Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 29(2); 2016 > Article
-
Review Article
- Current Concepts of Fractures and Dislocation of the Hand
- Yong-Cheol Yoon, M.D., Ph.D., Jong-Ryoon Baek, M.D., Ph.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2016;29(2):143-159.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.2.143
Published online: April 19, 2016
Gachon University Gil Hospital Trauma Center, Incheon, Korea.
*Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Jong-Ryoon Baek, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, 21 Namdong-daero 774beon-gil, Namdong-gu, Incheon 21565, Korea. Tel: 82-32-460-3384, Fax: 82-32-423-3384 baekjr@gilhospital.com
Copyright © 2016 The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 951 Views
- 11 Download
- 2 Crossref
Abstract
- Fractures and dislocation of the hand is a body injury involving complex structures and multiple functions, which frequently occur as they represent 10%-30% of all fractures. Such fractures and dislocation of the hand should be treated in the context of stability and flexibility; and tailored treatment is required in order to achieve the most optimal functional performance in each patient since deformation may occur if not treated, stiffness may occur with unnecessarily excessive treatment, and both deformation and stiffness may occur coincidently with inappropriate treatment. Stable injuries can be fixed with splintage whereas surgery is actively considered for unstable injuries. In addition, surgeons should keep in mind that as the surgical intervention is done aggressively, aggressive rehabilitation must be followed in correspondence with the surgical intervention. Successful outcome requires effort to prevent any potential complication including nerve hypersensitivity and infection. Finally, it is also important that the patient to know that swelling, stiffness, and pain may last for a long period of time until the recovery of fractures and dislocation of the hand.
- 1. Brunet ME, Haddad RJ Jr. Fractures and dislocations of the metacarpals and phalanges. Clin Sports Med, 1986;5:773-781.Article
- 2. Diwaker HN, Stothard J. The role of internal fixation in closed fractures of the proximal phalanges and metacarpals in adults. J Hand Surg Br, 1986;11:103-108.ArticlePDF
- 3. Court-Brown CM, Wood AM, Aitken S. The epidemiology of acute sports-related fractures in adults. Injury, 2008;39:1365-1372.Article
- 4. Oetgen ME, Dodds SD. Non-operative treatment of common finger injuries. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med, 2008;1:97-102.ArticlePDF
- 5. Singh J, Jain K, Mruthyunjaya , Ravishankar R. Outcome of closed proximal phalangeal fractures of the hand. Indian J Orthop, 2011;45:432-438.ArticlePDF
- 6. Yoong P, Goodwin RW, Chojnowski A. Phalangeal fractures of the hand. Clin Radiol, 2010;65:773-780.Article
- 7. Chim H, Teoh LC, Yong FC. Open reduction and interfragmentary screw fixation for symptomatic nonunion of distal phalangeal fractures. J Hand Surg Eur Vol, 2008;33:71-76.ArticlePDF
- 8. Gaheer RS, Ferdinand RD. Fracture dislocation of carpometacarpal joints: a missed injury. Orthopedics, 2011;34:399. Article
- 9. Meals C, Meals R. Hand fractures: a review of current treatment strategies. J Hand Surg Am, 2013;38:quiz 1031. 1021-1031.Article
- 10. Tuncer S, Aksu N, Dilek H, Ozkan T, Hamzaoglu A. Fractures of the fingers missed or misdiagnosed on poorly positioned or poorly taken radiographs: a retrospective study. J Trauma, 2011;71:649-655.Article
- 11. Federation of the European Societies for Surgery of the Hand 6th Congress Instructional Course. Fractures of the metacarpals and phalanges in adults and children. Bonn, Germany, 26-29 May 1999. Abstracts. J Hand Surg Br, 1999;24:Suppl 1. 1-30.Article
- 12. del Piñal F, Moraleda E, Rúas JS, de Piero GH, Cerezal L. Minimally invasive fixation of fractures of the phalanges and metacarpals with intramedullary cannulated headless compression screws. J Hand Surg Am, 2015;40:692-700.Article
- 13. Le Nen D. Extra-articular fractures of the digital metacarpals and phalanges of the long fingers. Chir Main, 2014;33:1-12.Article
- 14. Lautenbach M, Eisenschenk A, Sparmann M. Surgical and conservative treatment distal phalangeal fractures. Kongressbd Dtsch Ges Chir Kongr, 2002;119:519-525.Article
- 15. Ugurlar M, Saka G, Saglam N, Milcan A, Kurtulmus T, Akpınar F. Distal phalanx fracture in adults: Seymourtype fracture. J Hand Surg Eur Vol, 2014;39:237-241.ArticlePDF
- 16. Apic G, Mentzel M, Röhm A, Schöll H, Gülke J. Distal phalangeal fractures of the finger. Results of conservative and surgical treatment. Unfallchirurg, 2014;117:533-538.ArticlePDF
- 17. Valdes K, Naughton N, Algar L. Conservative treatment of mallet finger: a systematic review. J Hand Ther, 2015;28:237-245. quiz 246. Article
- 18. Richards SD, Kumar G, Booth S, Naqui SZ, Murali SR. A model for the conservative management of mallet finger. J Hand Surg Br, 2004;29:61-63.ArticlePDF
- 19. Auchincloss JM. Mallet-finger injuries: a prospective, controlled trial of internal and external splintage. Hand, 1982;14:168-173.ArticlePDF
- 20. Geyman JP, Fink K, Sullivan SD. Conservative versus surgical treatment of mallet finger: a pooled quantitative literature evaluation. J Am Board Fam Pract, 1998;11:382-390.Article
- 21. Horiuchi Y, Itoh Y, Sasaki T, Tasaki K, Iijima K, Uchinishi K. Dorsal dislocation of the D.I.P. joint with fracture of the volar base of the distal phalanx. J Hand Surg Br, 1989;14:177-182.ArticlePDF
- 22. Kapur B, Paniker J, Casaletto J. An alternative technique for external fixation of traumatic intra-articular fractures of proximal and middle phalanx. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg, 2015;19:163-167.Article
- 23. Hornbach EE, Cohen MS. Closed reduction and percutaneous pinning of fractures of the proximal phalanx. J Hand Surg Br, 2001;26:45-49.ArticlePDF
- 24. Oxford KL, Hildreth DH. Fracture bracing for proximal phalanx fractures. J Hand Ther, 1996;9:404-405.Article
- 25. Figl M, Weninger P, Hofbauer M, Pezzei C, Schauer J, Leixnering M. Results of dynamic treatment of fractures of the proximal phalanx of the hand. J Trauma, 2011;70:852-856.Article
- 26. Mikami Y, Takata H, Oishi Y. Kirschner wire stabilization of collateral ligament avulsion fractures of the base of the proximal phalanx. J Hand Surg Eur Vol, 2011;36:78-79.ArticlePDF
- 27. Nuland K, Charette R, Rodner CM. Operative Treatment of Unstable Long Oblique Proximal Phalanx Fractures. J Hand Surg Am, 2016;41:120-121.Article
- 28. Duncan KH, Jupiter JB. Intraarticular osteotomy for malunion of metacarpal head fractures. J Hand Surg Am, 1989;14:888-893.Article
- 29. Prokop A, Helling HJ, Kulus S, Rehm KE. Conservative treatment of metacarpal fracture. Kongressbd Dtsch Ges Chir Kongr, 2002;119:532-535.Article
- 30. Gajendran VK, Szabo RM, Myo GK, Curtiss SB. Biomechanical comparison of double-row locking plates versus single- and double-row non-locking plates in a comminuted metacarpal fracture model. J Hand Surg Am, 2009;34:1851-1858.Article
- 31. Facca S, Ramdhian R, Pelissier A, Diaconu M, Liverneaux P. Fifth metacarpal neck fracture fixation: Locking plate versus K-wire? Orthop Traumatol Surg Res, 2010;96:506-512.Article
- 32. Malasitt P, Owen JR, Tremblay MA, Wayne JS, Isaacs JE. Fixation for metacarpal neck fracture: a biomechanical study. Hand (N Y), 2015;10:438-443.ArticlePDF
- 33. Lee SG, Jupiter JB. Phalangeal and metacarpal fractures of the hand. Hand Clin, 2000;16:323-332. vii. Article
- 34. Miller RJ. Dislocations and fracture dislocations of the metacarpophalangeal joint of the thumb. Hand Clin, 1988;4:45-65.Article
- 35. Keramidas EG, Miller G. The Suzuki frame for complex intraarticular fractures of the thumb. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2005;116:1326-1331.Article
- 36. Ostrowski DM. Irreducible dorsoulnar dislocation of the proximal phalanx of the thumb. J Hand Surg Am, 1991;16:121-124.Article
- 37. Romo Rodríguez R, Fernández Vázquez JM, Camacho Galindo J, Tarazona Velutini P, Quinzaños Fresnedo J. Fracture dislocation of the proximal interphalangeal joint. Acta Ortop Mex, 2010;24:252-259.Article
- 38. Williams CS 4th. Proximal interphalangeal joint fracture dislocations: stable and unstable. Hand Clin, 2012;28:409-416. xi. Article
- 39. Elfar J, Mann T. Fracture-dislocations of the proximal interphalangeal joint. J Am Acad Orthop Surg, 2013;21:88-98.Article
- 40. Chamseddine AH, Jawish R, Zein H. Irreducible volar dislocation of the proximal interphalangeal finger joint. Chir Main, 2009;28:255-259.Article
- 41. Hamilton SC, Stern PJ, Fassler PR, Kiefhaber TR. Mini-screw fixation for the treatment of proximal interphalangeal joint dorsal fracture-dislocations. J Hand Surg Am, 2006;31:1349-1354.Article
- 42. Paul H, Albouni S, Mauger S, Heissler P. Palmar dislocation of the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint of the long finger. A case report. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol, 1995;5:97-100.Article
- 43. Ozçelik IB, Kabakas F, Mersa B, Purisa H, Sezer I, Ertürer E. Treatment of nonunions of the distal phalanx with olecranon bone graft. J Hand Surg Eur Vol, 2009;34:638-642.ArticlePDF
- 44. Meijs CM, Verhofstad MH. Symptomatic nonunion of a distal phalanx fracture: treatment with a percutaneous compression screw. J Hand Surg Am, 2009;34:1127-1129.Article
- 45. Hsu LP, Schwartz EG, Kalainov DM, Chen F, Makowiec RL. Complications of K-wire fixation in procedures involving the hand and wrist. J Hand Surg Am, 2011;36:610-616.Article
- 46. Nijhuis TH, Smits ES, Jaquet JB, Van Oosterom FJ, Selles RW, Hovius SE. Prevalence and severity of cold intolerance in patients after hand fracture. J Hand Surg Eur Vol, 2010;35:306-311.ArticlePDF
- 47. Smits ES, Nijhuis TH, Huygen FJ, Selles RW, Hovius SE, Niehof SP. Rewarming patterns in hand fracture patients with and without cold intolerance. J Hand Surg Am, 2011;36:670-676.Article
REFERENCES
Fig. 1

(A) The rotational deformity of the 4th finger nail plate was noted. (B) The deformity was aggravated with finger flexion.

Fig. 2

(A) We cannot see the specific fracture line on plain X-ray postero-anterior view. (B) The hamated fracture line was observed on a computed tomography imaging (arrow).

Fig. 3

(A) Damaged skin and soft tissue of the left hand was observed. (B) The reversed flow radial forearm flap was harvested. (C) Five months after flap surgery.

Fig. 4

Various treatments for distal phalangeal fractures. (A-C) Distal phalangeal fracture with nail bed injury. After closed reduction and K-wire fixation, the nail bed was repaired. Finally, the nail was reinserted and tied. (D, E) The avulsed fragment of the distal phalanx base dorsal aspect was noted. Extension block K-wiring was used. (F, G) Flexor digitorum profundus avulsion fracture at the distal phalanx was observed. Open reduction and hook plate fixation was performed.

Fig. 5

Various situations and treatment of middle, proximal phalangeal fracture. (A) Due to interaction of flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS) and extensor tendon central slip, dorsal angulation deformity was made at the middle phalangeal base fracture. (B) Because of traction of FDS, volar angulation was made at the middle phalangeal neck fracture. (C, D) Angulated and comminuted fracture of the proximal phalanx. Complete union was achieved with open reduction and plate fixation. (E-H) Crush injury at the middle phalanx. An open comminuted fracture and a severely damaged, dirty wound was observed. After dirty and devitalized tissue was debrided, temporary K-wire fixation was performed. At 2nd stage operation, auto iliac bone block graft and plate fixation was performed. A flap was required for skin coverage.

Fig. 6

Example of metacarpal fracture treatments. (A, B) A proximal phalanx collateral ligament avulsion fracture was observed. Closed reduction and K-wire fixation was performed. (C, D) A displaced, comminuted 2nd metacarpal head fracture. One headless screw and 1 miniscrew were used for fixation. (E, F) Multiple metacarpal neck fractures. Intramedullary nailing was performed at the 2, 3, and 5th metacarpal neck fracture. (G, H) Angulated and comminuted 5th metacarpal neck fracture. Intramedullary nailing with bouquet technique was performed. (I, J) Angulated and comminuted 5th metacarpal neck fracture. Transverse K-wire fixation was performed to the adjacent intact 4th metacarpal bone shaft. (K, L) Multiple metacarpal shaft fractures were noted. Plate fixation for the 2nd metacarpal bone, 3 lag screws for the 3rd metacarpal bone, and intramedullary nailing for the 4th metacarpal bone were used for each fracture. (M, N) Multiple comminuted metacarpal fractures. Complete union was achieved by locking plate.

Fig. 7

Various treatments of 1st metacarpal fractures. (A, B) A comminuted fracture of the 1st metacarpal shaft. Bony union was observed with plate fixation. (C, D) A 1st metacarpal base intraarticular fracture (Bennett fracture) was observed on a computed tomography image. After achieving satisfactory reduction with closed method, K-wire fixation was performed. (E, F) A 1st metacarpal base intraarticular comminuted fracture. Closed reduction was attempted, but failed. Therefore, open reduction and 2 screws fixation were performed. (G, H) A 1st metacarpal base intraarticular comminuted fracture. Comminution is very severe. We tried with limited minimal open reduction to achieve joint congruency and additional K-wire fixation and external fixation was applied.

Fig. 8

(A) Proximal interphalangeal joint flexion, distal interphalangeal joint joint hyperextension deformity (buttonhole deformity). (B) Severe valgus instability was checked on physical examination, which indicates a complete radial collateral ligament tear. (C-E) Second metacarpophalangeal joint dorsal dislocation was observed on imaging study. In the operating room, metacarpal head buttonholes into the palm (Kaplan deformity) was observed. The volar plate is interposed between the base of the proximal phalanx and metacarpal head. Lumbricalis is on the radial side, flexor tendon is on the ulnar side of the protruded metacarpal head. (F) Interposition of the adductor aponeurosis between the distal site of attachment of the ruptured ligament and the detached ligament, thus preventing ligamentous healing and restoration of joint stability. In this situation, only operative intervention will allow apposition and healing of the ligament in an anatomic position (arrow).

Table 1
![jkfs-29-143-i001.jpg]()
Examination and Management of Finger Dislocations and Fractures
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Current concepts in the management of phalangeal fractures in the hand
Hyun Tak Kang, Jun-Ku Lee
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(3): 109. CrossRef - Current Concepts in Management of Phalangeal Fractures
Yohan Lee, Sunghun Park, Jun-Ku Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2022; 35(4): 169. CrossRef
Current Concepts of Fractures and Dislocation of the Hand
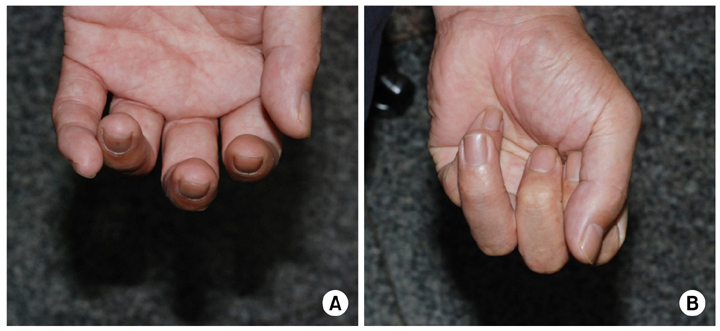
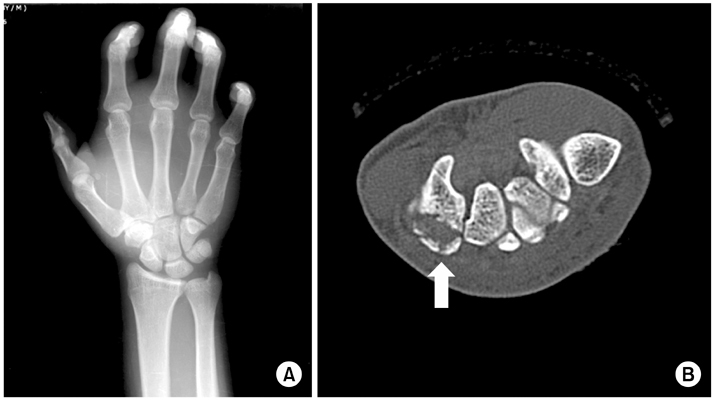
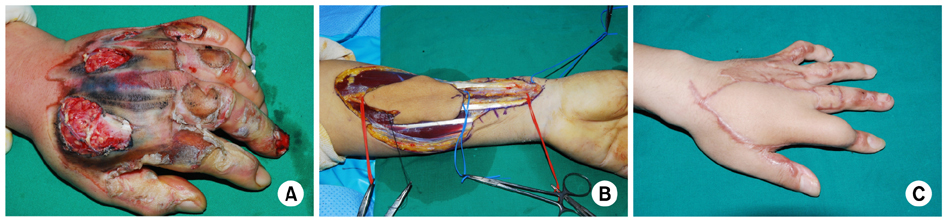
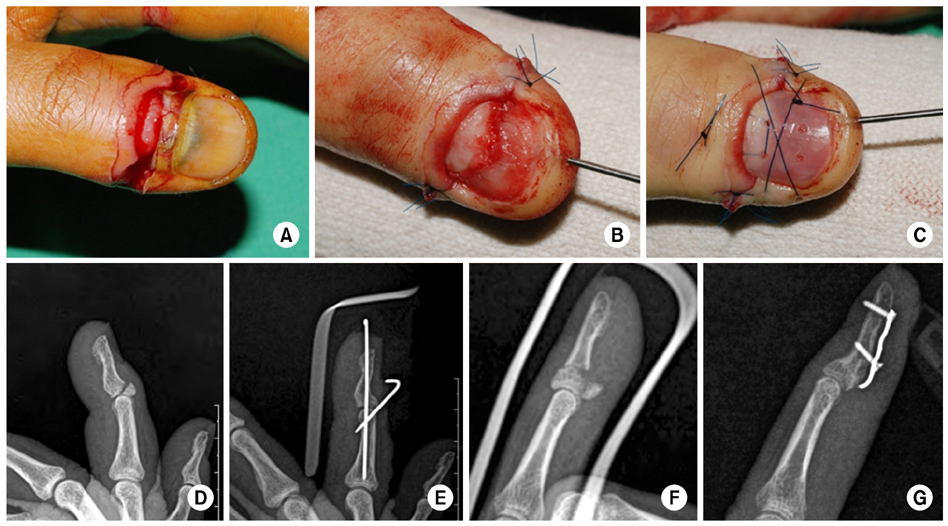
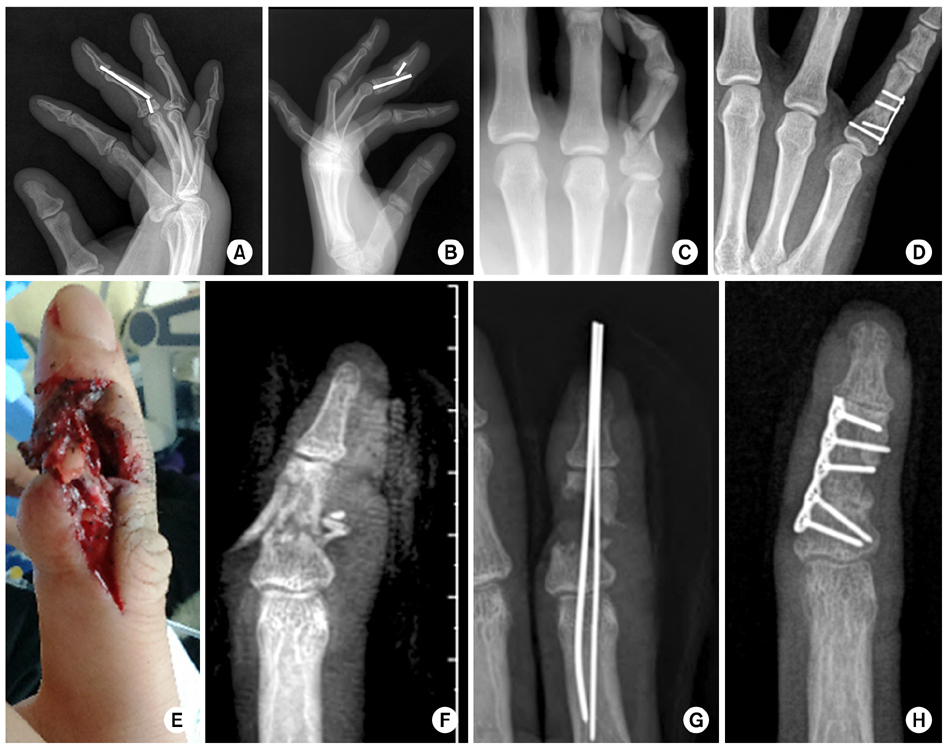
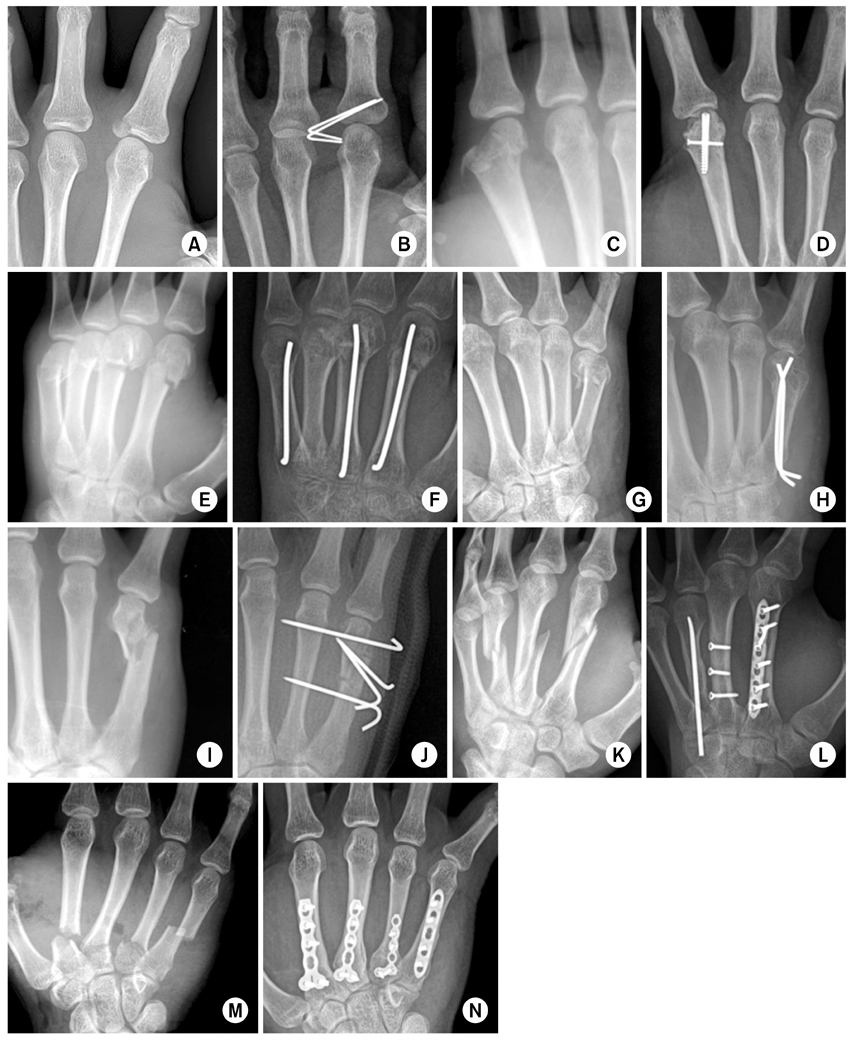
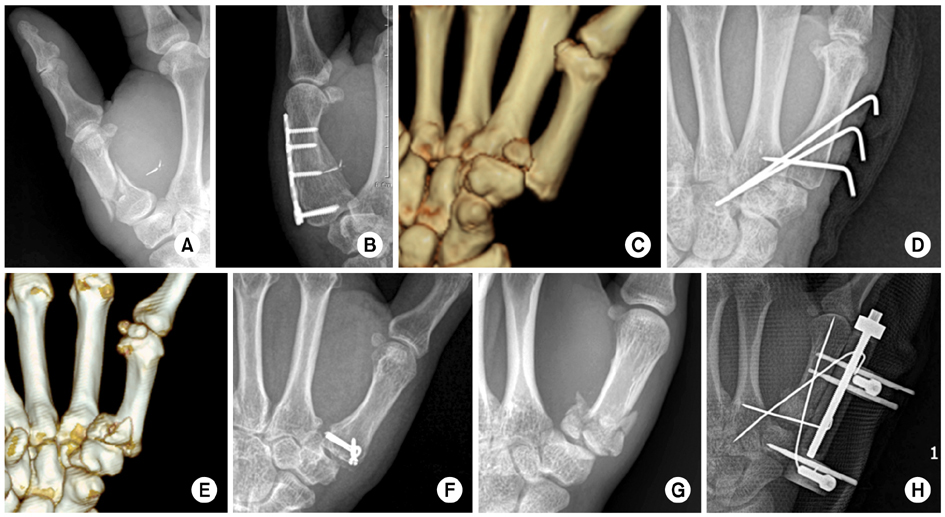
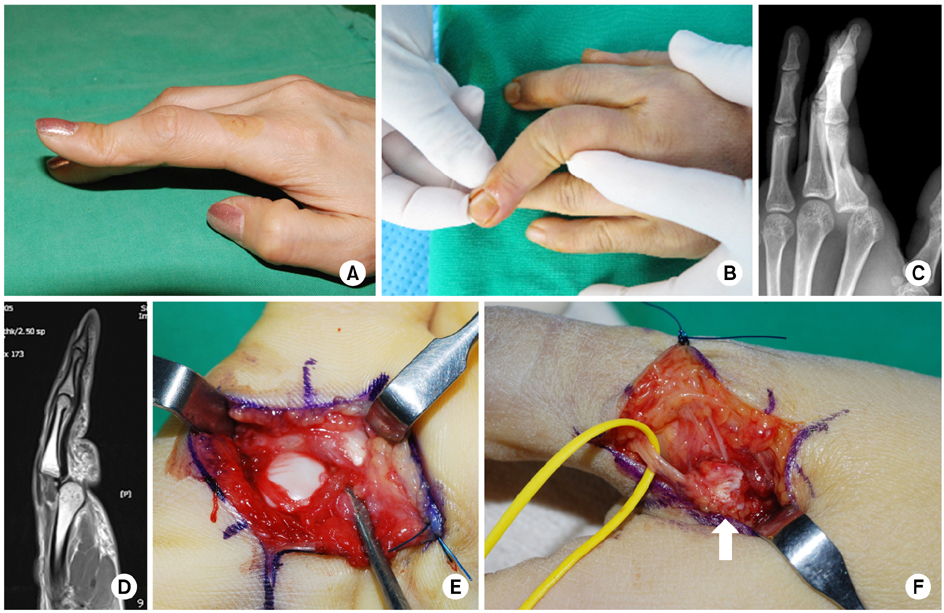
Fig. 1
(A) The rotational deformity of the 4th finger nail plate was noted. (B) The deformity was aggravated with finger flexion.
Fig. 2
(A) We cannot see the specific fracture line on plain X-ray postero-anterior view. (B) The hamated fracture line was observed on a computed tomography imaging (arrow).
Fig. 3
(A) Damaged skin and soft tissue of the left hand was observed. (B) The reversed flow radial forearm flap was harvested. (C) Five months after flap surgery.
Fig. 4
Various treatments for distal phalangeal fractures. (A-C) Distal phalangeal fracture with nail bed injury. After closed reduction and K-wire fixation, the nail bed was repaired. Finally, the nail was reinserted and tied. (D, E) The avulsed fragment of the distal phalanx base dorsal aspect was noted. Extension block K-wiring was used. (F, G) Flexor digitorum profundus avulsion fracture at the distal phalanx was observed. Open reduction and hook plate fixation was performed.
Fig. 5
Various situations and treatment of middle, proximal phalangeal fracture. (A) Due to interaction of flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS) and extensor tendon central slip, dorsal angulation deformity was made at the middle phalangeal base fracture. (B) Because of traction of FDS, volar angulation was made at the middle phalangeal neck fracture. (C, D) Angulated and comminuted fracture of the proximal phalanx. Complete union was achieved with open reduction and plate fixation. (E-H) Crush injury at the middle phalanx. An open comminuted fracture and a severely damaged, dirty wound was observed. After dirty and devitalized tissue was debrided, temporary K-wire fixation was performed. At 2nd stage operation, auto iliac bone block graft and plate fixation was performed. A flap was required for skin coverage.
Fig. 6
Example of metacarpal fracture treatments. (A, B) A proximal phalanx collateral ligament avulsion fracture was observed. Closed reduction and K-wire fixation was performed. (C, D) A displaced, comminuted 2nd metacarpal head fracture. One headless screw and 1 miniscrew were used for fixation. (E, F) Multiple metacarpal neck fractures. Intramedullary nailing was performed at the 2, 3, and 5th metacarpal neck fracture. (G, H) Angulated and comminuted 5th metacarpal neck fracture. Intramedullary nailing with bouquet technique was performed. (I, J) Angulated and comminuted 5th metacarpal neck fracture. Transverse K-wire fixation was performed to the adjacent intact 4th metacarpal bone shaft. (K, L) Multiple metacarpal shaft fractures were noted. Plate fixation for the 2nd metacarpal bone, 3 lag screws for the 3rd metacarpal bone, and intramedullary nailing for the 4th metacarpal bone were used for each fracture. (M, N) Multiple comminuted metacarpal fractures. Complete union was achieved by locking plate.
Fig. 7
Various treatments of 1st metacarpal fractures. (A, B) A comminuted fracture of the 1st metacarpal shaft. Bony union was observed with plate fixation. (C, D) A 1st metacarpal base intraarticular fracture (Bennett fracture) was observed on a computed tomography image. After achieving satisfactory reduction with closed method, K-wire fixation was performed. (E, F) A 1st metacarpal base intraarticular comminuted fracture. Closed reduction was attempted, but failed. Therefore, open reduction and 2 screws fixation were performed. (G, H) A 1st metacarpal base intraarticular comminuted fracture. Comminution is very severe. We tried with limited minimal open reduction to achieve joint congruency and additional K-wire fixation and external fixation was applied.
Fig. 8
(A) Proximal interphalangeal joint flexion, distal interphalangeal joint joint hyperextension deformity (buttonhole deformity). (B) Severe valgus instability was checked on physical examination, which indicates a complete radial collateral ligament tear. (C-E) Second metacarpophalangeal joint dorsal dislocation was observed on imaging study. In the operating room, metacarpal head buttonholes into the palm (Kaplan deformity) was observed. The volar plate is interposed between the base of the proximal phalanx and metacarpal head. Lumbricalis is on the radial side, flexor tendon is on the ulnar side of the protruded metacarpal head. (F) Interposition of the adductor aponeurosis between the distal site of attachment of the ruptured ligament and the detached ligament, thus preventing ligamentous healing and restoration of joint stability. In this situation, only operative intervention will allow apposition and healing of the ligament in an anatomic position (arrow).
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Fig. 6
Fig. 7
Fig. 8
Current Concepts of Fractures and Dislocation of the Hand
Examination and Management of Finger Dislocations and Fractures
| Diagnosis | Examination and initial treatment | Management | Recommendations for operation |
|---|---|---|---|
| PIP dislocation | Identify direction (dorsal, volar, lateral) | Dorsal: Splint and early range of motion | Fractures involving greater than 30%-40% of the intra-articular surface, reduction is difficult or unsuccessful, the patient is unable to obtain full extension following reduction |
| Attempt reduction | Volar: Splint in extension if there is an associated central slip | ||
| Check for neurovascular status and soft tissue injuries (volar plate in dorsal dislocation, central slip in volar dislocation) | |||
| Obtain postreduction radiographs | |||
| MCP dislocation (especially in the thumb) | Attempt reduction | Splint and early range of motion for simple dislocations | Reductions requiring anesthesia, open reductions |
| Check for neurovascular status and soft tissue injuries | |||
| Obtain postreduction radiographs (soft tissue injuries often impede reduction) | |||
| DIP dislocation | Attempt reduction | Splint and early range of motion | Complicated injuries |
| Check for neurovascular status and soft tissue injuries | |||
| Obtain postreduction radiographs | |||
| Distal phalanx fracture (tuft fracture) | Common in crush injuries | Splint for two to four weeks followed by range of motion; hyperesthesia, pain, and numbness common for up to six months following injury | Rarely needed |
| Assess for tenderness at distal phalanx | |||
| Obtain radiographs | |||
| Mallet fracture | Assess for inability to extend at DIP joint | Splint DIP joint in extension for eight weeks | Conservative treatment is ineffective; large displaced bony fragment or significant volar subluxation |
| Radiographs show a bony fragment at dorsal surface of the proximal distal phalanx | |||
| Flexor digitorum profundus avulsion fracture | Assess for inability to flex at the DIP joint | Referral recommended (possible flexor digitorum profundus retraction) | All injuries |
| Radiographs show a bony fragment at volar surface of the proximal distal phalanx | |||
| Middle or proximal phalanx fracture | Assess for tenderness over phalanx | Buddy taping and early range of motion | Displaced, oblique, or spiral fractures |
| Radiographs confirm diagnosis |
PIP: Proximal interphalangeal, MCP: Metacarpophalangeal, DIP: Distal interphalangeal.
Table 1
Examination and Management of Finger Dislocations and Fractures
PIP: Proximal interphalangeal, MCP: Metacarpophalangeal, DIP: Distal interphalangeal.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

