Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Acute Compartment Syndrome of Thigh: Ten-Year Experiences from a Level I Trauma Center
- Hyung Keun Song, Won-Tae Cho, Wan-Sun Choi, Seung-Yeob Sakong, Sumin Im
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2024;37(4):171-174. Published online October 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2024.37.4.171
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
To assess the demographics, injury mechanisms, treatments, and outcomes of traumatic acute compartment syndrome in the thigh.
Materials and Methods
Patients diagnosed with thigh compartment syndrome were analyzed retrospectively at the authors’ level I trauma center from March 2012 to February 2022. Data were collected from medical and radiological records, focusing on demographics, injury details, treatment timelines, and clinical outcomes.
Results
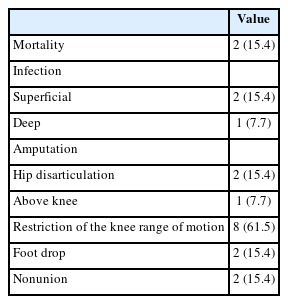
The cohort included 13 patients (11 males and 2 females) with a mean age of 46 years. Injuries primarily resulted from falls (6 patients) and vehicle accidents (5 patients). Fractures were noted in 11 patients, with seven involving the lower extremities and seven having open fractures; three of these were severe enough to be classified as Gustilo–Anderson type IIIc with associated femoral artery injuries. Time from the injury to fasciotomy ranged from within six hours to more than 24 hours. Fasciotomies were mainly single-sided (10 patients), targeting primarily the anterior compartments, and bilateral in three cases. Wound closures were performed using delayed primary closure (four patients) and partial- thickness skin grafts (five patients). Two patients died from multi-organ failure; other complications included infections (three patients), amputations (three patients), and long-term disabilities like drop foot (two patients), sensory deficits, joint stiffness (eight patients), and fracture non-unions requiring additional surgery (two patients).
Conclusion
Thigh-compartment syndrome, though infrequent, poses significant risks of mortality and chronic disability. This underscores the importance of prompt diagnosis and intervention.
- 1,507 View
- 48 Download

- Comparison of the Clinical and Radiographic Results between 125° and 130° Caput-Collum-Diaphyseal Angle Proximal Femoral Nail Anti-Rotation II in Patients with Intertrochanteric Fracture
- Soo Jae Yim, Yong Bok Park, Hyun Kwon Kim, Sin Hyung Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(4):210-216. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.4.210
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study compared the clinical and radiographic results of two proximal femoral nail antirotation II (PFNA-II) angled by 125° and 130° in patients with intertrochanteric fractures.
Materials and Methods
From March in 2015 to September in 2016, 65 patients who underwent a closed reduction and internal fixation with PFNA-II for a femoral intertrochanteric fracture were evaluated retrospectively. The minimum follow-up period was two years. Of those, 30 and 35 patients underwent 125° angled PFNA-II and 130° angled PFNA-II, respectively. The clinical performance was evaluated using the Harris hip score, WOMAC (Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthrtis Index), and UCLA (University of California Los Angeles) score. Radiographic analyses were performed using standardized anteroposterior and lateral radiographs to assess the implant position and quality of reduction. The blade length, distance between the blade tip and the tip of the greater trochanter, and distance between the blade tip and the most lateral protrusion point of the greater trochanter in the two groups were measured and compared.
Results
The clinical results, including the Harris hip score, WOMAC, and UCLA, were similar in the two groups at the last follow-up postoperatively. In the radiography evaluation, the implant position, quality of reduction, and the blade length were similar in the two groups. The distances between the blade tip and the tip of the greater trochanter were 52.60±3.53 mm and 58.07±5.54 mm in the 125° angled PFNA-II and 130° angled PFNA-II groups, respectively. The distance between the blade tip and the most lateral protrusion point of greater trochanter were 16.48±2.54 mm and 21.19±4.43 mm in the 125° angled PFNA-II and 130° angled PFNA-II groups, respectively. The differences were significant (p=0.031, p=0.012).
Conclusion
The operation with the 125° angled PFNA-II showed a more superior and lateral position of the blade than that with the 130° angled PFNA-II. Nevertheless, lateral thigh pain can occur when the blade is positioned superolaterally.
- 464 View
- 2 Download

Case Report
- Acute Compartment Syndrome of the Thigh Caused by Contusion: 4 Cases Report
- Oog Jin Shon, Gi Beom Kim, Chul Hyun Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(3):215-218. Published online July 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.3.215
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Acute compartment syndrome of the thigh, which usually occurs in the anterior compartment, is a rare condition. It can have various causes including femur fractures, vessel injury, pseudoaneurysm of the femoral or popliteal artery, and use of anticoagulant. However, there have been few reports of acute compartment syndrome of the thigh without fracture caused by blunt trauma. We report 4 cases of acute compartment syndrome of the thigh without fracture caused by blunt trauma, in which three patients were treated with fasciotomy and a Vacuum-Assisted wound Closure system and the other one had a delayed diagnosis, and eventually underwent above-knee amputation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Clinical Case Study of Residual Symptoms after Decompression of Traumatic Compartment Syndrome
Min Jung Ji, Seong Chul Lim, Jae Soo Kim, Hyun Jong Lee, Yun Kyu Lee
The Acupuncture.2015; 32(3): 197. CrossRef - Clinical Outcomes of Fasciotomy for Acute Compartment Syndrome
Ji Yong Park, Young Chang Kim, Ji Wan Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2015; 28(4): 223. CrossRef
- A Clinical Case Study of Residual Symptoms after Decompression of Traumatic Compartment Syndrome
- 610 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

Original Articles
- The Usefulness of Hip to Thigh Ratio as an Anthropometric Indicator for the Incidence of Hip Fracture
- Jin Park, Kyu Hyun Yang, Seong Hwan Moon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(1):1-5. Published online January 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To compare anthropometric indicators around the hip between osteoporotic fracture group and control group.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty patients for osteoporotic hip fracture and the same number of patients for spine fracture who admitted our institute from November 2006 to March 2007 were matched with control patients without osteoporotic fracture. The waist circumference (WC), hip circumference (HC), thigh circumference (TC), and height were measured. From these measurements, waist to hip ratio (WHR), waist to thigh ratio (WTR), hip to thigh ratio (HTR), waist to height ratio (WHtR), hip to height ratio (HHtR), and thigh to height ratio (THtR) were calculated. All these indicators were compared between hip fracture and control group, and between spine fracture and control group.
RESULTS
Comparison between spine fracture and control group showed that the WC, WHR, WHtR were statistically significant, but all indicators failed to show accuracy in the ROC analysis. Comparison between hip fracture and control group demonstrated the TC, WTR, HTR, WHtR, HHtR, THtR were statistically significant. However, only the HTR showed fair accuracy in the ROC analysis. The area under the curve (AUC) of the HTR was 0.75 (95% confidence interval, 0.62 to 0.87) (p=0.001).
CONCLUSION
The HTR was fairly accurate in predicting the incidence of hip fracture compared with any other anthropometric indicators. Therefore, we can consider that the HTR has clinical usefulness.
- 507 View
- 0 Download

- Anterolateral Thigh Island Flap
- Jae Hoon Lee, Il Hoen Choi
- J Korean Fract Soc 2008;21(3):207-212. Published online July 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.3.207
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To present the author's experience using the anterolateral thigh island flap for reconstruction of soft tissue defects around the hip and perineum.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Proximal based anterolateral thigh island flaps were performed to reconstruct the soft tissue defects at the perineum (3 patients) and the greater trochanter of the hip (one patient) in 4 patients. All patients were male. Mean age was 43 years (range, 32 to 50 years) and mean follow-up was 8 months (range, 6 to 13 months). The causes of the defects were traffic accident in 2 cases, necrotizing fasciitis 1 case, and pressure sore 1 case. Average size of the flap was 14x9 cm. Fasciocutaneous flaps were performed in 3 patients and musculocutaneous flap was performed in one patient.
RESULTS
All flaps were survived. There were no necrosis of the flaps. One flap presented venous congestion after surgery, which resolved with the decompression of the pedicle. Reconstruction with the anterolateral thigh island flap resulted in no recurrence of the infection or ulcer and good esthetic contour.
CONCLUSION
The anterolateral thigh island flap is a reliable flap for reconstruction around the perineum and hip joint.
- 339 View
- 0 Download

Case Report
- Posterior Thigh Compartment Syndrome as a Result of Pseudoaneurysm of the Popliteal Artery in the Distal Femoral Fracture: A Case Report
- Seoung Jun Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(3):277-281. Published online July 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.3.277
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Compartment syndrome of the thigh is a rare condition and usually occurs in the anterior compartment. It is frequently caused by muscle injury, femur fracture, muscle overuse and vessel injury, but there have been few reports about posterior thigh compartment syndrome caused by pseudoaneurysm of the popliteal artery after fixation of distal femoral fracture with the retrograde intramedullary nail. We report a case of posterior thigh compartment syndrome caused by pseudoaneurysm of the popliteal artery, and report the clinical progression and result of our case.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Huge Pseudoaneurysm of Popliteal Artery Following Conservative Treatment of a Distal Femur Fracture: A Case Report
Won-Chul Cho, Chong Bin Park, Young-Jun Choi, Hyun-Il Lee, Hee-Jae Won, Jae-Kwang Hwang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2016; 29(2): 137. CrossRef - Is CT Angiography a Reliable Tool for Diagnosis of Traumatic Vessel Injury in the Lower Extremities?
Jong-Hyuk Park, Kwang-Bok Lee, Hyuk Park, Jun-Mo Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2012; 25(1): 26. CrossRef
- Huge Pseudoaneurysm of Popliteal Artery Following Conservative Treatment of a Distal Femur Fracture: A Case Report
- 457 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


