Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 23(1); 2010 > Article
-
Original Article
- Treatment of Proximal Tibia Fractures Using LCP by MIPO Technique
- Sang-Ho Ha, M.D., Dong-Hui Kim, M.D., Jun-Young Lee, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2010;23(1):34-41.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.1.34
Published online: January 31, 2010
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Jun-Young Lee, M.D. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chosun University Hospital, 588, Seosuk-dong, Dong-gu, Gwangju 501-717, Korea. Tel: 82-62-220-3147, Fax: 82-62-226-3379, leejy88@chosun.ac.kr
Copyright © 2010 The Korean Fracture Society
- 836 Views
- 10 Download
- 3 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- We wanted to evaluate the efficacy of MIPO (minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis) technique by LCP (locking compression plate) for treating proximal tibia fractures.
-
Materials and Methods
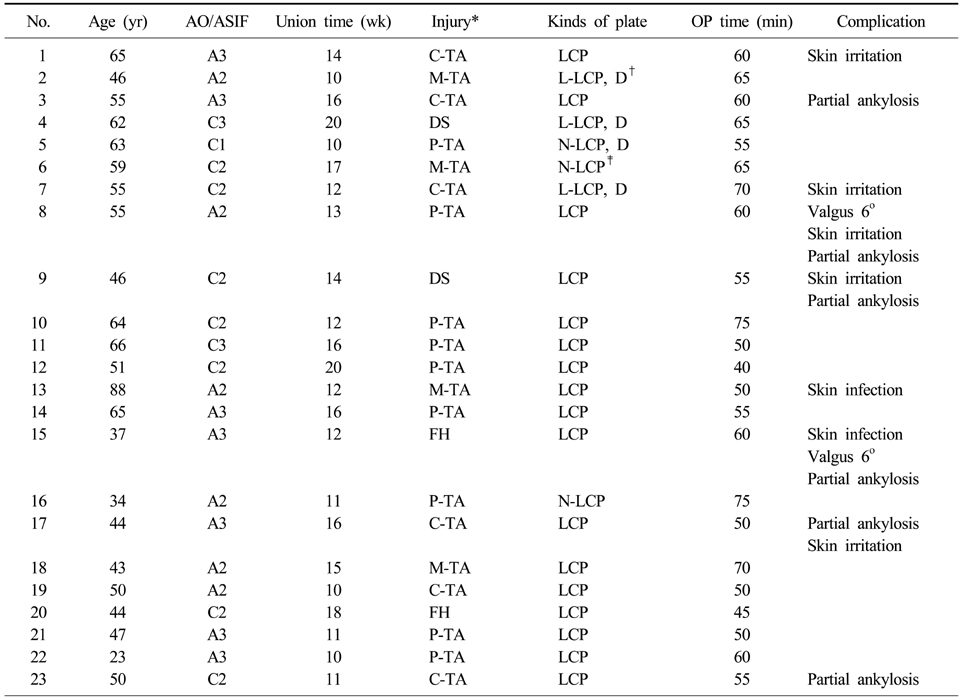
- Twenty-three patients, who had operation due to proximal tibia fracture and available for follow up for more than 1 year were included in this study. Cause of injury and accompanied injuries were checked. Operation time, period to bone union, range of joint motion and alignment were evaluated with complications.
-
Results
- Mean bone union time was 13.7 weeks (10~20). Twenty-one cases of the patients showed angulation of less than 5 degrees and 17 cases had normal range of motion. Five cases showed skin irritation by the plate and 2 cases had superficial infection.
-
Conclusion
- LCP by MIPO technique for treating proximal tibia fracture showed excellent results. Delicate technique is required for the proper adjustment of LCP and the alignment of the lower leg.
- 1. Baumgaertel F, Buhl M, Rahn BA. Fracture healing in biological plate osteosynthesis. Injury, 1998;29:Suppl 3. C3-C6.Article
- 2. Bolhofner BR. Indirect reduction and composite fixation of extraarticular proximal tibial fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1995;315:75-83.Article
- 3. Bone LB, Johnson KD. Treatment of tibial fractures by reaming and intramedullary nailing. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1986;68:877-887.Article
- 4. Buehler KC, Green J, Woll TS, Duwelius PJ. A technique for intramedullary nailing of proximal third tibia fractures. J Orthop Trauma, 1997;11:218-223.Article
- 5. Canadian Orthopaedic Trauma Society. Open reduction and internal fixation compared with circular fixator application for bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. Results of a multicenter, prospective, randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2006;88:2613-2623.Article
- 6. Court-Brown CM, Christie J, McQueen MM. Closed intramedullary tibial nailing. Its use in closed and type I open fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1990;72:605-611.ArticlePDF
- 7. Duwelius PJ, Rangitsch MR, Colville MR, Woll TS. Treatment of tibial plateau fractures by limited internal fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1997;339:47-57.Article
- 8. Egol KA, Tejwani NC, Capla EL, Wolinsky PL, Koval KJ. Staged management of high-energy proximal tibia fractures (OTA types 41): the results of a prospective, standardized protocol. J Orthop Trauma, 2005;19:448-455. discussion 456.Article
- 9. Gaudinez RF, Mallik AR, Szporn M. Hybrid external fixation of comminuted tibial plateau fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1996;328:203-210.Article
- 10. Gerher A, Ganz R. Combined internal and external osteosynthesis a biological approach to the treatment of complex fractures of the proximal tibia. Injury, 1998;29:Suppl 3. C22-C28.Article
- 11. Henley MB. Intramedullary divices for tibia fracture stabilization. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1989;(240):87-96.Article
- 12. Hutson JJ Jr, Zych GA. Infections in periarticular fractures of the lower extremity treated with tensioned wire hybrid fixators. J Orthop Trauma, 1998;12:214-218.Article
- 13. Kumar A, Whittle AP. Treatment of complex (Schatzker Type VI) fractures of the tibial plateau with circular wire external fixation: retrospective case review. J Orthop Trauma, 2000;14:339-344.Article
- 14. Lang GJ, Cohen BE, Bosse MJ, Kellam JF. Proximal third tibial shaft fractures. Should they be nailed? Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1995;315:64-74.Article
- 15. Lee BK, Jo H, Eom GS, Kim JW. Treatment of comminuted fractures of proximal tibia using MIPO technique. J Korean Soc Fract, 2002;15:243-250.Article
- 16. Miclau T, Martin RE. The evolution of modern plate osteosynthesis. Injury, 1997;28:Suppl 1. A3-A6.Article
- 17. Muller ME, Allgower M, Schneider R, Willenegger H. Manual of internal fixation. Techniques Recommended By the AOASIF. 1990;3rd ed. Berlin, Springer-Verlag. 574-576.Article
- 18. Oh CW, Oh JK, Jeon IH, et al. Double plating of proximal tibial fractures using minimally invasive percutaneous osteosynthesis technique. J Korean Fract Soc, 2005;18:250-255.Article
- 19. Peindl RD, Zura RD, Vincent A, Coley ER, Bosse MJ, Sims SH. Unstable proximal extraarticular tibia fractures: a biomechanical evaluation of four methods of fixation. J Orthop Trauma, 2004;18:540-545.Article
- 20. Perren SM. Minimally invasive internal fixation history, essence and potential of a new approach. Injury, 2001;32:Suppl 1. SA1-SA3.Article
- 21. Phisitkul P, McKinley TO, Nepola JV, Marsh JL. Complications of locking plate fixation in complex proximal tibia injuries. J Orthop Trauma, 2007;21:83-91.Article
- 22. Sarmiento A, Gersten LM, Sobol PA, Shankwiler JA, Vangsness CT. Tibial shaft fractures treated with functional braces. Experience with 780 fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1989;71:602-609.ArticlePDF
- 23. Schatzker J, Lambert DC. Supracondylar fractures of the femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1979;138:77-83.Article
- 24. Stamer DT, Schenk R, Staggers B, Aurori K, Aurori B, Behrens FF. Bicondylar tibial plateau fractures treated with a hybrid ring external fixator: a preliminary study. J Orthop Trauma, 1994;8:455-461.Article
- 25. Stokel EA, Sadasivan KK. Tibial plateau fractures: standardized evaluation of operative results. Orthopedics, 1991;14:263-270.Article
- 26. Tornetta P 3rd, Collins E. Semiextended position of intramedullary nailing of the proximal tibia. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1996;328:185-189.Article
- 27. Young MJ, Barrack RL. Complications of internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures. Orthop Rev, 1994;23:149-154.Article
REFERENCES
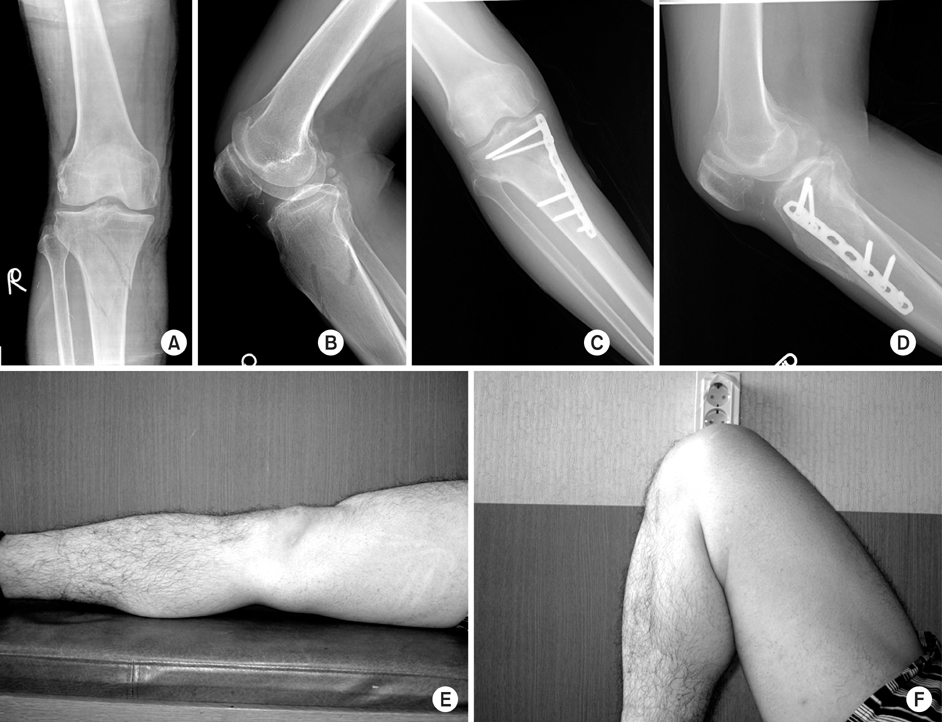
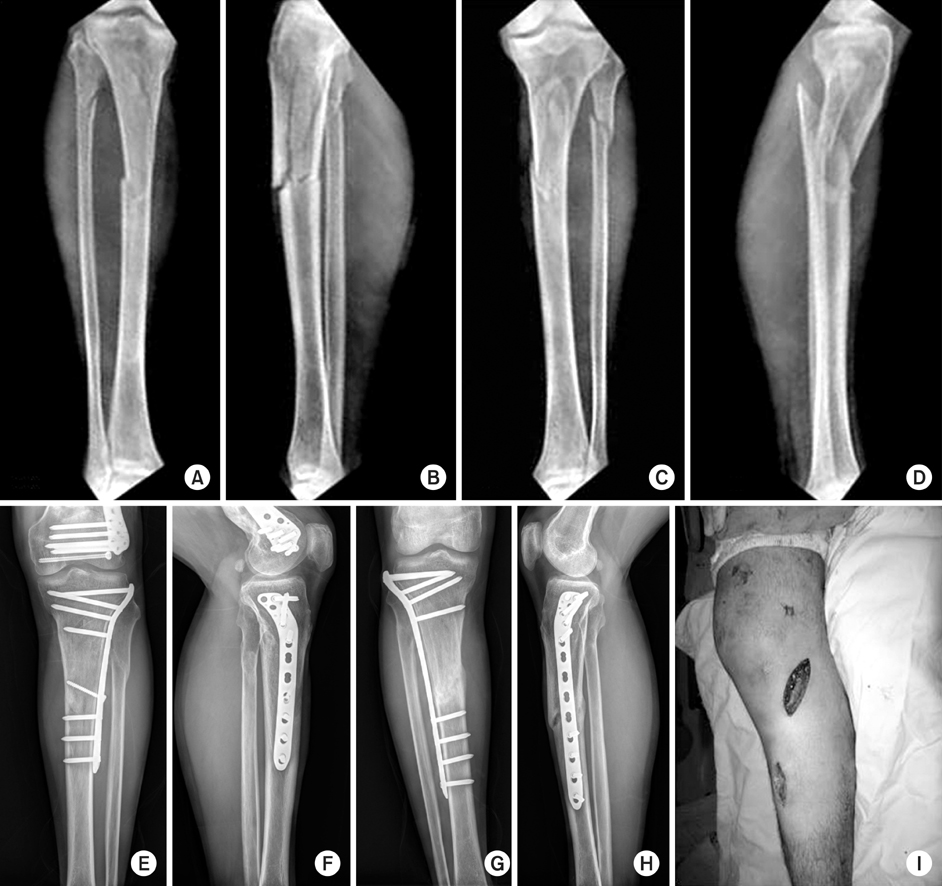
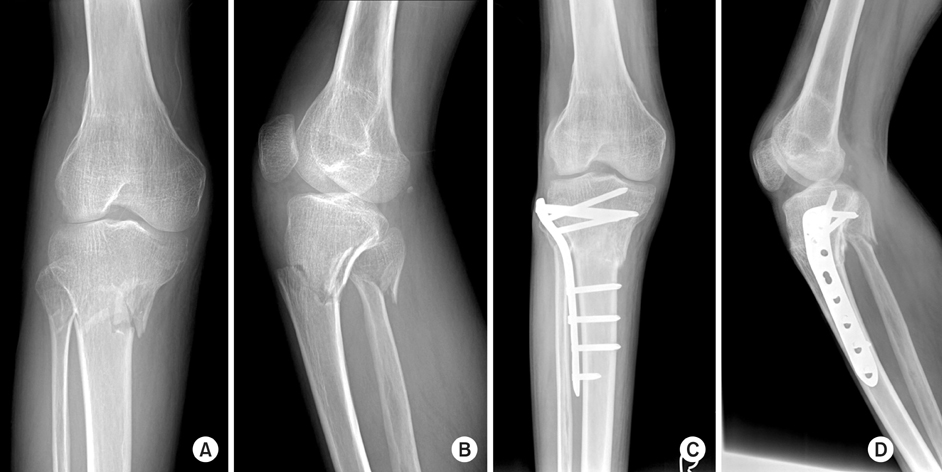
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- EVALUATION OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF SURGICAL TREATMENT FOR FRACTURE AROUND KNEE WITH LOCKING PLATE
VIKAS KUNTWAD, AMOL WAGH, SATYAJEET A HORE
Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research.2023; : 213. CrossRef - Medial Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis in Proximal Tibial Comminuted Fractures
Jae-Ang Sim, Kwang-Hui Kim, Yong-Seuk Lee, Sang-Jin Lee, Beom-Koo Lee
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2014; 49(4): 278. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Stabilization Using a Medial Locking Plate for Proximal Tibial Fractures - Technical Note -
Jae Ang Sim, Beom Koo Lee, Kwang Hui Kim, Yong Seuk Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2013; 26(4): 327. CrossRef
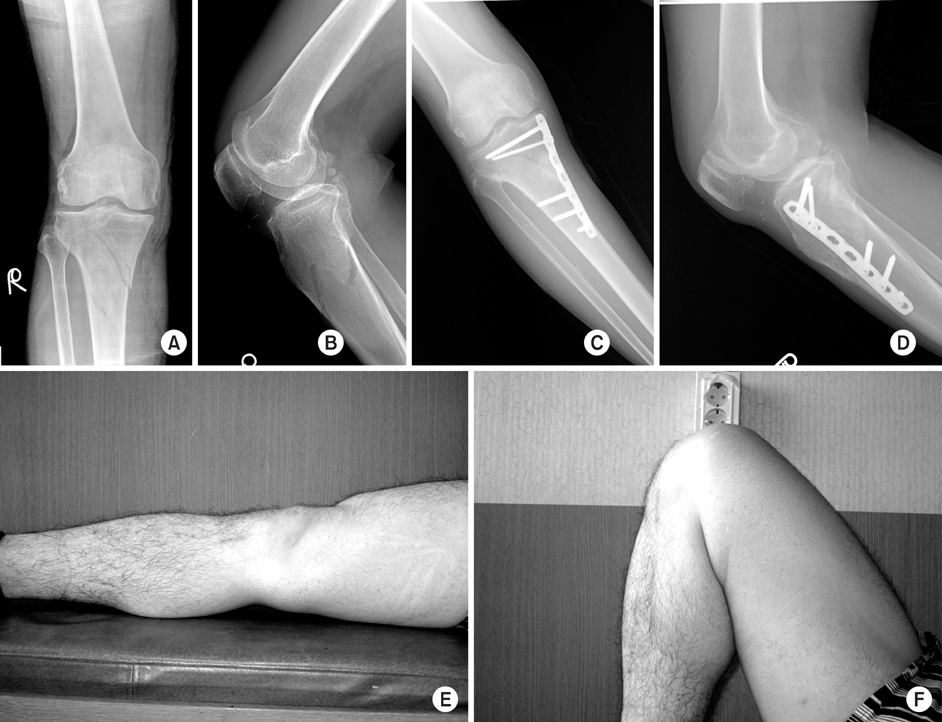
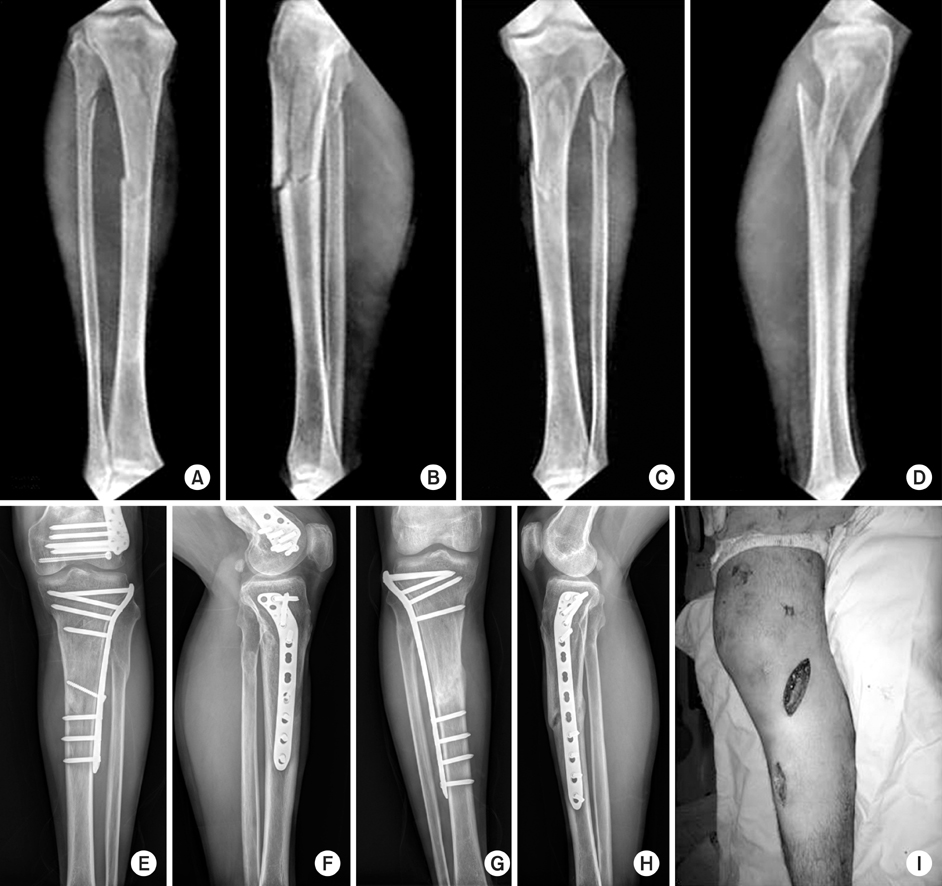
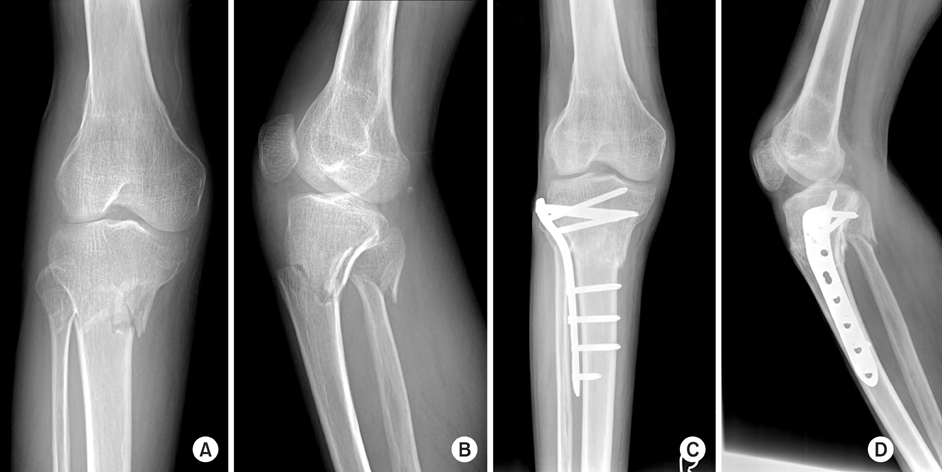
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Proximal tibial fractures treated with locking compressive plate using minimally invasive percutaneous osteosynthesis technique
*In injury mechanism, there were FH (fall from a height), DS (direct stroke), M-TA (motor cycle accident), C-TA (in car accident), and P-TA (pedestrian traffic accident), †Dual plating, ‡Narrow LCP.
Radiologic alignment of knee
Knee ROM
ROM: Range of motion.
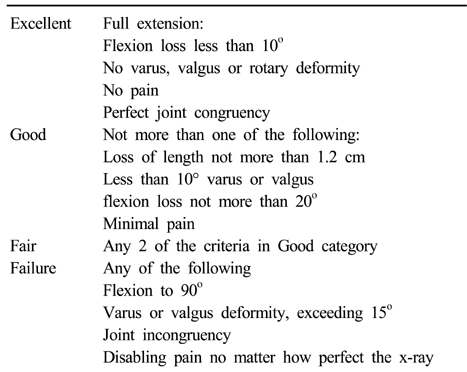
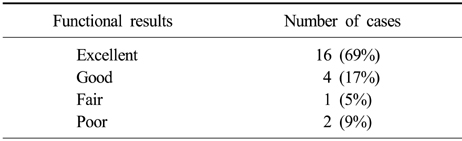
Schatzker and lambert assessment
The results of the schatzker and lambert assessment
*In injury mechanism, there were FH (fall from a height), DS (direct stroke), M-TA (motor cycle accident), C-TA (in car accident), and P-TA (pedestrian traffic accident), †Dual plating, ‡Narrow LCP.
ROM: Range of motion.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS


 Cite
Cite

