Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 24(3); 2011 > Article
-
Review Article from Symposium
- Treatment of Distal Femur Fracture
- Jung Jae Kim, M.D., Ji Ho Choi, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2011;24(3):288-293.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.3.288
Published online: July 15, 2011
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Jung Jae Kim, M.D. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Asan Medical Center, 88, Olympic-ro 43-gil, Songpa-gu, Seoul 138-736, Korea. Tel: 82-2-3010-3530, Fax: 82-2-488-7877, jjkim2@amc.seoul.kr
Copyright © 2011 The Korean Fracture Society
- 919 Views
- 5 Download
- 3 Crossref
- 1. Arneson TJ, Melton LJ 3rd, Lewallen DG, O'Fallon WM. Epidemiology of diaphyseal and distal femoral fractures in Rochester, Minnesota, 1965-1984. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1988;234:188-194.Article
- 2. Butt MS, Krikler SJ, Ali MS. Displaced fractures of the distal femur in elderly patients. Operative versus non-operative treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1996;78:110-114.
- 3. Court-Brown CM, Caesar B. Epidemiology of adult fractures: a review. Injury, 2006;37:691-697.Article
- 4. Healy WL, Brooker AF Jr. Distal femoral fractures. Comparison of open and closed methods of treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1983;174:166-171.
- 5. Heiney JP, Barnett MD, Vrabec GA, Schoenfeld AJ, Baji A, Njus GO. Distal femoral fixation: a biomechanical comparison of trigen retrograde intramedullary (i.m.) nail, dynamic condylar screw (DCS), and locking compression plate (LCP) condylar plate. J Trauma, 2009;66:443-449.
- 6. Higgins TF, Pittman G, Hines J, Bachus KN. Biomechanical analysis of distal femur fracture fixation: fixed-angle screw-plate construct versus condylar blade plate. J Orthop Trauma, 2007;21:43-46.
- 7. Kolb W, Guhlmann H, Windisch C, Marx F, Kolb K, Koller H. Fixation of distal femoral fractures with the Less Invasive Stabilization System: a minimally invasive treatment with locked fixed-angle screws. J Trauma, 2008;65:1425-1434.
- 8. Martinet O, Cordey J, Harder Y, Maier A, Bühler M, Barraud GE. The epidemiology of fractures of the distal femur. Injury, 2000;31:Suppl 3. C62-C63.
- 9. Merchan EC, Maestu PR, Blanco RP. Blade-plating of closed displaced supracondylar fractures of the distal femur with the AO system. J Trauma, 1992;32:174-178.
- 10. Neer CS 2nd, Grantham SA, Shelton ML. Supracondylar fracture of the adult femur. A study of one hundred and ten cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1967;49:591-613.
- 11. Papadokostakis G, Papakostidis C, Dimitriou R, Giannoudis PV. The role and efficacy of retrograding nailing for the treatment of diaphyseal and distal femoral fractures: a systematic review of the literature. Injury, 2005;36:813-822.
- 12. Pettine KA. Supracondylar fractures of the femur: long-term follow-up of closed versus nonrigid internal fixation. Contemp Orthop, 1990;21:253-261.
- 13. Sanders R, Regazzoni P, Ruedi TP. Treatment of supracondylar-intracondylar fractures of the femur using the dynamic condylar screw. J Orthop Trauma, 1989;3:214-222.
- 14. Sanders R, Swiontkowski M, Rosen H, Helfet D. Double-plating of comminuted, unstable fractures of the distal part of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1991;73:341-346.
- 15. Shewring DJ, Meggitt BF. Fractures of the distal femur treated with the AO dynamic condylar screw. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1992;74:122-125.PDF
- 16. Weight M, Collinge C. Early results of the less invasive stabilization system for mechanically unstable fractures of the distal femur (AO/OTA types A2, A3, C2, and C3). J Orthop Trauma, 2004;18:503-508.
- 17. Yang RS, Liu HC, Liu TK. Supracondylar fractures of the femur. J Trauma, 1990;30:315-319.
- 18. Zlowodzki M, Bhandari M, Marek DJ, Cole PA, Kregor PJ. Operative treatment of acute distal femur fractures: systematic review of 2 comparative studies and 45 case series (1989 to 2005). J Orthop Trauma, 2006;20:366-371.
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Comparative study of retrograde intramedullary nailing versus locking extramedullary plating in complete articular fractures with metaphyseal comminution of the distal femur
Yong-Cheol Yoon, Youngwoo Kim, Benjamin D. Pesante, You Seung Chun, Sang Ho Lee, Hoon-Sang Sohn
Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery.2024; 144(5): 2109. CrossRef - Efficacy of Integrated Korean Medicine Treatment Including Motion-Style Acupuncture Treatment for L1 Burst Fracture and Bilateral Femoral Condyle, Proximal Tibial, and Proximal Fibular Comminuted Fractures: A Case Report
Da Dam Kim, Seong Hyeon Jeon, Woo Young Kim
Journal of Acupuncture Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Mid-Term Result after Osteosynthesis of Intra-Articular Fractures of Distal Femur
Sam Guk Park, Jeong Jae Moon, Oog Jin Shon
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2016; 29(4): 242. CrossRef
Treatment of Distal Femur Fracture
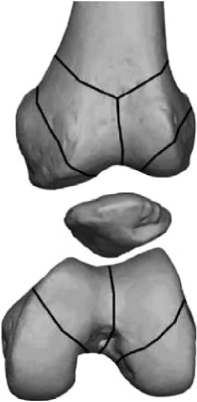
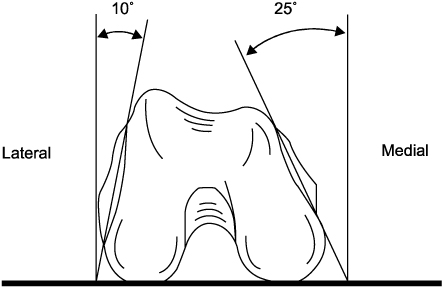
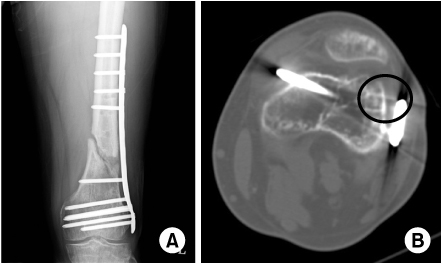
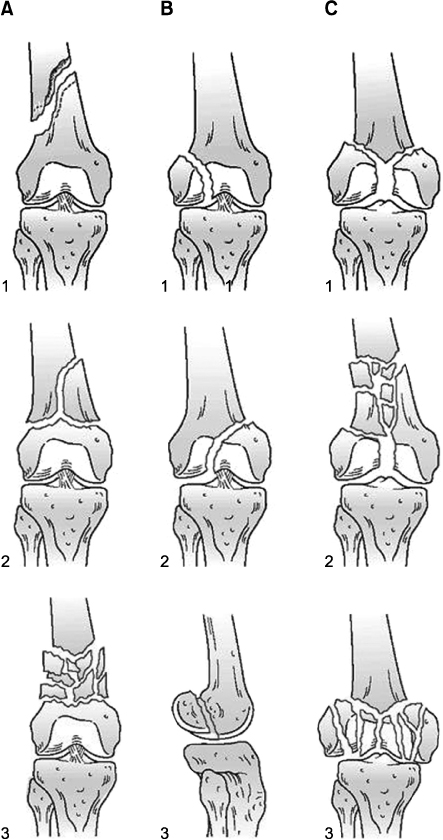
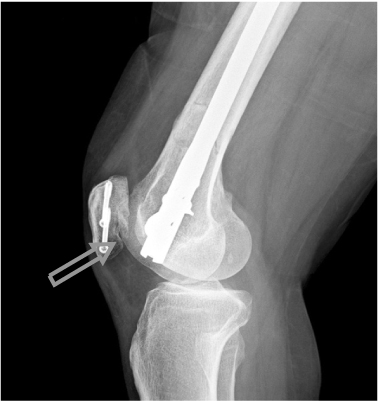
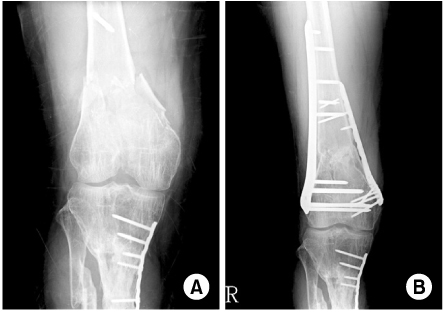
Fig. 1
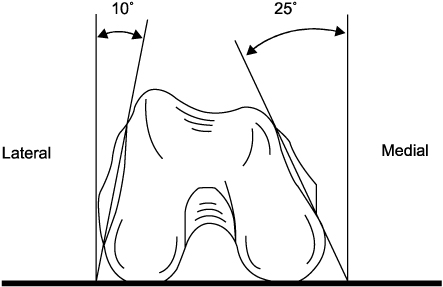
Lines of weakness on the distal femur.
Fig. 2
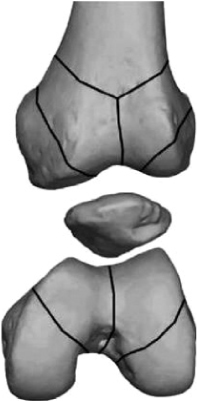
Anatomy of distal femur.
Fig. 3
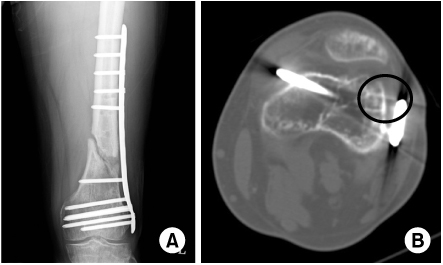
(A) Implant (distal screws) that appear of appropriate length.
(B) Distal screw is too long and cause painful medial irritation/poor plate position cause painful lateral irritation.
Fig. 4
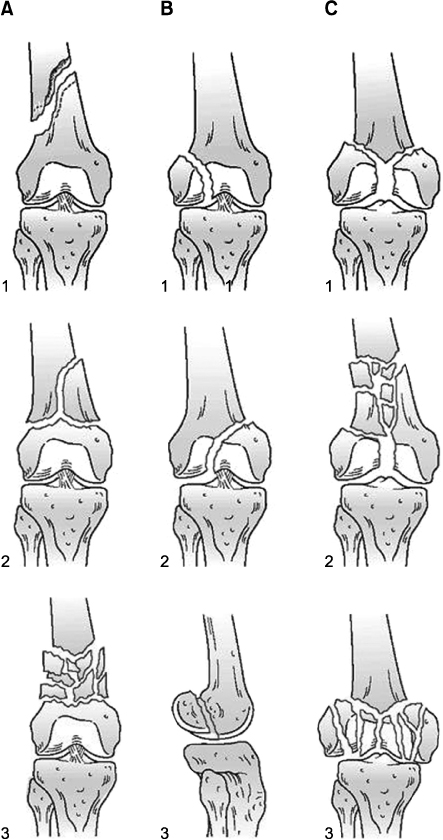
AO/OTA classification.
Fig. 5
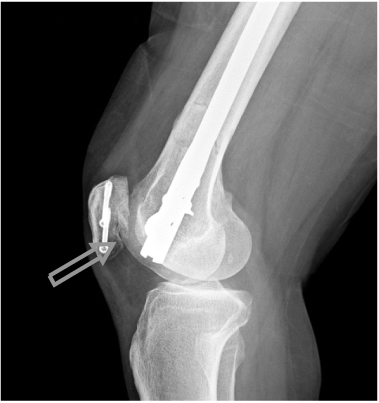
Improper nail depth cause patella notching and anterior knee pain.
Fig. 6
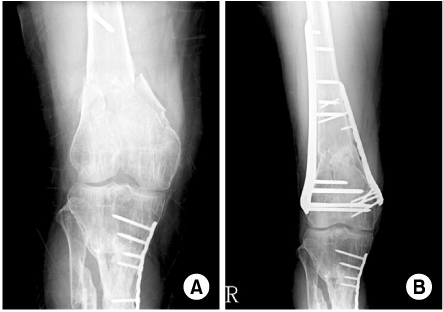
(A) AO/OTA classification type C/2 distal femur fracture.
(B) Medial augmentation with plate for extensive metaphyseal communition.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Fig. 6
Treatment of Distal Femur Fracture

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

