Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 23(4); 2010 > Article
-
Review Article from Symposium
- Acute Compartment Syndrome after Trauma
- Chang-Wug Oh, M.D., Hyun-Joo Lee, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2010;23(4):399-403.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.4.399
Published online: October 31, 2010
- Address reprint requests to: Chang-Wug Oh, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, 101, Dongin-dong 2-ga, Jung-gu, Daegu 700-422, Korea. Tel: 82-53-420-5630, Fax: 82-53-422-6605, cwoh@knu.ac.kr
Copyright © 2010 The Korean Fracture Society
- 546 Views
- 4 Download
- 8 Crossref
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Design and Feasibility Test of Motorized Hand-Held Devices for Intra-compartmental Pressure Monitoring
Bomi Yang, Jaeho Hyun, Jingyu Kim, Jihoon Kweon, Jaesoon Choi, Youngjin Moon, Ji Wan Kim
International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing.2024; 25(1): 99. CrossRef - Delayed Treatment of Foot Compartment Syndrome: A Case Report and Literature Review
Jihoon Jang, Young Choi
Journal of Korean Foot and Ankle Society.2021; 25(1): 46. CrossRef - Acute Compartment Syndrome after Anticoagulant Therapy to Misdiagnosed Deep Vein Thrombosis
Seok-Ha Hwang, Ho-Seung Jeon, Young-Kyun Woo, Seong-Tae Lim
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2019; 54(2): 177. CrossRef - A Clinical Case Study of Residual Symptoms after Decompression of Traumatic Compartment Syndrome
Min Jung Ji, Seong Chul Lim, Jae Soo Kim, Hyun Jong Lee, Yun Kyu Lee
The Acupuncture.2015; 32(3): 197. CrossRef - Diagnosis and Management of Acute Compartment Syndrome
Keun-Bae Lee, Seung-Hun Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2015; 28(1): 93. CrossRef - Clinical Outcomes of Fasciotomy for Acute Compartment Syndrome
Ji Yong Park, Young Chang Kim, Ji Wan Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2015; 28(4): 223. CrossRef - Compartment Syndrome of the Gluteus Medius Occurred without Bleeding or Trauma: A Case Report
Gyu-Min Kong, Yong-Uk Kwon, Jun-Ho Park
Hip & Pelvis.2015; 27(4): 278. CrossRef - Selection and Recommended Usage Guide of Temporary External Fixator
Seung-Jae Lim, Ki-Sun Sung, Chang-Wug Oh
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2013; 26(2): 164. CrossRef
Acute Compartment Syndrome after Trauma
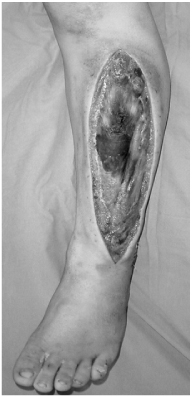
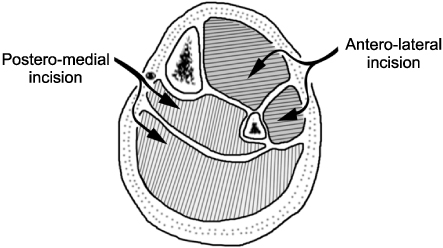
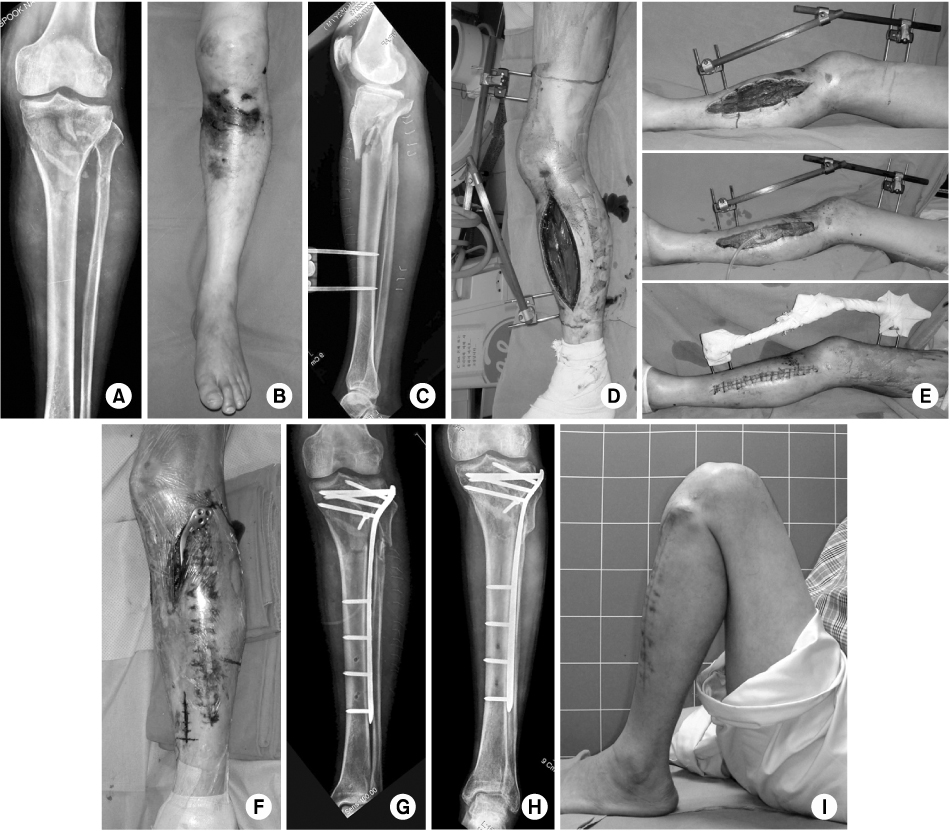
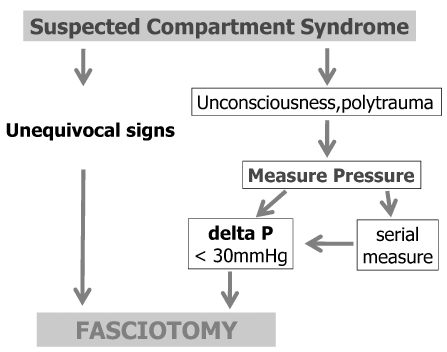
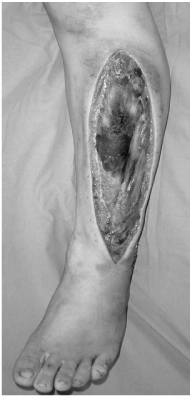
Fig. 1
The patient shows the necrosis of muscles in lateral compartment after compartment syndrome.
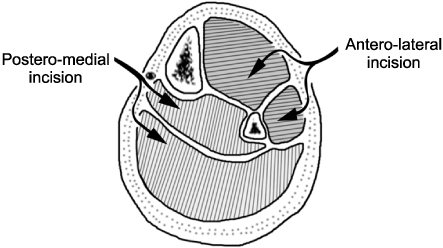
Fig. 2
Double incision technique to decompress the compartment syndrome.
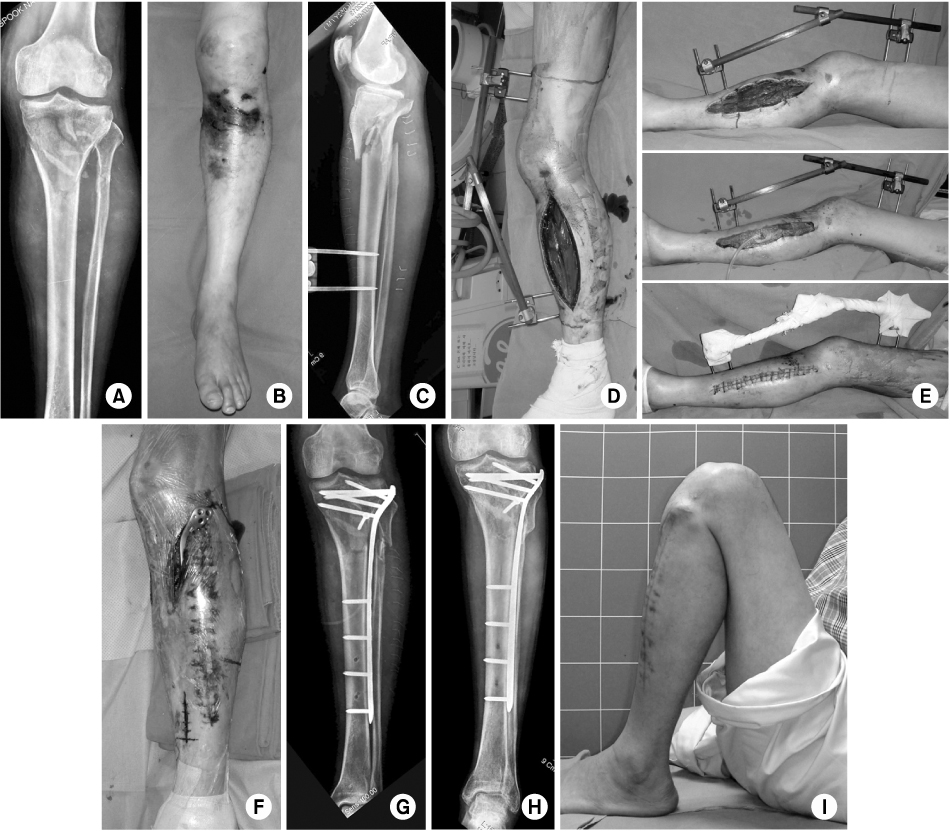
Fig. 3
The patient with a proximal tibia fracture (A) showed a severe swelling around the knee (B).
Fasciotomy was performed with the temporary external fixation (C, D).
The persisted swelling was handled by using vacuum-assisted wound closure. At 10 days after injury, the wound was closed successfully (E).
At 14 days, the fracture was stabilized with MIPO technique (F, G).
The fracture was united and the patient recovered the pre-injury function, at 1 year (H, I).
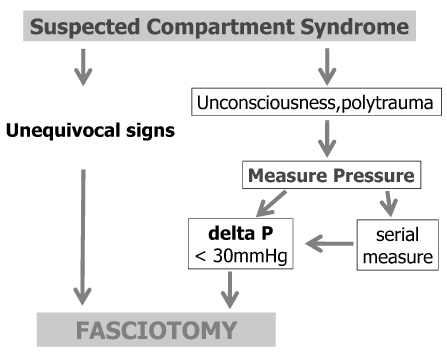
Fig. 4
Suggested diagram for the diagnosis and treatment for the compartment syndrome.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Acute Compartment Syndrome after Trauma
Risk factors of compartment syndrome
Table 1
Risk factors of compartment syndrome

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 Cite
Cite

