Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
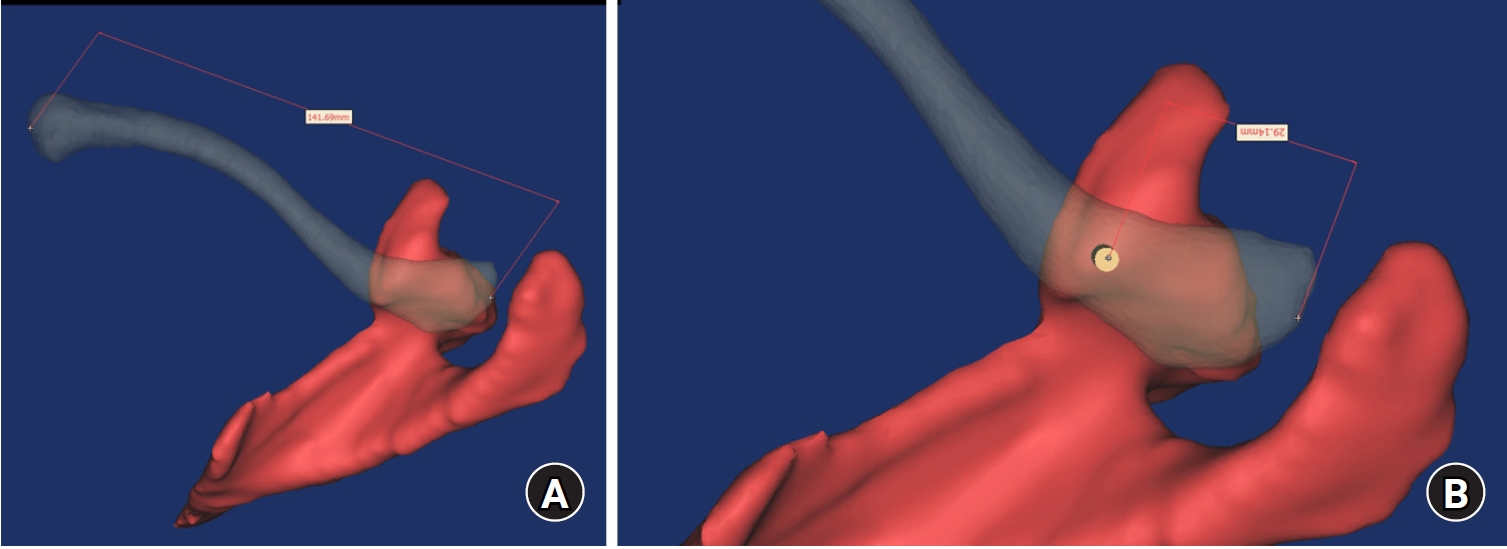
- Computational simulation of coracoclavicular screw insertion through the superior distal clavicular plate for clinical applications in Korean cadavers
- Hyung-Lae Cho, Ji Han Choi, Se-Lin Jeong, Gu-Hee Jung
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):143-151. Published online July 22, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00122
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The study was conducted to determine the practical area for inserting the coracoclavicular (CC) screw through the plate by analyzing three-dimensional (3D) shoulder models featuring virtually implanted, actual-size plates and screws.
Methods
Ninety cadaveric shoulders (41 males and 49 females) underwent continuous 1.0-mm slice computed tomography scans. The data were imported into image-processing software to generate a 3D shoulder model, including the scapula and clavicle. The overlapping area between the clavicle and the horizontal portion of the coracoid process (horizontal portion_CP) was analyzed in the cranial view. A curved pelvic recon plate was virtually placed on the upper surface of the distal clavicle, and an actual-size (3.5 mm) CC screw was inserted through the plate.
Results
The distal clavicle directly overlapped with the horizontal portion_CP in the vertical direction. The overlapping area was sufficient to place the 3.5 mm and 4.5 mm-sized screws. In all shoulder models, the CC screw could be inserted through the plate into the vertical direction, with an average length of 35.5 mm (range, 26.2–62.5 mm; standard deviation, 1.2 mm). In 87 models, the CC screw was inserted through the third hole from the lateral end of the plate. Two models were inserted through the second hole, and one model through the fourth hole.
Conclusions
The upper surface of the clavicle has sufficient overlapping area to place CC screws through the plate in the vertical direction in the corresponding hole. Supplemental CC screw fixation through the plate can be performed without additional or special equipment. Level of evidence: IV
- 646 View
- 21 Download

- Computational Simulation of Femoral Neck System and Additional Cannulated Screws Fixation for Unstable Femoral Neck Fractures and the Biomechanical Features for Clinical Applications
- Ju-Yeong Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(1):1-9. Published online January 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
To identify the biomechanical features for clinical applications through a computational simulation of the fixation of the Femoral Neck System (FNS) with additional cannulated screws for a Pauwels type III femoral neck fractures.
Materials and Methods
Thirty cadaveric femurs underwent computed tomography, and the images were transferred to the Mimics ® program, resulting in three-dimensional proximal femur models. A three-dimensional scan of the FNS and 6.5 mm and 7.0 mm cannulated screws was performed to enable computerized virtual fixation of FNS with additional cannulated screws for unstable femoral neck fractures. Furthermore, the cannulated screw used for additional fixation was modeled and used as a cylinder within the Ansys program. The biomechanical characteristics of these models were investigated by applying a physiological load virtually.
Results
The maximum von Mises stress value at bone was 380.14 MPa in FNS and 297.87 MPa in FNS+7.0 mm full-thread cannulated screw. The maximum von Mises stress value at FNS was 786.83 MPa in FNS and 435.62 MPa in FNS+7.0 mm full-thread cannulated screw. The FNS group showed the highest maximum von Mises stress values at bone and FNS. For total deformation, the maximum deformation value was 10.0420 mm in FNS and 9.2769 mm in FNS+7.0 mm full-thread cannulated screws. The FNS group represented the highest maximum deformation compared to the other groups.
Conclusion
Considering the anatomical spatiality and biomechanical characteristics of the FNS in unstable femoral neck fractures, when one 7.0 mm full thread cannulated screw was also fixed to the anterosuperior portion of the FNS, significant biomechanical stability was demonstrated.
- 737 View
- 10 Download

- Minimal Invasive Fixation Methods for the Metacarpal Fracture
- Ki Youn Kwon, Jin Rok Oh, Ji Woong Kwak
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(1):9-15. Published online January 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.1.9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study compared the radiologic and clinical outcomes of metacarpal fractures treated with two minimally invasive surgical techniques: Kirschner wire (K-wire) fixation and headless screw fixation.
Materials and Methods
This study included 52 patients (46 males and 6 females; age 18-55 years) with distal metacarpal fractures (middle and distal shaft, including the neck) who had undergone K-wire fixation or headless screw fixation. All subjects were followed up for at least six months. The radiologic assessments were performed to evaluate the angular deformity and shortenings. The total active motion (TAM), grip strength, and patients’ subjective functional assessment were measured to evaluate the hand function. The time taken to return to work (RTW) and adverse events were analyzed.
Results
Of the 52 cases, metacarpal fractures treated with headless screw fixation and K-wire fixation showed a significant difference associated with early RTW (p<0.05). There were no significant differences between the subjects treated with K-wire fixation and those with headless screw fixation in terms of the radiologic measurement, hand function examinations, complications, and adverse events (p>0.05).
Conclusion
After a six-month follow-up, minimally invasive K-wire fixation and headless screw fixation produced similar clinical and radiologic outcomes in subjects with metacarpal fractures. Compared to K-wire fixation, however, headless screw fixation led to earlier functional recovery and might be a better option for treating metacarpal fractures in this regard.
- 547 View
- 5 Download

- Comparing Outcomes of Screw Fixation and Non-Fixation for Small-Sized Posterior Malleolar Fragment in Ankle Trimalleolar Fractures
- Jee-Wook Ko, Gun-Woo Lee, Keun-Bae Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2021;34(1):8-15. Published online January 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2021.34.1.8
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study was undertaken to compare outcomes of screw fixation and non-fixation of a small-sized posterior malleolar fragment involving less than 25% articular surface in ankle trimalleolar fractures. Materials and Methods: A total of 32 consecutive ankles (32 patients), with posterior malleolar fragment involving 15%-25% of the joint surface, were enrolled in the study. Patients were divided into 2 groups according to whether the fragment was fixed or not (fixed: 20 ankles, non-fixed: 12 ankles). The minimum follow-up period was 12 months. Median size of the posterior malleolar fragment in the fixed and non-fixed groups were 24.6% (range, 22.3%-25.0%) and 22.1% (range, 17.4%-24.3%), respectively. Complications as well as clinical and radiographic outcomes were compared and analyzed between the two groups. Results: Clinical outcomes, including American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society (p=0.501), visual analogue scale (p=0.578), and ankle range of motion (p=0.552), showed no difference between groups at the final follow-up. No differences were obtained in the radiographic outcomes, including joint stepoff (p=0.289) and fragment gap (p=0.289). Complications, including 1 case of delayed union and 1 case of wound infection, were reported in the fixed group. Conclusion: Clinical outcomes and radiographic outcomes of the non-fixation group were satisfactory and comparable to the fixation group. Our results indicate that anatomical reduction with small-sized posterior malleolar fragment in ankle trimalleolar fractures is sufficient for satisfactory outcomes, without the need for additional internal fixation.
- 784 View
- 11 Download

- Comparison of Percutaneous versus Open Pedicle Screw Fixation for Treating Unstable Thoracolumbar Fractures
- Jin Young Han, Ki Youn Kwon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(1):1-8. Published online January 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study compared the clinical and radiological results between two groups of patients with percutaneous fixation or conventional fixation after hardware removal.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study analyzed 68 patients (43 open fixation and 43 percutaneous screw fixation [PSF] 25) who had undergone fixation for unstable thoracolumbar fractures. The radiologic results were obtained using the lateral radiographs taken before and after the fixation and at the time of hardware removal. The clinical results included the time of operation, blood loss, time to ambulation, duration of the hospital stay and the visual analogue scale.
RESULTS
The percutaneous pedicle screw fixation (PPSF) group showed better results than did the conventional posterior fixation (CPF) group (p<0.05) in regard to the perioperative data such as operation time, blood loss, and duration of the hospital stay. There were no significant differences in wedge angle, local kyphotic angle, and the ΔKyphotic angle on the postoperative plane radiographs between the two groups (p>0.05). There were no significant differences in the wedge angle and local kyphotic angle after implant removal (p>0.05) between the two groups as well. However, there were significant differences in the segmental montion angle (p<0.001), and the PPSF group showed a larger segmental motion angle than did the CPF group (CPF 1.7°±1.2° vs PPSF 5.9°±3.2°, respectively).
CONCLUSION
For the treatment of unstable thoracolumbar fractures, the PPSF technique could achieve better clinical results and an improved segmental motion angle after implant removal within a year than that of the conventional fixation method. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comparison of 2 Surgical Treatments for Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures: Temporary Osteosynthesis and Arthrodesis
Halil Ibrahim Süner, Rafael Luque Pérez, Daniel Garríguez-Pérez, Marta Echevarría Marín, Jose Luis Pérez, Ignacio Domínguez
World Neurosurgery.2022; 166: e419. CrossRef
- A Comparison of 2 Surgical Treatments for Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures: Temporary Osteosynthesis and Arthrodesis
- 1,458 View
- 22 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Report
- Spino-Pelvic Fixation in Unstable Sacral Fracture: A Case Report
- Jung Hwan Choi, Kyu Tae Hwang, Seung Gun Lee, Chang Nam Kang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(4):145-148. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.4.145
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 22-year-old female patient visited the emergency room (ER) after a pedestrian traffic accident in a drunken state. An examination at the ER revealed fractures at the right side of the sacral ala, sacral foramina, left anterior acetabulum, right inferior ramus, and right superior articular process of S1. She underwent spino-pelvic fixation and iliosacral (IS) screw fixation. One year later, bone union was completed and implant removal was performed and the treatment was completed without complications. The authors recommend spino-pelvic fixation and IS screw fixation for unstable sacral fractures as one of the excellent methods for obtaining posterior stability of the pelvis among the various treatments of unstable sacral fractures.
- 337 View
- 1 Download

Original Articles
- Computational Simulation of Multiple Cannulated Screw Fixation for Femoral Neck Fractures and the Anatomic Features for Clinical Applications
- Jin Hoon Jeong, Gu Hee Jung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(2):37-44. Published online April 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.2.37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To identify the anatomic features for clinical applications through a computational simulation of the fixation of three cannulated screws for a femoral neck fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty cadaveric femurs underwent computed tomography and the images were transferred to the Mimics® program, resulting in three-dimensional proximal femur models. A three-dimensional scan of the 7.0 mm cannulated screw was performed to enable computerized virtual fixation of multiple cannulated screws for femoral neck fractures. After positioning the screws definitively for cortical support, the intraosseous position of the cannulated screws was evaluated in the anteroposterior image and axial image direction.
RESULTS
Three cannulated screws located at the each ideal site showed an array of tilted triangles with anterior screw attachment and the shortest spacing between posterior and central screws. The central screw located at the lower side was placed in the mid-height of the lesser trochanter and slightly posterior, and directed toward the junction of femoral head and neck to achieve medial cortical support. All the posterior screws were limited in height by the trochanteric fossa and were located below the vastus ridge, but the anterior screws were located higher than the vastus ridge in 10 cases. To obtain the maximum spacing of the anterior and posterior screws on the axial plane, they should be positioned parallel to the cervical region nearest the cortical bone at a height not exceeding the vastus ridge.
CONCLUSION
The position of cannulated screws for cortical support were irregular triangular arrangements with the anterosuperior apex. The position of the ideal central screw in the anteroposterior view was at the mid-height of the lesser trochanter toward the junction of the femoral head and neck, and the anterior and posterior screws were parallel to the neck with a maximal spread just inferior to the vastus ridge. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Computational Simulation of Femoral Neck System and Additional Cannulated Screws Fixation for Unstable Femoral Neck Fractures and the Biomechanical Features for Clinical Applications
Ju-Yeong Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2023; 36(1): 1. CrossRef
- Computational Simulation of Femoral Neck System and Additional Cannulated Screws Fixation for Unstable Femoral Neck Fractures and the Biomechanical Features for Clinical Applications
- 665 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Treatment of Unstable Sacral Fractures Related to Spino-Pelvic Dissociations
- Hong Sik Kim, Jung Hwan Lee, Ki Chul Park, Ye Soo Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(3):178-183. Published online July 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.3.178
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the outcomes of surgical treatment modality in unstable sacral fractures combined with spinal and pelvic ring injury depending on the presence of spino-pelvic dissociations.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The subjects were 16 patients, with unstable sacral fractures combined with spinal and pelvic ring injuries, were operated from July 2004 to January 2011. The patients were divided into 2 groups depending on the presence of spino-pelvic dissociations: those with dissociations were group 1, and those without dissociations were group 2. Group 1 was treated with spino-pelvic fixations using iliac screw, while group 2 was treated with percutaneous iliosacral screw fixations. The availability of the radiological bony union with its application periods, and clinical results using visual analogue scale (VAS) and oswestry disability index (ODI) were evaluated, retrospectively.
RESULTS
Out of 16 patients, 8 patients in group 1 were treated with spino-pelvic fixation using iliac screw, and 8 patients in group 2 were treated with percutaneous iliosacral screw fixation. The mean bony union period was 17.4 weeks in group 1, and 19.6 weeks in group 2. The Mean VAS and ODI scores on the last follow-up were 2.5 points and 15.6 points in group 1, 2 points and 18.8 points in group 2, respectively. Both groups had favorable clinical results at the last follow-up.
CONCLUSION
For surgical treatments of unstable sacral fractures, spino-pelvic fixation using iliac screws is advised for cases with combined spino-pelvic dissociation, while percutaneous iliosacral screw fixation is advised for cases without combined dissociation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Integrative Korean Medicine Treatment for Sacral Fracture: Two Clinical Cases
Yeon Soo Kang, Pil Je Park, So Jeong Kim, Hyun Jin Jang, Min Ju Kim, Hyeon Kyu Choi, Jeong Kyo Jeong, Ju Hyun Jeon, Young Il Kim
Journal of Acupuncture Research.2023; 40(3): 281. CrossRef - Spino-Pelvic Fixation in Unstable Sacral Fracture: A Case Report
Jung-Hwan Choi, Kyu-Tae Hwang, Seung Gun Lee, Chang-Nam Kang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2018; 31(4): 145. CrossRef
- Integrative Korean Medicine Treatment for Sacral Fracture: Two Clinical Cases
- 681 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Anatomical Study of Symphysis Pubis Using 3 Dimensional Computed Tomography in Koreans
- Ji Wan Kim, Jung Min Park, Jae Suk Chang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(1):32-36. Published online January 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.1.32
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To acquire anatomical data for the normal pelvic bone structure using three-dimensional computed tomography (3D CT) and to propose the most appropriate angle and screw length for safe screw insertion during symphysis pubis plating.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We performed 3D CT analysis in 52 patients who required plating and selected a medial and lateral insertion point between the symphysis pubis and the pubic tubercle. Using a three-dimensional medical image analysis program, we evaluated the appropriate screw length, sagittal angle, and oblique angle at each point in this cohort.
RESULTS
At the medial point, the sagittal angle was determined to be 49.1degrees with an average screw length of 49.4 mm. At the lateral point, we calculated an average screw length of 49.1 mm, oblique angle of 23.2degrees, and sagittal angle of 45.7degrees. The screw length was longer in men than in women (4.6 mm and 7.3 mm, respectively) at the medial and lateral point.
CONCLUSION
At the symphysis pubis diastasis, we can insert the screw caudally at 49degrees with a minimal length of 37 mm at the medial point. We can insert the screw caudally at 46degrees, medially at 23degrees, with a minimal 34 mm length at the lateral point.
- 532 View
- 3 Download

- Anatomical Reduction of All Fracture Fragments and Fixation Using Inter-Fragmentary Screw and Plate in Comminuted and Displaced Clavicle Mid-Shaft Fracture
- Kyoung Hwan Koh, Min Soo Shon, Seung Won Lee, Jong Ho Kim, Jae Chul Yoo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(4):300-304. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.4.300
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To report the treatment results of anatomical reduction of all fracture fragments and internal fixation using an inter-fragmentary screw and plate in displaced mid-shaft clavicle fracture with comminution.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between June 2005 and August 2011, 13 consecutive displaced clavicle fractures with comminution (Edinburgh classification IIB2) treated by anatomic reduction and internal fixation using inter-fragmentary screw and plate were retrospectively evaluated. There were 11 male and 2 female patients with a mean age of 37.4 years (15~55 years). The right clavicle was injured in 4 patients and the dominant arm was involved in 46%. The mean duration from trauma to surgery was 7.0 days. The cause of injury was a traffic accident in three, a fall in two, and sports activity or direct injury in eight patients. All of the fracture pieces were anatomically reduced and fixed with inter-fragmentary screws. An additional plate was applied to maintain and reinforce the reduction of the fracture. Radiographic assessments for the numbers of fragments and the amount of shortening and displacement were performed. To verify the fracture healing and determine the time from fracture surgery to union and complications, all of the radiographs taken after surgery were evaluated.
RESULTS
The number of fragments was 2 in 7 cases, 3 in 5 cases, and 6 in one case. The mean shortening of the clavicle was 1.1 cm (0.3~2.1 cm) and mean displacement between the main fragments was 2.6 cm (1.3~4.5 cm). The mean duration of follow-up was 16.5 months (8~26 months). Radiographic union was achieved in all patients with a mean time to union of 10.8 weeks (8~14 weeks). There were no complications including metal failure, nonunion, or infection.
CONCLUSION
Anatomical reduction of all the fracture fragments and fixation using inter-fragmentary screws in addition to the usual plate fixation showed good fracture healing in displaced clavicle fracture with comminution. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Additional fixation using a metal plate with bioresorbable screws and wires for robinson type 2B clavicle fracture
Woo Jin shin, Young Woo Chung, Seon Do Kim, Ki-Yong An
Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow.2020; 23(4): 205. CrossRef - Use of Composite Wiring on Surgical Treatments of Clavicle Shaft Fractures
Kyung Chul Kim, In Hyeok Rhyou, Ji Ho Lee, Kee Baek Ahn, Sung Chul Moon
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2016; 29(3): 185. CrossRef
- Additional fixation using a metal plate with bioresorbable screws and wires for robinson type 2B clavicle fracture
- 817 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Treatment of Transverse Patellar Fracture with Cannulated Screws
- Jung Man Kim, Ju Seok Yoo, Yong Jin Kwon, Jang Ok Cheon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(2):149-153. Published online April 30, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.2.149
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To assess the indication and effect of screw fixation in the transverse patellar fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We analysed the results of 14 transverse patellar fractures fixed with screws from January 1991 to May 2005. Mean follow-up period was 47 months (range, 12~143 months). We analysed the radiologic union, operation time, ROM and postoperative Lysholm score.
RESULTS
All fractures healed uneventfully. The mean displacement was decreased from 2.2 mm preoperatively to 0.3 mm postoperatively (p=0.001, Wilcoxon signed rank test). The mean operation time was 34 minutes (range, 20 to 60 minutes). Normal range of motion was achieved in 13 knees (92.9%). Average Lysholm score was 95.9 at final follow-up.
CONCLUSION
Screw fixation seemed to be useful for treatment of transverse patellar fracture even in comminuted fractures with large fragments. The advantage of this technique was the preservation of extensor mechanism, simplicity, short operation time and good cosmesis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surgery of patellar fractures using a medial parapatellar approach
Yong-Cheol Yoon, Jae-Ang Sim, Jin-Hun Hong
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Results of Tension Band Wiring and Additional Circumferential Wiring in Treatment of Comminuted Patella Fracture
Young Min Lee, Kook Jin Chung, Ji Hyo Hwang, Hong Kyun Kim, Yong Hyun Yoon
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2014; 27(3): 206. CrossRef
- Surgery of patellar fractures using a medial parapatellar approach
- 703 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref

Case Report
- Old Atlantoaxial Rotary Subluxation Associated with High-riding Vertebral Arteries: Arthrodesis Using C1 Lateral Mass Screws and C2 Laminar Screws: A Case Report
- Kyeong Hwan Kim, Jin Sup Yeom, Kun Woo Park, Soon Woo Hong, Bong Soon Chang, Choon Ki Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(1):90-93. Published online January 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.1.90
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To the best of our knowledge, there has been no domestic report on posterior atlantoaxial fusion with segmental screw fixation using C2 laminar screws and C1 lateral mass screws for atlantoaxial subluxation. We report the result of this operation performed in a patient with old atlantoaxial rotary subluxation who required posterior fusion. We chose this technique in this patient because wire fixation was not suitable due to osteoporosis, and transarticular screw fixation and use of C2 pedicle screws were not feasible due to the peculiar bony anatomy of the axis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Indirect Decompression using Segmental Screw Fixation for Cervical Myelopathy Caused by C1-2 Subluxation - Technical Note -
Yoon Jong Kim, Kyeong Hwan Kim, Jong Hwa Won, Hak Jin Min, Ui Seong Yoon, Jin Sup Yeom
The Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2007; 42(6): 815. CrossRef
- Indirect Decompression using Segmental Screw Fixation for Cervical Myelopathy Caused by C1-2 Subluxation - Technical Note -
- 667 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Article
- Treatment of Acetabular Column Fractures with Limited Open Reduction and Screw Fixation
- Jung Jae Kim, Hyoung Keun Oh, Sung Yoon Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(1):26-32. Published online January 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.1.26
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the results of limited open reduction and screw fixation of acetabular fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Six acetabular fractures were treated with fluoroscopic guided screw fixation. The mean age was 46 years old and mean follow-up period was 18 months. There were 3 anterior column fractures, 2 transverse fractures and 1 both column fracture. Anterior column screw fixation was used in 5 cases and posterior column fixation in 1 case. Limited ilioinguinal approach was used in 4 cases and percutaneous screw fixation in 2 cases.
RESULTS
The mean union time was 16.6 weeks. The postoperative radiographic results revealed 2 cases with an anatomic reduction and 4 cases with an imperfect reduction. The clinical results showed 1 case with excellent, 4 cases with good and 1 case with fair. Regarding complication, there was 1 case of SI joint penestration without clinical symptoms.
CONCLUSION
Limited open reduction and screw fixation can be a useful alternative treatment for acetabular fractures in patients with minimally displaced fracture, severe multisystem trauma and soft tissue injury not suitable to traditional treatment.
- 623 View
- 1 Download

Case Reports
- Medial Plantar Nerve Injury after Screw Fixation of the Calcaneus Fracture
- Bong Cheol Kwon, Yong Woon Shin, Duck Joo Kwon, Nam Kyou Rhee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(2):288-290. Published online April 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.2.288
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- We present a case of medial plantar nerve injury by screw tip after open reduction and internal fixation of intraarticular calcaneus fracture. We reviewed the risk and prevention technique of medial plantar nerve injury in fixing the calcaneus fracture.
- 381 View
- 0 Download

- Transverse Fracture through Screw Site after Cannulated Screw Fixation in Vertical Patella Fracture: A Case Report
- Suk Kang, Phil Hyun Chung, Chung Soo Hwang, Jong Pil Kim, Young Sung Kim, Chong Suck Parke
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(1):96-99. Published online January 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.1.96
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- Many complications after operative treatment of patella including redisplacement of fracture, refracture, weakness of extensor muscles, patellofemoral joint arthritis, metal failure, malunion, infection, avascular necrosis were reported. We report a case of transverse fracture of patella through the cannulated screw fixation site used to fix previous vertical patella fracture with a review of the literatures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Results of Tension Band Wiring and Additional Circumferential Wiring in Treatment of Comminuted Patella Fracture
Young Min Lee, Kook Jin Chung, Ji Hyo Hwang, Hong Kyun Kim, Yong Hyun Yoon
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2014; 27(3): 206. CrossRef
- Results of Tension Band Wiring and Additional Circumferential Wiring in Treatment of Comminuted Patella Fracture
- 500 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- Development and Accuracy Test of a Robot-arm Type Image-guided Surgery System for Percutaneous Screw Fixation of the Sacro-iliac Joint
- Jin Sup Yeom, Won Sik Choy, Hayong Kim, Jong Won Kang, Kwang Won Lee, Whoan Jeang Kim, Jae Hoon Ahn, Seong Kyu Park, Jong Hwa Won, Hyungmin Kim, Namkug Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(2):191-197. Published online April 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.2.191
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To develop a robot-arm type image-guided surgery system for percuatneous screw fixation of the sacro-iliac joint and to evaluate its accuracy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We have developed an image-guided surgery system using a three-dimensional digitizer (Microscribe 3-D G2, Immersion, USA) and a personal computer. The registration error and target localization error at fiducial registration were measured 30 times for each using a phantom made with plastic pelvic bone model (Sawbones, USA). Sixteen 6.5 mm cannulated screws were inserted into four plastic bone models, and the accuracy was evaluated.
RESULTS
The target localization error was 1.46+/-0.47 mm while the registration error was 0.73+/-0.23 mm. All of the 16 screws were inserted well across the sacro-iliac joint, and there was neither cortical breach nor collision between screws or washers.
CONCLUSION
The accuracy of the developed system was similar to that of optical tracker-based navigation systems, and its helpfulness and usefulness was proven with simulation surgery using plastic bone models.
- 408 View
- 0 Download

- Development of a Computer-assisted Surgery System for Screw Fixation of the Sacro-iliac Joint
- Jin Sup Yeom, Won Sik Choy, Ha Yong Kim, Whoan Jeang Kim, Jong Won Kang, Yeongho Kim, Hyungmin Kim, Donghyun Seo, Seok Lee, Jae Bum Lee, Namkug Kim, Cheol Young Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(1):1-7. Published online January 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purposes of this study were to develop a computer-assisted surgery system for percutaneous screw fixation of the sacro-iliac joint and to evaluate its accuracy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We have developed a navigation system composed of an optical tracking device (Polaris, Northern Digital, Canada) and a personal computer. The registration error and target localization error at hybrid registration were measured using a phantom. The errors were measured 30 times for each. Sixteen 6.5 mm cannulated screws were inserted into four plastic bone models (Sawbones, USA), and the accuracy was evaluated.
RESULTS
The registration error was 0.76 +/-0.33 mm, and the target localization error was 1.43 +/-0.42 mm. All of the 16 screws were inserted well across the sacro-iliac joint, and there was neither penetration of the cortical bones nor collision between screws or washers.
CONCLUSION
The accuracy of the developed system was similar to existing ones, and its usefulness and helpfulness was proven with screw insertion into plastic bone models.
- 379 View
- 3 Download

- Result of Fibular Fixation Using Screw in Ankle Fracture
- Chung Soo Han, Yang Sun Im, Sun Teak Cheong
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(4):477-482. Published online October 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.4.477
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To compare the use of screw only fixation with lateral one-third tubular plate fixation of non-comminuted oblique fracture of the lateral malleous and report the advantages of screw only fixation MATERIALS AND METHODS: From January 1996 to January 2000, we had operated 44 cases of non-comminuted oblique fractures of the lateral malleous (Denis-Weber type B, Lange-Hausen classification supination-external rotation injury). All cases had a follow-up period of over 6 months. There were 21 cases of cortical or bone screw fixation (group I) and 23 cases of one third tubular plate fixation (group II). Radiologic and clinical outcome parameters were used to compare group I with group II.
RESULTS
There were no significant difference in bone union rate and period between group I and group II (group I : 92 days, group II : 89 days). All cases of both groups recovered a complete range of motion after cast off. There was 1 case superficial infection in group II.
CONCLUSION
The radiologic and clinical results and complications between screw only fixation and one-third tubular plate fixation at non-comminuted lateral fibular fracture have no difference. The advantage of screw only fixation at non-comminuted lateral malleolar fracture is a small incision, short operation time and decreased patient 's complaints as compared with a similar group of patients treated by fixation with a lateral one third tubular plate fixaiton. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Rehabilitation for Ankle Fracture in Korean Medicine: A Report of 4 Cases
Won-Bae Ha, Jong-Ha Lee, Yoon-Seung Lee, Dong-Chan Jo, Jin-Hyun Lee, Jung-Han Lee
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2017; 27(4): 171. CrossRef
- A Rehabilitation for Ankle Fracture in Korean Medicine: A Report of 4 Cases
- 563 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Radiologic Evaluation for the Safe Zone of Percutaneous Iliosacral Screw Fixation
- Jong Keon Oh, Su Young Bae, Jong Oh Kim, Kwon Jae Roh, Jeong Joon Lee, Sang Yeol Chang
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(3):336-341. Published online July 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.3.336
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the correlation of the safe zone of percutaneous iliosacral screw fixation with sacral dysmorphism and sacral alar slope variation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We studied the plain radiographs and the pelvic bone CT images of 52 patients. We reviewed each cases in terms of Routt 's dysmorphism and sacral alar slope variation(anterior, coplanar and posterior to inter-ICD line). We divided each cases into narrow and wide groups by the width of safe zone for the transverse 6.5mm cannulated cancellous screw. The data were analysed by McNemar x2-test and Cochran Q-test(p<0.05).
RESULTS
Typical sacral dysmorphism was found in five cases(9%). Four cases with dysmorphism(80%) and eighteen non-dysmorphic cases(38.2%) revealed narrow safe zones. The sacral slopes were anterior in 16 cases, coplanar in 25 cases, and posterior in 11 cases. The safe zone was significantly narrow in the group with anterior slope variation.
CONCLUSION
We could not found definite correlation between sacral dysmorphism and a narrow safe zone because the incidence of dysmorphism was too low in our study which differed from Routt 's report. An anterior sacral alar slope on CT can be a significant risk indicator for potential narrow safe zone and the risk of screw malposition. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Measurement of Optimal Insertion Angle for Iliosacral Screw Fixation Using Three-Dimensional Computed Tomography Scans
Jung-Jae Kim, Chul-Young Jung, Jonathan G. Eastman, Hyoung-Keun Oh
Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery.2016; 8(2): 133. CrossRef - Operative Treatment of Unstable Pelvic Ring Injury
Sang Hong Lee, Sang Ho Ha, Young Kwan Lee, Sung Won Cho, Sang Soo Park
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2012; 25(4): 243. CrossRef - Upper Sacral Morphology Related to Iliosacral Screw Fixation in Korean
Jung-Jae Kim, Chul-Young Jung, Hyoung-Keun Oh, Byoung-Se Yang, Jae-Suck Chang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2007; 20(2): 115. CrossRef
- Measurement of Optimal Insertion Angle for Iliosacral Screw Fixation Using Three-Dimensional Computed Tomography Scans
- 560 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Treatment of Distal Clavicle Fractures with Coracoclavicular ligament Injury
- Nam Yong Choi, Suk Ku Han, Seong Jin Park, Ki Ho Na, Young Hun Kim, Hyun Seok Somg, Yong Jin Kwon
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(1):21-27. Published online January 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.1.21
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the radiological and clinical results of the treatment of distal clavicular fractures with coracoclavicular ligament injury by coracoclavicular fixation with plating or repair of coracoclavicular ligament.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sixteen cases with minimum six months of follow-up were included in our study. Male was twelve and average age was 43(28-80). Ten cases of Craig type 2 were treated with coracoclavicular screw fixation with plating. Six cases of Craig type 5 were treated with coracoclavicular screw fixation with repair of coracoclavicular ligament. The radiologic assessment including coracoclavicular distance and union time and the clinical assessment including range of motion and degree of pain were evaluated.
RESULTS
Fifteen cases were united, but one case developed osteomyelitis and nonunion. Full range of motion was achieved in fifteen cases at last follow-up. Average coraco- clavicular distance compared to contralateral site in AP view was 2.1 mm increase in patients with plate fixation and 1.3 mm increase in patients with ligament repair. Average union time was 14.3 weeks and little differenece was noted between two groups(P>0.05).
CONCLUSION
Coracoclavicular screw fixation with plating or repair of coracoclavicular ligament were a useful method to treat distal clavicular fractures combined with coracoclavicular ligament injury.
- 432 View
- 3 Download

- Open Reduction and OA Miniscrew Fixation of the Hamate Fracture: A Case Report
- Myung Hwan Son, Mun Sik Pheo
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(4):992-995. Published online October 31, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.4.992
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The hamate fracture is very rare injury in carpal bone fractures. The mechanism of fracture may be attributed to indirect trauma with clenched fist. We have experienced a case of fracture of the body of the hamate bone. It was treated with open reduction and OA miniscrew fixation and plaster immobilization for four weeks and physical therapy. At 21 months follow-up, the result was satisfactory without traumatic arthritis, nonunion, ulnar nerve palsy, and limitation of motion. A case of fracture of the body of the hamate bone is reported with review of literatures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Operative treatment of hamate fractures with hamatometacarpal fracture dislocation using a self-designed dorsal buttress locking plate with trans-metacarpal pin insertion: short-term follow-up results
Seok-Won Kim, Hyung-Joon Lee, Ji-Kang Park, Dong-Min Chung
Archives of Hand and Microsurgery.2022; 27(3): 193. CrossRef - Screw Fixation Method through Temporary Kirschner Wire Hole for Coronal Hamate Fracture
Yong Gil Jo, Yohan Lee, Joonha Lee, Kee Jeong Bae, Min Bom Kim, Young Ho Lee
Archives of Hand and Microsurgery.2021; 26(4): 245. CrossRef
- Operative treatment of hamate fractures with hamatometacarpal fracture dislocation using a self-designed dorsal buttress locking plate with trans-metacarpal pin insertion: short-term follow-up results
- 499 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

- PROPER SCREW LENGTH FOR FIXATION OF THE MEDIAL MALLEOLAR FRACTURE OF ANKLE
- Dong Bae Shin, Soo Hong Han, Seung Soo Jeon
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(3):522-528. Published online July 31, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.3.522
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
There is rare report about screw length in ankle fracture in spite of the anatomical characteristic that distal densest area can give enough purchase of screw threads for fixation of medial malleolar fragment. Purpose of the current study is to evaluate the results of screw fixation and to estimate proper screw length in medial malleolar fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Authors retrospectively reviewed 136 cases of medial malleolar fracture which had been performed from Janurary 1985 to December 1997. The patients were divided into 3 groups according to screw length ; under 34mm screw length (9 cases), between 35mm and 45mm (76 cases), over 46mm (50 cases). Each group was evaluated bone union time, clinical outcomes and radiological results by Meyer and Kumler.
RESULTS
Good and excellent results were achieved 121 cases (89%) on clinical result and 125 cases (91.9%) on radiological result by Meyer criteria. There were no statistical differences between three group, but the 35mm-45mm screw length group showed slightly faster union tendency.
CONCLUSION
In the treatment of medial malleolar fracture, around 40mm length screw is sufficient for fixation and it doesn,t need to use the screw over 45mm length for more rigid fixation.
- 576 View
- 4 Download

- Arthroscopic Treatment of The Tibial Intercondylar Eminence Fractures
- Han Chul Kim, Beom Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(3):488-493. Published online July 31, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.3.488
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To compare operative results between pull-out wiring and retrograde screw fixation for displaced tibial intercondylar eminence fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From March 1997 to February 1999, authors carried out pull-out wiring in 3 patients and retrograde screw fixation in 5 patients who sustained typeII and typeIII displaced tibial intercondylar eminence fractures follow up for 16 months(mean).
RESULTS
The Union time was mean 7 wk in pull-out wiring and 6.5 wk in retrograde screw fixation. Limitation of knee motion(1 case) developed in retrograde screw fixation group and reoperated for adhesiolysis. Pull-out wiring group were all full motion recovered. Anterior instability(1 case) developed in retrograde screw fixation group and pull-out wiring group had no instability. Operation time for retrograde screw fixation group was mean 98min and pull-out wiring group was 105 min.
CONCLUSION
The outcome of pull-out wiring group were superior to retrograde screw fixation group. It can be stably fixed and allow early motion exercise. Besides, in case of small bony fragment, it is difficult for fixation with screw. And even impossible. In child cases, the multiple percutaneous pinning can lead to good result. So authors believe that pull-out wiring is worthy for tibial intercondylar eminence fracture.
- 396 View
- 0 Download

- Posterior Short Segment Instreumntation and Fusion for the Unstable Thoracolumbar Spine Fracture: A Comparative Study
- Ki Tack Kim, Gyu Pyo Hong, Dae Woo Hwang, Sang Un Lee, Sang Wook Bae
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(2):352-360. Published online April 30, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.2.352
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - INTRODUCTION : In treating of acute unstable thoracolumbar spine fractures, current trend is a toward short segment instrumentation to spare the motion segments. Many authors reported the result of short instrumentation and fusion, but there have been few reports about the effect of additional screw fixation at fractured vertebra in posterior short segment instrumentation and fusion. Therefore, the objective of this study is to compare the results of treatment between with/without screw fixation at the fractured vertebra in posterior short segment pedicle screw fixation.
MATERIAL AND METHODS : Twenty-three patients with unstable thoracolumbar spine fractures were treated with posterior short segment instrumentation and fusion. Eleven cases classified into group A were not fixed at the fractured vertebre. They were followed up to average 45 months(24-79). Twelve cases classified into group B were treated with screw fixation at the injured vertebra and followed up to average 38 months(14-78). Authors evaluated the radiologic assessment, such as wedge angle of fractured body, local kyphotic angle and wedge index(the ratio of anterior body height to posterior body height), the neurologic assessment by Frankel grade system and functional assessment by Denis system.
RESULTS
: There was no complication resulted from additional pedicle screw fixation at fractured level. In rediologic assessment, wedge angle were measured at preoperative, postoperative and last follow-up time as follows; in group A, 22.2degrees -11.3degrees -14.1degrees and in group B, 19.5degrees -8.8degrees -9.8degrees . The local kyphotic angle measured were 17.9degrees -7.0degrees -14degrees in group A and 17.1degrees -6.3degrees -7.9degrees in group B. The wedge index were 42.9%-22.6%-28.5% in group A and 40%-19.5%-22.4% in group B. At last follow-up time, eight eases showed Frankel grade E and three cases showed grade D in group A, and all cases of group B were Frankel E. Denis pain score were satisfctory in all of both group and Denis work score were also satisfactory in two group except one case of group A.
CONCLUSIONS
: Additional screw fixation at fractured verteba did not cause any complication. There was no significant difference in reduction rate between two groups(P>0.05), but group B showed better maintenance of correction of kyphotic deformity than that of group A(P<0.05). In conclusion, it seems that additional screw fixation at fractured level may be better method in maintaining asgittal alignment and decreasing the risk collapsing of body.
- 336 View
- 0 Download

- Lag Screw Fixation for the Multiple Spiral Metacarpal Fractures
- Jong Woong Park, Sung Kon Kim, Jung Ho Park, Joon Seok Hong, Jae Hun Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(1):152-157. Published online January 31, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.1.152
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
: We evaluated the results after the lag screw fixations using A.O. 2.0mm mini screws for the unstable multiple spiral metacarpal fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
: thirteen cases of multiple spiral metacarpal fractures were treated with the lag screw fixations using 2.0mm mini cortical screws by the recommended technique of AOASIF. TAM of each digit was measured at the time of last follow up and the result was compared with the contralateral normal digits. We also evaluated the amount of shortening, angulation or rotation at the fracture sites on the last follow-up radiographs.
RESULTS
: Complete radiological unions were obtained in all of the cases. TAM of the operated digits were above 90% compared with those of the contralateral normal digits except 1 case, which had an another fracture and deep laceration at the distal phalanx and proximal interphalangeal joint during the period of follow up. We could not find any shortening, angulation or rotation at the fracture sites on the last follow-up radiographs.
CONCLUSION
: When we consider that the goal of treatment of the metacarpal fracture is to obtain full motion of the digit through the early mobilization after injury, we think that the lag screw fixation using 2.0mm mini screw is a good treatment modality in the cases of unstable multiple spiral metacarpal fractures.
- 338 View
- 1 Download

- Open Reduction and AO Miniscrew Fixation of Displaced Radial Head Fractures in Adults
- Jae Do Kang, Kyung Chil Jung, Chi Wook Kyoung
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(1):146-151. Published online January 31, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.1.146
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
: To analyze the results of open reduction and AO miniscrew fisation in displaced radial head fractures in adults. Materials & Methods : We analyzed 10 cases of displaced radial head fractures who were operated with open reduction and AO miniscrew fixation from January 1996 to March 1998. All of the fractures were classified in the Mason classification. The functional rating index was used in follow-up assessment.
RESULTS
: Average flexion was 143.5degrees, and the mean fixed flexion deformity was 3.5 degrees. The average elbow score was 95.6 points Good or excellent results were achieved in 100%. No patient had evidence of valgus instability.
CONCLUSION
: We concluded that open reduction and internal fixation in Mason type II and reparable Mason type III radial head fractures gives satisfactory range of motion and stability in the elbow joint. We suggest that anatomical reduction of fracture fragments, rigid fixation, early mobilization and proper implant placement are important for the restoration of the elbow function
- 428 View
- 1 Download

- Arthroscopic Reduction and Percutaneous Cannulated Screw Fixation for Longitudinal Fractures of Patella
- Jung Han Yoo, Yung Khee Chung, Yong Wook Park, Jin Sub Kim, Deuk Soo Jun, Ho Jin Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(1):103-108. Published online January 31, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.1.103
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A variety of surgical modalities for fractures of patella have been described. We used arthroscopic reduction and percutaneous screw fixation for six cases of longitudinal fracture of patella. Ages of the patients ranged from 25 to 33 years. the postoperative regimen was one week long leg splint for reducing the pain, followed by continuous passive range of motion exercise of the knee including active one and quadriceps strengthening exercise until the full range of motion was gained, with progressive partial to full weight bearing with crutches. The follow-up period was from 12 to 54 monhts. Results were assessed subjectively and objectively with retrograde study. The full range of knee motion was recovered from 20 to 35 days postoperatively, The radiographic bone union was achieved from 31 to 42 days. And all patient had good results according to Lysholm and Gillquist scoring system. We had no experience of complication except one which is prominence of screw end. So, we believed that the arthroscopic reduction and percutaneous cannulated screw fixation for longitudinal fractures of patella is the useful surgical method.
- 316 View
- 0 Download

- HERBERT SCREW FIXATION FOR NON-COMMINUTED CLOSED MEDIAL MALLEOLAR FRACTURE
- Dong Man Park, Yong Jin Kim, Jea Won Chang, Jin Cheul Park
- J Korean Soc Fract 1999;12(3):638-644. Published online July 31, 1999
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1999.12.3.638
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - It is known that the Salter-Harris type I and II fractures of the distal tibial epiphysis usually Non-comminuted closed displaced medial malleolar fracture has been treated by open reduction and internal fixation. Since fracture fragment of medial malleolar is usually thiner and smaller than that of lateral malleolar, it is more difficult to fix firmly than that of lateral malleolar. In the treatment of medial malleolar fracture, although various fixation methods in the treatment of medial malleolar fracture have been reported, several complications have been reported. And then authors have been tried to find fixation methods and firm fixation material for medial malleolar fracture to minimize complications. The purpose of this paper is to compare operation time, duration of bone union, the presence of complication, and results by Meyer and Kumler criteria between Herbert and malleolar screw and to introduce percutaneous Herbert screw fixation technique. Since March 1996, forty-four patients had undergone surgical intervention for medial malleolar fractures. Twenty-three Herbert screw and twenty-one malleolar screws were used. The results were as follows; The operation time was shorter in Herbert screw fixation group. There were no complications such as pain and tenderness due to hardware protrusion and metal lossening in Herbert screw fixation group. We come to the coonclusion that the Herbert screw fixation method was a little better than the malleolar screw fixation method according to comparison by Meyer and Kumler ctireria. We concluded that Herbert screw fixation was a better method for non-comminuted closed displaced medial malleolar fracture to obtain early union and to prevent postoperative complications.
- 356 View
- 2 Download

- Operative Treaeent of Hohl II, III Plateau Fracture by Small Incision and Bone Window
- Jin Woo Kwon, Kyoung Tae Sohn, Sung Ho Shin, Woo Se Lee, Won Ho Jo, Jae Il Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1999;12(3):593-600. Published online July 31, 1999
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1999.12.3.593
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Severely depressed plateau fractures, especially Hohl I, III, can not be reduced by ligamentotaxis and require elevation through a cortical window, bone grafting, and fixation with either cancellous screws or a buttress plate. But traditional long lateral parapatellar incision and plate fixation method caused frequent wound dehiscence and deep infection. Thus to reduce the soft tissue problem we treated Hohl II, III plateau fractures by small anterolateral L-shaped incision, submeniscal exposure, reduction of depressed plateau and bone graft through bone window, and then cancellous screws fixation beneath the subchondral bone of elevated plateau. We anayzes 22 cases with Hohl II, III plateau fractures, which were treated by these method from February 1990 to December 1997 and followed more than 1 year. Males were 17, and females were 5. Average age of patients was 44.7 years. The most common cause of injury was traffic accidents(17 cases), and fracture type according to the Hohl classification was 14 cases of type II, 8 of type III. The associated injuries were 18 cases of meniscus tear, 13 of ligament injury(6 ACL, 7 MCL). The clinical results by Blokkers criteria were satisfactory 19 cases(86.3%) and unsatisfactory 3 cases(13.7%). We concluded that this method has following advantages; relatively firm fracture fixation, short operation time, low soft tissue problem.
- 335 View
- 1 Download

- Operative Treatment of the Condylnr Fractures of the Femur
- Moon Gu Choi, Youn Soo Kim, Kee Haeng Lee, Chang Hoon Chung, Hyoung Min Kim, Joong Hyuk Kwon
- J Korean Soc Fract 1999;12(3):523-528. Published online July 31, 1999
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1999.12.3.523
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the results of the the condylar fracture of the femur treated by open reduction and cancellous screw fixation. METERIALS AND METHODS: From April, 1994 to October, 1998, 9 cases of the condylar fracture of the femur were open reduced and internally fixed with cancellous screw. According to AO classification, B2 type, B3 type and C2 type were all three cases each. All intraarticular fragment of the 9 cases were fixed with cancellous screws fixation after open reduction. Additionally 2 cases were fixed with dynamic condylar screw and 1 case was fixed with supracondylar nail. Authors followed up from shortest one year one month to longist three year four month(average 2 years) and evaluated them by using the method of Schatzker and Lamberts.
RESULTS
Seven of 9 cases had reduced anatomically, and remained 2 case which were delayed to operation cannot reduced anatomically. In all case stable fixation of the intraarticular fragment was obtained by cancellous screw fixation without perioperative complication. Schatzker and Lamberts assesment shows excellent in four, good in one, fair in three and failure in one case. CONCLUSTION: In case of the condylar fracture of the femur, early and relatively simple screw fixation can obtain anotomical reduction and prevent complication caused by incongruent joint surface.
- 300 View
- 0 Download

- Treatment of High-Energy Tibial Plateau Fracture: A comparison of External Fixation with Limited Internal Fixation to Plate and Screw Fixation
- Suk Woong Yoon, Tae Sung Hwang, Byoung Gue Park
- J Korean Soc Fract 1998;11(4):769-777. Published online October 31, 1998
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1998.11.4.769
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - High energy tibial plateau fractures are associated with wevere articular depression, separation of both condyles, diaphyseal comminution and dissociation & loss of integrity of the soft tissue envelop. Thus it is very difficult to treat these fractures satisfactorily and severe complications may be developed. Authors carried out plate and screw fixation in 11 patients and external fixation(Ilizarov external fixator) with limited internal fixation in 8 patientsl who sustained high-energy tibial plateau fracture between Jan. 1992 and Feb. 1996. We compared the operative results of plate and screw fixation and external fixation with limited internal fixation in high-energy tibial plateau fractures which was follow up from 12months to 28months. The results were as follows; 1. The complications such as limitation of knee motion(3 cases), traumatic arthritis(1 case), angular deformity(2 cases), superficial infection(2 cases), deep infection(1 case), instability(1 case) were observed in plate fixation group. Limitation of knee motion(1 case), traumatic arthritis(1 case), delayed union(1 case) were developed in external fixation group. 2. According to Blokker's criteria, 6 cases(55%) among 11cases of plate and screw fixation group and 5 cases(63%) among 8 cases of Ilizarov external fixator group had satisfactory results. Ilizarov external fixation with limited internal fixation is useful method of treatment for high-energy tibial plateau fractures when extensive dissection and internal fixation are contraindicated due to comminution at the fracture site and compromise of the soft tissue.
- 495 View
- 0 Download

- Operative Treatment of the Humeral Shaft Fracture
- Suk Woong Yoon, Tae Sung Hwang, Bo Keun Jeon
- J Korean Soc Fract 1997;10(4):904-911. Published online October 31, 1997
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1997.10.4.904
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Most humeral shaft fractures can be managed nonoperatively. Recently improved results have been reported after internal fixation of the humeral shaft fractures, followed by early elbow and shoulder motion. Authors carried out True/Flex intramedullary nail in 14 patients and interlocking intramedullary nail in 12 patients and plate & screw fixation in 18 patients who sustained humerus shaft fracture between February 1992 and August 1996. We compared the operative results of intramedullary nailing and plate and screw fixation in humeral shaft fractures which was follow-up from 12 months to 21 months. The results were as follows ; 1) The mean union time was at 16.5 weeks in True/Flex group, at 16 weeks in interlocking nail group, and at 15.7 weeks in plate fixation group. 2) The complications such as angulation(3 cases), rotation(1 case), limitation of shoulder motion(2 cases), and delayed union(1 case) were observed in True/Flex group. Angulation(1 case), rotation(1 case), limitation of shoulder motion(3 cases), and nonunion (1 case) in interlocking nail group. Angulation (1 case), limitation of elbow motion(2 cases), nonunion(1 case), soft tissue infection(2 cases), and iatrogenic radial nerve palsy (2 cases) were developed in plate fixation group.
- 321 View
- 0 Download

- Miniplate and Miniscrew Fixation for the Metacarpal and Phalangeal Fractures
- Bu Hwan Kim, Jong In Yim, Deog Jeong Kang
- J Korean Soc Fract 1997;10(1):150-155. Published online January 31, 1997
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1997.10.1.150
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The functional end result is more important than fracture healing in the hand fracture treatment. Accurate open reduction and internal fixation with miniplate and miniscrew for metacarpal and phalangeal fractures of hand provides firm fixation and allows early postoperative mobilization which reduce the incidence of joint stiffness and tendon adhesion. The authors have reviewed 17 cases of metacarpal and phalangeal fractures of the hand in 13 patients which were treated with miniplate and miniscrew fixations in the department of orthopaedic surgery, Dae Dong General Hospital from Mar. 1994 to Feb. 1996. The following results were obtained. 1.The firm fixation allowed range-of-motion exercises in most patients between 3-14 days. 2.The roentgenographic union was obtained within 14.8 weeks in average. 3.The mean TAM(total active motion) range at last follow up was 247 in the metacarpal fracture and 226 in the phalangeal fracture. 4. The complications(tendon adhesion & loss of reduction) occurred in 2 cases(11.8%). In conclusion, fixation with miniplate and miniscrew for metacarpal and phalangeal fractures of the hand is considered to be an effective method in the treatment of metacarpal & phalangeal fractures.
- 417 View
- 2 Download

- Treatment of A-C joint dislocation with cannulated screw fixation under local anesthesia
- Bu Hwan Kim, Jong In Yim, Deog Jeong Kang
- J Korean Soc Fract 1996;9(1):185-192. Published online January 31, 1996
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1996.9.1.185
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In 1941, Bosworth used noncannulated coracoclavicular lag screw to Oeat acute A-C joint dislocation. In 1989, Tsou fixed coracoclavicular joint with percutaneous cannulated screw under general anesthesia in the treatment of acute A-C joint complete dislocations. We tried to treat 10 cases of acute A-C joint dislocations with cannulated screw fixation of C-C joint under local anesthesia, so we report the results with review of literatures. The results were as follows 1. Results of treatment were good in 7 cases, fair in 2 cases, and poor in 1 case by Weaver and Dunn evaluation criteria. 2. The operations were done under local anesthesia, but in two cases operation ended under general anesthesia due to discomfort of the patients. 3. In skeletally thin patient, it was very difficult to make accurate hole and we experienced an iatrogenic fracture of clavicle and coracoid process. This technique is not recommendable in skeletally thin patient. 4. Operation took 42 minutes on average(from 30 minutes to 105 minutes) though it took more time in the early cases. 5. We had several complications in 3 patients. Misdirection of screw(1 case), screw loosening and pull out(1 case), subluxation of A-C joint after removal of screw(2 cases), and iatrogenic fracture of clavicle and coracoid process(1 case) but no case of metal breakage or infection.
- 407 View
- 0 Download

- Surgical Treatment of Scaphoid Nonunion
- Jae Ik Thim, Taek Sun Kim, Sung Jong Lee, Suk Ha Lee, Chang Moo Yoo, Kil Joo Han
- J Korean Soc Fract 1996;9(1):15-23. Published online January 31, 1996
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1996.9.1.15
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The scaphoid fracture is the most common fracture of the carpal bone in young men and has high incidence of nonunion. Many methods of treatment for nonunion of the carpal scaphoid have been described; bone grafting, screw fixation, pulsed electromagnetic field and cast, percutaneous pinning and Herbert screw fixation. Two of the commonest methods of treatment are Matti-Russe procedure and Herbert screw fixation and this paper compares these two surgical treatments. At the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Korea Veterans Hospital, from October 1988 to October 1994, 11 cases of the scaphoid nonunion had been treated by Matti-Russe procedure only (4 cases), Matti-Russe procedure with K-wire (2 cases) and Bone graft with Herbert screw fixation (5 cases) and followed up more than 1 year. The results were as follows; 1. Among 11 cases, 10 cases were male and 1 case was female and the range of age was 19-46 years (Mean 26.2 years). 2. The sites of fracture were confined to the waist in 9 cases (82%) and prox 1/3 in 2 cases (18%). 3. The treatment methods were Matti-Russe only in 4 cases, Matti-Russe procedure with K-wire in 2 cases and Bone graft with Herbert screw fixation in 5 cases. 4. Postoperative cast immobilization was done for 16.5 weeks in the cases treated by Matti-Russe procedure and for 4 weeks in the cases treated by Bone graft with Herbert screw fixation. 5. The union rate was 91 % after postoperative 4 months (Mean 4.1 months). 6. The results of treatment were excellent in 7 cases (64%), good in 3 cases (27%) and fair in 1 case(9%). Therefore the Matti-Russe procedure and Bone graft with Herbert Screw fixation are good procedures in the treatment of scaphoid nonunion. But, Bone graft with Herbert screw fixation is more useful in young men because of short periods of immobilization and early returning to work.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Volar Percutaneous Cannulated Screw Fixation for Subacute Scaphoid Wasit Fracture
Jae Kwang Kim, Jong Oh Kim, Seung Yup Lee, Nam Hoon Do
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(2): 104. CrossRef
- Volar Percutaneous Cannulated Screw Fixation for Subacute Scaphoid Wasit Fracture
- 632 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Operative Treatment of the Shaft Fractures of the Forearm Bone
- Sang Won Park, Geol Choi
- J Korean Soc Fract 1995;8(1):199-205. Published online January 31, 1995
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1995.8.1.199
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The reduction and maintenance of the disphyseal fractures of the forearm bone are difficult due to the special rotational movement between two bones. Over the years various methods of operative treatment have been advocated, and good method must be selected as the fracture level, the fracture type, and the patients general condition. From May 1988 to August 1993, the authors have reviewed 50 patients of the forearm shaft fracture except the solitary radius or ulna fracture with minimum 1 year follow up which were treated in Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Korea University Hospital. The results obtained were as follows, 1. The most common cause of injury was the traffic accident(38%) and the next was the fall down(24%). The most frequent level of the fracture was middle one-third(54%) and the most common type of the fracture was transverse fracture(64%). The treatment methods were 32 cases of the compression plate and screw fuation in the radius and ulna, and 18 cases of the compression plate and screw fixation in radius and the intramedullary nailing in ulna. 2. The average duration of the radiological union of compression plate and screw fixation of radius and ulna was 12.5 weeks in radius and 12.1 weeks in ulna, and 12.8 weeks of radius and 15.2 weeks of ulna in cases of compression plate and screw fixation of radius and intramedullary nailing of ulna. 3. According to Grace and Eversmanns evaluation, satisfactory results (Excellent and Good) were 81.5% of compression plate and screw fixation and 83.3.To of compression plate and screw fixation of radius and intramedullary nailing of ulna. 4. Postoperative complication were 2 cases of superFicial wound infection and each 1 case of transient posterior interosseous nerve injury, non-union and non-union with metal failure in compression plate and screw fixation of both radius and ulna, and 1 case of non-union in intramedullary nailing of the ulna.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Locking versus Dynamic Compression Plates for Treatment of Diaphyseal Forearm Fracture
Yong Chan Lee, Hong Je Kang
Journal of the Korean Society for Surgery of the Hand.2015; 20(4): 168. CrossRef
- Comparison of Locking versus Dynamic Compression Plates for Treatment of Diaphyseal Forearm Fracture
- 505 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Operative Treatment of Intra-articular Calcaneal Fractures by Posterior Approaeh
- Youn Soo Kim, Ckoong Seo Park, In Tak Chu, Hyoung Min Kim, Jae Duk Ryu
- J Korean Soc Fract 1992;5(2):191-198. Published online November 30, 1992
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1992.5.2.191
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In contrast to the extra-articular calcaneal fractures, the treatment of intra-articular fractures is very difficult and the final result is not always satisfactory, because it has not only difficulties in the identification of the exact fracture pattern and an anatomical reduction of the fracture fragments, but also no principle of ideal treatment. Today, numerous controversies remain regarding the treatment of intra-articular calcaneal fractures, which include the need of reduction, the method of reduction, the surgical approach. the method of fixation, and the need of bone graft. We propose the posterior approach and longitudinal buttress screw fixation for the treatment of intra-articular calcaneal fractures. The posterior approach allows excellent visualization of the posterior facet of subtalar joint, and the longitudinal screw buttresses the posterior facrt fracture fragment of calcaneus. From Dec. 1990 to May 1992, 17 intra-articular calcaneal fractures out of 15 patients were treated by our surgical method and followed up (average, 9.2 months) in 12 cases out of 10 patients (2 bilateral cases). Seven cases were tongue type fractures and five were joint do- pression type. Operations were performed 5 to 15 days after accident(average, 92 days). Bone graft was performed only 3 cases. At last follow-up, there was no pain in 8 cases. intermittant dull pain in 3, and resting pain in 1. The Bohlers angle at post-accident and last follow-up were 5.9 and 30.7 in tongue type : 10.6 and 32.6 in joint depression type. The reduction of the fracturr fragments was maintained well and secondary deformities were not developed in all cases. Based on these findings in this study, most of the intra-articular calcaneal fractures can be reduced anatomically by posterior approach, and fracture fragment maintained by longitudinal buttress screw fixation.
- 360 View
- 1 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


