Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 29(4); 2016 > Article
-
Case Report
- Insufficiency Fracture of the Femoral Neck after Intramedullary Nailing for the Treatment of Atypical Femoral Fracture - A Case Report -
- Nam Hoon Moon, M.D., Jae Hoon Jang, M.D., Tae Hyuk Hwang, M.D., Ki Young Park, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2016;29(4):258-264.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.4.258
Published online: October 20, 2016
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Pusan National University Hospital, Korea.
*Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Good Sansun Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Nam Hoon Moon, M.D. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Pusan National University Hospital, 179 Gudeok-ro, Seo-gu, Busan 49241, Korea. Tel: 82-51-240-7248·Fax: 82-51-247-8395, namhoonmoon@gmail.com
• Received: January 5, 2016 • Revised: July 7, 2016 • Accepted: July 29, 2016
Copyright © 2016 The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 349 Views
- 3 Download
Abstract
- Although several publications have reported delayed or non-union, there is a consensus that the standard treatment for atypical femoral fracture (AFF) is an intramedullary nailing. However, no case of tensile insufficiency fracture of femoral neck associated with intramedullary nailing in patients with AFF have been reported. Here, we report an 82-year-old woman with tensile type of insufficiency fracture of the femoral neck after intramedullary nailing for the treatment of AFF.
- 1. Shane E, Burr D, Abrahamsen B, et al. Atypical subtrochanteric and diaphyseal femoral fractures: second report of a task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Miner Res, 2014;29:1-23.
- 2. Das De S, Setiobudi T, Shen L, Das De S. A rational approach to management of alendronate-related subtrochanteric fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2010;92:679-686.
- 3. Borrelli J Jr, Lane J, Bukata S, Egol K, Takemoto R, Slobogean G. Atypical femur fractures. J Orthop Trauma, 2014;28:S36-S42.
- 4. Visekruna M, Wilson D, McKiernan FE. Severely suppressed bone turnover and atypical skeletal fragility. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2008;93:2948-2952.Article
- 5. Weil YA, Rivkin G, Safran O, Liebergall M, Foldes AJ. The outcome of surgically treated femur fractures associated with long-term bisphosphonate use. J Trauma, 2011;71:186-190.Article
- 6. Egol KA, Park JH, Rosenberg ZS, Peck V, Tejwani NC. Healing delayed but generally reliable after bisphosphonate-associated complete femur fractures treated with IM nails. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 2014;472:2728-2734.Article
- 7. Bonifacio L, Syson P. Construct failure in an atypical femoral fracture treated with intramedullary nailing: a case report. Malays Orthop J, 2014;8:82-84.Article
- 8. Iwamoto J, Takeda T. Insufficiency fracture of the femoral neck during osteoporosis treatment: a case report. J Orthop Sci, 2002;7:707-712.Article
- 9. Kitajima I, Tachibana S, Mikami Y, Mori T, Hirota Y, Nakamichi K. Insufficiency fracture of the femoral neck after intramedullary nailing. J Orthop Sci, 1999;4:304-306.Article
- 10. Yang KH, Min BW, Ha YC. Atypical femoral fracture: 2015 position statement of the Korean society for bone and mineral research. J Bone Metab, 2015;22:87-91.Article
REFERENCES
Fig. 1
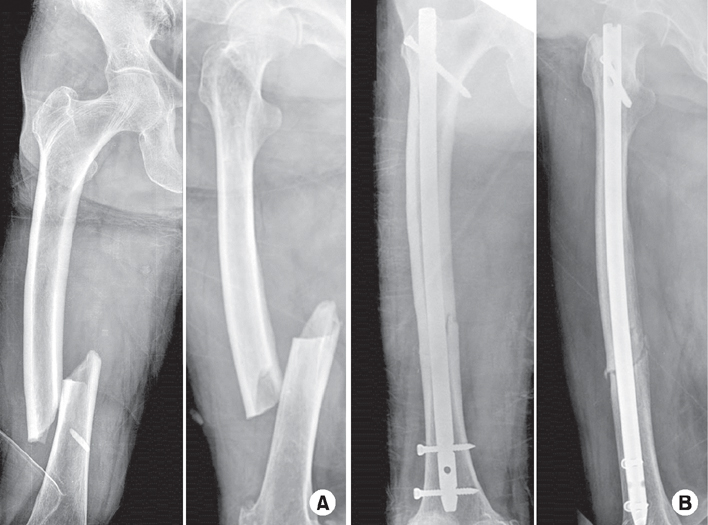
Representative radiographs of an 82-year-old female with atypical femoral fracture (AFF) treated with long-term bisphosphonate. (A) Preoperative radiographs demonstrate findings consistent with AFF, including transverse fracture lines with periosteal thickening of the lateral cortex, and non-comminuted complete fracture lines with medial spikes. (B) Internal fixation was performed using a standard intramedullary nail.

Fig. 2
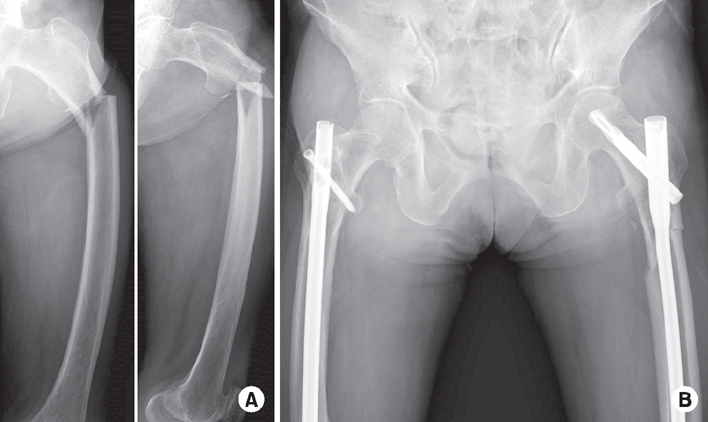
Patient had a subtrochanteric fracture on the contralateral side while weight bearing on the left leg. (A) Preoperative radiographs also demonstrate atypical femoral fracture. (B) Internal fixation was performed using a long proximal femoral nail anti-rotation 2.

Fig. 3
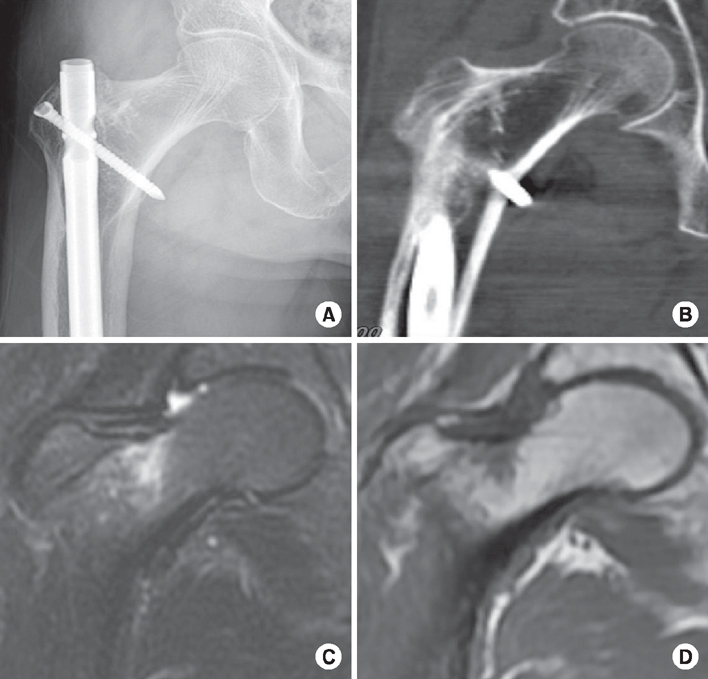
(A, B) Plain x-ray and computed tomography images showing no fracture line can be seen. (C) Coronal T1-weighted spin echo coronal image showing a focal area of low signal intensity on the tension side of the right femoral neck. (D) Coronal fat saturated T2-weighted image showing similar focal area of florid marrow edema on the tension side of the right femoral neck.

Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

Insufficiency Fracture of the Femoral Neck after Intramedullary Nailing for the Treatment of Atypical Femoral Fracture - A Case Report -
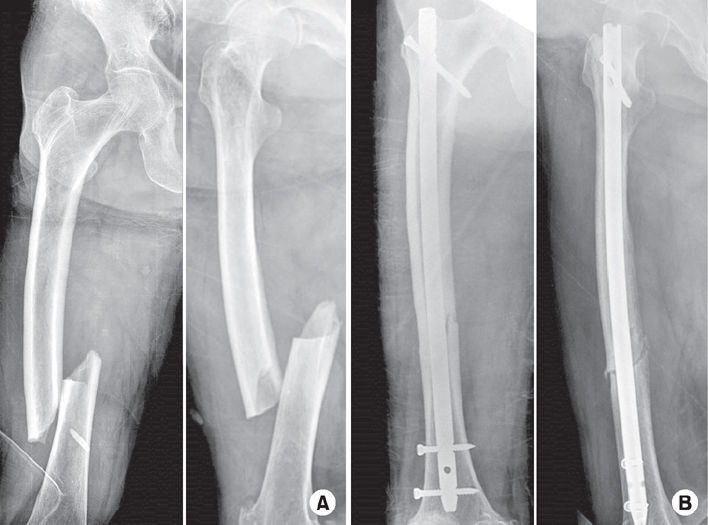
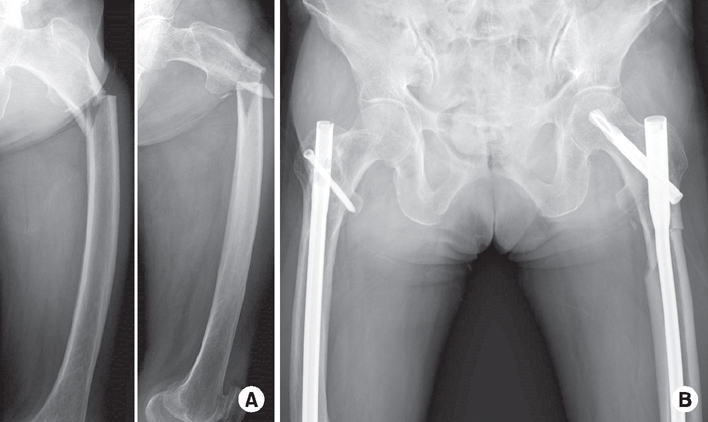
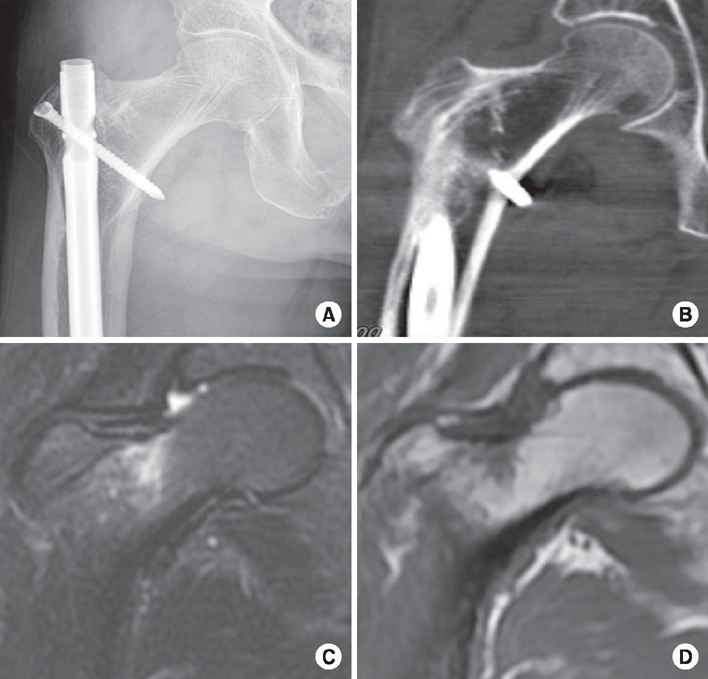
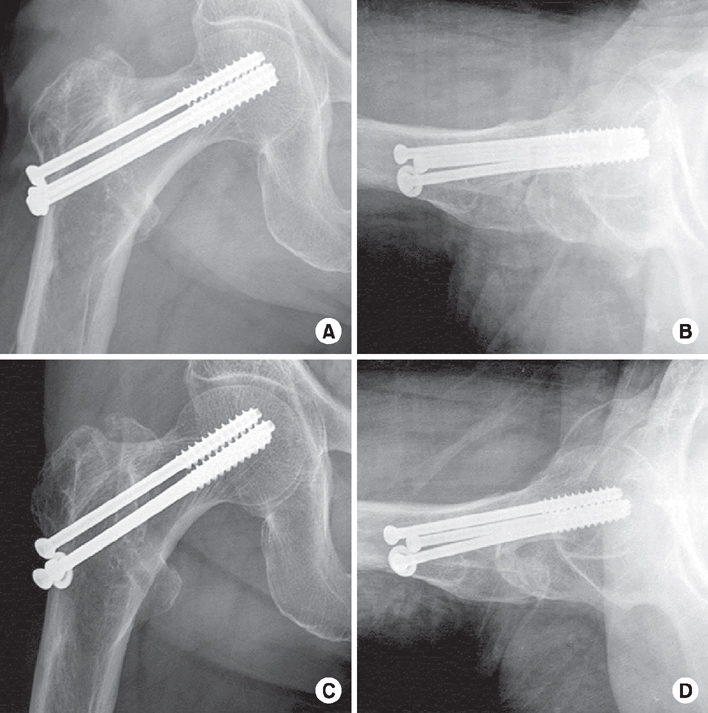
Fig. 1
Representative radiographs of an 82-year-old female with atypical femoral fracture (AFF) treated with long-term bisphosphonate. (A) Preoperative radiographs demonstrate findings consistent with AFF, including transverse fracture lines with periosteal thickening of the lateral cortex, and non-comminuted complete fracture lines with medial spikes. (B) Internal fixation was performed using a standard intramedullary nail.
Fig. 2
Patient had a subtrochanteric fracture on the contralateral side while weight bearing on the left leg. (A) Preoperative radiographs also demonstrate atypical femoral fracture. (B) Internal fixation was performed using a long proximal femoral nail anti-rotation 2.
Fig. 3
(A, B) Plain x-ray and computed tomography images showing no fracture line can be seen. (C) Coronal T1-weighted spin echo coronal image showing a focal area of low signal intensity on the tension side of the right femoral neck. (D) Coronal fat saturated T2-weighted image showing similar focal area of florid marrow edema on the tension side of the right femoral neck.
Fig. 4
(A, B) Postoperative radiographs presenting the internal fixation with multiple cannulated screws for the treatment of tensile type insufficiency fracture of the femoral neck. (C, D) At 6-month follow-up, there was no evidence of screw loosening or fixation loss.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Insufficiency Fracture of the Femoral Neck after Intramedullary Nailing for the Treatment of Atypical Femoral Fracture - A Case Report -

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
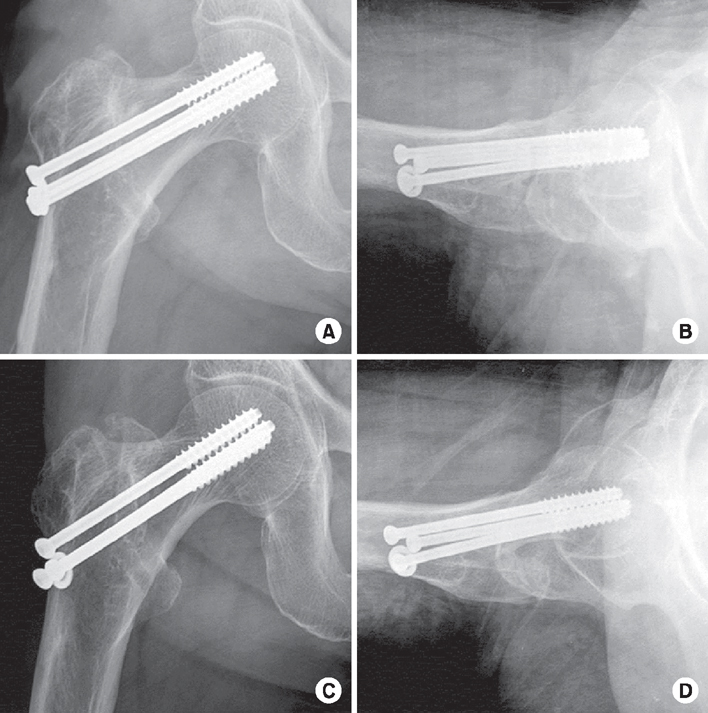
 Cite
Cite

