Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Comparative results of the femoral neck system versus the dynamic hip screw for stable femoral neck fractures in older adults in Korea: a retrospective cohort study
- Byung-Chan Choi, Byung-Woo Min, Kyung-Jae Lee, Jun-Sik Hong
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):203-211. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00276
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
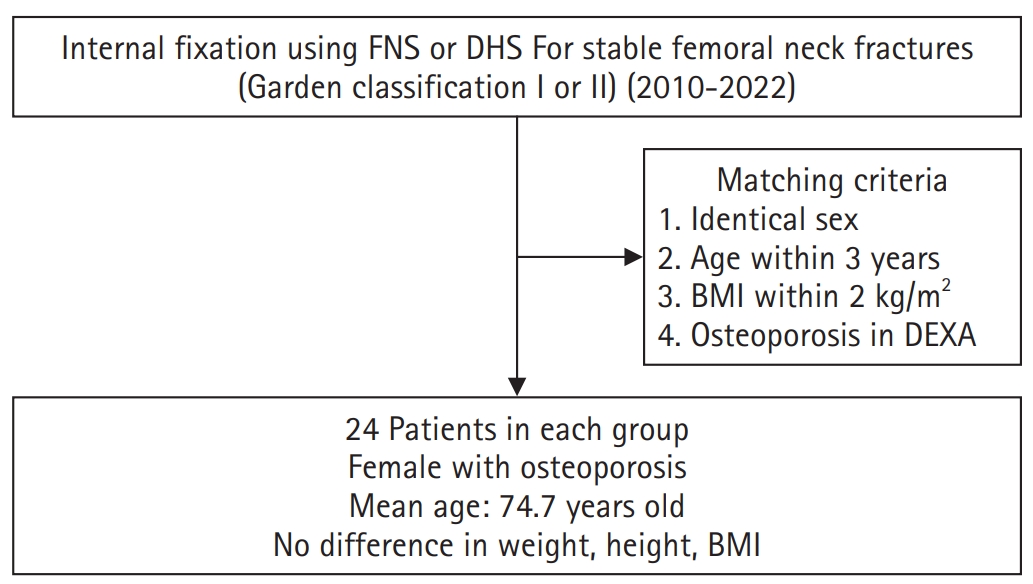
This study aimed to compare the clinical and radiological outcomes of the femoral neck system (FNS) and the dynamic hip screw (DHS) for the internal fixation of stable femoral neck fractures in older adults.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study included 48 matched older adult patients based on sex, age, BMI, and osteoporosis status, who had undergone internal fixation with either FNS or DHS for stable femoral neck fractures between January 2010 and December 2022. To minimize selection bias, a 1:1 case-control matching was performed based on sex, age, body mass index (BMI), and the presence of osteoporosis. A total of 48 patients (24 in each group) were included. We compared perioperative data (operation time, hemoglobin change, transfusion rate), functional outcomes using the Koval score, and radiological outcomes, including union rate, femoral neck shortening, and complication rates.
Results
The mean operation time was significantly shorter in the FNS group than in the DHS group (60.9 minutes vs. 70.8 minutes; P=0.007). There were no statistically significant differences between the two groups in the union rate (87.5% in FNS vs. 95.8% in DHS), femoral neck shortening, final Koval score distribution, or overall complication rates (12.5% in both groups).
Conclusions
For treating stable femoral neck fractures in older adults, the FNS demonstrated comparable clinical and radiological outcomes to the DHS, with the distinct advantage of a shorter operation time. While these findings suggest that the FNS is a promising and safe alternative that may reduce the surgical burden, definitive conclusions are precluded by the small sample size, warranting further research to corroborate these results. Level of evidence: IV.
- 1,387 View
- 20 Download

- The Role of Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate Graft in the Dynamic Hip Screw Fixation of Unstable Intertrochanter Fracture
- Chul Ho Kim, Ji Wan Kim, Eic Ju Lim, Jae Suk Chang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(4):250-257. Published online October 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.4.250
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to introduce our method of stabilizing unstable intertrochanteric fractures by using the dynamic hip screw (DHS) with a beta-tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP) graft and to compare the outcomes of this procedure with those of the conventional DHS without β-TCP.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients who underwent surgery by using DHS between March 2002 and January 2016 were retrospectively reviewed for analysis of the outcomes. The inclusion criteria were: 1) age of 60 years and older; 2) low-energy fracture resulting from a fall from no greater than the standing height; 3) multifragmentary pertrochanteric fracture (AO classification 31-A2.2, 2.3); and 4) follow-up of over 3 months. We compared 29 patients (29 hips) who underwent surgery, using DHS without β-TCP, with 29 age-sex matched patients (29 hips) who underwent surgery using DHS with grafted β-TCP granules to empty the trochanter area after reaming. We investigated the fracture union rate, union time, and length of lag screw sliding.
RESULTS
Bone union was achieved in all cases. The mean union time was 7.0 weeks in the β-TCP group and 8 .8 weeks in the non-β-TCP group. The length of lag screw sliding was 3.6 mm in the β-TCP group and 5 .5 mm in the non-β-TCP group. There were no implant failure cases in both groups.
CONCLUSION
The β-TCP graft for reinforcement DHS acquired satisfactory clinical outcomes for treating unstable intertrochanteric fractures.
- 404 View
- 3 Download

- Surgical Treatment for Stable 2-Part Intertrochanteric Femur Fracture Using Dynamic Hip Screw with 2-Hole Side Plate in Elderly Patients
- Kyung Hoon Lee, Suk Ku Han, Seung Jae Chung, Jongho Noh, Kee Haeng Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(3):192-199. Published online July 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.3.192
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the postoperative outcomes of elderly patients with stable 2-part intertrochanteric femur fractures surgically treated using dynamic hip screw with 2-hole side plate.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From February 2008 to January 2014, 50 patients older than the age of 65 years, who had been followed-up for more than 6 months after the operation at The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital were enrolled. A clinical evaluation of the skin incision length, operating time, and ambulatory status, using Clawson's Ambulation Capacity Classification, was performed, and a radiologic evaluation of Fogagnolo reduction quality, tip-apex distance (TAD), Cleveland index, sliding extent of lag screws, time duration till bony union, and complications was also done.
RESULTS
The mean skin incision length was 9.8 cm (range, 8-13 cm), the mean operating time was 41.4 minutes (range, 30-60 minutes), and 32 patients recovered their ambulatory function. Forty-eight patients gained bony union, and the time lapsed till union was average 10.6 weeks (range, 8-16 weeks). The evaluation of postoperative radiologic images showed the following reduction statuses by the Fogagnolo classification: 46 cases of "Good", 3 cases of "Acceptable," and 1 case of "Poor." Moreover, the mean TAD was 18.9 mm (range, 9.0-24.9 mm). While 45 cases fit into the zone 5 of the Cleveland index, other 3 were within zone 8 and the other 2 were within zone 6. The mean sliding length of the lag screws were 4.9 mm (range, 0.1-19.4 mm). There were a case of nonunion and a case of periprosthetic infection with nonunion as complications.
CONCLUSION
Using dynamic hip screws with 2-hole side plate for stable 2-part intertrochanteric femur fractures in elderly patients showed satisfactory results with respect to the recovery of ambulatory functions and bony union.
- 430 View
- 0 Download

- The Comparison between ITST(TM) (Intertrochanteric/Subtrochanteric) & DHS (Dynamic Hip Screw) in Unstable Femur Intertrochanteric Fracture
- Ho Seung Jeon, Byung Mun Park, Kyung Sub Song, Hyung Gyu Kim, Jong Ju Yun
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(3):131-137. Published online July 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.3.131
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate between DHS and ITST nail (2nd generation) on the treatment of unstable femur intertrochanteric fracture in patients over 70 years old.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
61 cases of unstable intertrochanteric fracture (grouped 37 patients with DHS and 24 patients with ITST) who were taken the operation from Mar. 2003 to Sep. 2007 were analysed regarding to union time, sliding length of lag screws, operation time, blood loss, postoperative complications and functional recovery score by Skovron.
RESULTS
The mean union time was 14.7 weeks in study group (ITST). The mean union time was 16.2 weeks in control group (DHS). The lag screw slidings were 7.2 mm in study group and 8.7 mm in control group. The operation times were 57.9 min in study group and 76.9 min in control group. The amount of blood loss were 67.7 ml in study group and 227.4 ml in control group. The complications were 4 cases in study group and 4 cases in control group. The Skovron recovery scores were 76.5% in study group and 73.7% in control group.
CONCLUSION
From a practical point of short operation time, less amount of bleeding and less complication, author think that the ITST nail is useful implant for treatment of unstable femur intertrochanteric fracture in patient of old age. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unstable Intertrochanteric Fracture Treated with ITST: A Comparative Study between Groups with and without Comminution of Greater Trochanter
Kyung-Sub Song, Sang-Ho Lee, Seong-Hun Jeong, Su-Keon Lee, Sung-Ha Hong
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2014; 27(1): 36. CrossRef - Treatment of the Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture with Proximal Femoral Nail: Nailing Using the Provisional K-wire Fixation
Gu-Hee Jung
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(3): 223. CrossRef
- Unstable Intertrochanteric Fracture Treated with ITST: A Comparative Study between Groups with and without Comminution of Greater Trochanter
- 667 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Treatment of Stable Intertrochanteric Fractures Using a Short Side Plate Dynamic Hip Screw
- Chong Kwan Kim, Jin Woo Jin, Sung Won Jung, Wan Sub Kwak, Jae Il Jo, Woo Sik Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(3):309-313. Published online July 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.3.309
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the usefulness of a 2 holes side plate dynamic hip screw for the treatment of stable intertrochanteric fracture of the femur.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between January 2000 and September 2004, 46 patients with intertrochanteric fracture of the femur were treated with 2 hole side plate dynamic hip screw (Group 1, 25 cases) or 4 hole side plate dynamic hip screw (Group 2, 21 cases). The mean age of the patient was 70 years, with a mean follow-up duration of 13 months. The time for operation, surgical incision length, blood loss, time for union, the sliding distance, change in the femoral neck-shaft angle and patient's walking ability were evaluated.
RESULTS
The mean operation time and mean incision length were shortened, and mean blood loss was decreased in Group 1 (p<0.01). There was no statistical difference in the union time, the mean change in the femoral neck-shaft angle and the mean sliding distance of the lag screw at the last follow-up. The mean mobility score of the Parker and Palmer was 8.0 points before the fracture and 7.2 points at the last follow-up.
CONCLUSION
Two-hole side plate dynamic hip screw is a useful device, in terms of the operation time, morbidity of operation site, satisfactory union rate and functional recovery of the patient in treatment of elderly patients with stable intertrochanteric fractures of the femur.
- 395 View
- 0 Download

- The Treatment of Unstable Intertrochanter Fracutures of Femur: Comparison between Proximal Femoral Nail and Dynamic Hip Screw
- Kyun Chul Kim, Hun Kyu Shin, Kyung Mo Son, Chun Seok Ko
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(4):369-374. Published online October 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.4.369
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analyze the results between PFN (Proximal Femoral Nail) and DHS (Dynamic Hip Screw) on the operative treatment of unstable intertrochanteric fractures retrospectively.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
35 cases of unstable intertrochanteric fractures (grouped 24 patients with DHS and 11 patients with PFN) who were taken the operations from Jan. 2001 to Mar. 2002 were analysed regarding to union state, union time, operation time, sliding length of lag screws, blood loss, postoperative complications and functional recovery scores by Sk?vron with ANOVA and multivariate linear regression.
RESULTS
The means of union time were 17.9 weeks (DHS) and 17.0 weeks (PFN), sliding length of lag screws were 3.9 mm (DHS) and 2.1 mm (PFN), perioperative blood losses were 743 cc (DHS) and 736 cc (PFN), operation time were 93.4 minutes (DHS) and 102 minutes (PFN), and the functional recovery scores by Sk?vron were 71.8% (DHS) and 76.8% (PFN), respectively. The results of our study indicate that there were not statistically significant differences between PFN and DHS groups in treatment of unstable intertrochanteric fractures (p>0.05). But, there was less sliding of lag screws in PFN group in statistical significance (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
Authors think that PFN is one of the useful implants in treating unstable intertrochanteric fractures of the femur in regarding to sliding. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty in Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures with an Effective Wiring Technique
Jae-Hwi Nho, Gi-Won Seo, Tae Wook Kang, Byung-Woong Jang, Jong-Seok Park, You-Sung Suh
Hip & Pelvis.2023; 35(2): 99. CrossRef - Comparison of the Gamma Nail and the Dynamic Hip Screw for Peritrochanteric Fracture
Seok Hyun Kweon
Hip & Pelvis.2011; 23(2): 124. CrossRef - The Efficiency of Additional Fixation of the Alternative Bone Substitute in Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures of Femur Treated with Gamma Nail
Jong-Oh Kim, Young-One Ko, Mi-Hyun Song
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(1): 1. CrossRef
- Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty in Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures with an Effective Wiring Technique
- 624 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Correlation between Anterior and Posterior Obliquity of the Sliding Lag Screw and Stability in Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures
- Kyu Hyun Yang, Je Hyun Yoo, Dong Joo Rhee, Jung Hoon Won, Dae Ya Kim, Dong Sik Sim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(4):308-313. Published online October 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.4.308
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To investigate the characteristics of the sliding pattern of the proximal fragment (head and neck) in unstable intertrochanteric fractures, which were fixed with a dynamic hip screw (DHS) with anterior to posterior or posterior to anterior insertion angle in the axial view.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
AO type A2.1 intertrochanteric fracture was reproduced in 10 proximal femur model (Synbone, Malans, Switzerland). Five fractured models were reduced and fixed using DHS with anterior to posterior insertion angle (group 1) and five models were fixed with posterior to anterior angle (group 2). Load of 500 N (30 cycles) was applied to the fracture fragment-plate complex using Instron 6022. Data on the distance of sliding and the angle of rotation of the proximal fragment were collected and analyzed.
RESULTS
No significant difference was noted statistically in the distance of sliding between the two groups (p=0.92). However, the mean angle of rotation was 13.4degrees and 8.0degrees in group 1 and 2, respectively and the difference was statistically significant (p=0.012). Anterior cortical fracture of distal fragment was noted in 3 cases of group 1. There was no fracture of the anterior cortex in group 2.
CONCLUSION
In unstable intertrochanteric fracture, the insertion angle of the lag screw in axial view does seem to play a role in the fate of bone-plate complex. Early eccentric contact of both fragments caused rotation of the proximal fragment in all cases and anterior cortical fracture of the distal fragment in 3 cases of group 1.
- 326 View
- 0 Download

- Treatment of Comminuted Trochanteric Fracture with Dynamic Hip Screw and Trochanteric Stabilizing Plate
- Seungki Baek, Youngjoon Choi, Chunghwan Kim, Yoojin Kim, Jaekwang Hwang, Hyungsun Ahn, Hyuntae Ahn, Kyungjun Park, Jaiwoo Cho
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(2):278-285. Published online April 30, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.2.278
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the results of treatment of comminuted femoral trochanteric fracture using dynamic hip screw(DHS) with trochanteric stabilizing plate(TSP) and DHS only.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
we analysed retrospectively 32 cases that has fracture extends over two or more levels of medial cortex(A2 of AO classification) and fracture extends through lateral cortex of femur(A3 of AO classicification) of femoral trochanteric fractures between 1997 and 2000. On simple AP radiograph of the DHS with TSP(n=16) and DHS only group(n=16), we reviewed bony union, slippage of lag screw, lateral displacement of greater trochanter.
RESULT
Bony union was observed in all cases. When bony union is done in follow up radiograph, Mean slippage of lag screw is 14.5mm in DHS only group, 12.6mm in DHS with TSP group and mean lateral displacement of greater trochanter is 9.8mm in DHS only group, 1.2mm in DHS with TSP group.
CONCLUSION
Use of DHS with TSP in comminuted femoral trochanteric fracture is lesser slippage of lag screw and lateral displacement of greater trochanter than DHS only used, and that is better method to maintain fracture reduction and internal fixation in treatment of comminuted femoral trochanteric fractures than DHS only. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Results of Use of Compression Hip Screw with Trochanter Stabilizing Plate for Reverse Oblique Intertrochanteric Fracture
Byung-Woo Min, Kyung-Jae Lee, Gyo-Wook Kim, Ki-Cheor Bae, Si-Wook Lee, Du-Han Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2014; 27(2): 120. CrossRef - A Comparison of Intramedullary and Extramedullary Fixations for the Treatment of Reverse Oblique or Transverse Intertrochanteric Femoral Fractures
Yerl-Bo Sung, Jung-Yun Choi, Eui-Yub Jung
Hip & Pelvis.2012; 24(2): 109. CrossRef
- Results of Use of Compression Hip Screw with Trochanter Stabilizing Plate for Reverse Oblique Intertrochanteric Fracture
- 577 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Crossref

- A Comparison study of the Gamma nail and the Dynamic Hip Screw for Peritrochanteric Fractures
- Dong Chul Lee, Sang Jae Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 1994;7(2):616-627. Published online November 30, 1994
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1994.7.2.616
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The peritrochanteric fractures had been very troublesome due to its complication in the treatment of the old patients in the pastdays. The Dynamic Hip Screw and the Gamma nail made the patients to mobilize early and decreased the complications. We have treated 44 cases of the peritrochanteric fractures using Gamma nail(25 cases) and Dynamic Hip Screw (19 cases) between Aug. 1989 and Nov 1993, and compared the results of each group. And obtained results were as follows 1. The traffic accident was constituted about one third proportion and unstable types of the peritrochanteric fractures were 25 cases among 44 cases(57%). 2. The Mean union time of the Gamma nail group was 10.4 weeks and the Dynamic Hip Screw group was about 13 weeks. There was statistically no significance in the mean union time between both groups. 3. There revealed significance(P<0.05) by statistical analysis in operation time, admission day, blood transfusion between both groups. 4. There revealed no signicance (p<0.05) by statistical analysis in degree of sliding of the lag screw and change of neck-shaft angle. 5. The complications in the Gamma nail group were varus in 3 cases and infection in 1 case, and in the Dynamic Hip Screw group there were varus in 3 cases, delayed union in 2 cases and refracture in 1 case.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Efficiency of Additional Fixation of the Alternative Bone Substitute in Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures of Femur Treated with Gamma Nail
Jong-Oh Kim, Young-One Ko, Mi-Hyun Song
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(1): 1. CrossRef
- The Efficiency of Additional Fixation of the Alternative Bone Substitute in Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures of Femur Treated with Gamma Nail
- 656 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Trochanteric fractures of the femur pitfalls of the treatment withdynamic hip screw in elderly patients
- Hyoun Oh Cho, Kyoung Duck Kwak, Sung Do Cho, Ang Hyoun Son
- J Korean Soc Fract 1992;5(1):111-120. Published online May 31, 1992
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1992.5.1.111
- 333 View
- 0 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


