Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Association between decreased bone mineral density and Pauwels angle in femoral neck fractures: a cross-sectional study
- Soo-Hwan Jung, Yong-Uk Kwon, Ji-Hun Park
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2026;39(1):20-29. Published online January 25, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00269
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
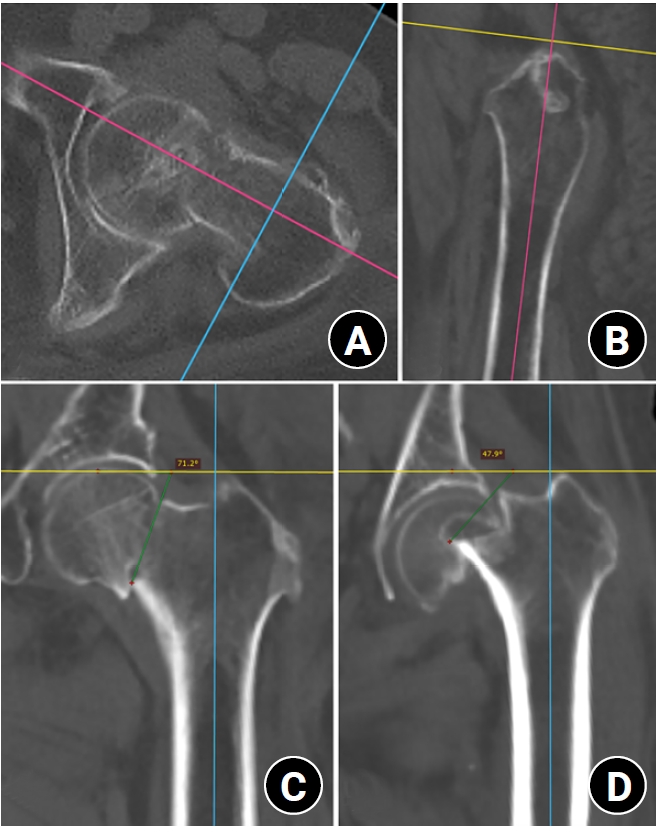
Progressive osteoporosis reduces the trabecular structures of the proximal femur, whereas the primary compression trabeculae (PCTs) are relatively preserved. We hypothesize that the loss of the vertically oriented PCTs in osteoporosis, which act as a mechanical barrier, affects fracture line propagation and influences the Pauwels angle. This study investigated the association between bone mineral density (BMD) and Pauwels angles in low-energy femoral neck fractures (FNFs).
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 150 patients (mean age, 75.3 years; range, 50–94 years) diagnosed with intracapsular FNFs between May 2019 and May 2023. BMD was measured within 1 month of the injury date using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, and modified Pauwels angles were assessed using a computed tomography-based multiplanar reconstruction program. Multiple linear regression analysis was performed to evaluate the factors influencing the Pauwels angles. The dependent variable was the Pauwels angle, while the independent variables included sex, age, height, body weight, body mass index, American Society of Anesthesiologists score, Charlson comorbidity index score, smoking status, alcohol use, preinjury walking ability, and femoral neck BMD T-scores.
Results
Higher femoral neck BMD T-scores were significantly associated with increased Pauwels angles (β=3.449, P<0.001). Greater body weight was independently associated with increased Pauwels angles (β=0.213, P=0.007).
Conclusions
The Pauwels angle demonstrated a significant association with BMD, with lower BMD associated with less steep Pauwels angles. In the absence of BMD measurement, the Pauwels angle may indicate osteoporosis severity in patients with low-energy FNFs. Level of evidence: III.
- 111 View
- 3 Download

- Computed tomography plane reformatting to reduce projection error in measuring Pauwels angle of femoral neck fractures: a cross-sectional study
- Gyu Min Kong, Jae-Young Lim, Se-Lin Jeong, Gu-Hee Jung
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2026;39(1):38-47. Published online January 25, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00038
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
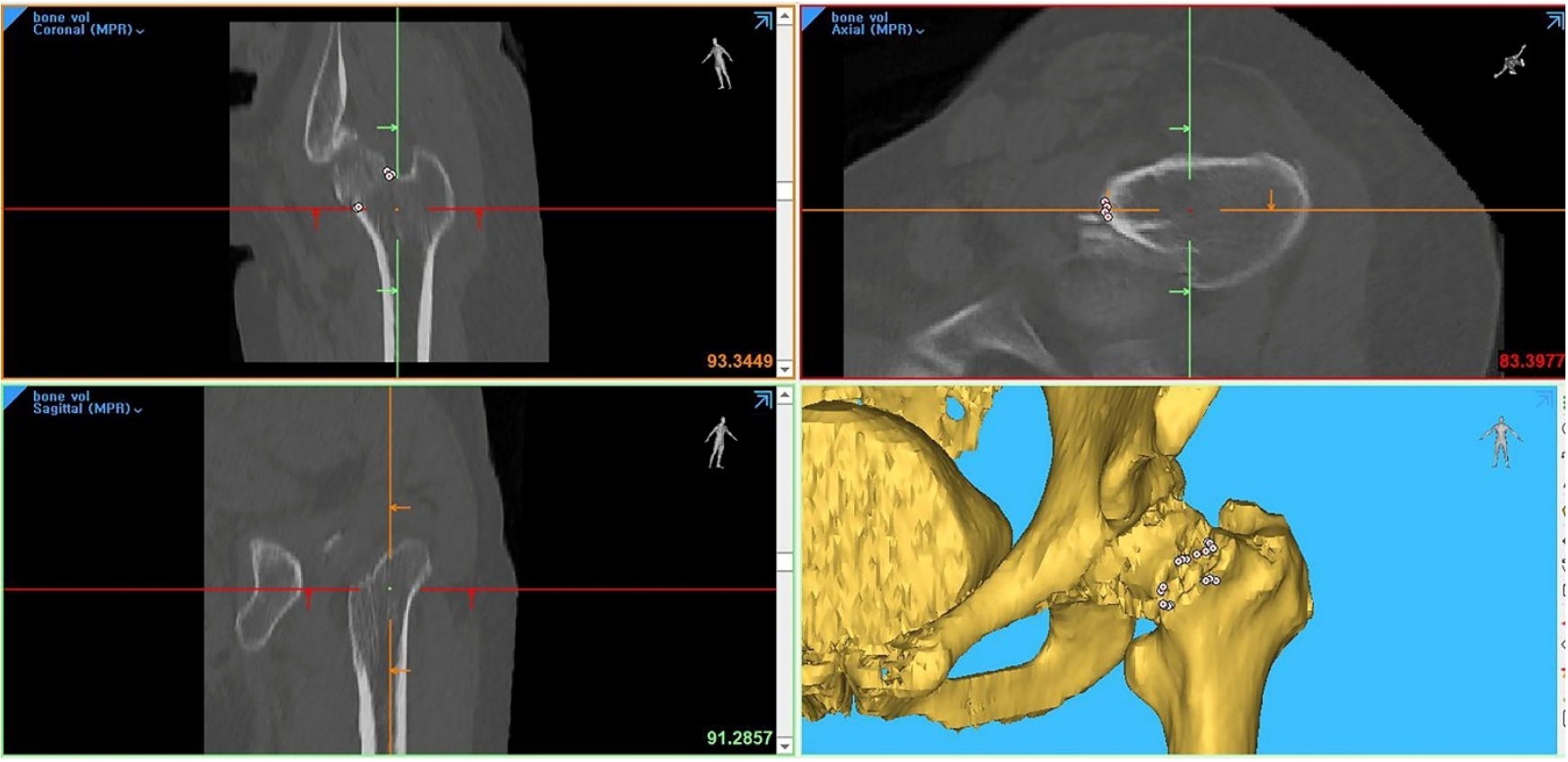
This study aimed to assess fracture verticality in both coronal and axial planes after eliminating projection error in femoral neck fractures among non-older adults, and to demonstrate its clinical utility using computed tomography (CT)-based modeling at actual size.
Methods
This retrospective observational study enrolled 57 patients (30 males and 27 females), aged 20–65 years, with displaced femoral neck fractures. Based on CT images, an actual-size fracture model was constructed. The CT scanning plane was reformatted with the neck-shaft fragment realigned vertically to the ground and parallel to the femoral neck axis. Three consecutive images were used to generate coronal reformats at the centerline and posterior border to measure central and posterior coronal plane verticality as Pauwels’ angle (PA). The central image of the reformatted axial plane was used to assess axial plane verticality. Differences in verticality were analyzed using analysis of variance.
Results
Three coronal morphology types were identified: linear (n=30), concave (n=25), and convex (n=2). Two axial morphology types were observed: cephalad (n=35) and trochanteric (n=22). The mean central PA, posterior PA, and axial verticality were 55.43°±13.79°, 51.44°±11.13°, and 85.74°±18.41°, respectively. Only the central PA showed a significant difference (P<0.001). The PA was significantly higher in the linear coronal type between images (P<0.05) and in the trochanteric axial type (P<0.05).
Conclusions
After reformatting the scanning plane, the central PA showed significant variation between images. Femoral neck fractures of the linear type in the coronal plane and the trochanteric type in the axial plane demonstrated greater verticality than other morphological types. Level of evidence:
- 115 View
- 4 Download

- Comparative results of the femoral neck system versus the dynamic hip screw for stable femoral neck fractures in older adults in Korea: a retrospective cohort study
- Byung-Chan Choi, Byung-Woo Min, Kyung-Jae Lee, Jun-Sik Hong
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):203-211. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00276
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This study aimed to compare the clinical and radiological outcomes of the femoral neck system (FNS) and the dynamic hip screw (DHS) for the internal fixation of stable femoral neck fractures in older adults.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study included 48 matched older adult patients based on sex, age, BMI, and osteoporosis status, who had undergone internal fixation with either FNS or DHS for stable femoral neck fractures between January 2010 and December 2022. To minimize selection bias, a 1:1 case-control matching was performed based on sex, age, body mass index (BMI), and the presence of osteoporosis. A total of 48 patients (24 in each group) were included. We compared perioperative data (operation time, hemoglobin change, transfusion rate), functional outcomes using the Koval score, and radiological outcomes, including union rate, femoral neck shortening, and complication rates.
Results
The mean operation time was significantly shorter in the FNS group than in the DHS group (60.9 minutes vs. 70.8 minutes; P=0.007). There were no statistically significant differences between the two groups in the union rate (87.5% in FNS vs. 95.8% in DHS), femoral neck shortening, final Koval score distribution, or overall complication rates (12.5% in both groups).
Conclusions
For treating stable femoral neck fractures in older adults, the FNS demonstrated comparable clinical and radiological outcomes to the DHS, with the distinct advantage of a shorter operation time. While these findings suggest that the FNS is a promising and safe alternative that may reduce the surgical burden, definitive conclusions are precluded by the small sample size, warranting further research to corroborate these results. Level of evidence: IV.
- 1,622 View
- 20 Download

- Risk factors of surgical complications after use of the femoral neck system: a random forest analysis
- Chul-Ho Kim, Hyun-Chul Shon, Han Soul Kim, Ji Wan Kim, Eic Ju Lim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):160-167. Published online July 23, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00157
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The femoral neck system (FNS), a novel fixation device for managing femoral neck fractures (FNFs), has gained popularity in recent years. However, analyses of the surgical complications and reoperation risks associated with the use of FNS remain limited.
Methods
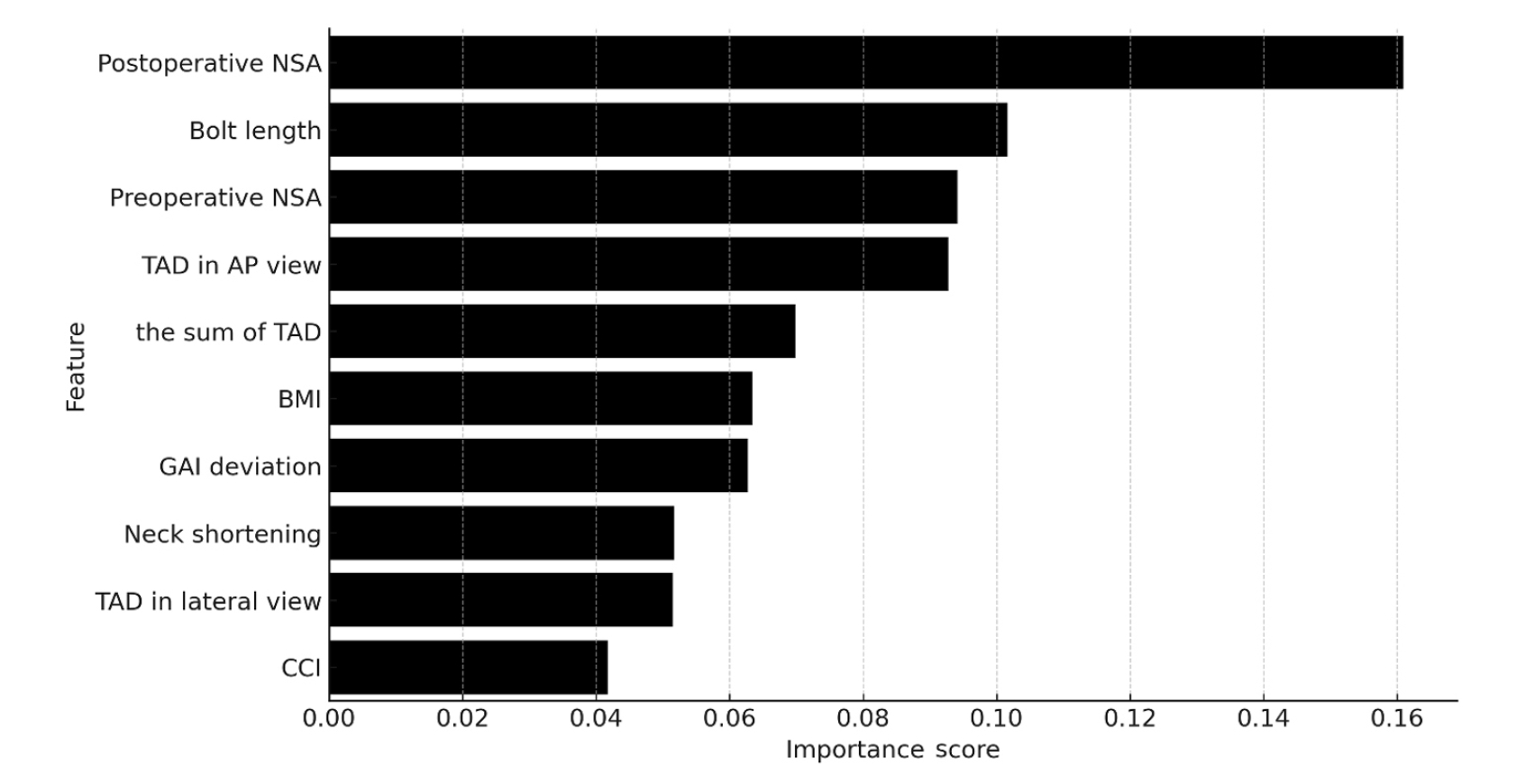
This retrospective observational study analyzed 57 patients who had undergone FNS fixation for FNF at two university hospitals between July 2019 and February 2024. Demographic, perioperative, and outcome variables, including age, sex, fracture classification (Garden, Pauwels, and AO), implant characteristics, tip-apex distance (TAD), neck shortening, and neck-shaft alignment, were analyzed. In addition to univariate analysis, a machine learning analysis was conducted using a random forest classifier with stratified sampling (80% training, 20% testing). The accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and area under the receiver’s operating curve were calculated to assess model performance.
Results
Ten patients experienced osteonecrosis of the femoral head (n=6), implant cut-out or penetration (n=3), and peri-implant fracture (n=1). Univariate analysis revealed that the TAD in the complication group was significantly shorter than that in the control group (12.1 vs. 16.7 mm; P=0.012). Additionally, neck shortening in the complication group was greater than that in the control group (4.9 vs. 2.3 mm; P=0.011). The random forest model achieved an accuracy of 83.3% and identified postoperative neck-shaft angle (NSA) as the most important predictor of complications (feature importance, 0.161), followed by bolt length (0.102) and preoperative NSA (0.094).
Conclusions
Risk factor analysis conducted using a random forest model identified postoperative NSA as the most important feature associated with postoperative complications following FNS. Therefore, care should be taken to normalize the postoperative NSA during FNF surgery. Level of Evidence: III. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Length-stable fixation reduces femoral neck shortening in unstable femoral neck fractures: A retrospective comparative study of length-stable dynamic hip screw versus femoral neck system fixation
Seonghyun Kang, Wonseok Choi, Jeong Seok Choi, Eic Ju Lim, SungJin Ahn, Jong-Keon Oh, William T. Kent, Whee Sung Son, Jae-Woo Cho
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Length-stable fixation reduces femoral neck shortening in unstable femoral neck fractures: A retrospective comparative study of length-stable dynamic hip screw versus femoral neck system fixation
- 1,191 View
- 43 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review Article
- Osteoporotic Hip Fracture: How We Make Better Results?
- Byung-Chan Choi, Kyung-Jae Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(1):52-59. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.1.52
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The prevalence of osteoporosis and incidence of osteoporotic fractures is increasing gradually as life expectancy is prolonged and the aged population increases. Osteoporotic hip fractures (femoral neck fractures and femoral intertrochanteric fractures) have high mortality because the patients with these fractures are elderly and have several comorbidities. Thorough preparation and a multidisciplinary approach in the preoperative period are critical, and early surgery is recommended. There are also several principles to treat osteoporotic hip fractures and prevent fixation failures. Many studies have suggested various treatment methods for femoral neck fractures and femoral intertrochanteric fractures. Functional recovery treatment is essential based on the patient’s health and activity levels. Finally, aggressive management of osteoporosis and the prevention of falling is needed to treat osteoporotic hip fractures successfully.
- 630 View
- 24 Download

Original Articles
- Comparison of Clinical Outcomes for Femoral Neck System and Cannulated Compression Screws in the Treatment of Femoral Neck Fracture
- Jae Kwang Hwang, KiWon Lee, Dong-Kyo Seo, Joo-Yul Bae, Myeong-Geun Song, Hansuk Choi
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(3):77-84. Published online July 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.3.77
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study compared the clinical and radiological results of the femoral neck system (FNS) and cannulated compression screws (CCS) for the fixation of femoral neck fractures.
Materials and Methods
Patients who underwent FNS or CCS internal fixation for femoral neck fractures between January 2016 and January 2022 were analyzed retrospectively. The hip joint function using the Harris hip score (HHS) was evaluated three months and one year after surgery. The operation time, fracture healing time, and associated surgical complications in the two groups were compared and analyzed statistically.
Results
Seventy-nine patients were categorized into 38 FNS and 41 CCS groups. The FNS group had a longer operation time and higher postoperative HHS at three months (p<0.01). Femoral neck shortening was lower in the FNS group (p=0.022). There were no significant differences in the fracture healing time and other complications.
Conclusion
There were no differences in most clinical outcomes and complications between the two groups except for the three-month HHS and femoral neck shortening. This study suggests that FNS could be an alternative to CCS for treating femoral neck fractures.
- 977 View
- 19 Download

- Computational Simulation of Femoral Neck System and Additional Cannulated Screws Fixation for Unstable Femoral Neck Fractures and the Biomechanical Features for Clinical Applications
- Ju-Yeong Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(1):1-9. Published online January 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
To identify the biomechanical features for clinical applications through a computational simulation of the fixation of the Femoral Neck System (FNS) with additional cannulated screws for a Pauwels type III femoral neck fractures.
Materials and Methods
Thirty cadaveric femurs underwent computed tomography, and the images were transferred to the Mimics ® program, resulting in three-dimensional proximal femur models. A three-dimensional scan of the FNS and 6.5 mm and 7.0 mm cannulated screws was performed to enable computerized virtual fixation of FNS with additional cannulated screws for unstable femoral neck fractures. Furthermore, the cannulated screw used for additional fixation was modeled and used as a cylinder within the Ansys program. The biomechanical characteristics of these models were investigated by applying a physiological load virtually.
Results
The maximum von Mises stress value at bone was 380.14 MPa in FNS and 297.87 MPa in FNS+7.0 mm full-thread cannulated screw. The maximum von Mises stress value at FNS was 786.83 MPa in FNS and 435.62 MPa in FNS+7.0 mm full-thread cannulated screw. The FNS group showed the highest maximum von Mises stress values at bone and FNS. For total deformation, the maximum deformation value was 10.0420 mm in FNS and 9.2769 mm in FNS+7.0 mm full-thread cannulated screws. The FNS group represented the highest maximum deformation compared to the other groups.
Conclusion
Considering the anatomical spatiality and biomechanical characteristics of the FNS in unstable femoral neck fractures, when one 7.0 mm full thread cannulated screw was also fixed to the anterosuperior portion of the FNS, significant biomechanical stability was demonstrated.
- 737 View
- 10 Download

Review Article
- Pediatric Femoral Neck Fracture
- Joo Hyung Han, Hoon Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2021;34(1):34-43. Published online January 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2021.34.1.34
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pediatric femoral neck fracture is an uncommon injury with a high complication rate, regardless of the appropriate diagnosis and management. The bony anatomy and blood supply of the proximal femur in a skeletally immature patient differ from those in adult patients. Generally, these fractures result from high-energy trauma, but pathologic hip fractures also occur, usually from low-energy trauma. Pediatric femoral neck fractures are categorized using the Delbet classification system. This classification guides management and aids clinicians in determining the risk of avascular osteonecrosis. The ideal surgical treatment is determined by the fracture type and the age of the patient. Reduction, which is achieved using a closed or open procedure, combined with stable fixation and/or cast immobilization, is recommended for most of these fractures. Anatomical reduction within 24 hours from the injury may result in a good surgical outcome. Although the effects of capsular decompression after reduction and fixation have not been established, decompression is easy to perform and may reduce the risk of avascular necrosis. Despite appropriate management, osteonecrosis can occur after all types of pediatric femur neck fractures. Other complications include coxa vara, nonunion, and premature physeal arrest.
- 1,369 View
- 29 Download

Original Article
- Clinical Outcomes and Radiologic Characteristics of Insufficiency Femoral Neck Fracture in Elderly Patients
- Hee-Uk Ye, Kyung-Jae Lee, Byung-Woo Min, Kyung-Hwan Lim, Beom-Soo Kim, Young-Hoon Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2021;34(1):1-7. Published online January 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2021.34.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
In elderly patients, femoral neck insufficiency fractures that occur without a history of trauma are difficult to diagnose and treat, so it is emphasized that early suspicion of fractures and additional diagnostic tests are conducted. Materials and Methods: Between December 2010 to December 2019, 12 femoral neck insufficiency fractures (group 1) were evaluated by comparing them with 50 traumatic femoral neck fractures of a similar age. Along with demographic data, neck cortical thickness, shaft cortical thickness, head diameter, neck width, trochanter width, shaft width, neck-shaft angle, hip axis length, femoral neck index on the simple radiographic image were compared. Results: Seven of the 12 cases were non-displaced fractures, and it took an average of 19.2 days to diagnose the fracture after the symptoms occurred. The height was smaller than the control group at 149.1 cm in group 1 and 157.2 cm in group 2 (p<0.001). The cortical thickness of the medial femoral neck showed significant differences between the two groups: 3.16 mm in group 1 and 4.11 mm in group 2 (p=0.004). There was no statistical difference in the other measurements. Conclusion: Femoral neck insufficiency fracture often has a delayed diagnosis because of the characteristics of the fracture. The cortical thickness of the medial femoral neck in simple radiographic images can help suspect femoral insufficiency fractures in elderly patients when considered with detailed medical history taking and a physical examination.
- 622 View
- 11 Download

Case Reports
- Rare Experience of Bilateral Femoral Neck and Shaft Fractures - A Case Report -
- DaeHyun Choe, Jae-Ho Lee, Ki-Chul Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(3):154-158. Published online July 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.3.154
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ipsilateral fractures of the femoral neck and shaft are relatively common injuries and accompany 2% to 9% of all femoral shaft fractures. On the other hand, it is extremely rare for these injuries to occur bilaterally. This paper reports the authors’ experience of a case with bilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures. The patient sustained multiple injuries, including liver laceration with hemoperitoneum, bilateral open fractures of the tibia, and bilateral femoral neck, and shaft fractures caused by a high-speed motor vehicle accident. Under the circumstances, damage-control orthopedic principles were applied, and external fixators were initially placed. After the patient’s general condition showed improvement, both femurs were fixed with a reconstruction nail. Fracture healing was achieved without complications, such as avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Despite the rare occurrence, this paper describes this case because these injuries must be managed with meticulous attention.
- 523 View
- 8 Download

- Insufficiency Fracture of the Femoral Neck after Intramedullary Nailing for the Treatment of Atypical Femoral Fracture - A Case Report -
- Nam Hoon Moon, Jae Hoon Jang, Tae Hyuk Hwang, Ki Young Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(4):258-264. Published online October 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.4.258
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Although several publications have reported delayed or non-union, there is a consensus that the standard treatment for atypical femoral fracture (AFF) is an intramedullary nailing. However, no case of tensile insufficiency fracture of femoral neck associated with intramedullary nailing in patients with AFF have been reported. Here, we report an 82-year-old woman with tensile type of insufficiency fracture of the femoral neck after intramedullary nailing for the treatment of AFF.
- 463 View
- 4 Download

Original Articles
- Treatment for Concurrent Ipsilateral Femoral Neck and Shaft Fractures Using Reconstruction Nail with Temporary K-Wires
- Sang Joon Lee, Sang Hong Lee, Sang Ho Ha, Gwang Chul Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2015;28(1):23-29. Published online January 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.1.23
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the results of operative treatment using a reconstruction nail after temporary K-wire fixation of the femoral neck for ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 11 cases were treated, which were followed-up for more than two years, between August 2007 and July 2012. The average age was 51 years (29-69 years) and men were dominant counting eight cases. All cases were operated with a reconstruction nail after temporary K-wire fixation of the femoral neck. Bone union periods, alignment, etc. were evaluated by radiological methods and accompanying damage and complications were also investigated. Functional evaluation was performed in accordance with Friedman and Wyman criteria at the last follow-up.
RESULTS
The average time for union of the femoral shaft was 22.5 weeks (12-32 weeks), and femoral neck was 13.1 weeks (8-20 weeks). There was no nonunion, and four femoral shaft fractures resulted in delayed union. There was one case of leg length discrepancy more than 2 cm long, but malalignment of more than 10 degrees was not observed. Avascular necrosis of the femoral head did not occur. Functional results were good in eight cases, fair in two cases, and poor in one case.
CONCLUSION
Treatment with reconstruction nailing after temporary K-wire fixation of the femoral neck is thought to be a good method which prevents neck displacement and has low complication rates.
- 649 View
- 6 Download

- Internal Fixation for Femoral Neck Fracture in Patients between the Ages of Twenty and Forty Years
- Ui Seoung Yoon, Jin Soo Kim, Hak Jin Min, Jae Seong Seo, Jong Pil Yoon, Joo Young Chung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2010;23(1):1-5. Published online January 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To retrospectively analysis of results of operatively treatment for femoral neck fracture occurred in twenties to thirties.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
20 patients were selected whom we were able to follow up at least 2 years after internal fixation for femoral neck fracture in twenties to thirties from 1998 to 2005. Mean age was 32.2 (21~39) and average follow up period was 26.3 (24~45) months. According to preoperative X-ray, there were 6 cases for Garden classification stage I, 10 for stage II and 4 for stage III, and 7 cases for subcapital fracture, 9 for transcervical fracture, 4 for basicervical fracture. In all cases, operations were performed within 12 hours after the injury. The operations were done after satisfying reduction with the Garden alignment index, with three cannulated screws for internal fixation. Postoperative results were analyzed by clinical symptoms and radiological examinations during follow up periods.
RESULTS
In immediately postoperative radiological examination, satisfying anatomical reduction with Garden alignment index was obtained in all cases, and unions were obtained within 4.5 months after the operation (3~6 month). Avascular necrosis of femoral head occurred in 7 cases of all patients (35.0%). The average time of occurrence of avascular necrosis of femoral head after operation was 10.7 months (9~15 months). Avascular necrosis was occutted 5 (31.3%) in fracture without displacement (Garden stage I, II), 2 (50.0%) in fracture with displacement (Garden stage III) and 4 in subcapital fracture, 3 in transcervical fracture.
CONCLUSION
The incidence of avascular necrosis of femoral head after the operation for displaced and nondisplaced femoral neck fracture between twenties and forty years was no significant difference. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Clinical Outcomes for Femoral Neck System and Cannulated Compression Screws in the Treatment of Femoral Neck Fracture
Jae Kwang Hwang, KiWon Lee, Dong-Kyo Seo, Joo-Yul Bae, Myeong-Geun Song, Hansuk Choi
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2023; 36(3): 77. CrossRef
- Comparison of Clinical Outcomes for Femoral Neck System and Cannulated Compression Screws in the Treatment of Femoral Neck Fracture
- 1,478 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Factors Predicting Complications after Internal Fixation of Femoral Neck Fractures
- Tae Ho Kim, Jong Oh Kim, Sung Sik Kang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(2):79-84. Published online April 30, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.2.79
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the factors predicting complications after internal fixation using multiple cannulated screws in the patients with femoral neck fracture, the authors performed a comparative study of a success group and a failure group and reviewed the literature.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sixty-eight patients with intracapsular femoral neck fractures were treated by multiple pinning from January 2000 to July 2007 and followed up more than one year. Relationships between the complications such as failure of union, collapse of femoral head due to osteonecrosis of femoral head and several affecting factors including the degree of displacement by Garden stage, state of reduction, position of screws, patient's age, time interval from injury to operation, anatomical fracture site and two weeks postoperative (99m)Tc-MDP bone scan were analyzed.
RESULTS
Statistically significant factors were the degree of displacement by Garden stage (p<0.001), reduction state (p<0.001) and postoperative two weeks (99m)Tc-MDP bone scan (p<0.001).
CONCLUSION
An accurate anatomical reduction is needed to decrease complications with multiple cannulated screws fixation of femoral neck fracture. Displacement of fracture by Garden stage and (99m)Tc-MDP bone scan are major factors predicting complications.
- 911 View
- 1 Download

- Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty for the Femoral Neck Fractures in Elderly Patients
- Woong Kyo Jeong, Sang Won Park, Soon Hyuck Lee, Jong Hoon Park, Suk Ha Lee, Ji Hoon Kang, Gi Won Choi, Won Noh
- J Korean Fract Soc 2008;21(1):8-12. Published online January 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.1.8
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the clinical results of bipolar hemiarthroplasty in elderly patients more than 65 years of age with a femoral neck fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Forty-six bipolar hemiarthroplasties in 43 patients more than 65 years of age which could be followed more than 3 years were included in this study. The clinical outcomes were evaluated using Harris hip score, pain score and support score. The radiological results were analyzed by femoral stem loosening and bipolar cup migration.
RESULTS
The average Harris hip score was 88.7 (62~96) points. An excellent score was recorded in 34 cases, good in 7 cases, fair in 3 cases and poor in 2 cases. The average pain score was 39.3 points and there were no pain in 20 cases, slight pain in 17 cases, mild pain in 6 cases and moderate pain in 2 cases. The average support score was 9.6 points and 32 patients could walk without the use of any assistive devices. Two cases were converted to total hip arthroplasty due to femoral stem loosening with or without bipolar cup migration.
CONCLUSION
For the early ambulation and functional recovery of elderly patients with femoral neck fracture, bipolar hemiarthroplasty was considered as one of recommendable methods.
- 757 View
- 7 Download

- Comparison of Operative Methods between Retrograde and Antegrade Nailing for Ipsilateral Femoral Shaft and Neck Fracture
- Chang Wug Oh, Jong Keon Oh, Woo Kie Min, Shin Yoon Kim, Seung Hoon Baek, Byung Chul Park, Hyung Soo Ahn, Tae Gong Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(2):135-140. Published online April 30, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.2.135
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To compare retrospectively the antegrade and retrograde nailing in the management of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty-two patients (thirty-three injuries) were included in this study. Mean age of patients was 38 years-old in the antegrade nailing group (16 injuries) and 44 years-old in the retrograde nailing group (17 injuries). We compared the union of fractures and complications between two groups, and investigated the influencing factors.
RESULTS
Femoral shaft fracture was united in 10 cases (63%) of antegrade group and 12 cases (71%) of retrograde group, at 28.2 and 27.3 weeks respectively. Nonunion was more prevalent in Winquist-Hansen III and IV (5 in antegrade nailing, 3 in retrograde nailing) than I and II. Femoral neck fracture was united with 1 case of nonunion in each group. Nonunion developed from Garden stage IV, but fractures of Garden stage I and II united regardless of methods.
CONCLUSION
In ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures, the kinds of methods did not affect the results of shaft fractures. Minimally displaced neck fractures also were not influenced by kinds of methods, but retrograde nailing may have a benefit in fixing the displaced neck fractures -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surgical management of bifocal femoral fractures: a systematic review and pooled analysis of treatment with a single implant versus double implants
J. D. Cnossen, Esther M. M. Van Lieshout, Michael H. J. Verhofstad
Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery.2023; 143(10): 6229. CrossRef - Retrograde Intramedullary Nailing or the Treatment of Segmental Femoral Shaft Fracture Including Distal Part
Jong-Ho Yoon, Byung-Woo Ahn, Chong-Kwan Kim, Jin-Woo Jin, Ji-Hoon Lee, Hyun-Ku Cho, Joo-Hyun Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(3): 145. CrossRef - The Treatment of IM Nailing of Femoral Shaft Fracture: Piriformis Fossa versus Trochanteric Entry Portal
Hyun Kook Youn, Oog Jin Shon, Dong Sung Han
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2008; 21(3): 200. CrossRef
- Surgical management of bifocal femoral fractures: a systematic review and pooled analysis of treatment with a single implant versus double implants
- 714 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Analysis of Affecting Factors of Fixation Failure of Femoral Neck Fractures Using Internal Fixation
- Soo Jae Yim, Seung Han Woo, Min Young Kim, Jong Seok Park, Eung Ha Kim, Yoo Sung Seo, Byung Il Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(3):297-302. Published online July 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.3.297
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the factors which influence on the fixation failure after internal fixation using multiple cannulated screws in the patients with femoral neck fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Ninty-six patients (male: 63, female: 33) who underwent closed reduction and internal fixation of femoral neck fracture between Feb. 1994 and Jun. 2002 with use of multiple cannulated screws. The mean age was 68 years (17~90) and mean follow-up period was average 50 months (36 months~6 years). The fixation failure was defined by change in fracture position above 10 mm, change in each screws position above 5%, backing above 20 mm, or perforation of the head, respectively. They were evaluated with the age, gender, fracture type, accuracy of reduction, placement of screws, posterior comminution and also studied the risk factors which influenced nonunion and the development of avascular necrosis.
RESULTS
Twenty-four patients out of 96 patients had radiographic signs of fixation failure. The incidence of nonunion in the fixation failure group was 41% (10/24) and AVN was 33% (8/24). There were statistically significant correlations between fixation failure and nonunion and that posterior comminution, poor reduction and improper placement of the screws were the major factors contributing to nonunion.
CONCLUSION
In case of femoral neck fracture of internal fixation using multiple cannulated screws, posterior comminution, poor reduction and improper placement of the screws were the major factors contributing to nonunion and fixation failure. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Results of Internal Fixation of Subcapital Femoral Neck Fractures
Joon Soon Kang, Kyoung Ho Moon, Joong Sup Shin, Eun Ho Shin, Chi Hoon Ahn, Geon Hong Choi
Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery.2016; 8(2): 146. CrossRef - Internal Fixation for Femoral Neck Fracture in Patients between the Ages of Twenty and Forty Years
Ui-Seoung Yoon, Jin-Soo Kim, Hak-Jin Min, Jae-Seong Seo, Jong-Pil Yoon, Joo-Young Chung
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(1): 1. CrossRef - Factors Predicting Complications after Internal Fixation of Femoral Neck Fractures
Tae-Ho Kim, Jong-Oh Kim, Sung-Sik Kang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(2): 79. CrossRef
- Clinical Results of Internal Fixation of Subcapital Femoral Neck Fractures
- 734 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Factors Predisposing to Complications After Internal Fixation of Femoral Neck Fracture
- Sang Won Park, Chang Yong Hur, Jong Ryoon Baek, Seong Jun Park
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(4):441-446. Published online October 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.4.441
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analyze the factors predisposing to complications after internal fixation of femoral neck fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed retrospectively the results of percutaneous internal fixation of femoral neck fracture using multiple pinning, in 52 cases who were treated from Jan. 1996 to Dec. 2001. Relationship between the complications and several factors such as the age, sex, time interval from injury to operation, Garden stage, Singh index, internal fixation device and state of redction were analyzed.
RESULTS
The functional results by Lunceford criteria were excellent in 23 cases (44%), good in 15 cases (29%), fair in 2 cases (3.8%) and poor in 12 cases (23.1%). The avascular necrosis of the femoral head were occured in 14 cases (26.9%). Among these, 1 case of non-union, 2 cases of mal-union were accompanied. No stastically significant relationship between the age, sex, time interval from injury to operation, Garden stage, Singh index, internal fixation device, state of redction and complication. However, there was 4 times higher complication rate in Garden stage 3 or 4 group than its rate in Garden stage 1 (odds ratio 3.889), and 3 times higher complication rate in non-anatomical reduction group (odds ratio 3.22).
CONCLUSION
Factors predisposing to complications after internal fixation of femoral neck fracture seemed to closely relate with Garden stage and state of reduction. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty for the Femoral Neck Fractures in Elderly Patients
Woong-Kyo Jeong, Sang-Won Park, Soon-Hyuck Lee, Jong-Hoon Park, Suk-Ha Lee, Ji-Hoon Kang, Gi-Won Choi, Won Noh
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2008; 21(1): 8. CrossRef
- Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty for the Femoral Neck Fractures in Elderly Patients
- 575 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Report
- Femoral Neck Fracture in Bilateral Above Knee Amputee: A Case Report
- Kye Young Han
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(1):116-119. Published online January 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.1.116
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Femoral neck fracture is a common fracture in elderly or osteoporotic women. But femoral neck fracture in previously amputed patients is rare, so the guideline of appropriate treatment is rarely discussed. Especially, femoral neck fracture in patients with above knee amputation was more rare. Hereby I report a case of femoral neck fracture occurred to 58-year-old male bilateral above knee amputee with the review of literatures.
- 388 View
- 2 Download

Original Articles
- Impacted Cancellous Allograft and Quadratus Femoris Pedicle Bone Graft of Femoral Neck Fracture Nonunion
- Soo Jae Yim, Seung Han Woo
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(4):519-525. Published online October 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.4.519
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The aim of this study was attempted to evaluate the effects of impacted cancellous allograft and quadratus femoris pedicle bone graft in the management of nonunion of femur neck fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between March 1998 and April 1999, 5 patients, rating from 36 to 45 years of age, were treated with impacted cancellous allograft and quadratus femoris pedicle bone graft and all cases were nonunion with displaced transcervical fracture whose primary treatment had been done with closed reduction and multiple pinning. The duration of follow-up was from 36 months to 48 months and the mean follow-up period was 40 months. Clinical evaluation was done according to Lunceford functional results and radiologically bone union was evaluated by 3 monthly X-ray check.
RESULTS
After follow-up from 36 months to 48 months, all cases resulted in the bone union. Four cases, radiologically bone union was progressed during 14 weeks, and the other, obtained at 6 months. All cases, at 18 months, radiologically complete bone union was obtained. Clinical result was above fair results and no one complaints pain and instability.
CONCLUSION
For patients with nonunion of femoral neck fracture, impacted cancellous allograft and quadratus femoris pedicle bone graft was provide a good result of union.
- 347 View
- 1 Download

- The Significance of Posterior Cortex in Complicated Femoral Neck Fractures which were Internal Fixated
- You Sung Suh, Seok Bong Jung, Soo Jae Yim, Jong Seok Park, Byung Ill Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(4):511-518. Published online October 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.4.511
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
When a surgeon carries out an operative treatment on a patient who has fractures of the femoral neck, he decides to do either the internal fixation for bony union or the aggressive treatment according to his experience and preparation, not according to the objective standard. The aim of this retrospective study is to prepare a guideline for the operative method.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We analyse possible factors of the patient who has nonunion, avascular necrosis and loss of fixation after doing internal fixation in femoral neck fractures RESULTS: In this treated case of femoral neck, the appearance of complications are influenced by the maintenance of internal fixation, shape of fractures, osteoporosis, and the position of fixations; but in the complicated cases without the loss of fixation, the shape of fractures always have posterior cortical communition.
CONCLUSION
When we choose between simple fixation and aggressive treatments in cases of fractures of the femoral neck, we must treat according to the patient 's condition, displacement of the fracture, operative technique and existence of a posterior cortical comminuted fracture.
- 391 View
- 0 Download

- Treatment of Pertrochanteric Fracture with Femoral Neck Fracture
- Weon Yoo Kim, Chang Whan Han, Woo Sung Choi, Jong Hoon Ji, Chang Youn Moon, Jin Young Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(3):307-311. Published online July 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.3.307
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
To establish the precise diagnosis of a comminuted pertrochanteric fracture with femoral neck fracture in a senile osteoporotic patient and report of a preliminary clinical results of early bipolar hemiarthroplasty. MATERIAL & METHODS: Consecutive seven cases of comminuted pertrochanteric fractures who were suspicious to have combination with femoral neck fracture were evaluated. All cases had routine radiographs and CT scans of proximal femur and performed with bipolar hemiarthroplasties. Observation of the retrieved femoral head to evaluate a fracture and recorded with photograph. Postoperative evaluation was done with Daubine & Postel clinical grading with medical recording and personal telephone. The clinical evaluation was focused on the recovery for preinjured walking distance.
RESULTS
All patients were proved to have combination with pertrochanteric fractures and femoral neck fractures. In addition, all patients were recovered to more than good in clinical grading and pre-injured walking distance.
CONCLUSION
To make a precise diagnosis of pertrochanteric fractures with femoral neck fracture it is recommended to perform the CT scan with prompt reading of the simple radiographs in suspicious case. An early bipolar hemiarthroplasty was also recommended to treat this kind of senile difficult fracture.
- 465 View
- 1 Download

- Complications and Affecting Factors for Intracapsular Femoral Neck Fractures Treated by Multiple Pinning
- Sung Jung Kim, Shin Yoon Kim, Gi Bong Cha, Chang Wug Oh, Il Hyung Park, Joo Chul Ihn
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(2):201-208. Published online April 30, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.2.201
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To investigate the relationship between the complications of intracapsular femoral neck fractures treated by multiple pinning and several affecting factors.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sixty-eight patients with intracapsular femoral neck fractures were treated by multiple pinning from March 1993 to January 2000 and followed at more than one year. Relationship between the complications such as failure of union, collapse of femoral head due to osteonecrosis of femoral head and several affecting factors including displacement of fracture according to Garden stage, state of reduction, position of screws, time interval from injury to operation, and fracture level were analyzed. The Fisher exact test, chi-square test, and multivariate logistic regression analysis were used to find the relevant factors influencing incidence of complications. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
RESULTS
Position of screw was the most important single factor affecting the results of treatment of intracapsular femoral neck fracture (p=0.046). Moreover, the Garden stage and position of screw were revealed affecting the incidence of complications together with other factors (each p value was 0.028 and 0.027).
CONCLUSION
We considered that satisfactory position of screw was important to reduce complications after multiple pinning for intracapsular femoral neck fracture. And the results of operation also seemed to closely relate with multiple factors including Garden stage and status of reduction. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Predicting Complications after Internal Fixation of Femoral Neck Fractures
Tae-Ho Kim, Jong-Oh Kim, Sung-Sik Kang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(2): 79. CrossRef
- Factors Predicting Complications after Internal Fixation of Femoral Neck Fractures
- 514 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Ipsilateral Femoral Neck and Shaft Fracture: Secondary Avascular Necrosis of Femoral Head
- Sung Taek Jung, Keun Bae Lee, Taek Lim Yoon, Sang Don Shim, Myung Seon Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 2001;14(4):609-615. Published online October 31, 2001
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2001.14.4.609
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the prognostic variables that influence the incidence of complication such as avascular necrosis of femoral head, nonunion of neck after the treatment of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fracture by the results and long term follow up. MATERIAL AND METHODS: We studied the 18 cases of 17 patients that could be follow up over 2 years among the patients received the treatment of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fracture from 1987 to 1998. The average follow up duration was 54.3 months (24-120) and all patients was men. The average age was 38.2 yrs(20-60). Fifteen cases of femoral neck fracture were treated with multiple pinning and 3 cases with the compression hip screw, 12 cases of femoral shaft fracture were treated with DCP, 5 cases by interlocking IM nailing and 1 case, open fracture, by external fixator. We evaluated the bone union and complication such as avascular necrosis of femoral head and nonunion.
RESULTS
For femoral neck fracture, resection arthroplasty was performed in 1 case and nonunion in 1 case. Bone union was obtained at average 4 months in 16 cases of femoral neck fracture, at 9 months in all cases of shaft fracture. The avascular necrosis of femoral head in 5 cases included 1 case of nonunion was found at minimal 20 months to maximal 59 months follows up.
DISCUSSION
All prognostic variables of the ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fracture, that is the Garden stage, Pauwels classification, delayed time to operation. had no statistical correlation with complication. Whenever possible the patients should be followed for a minimum 5 years to rule out avascular necrosis of femoral head.
- 391 View
- 1 Download

- The Relationship between the Variation of the femoral neckshaft angle according to Age and the Fracture of the Hip
- Jun Seop Jahng, Seong Hwan Moon, Jin Ho Che
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(4):702-708. Published online October 31, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.4.702
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
Femur neck-shaft angles were obtained from plain radiographs of the pelvis and their changes according to age were assessed along with their correlations to hip fracture incidence.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Forty-four patients who have received surgical treatments for femur neck or intertrochanteric fractures and 171 patients who performed bone densitometry at out patient clinic without any history of hip fractures were included in the study. All patients were older than 50 years. Standard value of 0.725 g/cm2 w a s used to separate the osteoporosis and non-osteoporosis groups. Femur neck-shaft angle was measured from standardized radiograph.
RESULTS
In the non-osteoporosis group, varization of femur neck-shaft angle was observed as age increased. No significant difference of the neck-shaft angle was proven between osteoporosis and non-osteoporosis group, and no correlation existed between the femoral neck bone mineral density and neck-shaft angle. Furthermore, fracture group and no fracture group showed no significant difference in neck-shaft angle.
CONCLUSION
The decrease in the neck-shaft angle with age increments has no effects on incidence of hip fracuture and factor most closely associated with fractures is bone mineral density.
- 496 View
- 1 Download

- The Clinical Resuts of Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty in Old Age-Femoral Neck Fracture vs. Intertrochanteric Fracture-
- Dong Heon Kim, Kyu Cheol Shin, Byeong Chun Chang, Dae Sul Kang
- J Korean Soc Fract 1999;12(3):509-515. Published online July 31, 1999
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1999.12.3.509
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The peritrochanteric fracture remains one of the most common and potentially devastating injuries in the geriatric population. The goal of treatment is early ambulation to prevent the complications such as pressure sore, pneumonia, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism and long time hospitalization by open reduction and internal fixation or closed reduction and internal rotation. In femoral neck fracture, many surgeons agree on the bipolar hemiarthroplasty but there is controversy about that treatment in intertrochanteric fracture. We have tried to assess the clinical outcome of bipolar hemiarthroplasty for the intertrochanteric fracture as compared with femoral neck fracture in old age. Ninty-five bipolar hemiarthroplasties were performed at our hospital, between January 1991 and February 1996. We selected 65 patients who had been followed for at least one year. Forty of sixty-five patients had femoral neck fractures and twenty-five of them intertrochanteric fractures. The results were as follows: 1. Regardless of using the cement, the partial weight bearing ambulation time after operation was 10.3 days in femoral neck fracture, 19.5 days in intertrichanteric fracture. 2. At one year follow-up the average Modified Harris Hip Score was 88.9 in femoral neck fracture, and 87.5 in intertrochanteric fracture. 3. Postoperative complications in case of femoral neck fracture included thigh pain in 4 patients, heterotopic ossification in 1, intraoperative fractures of the femoral shaft in 2, leg length inequality in 1 and dislocations after bipolar hemiarthroplasties in 3. And those in case of intertrochanteric fractures were thigh pain in 2 patients, heterotopic ossifications in 2, intraoperative fractures of the femoral shaft in 2 and dislocation after bipolar hemiarthroplasty in 1. 4. There were no statistically significant differences in the clinical functional score and complications between intertrochanteric and femoral neck fracture groups, therefore bipolar hemiarthroplasty can be recommended as one of the treatment of intertrochanteric fracture as well as femoral neck fracture in the elderly patient.
- 299 View
- 0 Download

- Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty for the Treatment of Displaced Femoral Neck Fracture in Elderly Patients: Uncemented versus Cemented femoral stems
- Jae Yeul Choi, Kyung Chul Kim, Hwa Jae Jeong, Bon Seop Koo, Ho Joong Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 1999;12(2):195-202. Published online April 30, 1999
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1999.12.2.195
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Forty five patients above the age of 60 with displaced femoral neck fractures were treated by bipolar hemiarthroplasty in Kangbuk Samsung hospital from January 1990 to January 1995. We evaluated these patients for comparison of the results between the cemented and uncemented femoral fixation, especially in elderly patients with medical illness or osteoporosis. During a follow up period of more than two years, the authors found less thigh pain(5.2% versus 38%) and slightly higher Harris hip scores(84.5 versus 80.0 points) in the cemented group in comparison with the uncemented group. Radiographic examination showed less radiolucent zones in the cemented group. Comparing the operative time(86.2 versus 83.8 minutes), hospital stay(4.7 weeks versus 5.3 weeks), blood loss(385 versus 381 ml) during the operation. The postoperative mortality rate was 2%, and the follow-up mortality rate was 11% in the first year. There was no significant difference between two groups in mortality rate. Thus in bipolar hemiarthroplasty in elderly patients with displaced femoral neck fracture, we have obtained satisfactory results despite of poor bone condition and osteoporosis except thigh pain. But the follow up period was too short to assess the late complications of the hemiarthroplasty such as acetabular erosion, implant loosening, so long-term follow up will be necessary
- 376 View
- 2 Download

- Treatment of Femoral Neck Fracture by Osteosynthesis
- Won Yong Sohn, Hong Chul Lim, Seung Joo Jeon, Ky Sung Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1999;12(1):6-12. Published online January 31, 1999
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1999.12.1.6
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We reviewed respectively the results of treatment of femotal neck fracture using ostesoynthetic methods, in 29 patients who were treated at the Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Guro hospital, Korea university, from January 1991 to December 1995. 20 cases were stabilized by cannulated hip screw, 6 cses by compression hip screw and 3 cases by Knowles pin. With the average follow up of 26 months (12-45 months), we analtzed the cauwe of injury with age, fracture types by Gardens method, the accuracy of reduction by Gardens alignment index and the functional results of the hip by Harris hip score and walking capacity. The adequacy of reduction by Gardens alignment index were as follows: anatsmical in 14, acceptable in 12 and poor in 3 cases. The fnetional results by Harris hip score and walking capacity were as follows : excellent in 21, good in 3, fair in 2 and poor in 3 cases. Complications after treatment of femoral neck fracture were one case of AVN, one case of non-union and two cases of combination of AVN and non-union. All these complications were developed in displaced femoral neck fracture with poor quality of reduction and directly correlated with initial displacement of fracture and reversely correlated with adequacy of reduction. Our concluwions are treatment of femoral neck fracture using osteosynthesis is favorable in young age regardless of intial displacement and in old age without osteoporosis and displacment and satisfactory results are produced from acceptable to anatomical reduction of fracture.
- 419 View
- 0 Download

- Clinical Analysis of Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head following femoral Neck Fracture
- You Sung Suh, Kyung Dae Min, Byung Joon Shin, Byung Ill Lee, Yeon Ill Kim, Soo Kyun Rah, Chang Uk Choi
- J Korean Soc Fract 1998;11(2):304-312. Published online April 30, 1998
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1998.11.2.304
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Post-traumatic avascular necrosis is a notorious complication of intracapsular fractures of the femoral neck, whether or not the fracture unites. The incidence of avascular necrosis of the femoral head following femoral neck fractures has been reported variably ranged from 7% to 84%. The purposes of this study are to analysis the clinical features of avascular necrosis of the femoral head following femoral neck fractures and to define causative factors of posttraumatic avascular necrosis. From May 1986 to May 1995, sixty-eight patients with intracapsular femoral neck fracture were operated on osteosynthesis in soonchunhyang University Hospital; we analysed retrospectively with follow-up more than two years, post-traumatic avascular necrosis(AVN) was developed in 13 patients(AVN group) and united forty-six patients were included non-avascular necrosis group, nine patients were excluded due to nonunion. Comparative study was performed between these two groups. The results were as follows: 1. The avascular necrosis of the femoral head following femoral neck fractures treated with osteosynthesis was noted in 13 cases (19%) 2. The eleven cases of 13 cases showed segmental collapse of the femoral head within 2 years. 3. Among the causative factors, age and sex, delay before operation and fixation device have no statistical significance(p>0.05) but type of fracture, initial displacement and quality of reduction showed to be statistical correlation(p<0.05). In conclusion, adequate reuction and internal fixation for the femoral neck fracture may essential to minimize avascular necrosis following osteosynthesis.
- 724 View
- 2 Download

- Structural Study of Proximal femur in the Elderly Femoral Neck & Trochanteric Fracture
- Byung Chul Park, Chang Wug Oh, Seung Hoon Oh
- J Korean Soc Fract 1998;11(1):175-180. Published online January 31, 1998
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1998.11.1.175
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The factors that determine whether a proximal femoral fracture is neck or trochanteric area are a matter of controversy. So we studied the BMD(bone mineral density) and the morphology of the contralateral femur in subcapital fracture and intertrochanteric fracture(Boyd - Griffin Type I,II). The bone density of femoral neck, Ward's triangle and trochanteric region was measured by dual energy X-ray absortiometry(DEXA) in 41 patients with femoral neck fracture value and fracture type in same patients, we calculate the femoral neck length from the plain X-ray film. The results were as follows. 1. The ratio of BMD in the neck and trochanter area was higher in the trochanter fracture group. 2. The level of BMD of the trochanter fracture group was lower than the neck fracture group in all opints of measurement. 3. In the measurement of femoral neck length at plain X-ray film, the neck length of trochanter fracture group was longer than the neck fracture group. It may be that difference in BMD and femoral neck length is related to the site at which a proximal femoral fracture occurs.
- 374 View
- 0 Download

- Treatment of Femoral Neck Fractures in the Elderly Patients Aged over 60 years: Comparative Study between Osteosynthesis and Bipola Arthroplasty
- You Sung Suh, Byung Woo Kim, Kyung Dae Min, Chi Soo Son, Soo Kyoon Rah, Chang Uk Choi
- J Korean Soc Fract 1998;11(1):153-158. Published online January 31, 1998
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1998.11.1.153
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - STUDY DESIGN: Seventy femoral neck fractures in the elderly patients aged over 60 years treated with osteosynthesis or primary biploar arthroplasty were assessed on complication and functional outcome at final follow up.
OBJECTIVE: To compare the results of femoral neck fractures in the elderly patients aged over 60 years treated with osteosynthesis or primary bipolar arthroplasty retrospectively. To know the indications of each method.
SUMMARY OF BACKGROUND DATA: Althrough the osteosynthesis method had preservation of hip joint, primary osteosynthesis method had possibility of major complications as nonunion and avascular necrosis of femoral head.
METHODS
Seventy patients with intra-articular femoral neck fracture were treated with osteosynthesis in 33 patients(group 1) and primary biploar arthroplasty in 37 patients(group 2). A comparartive analysis of age, sex, type of fracture, initial displacement of fracture, method of treatment, fixation device type, quality of reduction, operative time, blood loss at operation, complication and functional outcome at final follow up were performed.
RESULTS
The female was more three times than male. The mean ages were 70.1 years old in group 1 and 73.3 years old in group 2. In group 1, complications such as non-union and avascular necrosis of femoral head were significantly greater in the subcapital fractures and Garden's stage 3,4 than the transcapital fractures and Garden's stage 1,2. In operative method, blood loss and operative time were significantly greater in the group 2 than in the group 1. Seven major complications (avascular necrosis: 6 cases, non-union: 1 case) occurred in group 1, two major complications(death: 2 cases) occurred in group 2. The functional outcomes were superior to the group 2, but it may be due to high complication rates in group 1.
CONCLUSIONS
This study suggests that the important factors that influenced the clinical results were type of fracture, initial displacement of fracture, quality of reduction. So in relatively poor arthroplasty.
- 423 View
- 1 Download

- Multiple Pinning in Femoral Neck Fractures
- Kuen Tak Suh, Taek Geon Lee, Chang Il Yoo
- J Korean Soc Fract 1997;10(4):727-737. Published online October 31, 1997
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1997.10.4.727
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The incidence of femoral neck fracture has steadily increased with lengthening of the average life span. The end results of treatement have been improving with the development of internal fixation devices. However, the anatomic characteristics of femoral neck has made the complications of nonunion and avascular necrosis as a common result. Authors analysed 47 patients, with over 2 years follow-up on an average, who were more than twenty years old and treated with multiple Knowles pins or cannulated screws during the period from February 1988 to February 1994. Following results were obtained. 1. Among 47 patients, 23 cases(49%) were male and 24 cases(51%) were female. The highest incidence was found in the sixth decade. 2. The most common cause of femoral neck rracture was slip down(55%). 3. According to the Gardens classification, the displaced fracture(Garden stage III and IV) was more common (68%), and according to the anatomic classification, transcervical type was the most common (40%). 4. Among 47 patients, there were 1 case of nonunion(7%) and 2 cases of avascular necrosis of femoral head(13%) in the nondisplaced fractures(15 cases), compared to 6 cases of nonunion(19%) and 8 cases of avascular necrosis of femoral head(25%) in the displaced fractures(32 cases). There were 4 cases of nonunion(15%) and 5 cases of avascular necrosis of femoral head(19%) among the 26 patients treated with multiple Knowles pins, compared to 3 cases of nonunion(14%) and 5 cases of avascular necrosis of femoral head(28%) among the 21 patients treated with cannulated screws. 3 cases of nonunion(10%) and 4 cases of avascular necrosis of femoral head(13%) were developed among 30 cases in which acceptable reduction was achieved after closed reduction. 4 cases of nonunion(24%) and 6 cases of avascular necrosis of femoral head(35%) were developed among 17 cases in which poor reduction was achieved. 11 cases(42%) were complicated among 26 cases below Singh index grade 3 and 6 cases(29%) were complicat among 21 cases above Singh index grade 4. 5. Factors that may affect the success of treatment in femoral neck fracture are not the type of internal fixation device used, but rather anatomic site of fracture, the degree of displacement, degree of osteoporsis and accuracy of reduction.
- 417 View
- 1 Download

Case Report
- Fracture of Femur Neck Associated with Technical Errors in Closed Intramedullary Nailing of the Femur
- Yong Hoon Kim, Ki Chan Ahn, Sung Suk Seo, Young Chang Kim, Jang Suk Choi, Young Gu Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 1997;10(1):73-78. Published online January 31, 1997
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1997.10.1.73
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Closed intramedullary nailing has become increasingly popular in the management of fracture of the femur because of a high rate of union and a low rate of complications. Since the development, it has been widely used in more applicable level of femoral shaft fracture. Therefore, complications of intramedullary nailing was rarely seen, especially rare in case of fractures of the femoral neck associated with technical errors. The three cases of femoral neck fracture with technical errors during intramedullary nailing for treatment of femoral shaft fracture in Paik Hospital, Pusan from April 1994 to July 1995 are reported herein to document that this complication can occur. Three cases of the femoral neck fracture were treated by closed reduction and internal fixation with Knowles pin.
- 289 View
- 0 Download

Original Articles
- Multiple Knowles Pin Fixations of the Femoral Neck Fractures in Adults under 60 Years of Age
- Sang Won Park, Kwang Suk Lee, Dae Gon Wie
- J Korean Soc Fract 1996;9(4):859-868. Published online October 31, 1996
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1996.9.4.859
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Femoral neck fracture is more common in elderly even by minor trauma because of osteoporosis. In young adults, though the incidence is low, have a poor prognosis because of high incidence of non-union and aseptic necrosis. The treatment method of the femur neck fracture is widely divided into internal fination and replacelnent arthroplasty But there is still contrversies present in the treatment methods. The object of this study is to observe the relationships between the clinical outcomes and the age, the degree of displacement. the type of reduction, the time of operation and the bone density in the femoral neck fractures treated with mulliple Knowles pin fitation. The authors analyzed 29 cases of femoral neck fractures in adults under 60 years of age, who were treated with multiple pih (ixation and followed up more than 1 yearduration The results obtained were as follows; 1. The union of femoral neck fracture occured in 19 cases(65.5%) among the 19 cases and the mean duration of union was 4.8 months. 2. The complications were 8 cases(21.6%) of avascular necrosis, 2 cases(6.9%) of non-union, 2 cases of malunion and 1 case of post-traumatic arthritis. 3. The functional results by Lunceford criteria were satisfactory in 17 cases (58.6%). 4. In the patient group which were no avascular necrosis and non-union showed 89.5% of satisfactory functional end result. 5. There was a relationship between the complications such as avascular necrosis and non-union, and age of the patient, bone density, degree of initial displacement and type of reduction. But the duration between the injury and operation did not influence the complication rate. According to the above results, we concluded that multiple Knowles pin fination in femoral neck fracture is simple and safe method, and one of salvaging method of femoral head in adults under 60 years of age.
- 372 View
- 0 Download

- Concomitant Ipsilateral Femoral Neck and Shaft Fractures
- Kuen Tak Suh, Sang Jin Cheon, Chong Il Yoo
- J Korean Soc Fract 1996;9(2):458-465. Published online April 30, 1996
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1996.9.2.458
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Concomitant ipsilateral fractures of the femoral neck and shaft are rare, and present diagnostic difficulties and complex choices as to treatment. At the Department of Orthopedic surgery, Pusan National University Hospital, from April 1987 to June 1998, 18 cases of the concomitant ipsilateral fractures of the femoral neck and shaft had been treeated and followed up for 48.7 months in average (ranging from 12 months to 89 months). Initially one case of the femoral neck fracture was missed, which was a non-displaced fracture. Femoral reck fractures were treated with multiple screws or pins in all cases except two cases treated with recon struction nail. For the femoral shaft fractures, plate and screws were applied in 12 cases, Ender nails in three cases, reconstruction nail in two cases and skeletal traction in one case. Nonunion of femoral shaft fracture was developed in one case treated with skeletal fraction, metal loosening in one case treated with Ender nails, and limited motion of the knee in three cases which had knee injuries. But in our cases, avascular necrosis of femoral head and nonunion of the femoral neck and metal failure were not developed. The key factors of successful treatment for concomitant ipsilateral fractures of the femoral neck and shaft seemed to be careful evaluation of the associated hip injures in felnoral shaft fracture and early anatomical reduction and rigid fixation of fractures with early motion of joints.
- 416 View
- 5 Download

- Treatment of Femoral Neck Fractures in the Elderly Patiene
- Chung Nam Kang, Kwon Jae Roh, Yeo Hon Yun, Dong Jun Kim, Cheol Min Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1995;8(1):61-67. Published online January 31, 1995
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1995.8.1.61
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We analyzed 41 femoral neck fractures in 40 elderly patients aged over 65 years. All of them were treated by surgery and followed for average 22 months (range, 14 to 52 months) at the Ewha Womans University Hospital from 1988 to 1992. Of these, 15 cases were treated with internal fixation and 26 cases with endoprosthetic or total hip replacement arthroplasty For the level of fractures the most common features were subcapital, that were moderately to severely (Gardens stage III or IV) displaced. In the internal fuation group the results were unsatisfactory in the cases of subcapital type, moderate to severe (Gardens stage III or IV) displacement, Pauwels type III and those with osteoporosis (below stage III in Singh index). Our short term follow-up results showed that the prosthetic replacement group were generally superior in that they were not affected by the types of fractures and the degree of osteoporosis.
- 281 View
- 0 Download

- Ipsilateral Fracture of the Femoral Neck and Shaft
- Ho Jung Kang, Dae Yong Han, Dong Eun Shin
- J Korean Soc Fract 1994;7(2):246-255. Published online November 30, 1994
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1994.7.2.246
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ipsilateral fractures of the femoral neck and shaft are relatively uncommon infuries and usually the result of high-energy trauma in young adults. Frequently, the severe trauma responsible for this injury combination is also productive of associated injuries indeed life threatening. Several unique features of this injury have been recognized, including the high incidence of associated knee injuries, particulary fractures of the patella. This is thought to be due to a mechanism of injury in which the femur is longitudinally loaded at the flexed knee while positioned in neutral abduction. Also, this combination of injuries pose a difficult problem in management. The authors reviewed 14 cases of ipsilateral fracture of the femoral neck and shaft for the evaluation of the associated injury and method of ueatment from October 1986 to Febraury 1991 and the average follow-up period was 1.8 years. The results were as follows. 1. The site of the femoral neck and shaft fracture were mainly, basicervical and midshaft. 2. In two cases, the femoral neck fracture was not diagnosed initially. 3. Most of the associated fractures were patella and tibial fractures and PCL ruptures. 4. Complications Included three stiffness of the knee, two delayed union of the femoral shaft, one superficial wound infection and one delayed union with coxa vara deformity of the femoral neck.
- 297 View
- 0 Download

- Clinical study of femoral neck fracture treatment is delayed more than 7 days
- Dong Ki Lee, Taik Keun Ahn, Jong Oh Kim, Taik Seon Kim, Jai Ik Shim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1991;4(2):243-247. Published online November 30, 1991
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1991.4.2.243
- 501 View
- 0 Download

- Bipolar hemiarthroplasty as secondary procedure for femoral neck fractures in young adults
- Sung Joon Kim, Il Yong Choi, Heung Ryong Oh
- J Korean Soc Fract 1991;4(2):237-242. Published online November 30, 1991
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1991.4.2.237
- 346 View
- 1 Download

Case Report
- Delayed Femoral Neck Fracture in Interlocking Intramedullary Nailed Femur: A case report
- Sung Man Rowe, Eun Sun Moon, Eun Kyoo Song, Sung Taek Jung
- J Korean Soc Fract 1989;2(2):269-273. Published online November 30, 1989
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1989.2.2.269
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We report an uncommon complication following interlocking intramedullary nailing of the femur: delayed femoral neck fracture after 5 months of unevenful postoperative course. He was a 47-year-old laborer with good quality of bone, nevertheless he sustained femoral neck fracture after minor fall on the ground. We thought that loss of bone elasticity caused by interlocked nail in the whole femoral shaft including intertrochanteric portion made stress concentration on the femoral neck to develop a fracture with minor magnitude of traumatic force.
- 482 View
- 1 Download

Original Article
- Clinical Study on the Fractures of the Femoral Neck in Children
- Nyung Sik Park, Young Ok Cha
- J Korean Soc Fract 1988;1(1):91-101. Published online November 30, 1988
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1988.1.1.91
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The femoral neck fracture in children is rare and occurred by severe trauma and the treatment method & prognosis anre different from adult, and it is difficult to treat due to frequent complication, which is so called unsolved fracture. Twelve cases of childrens femoral neck fracture were treated at Chon buk National University Hospital from July, 1981 to May, 1988 were analysed clinically and radiologically and following results were obtained. 1. The commonest ang was between the age of 14 and 16 years and the ratio of boys & girls was 2:1. 2. The main cause of fracture was traffic accident(6 cases) and fall down was 5 cases and slip down was 1 case. 3. According to the Delbet & Colonas classification, the transcervical fracture was most common type and displaced fracture was 8 cases. 4. Associated injuries were extremity fracture(3 cases), etc. 5. Seven cases were treated by open reduction and internal fixation and five cases by cast immobilization after skin or skeletal traction. 6. The most common complication was coxa vara(5 cases) & other complications were avascular necrosis of femoral head(3 cases), premature epiphyseal closure(3 cases) and nonunion(2 cases). 7. According to Ratliffs assessment of results, eight cases were good, two fair & two poor. 8. Secondary operation(muscle pedicle bone graft, corrective subtrochanteric valgus osteotomy) was done in three cases and showed one good result, one fair result and one poor result.
- 352 View
- 1 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


