbidity and limited availability are the main problems. Allobone grafts are osteoconductive, but there are still concerns regarding the infection risks, costs, and donor availability issues. As an alternative, widely used ceramic-based synthetic bone substitutes are based alternatively on calcium (hydroxyapatite, tricalcium phosphate, calcium sulfate, calcium phosphate). Ceramic-based bone substitutes are osteoconductive, but they are weaker than cortical bone and are not osteoinductive. Bone morphogenic protein, demineralized bone matrix, and platelet-rich plasma are used to obtain an osteoinductive function. Recently, cell-based and gen-based bone substitutes were developed and studied. This paper reviews the basic information and the latest concepts on bone grafts and bone substitutes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Tannic acid-modified magnesium oxychloride bone cement with high water resistance and osteogenic properties
Junying Chen, Yijia Guan, Yue Yang, Tingting Ma, Jinlun Feng, Wenjie Guo, Qifang Wang, Yanru Zhang, Jianguo Liao
Ceramics International.2024; 50(24): 53407. CrossRef - Surface modification of magnesium with a novel composite coating for application in bone tissue engineering
Jorgimara de O. Braga, Diogo M.M. dos Santos, Fernando Cotting, Vanessa F.C. Lins, Nádia M. Leão, Daniel C.F. Soares, Eric M. Mazzer, Manuel Houmard, Roberto B. Figueiredo, Eduardo H.M. Nunes
Surface and Coatings Technology.2022; 433: 128078. CrossRef
- Tannic acid-modified magnesium oxychloride bone cement with high water resistance and osteogenic properties
- 1,069 View
- 12 Download
- 2 Crossref

Original Article
- Treatment of Type IIIb Open Tibial Fractures
- Seong Yeon Lim, Il Jae Lee, Jae Ho Joe, Hyung Keun Song
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(4):267-273. Published online October 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.4.267
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the outcome of treatment for patients with Type IIIb open tibial fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study targeted 35 adult patients for whom follow-up was possible over one year after undergoing surgical treatment. There were 29 males and six females with an average age of 45 years.
RESULTS
Fracture location was proximal in 10 cases, midshaft in 13 cases, and the distal part of the tibia in 12 cases. An average of 10 days was observed for definitive fixation with soft tissue coverage of the injury. The mean time to radiographic union was 27 weeks. Sixteen cases (45.7%) of complications were observed. Three cases of superficial infection, two cases of deep infection, four cases of partial flap necrosis, three cases of mal-alignment, three cases of joint stiffness, and one case of hardware breakage were observed. The mean lower extremity functional scale score was 68.5 and the factors influencing the clinical results were severity of open wound (p=0.000) and occurrence of complications (p=0.000) according to results of multiple regression analysis.
CONCLUSION
In treatment of Type IIIb open tibial fractures, good clinical results can be expected provided that complications are prevented through proper reduction, firm fixation, early soft tissue reconstruction, and early rehabilitation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Korean Medicine Treatments in Patients with Proximal Tibia Fracture: A Retrospective Observational Study
Jung Min Lee, Eun-Jung Lee
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2020; 30(3): 141. CrossRef
- Effect of Korean Medicine Treatments in Patients with Proximal Tibia Fracture: A Retrospective Observational Study
- 1,083 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

Published Erratum
- Erratum: Intermittent Parathyroid Hormone Treatment for Stimulation of Callus Formation in Elderly Patients
- Hyung Keun Song, Sung Jun Kim, Jae Hoo Lee, Kyu Hyun Yang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(2):170-171. Published online April 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.2.170
- Corrects: J Musculoskelet Trauma 2012;25(4):295
- 305 View
- 1 Download

Original Articles
- Intermittent Parathyroid Hormone Treatment for Stimulation of Callus Formation in Elderly Patients
- Hyung Keun Song, Sung Jun Kim, Jae Hoo Lee, Kyu Hyun Yang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(4):295-299. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.4.295
- Correction in: J Musculoskelet Trauma 2013;26(2):170
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of parathyroid hormone (PTH) on fracture healing in elderly patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We analyzed the radiologic results in 14 patients. Group I (n=7) was administrated intermittent PTH after surgical treatment and group II (n=7) was treated only with surgery. We checked the time of initial callus formation, bridging callus formation, and bone union through periodic follow-up radiographs by a radiologist who did not know the patient's information.
RESULTS
The mean time to initial callus formation was 6 weeks for group I, compared with 6.7 weeks for group II. The mean time to bridging callus formation was 15.9 weeks for group I, compared with 23.0 weeks for group II. The mean time to bone union was 28.7 weeks for group I, compared with 41.9 weeks for group II. The difference in the cumulative detection rate (CDR) of the initial callus formation of group I and II was not statistically significant (p=0.793). However, the CDR of the bridging callus formation and bone union for group I were higher than those of group II (p=0.008, p=0.001, respectively).
CONCLUSION
The intermittent PTH administration after surgical treatment and maximum possible preservation of the periosteum in elderly patients accelerates fracture healing. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Advances in Parathyroid Hormone-based medicines
Anne-Laure Bonnet, Lizaveta Aboishava, Michael Mannstadt
Journal of Bone and Mineral Research.2025; 40(11): 1195. CrossRef - Effects of Extracts from Cnidium officinale and Angelica sinensis on Bone Fusion in Mice with Femoral Fracture
Sang Woo Kim, Min-Seok Oh
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2024; 34(2): 1. CrossRef - Timing of osteoporosis therapies following fracture: the current status
Rajan Palui, Harsh Durgia, Jayaprakash Sahoo, Dukhabandhu Naik, Sadishkumar Kamalanathan
Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Postoperative Parathyroid Hormone Administration on Osteoporotic Intertrochanteric Fractures of Females
Hyun Cheol Oh, Ju Hyung Yoo, Joong Won Ha, Yung Park, Sang Hoon Park, Han Kook Yoon
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2020; 55(3): 237. CrossRef - The role of teriparatide in tuberosity healing after reverse shoulder arthroplasty in complex proximal humeral fragility fracture
Bancha Chernchujit, Renaldi Prasetia
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Bone Substitutes and the Advancement for Enhancing Bone Healing
Dong-Hyun Lee, Ji Wan Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2017; 30(2): 102. CrossRef - Current Role and Application of Teriparatide in Fracture Healing of Osteoporotic Patients: A Systematic Review
Sang-Min Kim, Kyung-Chung Kang, Ji Wan Kim, Seung-Jae Lim, Myung Hoon Hahn
Journal of Bone Metabolism.2017; 24(1): 65. CrossRef - The Effect of Teriparatide on Fracture Healing of Osteoporotic Patients: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Shenghan Lou, Houchen Lv, Guoqi Wang, Licheng Zhang, Ming Li, Zhirui Li, Lihai Zhang, Peifu Tang
BioMed Research International.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - A systematic review on the use of daily subcutaneous administration of teriparatide for treatment of patients with osteoporosis at high risk for fracture in Asia
J.F. Chen, K. H. Yang, Z.L. Zhang, H.C. Chang, Y. Chen, H. Sowa, S. Gürbüz
Osteoporosis International.2015; 26(1): 11. CrossRef
- Advances in Parathyroid Hormone-based medicines
- 675 View
- 8 Download
- 9 Crossref

- T Plate Fixation for Unstable Fracture of Distal Clavicle
- Ho Jung Kang, Kwan Kyu Park, Hong Kee Yoon, Hyung Keun Song, Soo Bong Hahn
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(3):329-334. Published online July 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.3.329
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To review clinical and radiological results after open reduction and internal fixation with T plate for unstable distal clavicle fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From July. 1999 to December 2002, nine patients with distal clavicle Neer type II fractures were treated by open reduction and internal fixation with T plate. The bony union was confirmed by plain radiography. The clinical results were analyzed according to the classification by Kona et al.
RESULTS
Average time to fracture union was 8 weeks in all cases. The functional results were as follows: excellent in 7 cases and good in 2 cases. Screw loosening occurred in one case, but bony union was achieved.
CONCLUSION
We recommend T plate fixation as another treatment method for unstable distal clavicle fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Usefulness of the Additional K-Wire Fixation and Suture for Reinforce the Treatment of Distal Clavicle Fracture Using Modified Tension Band Wiring
Seung-Bum Chae, Chang-Hyuk Choi, Dong-Young Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2016; 29(2): 107. CrossRef - Treatment of Distal Clavicle Fracture Using Hook Plate
Su-Han Ahn, Hyeong-Jo Yoon, Kwang-Yeol Kim, Hyung-Chun Kim, In-Yeol Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(1): 48. CrossRef - The Surgical Outcomes of Clavicle Lateral End Fractures Fixed with the Oblique T Locking Compession Plate
Seung-Oh Nam, Young-Soo Byun, Dong-Ju Shin, Jung-Hoon Shin, Chung-Yeol Lee, Tae-Gyun Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(1): 41. CrossRef - Results of Hook Plate Fixation of Unstable Distal Clavicle Fractures
Hoon-Sang Sohn, Byung Chul Jo
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(4): 335. CrossRef - Modified Spring Plate for Treatment of Unstable Distal Clavicle Fractures
Sang-Myung Lee, Il-Jung Park, Hyung-Min Kim, Jae-Chul Park, Sung-Gil Cho, Yoon-Chung Kim, Seung-Koo Rhee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(1): 64. CrossRef - Double Tension Band Wire Fixation for Unstable Fracture of the Distal Clavicle
Kyeong-Seop Song, Hyung-Gyu Kim, Byeong-Mun Park, Jong-Min Kim, Sung-Hoon Jung, Bong-Seok Yang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(1): 24. CrossRef
- Usefulness of the Additional K-Wire Fixation and Suture for Reinforce the Treatment of Distal Clavicle Fracture Using Modified Tension Band Wiring
- 522 View
- 0 Download
- 6 Crossref


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


